Vietnamese language and computers on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The
 Vietnamese often stacks diacritics, so typeface designers must take care to prevent stacked diacritics from colliding with adjacent letters or lines. When a tone mark is used together with another diacritic, offsetting the tone mark to the right preserves consistency and avoids slowing down saccades. In advertising signage and in
Vietnamese often stacks diacritics, so typeface designers must take care to prevent stacked diacritics from colliding with adjacent letters or lines. When a tone mark is used together with another diacritic, offsetting the tone mark to the right preserves consistency and avoids slowing down saccades. In advertising signage and in
 Unicode includes over 10,000 ' characters as part of Unicode's repertoire of
Unicode includes over 10,000 ' characters as part of Unicode's repertoire of
 A purely physical Vietnamese keyboard would be impractical, due to the sheer number of letter-diacritic-diacritic combinations in the alphabet e.g. á, à, ả, ã, ạ, â, ấ, etc. Instead, Vietnamese input relies on formulaic software-based keyboard layouts, virtual keyboards, or input methods (also known as IMEs).
A purely physical Vietnamese keyboard would be impractical, due to the sheer number of letter-diacritic-diacritic combinations in the alphabet e.g. á, à, ả, ã, ạ, â, ấ, etc. Instead, Vietnamese input relies on formulaic software-based keyboard layouts, virtual keyboards, or input methods (also known as IMEs).
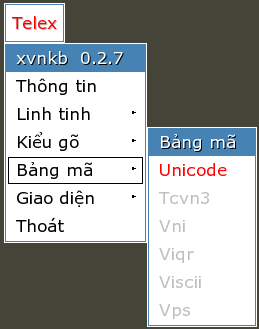 The three most common Vietnamese input methods are Telex, VNI, and VIQR. Telex indicates diacritics using letters that are unlikely to appear at the end of a word, while VNI repurposes the number keys or function keys and VIQR repurposes various punctuation marks. The Telex and VIQR conventions originated in an earlier era of telex machines and typewriters, respectively.
Support for these input methods is provided by input method editors (IMEs), which are known in Vietnamese as ', literally "peckers" or "percussion" in more general terms. IMEs may be provided by the operating system, installed as a third-party application, installed as a
The three most common Vietnamese input methods are Telex, VNI, and VIQR. Telex indicates diacritics using letters that are unlikely to appear at the end of a word, while VNI repurposes the number keys or function keys and VIQR repurposes various punctuation marks. The Telex and VIQR conventions originated in an earlier era of telex machines and typewriters, respectively.
Support for these input methods is provided by input method editors (IMEs), which are known in Vietnamese as ', literally "peckers" or "percussion" in more general terms. IMEs may be provided by the operating system, installed as a third-party application, installed as a  Borrowing a feature common amongst Chinese input methods, some Vietnamese IMEs allow one to skip diacritics altogether and instead, after typing the base letters, the user can select the accented word from a candidate list. In order to provide this autocomplete list, the IME may need to communicate with a Web service. Some IMEs also use candidate lists to allow the user to convert text from the Vietnamese alphabet to ', because there is no one-to-one correspondence between alphabetic words and ' characters.
Borrowing a feature common amongst Chinese input methods, some Vietnamese IMEs allow one to skip diacritics altogether and instead, after typing the base letters, the user can select the accented word from a candidate list. In order to provide this autocomplete list, the IME may need to communicate with a Web service. Some IMEs also use candidate lists to allow the user to convert text from the Vietnamese alphabet to ', because there is no one-to-one correspondence between alphabetic words and ' characters.
Computing in Vietnamese: Progress & Challenges
2005 International Macintosh Users Group presentation
Vietnamese Conversions
{snd online tool for recovering Vietnamese mojibake Natural language and computing Science and technology in Vietnam Vietnamese character input Vietnamese software
Vietnamese language
Vietnamese ( vi, tiếng Việt, links=no) is an Austroasiatic language originating from Vietnam where it is the national and official language. Vietnamese is spoken natively by over 70 million people, several times as many as the rest of the ...
is written with a Latin script
The Latin script, also known as Roman script, is an alphabetic writing system based on the letters of the classical Latin alphabet, derived from a form of the Greek alphabet which was in use in the ancient Greek city of Cumae, in southern ...
with diacritics ( accent tones) which requires several accommodations when typing on phone or computers. Software-based systems are a form of writing Vietnamese on phones or computers with software that can be installed on the device or from third party software such as UniKey. Telex is the oldest input method devised to encode the Vietnamese language with its tones. Other input methods may also include VNI (Number key-based keyboard) and VIQR. VNI input method is not to be confused with VNI code page.
Historically, Vietnamese was also written in ', which is mainly used for ceremonial and traditional purposes in recent times, and remains in the field of historians and philologists. There have been attempts to type chữ Hán
Chữ Hán (𡨸漢, literally "Chinese characters", ), Chữ Nho (𡨸儒, literally "Confucian characters", ) or Hán tự (漢字, ), is the Vietnamese term for Chinese characters, used to write Văn ngôn (which is a form of Classical Chinese ...
and chữ Nôm
Chữ Nôm (, ; ) is a logographic writing system formerly used to write the Vietnamese language. It uses Chinese characters ('' Chữ Hán'') to represent Sino-Vietnamese vocabulary and some native Vietnamese words, with other words represent ...
with existing Vietnamese input methods, but they are not widespread. Sometimes, Vietnamese can be typed without tone marks, which Vietnamese speakers can usually guess depending on context.
Fonts and character encodings
Vietnamese alphabet
Character encodings
There are as many as 46character encoding
Character encoding is the process of assigning numbers to graphical characters, especially the written characters of human language, allowing them to be stored, transmitted, and transformed using digital computers. The numerical values tha ...
s for representing the Vietnamese alphabet
The Vietnamese alphabet ( vi, chữ Quốc ngữ, lit=script of the National language) is the modern Latin writing script or writing system for Vietnamese. It uses the Latin script based on Romance languages originally developed by Portuguese m ...
. Unicode
Unicode, formally The Unicode Standard,The formal version reference is is an information technology standard for the consistent encoding, representation, and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems. The standard, ...
has become the most popular form for many of the world's writing systems, due to its great compatibility and software support. Diacritics may be encoded either as combining character
In digital typography, combining characters are characters that are intended to modify other characters. The most common combining characters in the Latin script are the combining diacritical marks (including combining accents).
Unicode al ...
s or as precomposed characters, which are scattered among the Latin Extended-A, Latin Extended-B
Latin Extended-B is the fourth block (0180-024F) of the Unicode Standard. It has been included since version 1.0, where it was only allocated to the code points 0180-01FF and contained 113 characters. During unification with ISO 10646 for versio ...
, and Latin Extended Additional blocks. The Vietnamese đồng
The dong ( Vietnamese: ''đồng'', Chữ Nôm: 銅) (; ; sign: ₫ or informally đ in Vietnamese; code: VND) has been the currency of Vietnam since 3 May 1978. It is issued by the State Bank of Vietnam. The dong was also the currency of the p ...
symbol is encoded in the Currency Symbols block. Historically, the Vietnamese language used other characters beyond the modern alphabet. The Middle Vietnamese letter B with flourish
B with flourish (Ꞗ, ꞗ) is the modern name for the third letter of the Middle Vietnamese alphabet, sorted between B and C. The B with flourish has a rounded hook that starts halfway up the stem (where the top of the bowl meets the ascender) ...
(ꞗ) is included in the Latin Extended-D block. The apex is not included in Unicode, but may serve as a rough approximation.
Early versions of Unicode assigned the characters and for the purpose of placing these marks beside a circumflex, as is common in Vietnamese typography. These two characters have been deprecated; and are now used regardless of any present circumflex.
For systems that lack support for Unicode, dozens of 8-bit Vietnamese code page
In computing, a code page is a character encoding and as such it is a specific association of a set of printable characters and control characters with unique numbers. Typically each number represents the binary value in a single byte. (In some c ...
s have been designed. The most commonly used of them were VISCII, VSCII (TCVN 5712:1993), VNI, VPS and Windows-1258. Where ASCII
ASCII ( ), abbreviated from American Standard Code for Information Interchange, is a character encoding standard for electronic communication. ASCII codes represent text in computers, telecommunications equipment, and other devices. Because ...
is required, such as when ensuring readability in plain text e-mail, Vietnamese letters are often encoded according to Vietnamese Quoted-Readable
Vietnamese Quoted-Readable (usually abbreviated VIQR), also known as Vietnet, is a convention for writing Vietnamese using ASCII characters encoded in only 7 bits, making possible for Vietnamese to be supported in computing and communication syste ...
(VIQR) or VSCII Mnemonic (VSCII-MNEM), though usage of either variable-width scheme has declined dramatically following the adoption of Unicode on the World Wide Web
The World Wide Web (WWW), commonly known as the Web, is an information system enabling documents and other web resources to be accessed over the Internet.
Documents and downloadable media are made available to the network through web ...
. For instance, support for all above mentioned 8-bit encodings, with the exception of Windows-1258, was dropped from Mozilla
Mozilla (stylized as moz://a) is a free software community founded in 1998 by members of Netscape. The Mozilla community uses, develops, spreads and supports Mozilla products, thereby promoting exclusively free software and open standards, ...
software in 2014.
Many Vietnamese fonts intended for desktop publishing
Desktop publishing (DTP) is the creation of documents using page layout software on a personal ("desktop") computer. It was first used almost exclusively for print publications, but now it also assists in the creation of various forms of online ...
are encoded in VNI or TCVN3 ( VSCII). Such fonts are known as "ABC fonts". Popular web browser
A web browser is application software for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's screen. Browsers are used o ...
s lack support for specialty Vietnamese encodings, so any webpage that uses these fonts appears as unintelligible '' mojibake'' on systems without them installed.
cursive
Cursive (also known as script, among other names) is any style of penmanship in which characters are written joined in a flowing manner, generally for the purpose of making writing faster, in contrast to block letters. It varies in functionali ...
handwriting, diacritics often take forms unfamiliar to other Latin alphabets. For example, the lowercase letter I retains its tittle in ''ì'', ''ỉ'', ''ĩ'', and ''í''. These nuances are rarely accounted for in computing environments.
Approaches to character encoding
Vietnamese writing requires 134 additional letters (between both cases) besides the 52 already present in ASCII. This exceeds the 128 additional characters available in a conventionalextended ASCII
Extended ASCII is a repertoire of character encodings that include (most of) the original 96 ASCII character set, plus up to 128 additional characters. There is no formal definition of "extended ASCII", and even use of the term is sometimes critic ...
encoding. Although this can be solved by using a variable-width encoding
A variable-width encoding is a type of character encoding scheme in which codes of differing lengths are used to encode a character set (a repertoire of symbols) for representation, usually in a computer. Most common variable-width encodings a ...
(as is done by UTF-8
UTF-8 is a variable-length character encoding used for electronic communication. Defined by the Unicode Standard, the name is derived from ''Unicode'' (or ''Universal Coded Character Set'') ''Transformation Format 8-bit''.
UTF-8 is capable of e ...
), a number of approaches have been used by other encodings to support Vietnamese without doing so:
* Replace at least six ASCII characters, selected either for being uncommon in Vietnamese, and/or for being non-invariant in ISO 646 or DEC NRCS (as in VNI for DOS).
* Drop the uppercase letters which are least frequently used, or all uppercase letters with tone marks (as in VSCII-3 (TCVN3)). These letters may still be supplied by means of all-capital fonts.
* Drop forms of the letter Y with tone marks, necessitating use of the letter in those circumstances. This approach was rejected by the designers of VISCII on the basis that a character encoding should not attempt to settle a spelling reform issue.
* Replace at least six C0 control characters (as in VISCII, VSCII-1 (TCVN1) and VPS).
* Use combining characters, allowing one vowel with accents to be fully represented using a sequence of characters (as in VNI, VSCII-2 (TCVN2), Windows-1258 and ANSEL
ANSEL, the American National Standard for Extended Latin Alphabet Coded Character Set for Bibliographic Use, was a character set used in text encoding. It provided a table of coded values for the representation of characters of the extended Latin ...
).
Font substitution
Many fonts support a subset of the Latin writing system that omits much of the Vietnamese alphabet. Due to the high density of Vietnamese-specific characters in Vietnamese text, Web browsers that implementfont substitution
Font substitution is the process of using one typeface in place of another when the intended typeface either is not available or does not contain glyphs for the required characters.
Font substitution can be aided by:
* classifying fonts into ge ...
reliably produce a ransom note effect
In typography, the ransom note effect is the result of using an excessive number of juxtaposed typefaces. It takes its name from the appearance of a stereotypical ransom note, with the message formed from words or letters cut randomly from a m ...
when the webpage specifies an inadequate font.
'
 Unicode includes over 10,000 ' characters as part of Unicode's repertoire of
Unicode includes over 10,000 ' characters as part of Unicode's repertoire of CJK Unified Ideographs
The Chinese, Japanese and Korean (CJK) scripts share a common background, collectively known as CJK characters. In the process called Han unification, the common (shared) characters were identified and named CJK Unified Ideographs. As of Unicode ...
. Of these characters, 10,082 can be found in the CJK Unified Ideographs Extension B
CJK Unified Ideographs Extension B is a Unicode block containing rare and historic CJK ideographs for Chinese, Japanese, Korean, and Vietnamese.
The block has dozens of variation sequences defined for standardized variants.
It also has thous ...
block, while the rest are distributed between the CJK Unified Ideographs
The Chinese, Japanese and Korean (CJK) scripts share a common background, collectively known as CJK characters. In the process called Han unification, the common (shared) characters were identified and named CJK Unified Ideographs. As of Unicode ...
, CJK Unified Ideographs Extension A
CJK Unified Ideographs Extension-A is a Unicode block containing rare Han ideographs.
The block has dozens of variation sequences defined for standardized variants.
It also has thousands of ideographic variation sequences registered in the Un ...
, and CJK Unified Ideographs Extension C
__FORCETOC__
CJK Unified Ideographs Extension C is a Unicode block containing rare and historic CJK ideographs for Chinese, Japanese, Korean, and Vietnamese.
The block has dozens of ideographic variation sequences registered in the Unicode I ...
blocks. A further 1,028 characters, including over 400 characters specific to the Tày language, are encoded in the CJK Unified Ideographs Extension E
CJK Unified Ideographs Extension E is a Unicode block containing rare and historic CJK ideographs for Chinese, Japanese, Korean, and Vietnamese.
The block has dozens of ideographic variation sequences registered in the Unicode Ideographic Vari ...
block. The characters are taken from the Vietnamese standards TCVN 5773:1993 and TCVN 6909:2001 rror for TCVN 6056:1995? as well as from research by the Han-Nom Research Institute and other groups. All the characters in TCVN 5773:1993 and about 95% of the characters in TCVN 6909:2001 rror for TCVN 6056:1995?have corresponding codepoints in Unicode 5.1, though TCVN 5773:1993 itself mapped most of its characters to the Private Use Area of Unicode. Unicode 13.0 added two diacritical characters to the Ideographic Symbols and Punctuation
Ideographic Symbols and Punctuation is a Unicode block containing symbols and punctuation marks used by ideographic scripts such as Tangut and Nüshu.
History
The following Unicode-related documents record the purpose and process of definin ...
block that were commonly used to indicate borrowed characters in .
The two most comprehensive ' fonts are the Vietnamese Nôm Preservation Foundation's '' Light'' and the community-developed ''HAN NOM A''/''HAN NOM B'', both of which place a large number of unstandardized characters in the Private Use Areas
In Unicode, a Private Use Area (PUA) is a range of code points that, by definition, will not be assigned characters by the Unicode Consortium. Three private use areas are defined: one in the Basic Multilingual Plane (), and one each in, and near ...
.
The Unicode Consortium's Unihan database includes Vietnamese readings of some characters but does not distinguish between Sino-Vietnamese and ' readings.
Like other CJKV writing systems, ' is traditionally written vertically, from top to bottom and right to left.
and may also be annotated using ruby character
Ruby characters or rubi characters () are small, annotative glosses that are usually placed above or to the right of logographic characters of languages in the East Asian cultural sphere, such as Chinese ''hanzi'', Japanese ''kanji'', and Ko ...
s, which is the same as chữ Quốc Ngữ for Vietnamese.
Text input
 A purely physical Vietnamese keyboard would be impractical, due to the sheer number of letter-diacritic-diacritic combinations in the alphabet e.g. á, à, ả, ã, ạ, â, ấ, etc. Instead, Vietnamese input relies on formulaic software-based keyboard layouts, virtual keyboards, or input methods (also known as IMEs).
A purely physical Vietnamese keyboard would be impractical, due to the sheer number of letter-diacritic-diacritic combinations in the alphabet e.g. á, à, ả, ã, ạ, â, ấ, etc. Instead, Vietnamese input relies on formulaic software-based keyboard layouts, virtual keyboards, or input methods (also known as IMEs).
Keyboard layouts
Vietnamese keyboard layouts rely on dead keys to compose letters with diacritics. Most desktop operating systems include a Vietnamese keyboard layout similar to , a Vietnamese national standard. Previously, typewriters used an AZERTY-based Vietnamese layout (AĐERTY).Input methods
 The three most common Vietnamese input methods are Telex, VNI, and VIQR. Telex indicates diacritics using letters that are unlikely to appear at the end of a word, while VNI repurposes the number keys or function keys and VIQR repurposes various punctuation marks. The Telex and VIQR conventions originated in an earlier era of telex machines and typewriters, respectively.
Support for these input methods is provided by input method editors (IMEs), which are known in Vietnamese as ', literally "peckers" or "percussion" in more general terms. IMEs may be provided by the operating system, installed as a third-party application, installed as a
The three most common Vietnamese input methods are Telex, VNI, and VIQR. Telex indicates diacritics using letters that are unlikely to appear at the end of a word, while VNI repurposes the number keys or function keys and VIQR repurposes various punctuation marks. The Telex and VIQR conventions originated in an earlier era of telex machines and typewriters, respectively.
Support for these input methods is provided by input method editors (IMEs), which are known in Vietnamese as ', literally "peckers" or "percussion" in more general terms. IMEs may be provided by the operating system, installed as a third-party application, installed as a browser extension
A browser extension is a small software module for customizing a web browser. Browsers typically allow a variety of extensions, including user interface modifications, cookie management, ad blocking, and the custom scripting and styling of web ...
, or provided by an individual website in the form of a script
Script may refer to:
Writing systems
* Script, a distinctive writing system, based on a repertoire of specific elements or symbols, or that repertoire
* Script (styles of handwriting)
** Script typeface, a typeface with characteristics of ha ...
. Common third-party applications include GoTiengViet, UniKey, VietKey, VPSKeys VPSKeys is a freeware input method editor developed and distributed by the Vietnamese Professionals Society (VPS). One of the first input method editors for Vietnamese, it allows users to add accent marks to Vietnamese text on computers running Mi ...
, WinVNKey, and xvnkb. On Unix-like
A Unix-like (sometimes referred to as UN*X or *nix) operating system is one that behaves in a manner similar to a Unix system, although not necessarily conforming to or being certified to any version of the Single UNIX Specification. A Unix-li ...
operating systems, the IBus and SCIM frameworks both support Vietnamese. IME scripts such as AVIM, Mudim, and VietTyping can be found on most Vietnamese message boards, the Vietnamese Wikipedia
The Vietnamese Wikipedia ( vi, Wikipedia tiếng Việt) is the Vietnamese-language edition of Wikipedia, a free, publicly editable, online encyclopedia supported by the Wikimedia Foundation. As with other language editions of Wikipedia, the p ...
, and other text-intensive websites. The Vietnamese Web browser Cốc Cốc comes with an input method built-in.
Input methods allow words to be composed in a more flexible order than keyboard layouts allow. For example, to enter the word "" using the TCVN 6064:1995 keyboard layout, one must type , in that order. By contrast, most IMEs permit the user to insert diacritics at the end of the word: in Telex, in VNI, or in VIQR. Some IMEs even allow diacritics to be entered before their base letters. Depending on an IME's implementation, it may also be possible to edit an existing word's diacritics without retyping the word.
Some virtual keyboards supplement the standard dead keys with dedicated shortcut keys. For example, with the VIQR keyboard built into iOS, it is possible to add a horn to "U" by tapping either or the dedicated key, which has no analogue on a physical keyboard.
 Borrowing a feature common amongst Chinese input methods, some Vietnamese IMEs allow one to skip diacritics altogether and instead, after typing the base letters, the user can select the accented word from a candidate list. In order to provide this autocomplete list, the IME may need to communicate with a Web service. Some IMEs also use candidate lists to allow the user to convert text from the Vietnamese alphabet to ', because there is no one-to-one correspondence between alphabetic words and ' characters.
Borrowing a feature common amongst Chinese input methods, some Vietnamese IMEs allow one to skip diacritics altogether and instead, after typing the base letters, the user can select the accented word from a candidate list. In order to provide this autocomplete list, the IME may need to communicate with a Web service. Some IMEs also use candidate lists to allow the user to convert text from the Vietnamese alphabet to ', because there is no one-to-one correspondence between alphabetic words and ' characters.
Other considerations
Typical Vietnamese text contains a high proportion of compound words. Compound words are never hyphenated in contemporary usage, sospell checker In software, a spell checker (or spelling checker or spell check) is a software feature that checks for misspellings in a text. Spell-checking features are often embedded in software or services, such as a word processor, email client, electronic ...
s are limited to checking individual syllables unless a statistical language model
A language model is a probability distribution over sequences of words. Given any sequence of words of length , a language model assigns a probability P(w_1,\ldots,w_m) to the whole sequence. Language models generate probabilities by training on ...
is consulted.
Vietnamese has rigid spelling rules and few exceptions, so text-to-speech engines may avoid dictionary lookups except when encountering a foreign loan word. TTS engines must account for tones, which are essential to the meaning of any Vietnamese word e.g. má (mother) is a different word to mà (but).
Internationalized user interfaces are generally unable to use the full complement of Vietnamese pronouns that would be expected in a traditional social setting, even when much is known about the user. Instead, user interfaces typically use generic pronouns such as and , some of which make potentially incorrect assumptions about the user's age and relationship to other users. For example, when a social media
Social media are interactive media technologies that facilitate the creation and sharing of information, ideas, interests, and other forms of expression through virtual communities and networks. While challenges to the definition of ''social me ...
platform notifies a user about a younger user, it may refer to the latter in the third person as instead of , leading the user to misinterpret the notification as a reference to someone else.
See also
* Chinese input methods for computers * Japanese language and computers * Korean language and computersReferences
Further reading
*External links
Computing in Vietnamese: Progress & Challenges
2005 International Macintosh Users Group presentation
Vietnamese Conversions
{snd online tool for recovering Vietnamese mojibake Natural language and computing Science and technology in Vietnam Vietnamese character input Vietnamese software