USS Montauk (1862) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The first USS ''Montauk'' was a single-

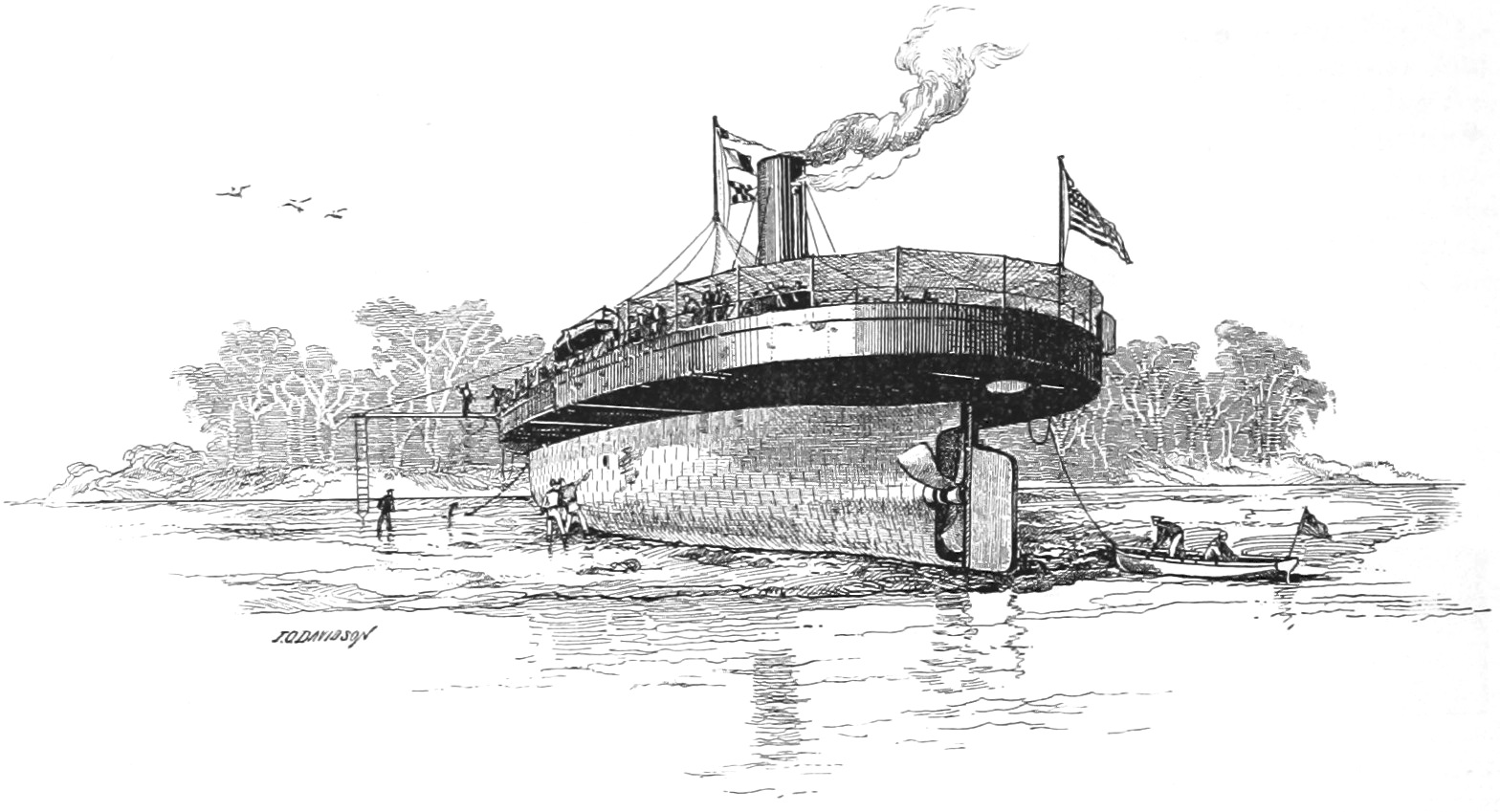 A principal
A principal  She was decommissioned at
She was decommissioned at
navsource.org: USS ''Montauk''Photograph of the U.S.S. Montauk from the Maine Memory Network
{{DEFAULTSORT:Montauk Passaic-class monitors Ships built in Brooklyn 1862 ships Ships of the Union Navy American Civil War monitors of the United States Spanish–American War monitors of the United States
turret
Turret may refer to:
* Turret (architecture), a small tower that projects above the wall of a building
* Gun turret, a mechanism of a projectile-firing weapon
* Objective turret, an indexable holder of multiple lenses in an optical microscope
* Mi ...
ed ''Passaic''-class monitor
Monitor or monitor may refer to:
Places
* Monitor, Alberta
* Monitor, Indiana, town in the United States
* Monitor, Kentucky
* Monitor, Oregon, unincorporated community in the United States
* Monitor, Washington
* Monitor, Logan County, West ...
in the Union Navy
), (official)
, colors = Blue and gold
, colors_label = Colors
, march =
, mascot =
, equipment =
, equipment_label ...
during the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
.
It saw action throughout the war. It was used as the floating prison for the conspirators in the Abraham Lincoln assassination
On April 14, 1865, Abraham Lincoln, the 16th president of the United States, was assassinated by well-known stage actor John Wilkes Booth, while attending the play ''Our American Cousin'' at Ford's Theatre in Washington, D.C.
Shot in the head ...
and was the site of the autopsy and identification of assassin John Wilkes Booth
John Wilkes Booth (May 10, 1838 – April 26, 1865) was an American stage actor who assassinated United States President Abraham Lincoln at Ford's Theatre in Washington, D.C., on April 14, 1865. A member of the prominent 19th-century Booth th ...
.
Construction
''Montauk'' was built byJohn Ericsson
John Ericsson (born Johan Ericsson; July 31, 1803 – March 8, 1889) was a Swedish-American inventor. He was active in England and the United States.
Ericsson collaborated on the design of the railroad steam locomotive ''Novelty'', which com ...
at Continental Iron Works
The Continental Iron Works was an American shipbuilding and engineering company founded in Greenpoint, Brooklyn, in 1861 by Thomas F. Rowland. It is best known for building a number of monitor warships for the United States Navy during the Am ...
, Greenpoint, Brooklyn
Greenpoint is the northernmost neighborhood in the New York City borough of Brooklyn, in the U.S. state of New York. It is bordered on the southwest by Williamsburg at Bushwick Inlet Park and McCarren Park; on the southeast by the Brooklyn� ...
; launched on October 9, 1862; and commissioned at New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
on December 14, 1862, Commander
Commander (commonly abbreviated as Cmdr.) is a common naval officer rank. Commander is also used as a rank or title in other formal organizations, including several police forces. In several countries this naval rank is termed frigate captain.
...
John L. Worden
John Lorimer Worden (March 12, 1818 – October 19, 1897) was a U.S. Navy officer in the American Civil War, who took part in the Battle of Hampton Roads, the first-ever engagement between Ironclad warship, ironclad steamships at Hampton Roads, V ...
in command.
Service

 A principal
A principal ironclad
An ironclad is a steam engine, steam-propelled warship protected by Wrought iron, iron or steel iron armor, armor plates, constructed from 1859 to the early 1890s. The ironclad was developed as a result of the vulnerability of wooden warships ...
in the naval attack on Charleston, South Carolina
Charleston is the largest city in the U.S. state of South Carolina, the county seat of Charleston County, and the principal city in the Charleston–North Charleston metropolitan area. The city lies just south of the geographical midpoint o ...
, ''Montauk'' departed New York on December 24, 1862, arriving Port Royal, South Carolina
Port Royal is a List of cities and towns in South Carolina, town on Port Royal Island in Beaufort County, South Carolina, Beaufort County, South Carolina, United States. The population was 14,220 at the 2020 census. It is part of the Hilton Head Is ...
on January 19, 1863, to join the South Atlantic Blockading Squadron
The Union blockade in the American Civil War was a naval strategy by the United States to prevent the Confederacy from trading.
The blockade was proclaimed by President Abraham Lincoln in April 1861, and required the monitoring of of Atlantic ...
. Taking advantage of the opportunity to test the XV-inch Dahlgren gun
Dahlgren guns were muzzle-loading naval artillery designed by Rear Admiral John A. Dahlgren USN (November 13, 1809 – July 12, 1870), mostly used in the period of the American Civil War. Dahlgren's design philosophy evolved from an accidental ...
and armor of the ''Passaic''-class ironclad for the first time, on January 27, Rear Admiral
Rear admiral is a senior naval flag officer rank, equivalent to a major general and air vice marshal and above that of a commodore and captain, but below that of a vice admiral. It is regarded as a two star "admiral" rank. It is often regarde ...
Samuel F. Du Pont
Samuel Francis Du Pont (September 27, 1803 – June 23, 1865) was a rear admiral in the United States Navy, and a member of the prominent Du Pont family. In the Mexican–American War, Du Pont captured San Diego, and was made commander of the Ca ...
sent ''Montauk'', with the gunboats , , and mortar schooner to bombard Fort McAllister
Fort McAllister was a Confederate earthen-work fort used to defend Savannah, Georgia during the American Civil War. It was the southernmost of the forts defending Savannah and was involved in the most battles. It was located on the Ogeechee Rive ...
, Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
. Although hit 13 times, ''Montauk'' was undamaged. The ironclad made a second attack on February 1, badly battering the fort; but ''Montauk'' was hit 48 times. She destroyed the blockade runner
A blockade runner is a merchant vessel used for evading a naval blockade of a port or strait. It is usually light and fast, using stealth and speed rather than confronting the blockaders in order to break the blockade. Blockade runners usuall ...
''Rattlesnake
Rattlesnakes are venomous snakes that form the genera ''Crotalus'' and ''Sistrurus'' of the subfamily Crotalinae (the pit vipers). All rattlesnakes are vipers. Rattlesnakes are predators that live in a wide array of habitats, hunting small anim ...
'' on February 28 in Ogeechee River
The Ogeechee River is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed April 26, 2011 blackwater river in the U.S. state of Georgia. It heads at the confluence of its North and South ...
but while descending the river was herself damaged by a torpedo (mine) which exploded under her.
''Montauk'' steamed into the North Fork of the Edisto River
The Edisto River is one of the longest free-flowing blackwater rivers in North America, flowing over 250 meandering miles from its sources in Saluda and Edgefield counties, to its Atlantic Ocean mouth at Edisto Beach, South Carolina. It rises in ...
on April 1 in preparation for the attack on Charleston. At midafternoon on April 7, Admiral Du Pont's ironclads attacked Fort Sumter
Fort Sumter is a sea fort built on an artificial island protecting Charleston, South Carolina from naval invasion. Its origin dates to the War of 1812 when the British invaded Washington by sea. It was still incomplete in 1861 when the Battl ...
. The Union ships braved intense fire from Confederates coastal artillery, and kept their own guns operating effectively until withdrawing toward evening. Damage to the monitors prevented Du Pont from resuming the attack the next day with ''Montauk'' taking 20 hits.
The ironclads launched an attack on Fort Wagner
Fort Wagner or Battery Wagner was a beachhead fortification on Morris Island, South Carolina, that covered the southern approach to Charleston Harbor. It was the site of two American Civil War battles in the campaign known as Operations Agai ...
, Morris Island
Morris Island is an 840-acre (3.4 km²) uninhabited island in Charleston Harbor in South Carolina, accessible only by boat. The island lies in the outer reaches of the harbor and was thus a strategic location in the American Civil War. The ...
on July 10. Capturing this island was important as it would permit access to the interior defenses of Charleston Harbor. Assuming command of the naval forces, John Dahlgren boarded ''Montauk'' on July 16 and after consultation with the captains, renewed the attack on Fort Wagner and bombarded it daily until it was evacuated by the Confederates on September 6. The ships then turned their attention to Fort Sumter and Fort Moultrie
Fort Moultrie is a series of fortifications on Sullivan's Island, South Carolina, built to protect the city of Charleston, South Carolina. The first fort, formerly named Fort Sullivan, built of palmetto logs, inspired the flag and n ...
operating for the rest of the year against these fortifications which guarded the Cradle of the Rebellion. However, the Confederate
Confederacy or confederate may refer to:
States or communities
* Confederate state or confederation, a union of sovereign groups or communities
* Confederate States of America, a confederation of secessionist American states that existed between 1 ...
works would never be taken by sea.
''Montauk'' remained off Charleston until July 1864, when she shifted operations to the Stono River
The Stono River or Creek is a tidal channel in southeast South Carolina, located southwest of Charleston. The channel runs southwest to northeast between the mainland and Wadmalaw Island and Johns Island, from north Edisto River between Johns ...
. In February 1865, she transferred to the Cape Fear River
The Cape Fear River is a long blackwater river in east central North Carolina. It flows into the Atlantic Ocean near Cape Fear, from which it takes its name. The river is formed at the confluence of the Haw River and the Deep River (North Carol ...
. Proceeding to the Washington Navy Yard
The Washington Navy Yard (WNY) is the former shipyard and ordnance plant of the United States Navy in Southeast Washington, D.C. It is the oldest shore establishment of the U.S. Navy.
The Yard currently serves as a ceremonial and administrativ ...
after the end of the conflict, she served as a floating bier for assassin John Wilkes Booth
John Wilkes Booth (May 10, 1838 – April 26, 1865) was an American stage actor who assassinated United States President Abraham Lincoln at Ford's Theatre in Washington, D.C., on April 14, 1865. A member of the prominent 19th-century Booth th ...
on April 27 and a floating prison for six accomplices.
 She was decommissioned at
She was decommissioned at Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
, in 1865. She remained there until sold to Frank Samuel
Frank Samuel (1889–1954) was a British businessman, inventor and philanthropist who was a managing director and later chairman of the United Africa Company (UAC).
Life
Samuel was born into a family that ran a music business, the business manufac ...
on April 14, 1904, except for a stint from May 1898 to March 1899, when she served with a crew primarily consisting of local naval reservists to protect the harbor of Portland, Maine
Portland is the largest city in the U.S. state of Maine and the seat of Cumberland County. Portland's population was 68,408 in April 2020. The Greater Portland metropolitan area is home to over half a million people, the 104th-largest metropol ...
during the Spanish–American War
, partof = the Philippine Revolution, the decolonization of the Americas, and the Cuban War of Independence
, image = Collage infobox for Spanish-American War.jpg
, image_size = 300px
, caption = (clock ...
.
References
Bibliography
* *''Additional technical data from'' * *External links
navsource.org: USS ''Montauk''
{{DEFAULTSORT:Montauk Passaic-class monitors Ships built in Brooklyn 1862 ships Ships of the Union Navy American Civil War monitors of the United States Spanish–American War monitors of the United States