VERITAS (spacecraft) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
VERITAS (Venus Emissivity, Radio Science, InSAR, Topography, and Spectroscopy) is an upcoming mission from
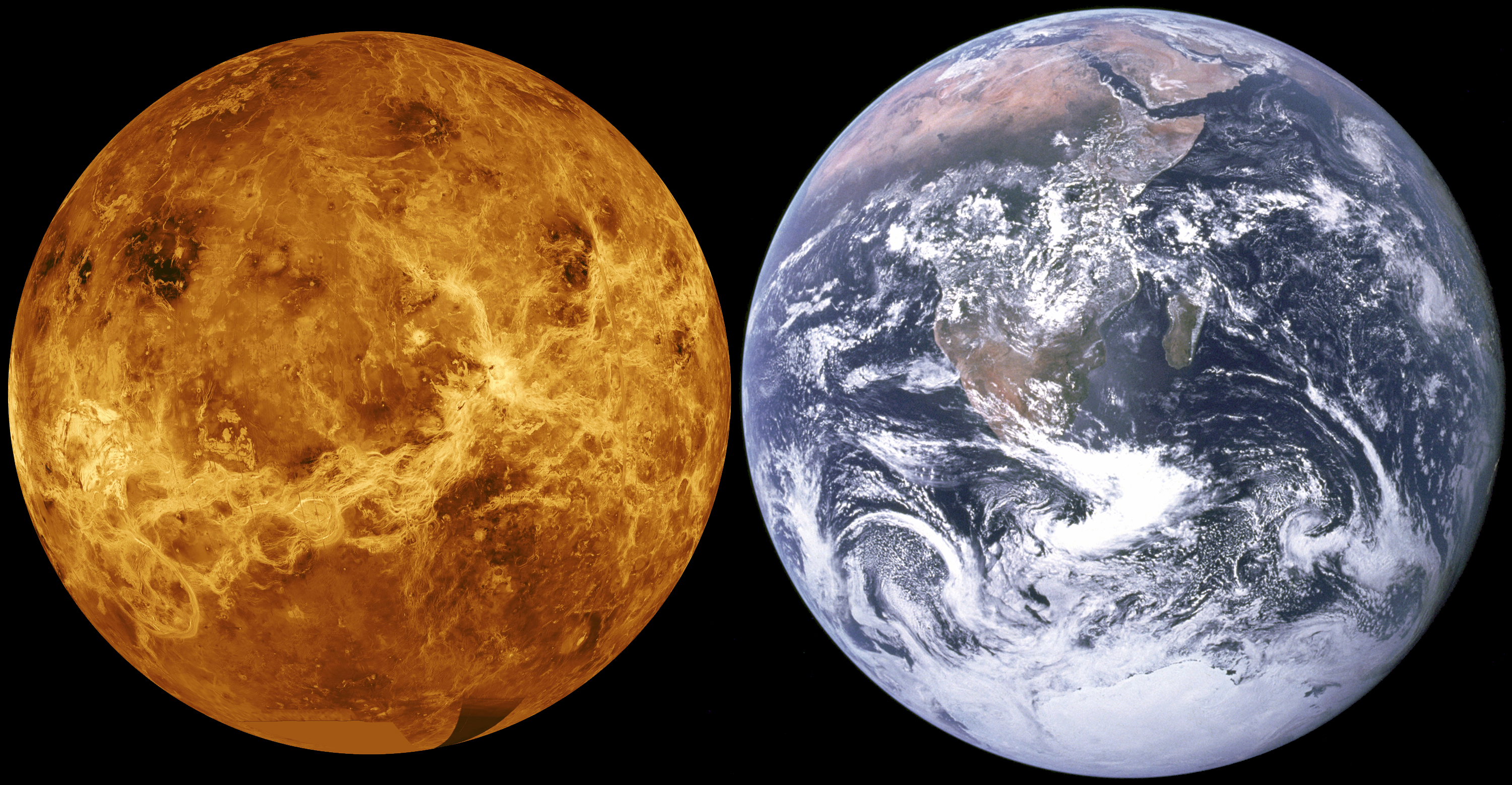 VERITAS will gather data to help scientists to answer three primary questions about Venus:
# How has its geology evolved over time?
# What geologic processes are currently operating on it?
# Has water been present on or near its surface?
Understanding Venus's geology is of significant scientific interest because of its similarities to Earth. Venus's size, age, and composition are all broadly similar to Earth's, but its environment is significantly different and less hospitable to life. Understanding Venus's geologic evolution therefore will help answer questions about the formation of planets hospitable to life. A key step in developing an understanding of this evolution is an investigation of Venus's current geology. Current data is highly suggestive of recent and active volcanism on Venus, but the extent of this volcanic activity is not completely known. Moreover, it is unknown to what degree surface water was historically present on Venus and what role subsurface water plays in Venus's modern geology.
VERITAS will gather data to help scientists to answer three primary questions about Venus:
# How has its geology evolved over time?
# What geologic processes are currently operating on it?
# Has water been present on or near its surface?
Understanding Venus's geology is of significant scientific interest because of its similarities to Earth. Venus's size, age, and composition are all broadly similar to Earth's, but its environment is significantly different and less hospitable to life. Understanding Venus's geologic evolution therefore will help answer questions about the formation of planets hospitable to life. A key step in developing an understanding of this evolution is an investigation of Venus's current geology. Current data is highly suggestive of recent and active volcanism on Venus, but the extent of this volcanic activity is not completely known. Moreover, it is unknown to what degree surface water was historically present on Venus and what role subsurface water plays in Venus's modern geology.
 VERITAS will collect data to help answer these questions in several ways. High-resolution imagery will be obtained using an X-band radar configured as a single pass
VERITAS will collect data to help answer these questions in several ways. High-resolution imagery will be obtained using an X-band radar configured as a single pass
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
's Jet Propulsion Laboratory
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) is a federally funded research and development center and NASA field center in the City of La Cañada Flintridge, California, United States.
Founded in the 1930s by Caltech researchers, JPL is owned by NASA an ...
(JPL) to map the surface of planet Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never f ...
in high resolution. The combination of topography, near-infrared spectroscopy, and radar image data will provide knowledge of Venus's tectonic and impact history, gravity, geochemistry, the timing and mechanisms of volcanic resurfacing, and the mantle processes responsible for them.
Proposal history
VERITAS was one of dozens of proposals submitted in 2015 to potentially become the 13th mission ofNASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
’s Discovery Program. Suzanne Smrekar of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) is a federally funded research and development center and NASA field center in the City of La Cañada Flintridge, California, United States.
Founded in the 1930s by Caltech researchers, JPL is owned by NASA an ...
(JPL) would serve as the principal investigator
In many countries, the term principal investigator (PI) refers to the holder of an independent grant and the lead researcher for the grant project, usually in the sciences, such as a laboratory study or a clinical trial. The phrase is also often us ...
, and JPL would be the managing agency. On 30 September 2015, VERITAS was selected as one of five finalists. On 4 January 2017, two other proposals to study small bodies, ''Lucy'' and ''Psyche'', were selected as the 13th and 14th Discovery missions, respectively.
VERITAS was again proposed for the Discovery Program in 2019, and was selected for Phase A funding on 13 February 2020. On 2 June 2021, it was selected, along with '' DAVINCI+'', to fly as one of the next Discovery missions. Each mission will get approximately US$500 million in funding. VERITAS was originally planned to be launched between the years 2028 and 2030. However, work on the mission was put on hold in November 2022, and the launch was delayed by at least three years (to no earlier than 2031), after an independent review of the ''Psyche'' mission found significant institutional issues at NASA and JPL.
Mission
 VERITAS will gather data to help scientists to answer three primary questions about Venus:
# How has its geology evolved over time?
# What geologic processes are currently operating on it?
# Has water been present on or near its surface?
Understanding Venus's geology is of significant scientific interest because of its similarities to Earth. Venus's size, age, and composition are all broadly similar to Earth's, but its environment is significantly different and less hospitable to life. Understanding Venus's geologic evolution therefore will help answer questions about the formation of planets hospitable to life. A key step in developing an understanding of this evolution is an investigation of Venus's current geology. Current data is highly suggestive of recent and active volcanism on Venus, but the extent of this volcanic activity is not completely known. Moreover, it is unknown to what degree surface water was historically present on Venus and what role subsurface water plays in Venus's modern geology.
VERITAS will gather data to help scientists to answer three primary questions about Venus:
# How has its geology evolved over time?
# What geologic processes are currently operating on it?
# Has water been present on or near its surface?
Understanding Venus's geology is of significant scientific interest because of its similarities to Earth. Venus's size, age, and composition are all broadly similar to Earth's, but its environment is significantly different and less hospitable to life. Understanding Venus's geologic evolution therefore will help answer questions about the formation of planets hospitable to life. A key step in developing an understanding of this evolution is an investigation of Venus's current geology. Current data is highly suggestive of recent and active volcanism on Venus, but the extent of this volcanic activity is not completely known. Moreover, it is unknown to what degree surface water was historically present on Venus and what role subsurface water plays in Venus's modern geology.
 VERITAS will collect data to help answer these questions in several ways. High-resolution imagery will be obtained using an X-band radar configured as a single pass
VERITAS will collect data to help answer these questions in several ways. High-resolution imagery will be obtained using an X-band radar configured as a single pass interferometric synthetic aperture radar Interferometric synthetic aperture radar, abbreviated InSAR (or deprecated IfSAR), is a radar technique used in geodesy and remote sensing. This geodetic method uses two or more synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images to generate maps of surface defo ...
(InSAR). This radar data will be coupled with a multispectral
Multispectral imaging captures image data within specific wavelength ranges across the electromagnetic spectrum. The wavelengths may be separated by filters or detected with the use of instruments that are sensitive to particular wavelengths, ...
near-infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of Light, visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from ...
(NIR) emissivity mapping capability. VERITAS will map surface topography with a spatial resolution of 250m and 5m vertical accuracy, and generate radar imagery with 30m spatial resolution. This high-resolution imaging data will allow scientists to locate active volcanic eruptions, to understand the age and composition of features on the planet's surface, and better understand the planet's overall geology. The spacecraft's communication system will also be used to perform a gravity science experiment to investigate variations in Venus' gravitational field. The spacecraft's telecom system will be used to map gravity strength at Venus' surface, providing a uniform resolution of better than 160 km. The data will provide an estimate of Venus' core size and information about topographic features that lie underneath the planet's surface.
Spacecraft
VERITAS is designed to produce global, high-resolutiontopography
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the land forms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps.
Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary sc ...
and imaging of Venus' surface and produce the first maps of deformation and global surface composition, thermal emissivity, and gravity fields. Onboard the spacecraft will be two scientific instrument
A scientific instrument is a device or tool used for scientific purposes, including the study of both natural phenomena and theoretical research.
History
Historically, the definition of a scientific instrument has varied, based on usage, laws, an ...
s, the Venus Emissivity Mapper (VEM) and Venus Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (VISAR).
* VEM (Venus Emissivity Mapper) is designed to map the surface emissivity using six spectral bands in five atmospheric windows that see through the clouds. It will be built by the German Aerospace Center
The German Aerospace Center (german: Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt e.V., abbreviated DLR, literally ''German Center for Air- and Space-flight'') is the national center for aerospace, energy and transportation research of Germany ...
(DLR). VEM also carries eight atmospheric bands for calibration and detection of near-surface water vapor
(99.9839 °C)
, -
, Boiling point
,
, -
, specific gas constant
, 461.5 J/( kg·K)
, -
, Heat of vaporization
, 2.27 MJ/kg
, -
, Heat capacity
, 1.864 kJ/(kg·K)
Water vapor, water vapour or aqueous vapor is the gaseous p ...
.
* VISAR (Venus Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar) is designed to generate global data sets for topography (250 m horizontal by 5 m vertical accuracy) and SAR imaging at 30 m resolution with targeted resolution at 15 m. It will create the first planetary active surface deformation map (1.5 cm vertical).
In addition to these two instruments, the spacecraft will also carry the Deep Space Atomic Clock-2 as a secondary payload. The Deep Space Atomic Clock-2 is the successor to the Deep Space Atomic Clock payload flown on the STP-2
The Space Test Program (STP) is the primary provider of spaceflight for the United States Department of Defense (DoD) space science and technology community. STP is managed by a group within the Advanced Systems and Development Directorate, a d ...
mission in June 2019, and is intended to provide highly precise timing for deep space missions.
See also
*List of missions to Venus
There have been 46 (including gravity-assist flybys) space missions to the planet Venus. Missions to Venus constitute part of the exploration of Venus.
List
As of 2020, the Soviet Union, United States, European Space Agency and Japan have con ...
* ''Magellan
Ferdinand Magellan ( or ; pt, Fernão de Magalhães, ; es, link=no, Fernando de Magallanes, ; 4 February 1480 – 27 April 1521) was a Portuguese explorer. He is best known for having planned and led the 1519 Spanish expedition to the East ...
'', the most recent previous NASA mission dedicated to Venus (1989-1993)
* '' DAVINCI+'', a Venus atmospheric probe, selected alongside VERITAS for the Discovery program
* ''EnVision
Envision may refer to:
Organizations
* Envision EMI, a management company based in Virginia, USA
* Envision Energy, a wind turbine manufacturer and energy technology company based in Shanghai, China
* Envision Financial, a financial institution ...
'', an ESA
, owners =
, headquarters = Paris, Île-de-France, France
, coordinates =
, spaceport = Guiana Space Centre
, seal = File:ESA emblem seal.png
, seal_size = 130px
, image = Views in the Main Control Room (120 ...
mission to Venus in the same timeframe
References
{{Planetary Missions Program Office, Discovery=y Discovery program proposals Proposed space probes Missions to Venus 2031 in science