Uttrakhand on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Uttarakhand ( , or ; , ), also known as Uttaranchal ( ; the official name until 2007), is a

 By the medieval period, the region was consolidated under the
By the medieval period, the region was consolidated under the  Uttarakhand is also well known for the mass agitation of the 1970s that led to the formation of the Chipko environmental movement and other social movements. Though primarily a
Uttarakhand is also well known for the mass agitation of the 1970s that led to the formation of the Chipko environmental movement and other social movements. Though primarily a
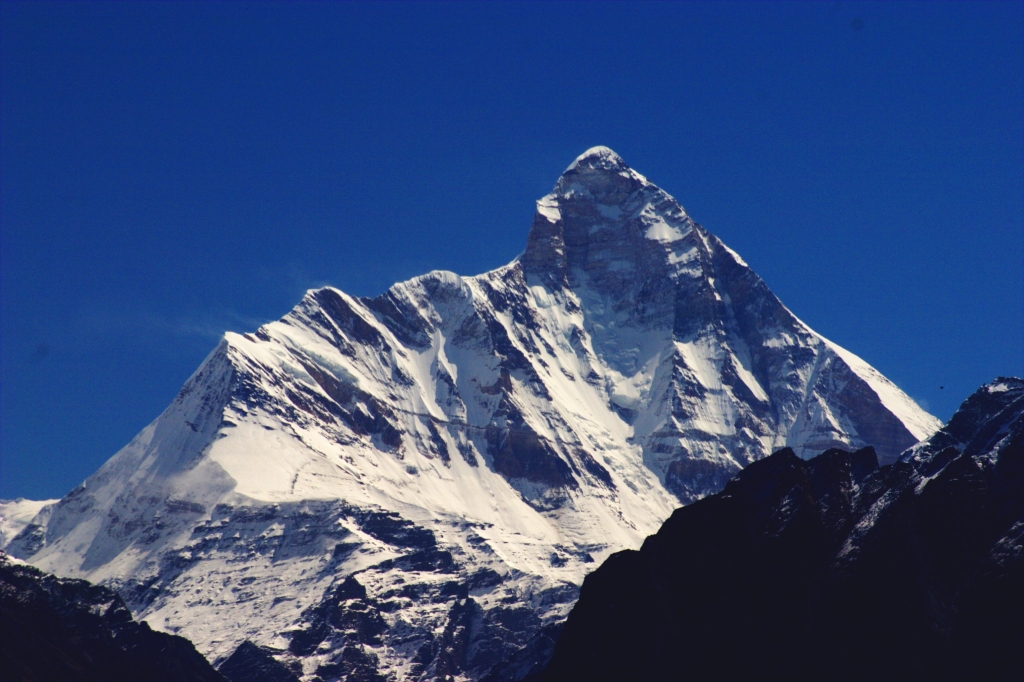 Uttarakhand has a total area of , of which 86% is mountainous and 65% is covered by forest. Most of the northern part of the state is covered by high
Uttarakhand has a total area of , of which 86% is mountainous and 65% is covered by forest. Most of the northern part of the state is covered by high  Uttarakhand lies on the southern slope of the Himalaya range, and the climate and vegetation vary greatly with elevation, from glaciers at the highest elevations to subtropical forests at the lower elevations. The highest elevations are covered by ice and bare rock. Below them, between are the
Uttarakhand lies on the southern slope of the Himalaya range, and the climate and vegetation vary greatly with elevation, from glaciers at the highest elevations to subtropical forests at the lower elevations. The highest elevations are covered by ice and bare rock. Below them, between are the
Moschus chrysogaster.jpg, Alpine Musk Deer (''Moschus chrysogaster'')
Golden mahseer (Tor putitora) Babai River.jpg,
Uttarakhand has a diversity of flora and fauna. It has a recorded forest area of , which constitutes 65% of the total area of the state. Uttarakhand is home to rare species of plants and animals, many of which are protected by sanctuaries and reserves.
Brahmakamal Kaluvinayak Chamoli Uttarakhand 2014-08-23.jpg, Brahma Kamal (''Saussurea obvallata'')
Rhododendron in full bloom! (8620051426).jpg, Burans (''Rhododendron arboreum'')
Kafal(blackberry) 2014-06-04 08-48.jpg,
state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
in the northern part of India. It is often referred to as the "Devbhumi" (literally 'Land of the Gods') due to its religious significance and numerous Hindu temple
A Hindu temple, or ''mandir'' or ''koil'' in Indian languages, is a house, seat and body of divinity for Hindus. It is a structure designed to bring human beings and gods together through worship, sacrifice, and devotion.; Quote: "The Hin ...
s and pilgrimage centres found throughout the state. Uttarakhand is known for the natural environment of the Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 10 ...
, the Bhabar and the Terai
, image =Terai nepal.jpg
, image_size =
, image_alt =
, caption =Aerial view of Terai plains near Biratnagar, Nepal
, map =
, map_size =
, map_alt =
, map_caption =
, biogeographic_realm = Indomalayan realm
, global200 = Terai-Duar savanna a ...
regions. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region
The Tibet Autonomous Region or Xizang Autonomous Region, often shortened to Tibet or Xizang, is a province-level autonomous region of the People's Republic of China in Southwest China. It was overlayed on the traditional Tibetan regions of � ...
of China to the north; the Sudurpashchim Province of Nepal
Nepal (; ne, :ne:नेपाल, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in S ...
to the east; the Indian states of Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh (; , 'Northern Province') is a state in northern India. With over 200 million inhabitants, it is the most populated state in India as well as the most populous country subdivision in the world. It was established in 1950 ...
to the south and Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh (; ; "Snow-laden Mountain Province") is a state in the northern part of India. Situated in the Western Himalayas, it is one of the thirteen mountain states and is characterized by an extreme landscape featuring several peaks ...
to the west and north-west. The state is divided into two divisions, Garhwal and Kumaon Kumaon or Kumaun may refer to:
* Kumaon division, a region in Uttarakhand, India
* Kumaon Kingdom, a former country in Uttarakhand, India
* Kumaon, Iran, a village in Isfahan Province, Iran
* , a ship of the Royal Indian Navy during WWII
See also
...
, with a total of 13 districts. The winter capital of Uttarakhand is Dehradun, the largest city of the state, which is a rail head. Bhararisain
Bhararisain is the summer capital of the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It is located in Chamoli district's Gairsain tehsil, around 14 km from the town of Gairsain.
History
On Uttarakhand's statehood, some activists considered Gairsain an idea ...
, a town in Chamoli district
Chamoli district is a district of the Uttarakhand state of India. It is bounded by the Tibet region to the north, and by the Uttarakhand districts of Pithoragarh and Bageshwar to the east, Almora to the south, Pauri Garhwal to the southwest, ...
, is the summer capital of Uttarakhand. The High Court of the state is located in Nainital
Nainital ( Kumaoni: ''Naintāl''; ) is a city and headquarters of Nainital district of Kumaon division, Uttarakhand, India. It is the judicial capital of Uttarakhand, the High Court of the state being located there and is the headquarters o ...
.
Archaeological evidence supports the existence of humans in the region since prehistoric times. The region formed a part of the Uttarakuru
Uttarakuru ( sa, उत्तर कुरु; ) is the name of a dvipa ("continent") in ancient Hindu and Buddhist mythology as well as Jain cosmology. The Uttarakuru country or Uttara Kuru Kingdom and its people are sometimes described as belong ...
Kingdom during the Vedic age
The Vedic period, or the Vedic age (), is the period in the late Bronze Age and early Iron Age of the history of India when the Vedic literature, including the Vedas (ca. 1300–900 BCE), was composed in the northern Indian subcontinent, betw ...
of Ancient India
According to consensus in modern genetics, anatomically modern humans first arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa between 73,000 and 55,000 years ago. Quote: "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by m ...
. Among the first major dynasties of Kumaon were the Kuninda
The Kingdom of Kuninda (or Kulinda in ancient literature) was an ancient central Himalayan kingdom documented from around the 2nd century BCE to the 3rd century, located in the southern areas of modern Himachal Pradesh and far western areas of U ...
s in the second century BCE who practiced an early form of Shaivism
Shaivism (; sa, शैवसम्प्रदायः, Śaivasampradāyaḥ) is one of the major Hindu traditions, which worships Shiva as the Supreme Being. One of the largest Hindu denominations, it incorporates many sub-traditions rangi ...
. Ashokan edicts
The Edicts of Ashoka are a collection of more than thirty inscriptions on the Pillars of Ashoka, as well as boulders and cave walls, attributed to Emperor Ashoka of the Maurya Empire who reigned from 268 BCE to 232 BCE. Ashoka used the expre ...
at Kalsi show the early presence of Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religions, Indian religion or Indian philosophy#Buddhist philosophy, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha. ...
in this region. During the medieval period, the region was consolidated under the Katyuri rulers of Kumaon also known as 'Kurmanchal Kingdom'. After the fall of Katyuris, the region was divided into the Kumaon Kingdom
Kumaon Kingdom was an independent Himalayan kingdom in the eastern region of present-day Uttarakhand state of India. It was established around 7th century and remained an independent and sovereign kingdom until 1791.
Etymology
Kumaon is beli ...
and the Garhwal Kingdom
Garhwal Kingdom was an independent Himalayan kingdom in the current north-western Himalayan state of Uttarakhand, India, founded in 688 CE by Kanak Pal, the progenitor of the Panwar dynasty that ruled over the kingdom uninterrupted until ...
. In 1816, most of modern Uttarakhand was ceded to the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
as part of the Treaty of Sugauli
The Treaty of Sugauli (also spelled Sugowlee, Sagauli and Segqulee), the treaty that established the boundary line of Nepal, was signed on 4 March 1816 between the East India Company and Guru Gajaraj Mishra following the Anglo-Nepalese War ...
. Although the erstwhile hill kingdoms of Garhwal and Kumaon were traditional rivals, the proximity of different neighbouring ethnic groups and the inseparable and complementary nature of their geography, economy, culture, language, and traditions created strong bonds between the two regions, which further strengthened during the Uttarakhand movement
The
Uttarakhand movement refers to the events of statehood activism within the undivided state of Uttar Pradesh which ultimately resulted in the formation of Uttarakhand, India as a separate state. Uttarakhand became a state on 9 November 2000. ...
for statehood in the 1990s.
The natives of the state are generally called Uttarakhandi, or more specifically either Garhwali or Kumaoni by their region of origin. According to the 2011 Census of India
The 2011 Census of India or the 15th Indian Census was conducted in two phases, house listing and population enumeration. The House listing phase began on 1 April 2010 and involved the collection of information about all buildings. Information ...
, Uttarakhand has a population of 10,086,292, making it the 20th most populous state in India.
Etymology
Uttarakhand's name is derived from theSanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
words ''uttara'' () meaning 'north', and ''khaṇḍa'' () meaning 'land', altogether simply meaning 'Northern Land'. The name finds mention in early Hindu scriptures
Hindu texts are manuscripts and voluminous historical literature which are related to any of the diverse traditions within Hinduism. A few of these texts are shared across these traditions and they are broadly considered Hindu scriptures. These ...
as the combined region of "Kedarkhand" (present day Garhwal) and "Manaskhand" (present day Kumaon Kumaon or Kumaun may refer to:
* Kumaon division, a region in Uttarakhand, India
* Kumaon Kingdom, a former country in Uttarakhand, India
* Kumaon, Iran, a village in Isfahan Province, Iran
* , a ship of the Royal Indian Navy during WWII
See also
...
). Uttarakhand was also the ancient Puranic
Purana (; sa, , '; literally meaning "ancient, old"Merriam-Webster's Encyclopedia of Literature (1995 Edition), Article on Puranas, , page 915) is a vast genre of Indian literature about a wide range of topics, particularly about legends an ...
term for the central stretch of the Indian Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 10 ...
.Kandari, O. P., & Gusain, O. P. (Eds.). (2001). Garhwal Himalaya: Nature, Culture & Society. Srinagar, Garhwal: Transmedia.
However, the region was given the name ''Uttaranchal'' by the Bharatiya Janata Party
The Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP; ; ) is a political party in India, and one of the two major Indian political parties alongside the Indian National Congress. Since 2014, it has been the ruling political party in India under Narendra Mod ...
-led union government
The Government of India ( ISO: ; often abbreviated as GoI), known as the Union Government or Central Government but often simply as the Centre, is the national government of the Republic of India, a federal democracy located in South Asia, ...
and Uttarakhand state government when they started a new round of state reorganisation in 1998. Chosen for its allegedly less-separatist connotations, the name change generated enormous controversy among many activists for a separate state who saw it as a political act. The name Uttarakhand remained popular in the region, even while Uttaranchal was promulgated through official usage.
In August 2006, Union Council of Ministers
The Union Council of Ministers Article 58 of the ''Constitution of India'' is the principal executive organ of the Government of India, which is responsible for being the senior decision making body of the executive branch. It is chaired by t ...
assented to the demands of the Uttaranchal Legislative Assembly and leading members of the Uttarakhand statehood movement to rename Uttaranchal state as Uttarakhand. Legislation to that effect was passed by the Uttaranchal Legislative Assembly in October 2006, and the Union Council of Ministers brought in the bill in the winter session of Parliament. The bill was passed by Parliament and signed into law by then President A. P. J. Abdul Kalam in December 2006, and since 1 January 2007 the state has been known as Uttarakhand.
History
Ancient rock paintings, rock shelters,paleolithic age
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic (), also called the Old Stone Age (from Greek: παλαιός ''palaios'', "old" and λίθος '' lithos'', "stone"), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone to ...
stone tools (hundreds of thousands of years old), and megaliths
A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. There are over 35,000 in Europe alone, located widely from Sweden to the Mediterranean sea.
The ...
provide evidence that the mountains of the region have been inhabited since prehistoric times. There are also archaeological remains that show the existence of early Vedic
upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the '' Atharvaveda''.
The Vedas (, , ) are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed in Vedic Sanskrit, the texts constitute the ...
(c. 1500 BCE) practices in the area.
The Pauravas
The Pauravas were an ancient dynasty on the Indus (present-day India and Pakistan) to which King Porus may have belonged.
Porus and the Pauravas
The origins of the Pauravas are still disputed. The Pauravas may be related to the Puru tribe, du ...
, Khasas
Khasas (Devanāgarī: खश; ') were an ancient Indo-Aryan tribe and a late Janapada kingdom from Himalayan regions of northern Indian subcontinent mentioned in the various historical Indian inscriptions and ancient Indian Hindu and Tibetan lite ...
, Kirata
The Kirāta ( sa, किरात) is a generic term in Sanskrit literature for people who had territory in the mountains, particularly in the Himalayas and Northeast India and who are believed to have been Sino-Tibetan in origin. The meaning o ...
s, Nandas
The Nanda dynasty ruled in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent during the fourth century BCE, and possibly during the fifth century BCE. The Nandas overthrew the Shaishunaga dynasty in the Magadha region of eastern India, and expanded ...
, Mauryas
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until 1 ...
, Kushanas
The Kushan Empire ( grc, Βασιλεία Κοσσανῶν; xbc, Κυϸανο, ; sa, कुषाण वंश; Brahmi: , '; BHS: ; xpr, 𐭊𐭅𐭔𐭍 𐭇𐭔𐭕𐭓, ; zh, 貴霜 ) was a syncretic empire, formed by the Yuezhi, i ...
, Kunindas, Guptas, Karkotas, Palas
A ''palas'' () is a German term for the imposing or prestigious building of a medieval ''Pfalz'' or castle that contained the great hall. Such buildings appeared during the Romanesque period (11th to 13th century) and, according to Thompson ...
, Gurjara-Pratiharas, Katyuris, Raikas, Chands, Parmar
Parmar is a Rajput clan found in Northern and Central India, especially in Rajasthan, Punjab, Haryana, Kutch, Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh and North Maharashtra.
See also
* Paramara Dynasty
* Panwar Dynasty
* Pawar
* Pan ...
s or Panwars, Mallas, Shahs and the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
have ruled Uttarakhand in turns.
Among the first major dynasties of Garhwal and Kumaon were the Kunindas in the second century BCE who practised an early form of Shaivism
Shaivism (; sa, शैवसम्प्रदायः, Śaivasampradāyaḥ) is one of the major Hindu traditions, which worships Shiva as the Supreme Being. One of the largest Hindu denominations, it incorporates many sub-traditions rangi ...
and traded salt with Western Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa, Taman ...
. It is evident from the Ashoka
Ashoka (, ; also ''Asoka''; 304 – 232 BCE), popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was the third emperor of the Maurya Empire of Indian subcontinent during to 232 BCE. His empire covered a large part of the Indian subcontinent, s ...
n edict at Kalsi in Western Garhwal that Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religions, Indian religion or Indian philosophy#Buddhist philosophy, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha. ...
made inroads in this region. Shamanic Hindu practices deviating from Hindu orthodoxy also persisted here. However, Garhwal and Kumaon were restored to nominal Vedic Hindu rule due to the travels of Shankaracharya
Shankaracharya ( sa, शङ्कराचार्य, , " Shankara-''acharya''") is a religious title used by the heads of amnaya monasteries called mathas in the Advaita Vedanta tradition of Hinduism. The title derives from Adi Shankara; te ...
and the arrival of migrants from the plains.
Between the 4th and 14th centuries, the Katyuri dynasty dominated lands of varying extent from the Katyur valley (modern-day Baijnath) in Kumaon. The historically significant temples at Jageshwar are believed to have been built by the Katyuris and later remodelled by the Chands. Other peoples of the Tibeto-Burman
The Tibeto-Burman languages are the non- Sinitic members of the Sino-Tibetan language family, over 400 of which are spoken throughout the Southeast Asian Massif ("Zomia") as well as parts of East Asia and South Asia. Around 60 million people spea ...
group known as Kirata
The Kirāta ( sa, किरात) is a generic term in Sanskrit literature for people who had territory in the mountains, particularly in the Himalayas and Northeast India and who are believed to have been Sino-Tibetan in origin. The meaning o ...
are thought to have settled in the northern highlands as well as in pockets throughout the region, and are believed to be ancestors of the modern day Bhotiya
Bhotiya or Bhot ( ne, भोटिया, ) are groups of ethno-linguistically related Tibetan people living in the Transhimalayan region that divides India from Tibet. The word ''Bhotiya'' comes from the classical Tibetan name for Tibet, , . ...
, Raji, Jad, and Banrawat people.

 By the medieval period, the region was consolidated under the
By the medieval period, the region was consolidated under the Garhwal Kingdom
Garhwal Kingdom was an independent Himalayan kingdom in the current north-western Himalayan state of Uttarakhand, India, founded in 688 CE by Kanak Pal, the progenitor of the Panwar dynasty that ruled over the kingdom uninterrupted until ...
in the west and the Kumaon Kingdom
Kumaon Kingdom was an independent Himalayan kingdom in the eastern region of present-day Uttarakhand state of India. It was established around 7th century and remained an independent and sovereign kingdom until 1791.
Etymology
Kumaon is beli ...
in the east. During this period, learning and new forms of painting (the Pahari school of art) developed. Modern-day Garhwal was likewise unified under the rule of Parmars who, along with many Brahmins
Brahmin (; sa, ब्राह्मण, brāhmaṇa) is a varna as well as a caste within Hindu society. The Brahmins are designated as the priestly class as they serve as priests ( purohit, pandit, or pujari) and religious teachers (guru ...
and Rajputs
Rajput (from Sanskrit ''raja-putra'' 'son of a king') is a large multi-component cluster of castes, kin bodies, and local groups, sharing social status and ideology of genealogical descent originating from the Indian subcontinent. The term Ra ...
, also arrived from the plains. In 1791, the expanding Gorkha Empire of Nepal
Nepal (; ne, :ne:नेपाल, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in S ...
overran Almora
Almora ( Kumaoni: ''Almāḍ'') is a municipal board and a cantonment town in the state of Uttarakhand, India. It is the administrative headquarters of Almora district. Almora is located on a ridge at the southern edge of the Kumaon Hills of th ...
, the seat of the Kumaon Kingdom. It was annexed to the Kingdom of Nepal
The Kingdom of Nepal ( ne, नेपाल अधिराज्य), also known as the Gorkha Empire ( ne, गोरखा अधिराज्य) or Asal Hindustan ( ne, असल हिन्दुस्तान)(), was a Hindu king ...
by Amar Singh Thapa
Amar Singh Thapa Chhetri distinguished as Badakaji Amar Singh Thapa( ne, बडाकाजी अमर सिंह थापा क्षेत्री), or Amar Singh Thapa The Elder, (also spelled Ambar Simha) also known by the honorific nam ...
. In 1803, the Garhwal Kingdom also fell to the Gurkhas. After the Anglo-Nepalese War
The Anglo-Nepalese War (1 November 1814 – 4 March 1816), also known as the Gorkha War, was fought between the Gorkhali army of the Kingdom of Nepal (present-day Nepal) and the British forces of the East India Company (EIC, present-day In ...
, this region was ceded to the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
as part of the Treaty of Sugauli
The Treaty of Sugauli (also spelled Sugowlee, Sagauli and Segqulee), the treaty that established the boundary line of Nepal, was signed on 4 March 1816 between the East India Company and Guru Gajaraj Mishra following the Anglo-Nepalese War ...
and the erstwhile Kumaon Kingdom along with the eastern region of Garhwal Kingdom was merged with the Ceded and Conquered Provinces
The Ceded and Conquered Provinces constituted a region in northern India that was ruled by the British East India Company from 1805 to 1834; it corresponded approximately—in present-day India—to all regions in Uttar Pradesh sta ...
. In 1816, the Garhwal Kingdom was re-established from a smaller region in Tehri
New Tehri is a city and a municipal board in Tehri Garhwal District in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It is the administrative headquarters of Tehri Garhwal District. This urban municipality area has 11 wards, from Vidhi Vihar to Vishwakarma P ...
as a princely state. In the southern part of Uttarakhand in Haridwar District (earlier part of saharanpur till 1988), the dominance and kingship (rajya) was exercises by Gujar chiefs, the area was under control of Parmar (Panwar or Khubars) Gujars in eastern Saharanpur including Haridwar in kingship of Raja Sabha Chandra of Jabarhera (Jhabrera). Gujars of the Khubar (Panwar) gotra held more than 500 villages there in upper Doab, and that situation was confirmed in 1759 in a grant by a Rohilla governor of 505 villages and 31 hamlets to one Manohar Singh Gujar (written in some records as Raja Nahar Singh son of Sabha Chandra). In 1792 Ram Dayal and his son Sawai Singh were ruling the area but due to some family reasons Ramdayal left Jhabrera and went to Landhaura village, now some villages were under control of Raja Ramdayal singh at Landhaura and some under his son Sawai Singh at Jhabrera. Hence, there were two branches of Jabarhera estate (riyasat) main branch at Jabarhera and second one at Landhaura, both father and son were ruling simultaneously without any conflicts till death of Raja Sawai Singh of Jabarhera in 1803. After death of Sawai Singh total control of powers transferred to Ram Dayal Singh at Landhaura, but some villages were given to descendants of Sawai Singh and her widow to collect revenue. By 1803 the Landhaura villages numbered 794 under Raja Ram Dayal Singh. Raja Ram Dayal Singh died on 29 March 1813. These holdings, at least those in the original grant made by the Rohilla governor, were initially recognized by the British in land settlements concluded with Ram Dayal and his heirs. As the years passed, more and more settlements appear to have been made with the village communities, however, and by 1850 little remained of the once vast estate of the Landhaura Khübars.
After India attained independence from the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
, the Garhwal Kingdom was merged into the state of Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh (; , 'Northern Province') is a state in northern India. With over 200 million inhabitants, it is the most populated state in India as well as the most populous country subdivision in the world. It was established in 1950 ...
, where Uttarakhand composed the Garhwal and Kumaon Divisions. Until 1998, Uttarakhand was the name most commonly used to refer to the region, as various political groups, including the Uttarakhand Kranti Dal
The Uttarakhand Kranti Dal (translation: Uttarakhand Revolutionary Party; UKD), is a registered unrecognised regional political party in Uttarakhand, India. It bills itself as the only regional party of the Uttarakhand in contrast to the nat ...
(Uttarakhand Revolutionary Party), began agitating for separate statehood under its banner. Although the erstwhile hill kingdoms of Garhwal and Kumaon were traditional rivals the inseparable and complementary nature of their geography, economy, culture, language, and traditions created strong bonds between the two regions. These bonds formed the basis of the new political identity of Uttarakhand, which gained significant momentum in 1994, when demand for separate statehood achieved almost unanimous acceptance among both the local populace and national political parties.
The most notable incident during this period was the Rampur Tiraha firing case on the night of 1 October 1994, which led to a public uproar. On 24 September 1998, the Uttar Pradesh Legislative Assembly
The Uttar Pradesh Legislative Assembly (Hindi: ''Uttar Pradesh Vidhan Sabha'') is the lower house of the bicameral legislature of Uttar Pradesh. There are 403 seats in the house filled by direct election using a single-member first-past-the- ...
and Uttar Pradesh Legislative Council
The Uttar Pradesh Legislative Council (Hindi: ''Uttar Pradesh Vidhan Parishad'') is the upper house of the bicameral legislature of Uttar Pradesh, a state in India. Uttar Pradesh is one of the six states in India, where the state legislature is ...
passed the Uttar Pradesh Reorganisation Bill, which began the process of forming a new state. Two years later the Parliament of India
The Parliament of India ( IAST: ) is the supreme legislative body of the Republic of India. It is a bicameral legislature composed of the president of India and two houses: the Rajya Sabha (Council of States) and the Lok Sabha (House of the ...
passed the Uttar Pradesh Reorganisation Act, 2000
Uttar Pradesh Reorganisation Act, 2000 is an Act of the Parliament of India enacted in 2000 for creation of the state of Uttarakhand, then tentatively named Uttaranchal, out of Uttar Pradesh. The law was introduced by NDA government headed b ...
and thus, on 9 November 2000, Uttarakhand became the 27th state of the Republic of India.
livelihood
A person's livelihood (derived from ''life-lode'', "way of life"; cf. OG ''lib-leit'') refers to their "means of securing the basic necessities (food, water, shelter and clothing) of life". Livelihood is defined as a set of activities essential t ...
movement rather than a forest conservation movement, it went on to become a rallying point for many future environmentalists
An environmentalist is a person who is concerned with and/or advocates for the protection of the environment. An environmentalist can be considered a supporter of the goals of the environmental movement, "a political and ethical movement that se ...
, environmental protests, and movements the world over and created a precedent for non-violent protest. It stirred up the existing civil society in India, which began to address the issues of tribal and marginalised people. So much so that, a quarter of a century later, ''India Today
''India Today'' is a weekly Indian English-language news magazine published by Living Media India Limited. It is the most widely circulated magazine in India, with a readership of close to 8 million. In 2014, ''India Today'' launched a new o ...
'' mentioned the people behind the "forest satyagraha" of the Chipko movement as among "100 people who shaped India". One of Chipko's most salient features was the mass participation of female villagers. It was largely female activists that played pivotal role in the movement. Gaura Devi was the leading activist who started this movement, other participants were Chandi Prasad Bhatt
Chandi Prasad Bhatt (born 23 June 1934) is an Indian Gandhian environmentalist and social activist, who founded Dasholi Gram Swarajya Sangh (DGSS) in Gopeshwar in 1964, which later became a mother-organization to the Chipko Movement, in which ...
, Sunderlal Bahuguna, and Ghanshyam Raturi, the popular Chipko poet.
Geography
 Uttarakhand has a total area of , of which 86% is mountainous and 65% is covered by forest. Most of the northern part of the state is covered by high
Uttarakhand has a total area of , of which 86% is mountainous and 65% is covered by forest. Most of the northern part of the state is covered by high Himalaya
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 100 ...
n peaks and glaciers. In the first half of the nineteenth century, the expanding development of Indian roads, railways and other physical infrastructure was giving rise to concerns over indiscriminate logging, particularly in the Himalaya
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 100 ...
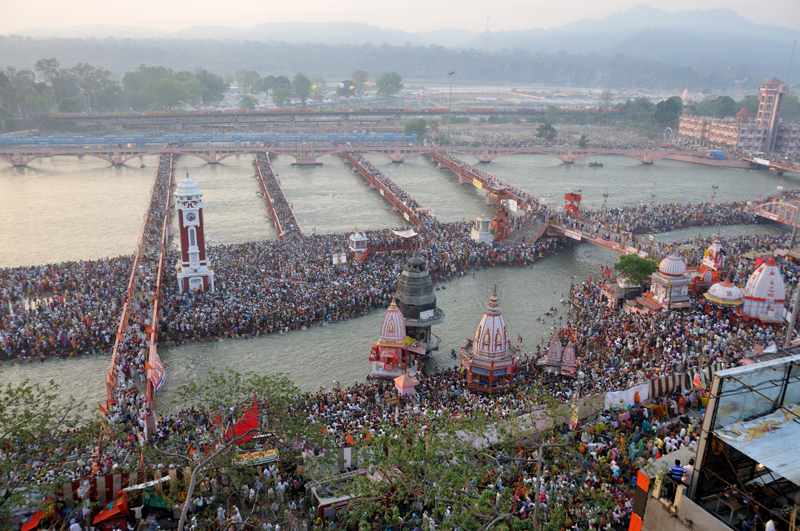
. Two of the most important rivers in Hinduism originate in the glaciers of Uttarakhand, the Ganges
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is ...
at Gangotri and the Yamuna
The Yamuna ( Hindustani: ), also spelt Jumna, is the second-largest tributary river of the Ganges by discharge and the longest tributary in India. Originating from the Yamunotri Glacier at a height of about on the southwestern slopes of B ...
at Yamunotri. They are fed by myriad lakes, glacial melts and streams. These two along with Badrinath
Badrinath is a town and nagar panchayat in Chamoli district in the state of Uttarakhand, India. A Hindu holy place, it is one of the four sites in India's Char Dham pilgrimage and is also part of India's Chota Char Dham pilgrimage circuit. ...
and Kedarnath
Kedarnath is a town and Nagar Panchayat in Rudraprayag district of Uttarakhand, India, known primarily for the Kedarnath Temple. It is approximately 86 kilometres from Rudraprayag, the district headquarter. Kedarnath is the most remote of t ...
form the Chota Char Dham
The Chota Char Dham (literally translated as 'the small four abodes/seats', meaning 'the small circuit of four abodes/seats'), is an important Hindu pilgrimage circuit in Uttarakhand, in the Indian Himalayas. Located in the Garhwal region ...
, a holy pilgrimage for the Hindus.
The state hosts the Bengal tiger
The Bengal tiger is a population of the '' Panthera tigris tigris'' subspecies. It ranks among the biggest wild cats alive today. It is considered to belong to the world's charismatic megafauna.
The tiger is estimated to have been present in ...
in Jim Corbett National Park
Jim Corbett National Park is a national park in India located in the Nainital district of Uttarakhand state. The first national park in India, it was established in 1936 during the British Raj and named ''Hailey National Park'' after Willia ...
, the oldest national park of the Indian subcontinent. The Nanda Devi and Valley of Flowers National Parks
The Nanda Devi National Park and Valley of Flowers National Parks is an UNESCO World Heritage Site in Uttarakhand, India. It possesses of two core areas about 20 km apart, made up by the Nanda Devi National Park and the Valley of Flowers Natio ...
, a UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
located in the upper expanses of Bhyundar Ganga near Joshimath
Joshimath, also known as Jyotirmath, is a city and a municipal board in Chamoli District in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. Located at a height of 6150 feet (1875 m), it is a gateway to several Himalayan mountain climbing expeditions, trekki ...
in Gharwal region, is known for the variety and rarity of its flowers and plants. One who raised this was Sir Joseph Dalton Hooker
Sir Joseph Dalton Hooker (30 June 1817 – 10 December 1911) was a British botanist and explorer in the 19th century. He was a founder of geographical botany and Charles Darwin's closest friend. For twenty years he served as director of ...
, Director of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew
Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew is a non-departmental public body in the United Kingdom sponsored by the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs. An internationally important botanical research and education institution, it employs 1,10 ...
, who visited the region. As a consequence, Lord Dalhousie
James Andrew Broun-Ramsay, 1st Marquess of Dalhousie (22 April 1812 – 19 December 1860), also known as Lord Dalhousie, styled Lord Ramsay until 1838 and known as The Earl of Dalhousie between 1838 and 1849, was a Scottish statesman and co ...
issued the Indian Forest Charter in 1855, reversing the previous laissez-faire policy. The following Indian Forest Act of 1878 put Indian forestry on a solid scientific basis. A direct consequence was the founding of the Imperial Forest School at Dehradun by Dietrich Brandis in 1878. Renamed the 'Imperial Forest Research Institute' in 1906, it is now known as the Forest Research Institute.
The model "Forest Circles" around Dehradun, used for training, demonstration and scientific measurements, had a lasting positive influence on the forests and ecology of the region. The Himalayan ecosystem provides habitat for many animals (including bharal
The bharal (''Pseudois nayaur''), also called the blue sheep, is a caprine native to the high Himalayas. It is the only member of the genus ''Pseudois.'' It occurs in India, Bhutan, China (in Gansu, Ningxia, Sichuan, Tibet, and Inner Mongolia), ...
, snow leopard
The snow leopard (''Panthera uncia''), also known as the ounce, is a felid in the genus '' Panthera'' native to the mountain ranges of Central and South Asia. It is listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List because the global population is es ...
s, leopards and tigers), plants, and rare herbs.
western Himalayan alpine shrub and meadows
The Western Himalayan alpine shrub and meadows is a montane grasslands and shrublands ecoregion of Nepal, India, and Tibet, which lies between the tree line and snow line in the western portion of the Himalaya Range.
Setting
The Western Himalayan ...
. The temperate western Himalayan subalpine conifer forests
The Western Himalayan subalpine conifer forests is a temperate coniferous forests ecoregion of the middle and upper elevations of the western Middle Himalayas of Nepal, India, and Pakistan.
Setting
The ecoregion forms a belt of coniferous fores ...
grow just below the tree line. At elevation they transition to the temperate western Himalayan broadleaf forests
The Western Himalayan broadleaf forests is a temperate broadleaf and mixed forest ecoregion which is found in the middle elevations of the western Himalayas, including parts of Nepal, India, and Pakistan.
Setting
The ecoregion forms an area of te ...
, which lie in a belt from elevation. Below elevation lie the Himalayan subtropical pine forests
The Himalayan subtropical pine forests are a large subtropical coniferous forest ecoregion covering portions of Bhutan, India, Nepal, and Pakistan.
Geography
This huge pine forest stretches for 3000 km across the lower elevations of the gre ...
. The Upper Gangetic Plains moist deciduous forests
The Upper Gangetic Plains moist deciduous forests is a tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests ecoregion of northern India.
Geography
It lies on the alluvial plain of the Ganges and Yamuna rivers, with an area of , covering most of t ...
and the drier Terai-Duar savanna and grasslands cover the lowlands along the Uttar Pradesh border in a belt locally known as Bhabar. These lowland forests have mostly been cleared for agriculture, but a few pockets remain.
In June 2013 several days of extremely heavy rain caused devastating floods in the region, resulting in more than 5000 people missing and presumed dead. The flooding was referred to in the Indian media as a "Himalayan Tsunami".
On 7 February 2021, flood
A flood is an overflow of water ( or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are an area of study of the discipline hydrol ...
s emerged from the Nanda Devi
Nanda Devi is the second-highest mountain in India, after Kangchenjunga, and the highest located entirely within the country (Kangchenjunga is on the border of India and Nepal). It is the 23rd-highest peak in the world.
Nanda Devi was consi ...
mountain glaciers, devastating locations along the Rishi Ganga
Rishiganga is a river in the Chamoli district, Uttarakhand, India. It springs from the Uttari Nanda Devi Glacier on the Nanda Devi mountain. It is also fed from the Dakshini Nanda Devi Glacier. Continuing through the Nanda Devi National Park, ...
, Dhauli Ganga and Alaknanda River
The Alaknanda is a Himalayan river in the Indian state of Uttarakhand and one of the two headstreams of the Ganges, the major river of Northern India and the holy river of Hinduism. In hydrology, the Alaknanda is considered the source stream ...
s, resulting in many people reported missing or killed, yet to be numbered. The damages include Rini village, several river dams and the Tapovan Vishnugad Hydropower Plant
The Tapovan Vishnugad Hydropower Plant is a 520 MW run-of-river hydroelectric project being constructed on Dhauliganga River in Chamoli District of Uttarakhand, India. The plant is expected to generate over 2.5 TWh of electricity annually.
Ta ...
.
Flora and fauna
Golden Mahseer
''Tor putitora'', the Putitor mahseer, Himalayan mahseer, or golden mahseer, is an endangered species of cyprinid fish that is found in rapid streams, riverine pools, and lakes in the Himalayan region. Its native range is within the basins of th ...
(''Tor putitora'')
Himalayan Monal, Male (28466143101).jpg, Himalayan Monal
The Himalayan monal (''Lophophorus impejanus''), also called Impeyan monal and Impeyan pheasant, is a pheasant native to Himalayan forests and shrublands at elevations of . It is part of the family Phasianidae and is listed as Least Concern on th ...
(''Lophophorus impejanus'')
Davidraju Common peacock-shillong.jpg, West Himalayan Common Peacock (''Papilio bianor polyctor'')
National parks
A national park is a natural park in use for conservation purposes, created and protected by national governments. Often it is a reserve of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that a sovereign state declares or owns. Although individua ...
in Uttarakhand include the Jim Corbett National Park
Jim Corbett National Park is a national park in India located in the Nainital district of Uttarakhand state. The first national park in India, it was established in 1936 during the British Raj and named ''Hailey National Park'' after Willia ...
(the oldest national park of India) in Nainital
Nainital ( Kumaoni: ''Naintāl''; ) is a city and headquarters of Nainital district of Kumaon division, Uttarakhand, India. It is the judicial capital of Uttarakhand, the High Court of the state being located there and is the headquarters o ...
and Pauri Garhwal District
Pauri Garhwal is a district in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. Its headquarters is in the town of Pauri. It is sometimes referred to simply as Garhwal district, though it should not be confused with the larger Garhwal region of which it is ...
, and Valley of Flowers National Park
Valley of Flowers National Park is an Indian National parks of India, national park which was established in 1982. It is located in Chamoli in the state of Uttarakhand and is known for its meadows of Endemism, endemic alpine flowers and the var ...
& Nanda Devi National Park
The Nanda Devi National Park or Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve, established in 1982 is a national park situated around the peak of Nanda Devi (7816 m) in Chamoli Garhwal district of Uttarakhand, in northern India. The entire park lies at an ele ...
in Chamoli District
Chamoli district is a district of the Uttarakhand state of India. It is bounded by the Tibet region to the north, and by the Uttarakhand districts of Pithoragarh and Bageshwar to the east, Almora to the south, Pauri Garhwal to the southwest, ...
, which together are a UNESCO World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
. A number of plant species in the valley are internationally threatened, including several that have not been recorded from elsewhere in Uttarakhand. Rajaji National Park
Rajaji National Park is an Indian national park and tiger reserve that encompasses the Shivaliks, near the foothills of the Himalayas. It is spread over 820 km2 and includes three districts of Uttarakhand: Haridwar, Dehradun and Pauri G ...
in Haridwar
Haridwar (; ) is a city and municipal corporation in the Haridwar district of Uttarakhand, India. With a population of 228,832 in 2011, it is the second-largest city in the state and the largest in the district.
The city is situated on the ri ...
, Dehradun and Pauri Garhwal District
Pauri Garhwal is a district in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. Its headquarters is in the town of Pauri. It is sometimes referred to simply as Garhwal district, though it should not be confused with the larger Garhwal region of which it is ...
and Govind Pashu Vihar National Park & Gangotri National Park
Gangotri National Park is a national park in Uttarkashi District of Uttarakhand in India, covering about . Its habitat consists of coniferous forests, alpine meadows and glaciers. Gaumukh at Gangotri glacier, the origin of river Ganga, is loc ...
in Uttarkashi District
Uttarkashi District is a district of Garhwal division of the Uttarakhand state in northern India, and has its headquarters at Uttarkashi city. It has six Tehsils namely Barkot, Dunda, Bhatwadi, Chinyalisaur, Purola and Mori.
The district conta ...
are some other protected areas in the state.
Leopards
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant species in the genus ''Panthera'', a member of the cat family, Felidae. It occurs in a wide range in sub-Saharan Africa, in some parts of Western and Central Asia, Southern Russia, a ...
are found in areas that are abundant in hills but may also venture into the lowland jungles. Smaller felines include the jungle cat
The jungle cat (''Felis chaus''), also called reed cat, swamp cat and jungle lynx, is a medium-sized cat native to the Middle East, the Caucasus, South and Southeast Asia and southern China. It inhabits foremost wetlands like swamps, littoral ...
, fishing cat
The fishing cat (''Prionailurus viverrinus'') is a medium-sized wild cat of South and Southeast Asia. Since 2016, it is listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List. Fishing cat populations are threatened by destruction of wetlands and have declin ...
, and leopard cat
The leopard cat (''Prionailurus bengalensis'') is a small wild cat native to continental South, Southeast, and East Asia. Since 2002 it has been listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List as it is widely distributed although threatened by hab ...
. Other mammals include four kinds of deer (barking
Barking may refer to:
Places
* Barking, London, a town in East London, England
** London Borough of Barking and Dagenham, a local government district covering the town of Barking
** Municipal Borough of Barking, a historical local government dist ...
, sambar, hog and chital
The chital or cheetal (''Axis axis''; ), also known as the spotted deer, chital deer, and axis deer, is a deer species native to the Indian subcontinent. It was first described and given a binomial name by German naturalist Johann Christian Po ...
), sloth
Sloths are a group of Neotropical xenarthran mammals constituting the suborder Folivora, including the extant arboreal tree sloths and extinct terrestrial ground sloths. Noted for their slowness of movement, tree sloths spend most of their l ...
, Brown
Brown is a color. It can be considered a composite color, but it is mainly a darker shade of orange. In the CMYK color model used in printing or painting, brown is usually made by combining the colors orange and black. In the RGB color model us ...
and Himalayan black bears, Indian grey mongoose
The Indian grey mongoose (''Urva edwardsii'') is a mongoose species native to the Indian subcontinent and West Asia. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List.
The grey mongoose inhabits open forests, scrublands and cultivated fields ...
s, otters, yellow-throated martens, bharal
The bharal (''Pseudois nayaur''), also called the blue sheep, is a caprine native to the high Himalayas. It is the only member of the genus ''Pseudois.'' It occurs in India, Bhutan, China (in Gansu, Ningxia, Sichuan, Tibet, and Inner Mongolia), ...
, Indian pangolin
The Indian pangolin (''Manis crassicaudata''), also called thick-tailed pangolin and scaly anteater is a pangolin native to the Indian subcontinent.
Like other pangolins, it has large, overlapping scales on its body which act as armour. The colou ...
s, and langur
The Colobinae or leaf-eating monkeys are a subfamily of the Old World monkey family that includes 61 species in 11 genera, including the black-and-white colobus, the large-nosed proboscis monkey, and the gray langurs. Some classifications sp ...
and rhesus monkeys. In the summer, elephants can be seen in herds of several hundred. Marsh crocodile
The mugger crocodile (''Crocodylus palustris'') is a medium-sized broad- snouted crocodile, also known as mugger and marsh crocodile. It is native to freshwater habitats from southern Iran to the Indian subcontinent, where it inhabits marshes ...
s (''Crocodylus palustris''), gharials (''Gavialis gangeticus'') and other reptiles are also found in the region. Local crocodiles were saved from extinction by captive breeding programs and subsequently re-released into the Ramganga river. Several freshwater terrapins and turtles like the Indian sawback turtle (''Kachuga tecta''), brahminy river turtle
The brahminy river turtle or crowned river turtle (''Hardella thurjii'') is a species of turtle in the family Geoemydidae. The species is endemic to South Asia.
Taxonomy
The genus ''Hardella'', to which the species ''Hardella thurjii'' belongs, ...
(''Hardella thurjii''), and Ganges softshell turtle (''Trionyx gangeticus'') are found in the rivers. Butterflies and birds of the region include red helen (''Papilio helenus''), the great eggfly (''Hypolimnos bolina''), common tiger (''Danaus genutia''), pale wanderer (''Pareronia avatar''), jungle babbler
The jungle babbler (''Argya striata'') is a member of the family Leiothrichidae found in the Indian subcontinent. Jungle babblers are gregarious birds that forage in small groups of six to ten birds, a habit that has given them the popular name ...
, tawny-bellied babbler
The tawny-bellied babbler (''Dumetia hyperythra'') also known in older Indian works as the rufous-bellied babbler is a small babbler that forages in small groups in low scrub forests. Like other members of the large Old World babbler family they ...
, great slaty woodpecker
The great slaty woodpecker (''Mulleripicus pulverulentus'') is a species of bird in the family Picidae. It is found across the Indian Subcontinent and Southeast Asia. A unique and basically unmistakable bird, it is the largest species of woodpeck ...
, red-breasted parakeet, orange-breasted green pigeon and chestnut-winged cuckoo. In 2011, a rare migratory bird, the bean goose, was also seen in the Jim Corbett National Park
Jim Corbett National Park is a national park in India located in the Nainital district of Uttarakhand state. The first national park in India, it was established in 1936 during the British Raj and named ''Hailey National Park'' after Willia ...
. A critically endangered bird, last seen in 1876 is the Himalayan quail endemic to the western Himalayas of the state.
Evergreen oaks, rhododendrons
''Rhododendron'' (; from Ancient Greek ''rhódon'' "rose" and ''déndron'' "tree") is a very large genus of about 1,024 species of woody plants in the heath family (Ericaceae). They can be either evergreen or deciduous. Most species are nati ...
, and conifers predominate in the hills. '' sal'' (''Shorea robusta''), silk cotton tree (''Bombax ciliata''), ''Dalbergia sissoo
''Dalbergia sissoo'', known commonly as North Indian rosewood or ''shisham'', is a fast-growing, hardy, deciduous rosewood tree native to the Indian subcontinent and southern Iran. ''D. sissoo'' is a large, crooked tree with long, leathery leav ...
'', '' Mallotus philippensis'', '' Acacia catechu'', ''Bauhinia racemosa
''Bauhinia racemosa'', commonly known as the bidi leaf tree, is a rare medicinal species of flowering shrub with religious significance. It is a small crooked tree with drooping branches that grows tall and flowers between February and May. It i ...
'', and '' Bauhinia variegata'' (camel's foot tree) are some other trees of the region. '' Albizia chinensis'', the sweet sticky flowers of which are favoured by sloth bears, are also part of the region's flora. A decade long study by Prof. Chandra Prakash Kala concluded that the Valley of Flowers is endowed with 520 species of higher plants ('' angiosperms'', ''gymnosperm
The gymnosperms ( lit. revealed seeds) are a group of seed-producing plants that includes conifers, cycads, '' Ginkgo'', and gnetophytes, forming the clade Gymnospermae. The term ''gymnosperm'' comes from the composite word in el, γυμν ...
s'' and '' pteridophytes''), of these 498 are flowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants th ...
s. The park has many species of medicinal plants including ''Dactylorhiza hatagirea
''Dactylorhiza hatagirea'' is a species of orchid generally found growing in the Himalayas, from Pakistan to SE Tibet, at altitudes of . It is locally called 'salam panja' or 'hatta haddi'. It is called 'panchaule' (पाँचऔंले) in ...
'', '' Picrorhiza kurroa'', '' Aconitum violaceum'', '' Polygonatum multiflorum'', '' Fritillaria roylei'', and '' Podophyllum hexandrum''. In the summer season of 2016, a large portion of forests in Uttarakhand caught fires and rubbled to ashes during Uttarakhand forest fires incident, which resulted in the damage of forest resources worth billions of rupees and death of 7 people with hundreds of wild animals died during fires. During the 2021 Uttarakhand forest fires, there was widespread damage to the forested areas in Tehri district.
A number of native plants are deemed to be of medicinal value. The government-run Herbal Research and Development Institute carries out research and helps conserve medicinal herbs that are found in abundance in the region. Local traditional healers still use herbs, in accordance with classical Ayurvedic texts, for diseases that are usually cured by modern medicine.
Kaphal
''Myrica esculenta'' is a tree or large shrub native to the hills of northern India, southern Bhutan and Nepal. Its common names include box myrtle, bayberry and kaphal. Its berries are edible and are consumed locally. It is the state fruit ...
(''Myrica esculenta'')
Brännässla (Urtica Dioica).jpg, Kandali (''Urtica dioica'')
Demographics
The native people of Uttarakhand are generally called Uttarakhandi and sometimes specifically eitherGarhwali Garhwali may refer to:
* Garhwali people, an ethno-linguistic group who live in northern India
* Garhwali language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by Garhwali people
* anything from or related to:
**Garhwal division, a region in state of Uttarakhan ...
or Kumaoni depending on their place of origin in either the Garhwal or Kumaon Kumaon or Kumaun may refer to:
* Kumaon division, a region in Uttarakhand, India
* Kumaon Kingdom, a former country in Uttarakhand, India
* Kumaon, Iran, a village in Isfahan Province, Iran
* , a ship of the Royal Indian Navy during WWII
See also
...
region. According to the 2011 Census of India
The 2011 Census of India or the 15th Indian Census was conducted in two phases, house listing and population enumeration. The House listing phase began on 1 April 2010 and involved the collection of information about all buildings. Information ...
, Uttarakhand has a population of 10,086,292 comprising 5,137,773 males and 4,948,519 females, with 69.77% of the population living in rural areas. The state is the 20th most populous state of the country having 0.83% of the population on 1.63% of the land. The population density of the state is 189 people per square kilometre having a 2001–2011 decadal growth rate of 18.81%. The gender ratio is 963 females per 1000 males. The crude birth rate in the state is 18.6 with the total fertility rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that would be born to a woman over her lifetime if:
# she were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through her lifetime
# she were t ...
being 2.3. The state has an infant mortality rate
Infant mortality is the death of young children under the age of 1. This death toll is measured by the infant mortality rate (IMR), which is the probability of deaths of children under one year of age per 1000 live births. The under-five morta ...
of 43, a maternal mortality rate
Maternal death or maternal mortality is defined in slightly different ways by several different health organizations. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines maternal death as the death of a pregnant mother due to complications related to p ...
of 188 and a crude death rate of 6.6.
Ethnic groups
Uttarakhand has a multiethnic population spread across two geocultural regions: the Garhwal, and the Kumaon. A large portion of the population isKshatriya
Kshatriya ( hi, क्षत्रिय) (from Sanskrit ''kṣatra'', "rule, authority") is one of the four varna (social orders) of Hindu society, associated with warrior aristocracy. The Sanskrit term ''kṣatriyaḥ'' is used in the con ...
(various clans of erstwhile landowning rulers and their descendants), including members of the native Garhwali Garhwali may refer to:
* Garhwali people, an ethno-linguistic group who live in northern India
* Garhwali language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by Garhwali people
* anything from or related to:
**Garhwal division, a region in state of Uttarakhan ...
, and Kumaoni as well as a number of migrants. According to a 2007 study by Centre for the Study of Developing Societies
The Centre for the Study of Developing Societies (CSDS) is an Indian research institute for the social sciences and humanities. It was founded in 1963 by Rajni Kothari and is largely funded by the Indian Council of Social Science Research Govt ...
, Uttarakhand has the highest percentage of Brahmin
Brahmin (; sa, ब्राह्मण, brāhmaṇa) is a varna as well as a caste within Hindu society. The Brahmins are designated as the priestly class as they serve as priests (purohit, pandit, or pujari) and religious teachers (gur ...
s of any state in India, with approximately 25-28% of the population being Brahmin. 18.3% of the population is classified as Other Backward Class
The Other Backward Class is a collective term used by the Government of India to classify castes which are educationally or socially backward. It is one of several official classifications of the population of India, along with General castes, ...
es (OBCs). 18.76% of the population belongs to the Scheduled Castes
The Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs) are officially designated groups of people and among the most disadvantaged socio-economic groups in India. The terms are recognized in the Constitution of India and the groups are designa ...
(an official term for the lower castes in the traditional caste system in India). Scheduled Tribes such as the Jaunsari, Bhotiya
Bhotiya or Bhot ( ne, भोटिया, ) are groups of ethno-linguistically related Tibetan people living in the Transhimalayan region that divides India from Tibet. The word ''Bhotiya'' comes from the classical Tibetan name for Tibet, , . ...
, Tharu, Buksa, Raji, Jad and Banrawat constitute 2.89% of the population.
Languages
The official language of Uttarakhand isHindi
Hindi ( Devanāgarī: or , ), or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi (Devanagari: ), is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in the Hindi Belt region encompassing parts of northern, central, eastern, and western India. Hindi has been ...
, which is spoken natively by % of the population (primarily concentrated in the south), Figures for Jaunsari also include speakers of Jaunpuri. and also used throughout the state as a lingua franca.
Additionally, the classical language Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
has been declared a second official language, although it has no native speakers and its use is constrained to educational and religious settings.
The other major regional languages of Uttarakhand are Garhwali Garhwali may refer to:
* Garhwali people, an ethno-linguistic group who live in northern India
* Garhwali language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by Garhwali people
* anything from or related to:
**Garhwal division, a region in state of Uttarakhan ...
, which is spoken by % of the population mostly in the western half of the state, Kumaoni, spoken in the eastern half and native to %, and Jaunsari, whose speakers are concentrated in Dehradun district in the southwest and make up % of the state's population. These three languages are closely related, with Garhwali and Kumaoni in particular making up the Central Pahari language subgroup. There are also sizeable populations of speakers of some of India's other major languages: Urdu
Urdu (;"Urdu"
'' Punjabi (%), both mostly found in the southern districts,
 There are 13 districts in Uttarakhand, which are grouped into two divisions,
There are 13 districts in Uttarakhand, which are grouped into two divisions,
Hanol Mahasu04.jpg,
Among the prominent local crafts is
 Uttarakhand's diverse ethnicities have created a rich literary tradition in languages including Hindi, Garhwali, Kumaoni, Jaunsari, and Tharu. Many of its traditional tales originated in the form of lyrical
Uttarakhand's diverse ethnicities have created a rich literary tradition in languages including Hindi, Garhwali, Kumaoni, Jaunsari, and Tharu. Many of its traditional tales originated in the form of lyrical
 The primary food of Uttarakhand is vegetables with wheat being a staple, although non-vegetarian food is also served. A distinctive characteristic of Uttarakhand cuisine is the sparing use of tomatoes, milk, and milk-based products. Coarse grain with high fibre content is very common in Uttarakhand due to the harsh terrain. Crops most commonly associated with Uttarakhand are
The primary food of Uttarakhand is vegetables with wheat being a staple, although non-vegetarian food is also served. A distinctive characteristic of Uttarakhand cuisine is the sparing use of tomatoes, milk, and milk-based products. Coarse grain with high fibre content is very common in Uttarakhand due to the harsh terrain. Crops most commonly associated with Uttarakhand are
 The dances of the region are connected to life and human existence and exhibit myriad human emotions. Langvir Nritya is a dance form for males that resembles gymnastic movements. Barada Nati folk dance is another dance of
The dances of the region are connected to life and human existence and exhibit myriad human emotions. Langvir Nritya is a dance form for males that resembles gymnastic movements. Barada Nati folk dance is another dance of
 One of the major
One of the major
 The Uttarakhand state is the second fastest growing state in India. Its gross state domestic product (GSDP) (at constant prices) more than doubled from 24,786 crore in FY2005 to 60,898 crore in FY2012. The real GSDP grew at 13.7% (CAGR) during the FY2005–FY2012 period. The contribution of the service sector to the GSDP of Uttarakhand was just over 50% during FY 2012. Per capita income in Uttarakhand is 198738 (FY 2018–19), which is higher than the national average of 126406 (FY 2018–19). According to the
The Uttarakhand state is the second fastest growing state in India. Its gross state domestic product (GSDP) (at constant prices) more than doubled from 24,786 crore in FY2005 to 60,898 crore in FY2012. The real GSDP grew at 13.7% (CAGR) during the FY2005–FY2012 period. The contribution of the service sector to the GSDP of Uttarakhand was just over 50% during FY 2012. Per capita income in Uttarakhand is 198738 (FY 2018–19), which is higher than the national average of 126406 (FY 2018–19). According to the
 Uttarakhand has of roads, of which are national highways and are state highways. The State Road Transport Corporation (SRTC), which has been reorganised in Uttarakhand as the
Uttarakhand has of roads, of which are national highways and are state highways. The State Road Transport Corporation (SRTC), which has been reorganised in Uttarakhand as the
Valley of flowers uttaranchal full view.JPG,
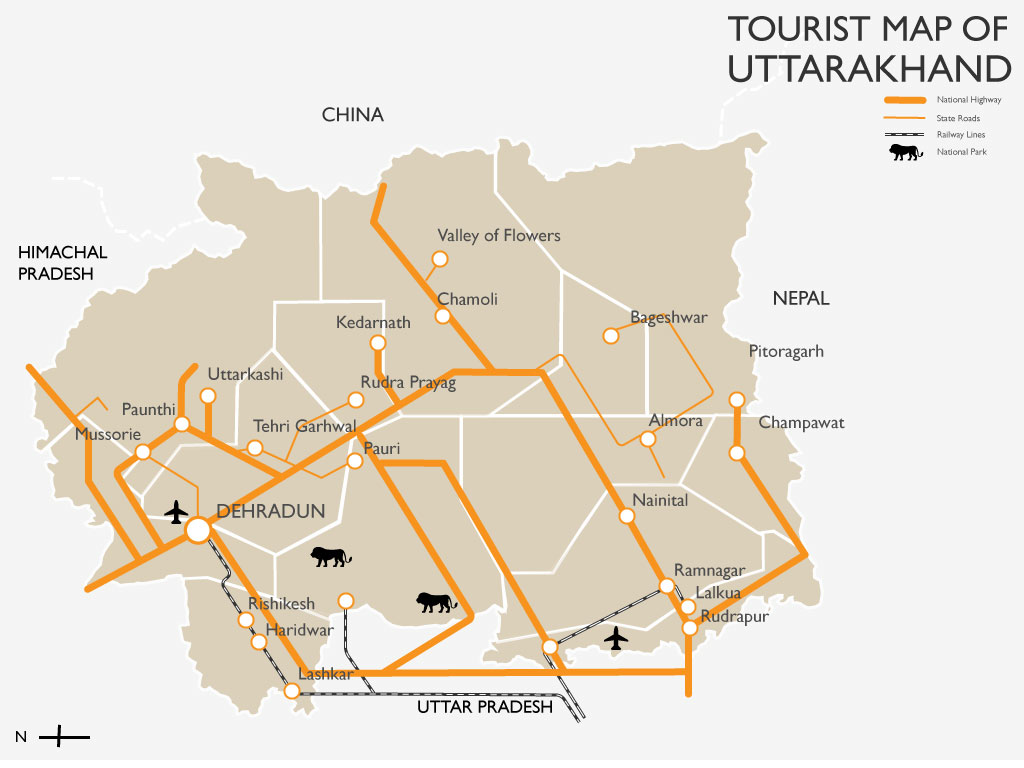 Uttarakhand has many tourist spots due to its location in the Himalayas. There are many ancient temples, forest reserves, national parks, hill stations, and mountain peaks that draw large number of tourists. There are 44 nationally protected monuments in the state. Oak Grove School in the state is on the tentative list for World Heritage Sites. Two of the most holy rivers in
Uttarakhand has many tourist spots due to its location in the Himalayas. There are many ancient temples, forest reserves, national parks, hill stations, and mountain peaks that draw large number of tourists. There are 44 nationally protected monuments in the state. Oak Grove School in the state is on the tentative list for World Heritage Sites. Two of the most holy rivers in 
 The high mountains and rivers of Uttarakhand attract many tourists and adventure seekers. It is also a favourite destination for adventure sports, such as
The high mountains and rivers of Uttarakhand attract many tourists and adventure seekers. It is also a favourite destination for adventure sports, such as
History of Uttaranchal
'. Indus Publishing. . * Husain, Z. (1995). ''Uttarakhand Movement: The Politics of Identity and Frustration, A Psycho-Analytical Study of the Separate State Movement, 1815–1995''. Bareilly: Prakash Book Depot. * Sharma, D. (1989). ''Tibeto-Himalayan languages of Uttarakhand''. Studies in Tibeto-Himalayan languages, 3. New Delhi, India: Mittal Publications. * Phonia, Kedar Singh (1987). ''Uttarakhand: The Land of Jungles, Temples and Snows''. New Delhi, India: Lancer Books. * Mukhopadhyaya, R. (1987). ''Uttarakhand Movement: A Sociological Analysis''. Centre for Himalayan Studies special lecture, 8. Raja Rammohunpur, Distt. Darjeeling: University of North Bengal. * Thapliyal, Uma Prasad (2005). ''Uttaranchal: Historical and Cultural Perspectives''. B. R. Pub. Corp., . * Negi, Vijaypal Singh, Jawaharnagar, P.O. Agastyamuni, Distt. Rudraprayag, ''The Great Himalayas'' 1998,
Uttarakhand Government Portal
Uttarakhand Tourism
Map of Uttarakhand
with places of interest and historical attractions, mountainshepherds.com. * * {{Authority control Uttarakhand North India States and union territories of India States and territories established in 2000 2000 establishments in India
'' Punjabi (%), both mostly found in the southern districts,
Bengali
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:
*something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia
* Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region
* Bengali language, the language they speak
** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
(%) and Bhojpuri (%), both mainly present in Udham Singh Nagar district in the south-east, and Nepali (%, found throughout the state, but most notably in Dehradun and Uttarkashi).
All the languages enumerated so far belong to the Indo-Aryan family. Apart from a few other minority Indo-Aryan languages, like Buksa Tharu and Rana Tharu (of Udham Singh Nagar district in the south-east), Mahasu Pahari
Mahasu Pahari ( Takri: ) is a Western Pahari (Himachali, Takri: ) language spoken in Himachal Pradesh. It is also known as Mahasui or Mahasuvi. The speaking population is about 1,000,000 (2001). It is more commonly spoken in the Himachal Pradesh ...
(found in Uttarkashi in the north-west), and Doteli
Doteli, or Dotyali () is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by about 800,000 people, most of whom live in Nepal. It is a dialect of Khas, which is an ancient form of the modern Nepali language, and is written in the Devanagari script. It has official ...
, Uttarakhand is also home to a number of indigenous Sino-Tibetan languages
Sino-Tibetan, also cited as Trans-Himalayan in a few sources, is a family of more than 400 languages, second only to Indo-European in number of native speakers. The vast majority of these are the 1.3 billion native speakers of Chinese languages. ...
, most of which are spoken in the north of the state. These include Jad (spoken in Uttarkashi district in the north-west), Rongpo (of Chamoli district), and several languages of Pithoragarh district in the north-east: Byangsi, Chaudangsi, Darmiya, Raji and Rawat. Another indigenous Sino-Tibetan language, Rangas, became extinct by the middle of the 20th century. Additionally, two non-indigenous Sino-Tibetan languages are also represented: Kulung (otherwise native to Nepal) and Tibetan.
Religion
More than four-fifths of Uttarakhand's residents areHindus
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
. Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
, Sikhs, Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words '' Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρ ...
, Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
s, and Jain
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle being ...
s make up the remaining population, with the Muslims being the largest minority. Hill regions are almost entirely Hindu, while the plains regions have a significant minority of Muslims and Sikhs.
Government and politics
Following theConstitution of India
The Constitution of India ( IAST: ) is the supreme law of India. The document lays down the framework that demarcates fundamental political code, structure, procedures, powers, and duties of government institutions and sets out fundamental ...
, Uttarakhand, like all Indian states, has a parliamentary system
A parliamentary system, or parliamentarian democracy, is a system of democratic governance of a state (or subordinate entity) where the executive derives its democratic legitimacy from its ability to command the support ("confidence") of th ...
of representative democracy
Representative democracy, also known as indirect democracy, is a type of democracy where elected people represent a group of people, in contrast to direct democracy. Nearly all modern Western-style democracies function as some type of represe ...
for its government.
The Governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
is the constitutional and formal head of the government and is appointed for a five-year term by the President of India
The president of India ( IAST: ) is the head of state of the Republic of India. The president is the nominal head of the executive, the first citizen of the country, as well as the commander-in-chief of the Indian Armed Forces. Droupadi Mur ...
on the advice of the Union government
The Government of India ( ISO: ; often abbreviated as GoI), known as the Union Government or Central Government but often simply as the Centre, is the national government of the Republic of India, a federal democracy located in South Asia, ...
. The present Governor of Uttarakhand is Gurmit Singh
Gurmit Singh Virk Chainchal Singh (born 24 March 1965; pa, ਗੁਰਮੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ, Gurmīt Siṅgh; ) is a Singaporean actor, comedian and television personality. He was prominently a full-time Mediacorp artiste from 1994 to 2014. A f ...
. The Chief Minister
A chief minister is an elected or appointed head of government of – in most instances – a sub-national entity, for instance an administrative subdivision or federal constituent entity. Examples include a state (and sometimes a union terri ...
, who holds the real executive powers, is the head of the party or coalition garnering the majority in the state elections. The current Chief Minister of Uttarakhand
The chief minister of Uttarakhand is the chief executive of the Indian state of Uttarakhand. In accordance with the Constitution of India, the governor is a state's ''de jure'' head, but ''de facto'' executive authority rests with the chief mi ...
is Pushkar Singh Dhami.
The unicameral
Unicameralism (from ''uni''- "one" + Latin ''camera'' "chamber") is a type of legislature, which consists of one house or assembly, that legislates and votes as one.
Unicameral legislatures exist when there is no widely perceived need for multi ...
Uttarakhand Legislative Assembly
The Uttarakhand Legislative Assembly, also known as the Uttarakhand Vidhan Sabha, is a unicameral governing and law making body of Uttarakhand, one of the 28 states of India. It is seated at Dehradun, the winter capital, and Bhararisain, the sum ...
consists of 70 members, known as Members of the Legislative Assembly
A member of the Legislative Assembly (MLA) is a representative elected by the voters of a constituency to a legislative assembly. Most often, the term refers to a subnational assembly such as that of a state, province, or territory of a country. ...
or MLAs, and special office bearers such as the Speaker
Speaker may refer to:
Society and politics
* Speaker (politics), the presiding officer in a legislative assembly
* Public speaker, one who gives a speech or lecture
* A person producing speech: the producer of a given utterance, especially:
** I ...
and Deputy Speaker, elected by the members. Assembly meetings are presided over by the Speaker, or the Deputy Speaker in the Speaker's absence. The Uttarakhand Council of Ministers is appointed by the Governor of Uttarakhand on the advice of the Chief Minister of Uttarakhand and reports to the Legislative Assembly. Leader of the Opposition leads the Official Opposition in the Legislative Assembly. Auxiliary authorities that govern at a local level are known as gram panchayat
Gram Panchayat () is a basic village-governing institute in Indian villages. It is a democratic structure at the grass-roots level in India. It is a political institute, acting as cabinet of the village. The Gram Sabha work as the general bo ...
s in rural areas, municipalities
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality'' may also mean the go ...
in urban areas and municipal corporations
A municipal corporation is the legal term for a local governing body, including (but not necessarily limited to) cities, counties, towns, townships, charter townships, villages, and boroughs. The term can also be used to describe municipally owne ...
in metro areas. All state and local government offices have a five-year term. The state also elects 5 members to Lok Sabha
The Lok Sabha, constitutionally the House of the People, is the lower house of India's bicameral Parliament, with the upper house being the Rajya Sabha. Members of the Lok Sabha are elected by an adult universal suffrage and a first-p ...
and 3 seats to Rajya Sabha
The Rajya Sabha, constitutionally the Council of States, is the upper house of the bicameral Parliament of India. , it has a maximum membership of 245, of which 233 are elected by the legislatures of the states and union territories using si ...
of the Parliament of India
The Parliament of India ( IAST: ) is the supreme legislative body of the Republic of India. It is a bicameral legislature composed of the president of India and two houses: the Rajya Sabha (Council of States) and the Lok Sabha (House of the ...
. The judiciary consists of the Uttarakhand High Court
The Uttarakhand High Court is the High Court of the state of Uttarakhand in India. The building of Uttarakhand High Court was constructed by Santoni MacDonald in 1900.
The Uttarakhand State was carved out from the State of Uttar Pradesh on ...
, located at Nainital
Nainital ( Kumaoni: ''Naintāl''; ) is a city and headquarters of Nainital district of Kumaon division, Uttarakhand, India. It is the judicial capital of Uttarakhand, the High Court of the state being located there and is the headquarters o ...
, and a system of lower courts. The incumbent Acting Chief Justice of Uttarakhand is Sanjaya Kumar Mishra.
Politics in Uttarakhand is dominated by the Indian National Congress
The Indian National Congress (INC), colloquially the Congress Party but often simply the Congress, is a political party in India with widespread roots. Founded in 1885, it was the first modern nationalist movement to emerge in the British E ...
and the Bharatiya Janata Party
The Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP; ; ) is a political party in India, and one of the two major Indian political parties alongside the Indian National Congress. Since 2014, it has been the ruling political party in India under Narendra Mod ...
. Since the formation of the state these two parties have ruled the state in turns. Following the hung mandate in the 2012 Uttarakhand Legislative Assembly election
The 2012 Uttarakhand Legislative Assembly election were the 3rd Vidhan Sabha ( Legislative Assembly) election of the state of Uttarakhand in India. Elections were held on 30 January 2012 when Indian National Congress emerged as the largest par ...
, the Indian National Congress, having the maximum number of seats, formed a coalition government headed by Harish Rawat
Harish Singh Rawat (born 27 April 1948) is an Indian politician who was Chief Minister of Uttarakhand from 2014 to 2017. A five-time Member of Parliament, Rawat is a leader of the Indian National Congress party. As a member of 15th Lok Sabha, ...
that collapsed on 27 March 2016, following the political turmoil as about nine MLAs of INC rebelled against the party and supported the opposition party BJP
The Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP; ; ) is a political party in India, and one of the two major Indian political parties alongside the Indian National Congress. Since 2014, it has been the ruling political party in India under Narendra Mo ...
, causing Harish Rawat government to lose the majority in assembly. However, on 21 April 2016 the High Court of Uttarakhand quashed the President's rule questioning its legality and maintained a status quo prior to 27 March 2016 when 9 rebel MLAs of INC voted against the Harish Rawat
Harish Singh Rawat (born 27 April 1948) is an Indian politician who was Chief Minister of Uttarakhand from 2014 to 2017. A five-time Member of Parliament, Rawat is a leader of the Indian National Congress party. As a member of 15th Lok Sabha, ...
government in assembly on state's money appropriation bill. On 22 April 2016 the Supreme Court of India stayed the order of High Court till 27 April 2016, thereby once again reviving the President's rule. In later developments regarding this matter, the Supreme Court ordered a floor test to be held on 10 May with the rebels being barred from voting. On 11 May at the opening of sealed result of the floor test, under the supervision of Supreme Court, the Harish Rawat government was revived following the victory in floor test held in Uttarakhand Legislative Assembly.
Subdivisions
 There are 13 districts in Uttarakhand, which are grouped into two divisions,
There are 13 districts in Uttarakhand, which are grouped into two divisions, Kumaon Kumaon or Kumaun may refer to:
* Kumaon division, a region in Uttarakhand, India
* Kumaon Kingdom, a former country in Uttarakhand, India
* Kumaon, Iran, a village in Isfahan Province, Iran
* , a ship of the Royal Indian Navy during WWII
See also
...
and Garhwal. Each division is administered by a divisional commissioner. Four new districts named Didihat
Didihat is a town and a Nagar Palika in Pithoragarh District in the state of Uttarakhand, India. It is one of the eleven Tehsils of India, administrative subdivisions of Pithoragarh district and also serves as its administrative headquarter. Wit ...
, Kotdwar
Kotdwar is a city, municipal corporation in Pauri Garhwal district of Uttarakhand, India. It's just 101 km from Pauri town , the district headquarter. It is the eighth-largest city in Uttarakhand. Its old name was "Khohdwar", which means the g ...
, Ranikhet
Ranikhet ( Kumaoni: ) is a hill station and cantonment town, nearby Almora Town in Almora district in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It is the home for the Military Hospital, Kumaon Regiment (KRC) and Naga Regiment and is maintained by the In ...
, and Yamunotri were declared by then Chief Minister of Uttarakhand, Ramesh Pokhriyal, on 15 August 2011 but yet to be officially formed.
Each district is administered by a district magistrate
A District Collector-cum-District Magistrate (also known as Deputy Commissioner in some states) is an All India Service officer of the Indian Administrative Service (IAS) cadre who is responsible for ''land revenue collection'', ''canal reve ...
. The districts are further divided into sub-divisions, which are administered by sub-divisional magistrates; sub-divisions comprise tehsil
A tehsil (, also known as tahsil, taluka, or taluk) is a local unit of administrative division in some countries of South Asia. It is a subdistrict of the area within a district including the designated populated place that serves as its administ ...
s which are administered by a tehsildar
In India and Pakistan, a Tehsildar or Mamlatdar is a tax officer accompanied by revenue inspectors. They are in charge of obtaining taxes from a tehsil with regard to land revenue. A tehsildar is also known as an executive magistrate of the relev ...
and community development block
In India, a Community development block (CD block) or simply Block is a sub-division of Tehsil, administratively earmarked for planning and development. The area is administered by a Block Development Officer (BDO), supported by several techni ...
s, each administered by a block development officer
A block is an administrative division of some South Asian countries.
Bhutan
In Bhutan, a block is called a gewog. It is essentially for oil a group of villages. Gewogs are official administrative units of Bhutan. The country is composed of ...
.
Urban areas
An urban area, built-up area or urban agglomeration is a human settlement with a high population density and infrastructure of built environment. Urban areas are created through urbanization and are categorized by urban morphology as cities, ...
are categorised into three types of municipalities based on their population; municipal corporations
A municipal corporation is the legal term for a local governing body, including (but not necessarily limited to) cities, counties, towns, townships, charter townships, villages, and boroughs. The term can also be used to describe municipally owne ...
, each administered by a municipal commissioner, municipal councils and, nagar panchayat
A nagar panchayat (town panchayat; ) or Notified Area Council (NAC) in India is a settlement in transition from rural to urban and therefore a form of an urban political unit comparable to a municipality. An urban centre with more than 12,000 ...
s (town councils), each of them administered by a chief executive officer
A chief executive officer (CEO), also known as a central executive officer (CEO), chief administrator officer (CAO) or just chief executive (CE), is one of a number of corporate executives charged with the management of an organization especial ...
. Rural areas
In general, a rural area or a countryside is a geographic area that is located outside towns and cities. Typical rural areas have a low population density and small settlements. Agricultural areas and areas with forestry typically are describ ...
comprise the three tier administration; district councils, block panchayats (block councils) and gram panchayat
Gram Panchayat () is a basic village-governing institute in Indian villages. It is a democratic structure at the grass-roots level in India. It is a political institute, acting as cabinet of the village. The Gram Sabha work as the general bo ...
s (village councils).
According to the 2011 census, Haridwar, Dehradun, and Udham Singh Nagar are the most populous districts, each of them having a population of over one million.
Settlements
The isolated Himalayan village of Bemni is located here.Culture
Architecture and crafts
Mahasu Devta Temple
Mahasu Devta Temple ( Mahasui: 𑚢𑚩𑚭𑚨𑚱 𑚛𑚲𑚦𑚙𑚭 𑚢𑚫𑚛𑚮𑚤, hi, महासू देवता मंदिर), is located on the Tuini-Mori road at Hanol, Dehradun district, Uttarakhand,India and was bu ...
at Hanol is notable for its traditional wooden architecture.
Architectural details of a Dharamshala, estb. 1822, Haridwar.jpg, Architectural details of a Dharamshala
Dharamshala (; also spelled Dharamsala) is the winter capital of Himachal Pradesh, India. It serves as administrative headquarters of the Kangra district after being relocated from Kangra, a city located away from Dharamshala, in 1855.
The ...
, established 1822, Haridwar.
Abhisarika-nayika-mola-ram.jpg, ''Abhisarika Nayika'', a painting by Mola Ram
Mola Ram or Maula Ram ( deva, मौला राम) (1743–1833), p.119 was an Indian painter, who originated the Garhwal branch of the Kangra school of painting., pp.75–76 He was also a poet, historian and diplomat., p.25 Much researc ...
.
The Deputy Chairman, Planning Commission, Shri K.C. Pant speaking at the releasing of the Uttaranchal crafts map at the exhibition of "Artistic Crafts Maps of Jharkhand.jpg, The releasing of the Uttaranchal crafts map
wood carving
Wood carving is a form of woodworking by means of a cutting tool (knife) in one hand or a chisel by two hands or with one hand on a chisel and one hand on a mallet, resulting in a wooden figure or figurine, or in the sculptural ornamentation ...
, which appears most frequently in the ornately decorated temples of Uttarakhand. Intricately carved designs of floral patterns, deities, and geometrical motifs also decorate the doors, windows, ceilings, and walls of village houses. Paintings and murals are used to decorate both houses and temples. Pahari painting
Pahari painting (literally meaning a painting from the mountainous regions: ''pahar'' means a mountain in Hindi) is an umbrella term used for a form of Indian painting, done mostly in miniature forms, originating from Himalayan hill kingdoms ...
is a form of painting that flourished in the region between the 17th and 19th century. Mola Ram
Mola Ram or Maula Ram ( deva, मौला राम) (1743–1833), p.119 was an Indian painter, who originated the Garhwal branch of the Kangra school of painting., pp.75–76 He was also a poet, historian and diplomat., p.25 Much researc ...
started the Garhwal Branch of the Kangra school of painting. Guler State
Guler was a small precolonial Indian hill state in the Lower Himalayas. Its capital was the town of Haripur Guler, in modern-day Himachal Pradesh. The kingdom was founded in 1415 by Raja Hari Chand, a scion of the ancient royal family of Kang ...
was known as the "cradle of Kangra paintings". Kumaoni art often is geometrical in nature, while Garhwali art is known for its closeness to nature. Other crafts of Uttarakhand include handcrafted gold jewellery
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile met ...
, basketry from Garhwal, woollen shawls, scarves
A scarf, plural ''scarves'', is a piece of fabric worn around the neck or head for warmth, sun protection, cleanliness, fashion, religious reasons, or used to show the support for a sports club or team. They can be made in a variety of diffe ...
, and rugs
Rug or RUG may refer to:
* Rug, or carpet, a textile floor covering
* Rug, slang for a toupée
* Ghent University (''Rijksunversiteit Gent'', or RUG)
* Really Useful Group, or RUG, a company set up by Andrew Lloyd Webber
* Rugby railway station, N ...
. The latter are mainly produced by the Bhotiyas of northern Uttarakhand.
Arts and literature
 Uttarakhand's diverse ethnicities have created a rich literary tradition in languages including Hindi, Garhwali, Kumaoni, Jaunsari, and Tharu. Many of its traditional tales originated in the form of lyrical
Uttarakhand's diverse ethnicities have created a rich literary tradition in languages including Hindi, Garhwali, Kumaoni, Jaunsari, and Tharu. Many of its traditional tales originated in the form of lyrical ballad
A ballad is a form of verse, often a narrative set to music. Ballads derive from the medieval French ''chanson balladée'' or ''ballade'', which were originally "dance songs". Ballads were particularly characteristic of the popular poetry and ...
s and chanted by itinerant singers and are now considered classics of Hindi literature
Hindi literature ( hi, हिन्दी साहित्य, translit=hindī sāhitya) includes literature in the various Hindi language which have writing systems. Earliest forms of Hindi literature are attested in poetry of Apabhraṃś ...
. Abodh Bandhu Bahuguna, Badri Datt Pandey, Ganga Prasad Vimal; Mohan Upreti
Mohan Upreti (1928–1997) was an Indian theatre director, playwright and a music composer, considered one of the pioneers in Indian theatre music.
A popular figure in Kumaon, Mohan Upreti is remembered for his immense contribution towards the ...
, Naima Khan Upreti
Naima Khan Upreti ( hi, नईमा खान उप्रेती; 25 May 1938 – 15 June 2018) was an Indian theatre actor, singer and a producer at Doordarshan. She was also the wife of Mohan Upreti, considered to be one of the pioneer ...
, Prasoon Joshi
Prasoon Joshi (born 16 September 1971) is an Indian poet, writer, lyricist, screenwriter, and communication specialist and marketer. He is the CEO of McCann World group India and Chairman APAC (Asia Pacific), a subsidiary of the global marke ...
, Shailesh Matiyani, Shekhar Joshi, Shivani, Taradutt Gairola, Tom Alter
Thomas Beach Alter (22 June 1950 – 29 September 2017) was an Indian actor. He was best known for his works in Hindi cinema, and Indian theatre. In 2008, he was awarded the Padma Shri by the Government of India.
Early life
Born in Mussoorie ...
; Lalit Kala Akademi fellow – Ranbir Singh Bisht; Sangeet Natak Akademi Awardees – B. M. Shah, Narendra Singh Negi; Sahitya Akademi Award
The Sahitya Akademi Award is a literary honour in India, which the Sahitya Akademi, India's National Academy of Letters, annually confers on writers of the most outstanding books of literary merit published in any of the 22 languages of the ...
ees – Leeladhar Jagudi, Shivprasad Dabral Charan, Manglesh Dabral, Manohar Shyam Joshi
Manohar Shyam Joshi (9 August 1933 – 30 March 2006) was a Hindi writer, journalist and scriptwriter, most well known as the writer of Indian television's first soap opera, '' Hum Log'' (1984) and his early hits ''Buniyaad'' (1987), '' Kakaji ...
, Ramesh Chandra Shah, Ruskin Bond
Ruskin Bond (born 19 May 1934) is an Anglo-Indian author . His first novel, '' The Room on the Roof'', was published in 1956, and it received the John Llewellyn Rhys Prize in 1957. Bond has authored more than 500 short stories, essays, and ...
and Viren Dangwal; Jnanpith Award
The Jnanpith Award is the oldest and the highest Indian literary award presented annually by the Bharatiya Jnanpith to an author for their "outstanding contribution towards literature". Instituted in 1961, the award is bestowed only on Indian w ...
ee and Sahitya Akademi fellow Sumitranandan Pant
Sumitranandan Pant (20 May 1900 – 28 December 1977) was an Indian poet. He was one of the most celebrated 20th century poets of the Hindi language and was known for romanticism in his poems which were inspired by nature, people and beauty wit ...
are some major literary, artistic and theatre personalities from the state. prominent philosophers, Indian independence activists and social-environmental activists; Anil Prakash Joshi
Dr. Anil Prakash Joshi is an environmentalist, green activist, and the founder of Himalayan Environmental Studies and Conservation Organization (HESCO), a Dehradun-based voluntary organization. His work majorly includes developing sustainable t ...
, Basanti Devi
Basanti Devi (23 March 1880 – 7 May 1974) was an Indian independence activist during the British rule in India. She was the wife of activist Chittaranjan Das. After Das' arrest in 1921 and death in 1925, she took an active part in various po ...
, Gaura Devi, Govind Ballabh Pant
Govind Ballabh Pant (10 September 1887 – 7 March 1961) was an Indian freedom fighter and the first chief minister of Uttar Pradesh. Alongside Mahatma Gandhi, Jawaharlal Nehru and Vallabhbhai Patel, Vallabh Bhai Patel, Pant was a key figure i ...
, Chandi Prasad Bhatt
Chandi Prasad Bhatt (born 23 June 1934) is an Indian Gandhian environmentalist and social activist, who founded Dasholi Gram Swarajya Sangh (DGSS) in Gopeshwar in 1964, which later became a mother-organization to the Chipko Movement, in which ...
, Deep Joshi
Deep Joshi is an Indian social worker and NGO activist and a recipient of the Magsaysay award in 2009. He is recognised for his leadership in bringing professionalism to the NGO movement in India. He co-founded a non-profit organisation, Profe ...
, Hargovind Pant, Kalu Singh Mahara
Kalu Singh Mahara was a Kumaoni(Kumauni) leader during the Indian Rebellion of 1857. He is known as a freedom fighter from the state of Uttarakhand, then in the United Province.
Kalu Singh began a campaign named as Krantiveer. It became was popu ...
, Kunwar Singh Negi, Mukandi Lal
Mukandi Lal (14 October 1885 - 10 January 1982) was an Indian advocate, judge, freedom fighter, politician, writer and art critic from Garhwal.
Early life
Mukandi Lal was born in Patali village, Malla Nagpur patti in Chamoli, Garhwal in the ...
, Nagendra Saklani, Sri Dev Suman, Ram Prasad Nautiyal, Sunderlal Bahuguna and Vandana Shiva
Vandana Shiva (born 5 November 1952) is an Indian scholar, environmental activist, food sovereignty advocate, ecofeminist and anti-globalisation author. Based in Delhi, Shiva has written more than 20 books. She is often referred to as "Gandh ...
are also from Uttarakhand.
Cuisine
 The primary food of Uttarakhand is vegetables with wheat being a staple, although non-vegetarian food is also served. A distinctive characteristic of Uttarakhand cuisine is the sparing use of tomatoes, milk, and milk-based products. Coarse grain with high fibre content is very common in Uttarakhand due to the harsh terrain. Crops most commonly associated with Uttarakhand are
The primary food of Uttarakhand is vegetables with wheat being a staple, although non-vegetarian food is also served. A distinctive characteristic of Uttarakhand cuisine is the sparing use of tomatoes, milk, and milk-based products. Coarse grain with high fibre content is very common in Uttarakhand due to the harsh terrain. Crops most commonly associated with Uttarakhand are Buckwheat
Buckwheat (''Fagopyrum esculentum''), or common buckwheat, is a flowering plant in the knotweed family Polygonaceae cultivated for its grain-like seeds and as a cover crop. The name "buckwheat" is used for several other species, such as ''Fagopy ...
(locally called ''Kotu'' or ''Kuttu'') and the regional crops, ''Maduwa'' and ''Jhangora'', particularly in the interior regions of Kumaon and Garhwal. Generally, either Desi Ghee or Mustard oil
Mustard oil can mean either the pressed oil used for cooking, or a pungent essential oil also known as volatile oil of mustard. The essential oil results from grinding mustard seed, mixing the grounds with water, and extracting the resulting vola ...
is used for the purpose of cooking food. Simple recipes are made interesting with the use of hash seeds '' Jakhya'' as spice, chutney
A chutney is a spread in the cuisines of the Indian subcontinent. Chutneys are made in a wide variety of forms, such as a tomato relish, a ground peanut garnish, yogurt or curd, cucumber, spicy coconut, spicy onion or mint dipping sa ...
made of Bhang
Bhang (IAST: ''Bhāṅg'') is an edible preparation made from the leaves of the cannabis plant originating from the Indian subcontinent. It has been used in food and drink as early as 1000 BC in ancient India. Bhang is traditionally distribu ...
is also a regional cuisine. Bal Mithai is a popular fudge-like sweet. Other popular dishes include Dubuk, Chains, Kap, Bhatiya, Jaula, Phana, Paliyo, Chutkani and Sei. In sweets; Swal, Ghughut/Khajur, Arsa, Mishri, Gatta and Gulgulas are popular. A regional variation of Kadhi
Kadhi or karhi is a dish popularly consumed in South Asia. It consists of a thick gravy based on gram flour, and contains vegetable fritters called pakoras, to which dahi (yogurt) is added to give it a bit of sour taste. It is often eaten wit ...
called ''Jhoi'' or ''Jholi'' is also popular.
Dances and music
 The dances of the region are connected to life and human existence and exhibit myriad human emotions. Langvir Nritya is a dance form for males that resembles gymnastic movements. Barada Nati folk dance is another dance of
The dances of the region are connected to life and human existence and exhibit myriad human emotions. Langvir Nritya is a dance form for males that resembles gymnastic movements. Barada Nati folk dance is another dance of Jaunsar-Bawar
Jaunsar-Bawar is a hilly region in Garhwal division of Uttarakhand, northern India. It is located in the north-west of Dehradun district, along the border with the state of Himachal Pradesh.
Ethnically, Jaunsar-Bawar comprises two regions, inh ...
, which is practised during some religious festivals. Other well-known dances include Hurka Baul, Jhora-Chanchri, Chhapeli, Thadya, Jhumaila, Pandav
The Pandavas (Sanskrit: पाण्डव, IAST: Pāṇḍava) refers to the five legendary brothers— Yudhishthira, Bhima, Arjuna, Nakula and Sahadeva—who are the central characters of the Hindu epic ''Mahabharata''. They are acknowledged ...
, Chauphula, and Chholiya
Chholiya (or Chhaliya; Kumaoni: ) or Hudkeli (or Hudke; ) is a traditional folk dance form originated in the Kumaon division of the Indian state of Uttarakhand and Sudurpashchim province of Nepal. It has today become a symbol of Kumaoni and ...
. Music is an integral part of the Uttarakhandi culture. Popular types of folk songs include Mangal, Basanti, Khuder and Chhopati. These folk songs are played on instruments including Dhol
Dhol (IPA: ) can refer to any one of a number of similar types of double-headed drum widely used, with regional variations, throughout the Indian subcontinent. Its range of distribution in India, Bangladesh and Pakistan primarily includes nort ...
, Damau, Turri, Ransingha, Dholki, Daur, Thali
Thali (meaning "plate"), Bhojanam (meaning "full meal") or Chakluk is a round platter used to serve food in South Asia, Southeast Asia and the Caribbean. Thali is also used to refer to an Indian-style meal made up of a selection of various d ...
, Bhankora, Mandan and Mashakbaja. "Bedu Pako Baro Masa
''Bedu Pako Baro Masa'' (English: ''Figs do ripen round the year'') is a Kumaoni folk song in Kumaoni language which was composed by Mohan Upreti, B. M. Shah and written by Brijendra Lal Shah. This Kumaoni song was composed, written and first ...
" is a popular folk song of Uttarakhand with international fame and legendary status within the state. It serves as the cultural anthem of Uttarakhandi people worldwide. Music is also used as a medium through which the gods are invoked. '' Jagar'' is a form of spirit worship in which the singer, or ''Jagariya'', sings a ballad of the gods, with allusions to great epics, like Mahabharat
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; sa, महाभारतम्, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the '' Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the struggle between two groups of cousins in the Kuru ...
and Ramayana
The ''Rāmāyana'' (; sa, रामायणम्, ) is a Sanskrit literature, Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epic composed over a period of nearly a millennium, with scholars' estimates for the earliest stage of the text ranging from the 8th ...
, that describe the adventures and exploits of the god being invoked. B. K. Samant, Basanti Bisht, Chander Singh Rahi, Girish Tiwari 'Girda', Gopal Babu Goswami, Heera Singh Rana, Jeet Singh Negi, Meena Rana, Mohan Upreti
Mohan Upreti (1928–1997) was an Indian theatre director, playwright and a music composer, considered one of the pioneers in Indian theatre music.
A popular figure in Kumaon, Mohan Upreti is remembered for his immense contribution towards the ...
, Narendra Singh Negi and Pritam Bhartwan are popular folk singers
Folk music is a music genre that includes traditional folk music and the contemporary genre that evolved from the former during the 20th-century folk revival. Some types of folk music may be called world music. Traditional folk music has be ...
and musicians from the state, so are Bollywood
Hindi cinema, popularly known as Bollywood and formerly as Bombay cinema, refers to the film industry based in Mumbai, engaged in production of motion pictures in Hindi language. The popular term Bollywood, is a portmanteau of "Bombay" (fo ...
singer Jubin Nautiyal
Jubin Nautiyal (born 14 June 1989) is an Indian playback singer and live performer. In June 2022, he won the IIFA award for “Playback Singer (Male)” for the song “Raataan Lambiyan.” He was awarded Upcoming Male Vocalist of the Year at ...
and country
A country is a distinct part of the world, such as a state, nation, or other political entity. It may be a sovereign state or make up one part of a larger state. For example, the country of Japan is an independent, sovereign state, while ...
singer Bobby Cash.
Fairs and festivals
 One of the major
One of the major Hindu pilgrimages
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
, Haridwar Kumbh Mela
The Kumbh Mela at Haridwar is a mela held every 12 years at Haridwar, India. The exact date is determined according to Hindu astrology: the Mela is held when Jupiter is in Aquarius and the Sun enters Aries.
The event possesses deep religious s ...
, takes place in Uttarakhand. Haridwar
Haridwar (; ) is a city and municipal corporation in the Haridwar district of Uttarakhand, India. With a population of 228,832 in 2011, it is the second-largest city in the state and the largest in the district.
The city is situated on the ri ...
is one of the four places in India where this mela is organised. Haridwar most recently hosted the Purna Kumbh Mela from Makar Sankranti (14 January 2010) to Vaishakh Purnima Snan (28 April 2010). Hundreds of foreigners joined Indian pilgrims in the festival, which is considered the largest religious gathering in the world., The Independent
''The Independent'' is a British online newspaper. It was established in 1986 as a national morning printed paper. Nicknamed the ''Indy'', it began as a broadsheet and changed to tabloid format in 2003. The last printed edition was publish ...
, 14 April 2010
Kumauni Holi, in forms including Baithki Holi, Khari Holi, and Mahila Holi, all of which start from Vasant Panchami
Vasant Panchami, also called Saraswati Puja in honor of the Hindu goddess Saraswati, is a festival that marks the preparation for the arrival of spring. The festival is celebrated in Indian religions in different ways depending on the region. ...
, are festivals and musical affairs that can last almost a month. Ganga Dashahara, Vasant Panchami, Makar Sankranti, Ghee Sankranti, Khatarua, Vat Savitri, and Phul Dei (The festival of spring) are other major festivals. In addition, various fairs like Kanwar Yatra
The Kānvar (or Kānwar/ Kāvaḍ) Yātrā (Devanagari: कांवड़ यात्रा) is an annual pilgrimage of devotees of Shiva, known as ''Kānvarias''(कावड़िया) or "Bhole" (भोले), to Hindu pilgrimage plac ...
, Kandali Festival, Ramman
Hadad ( uga, ), Haddad, Adad ( Akkadian: 𒀭𒅎 '' DIM'', pronounced as ''Adād''), or Iškur ( Sumerian) was the storm and rain god in the Canaanite and ancient Mesopotamian religions.
He was attested in Ebla as "Hadda" in c. 2500 BCE. ...
, Harela Mela, Kauthig, Nauchandi Mela, Giddi Mela, Uttarayani Mela and Nanda Devi Raj Jat
The three-week-long Nanda Devi Raj Jat (नंदा देवी राज जात) is a pilgrimage and festival of Uttarakhand. India. The Raj-Jaat is celebrated in Chamoli Garhwal district, and traditionally only the deities of Garhwal Div ...
take place.
The festivals of Kumbh Mela at Haridwar
Haridwar (; ) is a city and municipal corporation in the Haridwar district of Uttarakhand, India. With a population of 228,832 in 2011, it is the second-largest city in the state and the largest in the district.
The city is situated on the ri ...
, Ramlila
Ramlila (Rāmlīlā) (literally 'Rama's lila or play') is any dramatic folk re-enactment of the life of Rama according to the ancient Hindu epic ''Ramayana'' or secondary literature based on it such as the ''Ramcharitmanas''. It particularly ...
, Ramman
Hadad ( uga, ), Haddad, Adad ( Akkadian: 𒀭𒅎 '' DIM'', pronounced as ''Adād''), or Iškur ( Sumerian) was the storm and rain god in the Canaanite and ancient Mesopotamian religions.
He was attested in Ebla as "Hadda" in c. 2500 BCE. ...
of Garhwal, the traditions of Vedic chant
The oral tradition of the Vedas (Śruti) consists of several pathas, "recitations" or ways of chanting the Vedic mantras. Such traditions of Vedic chant are often considered the oldest unbroken oral tradition in existence, the fixation of the Vedi ...
ings and Yoga
Yoga (; sa, योग, lit=yoke' or 'union ) is a group of physical, mental, and spiritual practices or disciplines which originated in ancient India and aim to control (yoke) and still the mind, recognizing a detached witness-consci ...
are included in the list of Intangible cultural heritage of the UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
.
Economy
 The Uttarakhand state is the second fastest growing state in India. Its gross state domestic product (GSDP) (at constant prices) more than doubled from 24,786 crore in FY2005 to 60,898 crore in FY2012. The real GSDP grew at 13.7% (CAGR) during the FY2005–FY2012 period. The contribution of the service sector to the GSDP of Uttarakhand was just over 50% during FY 2012. Per capita income in Uttarakhand is 198738 (FY 2018–19), which is higher than the national average of 126406 (FY 2018–19). According to the
The Uttarakhand state is the second fastest growing state in India. Its gross state domestic product (GSDP) (at constant prices) more than doubled from 24,786 crore in FY2005 to 60,898 crore in FY2012. The real GSDP grew at 13.7% (CAGR) during the FY2005–FY2012 period. The contribution of the service sector to the GSDP of Uttarakhand was just over 50% during FY 2012. Per capita income in Uttarakhand is 198738 (FY 2018–19), which is higher than the national average of 126406 (FY 2018–19). According to the Reserve Bank of India
The Reserve Bank of India, chiefly known as RBI, is India's central bank and regulatory body responsible for regulation of the Indian banking system. It is under the ownership of Ministry of Finance, Government of India. It is responsible f ...
, the total foreign direct investment in the state from April 2000 to October 2009 amounted to US$46.7 million.
Like most of India, agriculture is one of the most significant sectors of the economy of Uttarakhand. Basmati
Basmati, , is a variety of long, slender-grained aromatic rice which is traditionally grown in India, Pakistan, and Nepal.
rice, wheat, soybeans, groundnuts, coarse cereals, pulses, and oil seeds are the most widely grown crops. Fruits like apples, oranges, pears, peaches, lychees, and plums are widely grown and important to the large food processing industry. Agricultural export zones have been set up in the state for lychees, horticulture, herbs, medicinal plants, and basmati rice. During 2010, wheat production was 831 thousand tonnes and rice production was 610 thousand tonnes, while the main cash crop of the state, sugarcane, had a production of 5058 thousand tonnes. As 86% of the state consists of hills, the yield per hectare is not very high. 86% of all croplands are in the plains while the remaining is from the hills. The state also holds the GI tag for Tejpatta ( Cinnamomum tamala) or Indian bay leaf, which is known to add flavour to dishes and also possesses several medicinal properties.
Other key industries include tourism and hydropower, and there is prospective development in IT, ITES, biotechnology, pharmaceuticals and automobile industries. The service sector of Uttarakhand mainly includes tourism, information technology, higher education, and banking.
During 2005–2006, the state successfully developed three Integrated Industrial Estates (IIEs) at Haridwar
Haridwar (; ) is a city and municipal corporation in the Haridwar district of Uttarakhand, India. With a population of 228,832 in 2011, it is the second-largest city in the state and the largest in the district.
The city is situated on the ri ...
, Pantnagar
Pantnagar is a town and a university campus in Udham Singh Nagar district, Uttarakhand. Nainital, Kashipur, Rudrapur and Kiccha, Haldwani are the major cities surrounding Pantnagar.
The town is home to the first agricultural university of I ...
, and Sitarganj
Sitarganj is a city and a municipal board in Udham Singh Nagar district in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. Now it is home to the Integrated Industrial Estate Sitarganj (IIE) being developed by State Industrial Development Corporation of Uttarak ...
; Pharma City at Selakui; Information Technology Park at Sahastradhara ( Dehradun); and a growth centre at Sigaddi (Kotdwar
Kotdwar is a city, municipal corporation in Pauri Garhwal district of Uttarakhand, India. It's just 101 km from Pauri town , the district headquarter. It is the eighth-largest city in Uttarakhand. Its old name was "Khohdwar", which means the g ...
). Also in 2006, 20 industrial sectors in public private partnership mode were developed in the state.
Transport
 Uttarakhand has of roads, of which are national highways and are state highways. The State Road Transport Corporation (SRTC), which has been reorganised in Uttarakhand as the
Uttarakhand has of roads, of which are national highways and are state highways. The State Road Transport Corporation (SRTC), which has been reorganised in Uttarakhand as the Uttarakhand Transport Corporation
Uttarakhand Transport Corporation also referred to as UTC or Uttarakhand Roadways, is the state run bus service of Uttarakhand state of India. UTC buses serves routes to towns and cities within Uttarakhand and adjoining states and union territt ...
(UTC), is a major constituent of the transport system in the state. The corporation began to work on 31 October 2003 and provides services on interstate and nationalised routes. As of 2012, approximately 1000 buses are being plied by the UTC on 35 nationalised routes along with many other non-nationalised routes. There are also private transport operators operating approximately 3000 buses on non-nationalised routes along with a few interstate routes in Uttarakhand and the neighbouring state of U.P. For travelling locally, the state, like most of the country, has auto rickshaw
An auto rickshaw is a motorized version of the pulled rickshaw or cycle rickshaw. Most have three wheels and do not tilt. They are known by many terms in various countries including auto, auto rickshaw, baby taxi, mototaxi, pigeon, jonnybee, bajaj ...
s and cycle rickshaw
The cycle rickshaw is a small-scale local means of transport. It is a type of hatchback tricycle designed to carry passengers on a for-hire basis. It is also known by a variety of other names such as bike taxi, velotaxi, pedicab, bikecab, ...
s. In addition, remote towns and villages in the hills are connected to important road junctions and bus routes by a vast network of crowded share jeeps.
The air transport network in the state is gradually improving. Jolly Grant Airport in Dehradun, is the busiest airport in the state with six daily flights to Delhi Airport
Indira Gandhi International Airport is the primary international airport serving Delhi, the capital of India, and the National Capital Region (NCR). The airport, spread over an area of , is situated in Palam, Delhi, southwest of the New De ...
. Pantnagar Airport, located in Pantnagar
Pantnagar is a town and a university campus in Udham Singh Nagar district, Uttarakhand. Nainital, Kashipur, Rudrapur and Kiccha, Haldwani are the major cities surrounding Pantnagar.
The town is home to the first agricultural university of I ...
of the Kumaon region have 1 daily air service to Delhi and return too
. There government is planning to develop Naini Saini Airport in Pithoragarh
Pithoragarh ( Kumaoni: ''Pithor'garh'') is a Himalayan city with a Municipal Board in Pithoragarh district in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It is the fourth largest city of Kumaon and the largest in Kumaon hills. It is an education hub of t ...
, Bharkot Airport in Chinyalisaur in Uttarkashi district and Gauchar Airport
Gauchar is a Hill Town sort of a valley town located in Karnaprayag tehsil within Chamoli district of Uttarakhand state in India. Gauchar is situated on the left bank of river Alaknanda and is en route to the celebrated holy destination of Badrin ...
in Gauchar, Chamoli district.
There are plans to launch helipad service in Pantnagar and Jolly Grant Airports and other important tourist destinations like Ghangaria and Hemkund Sahib.
As over 86% of Uttarakhand's terrain consists of hills, railway services are very limited in the state and are largely confined to the plains. In 2011, the total length of railway tracks was about . Rail, being the cheapest mode of transport, is most popular. The most important railway station in Kumaun Division of Uttarakhand is at Kathgodam
Kathgodam is a suburb of Haldwani city in the Nainital district of Uttarakhand state of India. It used to be a part of the twin township of Haldwani-Kathgodam, and is immediately north of Haldwani. It is one of the important collection centres ...
, 35 kilometres away from Nainital. Kathgodam is the last terminus of the broad gauge line of North East Railways that connects Nainital with Delhi, Dehradun, and Howrah. Other notable railway stations are at Pantnagar
Pantnagar is a town and a university campus in Udham Singh Nagar district, Uttarakhand. Nainital, Kashipur, Rudrapur and Kiccha, Haldwani are the major cities surrounding Pantnagar.
The town is home to the first agricultural university of I ...
, Lalkuan
Lalkuan is a Nagar Panchayat in the Nainital district of the Indian state of Uttarakhand.
Demographics
In the 2011 India census, Lalkuan had a population of 7,644. Males constituted 55% of the population and females 45%. Lalkuan had an average l ...
and Haldwani
Haldwani ( Kumaoni: ''Haldvānī'') is the largest city of Kumaon. It is also the third most populous city and largest commercial market in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. Haldwani is said to be the financial capital of Uttarakhand, having the ...
.
Dehradun railway station
Dehradun Terminal railway station is a railway station in Dehradun, Uttarakhand, India, on the Northern line of the Northern Railway network. It is owned by Indian Railways.
It was established in 1899 by the British. Several lines which run t ...
is a railhead of the Northern Railways.
Haridwar station is situated on the Delhi–Dehradun and Howrah–Dehradun railway lines. One of the main railheads of the Northern Railways, Haridwar Junction Railway Station is connected by broad gauge line. Roorkee comes under Northern Railway region of Indian Railways on the main Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising a ...
– Mughal Sarai trunk route and is connected to major Indian cities.
Other railheads are Rishikesh, Kotdwar
Kotdwar is a city, municipal corporation in Pauri Garhwal district of Uttarakhand, India. It's just 101 km from Pauri town , the district headquarter. It is the eighth-largest city in Uttarakhand. Its old name was "Khohdwar", which means the g ...
and Ramnagar Ramnagar may refer to the following places:
Bangladesh
* Ramnagar, Bangladesh, a village in Chittagong Division
* Ramnagar Union, Jessore Sadar
India Jammu and Kashmir
* Ramnagar, Udhampur, a town in Jammu and Kashmir
** Ramnagar Fort Udha ...
linked to Delhi by daily trains.
Tourism
Valley of Flowers National Park
Valley of Flowers National Park is an Indian National parks of India, national park which was established in 1982. It is located in Chamoli in the state of Uttarakhand and is known for its meadows of Endemism, endemic alpine flowers and the var ...
Ali bugyal2.jpg, View of a Bugyal
Bugyals are alpine pasture lands, or meadows, in higher elevation range between and of the Himalayas in the Indian state of Uttarakhand, where they are called "nature’s own gardens". The topography of the terrain is either flat or sloped. Th ...
(meadow) in Uttarakhand
Har Ki Dun.jpg, Har Ki Doon
Har Ki Doon or Har Ki Dun is a cradle-shaped hanging valley in the Garhwal Himalayas of Uttarakhand, India. The region is surrounded with green Bugyals (High Altitude Meadows). It is surrounded by snow-covered peaks and alpine vegetation. It is ...
, a high-altitude hanging valley
A valley is an elongated low area often running between hills or mountains, which will typically contain a river or stream running from one end to the other. Most valleys are formed by erosion of the land surface by rivers or streams over ...
Rishikesh view across bridge.jpg, Rishikesh view and 13 stories Shiva temple across Lakshman Jhula bridge over the Ganges
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is ...
Kedarnath Temple - OCT 2014.jpg, Kedarnath Temple
Kedarnath Temple (Sanskrit: केदारनाथ मंदिर, IAST: ''Kēdāranātha Mandira'', ) is a Hindu temple roughly 1200 years old dedicated to Shiva. The temple is located on the Garhwal Himalayan range near the Mandakini river ...
is one of the 12 Jyotirlingas
 Uttarakhand has many tourist spots due to its location in the Himalayas. There are many ancient temples, forest reserves, national parks, hill stations, and mountain peaks that draw large number of tourists. There are 44 nationally protected monuments in the state. Oak Grove School in the state is on the tentative list for World Heritage Sites. Two of the most holy rivers in
Uttarakhand has many tourist spots due to its location in the Himalayas. There are many ancient temples, forest reserves, national parks, hill stations, and mountain peaks that draw large number of tourists. There are 44 nationally protected monuments in the state. Oak Grove School in the state is on the tentative list for World Heritage Sites. Two of the most holy rivers in Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
the Ganges
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is ...
and Yamuna
The Yamuna ( Hindustani: ), also spelt Jumna, is the second-largest tributary river of the Ganges by discharge and the longest tributary in India. Originating from the Yamunotri Glacier at a height of about on the southwestern slopes of B ...
, originate in Uttarakhand. Binsar Devta is a popular Hindu temple in the area.
Uttarakhand has long been called "Land of the Gods" as the state has some of the holiest Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
shrines, and for more than a thousand years, pilgrims have been visiting the region in the hopes of salvation and purification from sin. Gangotri and Yamunotri, the sources of the Ganges and Yamuna, dedicated to Ganga and Yamuna
The Yamuna ( Hindustani: ), also spelt Jumna, is the second-largest tributary river of the Ganges by discharge and the longest tributary in India. Originating from the Yamunotri Glacier at a height of about on the southwestern slopes of B ...
respectively, fall in the upper reaches of the state and together with Badrinath
Badrinath is a town and nagar panchayat in Chamoli district in the state of Uttarakhand, India. A Hindu holy place, it is one of the four sites in India's Char Dham pilgrimage and is also part of India's Chota Char Dham pilgrimage circuit. ...
(dedicated to Vishnu
Vishnu ( ; , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism.
Vishnu is known as "The Preserver" withi ...
) and Kedarnath
Kedarnath is a town and Nagar Panchayat in Rudraprayag district of Uttarakhand, India, known primarily for the Kedarnath Temple. It is approximately 86 kilometres from Rudraprayag, the district headquarter. Kedarnath is the most remote of t ...
(dedicated to Shiva
Shiva (; sa, शिव, lit=The Auspicious One, Śiva ), also known as Mahadeva (; ɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐ, or Hara, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions within Hindu ...
) form the Chota Char Dham
The Chota Char Dham (literally translated as 'the small four abodes/seats', meaning 'the small circuit of four abodes/seats'), is an important Hindu pilgrimage circuit in Uttarakhand, in the Indian Himalayas. Located in the Garhwal region ...
, one of Hinduism's most spiritual and auspicious pilgrimage circuits. Haridwar, meaning "Gateway to the God", is a prime Hindu destination. Haridwar
Haridwar (; ) is a city and municipal corporation in the Haridwar district of Uttarakhand, India. With a population of 228,832 in 2011, it is the second-largest city in the state and the largest in the district.
The city is situated on the ri ...
hosts the Haridwar Kumbh Mela
The Kumbh Mela at Haridwar is a mela held every 12 years at Haridwar, India. The exact date is determined according to Hindu astrology: the Mela is held when Jupiter is in Aquarius and the Sun enters Aries.
The event possesses deep religious s ...
every twelve years, in which millions of pilgrims take part from all parts of India and the world. Rishikesh near Haridwar is known as the preeminent yoga
Yoga (; sa, योग, lit=yoke' or 'union ) is a group of physical, mental, and spiritual practices or disciplines which originated in ancient India and aim to control (yoke) and still the mind, recognizing a detached witness-consci ...
centre of India. The state has an abundance of temples and shrines, many dedicated to local deities or manifestations of Shiva and Durga
Durga ( sa, दुर्गा, ) is a major Hindu goddess, worshipped as a principal aspect of the mother goddess Mahadevi. She is associated with protection, strength, motherhood, destruction, and wars.
Durga's legend centres around c ...
, references to many of which can be found in Hindu scriptures and legends. Uttarakhand is, however, a place of pilgrimage for the adherents of other religions too. Piran Kaliyar Sharif near Roorkee is a pilgrimage site to Muslims, Gurudwara Darbar Sahib, in Dehradun, Gurudwara Hemkund Sahib in Chamoli district
Chamoli district is a district of the Uttarakhand state of India. It is bounded by the Tibet region to the north, and by the Uttarakhand districts of Pithoragarh and Bageshwar to the east, Almora to the south, Pauri Garhwal to the southwest, ...
, Gurudwara Nanakmatta Sahib in Nanakmatta
Nanakmatta is a historical town named after the Sikh pilgrimage site, Gurdwara Nanak Mata Sahib, in the state of Uttarakhand in India. Sikh tradition records that the site was once called Gorakhmata, a centre of Siddh-jogis named after the fou ...
and Gurudwara Reetha Sahib in Champawat district
Champawat district is a district of Uttarakhand state in northern India. The town of Champawat is the administrative headquarters. The district of Champawat constituted in the year 1997. The district is divided into five tehsils: Barakot, Lohag ...
are pilgrimage centres for Sikhs. Tibetan Buddhism
Tibetan Buddhism (also referred to as Indo-Tibetan Buddhism, Lamaism, Lamaistic Buddhism, Himalayan Buddhism, and Northern Buddhism) is the form of Buddhism practiced in Tibet and Bhutan, where it is the dominant religion. It is also in majo ...
has also made its presence with the reconstruction of Mindrolling Monastery
Mindrolling Monastery (, English: "Sublime Island of Ripening Liberation"), is one of the "Six Mother Monasteries" of the Nyingma school in Tibet. It was founded by Rigzin Terdak Lingpa in 1676. Tendrak Lingpa's lineage is known as the ''Nyo'' ...
and its Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism.
According to Buddhist tradition, he was born in L ...
Stupa, described as the world's highest at Clement Town, Dehradun.
Auli and Munsiari
Munsiyari ( Kumaoni: ''Munsyār'') is the name of the sub-division headquarters, a conglomeration of revenue villages and it also refers to the entire region as Munsiyari Tehsil and Sub Division in the Pithoragarh District in the hill-state of ...
are well-known skiing resorts in the state.
The state has 12 National Parks and Wildlife Sanctuaries, which cover 13.8 per cent of the total area of the state. They are located at different altitudes varying from 800 to 5400 metres. The oldest national park on the Indian sub-continent, Jim Corbett National Park
Jim Corbett National Park is a national park in India located in the Nainital district of Uttarakhand state. The first national park in India, it was established in 1936 during the British Raj and named ''Hailey National Park'' after Willia ...
, is a major tourist attraction.
Vasudhara Falls, near Badrinath
Badrinath is a town and nagar panchayat in Chamoli district in the state of Uttarakhand, India. A Hindu holy place, it is one of the four sites in India's Char Dham pilgrimage and is also part of India's Chota Char Dham pilgrimage circuit. ...
is a waterfall with a height of set in a backdrop of snow-clad mountains.
The state has always been a destination for mountaineering, hiking
Hiking is a long, vigorous walk, usually on trails or footpaths in the countryside. Walking for pleasure developed in Europe during the eighteenth century.AMATO, JOSEPH A. "Mind over Foot: Romantic Walking and Rambling." In ''On Foot: A Histor ...
, and rock climbing in India. A recent development in adventure tourism
Adventure travel is a type of niche tourism, involving exploration or travel with a certain degree of risk (real or perceived), and which may require special skills and physical exertion. In the United States, adventure tourism has grown in r ...
in the region has been whitewater rafting
Rafting and whitewater rafting are recreational outdoor activities which use an inflatable raft to navigate a river or other body of water. This is often done on whitewater or different degrees of rough water. Dealing with risk is often a ...
in Rishikesh. Due to its proximity to the Himalaya ranges, the place is full of hills and mountains and is suitable for trekking, climbing, skiing, camping, rock climbing, and paragliding. Roopkund is a trekking site, known for the mysterious skeletons found in a lake, which was featured by National Geographic Channel in a documentary. The trek to Roopkund passes through the meadows of Bugyal
Bugyals are alpine pasture lands, or meadows, in higher elevation range between and of the Himalayas in the Indian state of Uttarakhand, where they are called "nature’s own gardens". The topography of the terrain is either flat or sloped. Th ...
.
New Tehri city has Tehri Dam
With a height of 260.5 m (855 ft) Tehri Dam is the tallest dam in India and 12th tallest dam in the world. With a total planned installed capacity of 2400 MW, it's the biggest Hydroelectric power plant in India. It is a multi-purpose rock and ea ...
, with a height of 260.5 m (855 ft) is the tallest dam in India. It is currently ranked No 10 on the List of Tallest Dams
This is a list of the tallest dams in the world over in height. The tallest dam in the world is the Jinping-I Dam, an arch dam in China at . The tallest embankment dam and second tallest dam in the world is the Nurek Dam in Tajikistan. The tal ...
in the world. Tehri Lake with a surface area of 52 km2, is the biggest lake in the state of Uttarakhand. It has good options for Adventure Sports and various water sports like Boating, Banana Boat, Bandwagon Boat, Jet Ski, Water Skiing, Para-sailing, Kayaking.
Education
On 30 September 2010 there were 15,331 primary schools with 1,040,139 students and 22,118 working teachers in Uttarakhand. At the 2011 census the literacy rate of the state was 78.82% with 87.4% literacy for males and 70% literacy for females. The language of instruction in the schools is either English orHindi
Hindi ( Devanāgarī: or , ), or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi (Devanagari: ), is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in the Hindi Belt region encompassing parts of northern, central, eastern, and western India. Hindi has been ...
. There are mainly government-run, private unaided (no government help), and private aided schools in the state. The main school affiliations are CBSE, CISCE or UBSE, the state syllabus defined by the Department of Education of the Government of Uttarakhand
The Government of Uttarakhand also known as the State Government of Uttarakhand, or locally as State Government, is the subnational government of the Indian state of Uttarakhand and its 13 Districts. It consists of an executive branch, led ...
.. Furthermore, there is an IIT in Roorkee, AIIMS
The All India Institutes of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) is a group of autonomous government public medical universities of higher education under the jurisdiction of Ministry of Health and Family Welfare , Government of India. These institutes h ...
in Rishikesh and an IIM
The Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs) are central government-owned-public business schools for management offering undergraduate, postgraduate, doctoral and executive programmes along with some additional courses in the field of busin ...
in Kashipur.
Sports
 The high mountains and rivers of Uttarakhand attract many tourists and adventure seekers. It is also a favourite destination for adventure sports, such as
The high mountains and rivers of Uttarakhand attract many tourists and adventure seekers. It is also a favourite destination for adventure sports, such as paragliding
Paragliding is the recreational and competitive adventure sport of flying paragliders: lightweight, free-flying, foot-launched glider aircraft with no rigid primary structure. The pilot sits in a harness or lies supine in a cocoon-like 'p ...
, sky diving
Parachuting, including also skydiving, is a method of transiting from a high point in the atmosphere to the surface of Earth with the aid of gravity, involving the control of speed during the descent using a parachute or parachutes.
For ...
, rafting
Rafting and whitewater rafting are recreational outdoor activities which use an inflatable raft to navigate a river or other body of water. This is often done on whitewater or different degrees of rough water. Dealing with risk is often a ...
and bungee jumping.
More recently, golf
Golf is a club-and-ball sport in which players use various clubs to hit balls into a series of holes on a course in as few strokes as possible.
Golf, unlike most ball games, cannot and does not use a standardized playing area, and coping ...
has also become popular with Ranikhet
Ranikhet ( Kumaoni: ) is a hill station and cantonment town, nearby Almora Town in Almora district in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It is the home for the Military Hospital, Kumaon Regiment (KRC) and Naga Regiment and is maintained by the In ...
being a favourite destination.
The Cricket Association of Uttarakhand is the governing body for cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by str ...
activities. The Uttarakhand cricket team
The Uttarakhand cricket team is a cricket team that represents the state of Uttarakhand in Indian domestic competitions.
Background
In July 2018, the Board of Control for Cricket in India (BCCI) named the team as one of the nine new sides that ...
represents Uttarakhand in Ranji Trophy, Vijay Hazare Trophy and Syed Mushtaq Ali Trophy
The Syed Mushtaq Ali Trophy is a domestic T-20 cricket championship in India, organized by the Board of Control for Cricket in India (BCCI), among the teams from the Ranji Trophy. It is named after Indian former test cricketer Syed Mushtaq Ali ...
. Rajiv Gandhi International Cricket Stadium in Dehradun is the home ground of Uttarakhand cricket team.
The Uttarakhand State Football Association
The Uttarakhand State Football Association (USFA) is the governing body of football activities in the Indian state of Uttarakhand and the Uttarakhand football team. It is affiliated with the All India Football Federation. It sends state teams ...
is the governing body for association football
Association football, more commonly known as football or soccer, is a team sport played between two teams of 11 players who primarily use their feet to propel the ball around a rectangular field called a pitch. The objective of the game is ...
. The Uttarakhand football team
The Uttarakhand football team is an Indian football team representing Uttarakhand in the Santosh Trophy.
Current squad
The following 22 players were called up for the 2022–23 Santosh Trophy.
Competitive record
...
represents Uttarakhand in the Santosh Trophy and other leagues. The Indira Gandhi International Sports Stadium
Indira Gandhi International Sports Stadium is located in Haldwani, Uttarakhand, India. It has a capacity of 25,000 people and was inaugurated on 18 December 2016 by Harish Rawat, the then Chief Minister of Uttarakhand. It is spread over an ar ...
in Haldwani
Haldwani ( Kumaoni: ''Haldvānī'') is the largest city of Kumaon. It is also the third most populous city and largest commercial market in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. Haldwani is said to be the financial capital of Uttarakhand, having the ...
is the home ground of Uttarakhand football team.
Notable people
* Ajit Kumar Doval, 5th National Security Adviser of India *Rifleman
A rifleman is an infantry soldier armed with a rifled long gun. Although the rifleman role had its origin with 16th century hand cannoneers and 17th century musketeers, the term originated in the 18th century with the introduction of the ri ...
Jaswant Singh Rawat
Rifleman Jaswant Singh Rawat, MVC (19 August 1941 – 17 November 1962) was an Indian Army soldier serving in the Garhwal Rifles who was awarded the prestigious Maha Vir Chakra posthumously as a result of his actions during the battle of Nura ...
, recipient of Maha Vir Chakra
The Maha Vir Chakra (MVC) () is the second highest military decoration in India, after the Param Vir Chakra, and is awarded for acts of conspicuous gallantry in the presence of the enemy, whether on land, at sea or in the air. It replaced the B ...
* General Bipin Chandra Joshi, Chief of Army Staff of Indian Army
* General
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry.
In some usages the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED ...
Bipin Rawat
General Bipin Rawat (16 March 1958 – 8 December 2021) was an Indian military officer who was a four-star general of the Indian Army. He served as the first Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) of the Indian Armed Forces from January 2020 u ...
– 1st Chief of Defence Staff of India
* General
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry.
In some usages the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED ...
Anil Chauhan
General Anil Chauhan (born 18 May 1961) is a four-star general of the Indian Army, who is the current and 2nd Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) of the Indian Armed Forces since 30 September 2022.
An alumnus of the National Defence Academy, Khadakw ...
– 2nd Chief of Defence Staff of India
See also
* Outline of Uttarakhand *Himalayan states
The term Himalayan states is used to group countries that straddle the Himalayas. It primarily denotes Bhutan, China, India, Nepal, and Pakistan; some definitions also include Afghanistan and Myanmar. Two countries—Bhutan and Nepal—are loc ...
* Indian Himalayan Region
The Indian Himalayan Region (abbreviated to IHR) is the section of the Himalayas within the Republic of India, spanning seven Indian states and union territories, namely Ladakh, Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, West B ...
*'' Mountain Temples and Temple Mountains''
References
Further reading
* * * * * Handa, Umachand (2002).History of Uttaranchal
'. Indus Publishing. . * Husain, Z. (1995). ''Uttarakhand Movement: The Politics of Identity and Frustration, A Psycho-Analytical Study of the Separate State Movement, 1815–1995''. Bareilly: Prakash Book Depot. * Sharma, D. (1989). ''Tibeto-Himalayan languages of Uttarakhand''. Studies in Tibeto-Himalayan languages, 3. New Delhi, India: Mittal Publications. * Phonia, Kedar Singh (1987). ''Uttarakhand: The Land of Jungles, Temples and Snows''. New Delhi, India: Lancer Books. * Mukhopadhyaya, R. (1987). ''Uttarakhand Movement: A Sociological Analysis''. Centre for Himalayan Studies special lecture, 8. Raja Rammohunpur, Distt. Darjeeling: University of North Bengal. * Thapliyal, Uma Prasad (2005). ''Uttaranchal: Historical and Cultural Perspectives''. B. R. Pub. Corp., . * Negi, Vijaypal Singh, Jawaharnagar, P.O. Agastyamuni, Distt. Rudraprayag, ''The Great Himalayas'' 1998,
External links
Government
Uttarakhand Government Portal
Uttarakhand Tourism
General information
Map of Uttarakhand
with places of interest and historical attractions, mountainshepherds.com. * * {{Authority control Uttarakhand North India States and union territories of India States and territories established in 2000 2000 establishments in India