V1494 Aquilae on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 V1494 Aquilae or Nova Aquilae 1999 b was a nova which occurred during 1999 in the constellation Aquila and reached a brightness of
V1494 Aquilae or Nova Aquilae 1999 b was a nova which occurred during 1999 in the constellation Aquila and reached a brightness of
www.tsm.toyama.toyama.jp
Simbad
Image V1494 Aquilae
V1494 Aql
International Variable Star Index
V1494 Aql
AAVSO comparison chart {{DEFAULTSORT:V1494 Aquilae Astronomical X-ray sources Novae Aquila (constellation) 1999 in science Aquilae, V1494
 V1494 Aquilae or Nova Aquilae 1999 b was a nova which occurred during 1999 in the constellation Aquila and reached a brightness of
V1494 Aquilae or Nova Aquilae 1999 b was a nova which occurred during 1999 in the constellation Aquila and reached a brightness of magnitude
Magnitude may refer to:
Mathematics
*Euclidean vector, a quantity defined by both its magnitude and its direction
*Magnitude (mathematics), the relative size of an object
*Norm (mathematics), a term for the size or length of a vector
*Order of ...
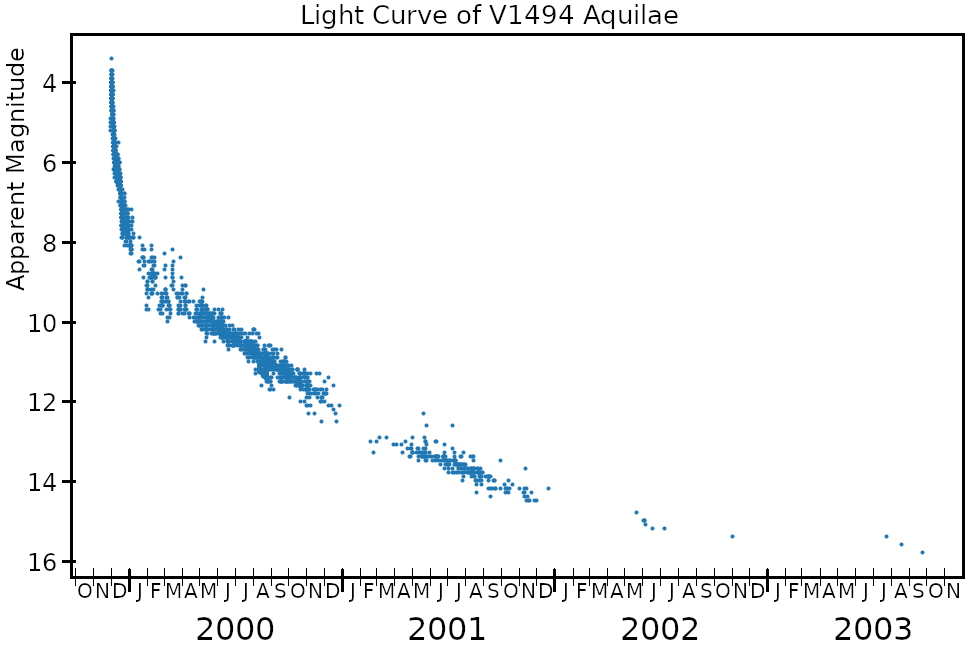
3.9 on 2 December 1999. making it easily visible to the naked eye. The nova was discovered with 14×100 binoculars by Alfredo Pereira of Cabo da Roca
Cabo da Roca () or Cape Roca is a cape which forms the westernmost point of the Sintra Mountain Range, of mainland Portugal, of continental Europe, and of the Eurasian landmass. It is situated in the municipality of Sintra, near Azóia, in th ...
, Portugal at 18:50 UT on 1 December 1999, when it had a visual magnitude of 6.0.
V1494 Aquilae is classified as a fast nova, meaning it faded from peak brightness by more than 3 magnitudes in less than 100 days. During its decline, V1494 Aql produced unusual variations in its x-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
radiation, including a bright burst lasting several minutes. During 2000, the x-ray spectrum developed from a hard (high energy) emission-line spectrum to a spectrum typical of a super soft X-ray source A luminous supersoft X-ray source (SSXS, or SSS) is an astronomical source that emits only low energy (i.e., soft) X-rays. Soft X-rays have energies in the 0.09 to 2.5 keV range, whereas hard X-rays are in the 1–20 keV range. SSSs emit few or no ...
. The x-ray intensity varied with a period of about 40 minutes, probably due to pulsations induced in the white dwarf by its re-kindled hydrogen fusion.
All novae are binary systems with two stars orbiting so close to each other that one star, the "donor" star transfers matter to the other star which is a white dwarf
A white dwarf is a stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very dense: its mass is comparable to the Sun's, while its volume is comparable to the Earth's. A white dwarf's faint luminosity comes ...
. In the case of V1494 the white dwarf has a mass of 1.20 , and it is accreting mass from the donor star at a rate of . The stars' orbital period is 3.23 hours, and the system is an eclipsing binary with two brightness minima each orbit, one 0.5 and one 0.1 magnitudes deep. This apparently is a measurement of two stars of approximately equal brightness, the nova and a companion to the south east. Measuring only the brightness of the nova, the eclipses are about two magnitudes deep. The white dwarf is probably an oxygen-neon-magnesium type.
Unlike some novae, the material ejected from V1494 Aquilae has not formed a visible nebula around the star. However, a shell approximately across has been detected spectroscopically in H-alpha
H-alpha (Hα) is a specific deep-red visible spectral line
A spectral line is a dark or bright line in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum, resulting from emission or absorption of light in a narrow frequency range, compared wit ...
emission.
The distance to V1494 Aquilae has been estimated by different methods. Early estimates were based on assumptions about the luminosity of the nova and gave distances around . Later models assumed distances of up to . Comparison of the measured shell size with the observed expansion velocity give a distance of . Gaia DR2
The ''Gaia'' catalogues are star catalogues created using the results obtained by '' Gaia'' space telescope.
The catalogues are released in stages that will contain increasing amounts of information; the early releases also miss some stars, espec ...
published a parallax of , corresponding to a distance of . Gaia EDR3
The ''Gaia'' catalogues are star catalogues created using the results obtained by '' Gaia'' space telescope.
The catalogues are released in stages that will contain increasing amounts of information; the early releases also miss some stars, espec ...
published a parallax of , corresponding to a distance around .
References
External links
www.tsm.toyama.toyama.jp
Simbad
Image V1494 Aquilae
V1494 Aql
International Variable Star Index
V1494 Aql
AAVSO comparison chart {{DEFAULTSORT:V1494 Aquilae Astronomical X-ray sources Novae Aquila (constellation) 1999 in science Aquilae, V1494