Via Clodia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
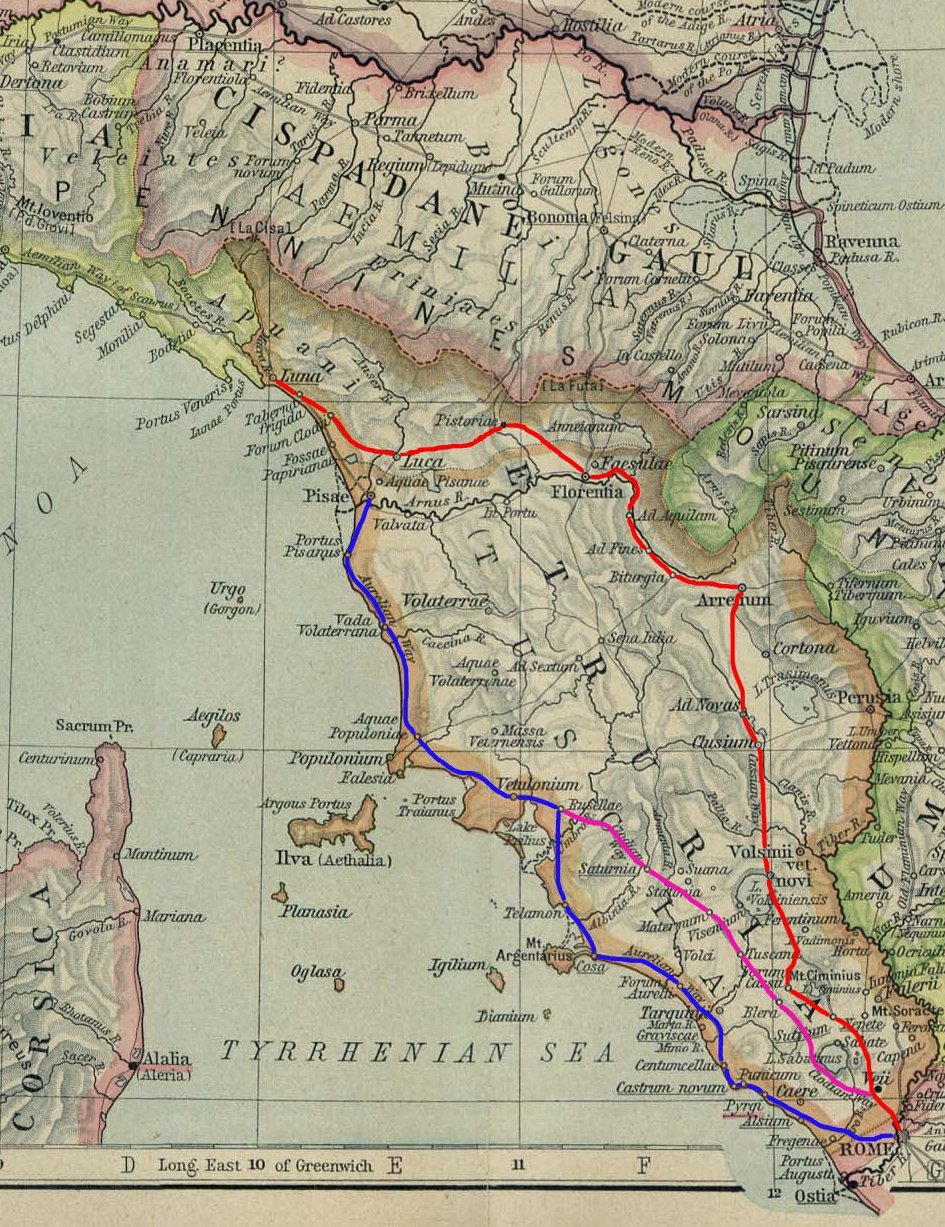
 The Via Clodia was an ancient high-road of
The Via Clodia was an ancient high-road of

 The Via Clodia was an ancient high-road of
The Via Clodia was an ancient high-road of Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
. Situated between the Via Cassia
The ''Via Cassia'' ("way of Cassius") was an important Roman road striking out of the ''Via Flaminia'' near the Milvian Bridge in the immediate vicinity of Rome and, passing not far from Veii, traversed Etruria. The ''Via Cassia'' passed through ...
and the Via Aurelia
The ''Via Aurelia'' (Latin for "Aurelian Way") is a Roman road in Italy constructed in approximately 241 BC. The project was undertaken by Gaius Aurelius Cotta, who at that time was censor.Hornblower, Simon, & Antony Spawforth. ''The Oxford Cla ...
, it is different from them notably in that the latter was designed primarily for military long-haul, irrespective of settlements they met, but the Via Clodia was of short-range, intended for commercial traffic with the colonies in Etruscan __NOTOC__
Etruscan may refer to:
Ancient civilization
*The Etruscan language, an extinct language in ancient Italy
*Something derived from or related to the Etruscan civilization
**Etruscan architecture
**Etruscan art
**Etruscan cities
** Etrusca ...
lands.
Its origin is uncertain, but most scholars agree that it was built by the Romans on an existing Etruscan route (between Pitigliano, Sorano and Sovana) on the path of the existing Etruscan "Via Cava"). However we can speak of the Via Clodia from the end of the 3rd century BC, and that from 225 BC it was paved. The existing road was probably used as a way of penetration and conquest of Etruria by the Roman army begun in 310 BC. The road never seems to have had heavy traffic, only connecting Rome with Etruria inner north-western cities. The stretch between Bracciano and Oriolo Romano continues a straight line whose paving stones are found here and there, often uprooted. Some basalt sections appear in the territory of Tuscania, Oriolo Romano, Vejano and Blera.
Its course, for the first 11 miles, was the same as that of the Via Cassia
The ''Via Cassia'' ("way of Cassius") was an important Roman road striking out of the ''Via Flaminia'' near the Milvian Bridge in the immediate vicinity of Rome and, passing not far from Veii, traversed Etruria. The ''Via Cassia'' passed through ...
; it then diverged in a northwest direction and ran on the west side of the Lacus Sabatinus, past Forum Clodii and Blera
Blera is a small town and ''comune'' in the northern Lazio region of Italy. It was known during the Middle Ages as Bieda, an evolved form of its ancient name, which was restored in the twentieth century. It is the birthplace of Pope Sabinian; Pop ...
. According to some it ended in Saturnia. At Forum Cassii Forum Cassii was an ancient town of Etruria, in central Italy, situated on the Via Cassia, with the formation of which, from its name, it was certainly connected. It is known to us from the Itineraries, which place it 11 Roman miles beyond Sutrium ...
it may have rejoined the Via Cassia, and it seems to have taken the same line as the latter as far as Florentia (Florence
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany Regions of Italy, region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilan ...
). However, beyond Florentia, between Luca (Lucca
Lucca ( , ) is a city and ''comune'' in Tuscany, Central Italy, on the Serchio River, in a fertile plain near the Ligurian Sea. The city has a population of about 89,000, while its province has a population of 383,957.
Lucca is known as one ...
) and Luna, we find another Forum Clodii, and the Antonine itinerary gives the route from Luca to Rome as being by the Via Clodia, wrongly as regards the portion from Florentia southwards, but perhaps rightly as regards that from Luca to Florentia. Clodius Vestalis (c. 43) was perhaps responsible for the construction of the first portion and of that from Florentia to Luca (and Luna). Moreover, he also founded the two Fora Clodii. The name seems, in imperial times, to have to some extent driven out that of the Cassia, and both roads were administered, with other minor roads, by the same curator.
Via Clodia Nova
The Via Clodia Nova extension was constructed in 183 BC by the consulMarcus Claudius Marcellus
Marcus Claudius Marcellus (; 270 – 208 BC), five times elected as consul of the Roman Republic, was an important Roman military leader during the Gallic War of 225 BC and the Second Punic War. Marcellus gained the most prestigious award a Roma ...
. It started from Lucca and climbed the valley on the right bank of the river Serchio, crossed the Garfagnana region to the Piazza al Serchio, then passed over the col of Tea (955m) and through Fosdinovo before joining the Via Cassia, Luni and the port.
Stages
According to theTabula Peutingeriana
' (Latin for "The Peutinger Map"), also referred to as Peutinger's Tabula or Peutinger Table, is an illustrated ' (ancient Roman road map) showing the layout of the '' cursus publicus'', the road network of the Roman Empire.
The map is a 13th-ce ...
, the stages on the Via Clodia are:
*''Sextum'' (in the current area of Rome called The Retort and where the Via Cassia separated)
*''Careias'' (in the current area of Rome called Santa Maria di Galeria)
*''ad Nonas'' (near Vigna di Valle
''Vigna'' is a genus of plants in the legume family, Fabaceae, with a pantropical distribution.Aitawade, M. M., et al. (2012)Section ''Ceratotropis'' of subgenus ''Ceratotropis'' of ''Vigna'' (Leguminosae–Papilionoideae) in India with a new ...
)
*''Forum Clodii'' (near San Liberato di Bracciano)
*''Olera'' (Blera
Blera is a small town and ''comune'' in the northern Lazio region of Italy. It was known during the Middle Ages as Bieda, an evolved form of its ancient name, which was restored in the twentieth century. It is the birthplace of Pope Sabinian; Pop ...
)
*''Tuscana'' (Tuscania
Tuscania is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Viterbo, Lazio Region, Italy. Until the late 19th century the town was known as Toscanella.
History
Antiquity
According to the legend, Tuscania was founded by Aeneas' son, Ascanius, whe ...
)
*'' Marta'' (on lago di Bolsena
Lake Bolsena ( it, Lago di Bolsena) is a lake of volcano, volcanic origin in the northern part of the province of Viterbo called ''Alto Lazio'' ("Upper Latium") or ''Tuscia'' in central Italy. It is the largest volcanic lake in Europe. Roman ...
)
*''Maternum'' (Canino
Canino is a town and ''comune'' of Italy, in the province of Viterbo (northern Lazio) in the internal part of Maremma Laziale. It is west of Valentano and northwest of Viterbo.
It is also near the ancient Etruscan town of Vulci, and the des ...
or Ischia di Castro
Ischia di Castro is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Viterbo in the Italian region Latium, located about northwest of Rome and about northwest of Viterbo.
Ischia di Castro borders the following municipalities: Canino, Cellere, Far ...
)
*''Saturnia
Saturnia () is a spa town in Tuscany in north-central Italy that has been inhabited since ancient times. It is a ''frazione'' of the ''comune'' of Manciano, in the province of Grosseto. Famous for the spa which gives it its name, its population ...
''
Roman bridges
There are the remains of severalRoman bridge
The ancient Romans were the first civilization to build large, permanent bridges. Early Roman bridges used techniques introduced by Etruscan immigrants, but the Romans improved those skills, developing and enhancing methods such as arches and ...
s along the road, including the Ponte Piro and Ponte della Rocca.
See also
* Roman road *Roman bridge
The ancient Romans were the first civilization to build large, permanent bridges. Early Roman bridges used techniques introduced by Etruscan immigrants, but the Romans improved those skills, developing and enhancing methods such as arches and ...
* Roman engineering
References
{{Coord missing, ItalyClodia
Clodius is an alternate form of the Roman '' nomen'' Claudius, a patrician '' gens'' that was traditionally regarded as Sabine in origin. The alternation of ''o'' and ''au'' is characteristic of the Sabine dialect. The feminine form is Clodia.
R ...