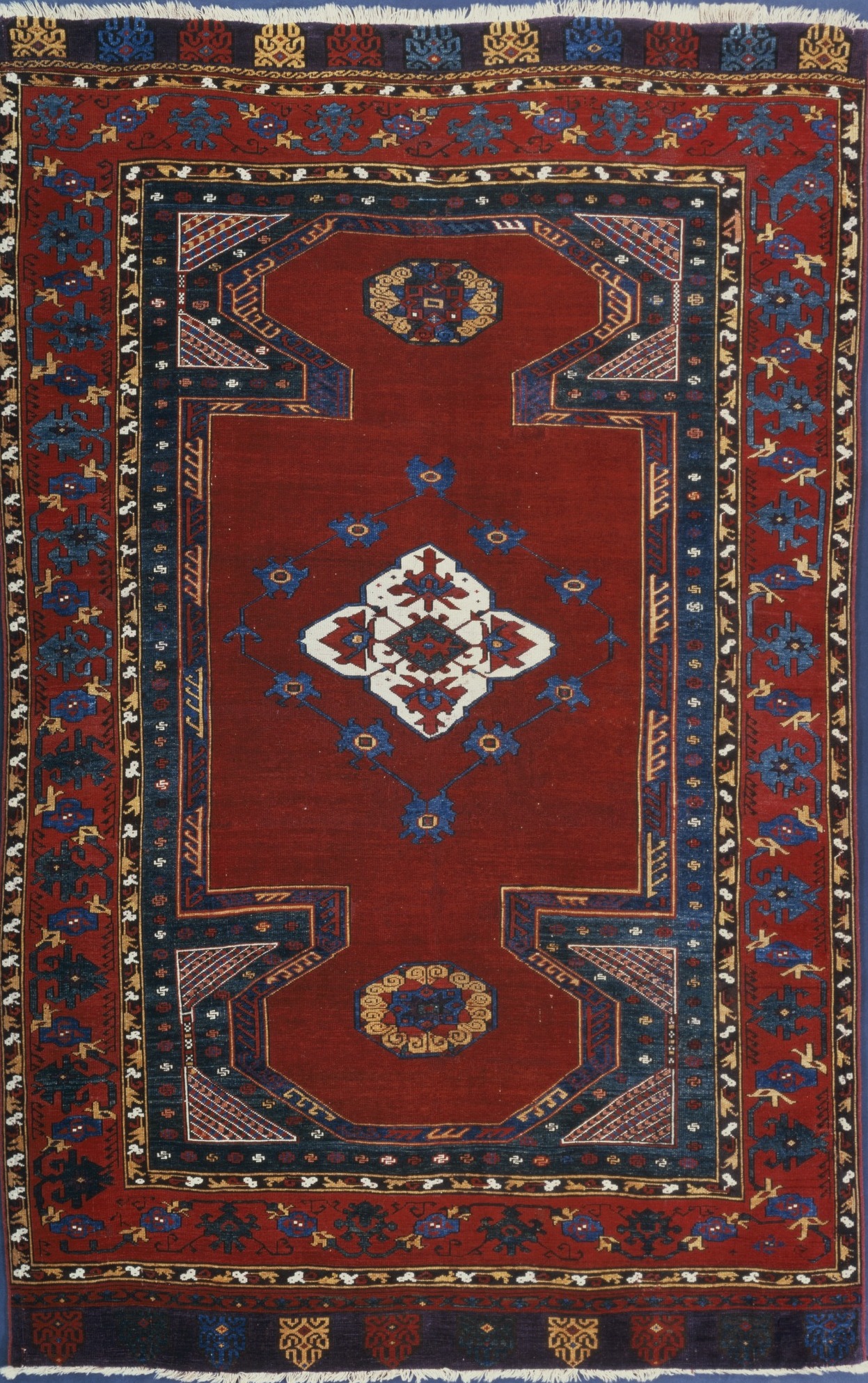


Anatolian rug is a term of convenience, commonly used today to denote rugs and carpets woven in
Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
and its adjacent regions. Geographically, its area of production can be compared to the territories which were historically dominated by the
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
. It denotes a knotted, pile-woven floor or wall covering which is produced for home use, local sale, and export. Together with the flat-woven
kilim
A kilim ( az, Kilim کیلیم; tr, Kilim; tm, Kilim; fa, گلیم ''Gilīm'') is a flat tapestry- woven carpet or rug traditionally produced in countries of the former Persian Empire, including Iran, the Balkans and the Turkic countries. Ki ...
, Anatolian rugs represent an essential part of the regional culture, which is officially understood as the
Culture of Turkey
The culture of Turkey ( tr, Türkiye Kültürü) combines a heavily diverse and heterogeneous set of elements that have been derived from the various cultures of the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Europe, Caucasia, Middle East and Central Asia t ...
today,
["The historical importance of rug and carpet weaving in Anatolia"](_blank)
Turkishculture.org. Retrieved on 2012-01-27. and derives from the ethnic, religious and cultural pluralism of one of the most ancient centres of human civilisation.
Rug weaving represents a traditional craft dating back to prehistoric times. Rugs were woven much earlier than even the oldest surviving rugs like the
Pazyryk rug would suggest. During its long history, the art and craft of the woven carpet has absorbed and integrated different cultural traditions. Traces of
Byzantine design can be observed in Anatolian rugs;
Turkic peoples
The Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West, Central, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose members speak languages belonging to ...
migrating from Central Asia, as well as Armenian people, Caucasian and Kurdic tribes either living in, or migrating to Anatolia at different times in history contributed their traditional motifs and ornaments. The arrival of Islam and the development of the
Islamic art
Islamic art is a part of Islamic culture and encompasses the visual arts produced since the 7th century CE by people who lived within territories inhabited or ruled by Muslim populations. Referring to characteristic traditions across a wide ra ...
has profoundly influenced the Anatolian rug design. Its ornaments and patterns thus reflect the political history and social diversity of the area. However, scientific research was unable, as yet, to attribute any particular design feature to any specific ethnic or regional tradition, or even to differentiate between nomadic and village design patterns.
Within the group of
oriental carpet
An oriental rug is a heavy textile made for a wide variety of utilitarian and symbolic purposes and produced in " Oriental countries" for home use, local sale, and export.
Oriental carpets can be pile woven or flat woven without pile, using v ...
s, the Anatolian rug is distinguished by particular characteristics of its dyes and colours, motifs, textures and techniques. Examples range in size from small pillows (') to large, room-sized carpets. The earliest surviving examples of Anatolian rugs known today date from the thirteenth century. Distinct types of rugs have been woven ever since in court manufactures and provincial workshops, village homes, tribal settlements, or in the nomad's tent. Rugs were simultaneously produced at all different levels of society, mainly using sheep wool, cotton and
natural dye
Natural dyes are dyes or colorants derived from plants, invertebrates, or minerals. The majority of natural dyes are vegetable dyes from plant sources— roots, berries, bark, leaves, and wood—and other biological sources such as fungi.
Ar ...
s. Anatolian rugs are most often tied with
symmetrical knots, which were so widely used in the area that Western rug dealers in the early 20th century adopted the term "Turkish" or "Ghiordes" knot for the technique. From the 1870s onwards, the Ottoman court manufactures also produced silk-piled rugs, sometimes with inwoven threads of gold or silver, but the traditional material of the majority of Anatolian rugs was
hand-spun, naturally-dyed wool.
In Europe, Anatolian rugs were frequently depicted in
Renaissance paintings, often in a context of dignity, prestige and luxury. Political contacts and trade intensified between Western Europe and the Islamic world after the 13th century AD. When direct trade was established with the Ottoman Empire during the 14th century, all kinds of carpets were at first indiscriminately given the trade name of "Turkish" carpets, regardless of their actual place of manufacture.
Since the late nineteenth century,
oriental
The Orient is a term for the East in relation to Europe, traditionally comprising anything belonging to the Eastern world. It is the antonym of '' Occident'', the Western World. In English, it is largely a metonym for, and coterminous with, the ...
rugs have been subject to art historic and scientific interest in the Western world.
The richness and cultural diversity of rug weaving were gradually better understood. More recently, also flat woven carpets (
Kilim
A kilim ( az, Kilim کیلیم; tr, Kilim; tm, Kilim; fa, گلیم ''Gilīm'') is a flat tapestry- woven carpet or rug traditionally produced in countries of the former Persian Empire, including Iran, the Balkans and the Turkic countries. Ki ...
,
Soumak, Cicim, Zili) have attracted the interest of collectors and scientists.
The art and craft of the Anatolian rug underwent serious changes by the introduction of
synthetic dyes
A dye is a colored substance that chemically bonds to the substrate to which it is being applied. This distinguishes dyes from pigments which do not chemically bind to the material they color. Dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution and ...
from the last third of the 19th century onwards. The mass production of cheap rugs designed for commercial success had brought the ancient tradition close to extinction. In the late twentieth century, projects like the
DOBAG Carpet Initiative have successfully revived the tradition of Anatolian rug weaving using hand-spun, naturally-dyed wool and traditional designs.
History

The origin of carpet weaving remains unknown, as carpets are subject to use, wear, and destruction by insects and rodents. Controversy arose over the accuracy of the claim that the oldest records of flat woven
kilim
A kilim ( az, Kilim کیلیم; tr, Kilim; tm, Kilim; fa, گلیم ''Gilīm'') is a flat tapestry- woven carpet or rug traditionally produced in countries of the former Persian Empire, including Iran, the Balkans and the Turkic countries. Ki ...
s come from the
Çatalhöyük
Çatalhöyük (; also ''Çatal Höyük'' and ''Çatal Hüyük''; from Turkish ''çatal'' "fork" + ''höyük'' "tumulus") is a tell of a very large Neolithic and Chalcolithic proto-city settlement in southern Anatolia, which existed from app ...
excavations, dated to circa 7000 BC.
The excavators' report
[Evidence for ancient kilim patterns found in Çatalhöyük](_blank)
Turkishculture.org. Retrieved on 2012-01-27. remained unconfirmed, as it states that the wall paintings depicting kilim motifs had disintegrated shortly after their exposure.
The history of rug weaving in Anatolia must be understood in the context of the country's political and social history. Anatolia was home to ancient civilizations, such as the
Hittites
The Hittites () were an Anatolian people who played an important role in establishing first a kingdom in Kussara (before 1750 BC), then the Kanesh or Nesha kingdom (c. 1750–1650 BC), and next an empire centered on Hattusa in north-cent ...
, the
Phrygians
The Phrygians ( Greek: Φρύγες, ''Phruges'' or ''Phryges'') were an ancient Indo-European speaking people, who inhabited central-western Anatolia (modern-day Turkey) in antiquity. They were related to the Greeks.
Ancient Greek authors use ...
, the
Assyrians, the
Ancient Persia
The history of Iran is intertwined with the history of a larger region known as Greater Iran, comprising the area from Anatolia in the west to the borders of Ancient India and the Syr Darya in the east, and from the Caucasus and the Eurasian Step ...
ns, the
Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, ''hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diaspora ...
, the
Ancient Greeks
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cult ...
, and the
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
. Rug weaving is assumed to already exist in Anatolia during this time, however there are no examples of pre-Turkic migration rugs in Anatolia. In 1071 AD, the
Seljuq Alp Arslan
Alp Arslan was the second Sultan of the Seljuk Empire and great-grandson of Seljuk, the eponymous founder of the dynasty. He greatly expanded the Seljuk territory and consolidated his power, defeating rivals to the south and northwest, and his ...
defeated the Roman Emperor
Romanos IV
Romanos IV Diogenes ( Greek: Ρωμανός Διογένης), Latinized as Romanus IV Diogenes, was a member of the Byzantine military aristocracy who, after his marriage to the widowed empress Eudokia Makrembolitissa, was crowned Byzantine ...
Diogenes at
Manzikert
The Battle of Manzikert or Malazgirt was fought between the Byzantine Empire and the Seljuk Empire on 26 August 1071 near Manzikert, theme of Iberia (modern Malazgirt in Muş Province, Turkey). The decisive defeat of the Byzantine army and th ...
. This is regarded as the beginning of the ascendancy of the
Seljuq Turks
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; fa, سلجوقیان ''Saljuqian'', alternatively spelled as Seljuqs or Saljuqs), also known as Seljuk Turks, Seljuk Turkomans "The defeat in August 1071 of the Byzantine emperor Romanos Diogenes
by the Turk ...
.
Seljuq rugs: Travelers' reports and the Konya fragments
In the early fourteenth century,
Marco Polo
Marco Polo (, , ; 8 January 1324) was a Venetian merchant, explorer and writer who travelled through Asia along the Silk Road between 1271 and 1295. His travels are recorded in '' The Travels of Marco Polo'' (also known as ''Book of the Marv ...
wrote in the account of his
travels:
''...et ibi fiunt soriani et tapeti pulchriores de mundo et pulchrioris coloris.''
"...and here they make the most beautiful silks and carpets in the world, and with the most beautiful colours."
Coming from Persia, Polo travelled from Sivas to Kayseri.
Abu'l-Fida
Ismāʿīl b. ʿAlī b. Maḥmūd b. Muḥammad b. ʿUmar b. Shāhanshāh b. Ayyūb b. Shādī b. Marwān ( ar, إسماعيل بن علي بن محمود بن محمد بن عمر بن شاهنشاه بن أيوب بن شادي بن مروان ...
, citing
Ibn Sa'id al-Maghribi refers to rug export from Anatolian cities in the late 13th century: "That's where Turkoman carpets are made, which are exported to all other countries". He and the Moroccan merchant
Ibn Battuta
Abu Abdullah Muhammad ibn Battutah (, ; 24 February 13041368/1369),; fully: ; Arabic: commonly known as Ibn Battuta, was a Berber Maghrebi scholar and explorer who travelled extensively in the lands of Afro-Eurasia, largely in the Muslim ...
mention Aksaray as a major rug weaving center in the early-to-mid-14th century.
The earliest surviving woven rugs were found in
Konya
Konya () is a major city in central Turkey, on the southwestern edge of the Central Anatolian Plateau, and is the capital of Konya Province. During antiquity and into Seljuk times it was known as Iconium (), although the Seljuks also called it D ...
,
Beyşehir
Beyşehir () is a large town and district of Konya Province in the Akdeniz region of Turkey. The town is located on the southeastern shore of Lake Beyşehir and is marked to the west and the southwest by the steep lines and forests of the Tauru ...
and
Fostat
Fusṭāṭ ( ar, الفُسطاط ''al-Fusṭāṭ''), also Al-Fusṭāṭ and Fosṭāṭ, was the first capital of Egypt under Muslim rule, and the historical centre of modern Cairo. It was built adjacent to what is now known as Old Cairo by ...
, and were dated to the 13th century. These carpets from the
Anatolian Seljuq Period (1243–1302) are regarded as the first group of Anatolian rugs. Eight fragments were found in 1905 by F.R. Martin in the
Alaeddin Mosque in Konya, four in the
Eşrefoğlu Mosque
Eşrefoğlu Mosque is a 13th-century mosque in Beyşehir, Konya Province, Turkey
It is situated north of the Beyşehir Lake
History
During the last years of Seljuks of Rum, various governors of Seljuks enjoyed a partial independency. They ...
in
Beyşehir
Beyşehir () is a large town and district of Konya Province in the Akdeniz region of Turkey. The town is located on the southeastern shore of Lake Beyşehir and is marked to the west and the southwest by the steep lines and forests of the Tauru ...
in Konya province by R.M. Riefstahl in 1925.
More fragments were found in
Fostat
Fusṭāṭ ( ar, الفُسطاط ''al-Fusṭāṭ''), also Al-Fusṭāṭ and Fosṭāṭ, was the first capital of Egypt under Muslim rule, and the historical centre of modern Cairo. It was built adjacent to what is now known as Old Cairo by ...
, today a suburb of the city of Cairo.
Judging by their original size (Riefstahl reports a carpet up to 6 m long), the Konya carpets must have been produced in town manufactories, as looms of this size can hardly have been set up in a nomadic or village home. Where exactly these carpets were woven is unknown. The field patterns of the Konya rugs are mostly geometric, and small in relation to the carpet size. Similar patterns are arranged in diagonal rows: Hexagons with plain, or hooked outlines; squares filled with stars, with interposed
kufic
Kufic script () is a style of Arabic script that gained prominence early on as a preferred script for Quran transcription and architectural decoration, and it has since become a reference and an archetype for a number of other Arabic scripts. It ...
-like ornaments; hexagons in diamonds composed of rhomboids filled with stylized flowers and leaves. Their main borders often contain kufic ornaments. The corners are not "resolved", which means that the border design is cut off, and does not continue diagonally around the corners. The colours (blue, red, green, to a lesser extent also white, brown, yellow) are subdued, frequently two shades of the same colour are opposed to each other. Nearly all carpet fragments show different patterns and ornaments.
The Beyşehir rugs are closely related to the Konya specimen in design and colour.
In contrast to the "
animal carpets" of the following period, depictions of animals are rarely seen in the Seljuq fragments. Rows of horned quadrupeds placed opposite to each other, or birds beside a tree can be recognized on some fragments.
The style of the Seljuq rugs has parallels amongst the architectural decoration of contemporaneous mosques such as those at
Divriği
Divriği (formerly Tephrike, Greek: Τεφρική) is a small town and district of Sivas Province of Turkey. The town lies on gentle slope on the south bank of the Çaltısuyu river, a tributary of the Karasu river. The Great Mosque and Hospit ...
,
Sivas
Sivas (Latin and Greek: ''Sebastia'', ''Sebastea'', Σεβάστεια, Σεβαστή, ) is a city in central Turkey and the seat of Sivas Province.
The city, which lies at an elevation of in the broad valley of the Kızılırmak river, is ...
, and
Erzurum
Erzurum (; ) is a city in eastern Anatolia, Turkey. It is the largest city and capital of Erzurum Province and is 1,900 meters (6,233 feet) above sea level. Erzurum had a population of 367,250 in 2010.
The city uses the double-headed eagle as ...
, and may be related to Byzantine art. Today, the rugs are kept at the
Mevlana Museum
Jalāl al-Dīn Muḥammad Rūmī ( fa, جلالالدین محمد رومی), also known as Jalāl al-Dīn Muḥammad Balkhī (), Mevlânâ/Mawlānā ( fa, مولانا, lit= our master) and Mevlevî/Mawlawī ( fa, مولوی, lit= my ma ...
in Konya, and at the
Turkish and Islamic Arts Museum
The Turkish and Islamic Arts Museum ( tr, ) is a museum located in Sultanahmet Square in Fatih district of Istanbul, Turkey. Constructed in 1524, the building was formerly the palace of Pargalı Ibrahim Pasha, who was the second grand vizier to S ...
in Istanbul.
File:Konya Ethnographical Museum - Carpet 1.png, Rug fragment from Eşrefoğlu Mosque
Eşrefoğlu Mosque is a 13th-century mosque in Beyşehir, Konya Province, Turkey
It is situated north of the Beyşehir Lake
History
During the last years of Seljuks of Rum, various governors of Seljuks enjoyed a partial independency. They ...
, Beysehir, Turkey. Seljuq Period, 13th century.
File:Seljuk Carpet Fragment 13th Century..png, Seljuq carpet, 320 x 240 cm, from Alaeddin Mosque, Konya, 13th century
File:Unknown, Turkey, 11th-13th Century - Carpet with Animal Design - Google Art Project.jpg, Animal carpet, dated to the 11th–13th century, Museum of Islamic Art, Doha
The Museum of Islamic Art (MIA) is a museum on one end of the Corniche in Doha, Qatar. As per the architect I. M. Pei's specifications, the museum is built on an island off an artificial projecting peninsula near the traditional '' dhow'' ha ...
Rugs of the Anatolian Beyliks
Early in the thirteenth century, the territory of Anatolia was invaded by
Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
. The weakening of Seljuq rule allowed Turkmen tribes known as the
Oghuz Turks
The Oghuz or Ghuzz Turks (Middle Turkic: ٱغُز, ''Oγuz'', ota, اوغوز, Oġuz) were a western Turkic people that spoke the Oghuz branch of the Turkic language family. In the 8th century, they formed a tribal confederation conven ...
to organize themselves into independent sovereignties, the
Beyliks
Anatolian beyliks ( tr, Anadolu beylikleri, Ottoman Turkish: ''Tavâif-i mülûk'', ''Beylik'' ) were small principalities (or petty kingdoms) in Anatolia governed by beys, the first of which were founded at the end of the 11th century. A secon ...
. These were later integrated into the Ottoman Empire by the sultans
Bayezid I
Bayezid I ( ota, بايزيد اول, tr, I. Bayezid), also known as Bayezid the Thunderbolt ( ota, link=no, یلدیرم بايزيد, tr, Yıldırım Bayezid, link=no; – 8 March 1403) was the Ottoman Sultan from 1389 to 1402. He adopted ...
(1389-1402),
Murad II
Murad II ( ota, مراد ثانى, Murād-ı sānī, tr, II. Murad, 16 June 1404 – 3 February 1451) was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1421 to 1444 and again from 1446 to 1451.
Murad II's reign was a period of important economic deve ...
(1421-1481),
Mehmed the Conqueror
Mehmed II ( ota, محمد ثانى, translit=Meḥmed-i s̱ānī; tr, II. Mehmed, ; 30 March 14323 May 1481), commonly known as Mehmed the Conqueror ( ota, ابو الفتح, Ebū'l-fetḥ, lit=the Father of Conquest, links=no; tr, Fâtih Su ...
(1451-1481), and
Selim I
Selim I ( ota, سليم الأول; tr, I. Selim; 10 October 1470 – 22 September 1520), known as Selim the Grim or Selim the Resolute ( tr, links=no, Yavuz Sultan Selim), was the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1512 to 1520. Despite las ...
(1512-1520).
Literary sources like the
Book of Dede Korkut
The ''Book of Dede Korkut'' or ''Book of Korkut Ata'' ( az, Kitabi-Dədə Qorqud, ; tk, Kitaby Dädem Gorkut; tr, Dede Korkut Kitabı) is the most famous among the epic stories of the Oghuz Turks. The stories carry morals and values signifi ...
confirm that the Turkoman tribes produced carpets in Anatolia. What types of carpets were woven by the Turkoman Beyliks remains unknown, since we are unable to identify them. One of the Turkoman tribes of the Beylik group, the
Tekke settled in South-western Anatolia in the eleventh century, and moved back to the Caspian sea later. The Tekke tribes of Turkmenistan, living around Merv and the Amu Darya during the 19th century and earlier, wove a distinct type of carpet characterized by stylized floral motifs called
guls in repeating rows.
Ottoman carpets
Around 1300 AD, a group of Turkmen tribes under Suleiman and Ertugrul moved westward. Under
Osman I
Osman I or Osman Ghazi ( ota, عثمان غازى, translit= ʿOsmān Ġāzī; tr, I. Osman or ''Osman Gazi''; died 1323/4), sometimes transliterated archaically as Othman, was the founder of the Ottoman Empire (first known as the Ottoman Bey ...
, they founded the
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
in northwestern
Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
; in 1326, the Ottomans conquered Bursa, which became the first capital of the Ottoman state. By the late 15th century, the Ottoman state had become a major power. In 1517, the Egyptian
Sultanate of the Mamluks was overthrown in the
Ottoman–Mamluk war.
Suleiman the Magnificent
Suleiman I ( ota, سليمان اول, Süleyman-ı Evvel; tr, I. Süleyman; 6 November 14946 September 1566), commonly known as Suleiman the Magnificent in the West and Suleiman the Lawgiver ( ota, قانونى سلطان سليمان, Ḳ ...
, the tenth
Sultan
Sultan (; ar, سلطان ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it c ...
(1520-1566), invaded Persia and forced the Persian Shah
Tahmasp (1524–1576) to move his capital from
Tabriz
Tabriz ( fa, تبریز ; ) is a city in northwestern Iran, serving as the capital of East Azerbaijan Province. It is the sixth-most-populous city in Iran. In the Quru River valley in Iran's historic Azerbaijan region between long ridges of vo ...
to
Qazvin
Qazvin (; fa, قزوین, , also Romanized as ''Qazvīn'', ''Qazwin'', ''Kazvin'', ''Kasvin'', ''Caspin'', ''Casbin'', ''Casbeen'', or ''Ghazvin'') is the largest city and capital of the Province of Qazvin in Iran. Qazvin was a capital of the ...
, until the
Peace of Amasya
The Peace of Amasya ( fa, پیمان آماسیه ("Peymān-e Amasiyeh"); tr, Amasya Antlaşması) was a treaty agreed to on May 29, 1555, between Shah Tahmasp of Safavid Iran and Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent of the Ottoman Empire at the cit ...
was agreed upon in 1555.
As the political and economical influence grew of the Ottoman Empire,
Istanbul
)
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code = 34000 to 34990
, area_code = +90 212 (European side) +90 216 (Asian side)
, registration_plate = 34
, blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD
, blank_i ...
became a meeting point of diplomats, merchants and artists. During Suleiman I.'s reign, artists and artisans of different specialities worked together in court manufactures (''Ehl-i Hiref'').
Calligraphy
Calligraphy (from el, link=y, καλλιγραφία) is a visual art related to writing. It is the design and execution of lettering with a pen, ink brush, or other writing instrument. Contemporary calligraphic practice can be defined ...
and
miniature painting Miniature painting may refer to:
* Miniature (illuminated manuscript), a small illustration used to decorate an illuminated manuscript
* Persian miniature, a small painting on paper in the Persian tradition, for a book or album
* Ottoman miniature, ...
were performed in the calligraphy workshops, or ', and influenced carpet weaving. Besides Istanbul, Bursa, Iznik, Kütahya and Ushak were homes to manufactories of different specializations.
Bursa
( grc-gre, Προῦσα, Proûsa, Latin: Prusa, ota, بورسه, Arabic:بورصة) is a city in northwestern Turkey and the administrative center of Bursa Province. The fourth-most populous city in Turkey and second-most populous in the ...
became known for its silk cloths and brocades,
Iznik and
Kütahya
Kütahya () (historically, Cotyaeum or Kotyaion, Greek: Κοτύαιον) is a city in western Turkey which lies on the Porsuk river, at 969 metres above sea level. It is inhabited by some 578,640 people (2022 estimate). The region of Kütahya ha ...
were famous for ceramics and
tile
Tiles are usually thin, square or rectangular coverings manufactured from hard-wearing material such as ceramic, stone, metal, baked clay, or even glass. They are generally fixed in place in an array to cover roofs, floors, walls, edges, or ...
s,
Uşak
Uşak (; el, Ουσάκειον, Ousakeion) is a city in the interior part of the Aegean Region of Turkey. The city has a population of 500,000 (2016 census) and is the capital of Uşak Province.
Uşak city is situated at a distance of from İz ...
,
Gördes
Gördes is a town and district of Manisa Province in the Aegean region of Turkey. According to the 2000 census, population of the district is 38,110 of which 10,809 live in the town of Gördes. The district covers an area of , and the town lies ...
, and
Ladik for their carpets. The Ushak region, one of the centers of Ottoman "court" production, produced some of the finest carpets of the sixteenth century.
Holbein and
Lotto carpet
A Lotto carpet is a hand-knotted, patterned Turkish carpet that was produced primarily during the 16th and 17th centuries along the Aegean coast of Anatolia, Turkey, although it was also copied in various parts of Europe. It is characterized by ...
s were woven here. Gold-brocaded silk velvet carpets known as ''Çatma'' are associated with the old Ottoman capital of Bursa, in Western Anatolia near the Sea of Marmara.
15th century "animal" rugs
Very few carpets still exist today which represent the transition between the late Seljuq and early Ottoman period. A traditional Chinese motif, the fight between phoenix and dragon, is seen in an Anatolian rug, today at the
Pergamon Museum
The Pergamon Museum (; ) is a listed building on the Museum Island in the historic centre of Berlin. It was built from 1910 to 1930 by order of German Emperor Wilhelm II according to plans by Alfred Messel and Ludwig Hoffmann in Stripped C ...
, Berlin. Radiocarbon dating confirmed that the "Dragon and Phoenix" carpet was woven in the mid 15th century, during the early Ottoman Empire. It is knotted with symmetric knots. The Chinese motif was probably introduced into Islamic art by the Mongols during the thirteenth century.
Another carpet showing two medallions with two birds besides a tree was found in the Swedish church of Marby. More fragments were found in
Fostat
Fusṭāṭ ( ar, الفُسطاط ''al-Fusṭāṭ''), also Al-Fusṭāṭ and Fosṭāṭ, was the first capital of Egypt under Muslim rule, and the historical centre of modern Cairo. It was built adjacent to what is now known as Old Cairo by ...
, today a suburb of the city of Cairo.
A carpet with serial bird-and-tree medallions is shown in
Sano di Pietro
Sano di Pietro or Ansano di Pietro di Mencio (1405–1481) was an Italian painter of the Sienese school of painting. He was active for about half a century during the Quattrocento period, and his contemporaries included Giovanni di Paolo and S ...
's painting "Marriage of the Virgin" (1448–52).
The "Dragon and Phoenix" and the "Marby" rugs were the only existing examples of Anatolian animal carpets known until 1988. Since then, seven more carpets of this type have been found. They survived in Tibetan monasteries and were removed by monks fleeing to Nepal during the
Chinese cultural revolution
The Cultural Revolution, formally known as the Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution, was a sociopolitical movement in the People's Republic of China (PRC) launched by Mao Zedong in 1966, and lasting until his death in 1976. Its stated goal ...
. One of these carpets was acquired by the Metropolitan Museum of Art
which parallels a painting by the Sienese artist
Gregorio di Cecco: "The Marriage of the Virgin", 1423. It shows large confronted animals, each with a smaller animal inside.
More animal carpets were depicted in Italian paintings of the 14th and 15th century, and thus represent the earliest Oriental carpets shown in Renaissance paintings. Although only few examples for early Anatolian carpets have survived, European paintings inform the knowledge about late Seljuk and early Ottoman carpets. By the end of the 15th century, geometrical ornaments became more frequent.
Holbein and Lotto carpets
Based on the distribution and size of their geometric medallions, a distinction is made between "large" and "small"
Holbein carpets. The small Holbein type is characterized by small octagons, frequently including a star, which are distributed over the field in a regular pattern, surrounded by
arabesques
The arabesque is a form of artistic decoration consisting of "surface decorations based on rhythmic linear patterns of scrolling and interlacing foliage, tendrils" or plain lines, often combined with other elements. Another definition is "Foli ...
. The large Holbein type show two or three large medallions, often including eight-pointed stars. Their field is often covered in minute floral ornaments. The
MAK in Vienna, the
Louvre
The Louvre ( ), or the Louvre Museum ( ), is the world's most-visited museum, and an historic landmark in Paris, France. It is the home of some of the best-known works of art, including the ''Mona Lisa'' and the '' Venus de Milo''. A central ...
in Paris, and the
Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 1000 ...
keep particularly beautiful Ushak carpets.
Lotto carpet
A Lotto carpet is a hand-knotted, patterned Turkish carpet that was produced primarily during the 16th and 17th centuries along the Aegean coast of Anatolia, Turkey, although it was also copied in various parts of Europe. It is characterized by ...
s show a yellow grid of geometric arabesques, with interchanging cruciform, octagonal, or diamond shaped elements. The oldest examples have "kufic" borders. The field is always red, and is covered with bright yellow leaves on an underlying rapport of octagonal or rhombiform elements. Carpets of various sizes up to 6 meters square are known. Ellis distinguishes three principal design groups for Lotto carpets: the Anatolian-style, kilim-style, and ornamental style.
Holbein and Lotto carpets have little in common with decorations and ornaments seen on Ottoman art objects other than carpets. Briggs demonstrated similarities between both types of carpets, and Timurid carpets depicted in miniature paintings. The Holbein and Lotto carpets may represent a design tradition dating back to the
Timurid period.
Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
, 16th century.
File:Inside the Harem, Topkapi Palace, Istanbul, Turkey (Nov 2009).jpg, The Harem Room, Topkapi Palace, carpet with a small-pattern "Holbein" design
File:Holbein carpet with large medallions 16th century Central Anatolia.jpg, Type IV large-pattern Holbein carpet, 16th century, Central Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
.
Image:Western Anatolian knotted woll carpet with 'Lotto' patern, 16th century, Saint Louis Art Museum.jpg, Western Anatolian ‘Lotto’-rug, 16th century, Saint Louis Art Museum
The Saint Louis Art Museum (SLAM) is one of the principal U.S. art museums, with paintings, sculptures, cultural objects, and ancient masterpieces from all corners of the world. Its three-story building stands in Forest Park in St. Louis, ...
Ushak carpets
Star Ushak carpets were woven in large formats. They are characterized by large dark blue star shaped primary medallions in infinite repeat on a red ground field containing a secondary floral scroll. The design was likely influenced by northwest Persian book design, or by Persian carpet medallions.
As compared to the medallion Ushak carpets, the concept of the infinite repeat in star Ushak carpets is more accentuated and in keeping with the early Turkish design tradition.
Because of their strong allusion to the infinite repeat, the star Ushak design can be used on carpets of various size and in many varying dimensions.

Medallion Ushak carpets usually have a red or blue field decorated with a floral trellis or leaf tendrils, ovoid primary medallions alternating with smaller eight-lobed stars, or lobed medallions, intertwined with floral tracery. Their border frequently contains palmettes on a floral and leaf scroll, and pseudo-kufic characters.
Medallion Ushak carpets with their curvilinear patterns significantly depart from the designs of earlier Turkish carpets. Their emergence in the sixteenth century hints at a potential impact of Persian designs. Since the Ottoman Turks occupied the former Persian capital of
Tabriz
Tabriz ( fa, تبریز ; ) is a city in northwestern Iran, serving as the capital of East Azerbaijan Province. It is the sixth-most-populous city in Iran. In the Quru River valley in Iran's historic Azerbaijan region between long ridges of vo ...
in the first half of the sixteenth century, they would have knowledge of, and access to Persian medallion carpets. Several examples are known to have been in Turkey at an early date, such as the carpet that Erdmann found in the Topkapı Palace. The Ushak carpet medallion, however, conceived as part of an endless repeat, represents a specific Turkish idea, and is different from the Persian understanding of a self-contained central medallion.
Star and medallion Ushaks represent an important innovation, as in them, floral ornaments appear in Turkish carpets for the first time. The replacement of floral and foliate ornaments by geometrical designs, and the substitution of the infinite repeat by large, centered compositions of ornaments, was termed by
Kurt Erdmann
Kurt Erdmann (9 September 1901, in Hamburg – 30 September 1964, in Berlin) was a German art historian who specialized in Sasanian and Islamic Art. He is best known for his scientific work on the history of the Oriental rug, which he establish ...
the "pattern revolution".
Another small group of Ushak carpets is called Double-niche Ushaks. In their design, the corner medallions have been moved closely together, so that they form a niche on both ends of the carpet. This has been understood as a prayer rug design, because a pendant resembling a mosque lamp is suspended from one of the niches. The resulting design scheme resembles the classical Persian medallion design. Counterintuitive to the prayer rug design, some of the double niche Ushaks have central medallions as well. Double niche Ushaks thus may provide an example for the integration of Persian patterns into an older Anatolian design tradition.
White ground (Selendi) rugs

Examples are also known of rugs woven in the Ushak area whose fields are covered by ornaments like the
Cintamani
Cintāmaṇi ( Sanskrit; Devanagari: चिंतामणि; Chinese: 如意寶珠; Pinyin: ''Rúyì bǎozhū''; Japanese Romaji: ''Nyoihōju; Tamil:சிந்தாமணி''), also spelled as Chintamani (or the ''Chintamani Stone''), i ...
motif, made of three coloured orbs arranged in triangles, often with two wavy bands positioned under each triangle. This motiv usually appears on a white ground. Together with the bird and a very small group of so-called scorpion rugs, they form a group of known as "white ground rugs". Bird rugs have an allover geometrical field design of repeating quatrefoils enclosing a rosette. Although geometric in design, the pattern has similarities to birds. The rugs of the white ground group have been attributed to the nearby town of Selendi, based on an Ottoman official price list ''(narh defter)'' of 1640 which mentions a "white carpet with leopard design".
Ottoman Cairene rugs
After the 1517 Ottoman conquest of the Mamluk Sultanate in Egypt, two different cultures merged, as is seen on Mamluk carpets woven after this date. The earlier tradition of the Mamluk carpet used "S" (clockwise) spun and "Z" (anti-clockwise)-plied wool, and a limited palette of colours and shades. After the conquest, the Cairene weavers adopted an Ottoman Turkish design.
The production of these carpets continued in Egypt, and probably also in Anatolia, into the early 17th century.
"Transylvanian" rugs
Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the A ...
, in present-day
Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, S ...
was part of the Ottoman Empire from 1526-1699. It was an important center for the carpet trade with Europe. Carpets were also valued in Transylvania, and Turkish carpets were used as decorative wall furnishings in Christian Protestant churches. Amongst others, the
Brașov
Brașov (, , ; german: Kronstadt; hu, Brassó; la, Corona; Transylvanian Saxon: ''Kruhnen'') is a city in Transylvania, Romania and the administrative centre of Brașov County.
According to the latest Romanian census (2011), Brașov has a pop ...
Black Church
The black church (sometimes termed Black Christianity or African American Christianity) is the faith and body of Christian congregations and denominations in the United States that minister predominantly to African Americans, as well as their ...
still shelters a variety of Anatolian carpets, called by convenience "Transylvanian carpets". By their preservation in Christian churches, unusual as the setting may be, the carpets were protected from wear and the changes of history, and often remained in excellent condition. Amongst these carpets are well-preserved Holbein, Lotto, and Bird Ushak carpets.
The carpets termed "Transsylvanian carpets" by convenience today are of Ottoman origin, and were woven in Anatolia.
Usually their format is small, with borders of oblong, angular cartouches whose centers are filled with stylized, counterchanging vegetal motifs, sometimes interspersed with shorter stellated rosettes or cartouches. Their field often has a prayer niche design, with two pairs of vases with flowering branches symmetrically arranged towards the horizontal axis. In other examples, the field decor is condensed into medallions of concentric lozenges and rows of flowers. The spandrels of the prayer niche contain stiff arabesques or geometrical rosettes and leaves. The ground colour is yellow, red, or dark blue. The Transylvanian church records, as well as Netherlandish paintings from the seventeenth century which depict in detail carpets with this design, allow for precise dating.
By the time "Transylvanian" carpets appear in Western paintings for the first time, royal and aristocratic subjects had mostly progressed to sit for portraits which depict Persian carpets. Less wealthy sitters are still shown with the Turkish types: The 1620 ''
Portrait of Abraham Grapheus'' by
Cornelis de Vos
Cornelis de Vos (1584 – 9 May 1651) was a Flemish painter, draughtsman and art dealer. He was one of the leading portrait painters in Antwerp and is best known for his sensitive portraits, in particular of children and families. He was ...
, and
Thomas de Keyser
Thomas de Keyser (c. 1596–1667) was a Dutch portrait painter, a dealer in Belgium bluestone and stone mason. He was the most in-demand portrait painter in the Netherlands until the 1630s, when Rembrandt eclipsed him in popularity. Rembrand ...
's "Portrait of an unknown man" (1626) and "Portrait of Constantijn Huyghens and his clerk" (1627) are amongst the earliest paintings depicting the "Transylvanian" types of Ottoman Turkish manufactory carpets. Transylvanian vigesimal accounts, customs bills, and other archived documents provide evidence that these carpets were exported to Europe in large quantities. Probably the increase in production reflects the increasing demand by an upper middle class who now could afford to buy these carpets.
Pieter de Hooch
Pieter de Hooch (, also spelled "Hoogh" or "Hooghe"; 20 December 1629 (baptized) – 24 March 1684 (buried)) was a Dutch Golden Age painter famous for his genre works of quiet domestic scenes with an open doorway. He was a contemporary of ...
s 1663 painting "Portrait of a family making music" depicts an Ottoman prayer rug of the "Transylvanian" type.
Anatolian carpets of the "Transylvanian" type were also kept in other European churches in Hungary, Poland, Italy and Germany, whence they were sold, and reached European and American museums and private collections. Aside from the Transylvanian churches, the
Brukenthal National Museum
The Brukenthal National Museum ( ro, Muzeul Național Brukenthal; german: Brukenthalmuseum) is a museum in Sibiu, Transylvania, Romania, established in the late 18th century by Samuel von Brukenthal (1721-1803) in his city palace. Baron Bruken ...
in Sibiu, Romania,
the
Museum of Fine Arts (Budapest)
The Museum of Fine Arts ( hu, Szépművészeti Múzeum �seːpmyveːsɛti ˈmuːzɛum is a museum in Heroes' Square, Budapest, Hungary, facing the Palace of Art.
It was built by the plans of Albert Schickedanz and Fülöp Herzog in an eclect ...
, the
Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 1000 ...
, and the
Skokloster Castle
Skokloster Castle ( sv, Skoklosters slott) is a Swedish Baroque castle built between 1654 and 1676 by Carl Gustaf Wrangel, located on a peninsula of Lake Mälaren between Stockholm and Uppsala. It became a state museum in the 1970s and displays co ...
near Stockholm in Sweden keep important collections of "Transylvanian" carpets.
Carpets are rarely found in Anatolia itself from the transitional period between the classical Ottoman era and the nineteenth century. The reason for this remains unclear. Carpets which can be reliably dated to the eighteenth century are of a small format. At the same time, western European residences were more sparely equipped with Oriental carpets. It seems likely that carpets were not exported in large scale during this time.
19th century: "''Mecidi''" style, and the Hereke court manufacture

By the end of the eighteenth century, the "turkish baroque" or "''mecidi''" style developed out of French baroque designs. Carpets were woven after the patterns of French
Savonnerie
The Savonnerie manufactory was the most prestigious European manufactory of knotted-pile carpets, enjoying its greatest period c. 1650–1685; the cachet of its name is casually applied to many knotted-pile carpets made at other centers. The manuf ...
and
Aubusson tapestry
Aubusson tapestry is tapestry manufactured at Aubusson, in the upper valley of the Creuse in central France. The term often covers the similar products made in the nearby town of Felletin, whose products are often treated as "Aubusson". The i ...
. Sultan
Abdülmecid I
Abdulmejid I ( ota, عبد المجيد اول, ʿAbdü'l-Mecîd-i evvel, tr, I. Abdülmecid; 25 April 182325 June 1861) was the 31st Sultan of the Ottoman Empire and succeeded his father Mahmud II on 2 July 1839. His reign was notable for the r ...
(1839–1861) built the
Dolmabahçe Palace
Dolmabahçe Palace ( tr, Dolmabahçe Sarayı, ) located in the Beşiktaş district of Istanbul, Turkey, on the European coast of the Bosporus strait, served as the main administrative center of the Ottoman Empire from 1856 to 1887 and from 1909 t ...
, modelled after the
Palace of Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; french: Château de Versailles ) is a former royal residence built by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, about west of Paris, France. The palace is owned by the French Republic and since 1995 has been managed, u ...
.
A weaving workshop was established in 1843 in
Hereke Hereke is a town in Kocaeli province, Turkey, located to the north of the Gulf of İzmit, near Istanbul. It is famous for Hereke carpets. It was bound to Gebze district until transferring to Körfez in 1987 and had municipality status until 2009 ...
, a coastal town 60 kilometers from Istanbul on the bay of
Izmit.
[Hereke Silk Carpet.com](_blank)
. Hereke Silk Carpet.com. Retrieved on 2012-01-27. It also supplied the royal palaces with silk brocades and other textiles. The Hereke Imperial Factory initially included looms producing cotton fabric. Silk brocades and velvets for drapes and upholstery were manufactured at a workshop known as the "''kamhane''". In 1850 the cotton looms were moved to a factory in Bakirköy, west of Istanbul, and jacquard looms were installed in Hereke. Although in the early years the factory produced exclusively for the Ottoman palaces, as production increased the woven products were available in the
Kapalıçarşı
The Grand Bazaar ( tr, Kapalıçarşı, meaning ‘Covered Market’; also , meaning ‘Grand Market’Müller-Wiener (1977), p. 345.) in Istanbul is one of the largest and oldest covered markets in the world, with 61 covered streets and over 4 ...
or Grand Bazaar, in the second half of the 19th century. In 1878 a fire in the factory caused extensive damage, and it was not reopened until 1882. Carpet production began in
Hereke Hereke is a town in Kocaeli province, Turkey, located to the north of the Gulf of İzmit, near Istanbul. It is famous for Hereke carpets. It was bound to Gebze district until transferring to Körfez in 1987 and had municipality status until 2009 ...
in 1891 and expert carpet weavers were brought in from the carpet weaving centers of
Sivas
Sivas (Latin and Greek: ''Sebastia'', ''Sebastea'', Σεβάστεια, Σεβαστή, ) is a city in central Turkey and the seat of Sivas Province.
The city, which lies at an elevation of in the broad valley of the Kızılırmak river, is ...
,
Manisa
Manisa (), historically known as Magnesia, is a city in Turkey's Aegean Region and the administrative seat of Manisa Province.
Modern Manisa is a booming center of industry and services, advantaged by its closeness to the international port ci ...
and
Ladik. The carpets were all hand woven, and in the early years they were either made for the Ottoman palaces or as gifts for visiting statesmen. Later, they were also woven for export.
Hereke carpets are known primarily for their fine weave. Silk thread or fine wool yarn and occasionally gold, silver and cotton thread are used in their production. Wool carpets produced for the palace had 60–65 knots per square centimeter, while silk carpets had 80–100 knots.
The oldest Hereke carpets, now exhibited in
Topkapı and other palaces in Istanbul, contain a wide variety of colours and designs. The typical "palace carpet" features intricate floral designs, including the tulip, daisy, carnation, crocus, rose, lilac, and hyacinth. It often has quarter medallions in the corners. The medallion designs of earlier Ushak carpets was widely used at the Hereke factory. These medallions are curved on the horizontal axis and taper to points on the vertical axis. Hereke prayer rugs feature patterns of geometric motifs, tendrils and lamps as background designs within the representation of a
mihrab
Mihrab ( ar, محراب, ', pl. ') is a niche in the wall of a mosque that indicates the ''qibla'', the direction of the Kaaba in Mecca towards which Muslims should face when praying. The wall in which a ''mihrab'' appears is thus the "qibla ...
(prayer niche). Once referring solely to carpets woven at Hereke, the term "Hereke carpet" now refers to any high quality carpet woven using similar techniques. Hereke carpets remain among the finest and most valuable examples of woven carpets in the world.
Modern history: Decline and revival
The modern history of carpets and rugs began in the nineteenth century when increasing demand for handmade carpets arose on the international market. However, the traditional, hand-woven, naturally dyed Turkish carpet is a very labour-intense product, as each step in its manufacture requires considerable time, from the preparation, spinning, dyeing of the wool to setting up the loom, knotting each knot by hand, and finishing the carpet before it goes to market. In an attempt to save on resources and cost, and maximise on profit in a competitive market environment, synthetic
dyes
A dye is a colored substance that chemically bonds to the substrate to which it is being applied. This distinguishes dyes from pigments which do not chemically bind to the material they color. Dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution an ...
, non-traditional weaving tools like the
power loom
A power loom is a mechanized loom, and was one of the key developments in the industrialization of weaving during the early Industrial Revolution. The first power loom was designed in 1786 by Edmund Cartwright and first built that same year. ...
, and standardized designs were introduced. This led to a rapid breakdown of the tradition, resulting in the degeneration of an art which had been cultivated for centuries. The process was recognized by art historians as early as in 1902. It is hitherto unknown when exactly this process of degeneration started, but it is observed mainly since the large-scale introduction of synthetic colours took place.
In the late twentieth century, the loss of cultural heritage was recognized, and efforts started to revive the tradition.
Initiatives
In political science, an initiative (also known as a popular initiative or citizens' initiative) is a means by which a petition signed by a certain number of registered voters can force a government to choose either to enact a law or hold a ...
were started aiming at re-establishing the ancient tradition of carpet weaving from handspun, naturally dyed wool.
The return to traditional dyeing and weaving by the producers, and the renewed customer interest in these carpets was termed by Eilland as the "Carpet Renaissance". Thus, Anatolian rugs remain distinguishable from rugs woven in other regions.
Carpet weaving: Materials, technique, processes
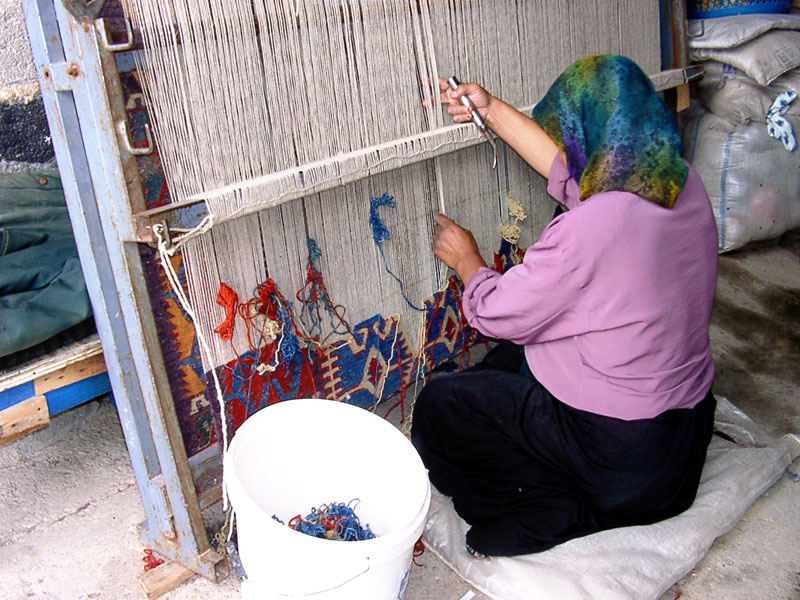

In traditional households, women and girls take up carpet and kilim weaving as a hobby as well as a means of earning money. Women learn their weaving skills at an early age, taking months or even years to complete the pile rugs and flat woven kilims that were created for their use in daily life. As is true in most weaving cultures, traditionally it is women and girls who are both artisan and weaver.
["Kilim Rugs: Timeless Beauty"](_blank)
kilims.org. Retrieved 2016-01-27.
Materials
Makers of handmade rugs use only natural fibres. The most common materials used for the pile are wool, silk and cotton. Nomadic and village weavers sometimes also use goat- and camel-hair. Traditionally, spinning is done by
hand
A hand is a prehensile, multi-fingered appendage located at the end of the forearm or forelimb of primates such as humans, chimpanzees, monkeys, and lemurs. A few other vertebrates such as the koala (which has two opposable thumbs on each "h ...
. Several strands of yarn are then
plied together so that the resulting yarn is strong enough to be used for weaving.
Sheep's wool is the most frequently used pile material in a Turkish rug because it is soft, durable, easy to work with and not too expensive. It is less susceptible to dirt than cotton, does not react electrostatically, and insulates against both heat and cold. This combination of characteristics is not found in other natural fibers. Wool comes from the coats of sheep. Natural wool comes in colors of white, brown, fawn, yellow and gray, which are sometimes used directly without going through a dyeing process. Sheep's wool also takes dyes well. Traditionally, wool used for Turkish carpets is
spun by hand. Before the yarn can be used for weaving, several strands have to be twisted together for additional strength.
Cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor pe ...
is used primarily in the foundation, the
warps and
wefts of rugs. Cotton is stronger than wool, and, when used for the foundation, makes a carpet lie flat on the ground, as it is not as easily distorted as woolen strings. Some weavers, such as Turkomans, also use cotton for weaving small white details into the rug in order to create contrast.
Wool-on-wool (wool pile on wool warp and weft): This is the most traditional type of Anatolian rug. Wool-on-wool carpet weaving dates back further and utilizes more traditional design-motifs than its counterparts. Because wool cannot be spun extra finely, the
knot count is often not as high as seen in a "wool-on-cotton" or "silk-on-silk" rug. Wool-on-wool carpets are more frequently attributed to tribal or nomadic production.
Wool-on-
cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor pe ...
(wool pile on cotton warp and weft): This particular combination facilitates a more intricate design-pattern than a "wool-on-wool carpet", as cotton can be finely spun which allows for a higher knot-count. A "wool-on-cotton" rug is often indicative of a town weaver. Due to their higher pile density, wool-on-cotton carpets are heavier than wool-on-wool rugs.
Silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from th ...
-on-silk (silk pile on silk warp and weft): This is the most intricate type of carpet, featuring a very fine weave. Knot counts on some superior-quality "silk-on-silk" rugs can be as high as 28×28 knots/cm
2. Knot counts for silk carpets intended for floor coverings should be no greater than 100 knots per square cm, or 10×10 knots/cm
2. Carpets woven with a knot count greater than 10×10 knots/cm
2 are intended to be used as a wall or pillow tapestry, because their fabric is less resistant to mechanical stress. These very fine, intricately-woven rugs and carpets are usually no larger than 3×3 m.
Dyes and dyeing

Traditional dyes used for Anatolian carpets are obtained from plants, insects and minerals. In 1856, the English chemist
William Henry Perkin
Sir William Henry Perkin (12 March 1838 – 14 July 1907) was a British chemist and entrepreneur best known for his serendipitous discovery of the first commercial synthetic organic dye, mauveine, made from aniline. Though he failed in trying ...
invented the first
aniline
Aniline is an organic compound with the formula C6 H5 NH2. Consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group, aniline is the simplest aromatic amine. It is an industrially significant commodity chemical, as well as a versatile starti ...
dye,
mauveine
Mauveine, also known as aniline purple and Perkin's mauve, was one of the first synthetic dyes. It was discovered serendipitously by William Henry Perkin in 1856 while he was attempting to synthesise the phytochemical quinine for the treatment of ...
. A variety of other synthetic
dyes
A dye is a colored substance that chemically bonds to the substrate to which it is being applied. This distinguishes dyes from pigments which do not chemically bind to the material they color. Dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution an ...
were invented thereafter. Cheap, readily prepared and easy to use as they were compared to natural dyes, their use is documented in Ushak carpets already by the mid 1860s. The tradition of natural dyeing was recently revived, based on chemical analyses of natural dyes from antique wool samples, and experimental re-creation of dyeing recipes and processes, in the early 1980s.
According to these analyses, natural dyes used in Anatolian rugs include:
* ''Red'' from
Madder (Rubia tinctorum) roots,
* ''Yellow'' from plants, including
onion (Allium cepa), several chamomile species (
Anthemis
''Anthemis'' is a genus of aromatic flowering plants in the family Asteraceae, closely related to '' Chamaemelum'', and like that genus, known by the common name chamomile; some species are also called dog-fennel or mayweed. ''Anthemis'' are nati ...
,
Matricaria chamomilla
''Matricaria chamomilla'' (synonym: ''Matricaria recutita''), commonly known as chamomile (also spelled camomile), German chamomile, Hungarian chamomile (kamilla), wild chamomile, blue chamomile, or scented mayweed, is an annual plant of the com ...
), and
Euphorbia
''Euphorbia'' is a very large and diverse genus of flowering plants, commonly called spurge, in the family Euphorbiaceae. "Euphorbia" is sometimes used in ordinary English to collectively refer to all members of Euphorbiaceae (in deference to t ...
,
* ''Black'':
Oak apple
Oak apple or oak gall is the common name for a large, round, vaguely apple-like gall commonly found on many species of oak. Oak apples range in size from in diameter and are caused by chemicals injected by the larva of certain kinds of gall ...
s,
Oak acorns,
Tanner's sumach,
* ''Green'' by double dyeing with
Indigo
Indigo is a deep color close to the color wheel blue (a primary color in the RGB color space), as well as to some variants of ultramarine, based on the ancient dye of the same name. The word "indigo" comes from the Latin word ''indicum'', ...
and yellow dye,
* ''Orange'' by double dyeing with madder red and yellow dye,
* ''Blue'':
Indigo
Indigo is a deep color close to the color wheel blue (a primary color in the RGB color space), as well as to some variants of ultramarine, based on the ancient dye of the same name. The word "indigo" comes from the Latin word ''indicum'', ...
gained from
Indigofera tinctoria
''Indigofera tinctoria'', also called true indigo, is a species of plant from the bean family that was one of the original sources of indigo dye.
Description
True indigo is a shrub one to two meters high. It may be an annual plant, annual, bi ...
.
The dyeing process involves the preparation of the yarn in order to make it susceptible for the proper dyes by immersion in a
mordant
A mordant or dye fixative is a substance used to set (i.e. bind) dyes on fabrics by forming a coordination complex with the dye, which then attaches to the fabric (or tissue). It may be used for dyeing fabrics or for intensifying stains in ...
, immersing the yarn in the dyeing solution, and leaving it to dry exposed to air and sunlight. Some colours, especially dark brown, require iron mordants, which can damage or fade the fabric. This often results in faster pile wear in areas dyed in dark brown colours, and may create a relief effect in antique Turkish carpets.
With modern synthetic
dyes
A dye is a colored substance that chemically bonds to the substrate to which it is being applied. This distinguishes dyes from pigments which do not chemically bind to the material they color. Dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution an ...
, nearly every colour and shade can be obtained so that it is nearly impossible to identify, in a finished carpet, whether natural or artificial dyes were used. Modern carpets can be woven with carefully selected synthetic colours, and provide artistic and utilitarian value.
The Anatolian rug is distinct from carpets of other provenience in that it makes more pronounced use of primary colours. Western Anatolian carpets prefer red and blue colours, whereas Central Anatolian use more red and yellow, with sharp contrasts set in white.
Weaving and finishing




A variety of tools are needed in the construction of a handmade rug. A
loom
A loom is a device used to weave cloth and tapestry. The basic purpose of any loom is to hold the warp threads under tension to facilitate the interweaving of the weft threads. The precise shape of the loom and its mechanics may vary, but t ...
, a horizontal or upright framework, is needed to mount the vertical
warps into which the pile nodes are knotted, and one or more shoots of horizontal
wefts are woven ("shot") in after each row of knots in order to further stabilize the fabric. Wefts can be either undyed or dyed, mostly in red and blue.
The pile knots are usually knotted by hand. Most rugs from Anatolia utilize the symmetrical
Turkish double knot. Each knot is made on two warps. With this form of knotting, each end of the pile thread is twisted around two warp threads at regular intervals, so that both ends of the knot come up between two strands on one side of the carpet. The thread is then pulled downwards and cut with a knife.
After a row of knots has been inserted, one or two, sometimes more, rows of wefts are woven in, and the fabric is compacted by beating with a heavy comb. Once the carpet is finished, it is cut from the loom. The sides or
selvages are usually overcast in wool. The selvages consist of up to ten warp threads. Especially village and nomadic rugs have flat-woven
kilim
A kilim ( az, Kilim کیلیم; tr, Kilim; tm, Kilim; fa, گلیم ''Gilīm'') is a flat tapestry- woven carpet or rug traditionally produced in countries of the former Persian Empire, including Iran, the Balkans and the Turkic countries. Ki ...
ends, sometimes including pile-woven tribal signs or village crests. The pile of the carpet is shorn with special knives in order to obtain an equal surface. In some carpets, a relief effect is obtained by clipping the pile unevenly. Finally, the carpet is washed before it is used, or goes to the market.
The upright pile of Turkish rugs usually falls in one direction, as knots are always pulled down before the string of pile yarn is cut off and work resumes on the next knot, piling row after row of knots on top of each other. When touching a carpet, this creates a feeling similar to stroking an animal's fur. This can be used to determine where the weaver has started knotting the pile. The pile in Turkish carpets is usually between 2 and 4 mm thick. Coarse nomadic rugs like the
Yürük rugs, can be as thick as 12 mm. A special bedding carpet called ''yatak'' may reach a pile thickness of 20 to 25 mm.
Origins and traditions of Anatolian rug design
Anatolian rug design integrates different strands of traditions. Specific elements are closely related to the history of
Turkic peoples
The Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West, Central, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose members speak languages belonging to ...
and their interaction with surrounding cultures, in their central Asian origin as well as during their migration, and in Anatolia itself. The most important cultural influences came from the Chinese culture, and from Islam.
Carpets from the
Bergama
Bergama is a populous district, as well as the center city of the same district, in İzmir Province in western Turkey. By excluding İzmir's metropolitan area, it is one of the prominent districts of the province in terms of population and is l ...
and
Konya
Konya () is a major city in central Turkey, on the southwestern edge of the Central Anatolian Plateau, and is the capital of Konya Province. During antiquity and into Seljuk times it was known as Iconium (), although the Seljuks also called it D ...
areas are considered as most closely related to earlier Anatolian rugs, and their significance in the history of the art is now better understood.
Central Asian traditions
The early history of the
Turkic peoples
The Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West, Central, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose members speak languages belonging to ...
in Central Asia is closely related to China. Contacts between Turks and China are documented since the early
Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
.
In his essay on centralized designs, Thompson relates the central medallion pattern, frequently found in Anatolian rugs to the "lotus pedestal" and "cloud collar (yun chien)" motifs, used in
the art of Buddhist Asia, which he dated back to
Yuan dynasty China. Recently, Brüggemann further elaborated on the relationship between Chinese and Turkic motifs like the "cloud band" ornament, the origin of which he relates to the
Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
. The early Anatolian "Phoenix and Dragon rug" depicts another traditional motif of Chinese mythology, the fight between the phoenix (
Fenghuang
''Fènghuáng'' (, ) are mythological birds found in Sinospheric mythology that reign over all other birds. The males were originally called ''fèng'' and the females ''huáng'', but such a distinction of gender is often no longer made and ...
) and the
dragon
A dragon is a reptilian legendary creature that appears in the folklore of many cultures worldwide. Beliefs about dragons vary considerably through regions, but dragons in western cultures since the High Middle Ages have often been depicted a ...
.
Romano-Hellenistic traditions
There are documentary records of carpets being used by the ancient Greeks.
Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
writes in
Ilias
Ilias may refer to:
* the ''Iliad'', an ancient Greek epos
* Ilias (name), a personal name (including a list of people with the name)
* ILIAS, a web-based learning management system
* 6604 Ilias, an asteroid
See also
* Profitis Ilias (disambi ...
XVII,350 that the body of Patroklos is covered with a "splendid carpet". In
Odyssey
The ''Odyssey'' (; grc, Ὀδύσσεια, Odýsseia, ) is one of two major ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the '' Iliad'', ...
Book VII and X "carpets" are mentioned.
Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ' ...
wrote (
nat. VIII, 48) that carpets ("polymita") were invented in Alexandria. It is unknown whether these were flatweaves or pile weaves, as no detailed technical information can be gained from the texts.
Athenaeus of Naucratis
Athenaeus of Naucratis (; grc, Ἀθήναιος ὁ Nαυκρατίτης or Nαυκράτιος, ''Athēnaios Naukratitēs'' or ''Naukratios''; la, Athenaeus Naucratita) was a Greek rhetorician and grammarian, flourishing about the end of th ...
describes luxurious carpets in his
Deipnosophists
The ''Deipnosophistae'' is an early 3rd-century AD Greek work ( grc, Δειπνοσοφισταί, ''Deipnosophistaí'', lit. "The Dinner Sophists/Philosophers/Experts") by the Greek author Athenaeus of Naucratis. It is a long work of liter ...
, written about 230 AD.
"And under these there were strewed purple carpets of the finest wool, with the carpet pattern on both sides. And there were handsomely embroidered rugs very beautifully elaborated on them." (Book V, p. 314)
" ..to lie on a couch with silver feet, with a smooth Sardian carpet spread under it of the most expensive description." (Book VI, p. 401)
A carpet "with the pattern on both sides" could either be a flat-woven, or pile-woven carpet. Whether "purple" refers to the colour of the fabric or to the dyestuff (either
Tyrian purple
Tyrian purple ( grc, πορφύρα ''porphúra''; la, purpura), also known as Phoenician red, Phoenician purple, royal purple, imperial purple, or imperial dye, is a reddish-purple natural dye. The name Tyrian refers to Tyre, Lebanon. It is ...
or
madder red could have been used) remains unknown. The town of
Sardis
Sardis () or Sardes (; Lydian: 𐤳𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣 ''Sfard''; el, Σάρδεις ''Sardeis''; peo, Sparda; hbo, ספרד ''Sfarad'') was an ancient city at the location of modern ''Sart'' (Sartmahmut before 19 October 2005), near Salihli, ...
lies in Western Anatolia, thus, this may be the earliest reference to carpet production in the region of Asia minor.
Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
was ruled by the Roman Empire since 133 BCE. The
East Roman (Byzantine) and
Sasanian
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named ...
Empires have coexisted for more than 400 years. Artistically, both empires have developed similar styles and decorative vocabulary, as exemplified by mosaics and architecture of Roman
Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου, ''Antiókheia hē epì Oróntou'', Learned ; also Syrian Antioch) grc-koi, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου; or Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπ� ...
.
A Turkish carpet pattern depicted on
Jan van Eyck
Jan van Eyck ( , ; – July 9, 1441) was a painter active in Bruges who was one of the early innovators of what became known as Early Netherlandish painting, and one of the most significant representatives of Early Northern Renaissance art. A ...
's
"Paele Madonna" painting was traced back to late Roman origins and related to early Islamic floor mosaics found in the Umayyad palace of
Khirbat al-Mafjar
Hisham's Palace ( ar, قصر هشام '), also known as Khirbat al-Mafjar ( ar, خربة المفجر), is an important early Islamic archaeological site in the Palestinian city of Jericho, in the West Bank. Built by the Umayyad dynasty in the ...
.
The architectural elements seen in the Khirbat al-Mafjar complex are considered exemplary for the continuation of pre-Islamic, Roman designs in early Islamic art.
Islamic traditions

When
Turkic migrants moved from Central Asia to
Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
, they were migrating mainly through lands which had already adopted Islam. Depicting animals or humans is
prohibited in the Islamic tradition, which does not distinguish between religious and profane life. Since the codification of the
Quran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , ...
by
Uthman Ibn Affan in 651 AD/19 AH and the
Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan
Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan ibn al-Hakam ( ar, عبد الملك ابن مروان ابن الحكم, ʿAbd al-Malik ibn Marwān ibn al-Ḥakam; July/August 644 or June/July 647 – 9 October 705) was the fifth Umayyad caliph, ruling from April 685 ...
reforms,
Islamic art
Islamic art is a part of Islamic culture and encompasses the visual arts produced since the 7th century CE by people who lived within territories inhabited or ruled by Muslim populations. Referring to characteristic traditions across a wide ra ...
has focused on writing and ornament. The borders of Anatolian rugs frequently contain ornaments which were derived from
Islamic calligraphy
Islamic calligraphy is the artistic practice of handwriting and calligraphy, in the languages which use Arabic alphabet or the alphabets derived from it. It includes Arabic, Persian, Ottoman, and Urdu calligraphy.Chapman, Caroline (2012). ...
. Usually, these "kufic" borders consist of lam-alif- or alif-lam sequences in an interwoven pattern.
The main fields of Anatolian rugs are frequently filled with redundant, interwoven patterns in "infinite repeat". Thus, the rug represents a section of an infinite pattern, which is imagined as continuing beyond its borders and into the infinite.
Anatolian rugs of the
"Lotto" or
"Holbein" type provide examples for "infinite repeat" field patterns.
A specific Islamic pattern is the mihrab pattern which defines the
Prayer rug
A prayer rug or prayer mat is a piece of fabric, sometimes a pile carpet, used by Muslims, some Christians and some Baha'i during prayer.
In Islam, a prayer mat is placed between the ground and the worshipper for cleanliness during the various ...
. A prayer rug is characterized by a niche at one end, representing the
mihrab
Mihrab ( ar, محراب, ', pl. ') is a niche in the wall of a mosque that indicates the ''qibla'', the direction of the Kaaba in Mecca towards which Muslims should face when praying. The wall in which a ''mihrab'' appears is thus the "qibla ...
in every mosque, a directional point to direct the
worship
Worship is an act of religious devotion usually directed towards a deity. It may involve one or more of activities such as veneration, adoration, praise, and praying. For many, worship is not about an emotion, it is more about a recogni ...
per towards
Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow v ...
. The mihrab pattern in Turkish carpets is often modified and may consist of a single, double, or vertically or horizontally multiplied niche. Thus the niche pattern can range from a concrete, architectural to a more ornamental understanding of the design. Prayer rugs are often woven "upside down", as becomes apparent when the direction of the pile is felt by touching the carpet. This has both technical (the weaver can focus on the more complicated niche design first), and practical reasons (the pile inclines in the direction of the worshipper's prostration).
Other cultural influences

Large, geometric shapes are considered to be of Caucasian or
Turkmen origin. The Caucasian tradition may have been integrated either by migrating Turkish tribes, or by contact with Turkmen people already living in Anatolia.
A central medallion consisting of large, concentrically reduced rhomboid patterns with latch-hook ornaments is associated with the
Yörük nomads of Anatolia. The name Yürük is usually given to nomads whose way of life has changed least from its central Asian origin.
In Anatolia, several ethnic minorities have maintained separate traditions, e.g., the Greek, Armenians, and Kurds. Whilst Greeks and Armenians were involved in carpet weaving and trading in the past, no design motifs have been clearly associated with their distinct, Christian culture.
Kurdish rug design differs from Anatolian. Kurdish rugs are more often discussed together with
Persian carpet
A Persian carpet ( fa, فرش ایرانی, translit=farš-e irâni ) or Persian rug ( fa, قالی ایرانی, translit=qâli-ye irâni ),Savory, R., ''Carpets'',(Encyclopaedia Iranica); accessed January 30, 2007. also known as Iranian ...
s.
Social context: Court and town, village and nomadic production
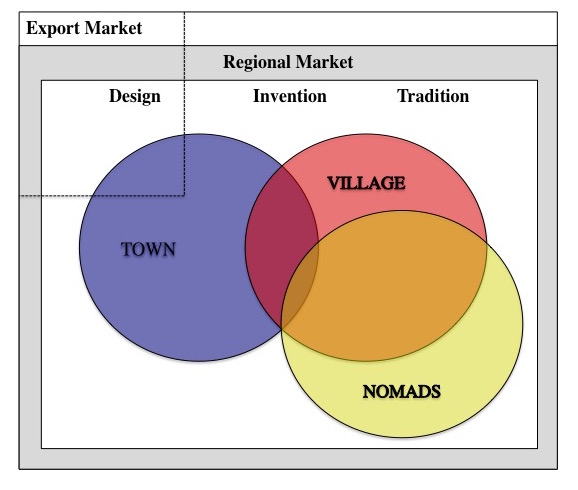
Carpets and rugs were simultaneously produced by and for the four different social levels of court, town, rural village, and tribe.
Elements of town design were often reproduced in rural production, and integrated by the village weavers into their own artistic tradition by a process called stylization.
Court manufacture
Representative "court" rugs were woven by special workshops, often founded and protected by the sovereign, with the intention to represent power and status. As such, representative carpets have developed a specific design tradition influenced by the courts of the surrounding empires. Rugs were produced in the court manufactures as special commissions or gifts. Their elaborate design required a division of work between an artist who created a design plan (termed "cartoon") on paper, and a weaver who was given the plan for execution on the loom. Thus, artist and weaver were separated.
Town and village production
Carpets were woven in town manufactures by organized manufactories. Usually, town manufactures have a larger range of patterns and ornaments and more artistically developed designs which can be executed by the weavers, the palette of colours is rich, and the weaving technique may be finer due to their access to high-quality wool, and the employment of specialized weavers. Larger formats can be produced on the larger, stationary looms. Carpets are woven from cartoons, using material provided by the manufacturer. The town manufactories may accept commissions even from foreign countries, and produce carpets for export.
Rugs produced in villages are often produced in individual homes, but at least partly commissioned and supervised by guilds or manufacturers. Home production may not require full-time labour, but could be performed when time allows, besides other household tasks. Village carpets as essential household items were part of a tradition that was at times influenced by, but essentially distinct from the invented designs of the workshop production. Frequently, mosques had acquired rural carpets as
charitable gifts, which provided material for studies.
Rural carpets rarely include cotton for warps and wefts, and almost never silk, as these materials had to be purchased on the market by the individual weaver.
Patterns and ornaments from court manufactory rugs were reproduced by smaller (town or village) workshops. This process is well documented for Ottoman prayer rugs.
As prototypical court designs were passed on to smaller workshops, and from one generation to the next, the design underwent a process termed stylization, comprizing series of small, incremental changes either in the overall design, or in details of smaller patterns and ornaments, over time. As a result, the prototype may be modified to an extent as to be barely recognizable. Initially misunderstood as the "degeneration" of a design, the process of stylization is now regarded as a genuine creative process within a distinct design tradition.
Stylization in Anatolian prayer rug design
File:The James F. Ballard Late 16th Century Bursa Prayer Rug.jpg, Ottoman court prayer rug, Bursa, late 16th century (James Ballard collection, Metropolitan Museum of Art)
File:Turkish - Prayer Rug - Google Art Project.jpg, Turkish prayer rug
File:Prayer rug, Turkey, Bergama, late 19th century, wool - Huntington Museum of Art - DSC04879.JPG, Bergama prayer rug, late 19th century
Nomadic and tribal production
With the end of the traditional
nomadic lifestyle in Anatolia, and the consequent loss of specific traditions, it has become difficult to identify a genuine "nomadic rug". Social or ethnic groups known for their nomadic lifestyle like the
Yürük or
Kurds ug:كۇردلار
Kurds ( ku, کورد ,Kurd, italic=yes, rtl=yes) or Kurdish people are an Iranian peoples, Iranian ethnic group native to the mountainous region of Kurdistan in Western Asia, which spans southeastern Turkey, northwestern Ir ...
in contemporary Turkey have in large parts acquired sedentary lifestyles. Some aspects of the tradition, like the use of specific materials, dyes, weaving or finishing techniques or designs may have been preserved, which can be identified as specifically nomadic or tribal.
Criteria for a nomadic production include:
* Unusual materials like warps made of goat's hair, or camel wool in the pile;
* high quality wool with long pile (Anatolian and Turkmen nomads);
* small format fitting for a horizontal loom;
* irregular format due to frequent re-assembly of the loom, resulting in irregular tension of the warps;
* pronounced abrash (irregularities within the same colour due to dyeing of yarn in small batches);
* inclusion of flat weaves at the ends.
Within the genre of carpet weaving, the most authentic village and nomadic products were those woven to serve the needs of the community, which were not intended for export or trade other than local. This includes specialized bags and bolster covers (') in Anatolia, which show designs adapted from the earliest weaving traditions.
Regions
Anatolia can be divided into three major areas of rug production, centered around local towns and marketplaces, which often lend their names to the rugs produced in the surrounding area. Western, Central, and Eastern Anatolia have distinct weaving traditions. However, commercially produced rugs are often woven irrespective of local design traditions. Preferential use of different materials and dyes, as well as characteristic designs, sometimes allow for a more specific assignment of a carpet to one of the three regions, or to a more specific weaving place.
Regional technical characteristics
Western Anatolia
As a group, Western Anatolian rugs often show a bright brick red and lighter reddish colours. White accents are prominent, and green and yellow are more frequently seen than in rugs from other regions of Anatolia. The wefts are often dyed red. The selvages are reinforced over 3-4 warp cords. The ends of the rug are often protected by flat weave
kilim
A kilim ( az, Kilim کیلیم; tr, Kilim; tm, Kilim; fa, گلیم ''Gilīm'') is a flat tapestry- woven carpet or rug traditionally produced in countries of the former Persian Empire, including Iran, the Balkans and the Turkic countries. Ki ...
s containing a small ornament woven in pile.
*
Istanbul
)
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code = 34000 to 34990
, area_code = +90 212 (European side) +90 216 (Asian side)
, registration_plate = 34
, blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD
, blank_i ...
is the largest city of Turkey. During the nineteenth century, the court manufactories of Topkapı, Üsküdar, and Kum Kapı produced silk carpets in "Safavid-Osmanic" designs modelled on those of the sixteenth century, employing Armenian (from the areas of Kayseri and Sivas), and Persian weavers. Kum Kapı was, in the nineteenth century, the Armenian quarter of Istanbul. The asymmetrical knot was used. Silk carpets produced here often were woven with silver and gold threads. Two of the most prominent designer weavers were Zareh Penyamian and Tossounian. Zareh is known for his prayer rugs, which often included the "Sultan's head" form of the mihrab, cloud bands in the prayer field, palmettes and arabesque patterns and
Quran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , ...
ic inscriptions. He often signed his carpets. Tossounian made silk rugs with high pile, glowing colours, and red kilim endings. The design was inspired by Persian animal carpets of the "Sanguszko" type. Colours are very elaborate, carmine red, jade green, yellow, and dark bright indigo.
*
Hereke Hereke is a town in Kocaeli province, Turkey, located to the north of the Gulf of İzmit, near Istanbul. It is famous for Hereke carpets. It was bound to Gebze district until transferring to Körfez in 1987 and had municipality status until 2009 ...
is a coastal town 60 kilometers from Istanbul on the bay of
Izmit. A weaving workshop was established in 1843 by Sultan
Abdülmecid I
Abdulmejid I ( ota, عبد المجيد اول, ʿAbdü'l-Mecîd-i evvel, tr, I. Abdülmecid; 25 April 182325 June 1861) was the 31st Sultan of the Ottoman Empire and succeeded his father Mahmud II on 2 July 1839. His reign was notable for the r ...
. Initially, the manufactory produced exclusively for the Ottoman court, which commissioned carpets for the
Dolmabahçe Palace
Dolmabahçe Palace ( tr, Dolmabahçe Sarayı, ) located in the Beşiktaş district of Istanbul, Turkey, on the European coast of the Bosporus strait, served as the main administrative center of the Ottoman Empire from 1856 to 1887 and from 1909 t ...
. Carpet production began in
Hereke Hereke is a town in Kocaeli province, Turkey, located to the north of the Gulf of İzmit, near Istanbul. It is famous for Hereke carpets. It was bound to Gebze district until transferring to Körfez in 1987 and had municipality status until 2009 ...
in 1891 and expert carpet weavers were brought in from the carpet weaving centers of
Sivas
Sivas (Latin and Greek: ''Sebastia'', ''Sebastea'', Σεβάστεια, Σεβαστή, ) is a city in central Turkey and the seat of Sivas Province.
The city, which lies at an elevation of in the broad valley of the Kızılırmak river, is ...
,
Manisa
Manisa (), historically known as Magnesia, is a city in Turkey's Aegean Region and the administrative seat of Manisa Province.
Modern Manisa is a booming center of industry and services, advantaged by its closeness to the international port ci ...
and
Ladik. Hereke carpets are known primarily for their fine weave. Silk thread or fine wool yarn and occasionally gold, silver and cotton thread are used in their production. Hereke court carpets contain a wide variety of colours and designs. The medallion designs of earlier Ushak carpets was widely used at the Hereke factory. Once referring solely to carpets woven at Hereke, the term "Hereke carpet" is now used as a trade name for any high quality carpet woven with similar design.
*
Bergama
Bergama is a populous district, as well as the center city of the same district, in İzmir Province in western Turkey. By excluding İzmir's metropolitan area, it is one of the prominent districts of the province in terms of population and is l ...
is the capital town of a district in the
Izmir Province of northwest
Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula ...
. As a market place for the surrounding villages, the name of Bergama is used as a trade name. The history of carpet weaving in Bergama probably dates back to the 11th century. Bergama carpets survived which date from the early 15th century. The best known carpet type woven for export which is attributed to the Bergama region is the so-called "large pattern
Holbein Type", or Holbein Type III. A late descendant of the large-pattern Holbein design is often seen in Bergama carpets, called the "4+1" or "quincunxial" design, with a large square central medallion surrounded by four smaller squares placed at its corners. Also antique Anatolian carpets found in Transylvanian churches were likely woven in Bergama.
Bergama rugs typically have large geometric patterns (the "Caucasian" type) or more floral patterns, stylized in rectilinear design (the "Turkish" type). They use typical Western Anatolian colour schemes with dark red and blue, and accents set in white. Bridal carpets ("Kiz Bergama") often show rosettes arranged in a lozenge pattern in their field panels.
Village and peasant carpets from the Bergama area often show coarser knotting with bold, highly stylized designs and bright blue, red, and white colours in sharp contrast.
* The village of Kozak lies north of Bergama in the
Izmir Province of northwest
Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula ...
. By structure and colours they belong to the Bergama group. Small format rugs show geometrical designs, often adorned with latched hooks, which closely resembles Caucasian designs.
* Yagcibedir is not a town name, but a label for a carpet type woven in the
Balıkesir province in the
Marmara region. These carpets are characterized by their high knot density (1000-1400 per square meter), and subdued colours. They show geometrical patterns in dark red, brown, and black-blue. By their fine weaving, colours and design they resemble Caucasian designs, and are mainly woven by people of
Circassian and
Turkmen descent who migrated into this area.
*
Çanakkale lies on the eastern shore of the
Dardanelles
The Dardanelles (; tr, Çanakkale Boğazı, lit=Strait of Çanakkale, el, Δαρδανέλλια, translit=Dardanéllia), also known as the Strait of Gallipoli from the Gallipoli peninsula or from Classical Antiquity as the Hellespont (; ...
near ancient
Troy
Troy ( el, Τροία and Latin: Troia, Hittite: 𒋫𒊒𒄿𒊭 ''Truwiša'') or Ilion ( el, Ίλιον and Latin: Ilium, Hittite: 𒃾𒇻𒊭 ''Wiluša'') was an ancient city located at Hisarlik in present-day Turkey, south-west of Ç ...
. Carpets are mainly woven in smaller villages to the south of Çanakkale. They show large squares, rhombi or polygons in their fields and strong colours like brick red, bright dark blue, saffron yellow and white.
Ayvacık is a village south of Çanakkale and
Ezine
An online magazine is a magazine published on the Internet, through bulletin board systems and other forms of public computer networks. One of the first magazines to convert from a print magazine format to being online only was the computer magaz ...
near the ruins of
Assos
Assos (; grc-gre, Ἄσσος, la, Assus) is a beautiful small and historically important town on the Aegean coast in the Ayvacık district of Çanakkale province, Turkey. It is on the southern side of Biga Peninsula (better known by its anc ...
and
Troy
Troy ( el, Τροία and Latin: Troia, Hittite: 𒋫𒊒𒄿𒊭 ''Truwiša'') or Ilion ( el, Ίλιον and Latin: Ilium, Hittite: 𒃾𒇻𒊭 ''Wiluša'') was an ancient city located at Hisarlik in present-day Turkey, south-west of Ç ...
. The carpets are of the Bergama type. Since 1981, the
DOBAG initiative runs workshops in the small hamlets around Ayvacık, which produce rugs in traditional designs and with natural dyes. The initiative also has workshops in the Yuntdağ area near Bergama, where people of
Turkmen descent weave robust, thick carpets in largely geometric designs. Floral or prayer rug designs are rare.
* The area between Balikesir and Eskisehir is inhabited mainly by a Turkish tribe called Karakecili. The rugs are often smaller, with cheerful bright red, light blue, white and pale green. The use of goats's hair for the warps hints at the nomadic origins of the tribe. The design is geometric, often combined with stylized floral motifs. The borders sometimes contain rows of lozenges, as also seen in more elaborate form in "Transylvanian" carpets.
*
Bandırma
Bandırma () is a city in northwestern Turkey with 161,894 inhabitants as of 2021 on the Sea of Marmara. Bandırma is a district of Balıkesir Province. Bandırma is located in the south of the Marmara Sea, in the bay with the same name, and is ...
is the capital town of the province to which it has given its name. The town lies on the
Marmara coast. Since the nineteenth century, intricately woven carpets are produced mainly in prayer rug design. The cotton foundation and finely knotted pile of wool and silk characterizes the Bandırma carpet as a product of town manufacture. Production declined during the late nineteenth century, with inferior or artificial silk and mercerized cotton being used. The name of the town and region is nowadays often used for cheap imitations sold by other manufacturers.
*
Gördes
Gördes is a town and district of Manisa Province in the Aegean region of Turkey. According to the 2000 census, population of the district is 38,110 of which 10,809 live in the town of Gördes. The district covers an area of , and the town lies ...
lies about 100 km north-east of
Izmir. Carpets were already produced there in the 16th century. Their largely floral, stylized patterns can be traced back to Ottoman floral designs of the sixteenth and seventeenth century. The main border is often composed of rows of three pomegranates, arranged like flowers in groups of three, held together by their stems. Typical is also a broad border of seven stripes ('). Gördes is mostly famous for its bridal and prayer carpets. The shapes of the mihrab niches vary from simple stepped arches to artistic architectural pillars, with a horizontal rectangular crossbar above the mihrab niche. Typical colours are cherry red, pastel pink, blue and green together with dark indigo blue. Early carpets of the Gördes type have a more lively colour. Since the 19th century, some pieces show spacious accents in white cotton, and the colours, overall, become more subdued.
*
Kula is the capital town of the
Manisa Province, and lies about 100 km east of Izmir on the road to Ușak. Together with Ușak, Gördes, Lâdik and Bergama it belongs to the most important rug weaving centers of Anatolia. Prayer rug designs are common, with straight-lined mihrab niches. Another specific design is called "'", or graveyard design, which is a subtype of the garden design. The particularly gloomy yet brilliant colour scheme caused one type of rugs from this area to be called "Kömürcü ("charcoal burner") Kula". A combination with predominantly yellow borders is characteristic for Kula carpets.
Unusual for Anatolian, and even for Oriental rugs, the rug type called "Kendirli" Kula makes use of hemp in its foundation. A number of "Transylvanian" rugs are attributed to the Kula area.
*
Uşak
Uşak (; el, Ουσάκειον, Ousakeion) is a city in the interior part of the Aegean Region of Turkey. The city has a population of 500,000 (2016 census) and is the capital of Uşak Province.
Uşak city is situated at a distance of from İz ...
lies north of
Denizli
Denizli is an industrial city in the southwestern part of Turkey and the eastern end of the alluvial valley formed by the river Büyük Menderes, where the plain reaches an elevation of about . Denizli is located in the country's Aegean Region.
...
in the
Aegean Region
The Aegean Region () is one of the 7 geographical regions of Turkey. The largest city in the region is İzmir. Other big cities are Manisa, Aydın, Denizli, Muğla, Afyonkarahisar and Kütahya.
Located in western Turkey, it is bordere ...
. It is one of the most renowned and important carpet centres. According to their structure and patterns there are several types of carpets called "star", "medallion" and "white-ground" Ușak carpets. Frequently depicted by European painters during the
Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ide ...
era, they are often given, as a term of convenience, the name of the painter on whose paintings corresponding carpets have been identified. The best known are
Holbein and
Lotto carpet
A Lotto carpet is a hand-knotted, patterned Turkish carpet that was produced primarily during the 16th and 17th centuries along the Aegean coast of Anatolia, Turkey, although it was also copied in various parts of Europe. It is characterized by ...
s.
*
Smyrna
Smyrna ( ; grc, Σμύρνη, Smýrnē, or , ) was a Greek city located at a strategic point on the Aegean coast of Anatolia. Due to its advantageous port conditions, its ease of defence, and its good inland connections, Smyrna rose to prom ...
carpets are woven in the surrounding of the town today known as
Izmir. Their more elaborate, curvilinear "town designs" distinguish Smyrna carpets from the products of other Anatolian centers. Single ornaments are directly related to Ottoman "court" carpets. In particular, the main borders often contain elongated cartouches like those seen in "Transylvanian" carpets.
*
Milas lies on the south-western coast of the
Aegean Region
The Aegean Region () is one of the 7 geographical regions of Turkey. The largest city in the region is İzmir. Other big cities are Manisa, Aydın, Denizli, Muğla, Afyonkarahisar and Kütahya.
Located in western Turkey, it is bordere ...
. Since the 18th century, predominantly carpets with a "prayer rug" design and characteristic "gathered" mihrabs are woven here. Other types include the Ada (island) Milas rugs from the area of Karaova, with vertically twisted polygons in their fields, and the rare medallion Milas rug with a mostly yellow-gold medallion on a red background. Their borders often show crystalline star shaped ornaments composed by arrow-like ornaments pointing towards the center. Similar designs are also found in Caucasian carpets. Commonly used colours include pale violet, warm yellow, and pale green. The field panel ground is often a brick red.
*
Megri lies on the Turkish south coast, opposite the island of
Rhodes
Rhodes (; el, Ρόδος , translit=Ródos ) is the largest and the historical capital of the Dodecanese islands of Greece. Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the S ...
. In 1923, it was renamed Fethiye. Megri rugs often show a division of the inner field into three different long fields, with floral patterns inscribed. Prayer rug designs with stepped gable bands are also seen. Typical colours are yellow, bright red, light and dark blue, and white. Megri rugs are also sold under the name of Milas, and it is sometimes difficult to differentiate these two products of town manufacture.
*
Isparta
Isparta is a city in western Turkey and the capital of Isparta Province. The city's population was 222,556 in 2010 and its elevation is 1035 m. It is known as the "City of Roses".
Isparta is well-connected to other parts of Turkey via roads. An ...
in Pisidia emerged as a new centre of Anatolian rug production in the late 1880s. The city, until then renowned for its rose production, developed into a competitive carpet weaving centre with significant export activity. A major role in this development was played by the Oriental Carpet Manufacturers one of the largest companies active in this field, which bought the carpets on a monopoly-based system, whereas it also provided the weavers with primary material, such as dyed yarns, and with technical assistance, namely specialized personnel who could improve the processes and final products. Isparta carpets came in a standard quality, which enhanced their commercial value and demand. Their main feature was the cotton weft and the use of asymmetric knots.
Many of them belonged to the prayer-rug type, with triangular patterns which remind of a mihrab. The Isparta type rug, considered by Kahramanos, a standardized product of the 19th century, is woven with double-stranded yarns and in a smaller number of knots; their initial patterns were imitating popular Asia Minor styles, particularly those of Usak, with a central medallion, decorated corners and lively colours. Soon, they turned to following Persian style, which proved much more popular in the western markets, particularly that of the United States.
Later, in the 1920s and 1930s they followed Sarouk patterns.
Initially yarns were dyed with natural, plant-based dyes, but soon, as elsewhere, they changed to chemically-dyed yarns. The original wool on wool fabric was replaced by a combination of lamb's wool for the weft and cotton or linen for the warp. Carpet production in Isparta followed the technologically innovative solutions of that time such as the aforementioned replacement of natural dyes by chemical ones, which were cheaper. The chemically prepared
aniline
Aniline is an organic compound with the formula C6 H5 NH2. Consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group, aniline is the simplest aromatic amine. It is an industrially significant commodity chemical, as well as a versatile starti ...
s used at first were proved to be inconsistent, but soon chemistry provided new synthetic dyes with steady and standardized colours; this made the reproduction of the same pattern over and over again possible. The use of millimetric paper for designing the patterns allowed workers to reproduce patterns exactly in all their details.
[Ppapadaki, I.A., " Spartali Iordanis Styloglou (1887-1948), contribution to the development of carpet weaving in Isparta, Asia Minor", Deltion tis Etairias Meletis tis Kath Imas Anatolis, 2 (2006), 161-175.] Isparta carpet weaving suffered a severe blow after the expulsion of the Greek Orthodox population in 1922, however Isparta remained a centre for washing and finishing carpets until today.
Central Anatolia


Central Anatolia is one of the main areas of carpet production in Turkey. Regional weaving centers with distinct designs and traditions are:
*
Konya
Konya () is a major city in central Turkey, on the southwestern edge of the Central Anatolian Plateau, and is the capital of Konya Province. During antiquity and into Seljuk times it was known as Iconium (), although the Seljuks also called it D ...
(Konya,
Konya-Derbent,
Selçuk
Selçuk is a town in İzmir Province in the Aegean Region of Turkey. It is located northeast of the ancient city of Ephesus, that was once home to the Temple of Artemis, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World.
Its previous Greek name, ...
, Keçimuslu, Ladik, Innice,
Obruk)
The town of Konya is the old capital of the Seljuq Empire. The
Mevlana Museum
Jalāl al-Dīn Muḥammad Rūmī ( fa, جلالالدین محمد رومی), also known as Jalāl al-Dīn Muḥammad Balkhī (), Mevlânâ/Mawlānā ( fa, مولانا, lit= our master) and Mevlevî/Mawlawī ( fa, مولوی, lit= my ma ...
in Konya has a large collection of Anatolian rugs, including some of the carpet fragments found in the
Alaeddin and
Eşrefoğlu Mosque
Eşrefoğlu Mosque is a 13th-century mosque in Beyşehir, Konya Province, Turkey
It is situated north of the Beyşehir Lake
History
During the last years of Seljuks of Rum, various governors of Seljuks enjoyed a partial independency. They ...
. Carpets from the Konya manufacture often show an elaborate prayer rug design, with a monochrome bright madder red field. Carpets from Konya-Derbent often have two floral medallions woven into the field below the mihrab. The Konya-Selçuk carpet tradition makes use of a lean octagonal medallion in the middle of the field, with three opposed geometrical forms crowned by tulips. Also typical is a broad ornamental main border with detailed, filigree patterns flanked by two secondary borders with meandering vines and flowers. Rugs from Keçimuslu are often sold as Konya rugs, and show a similar bright madder red field, but with prominent green colours in the main border.
Konya-Ladik rugs often show prayer rug designs. Their fields are mostly in bright madder red, with stepped mihrab designs. Opposite, and sometimes above, the prayer niche are smaller gables. The gables are often arranged in groups of three, each gable decorated with a stylized, geometric tulip ornament. The tulips are frequently shown upside down at the lower end of the prayer niche. The spandrels are often in golden yellow, and show water ewer ornaments. The "Ladik sinekli" design is also specific for Ladik. On a white or cream white field, a multitude of small black ornaments is arranged, which resemble flies (Turk.: "''sinek''"). Innice rugs resemble Ladik rugs in their use of tulip ornaments, the bold red field complemented by the bright green foundation of the spandrels. Obruk rugs show the typical Konya design and colours, but their ornaments are more bold and stylized, resembling the Yürük traditions of the weavers from this village. Obruk rugs are sometimes also sold in Kayseri.
*
Kayseri
Kayseri (; el, Καισάρεια) is a large industrialised city in Central Anatolia, Turkey, and the capital of Kayseri province. The Kayseri Metropolitan Municipality area is composed of five districts: the two central districts of Kocasina ...
(Kayseri,
Avanos
Avanos is a town and district of Nevşehir Province in the Cappadocia region of Central Anatolia, Turkey, located north of Nevşehir, the capital city of the province. In 2011 the population of Avanos town was 16,000. Historically known as Vene ...
,
Ürgüp
Ürgüp ( el, Προκόπιο ''Prokópio,'' or Cappadocian Greek: ''Prokópi'', ota, Burgut Kalesi) is a town and district of Nevşehir Province in the Central Anatolia region of Turkey. It is located in the historical region of Cappadocia, a ...
,
Kırşehir
Kırşehir, formerly Mocissus ( grc, Μωκισσός) and Justinianopolis (Ἰουστινιανούπολις), is a city in Turkey. It is the capital district of the Kırşehir Province. According to the 2000 census, the population of the distr ...
,
Mucur
Mucur is a town and district of Kırşehir Province in the Central Anatolia region of Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainl ...
,
Ortaköy
Ortaköy ( ''Middle Village)'' is a neighbourhood within the Beşiktaş district of Istanbul, Turkey, on the European shore of the Bosphorus. it was originally a small fishing village, known in Greek as Agios Fokas (Άγιος Φωκάς) in t ...
,
İncesu)
Kayseri rugs are distinguished by their fine weaving which characterizes the manufactory production, which is prevalent in this area. The rugs are produced mainly for export, and imitate designs from other regions. Wool, silk, and artificial silk are used. The top products of the Kayseri manufactures come very close to those from Hereke and Kum-Kapı. Ürgüp, Avanos and İncesu are
Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Revo ...
n towns.
Carpets from Avanos, often in prayer rug design, are distinguished by their dense weaving. Typically, an elaborate pendant representing either a
Mosque lamp
Mosque lamps of enamelled glass, often with gilding, survive in considerable numbers from the Islamic art of the Middle Ages, especially the 13th and 14th centuries, with Cairo in Egypt and Aleppo and Damascus in Syria the most important centres ...
or a triangular protective amulet ("''mosca''") hanging from the prayer niche adorns the field. The prayer niches are often stepped, or drawn in at its sides in the classical "head-and-shoulders" shape. The field is often in bright red, and surrounded by golden yellow spandrels and borders. The fine weaving allows for elaborate ornamental patterns, which make the Avanos carpet easy to identify amongst other rugs.
Ürgüp carpets are distinguished by their colours. Brown-gold is dominant, bright orange and yellow are often seen. A medallion within a medallion frequently is set into the field, which is of a typical "Ürgüp red" colour, adorned with floral motifs. Palmettes fill the corner medallions and the main borders. The outermost secondary border often has reciprocal crenellations.
Rugs from Kırşehir, Mucur and Ortaköy are closely related, and not easily distinguished from each other. Prayer and medallion designs are woven, as well as garden ("''mazarlik''", or "graveyard") designs. Pale turquois blue, pale green and rose colours are prevalent. Rugs from Ortaköy show a hexagonal central ornament, often including a cruciform pattern. The borders show stylized carnations arranged in a row of square compartments. Mucur carpets often show a stepped "prayer niche within a prayer niche" design, with contrasting bright madder red and light indigo colours separated by yellow outlines. The borders are composed of rows of squares filled with geometric diamond or rhomboid patterns. Mucur and Kırşehir are also known for their multiple-niche prayer rugs, or ''"saph"''.
*
Niğde
Niğde (; grc, Νίγδη; Hittite: Nahita, Naxita) is a city and the capital of Niğde province in the Central Anatolia region of Turkey at an elevation of 1,299 m. In 2017 the city population was 141,010 people.
The city is small with plenty ...
(Niğde,
Taşpınar,
Fertek
Fertek is an Anatolian town in Niğde Province, Turkey. It has a history going back to 3rd century, starting with the settlement of Karamanlides. The town went through Byzantine, Seljuk, and Ottoman histories.
History
In Turkish, Arabic, a ...
, Maden,
Yahyalı,
Yeşilhisar,
Karapinar,
Karaman
Karaman, historically known as Laranda ( Greek: Λάρανδα), is a city in south central Turkey, located in Central Anatolia, north of the Taurus Mountains, about south of Konya. It is the capital district of the Karaman Province. Accordin ...
)
Niğde is the market place for the surrounding area, and many rugs woven in the surrounding villages are sold under the trade name of Niğde. If a prayer rug design is used, the niche and spandrels are typically tall and narrow. Likewise, the central field is not substantially larger than the main border. Typical for Taşpınar are elongated, almost ogival central medallions, the dominant colours are warm red, blue, and light green. Fertek rugs are distinguished by their simple, floral ornaments. The main field is often not separated from the main border, as usual, by a smaller secondary border. The outermost secondary border often has reciprocal crenellation patterns. The colour composition often contains soft reds, dark olive greens, and blue. Maden rugs used cochineal red for their main fields, which are narrow and slim, as typical for Niğde rugs. The foundation of their main border is often dyed in corrosive brown, which caused deterioration of the carpet pile in these areas, and produces a relief effect. Yahali is a regional center and market place for its surroundings. Carpets from this region often have a hexagonal central medallion, with double-hooked ornaments in the fields and carnations in the main border.
Carpets from Karapinar and Karaman geographically belong to the Konya area, but their design is more similar to the rugs woven in the Niğde area. The design of some Karapinar rugs shows similarities, but is not related, to Turkmen door rugs (''"ensi"''), as three columns crowned by double hooks ("''kotchak''") frequently form the prayer niche. Opposed "double hook" ornaments fill the columns both in Karapinar and Karaman rugs. Another type of design often seen in Karapinar runners is composed of geometric hexagonal primary motifs arranged on top of each other, in subdued red, yellow, green, and white.
*
Sivas
Sivas (Latin and Greek: ''Sebastia'', ''Sebastea'', Σεβάστεια, Σεβαστή, ) is a city in central Turkey and the seat of Sivas Province.
The city, which lies at an elevation of in the broad valley of the Kızılırmak river, is ...
(Sivas,
Zara,
Kangal
Kangal is a town and a district of Sivas Province in Turkey. The current mayor is Ahmet Kürşad Apaydın from the Great Unity Party (BBP). As Kaymakam was appointed Erinç Demir.
Demographics
The town is populated by Sunni Kurds ug:كۇرد� ...
)

State-owned manufactories, some of them organized as weaving schools, produce rugs in Sivas. The design imitates carpets from other regions, especially Persian designs. Traditional Sivas carpets were distinguished by their dense and short, velvet-like pile in elaborate designs which are characteristic for a "town manufactory". The main border is typically composed of rows of three carnations, held together by a stem. Zara, 70 km east of Sivas, has an Armenian colony which produces rugs in a characteristic design composed of row after row of vertical stripes extending over the entire field. Each stripe is filled with elaborate floral arabesques. The pile is clipped very short so that the detailed patterns can be clearly seen.
Eastern Anatolia
We are currently unable to recognize specific local designs in east Anatolian carpets. Until the
Armenian genocide
The Armenian genocide was the systematic destruction of the Armenian people and identity in the Ottoman Empire during World War I. Spearheaded by the ruling Committee of Union and Progress (CUP), it was implemented primarily through t ...
in 1915, East Anatolia had a large Armenian population, and sometimes carpets are identified as of Armenian production by their inscriptions. Information is also lacking with regard to the Kurdish and Turkish carpet production. Research in the 1980s has come to the conclusion that the tradition of weaving has almost vanished, and more specific information may be lost.
*
Kars
Kars (; ku, Qers; ) is a city in northeast Turkey and the capital of Kars Province. Its population is 73,836 in 2011. Kars was in the ancient region known as ''Chorzene'', (in Greek Χορζηνή) in classical historiography (Strabo), part of ...
is the capital of
Kars Province
Kars Province ( tr, Kars ili; ku, Parêzgeha Qersê; hy, Կարսի նահանգ) is a province of Turkey, located in the northeastern part of the country. It shares part of its closed border with Armenia. The provincial capital is the city o ...
in northeastern Anatolia. Carpets produced around the town are similar to Caucasian rugs, with their colours more subdued. Kars is also used as a trade name, related to the quality of the weaving. Carpets of lower quality woven in the Kars region are sometimes called "Hudut" (i.e., frontier) carpets, which are woven in the frontier area between Turkey, Iran, Armenia and Georgia. Typical designs closely resemble the neighbouring Caucasian regions. Kars rugs often show "Kasak" designs as seen in Fachralo, Gendje, and Akstafa rugs, but their structure and materials are different. Kars or Hudut rugs often have goat's hair in pile and foundation.
Other East Anatolian rugs are usually not attributed to a specific location, but are classified according to their tribal provenience. As the Kurdish and
Yürük tribes were living as nomads for most of their history, they tended to weave traditional tribal, rather than any local, design. If a rug with an overall Yürük design can be attributed to a specific region (as Yürüks also live in other regions of Anatolia), the name "Yürük" sometimes precedes the regional name. The region around the towns of
Diyarbakır
Diyarbakır (; ; ; ) is the largest Kurdish-majority city in Turkey. It is the administrative center of Diyarbakır Province.
Situated around a high plateau by the banks of the Tigris river on which stands the historic Diyarbakır Fortres ...
,
Hakkâri, and the
Van province
Van Province ( tr, Van ili, ku, Parezgêha Wanê, Armenian: Վանի մարզ) is a province in the Eastern Anatolian region of Turkey, between Lake Van and the Iranian border. It is 19,069 km2 in area and had a population of 1,035,418 a ...
has a large Kurdish population. The towns of Hakkâri and
Erzurum
Erzurum (; ) is a city in eastern Anatolia, Turkey. It is the largest city and capital of Erzurum Province and is 1,900 meters (6,233 feet) above sea level. Erzurum had a population of 367,250 in 2010.
The city uses the double-headed eagle as ...
were market places for Kurdish kilims, rugs and smaller weavings like cradles, bags (''heybe'') and tent decorations.
Thematic galleries
Patterns of Central Asian origin: cloud band, lotus seat, cloud collar
File:Antique Red Turkish Oushak Carpet.jpg, Ushak carpet with a ''"cloud band" border and field'', Mecidi period design
File:Transylvanian carpet Met 22.100.91.jpg, "Transylvanian" double-niche carpet with a ''central medallion''
Patterns of Islamic origin: Calligraphic borders, infinite repeat field, prayer niche design
File:Small_pattern_Holbein_carpet_Anatolia_16th_century.jpg, Type I small-pattern Holbein carpet with ''"kufic" main border and "infinite repeat" field pattern'', Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
, 16th century.
Image:Western Anatolian knotted woll carpet with 'Lotto' patern, 16th century, Saint Louis Art Museum.jpg, Western Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
n ‘Lotto carpet’ with ''"kufic" main border and "infinite repeat" field pattern'', 16th century, Saint Louis Art Museum
The Saint Louis Art Museum (SLAM) is one of the principal U.S. art museums, with paintings, sculptures, cultural objects, and ancient masterpieces from all corners of the world. Its three-story building stands in Forest Park in St. Louis, ...
.
File:Urgup_Region_Rug_with_Kufic_inner_border._CL_Lane_Collection.jpg, Urgup rug with ''"kufic" inner border''
File:Turkey Prayer rug.jpg, 17th-century Turkish prayer rug with a ''single niche''; National Museum, Warsaw
The National Museum in Warsaw ( pl, Muzeum Narodowe w Warszawie), popularly abbreviated as MNW, is a national museum in Warsaw, one of the largest museums in Poland and the largest in the capital. It comprises a rich collection of ancient art ( Eg ...
File:Turkey.Konya004.jpg, Kirşehir ''single niche'' prayer rug, Tilavet room, Mevlâna Mausoleum, Konya
File:Turkey.Konya031.jpg, Kirşehir ''single niche'' prayer rug, 18th century, Mevlâna Mausoleum, Konya
File:Vintage Konya Prayer Seccade. CL Lane Collection.jpg, Konya ''single niche'' prayer rug
File:Antique Gaziantep Double Prayer Rug.jpg, Gaziantep ''double-niche'' prayer rug
File:Vintage Central Anatolian Tribal Rug.JPG, Central Anatolian ''double-niche'' prayer rug
File:Little world, Aichi prefecture - Turkish culture exhibition - Turkish carpet - Made in Nuzumla.jpg, Prayer rug with ''multiplied niches''
File:Selimiye-Mosque-interior.jpg, Edirne Selimiye Mosque interior with ''multiple-niche'' prayer rug (saph)
File:TheSultanAhmetCamiiPrayerRugSaphThe Blue Mosque Istanbul2006creditjancadoret.jpg, The Sultan Ahmed Mosque
The Blue Mosque in Istanbul, also known by its official name, the Sultan Ahmed Mosque ( tr, Sultan Ahmet Camii), is an Ottoman-era historical imperial mosque located in Istanbul, Turkey. A functioning mosque, it also attracts large numbers ...
''multiple-niche'' prayer rug (saph).
See also
*
Carpet weaving in Isparta
Types
*
Bergama carpet
*
Hereke carpet
Hereke carpets are Turkish handmade carpets produced and sold in Hereke, a coastal town in Turkey. For a long time, they used to be produced only in Hereke, 60 km from Istanbul. The materials used are silk, a combination of wool and cotton ...
*
Konya Carpets and Rugs
*
Milas carpet
*
Ushak carpet
Uşak carpets, Ushak carpets or Oushak Carpets ( tr, Uşak Halısı) are Turkish carpets that use a particular family of designs, called by convention after the city of Uşak, Turkey – one of the larger towns in Western Anatolia, which was ...
*
Yürük rug
A Yürük rug is a traditional Tribe, tribal Carpet, rug woven in Anatolia by the Yörüks, a Turkish ethnic subgroup.
Yürük rugs have a long shaggy Knotted-pile carpet, pile, tied with Knotted-pile carpet#Ghiordes, Ghiordes knots. The Warp an ...
Other related rugs and carpets
*
Oriental carpet
An oriental rug is a heavy textile made for a wide variety of utilitarian and symbolic purposes and produced in " Oriental countries" for home use, local sale, and export.
Oriental carpets can be pile woven or flat woven without pile, using v ...
*
Armenian carpet
The term Armenian carpet designates, but is not limited to, tufted rugs or knotted carpets woven in Armenia or by Armenians from pre-Christian times to the present. It also includes a number of flat woven textiles. The term covers a large variet ...
*
Kurdish rugs
Kurdish rugs ( ku, قالی کوردی) are rugs woven by Kurds in Kurdistan.Neff, Ivan C. and Carol V. Maggs. Dictionary of Oriental Rugs. London: AD. Donker LTD, 1977. When referring to Kurdish rugs within the rug industry, one is referring to ...
*
Persian rug
A Persian carpet ( fa, فرش ایرانی, translit=farš-e irâni ) or Persian rug ( fa, قالی ایرانی, translit=qâli-ye irâni ),Savory, R., ''Carpets'',(Encyclopaedia Iranica); accessed January 30, 2007. also known as Iranian ...
*
Turkmen rug
References
External links
Anatolian Carpets and Kilims: The Turkish Cultural FoundationOttoman carpets in the Metropolitan MuseumOttoman Silk Velvets at Shangri LaOver 170 pictures from Istanbul carpet museum
{{Rugs and carpets
Turkish art
Turkish culture
Turkish inventions
Oriental rugs and carpets
Turkish rugs and carpets

 The origin of carpet weaving remains unknown, as carpets are subject to use, wear, and destruction by insects and rodents. Controversy arose over the accuracy of the claim that the oldest records of flat woven
The origin of carpet weaving remains unknown, as carpets are subject to use, wear, and destruction by insects and rodents. Controversy arose over the accuracy of the claim that the oldest records of flat woven  Medallion Ushak carpets usually have a red or blue field decorated with a floral trellis or leaf tendrils, ovoid primary medallions alternating with smaller eight-lobed stars, or lobed medallions, intertwined with floral tracery. Their border frequently contains palmettes on a floral and leaf scroll, and pseudo-kufic characters.
Medallion Ushak carpets with their curvilinear patterns significantly depart from the designs of earlier Turkish carpets. Their emergence in the sixteenth century hints at a potential impact of Persian designs. Since the Ottoman Turks occupied the former Persian capital of
Medallion Ushak carpets usually have a red or blue field decorated with a floral trellis or leaf tendrils, ovoid primary medallions alternating with smaller eight-lobed stars, or lobed medallions, intertwined with floral tracery. Their border frequently contains palmettes on a floral and leaf scroll, and pseudo-kufic characters.
Medallion Ushak carpets with their curvilinear patterns significantly depart from the designs of earlier Turkish carpets. Their emergence in the sixteenth century hints at a potential impact of Persian designs. Since the Ottoman Turks occupied the former Persian capital of  Examples are also known of rugs woven in the Ushak area whose fields are covered by ornaments like the
Examples are also known of rugs woven in the Ushak area whose fields are covered by ornaments like the  By the end of the eighteenth century, the "turkish baroque" or "''mecidi''" style developed out of French baroque designs. Carpets were woven after the patterns of French
By the end of the eighteenth century, the "turkish baroque" or "''mecidi''" style developed out of French baroque designs. Carpets were woven after the patterns of French  In traditional households, women and girls take up carpet and kilim weaving as a hobby as well as a means of earning money. Women learn their weaving skills at an early age, taking months or even years to complete the pile rugs and flat woven kilims that were created for their use in daily life. As is true in most weaving cultures, traditionally it is women and girls who are both artisan and weaver."Kilim Rugs: Timeless Beauty"
In traditional households, women and girls take up carpet and kilim weaving as a hobby as well as a means of earning money. Women learn their weaving skills at an early age, taking months or even years to complete the pile rugs and flat woven kilims that were created for their use in daily life. As is true in most weaving cultures, traditionally it is women and girls who are both artisan and weaver."Kilim Rugs: Timeless Beauty" Traditional dyes used for Anatolian carpets are obtained from plants, insects and minerals. In 1856, the English chemist
Traditional dyes used for Anatolian carpets are obtained from plants, insects and minerals. In 1856, the English chemist 


 A variety of tools are needed in the construction of a handmade rug. A
A variety of tools are needed in the construction of a handmade rug. A  When Turkic migrants moved from Central Asia to
When Turkic migrants moved from Central Asia to  Large, geometric shapes are considered to be of Caucasian or Turkmen origin. The Caucasian tradition may have been integrated either by migrating Turkish tribes, or by contact with Turkmen people already living in Anatolia.
A central medallion consisting of large, concentrically reduced rhomboid patterns with latch-hook ornaments is associated with the Yörük nomads of Anatolia. The name Yürük is usually given to nomads whose way of life has changed least from its central Asian origin.
In Anatolia, several ethnic minorities have maintained separate traditions, e.g., the Greek, Armenians, and Kurds. Whilst Greeks and Armenians were involved in carpet weaving and trading in the past, no design motifs have been clearly associated with their distinct, Christian culture. Kurdish rug design differs from Anatolian. Kurdish rugs are more often discussed together with
Large, geometric shapes are considered to be of Caucasian or Turkmen origin. The Caucasian tradition may have been integrated either by migrating Turkish tribes, or by contact with Turkmen people already living in Anatolia.
A central medallion consisting of large, concentrically reduced rhomboid patterns with latch-hook ornaments is associated with the Yörük nomads of Anatolia. The name Yürük is usually given to nomads whose way of life has changed least from its central Asian origin.
In Anatolia, several ethnic minorities have maintained separate traditions, e.g., the Greek, Armenians, and Kurds. Whilst Greeks and Armenians were involved in carpet weaving and trading in the past, no design motifs have been clearly associated with their distinct, Christian culture. Kurdish rug design differs from Anatolian. Kurdish rugs are more often discussed together with  Carpets and rugs were simultaneously produced by and for the four different social levels of court, town, rural village, and tribe. Elements of town design were often reproduced in rural production, and integrated by the village weavers into their own artistic tradition by a process called stylization.
Carpets and rugs were simultaneously produced by and for the four different social levels of court, town, rural village, and tribe. Elements of town design were often reproduced in rural production, and integrated by the village weavers into their own artistic tradition by a process called stylization.
 Anatolia can be divided into three major areas of rug production, centered around local towns and marketplaces, which often lend their names to the rugs produced in the surrounding area. Western, Central, and Eastern Anatolia have distinct weaving traditions. However, commercially produced rugs are often woven irrespective of local design traditions. Preferential use of different materials and dyes, as well as characteristic designs, sometimes allow for a more specific assignment of a carpet to one of the three regions, or to a more specific weaving place.
Anatolia can be divided into three major areas of rug production, centered around local towns and marketplaces, which often lend their names to the rugs produced in the surrounding area. Western, Central, and Eastern Anatolia have distinct weaving traditions. However, commercially produced rugs are often woven irrespective of local design traditions. Preferential use of different materials and dyes, as well as characteristic designs, sometimes allow for a more specific assignment of a carpet to one of the three regions, or to a more specific weaving place.
 Central Anatolia is one of the main areas of carpet production in Turkey. Regional weaving centers with distinct designs and traditions are:
*
Central Anatolia is one of the main areas of carpet production in Turkey. Regional weaving centers with distinct designs and traditions are:
*  State-owned manufactories, some of them organized as weaving schools, produce rugs in Sivas. The design imitates carpets from other regions, especially Persian designs. Traditional Sivas carpets were distinguished by their dense and short, velvet-like pile in elaborate designs which are characteristic for a "town manufactory". The main border is typically composed of rows of three carnations, held together by a stem. Zara, 70 km east of Sivas, has an Armenian colony which produces rugs in a characteristic design composed of row after row of vertical stripes extending over the entire field. Each stripe is filled with elaborate floral arabesques. The pile is clipped very short so that the detailed patterns can be clearly seen.
State-owned manufactories, some of them organized as weaving schools, produce rugs in Sivas. The design imitates carpets from other regions, especially Persian designs. Traditional Sivas carpets were distinguished by their dense and short, velvet-like pile in elaborate designs which are characteristic for a "town manufactory". The main border is typically composed of rows of three carnations, held together by a stem. Zara, 70 km east of Sivas, has an Armenian colony which produces rugs in a characteristic design composed of row after row of vertical stripes extending over the entire field. Each stripe is filled with elaborate floral arabesques. The pile is clipped very short so that the detailed patterns can be clearly seen.