Type 1a supernova on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A Type Ia supernova (read: "type one-A") is a type of supernova that occurs in
 The Type Ia supernova is a subcategory in the Minkowski–Zwicky supernova classification scheme, which was devised by German-American astronomer
The Type Ia supernova is a subcategory in the Minkowski–Zwicky supernova classification scheme, which was devised by German-American astronomer  Once fusion begins, the temperature of the white dwarf increases. A main sequence star supported by
Once fusion begins, the temperature of the white dwarf increases. A main sequence star supported by
 Unlike the other types of supernovae, Type Ia supernovae generally occur in all types of galaxies, including ellipticals. They show no preference for regions of current stellar formation. As white dwarf stars form at the end of a star's main sequence evolutionary period, such a long-lived star system may have wandered far from the region where it originally formed. Thereafter a close binary system may spend another million years in the mass transfer stage (possibly forming persistent nova outbursts) before the conditions are ripe for a Type Ia supernova to occur.
A long-standing problem in astronomy has been the identification of supernova progenitors. Direct observation of a progenitor would provide useful constraints on supernova models. As of 2006, the search for such a progenitor had been ongoing for longer than a century. Proceedings of the conference held 12–14 June 2007, at Keele University, Keele, United Kingdom. Observation of the supernova SN 2011fe has provided useful constraints. Previous observations with the Hubble Space Telescope did not show a star at the position of the event, thereby excluding a red giant as the source. The expanding plasma from the explosion was found to contain carbon and oxygen, making it likely the progenitor was a white dwarf primarily composed of these elements.
Similarly, observations of the nearby SN PTF 11kx, discovered January 16, 2011 (UT) by the Palomar Transient Factory (PTF), lead to the conclusion that this explosion arises from single-degenerate progenitor, with a red giant companion, thus suggesting there is no single progenitor path to SN Ia. Direct observations of the progenitor of PTF 11kx were reported in the August 24 edition of Science and support this conclusion, and also show that the progenitor star experienced periodic nova eruptions before the supernova – another surprising discovery.
However, later analysis revealed that the circumstellar material is too massive for the single-degenerate scenario, and fits better the core-degenerate scenario.
Unlike the other types of supernovae, Type Ia supernovae generally occur in all types of galaxies, including ellipticals. They show no preference for regions of current stellar formation. As white dwarf stars form at the end of a star's main sequence evolutionary period, such a long-lived star system may have wandered far from the region where it originally formed. Thereafter a close binary system may spend another million years in the mass transfer stage (possibly forming persistent nova outbursts) before the conditions are ripe for a Type Ia supernova to occur.
A long-standing problem in astronomy has been the identification of supernova progenitors. Direct observation of a progenitor would provide useful constraints on supernova models. As of 2006, the search for such a progenitor had been ongoing for longer than a century. Proceedings of the conference held 12–14 June 2007, at Keele University, Keele, United Kingdom. Observation of the supernova SN 2011fe has provided useful constraints. Previous observations with the Hubble Space Telescope did not show a star at the position of the event, thereby excluding a red giant as the source. The expanding plasma from the explosion was found to contain carbon and oxygen, making it likely the progenitor was a white dwarf primarily composed of these elements.
Similarly, observations of the nearby SN PTF 11kx, discovered January 16, 2011 (UT) by the Palomar Transient Factory (PTF), lead to the conclusion that this explosion arises from single-degenerate progenitor, with a red giant companion, thus suggesting there is no single progenitor path to SN Ia. Direct observations of the progenitor of PTF 11kx were reported in the August 24 edition of Science and support this conclusion, and also show that the progenitor star experienced periodic nova eruptions before the supernova – another surprising discovery.
However, later analysis revealed that the circumstellar material is too massive for the single-degenerate scenario, and fits better the core-degenerate scenario.
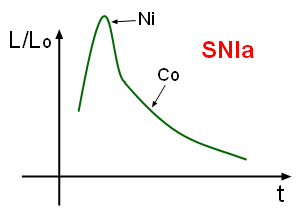 Type Ia supernovae have a characteristic
Type Ia supernovae have a characteristic
 There is significant diversity within the class of Type Ia supernovae. Reflecting this, a plethora of sub-classes have been identified. Two prominent and well-studied examples include 1991T-likes, an overluminous subclass that exhibits particularly strong iron
There is significant diversity within the class of Type Ia supernovae. Reflecting this, a plethora of sub-classes have been identified. Two prominent and well-studied examples include 1991T-likes, an overluminous subclass that exhibits particularly strong iron
List of all known Type Ia supernovae
a
The Open Supernova Catalog
* * * * (A Type Ia progenitor found) *
SNFactory Shows Type Ia ‘Standard Candles’ Have Many Masses
(March 4, 2014) {{DEFAULTSORT:Type Ia Supernova Type 1a Supernova Articles containing video clips
binary system
A binary system is a system of two astronomical bodies which are close enough that their gravitational attraction causes them to orbit each other around a barycenter ''(also see animated examples)''. More restrictive definitions require that th ...
s (two stars orbiting one another) in which one of the stars is a white dwarf
A white dwarf is a stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very dense: its mass is comparable to the Sun's, while its volume is comparable to the Earth's. A white dwarf's faint luminosity comes ...
. The other star can be anything from a giant star
A giant star is a star with substantially larger radius and luminosity than a main-sequence (or ''dwarf'') star of the same surface temperature.Giant star, entry in ''Astronomy Encyclopedia'', ed. Patrick Moore, New York: Oxford University Press ...
to an even smaller white dwarf.
Physically, carbon–oxygen white dwarfs with a low rate of rotation are limited to below 1.44 solar masses ().
Beyond this "critical mass
In nuclear engineering, a critical mass is the smallest amount of fissile material needed for a sustained nuclear chain reaction. The critical mass of a fissionable material depends upon its nuclear properties (specifically, its nuclear fi ...
", they reignite and in some cases trigger a supernova explosion; this critical mass is often referred to as the Chandrasekhar mass, but is marginally different from the absolute Chandrasekhar limit
The Chandrasekhar limit () is the maximum mass of a stable white dwarf star. The currently accepted value of the Chandrasekhar limit is about ().
White dwarfs resist gravitational collapse primarily through electron degeneracy pressure, compa ...
, where electron degeneracy pressure
Electron degeneracy pressure is a particular manifestation of the more general phenomenon of quantum degeneracy pressure. The Pauli exclusion principle disallows two identical half-integer spin particles (electrons and all other fermions) from si ...
is unable to prevent catastrophic collapse. If a white dwarf gradually accretes mass from a binary companion, or merges with a second white dwarf, the general hypothesis is that a white dwarf's core will reach the ignition temperature for carbon fusion as it approaches the Chandrasekhar mass. Within a few seconds of initiation of nuclear fusion, a substantial fraction of the matter in the white dwarf undergoes a runaway reaction, releasing enough energy (1–)
to unbind the star in a supernova explosion.
The Type Ia category of supernova produces a fairly consistent peak luminosity because of this fixed critical mass at which a white dwarf will explode. Their consistent peak luminosity allows these explosions to be used as standard candle
The cosmic distance ladder (also known as the extragalactic distance scale) is the succession of methods by which astronomers determine the distances to celestial objects. A ''direct'' distance measurement of an astronomical object is possible o ...
s to measure the distance to their host galaxies: the visual magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the brightness of a star or other astronomical object observed from Earth. An object's apparent magnitude depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance from Earth, and any extinction of the object's lig ...
of a type Ia supernova, as observed from Earth, indicates its distance from Earth.
In May 2015, NASA reported that the ''Kepler'' space observatory observed KSN 2011b, a Type Ia supernova in the process of exploding. Details of the pre-nova moments may help scientists better judge the quality of Type Ia supernovae as standard candles, which is an important link in the argument for dark energy
In physical cosmology and astronomy, dark energy is an unknown form of energy that affects the universe on the largest scales. The first observational evidence for its existence came from measurements of supernovas, which showed that the univ ...
.
In September 2021, astronomers reported that the Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (often referred to as HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most vers ...
had taken three images of a Type Ia supernova through a gravitational lens
A gravitational lens is a distribution of matter (such as a cluster of galaxies) between a distant light source and an observer that is capable of bending the light from the source as the light travels toward the observer. This effect is known ...
. This supernova appeared at three different times in the evolution of its brightness due to the differing path length of the light in the three images; at −24, 92, and 107 days from peak luminosity. A fourth image will appear in 2037 allowing observation of the entire luminosity cycle of the supernova.
Consensus model
Rudolph Minkowski
Rudolph Minkowski (born Rudolf Leo Bernhard Minkowski ; ; May 28, 1895 – January 4, 1976) was a German-American astronomer.
Biography
Minkowski was the son of Marie Johanna Siegel and physiologist Oskar Minkowski. His uncle was Hermann Min ...
and Swiss astronomer Fritz Zwicky
Fritz Zwicky (; ; February 14, 1898 – February 8, 1974) was a Swiss astronomer. He worked most of his life at the California Institute of Technology in the United States of America, where he made many important contributions in theoretical an ...
. There are several means by which a supernova of this type can form, but they share a common underlying mechanism. Theoretical astronomers long believed the progenitor star for this type of supernova is a white dwarf
A white dwarf is a stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very dense: its mass is comparable to the Sun's, while its volume is comparable to the Earth's. A white dwarf's faint luminosity comes ...
, and empirical evidence for this was found in 2014 when a Type Ia supernova was observed in the galaxy Messier 82
Messier 82 (also known as NGC 3034, Cigar Galaxy or M82) is a starburst galaxy approximately 12 million light-years away in the constellation Ursa Major. It is the second-largest member of the M81 Group, with the D25 isophotal diameter of . It ...
. When a slowly-rotating carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon mak ...
–oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as ...
white dwarf accretes matter from a companion, it can exceed the Chandrasekhar limit of about , beyond which it can no longer support its weight with electron degeneracy pressure.
In the absence of a countervailing process, the white dwarf would collapse to form a neutron star
A neutron star is the collapsed core of a massive supergiant star, which had a total mass of between 10 and 25 solar masses, possibly more if the star was especially metal-rich. Except for black holes and some hypothetical objects (e.g. w ...
, in an accretion-induced non-ejective process, as normally occurs in the case of a white dwarf that is primarily composed of magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ta ...
, neon, and oxygen.
The current view among astronomers who model Type Ia supernova explosions, however, is that this limit is never actually attained and collapse is never initiated. Instead, the increase in pressure and density due to the increasing weight raises the temperature of the core, and as the white dwarf approaches about 99% of the limit, a period of convection
Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy). When the cause of the conve ...
ensues, lasting approximately 1,000 years.
At some point in this simmering phase, a deflagration flame front is born, powered by carbon fusion. The details of the ignition are still unknown, including the location and number of points where the flame begins. Oxygen fusion is initiated shortly thereafter, but this fuel is not consumed as completely as carbon.
 Once fusion begins, the temperature of the white dwarf increases. A main sequence star supported by
Once fusion begins, the temperature of the white dwarf increases. A main sequence star supported by thermal pressure
In thermodynamics, thermal pressure (also known as the thermal pressure coefficient) is a measure of the relative pressure change of a fluid or a solid as a response to a temperature change at constant volume. The concept is related to the Pressur ...
can expand and cool which automatically regulates the increase in thermal energy. However, degeneracy pressure
Degenerate matter is a highly dense state of fermionic matter in which the Pauli exclusion principle exerts significant pressure in addition to, or in lieu of, thermal pressure. The description applies to matter composed of electrons, protons, ne ...
is independent of temperature; white dwarfs are unable to regulate temperature in the manner of normal stars, so they are vulnerable to runaway fusion reactions. The flare accelerates dramatically, in part due to the Rayleigh–Taylor instability
The Rayleigh–Taylor instability, or RT instability (after Lord Rayleigh and G. I. Taylor), is an instability of an interface between two fluids of different densities which occurs when the lighter fluid is pushing the heavier fluid.
Drazin ( ...
and interactions with turbulence
In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is fluid motion characterized by chaotic changes in pressure and flow velocity. It is in contrast to a laminar flow, which occurs when a fluid flows in parallel layers, with no disruption between ...
. It is still a matter of considerable debate whether this flare transforms into a supersonic detonation
Detonation () is a type of combustion involving a supersonic exothermic front accelerating through a medium that eventually drives a shock front propagating directly in front of it. Detonations propagate supersonically through shock waves with s ...
from a subsonic deflagration.
Regardless of the exact details of how the supernova ignites, it is generally accepted that a substantial fraction of the carbon and oxygen in the white dwarf fuses into heavier elements within a period of only a few seconds, with the accompanying release of energy increasing the internal temperature to billions of degrees. The energy released (1–) is more than sufficient to unbind the star; that is, the individual particles making up the white dwarf gain enough kinetic energy
In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the energy that it possesses due to its motion.
It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its acc ...
to fly apart from each other. The star explodes violently and releases a shock wave
In physics, a shock wave (also spelled shockwave), or shock, is a type of propagating disturbance that moves faster than the local speed of sound in the medium. Like an ordinary wave, a shock wave carries energy and can propagate through a me ...
in which matter is typically ejected at speeds on the order of , roughly 6% of the speed of light
The speed of light in vacuum, commonly denoted , is a universal physical constant that is important in many areas of physics. The speed of light is exactly equal to ). According to the special theory of relativity, is the upper limit ...
. The energy released in the explosion also causes an extreme increase in luminosity. The typical visual absolute magnitude
Absolute magnitude () is a measure of the luminosity of a celestial object on an inverse logarithmic astronomical magnitude scale. An object's absolute magnitude is defined to be equal to the apparent magnitude that the object would have if it ...
of Type Ia supernovae is ''M''v = −19.3 (about 5 billion times brighter than the Sun), with little variation.
The theory of this type of supernova is similar to that of novae, in which a white dwarf accretes matter more slowly and does not approach the Chandrasekhar limit. In the case of a nova, the infalling matter causes a hydrogen fusion surface explosion that does not disrupt the star.
Type Ia supernovae differ from Type II supernovae, which are caused by the cataclysmic explosion of the outer layers of a massive star as its core collapses, powered by release of gravitational potential energy
Gravitational energy or gravitational potential energy is the potential energy a massive object has in relation to another massive object due to gravity. It is the potential energy associated with the gravitational field, which is released (conver ...
via neutrino
A neutrino ( ; denoted by the Greek letter ) is a fermion (an elementary particle with spin of ) that interacts only via the weak interaction and gravity. The neutrino is so named because it is electrically neutral and because its rest mass ...
emission.
Formation
Single degenerate progenitors
One model for the formation of this category of supernova is a close binary star system. The progenitor binary system consists of main sequence stars, with the primary possessing more mass than the secondary. Being greater in mass, the primary is the first of the pair to evolve onto the asymptotic giant branch, where the star's envelope expands considerably. If the two stars share a common envelope then the system can lose significant amounts of mass, reducing theangular momentum
In physics, angular momentum (rarely, moment of momentum or rotational momentum) is the rotational analog of linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity because it is a conserved quantity—the total angular momentum of a closed syst ...
, orbital radius and period
Period may refer to:
Common uses
* Era, a length or span of time
* Full stop (or period), a punctuation mark
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Period (music), a concept in musical composition
* Periodic sentence (or rhetorical period), a concept ...
. After the primary has degenerated into a white dwarf, the secondary star later evolves into a red giant and the stage is set for mass accretion onto the primary. During this final shared-envelope phase, the two stars spiral in closer together as angular momentum is lost. The resulting orbit can have a period as brief as a few hours. If the accretion continues long enough, the white dwarf may eventually approach the Chandrasekhar limit
The Chandrasekhar limit () is the maximum mass of a stable white dwarf star. The currently accepted value of the Chandrasekhar limit is about ().
White dwarfs resist gravitational collapse primarily through electron degeneracy pressure, compa ...
.
The white dwarf companion could also accrete matter from other types of companions, including a subgiant
A subgiant is a star that is brighter than a normal main-sequence star of the same spectral class, but not as bright as giant stars. The term subgiant is applied both to a particular spectral luminosity class and to a stage in the evolution ...
or (if the orbit is sufficiently close) even a main sequence star. The actual evolutionary process during this accretion stage remains uncertain, as it can depend both on the rate of accretion and the transfer of angular momentum to the white dwarf companion.
It has been estimated that single degenerate progenitors account for no more than 20% of all Type Ia supernovae. See also lay reference:
Double degenerate progenitors
A second possible mechanism for triggering a Type Ia supernova is the merger of two white dwarfs whose combined mass exceeds the Chandrasekhar limit. The resulting merger is called a super-Chandrasekhar mass white dwarf. In such a case, the total mass would not be constrained by the Chandrasekhar limit. Collisions of solitary stars within the Milky Way occur only once every to ; far less frequently than the appearance of novae. Collisions occur with greater frequency in the dense core regions ofglobular cluster
A globular cluster is a spheroidal conglomeration of stars. Globular clusters are bound together by gravity, with a higher concentration of stars towards their centers. They can contain anywhere from tens of thousands to many millions of membe ...
s (''cf.'' blue straggler
A blue straggler is a main-sequence star in an open or globular cluster that is more luminous and bluer than stars at the main sequence turnoff point for the cluster. Blue stragglers were first discovered by Allan Sandage in 1953 while perform ...
s). A likely scenario is a collision with a binary star system, or between two binary systems containing white dwarfs. This collision can leave behind a close binary system of two white dwarfs. Their orbit decays and they merge through their shared envelope. A study based on SDSS spectra found 15 double systems of the 4,000 white dwarfs tested, implying a double white dwarf merger every 100 years in the Milky Way: this rate matches the number of Type Ia supernovae detected in our neighborhood.
A double degenerate scenario is one of several explanations proposed for the anomalously massive () progenitor of SN 2003fg. It is the only possible explanation for SNR 0509-67.5, as all possible models with only one white dwarf have been ruled out. It has also been strongly suggested for SN 1006, given that no companion star remnant has been found there. Observations made with NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
's Swift
Swift or SWIFT most commonly refers to:
* SWIFT, an international organization facilitating transactions between banks
** SWIFT code
* Swift (programming language)
* Swift (bird), a family of birds
It may also refer to:
Organizations
* SWIFT, ...
space telescope ruled out existing supergiant or giant companion stars of every Type Ia supernova studied. The supergiant companion's blown out outer shell should emit X-rays
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nbs ...
, but this glow was not detected by Swift's XRT (X-ray telescope) in the 53 closest supernova remnants. For 12 Type Ia supernovae observed within 10 days of the explosion, the satellite's UVOT (ultraviolet/optical telescope) showed no ultraviolet radiation originating from the heated companion star's surface hit by the supernova shock wave, meaning there were no red giants or larger stars orbiting those supernova progenitors. In the case of SN 2011fe, the companion star must have been smaller than the Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
, if it existed. The Chandra X-ray Observatory
The Chandra X-ray Observatory (CXO), previously known as the Advanced X-ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF), is a Flagship-class space telescope launched aboard the during STS-93 by NASA on July 23, 1999. Chandra is sensitive to X-ray sources 1 ...
revealed that the X-ray radiation of five elliptical galaxies
An elliptical galaxy is a type of galaxy with an approximately ellipsoidal shape and a smooth, nearly featureless image. They are one of the four main classes of galaxy described by Edwin Hubble in his Hubble sequence and 1936 work ''The Real ...
and the bulge of the Andromeda Galaxy
The Andromeda Galaxy (IPA: ), also known as Messier 31, M31, or NGC 224 and originally the Andromeda Nebula, is a barred spiral galaxy with the diameter of about approximately from Earth and the nearest large galaxy to the Milky Way. The gal ...
is 30–50 times fainter than expected. X-ray radiation should be emitted by the accretion discs of Type Ia supernova progenitors. The missing radiation indicates that few white dwarfs possess accretion disc
An accretion disk is a structure (often a circumstellar disk) formed by diffuse material in orbital motion around a massive central body. The central body is typically a star. Friction, uneven irradiance, magnetohydrodynamic effects, and other ...
s, ruling out the common, accretion-based model of Ia supernovae. Inward spiraling white dwarf pairs are strongly-inferred candidate sources of gravitational waves, although they have not been directly observed.
Double degenerate scenarios raise questions about the applicability of Type Ia supernovae as standard candle
The cosmic distance ladder (also known as the extragalactic distance scale) is the succession of methods by which astronomers determine the distances to celestial objects. A ''direct'' distance measurement of an astronomical object is possible o ...
s, since total mass of the two merging white dwarfs varies significantly, meaning luminosity also varies.
Type Iax
It has been proposed that a group of sub-luminous supernovae that occur when helium accretes onto a white dwarf should be classified as Type Iax. This type of supernova may not always completely destroy the white dwarf progenitor, but instead leave behind a zombie star.Observation
 Unlike the other types of supernovae, Type Ia supernovae generally occur in all types of galaxies, including ellipticals. They show no preference for regions of current stellar formation. As white dwarf stars form at the end of a star's main sequence evolutionary period, such a long-lived star system may have wandered far from the region where it originally formed. Thereafter a close binary system may spend another million years in the mass transfer stage (possibly forming persistent nova outbursts) before the conditions are ripe for a Type Ia supernova to occur.
A long-standing problem in astronomy has been the identification of supernova progenitors. Direct observation of a progenitor would provide useful constraints on supernova models. As of 2006, the search for such a progenitor had been ongoing for longer than a century. Proceedings of the conference held 12–14 June 2007, at Keele University, Keele, United Kingdom. Observation of the supernova SN 2011fe has provided useful constraints. Previous observations with the Hubble Space Telescope did not show a star at the position of the event, thereby excluding a red giant as the source. The expanding plasma from the explosion was found to contain carbon and oxygen, making it likely the progenitor was a white dwarf primarily composed of these elements.
Similarly, observations of the nearby SN PTF 11kx, discovered January 16, 2011 (UT) by the Palomar Transient Factory (PTF), lead to the conclusion that this explosion arises from single-degenerate progenitor, with a red giant companion, thus suggesting there is no single progenitor path to SN Ia. Direct observations of the progenitor of PTF 11kx were reported in the August 24 edition of Science and support this conclusion, and also show that the progenitor star experienced periodic nova eruptions before the supernova – another surprising discovery.
However, later analysis revealed that the circumstellar material is too massive for the single-degenerate scenario, and fits better the core-degenerate scenario.
Unlike the other types of supernovae, Type Ia supernovae generally occur in all types of galaxies, including ellipticals. They show no preference for regions of current stellar formation. As white dwarf stars form at the end of a star's main sequence evolutionary period, such a long-lived star system may have wandered far from the region where it originally formed. Thereafter a close binary system may spend another million years in the mass transfer stage (possibly forming persistent nova outbursts) before the conditions are ripe for a Type Ia supernova to occur.
A long-standing problem in astronomy has been the identification of supernova progenitors. Direct observation of a progenitor would provide useful constraints on supernova models. As of 2006, the search for such a progenitor had been ongoing for longer than a century. Proceedings of the conference held 12–14 June 2007, at Keele University, Keele, United Kingdom. Observation of the supernova SN 2011fe has provided useful constraints. Previous observations with the Hubble Space Telescope did not show a star at the position of the event, thereby excluding a red giant as the source. The expanding plasma from the explosion was found to contain carbon and oxygen, making it likely the progenitor was a white dwarf primarily composed of these elements.
Similarly, observations of the nearby SN PTF 11kx, discovered January 16, 2011 (UT) by the Palomar Transient Factory (PTF), lead to the conclusion that this explosion arises from single-degenerate progenitor, with a red giant companion, thus suggesting there is no single progenitor path to SN Ia. Direct observations of the progenitor of PTF 11kx were reported in the August 24 edition of Science and support this conclusion, and also show that the progenitor star experienced periodic nova eruptions before the supernova – another surprising discovery.
However, later analysis revealed that the circumstellar material is too massive for the single-degenerate scenario, and fits better the core-degenerate scenario.
Light curve
 Type Ia supernovae have a characteristic
Type Ia supernovae have a characteristic light curve
In astronomy, a light curve is a graph of light intensity of a celestial object or region as a function of time, typically with the magnitude of light received on the y axis and with time on the x axis. The light is usually in a particular frequ ...
, their graph of luminosity as a function of time after the explosion. Near the time of maximal luminosity, the spectrum contains lines of intermediate-mass elements from oxygen to calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar t ...
; these are the main constituents of the outer layers of the star. Months after the explosion, when the outer layers have expanded to the point of transparency, the spectrum is dominated by light emitted by material near the core of the star, heavy elements synthesized during the explosion; most prominently isotopes close to the mass of iron ( iron-peak elements). The radioactive decay of nickel-56
Naturally occurring nickel (28Ni) is composed of five stable isotopes; , , , and , with being the most abundant (68.077% natural abundance). 26 radioisotopes have been characterised with the most stable being with a half-life of 76,000 years, ...
through cobalt-56 to iron-56
Iron-56 (56Fe) is the most common isotope of iron. About 91.754% of all iron is iron-56.
Of all nuclides, iron-56 has the lowest mass per nucleon. With 8.8 MeV binding energy per nucleon, iron-56 is one of the most tightly bound nuclei.
N ...
produces high-energy photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they a ...
s, which dominate the energy output of the ejecta at intermediate to late times.
The use of Type Ia supernovae to measure precise distances was pioneered by a collaboration of Chilean and US astronomers, the Calán/Tololo Supernova Survey. In a series of papers in the 1990s the survey showed that while Type Ia supernovae do not all reach the same peak luminosity, a single parameter measured from the light curve can be used to correct unreddened Type Ia supernovae to standard candle values. The original correction to standard candle value is known as the Phillips relationship
and was shown by this group to be able to measure relative distances to 7% accuracy. The cause of this uniformity in peak brightness is related to the amount of nickel-56 produced in white dwarfs presumably exploding near the Chandrasekhar limit.
The similarity in the absolute luminosity profiles of nearly all known Type Ia supernovae has led to their use as a secondary standard candle in extragalactic astronomy.
Improved calibrations of the Cepheid variable
A Cepheid variable () is a type of star that pulsates radially, varying in both diameter and temperature and producing changes in brightness with a well-defined stable period and amplitude.
A strong direct relationship between a Cepheid vari ...
distance scale and direct geometric distance measurements to NGC 4258 from the dynamics of maser
A maser (, an acronym for microwave amplification by stimulated emission of radiation) is a device that produces coherent electromagnetic waves through amplification by stimulated emission. The first maser was built by Charles H. Townes, Ja ...
emission
when combined with the Hubble diagram of the Type Ia supernova distances have led to an improved value of the Hubble constant
Hubble's law, also known as the Hubble–Lemaître law, is the observation in physical cosmology that galaxies are moving away from Earth at speeds proportional to their distance. In other words, the farther they are, the faster they are moving ...
.
In 1998, observations of distant Type Ia supernovae indicated the unexpected result that the universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents, including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy. The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological description of the development of the universe. ...
seems to undergo an accelerating expansion.
Three members from two teams were subsequently awarded Nobel Prizes for this discovery.
Subtypes
 There is significant diversity within the class of Type Ia supernovae. Reflecting this, a plethora of sub-classes have been identified. Two prominent and well-studied examples include 1991T-likes, an overluminous subclass that exhibits particularly strong iron
There is significant diversity within the class of Type Ia supernovae. Reflecting this, a plethora of sub-classes have been identified. Two prominent and well-studied examples include 1991T-likes, an overluminous subclass that exhibits particularly strong iron absorption lines
A spectral line is a dark or bright line in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum, resulting from emission or absorption of light in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies. Spectral lines are often used to identi ...
and abnormally small silicon features, and 1991bg-likes, an exceptionally dim subclass characterized by strong early titanium absorption features and rapid photometric and spectral evolution. Despite their abnormal luminosities, members of both peculiar groups can be standardized by use of the Phillips relation to determine distance
Distance is a numerical or occasionally qualitative measurement of how far apart objects or points are. In physics or everyday usage, distance may refer to a physical length or an estimation based on other criteria (e.g. "two counties over"). ...
.
See also
*Carbon detonation
Carbon detonation or carbon deflagration is the violent reignition of thermonuclear fusion in a white dwarf star that was previously slowly cooling. It involves a runaway thermonuclear process which spreads through the white dwarf in a matter of se ...
* Cosmic distance ladder
The cosmic distance ladder (also known as the extragalactic distance scale) is the succession of methods by which astronomers determine the distances to celestial objects. A ''direct'' distance measurement of an astronomical object is possible o ...
* History of supernova observation
The known history of supernova observation goes back to 185 AD, when supernova SN 185 appeared; which is the oldest appearance of a supernova recorded by mankind. Several additional supernovae within the Milky Way galaxy have been recorded since t ...
* List of supernova remnants
This is a list of observed supernova remnants (SNRs) in the Milky Way, as well as galaxies nearby enough to resolve individual nebulae, such as the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds and the Andromeda Galaxy.
Supernova remnants typically only survi ...
* Near-Earth supernova
A near-Earth supernova is an explosion resulting from the death of a star that occurs close enough to the Earth (roughly less than 10 to 300 parsecs (30 to 1000 light-years) away) to have noticeable effects on Earth's biosphere.
An estima ...
* Supernova remnant
A supernova remnant (SNR) is the structure resulting from the explosion of a star in a supernova. The supernova remnant is bounded by an expanding shock wave, and consists of ejected material expanding from the explosion, and the interstellar mat ...
References
External links
List of all known Type Ia supernovae
a
The Open Supernova Catalog
* * * * (A Type Ia progenitor found) *
SNFactory Shows Type Ia ‘Standard Candles’ Have Many Masses
(March 4, 2014) {{DEFAULTSORT:Type Ia Supernova Type 1a Supernova Articles containing video clips