Vi–ii–V–I on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
__NOTOC__In  The circle progression is commonly a succession through all seven
The circle progression is commonly a succession through all seven
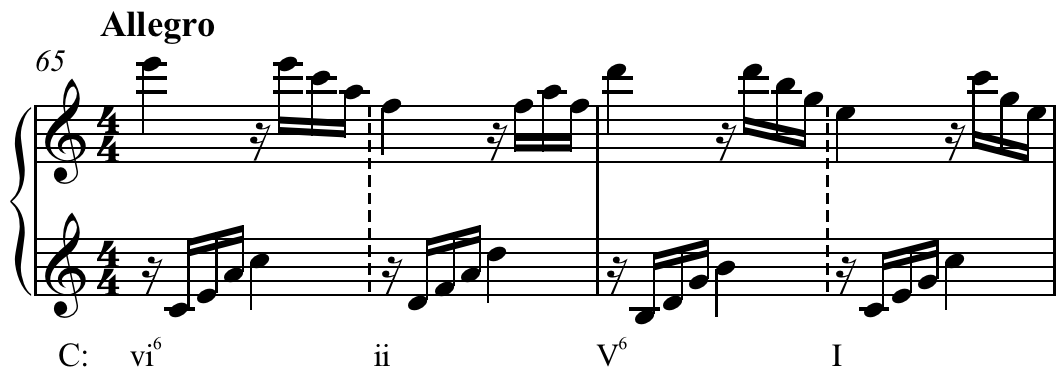 Pop songs that include the vi–ii–V–I progression include
Pop songs that include the vi–ii–V–I progression include
music
Music is generally defined as the art of arranging sound to create some combination of form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise expressive content. Exact definitions of music vary considerably around the world, though it is an aspe ...
, the vi–ii–V–I progression is a chord progression
In a musical composition, a chord progression or harmonic progression (informally chord changes, used as a plural) is a succession of chords. Chord progressions are the foundation of harmony in Western musical tradition from the common practice ...
(also called the circle progression for the circle of fifths
In music theory, the circle of fifths is a way of organizing the 12 chromatic pitches as a sequence of perfect fifths. (This is strictly true in the standard 12-tone equal temperament system — using a different system requires one interval of ...
, along which it travels). A vi–ii–V–I progression in C major (with inverted chords) is shown below.
It is "undoubtedly the most common and the strongest of all harmonic progressions" and consists of "adjacent roots
A root is the part of a plant, generally underground, that anchors the plant body, and absorbs and stores water and nutrients.
Root or roots may also refer to:
Art, entertainment, and media
* ''The Root'' (magazine), an online magazine focusing ...
in ascending fourth or descending fifth relationship", with movement by ascending perfect fourth
A fourth is a musical interval encompassing four staff positions in the music notation of Western culture, and a perfect fourth () is the fourth spanning five semitones (half steps, or half tones). For example, the ascending interval from C to ...
being equivalent to movement by descending perfect fifth
In music theory, a perfect fifth is the musical interval corresponding to a pair of pitches with a frequency ratio of 3:2, or very nearly so.
In classical music from Western culture, a fifth is the interval from the first to the last of five ...
due to inversion
Inversion or inversions may refer to:
Arts
* , a French gay magazine (1924/1925)
* ''Inversion'' (artwork), a 2005 temporary sculpture in Houston, Texas
* Inversion (music), a term with various meanings in music theory and musical set theory
* ...
.Bruce Benward and Marilyn Nadine Saker, ''Music In Theory and Practice'', seventh edition, 2 vols. + 2 sound discs (Boston: McGraw-Hill, 2003) 1:178. . For instance, in C major, the chords are Am–Dm–G–C, which have roots that descend by perfect fifth (or ascend by fourth), as shown below.William G Andrews and Molly Sclater (2000). ''Materials of Western Music Part 1'', p.227. .
: The circle progression is commonly a succession through all seven
The circle progression is commonly a succession through all seven diatonic
Diatonic and chromatic are terms in music theory that are most often used to characterize scales, and are also applied to musical instruments, intervals, chords, notes, musical styles, and kinds of harmony. They are very often used as a ...
chords of a diatonic scale
In music theory, a diatonic scale is any heptatonic scale that includes five whole steps (whole tones) and two half steps (semitones) in each octave, in which the two half steps are separated from each other by either two or three whole st ...
by fifths, including one progression by diminished fifth
Diminished may refer to:
*Diminution
In Western music and music theory, diminution (from Medieval Latin ''diminutio'', alteration of Latin ''deminutio'', decrease) has four distinct meanings. Diminution may be a form of embellishment in whic ...
, (in C: between F and B) and one diminished chord
In music theory, a diminished triad (also known as the minor flatted fifth) is a triad consisting of two minor thirds above the root. It is a minor triad with a lowered ( flattened) fifth. When using chord symbols, it may be indicated by the ...
(in C major, B), returning to the tonic at the end. A circle progression in C major is shown below.
Shorter progressions may be derived from this by selecting certain specific chords from the progression through all seven diatonic chords. The ii–V–I turnaround lies at the end of the circle progression, as does the vi–ii–V–I progression of root movement by descending fifths, which establishes tonality and also strengthens the key through the contrast of minor and major.
Examples
Examples of vi–ii–V–I are shown below. Pop songs that include the vi–ii–V–I progression include
Pop songs that include the vi–ii–V–I progression include Weezer
Weezer is an American rock band formed in Los Angeles, California, in 1992. Since 2001, the band has consisted of Rivers Cuomo (vocals, guitar, keyboards), Patrick Wilson (drums, backing vocals), Scott Shriner (bass guitar, keyboards, backing ...
's " Island in the Sun"
I‚àívi‚àíii‚àíV
I‚àívi‚àíii‚àíV is one of the most common chord progressions injazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with its roots in blues and ragtime. Since the 1920s Jazz Age, it has been recognized as a m ...
. The progression is often used as a turnaround, occurring as the last two bars of a chorus
Chorus may refer to:
Music
* Chorus (song) or refrain, line or lines that are repeated in music or in verse
* Chorus effect, the perception of similar sounds from multiple sources as a single, richer sound
* Chorus form, song in which all verse ...
or section. The I‚àívi‚àíii‚àíV chord progression occurs as a two-bar pattern in the A section of the rhythm changes, the progression based on George Gershwin
George Gershwin (; born Jacob Gershwine; September 26, 1898 – July 11, 1937) was an American composer and pianist whose compositions spanned popular, jazz and classical genres. Among his best-known works are the orchestral compositions ' ...
's "I Got Rhythm
"I Got Rhythm" is a piece composed by George Gershwin with lyrics by Ira Gershwin and published in 1930, which became a jazz standard. Its chord progression, known as the " rhythm changes", is the foundation for many other popular jazz tunes suc ...
". It can be varied as well: according to Mark Levine
Mark Andrew LeVine is an American historian, musician, writer, and professor. He is a professor of history at the University of California, Irvine.
Education
LeVine received his B.A. in comparative religion and biblical studies from Hunter ...
, " day's players usually play a dominant 7th chord rather than a minor 7th chord as the VI chord in a I-VI-II-V."
In the jazz minor scale
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with its roots in blues and ragtime. Since the 1920s Jazz Age, it has been recognized as a major f ...
, the diatonic progression below is possible.Arnold, Bruce E. (2001). ''Music Theory Workbook for Guitar: Scale Construction'', p.12. .
:
:
See also
*Approach chord
In music, an approach chord (also chromatic approach chord and dominant approach chord) is a chord one half-step higher or lower than the goal, especially in the context of turnarounds and cycle-of-fourths progressions, for example the two ...
*Predominant chord
In music theory, a predominant chord (also pre-dominant) is any chord which normally resolves to a dominant chord.Benward & Saker (2009). ''Music in Theory and Practice: Volume II'', Glossary, p.359. Eighth Edition. . "Any chord in functional ...
*Dominant (music)
In music, the dominant is the fifth scale degree () of the diatonic scale. It is called the ''dominant'' because it is second in importance to the first scale degree, the tonic. In the movable do solfège system, the dominant note is sung as " ...
* Extended dominant
* Ragtime progression
*Tadd Dameron turnaround
In jazz, the Tadd Dameron turnaround, named for Tadd Dameron, "is a very common turnaround in the jazz idiom",Coker, et al (1982). ''Patterns for Jazz: A Theory Text for Jazz Composition and Improvisation'', p.118. . derived from a typical I‚à ...
Sources
{{DEFAULTSORT:Vi-ii-V-I Progression Chord progressions de:Quintfallsequenz fi:Jazzpiano#Kvinttiympyrä