Truncated cuboctahedron on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
 Like many other solids the truncated octahedron has full
Like many other solids the truncated octahedron has full
E.g. the 3 subgroups with 24 elements correspond to a nonuniform
Editable printable net of a truncated cuboctahedron with interactive 3D viewThe Uniform Polyhedra
The Encyclopedia of Polyhedra
{{Polyhedron navigator Uniform polyhedra Archimedean solids Truncated tilings Zonohedra
geometry
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is ...
, the truncated cuboctahedron is an Archimedean solid, named by Kepler as a truncation of a cuboctahedron
A cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with 8 triangular faces and 6 square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with 2 triangles and 2 squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such, it ...
. It has 12 square
In Euclidean geometry, a square is a regular quadrilateral, which means that it has four equal sides and four equal angles (90- degree angles, π/2 radian angles, or right angles). It can also be defined as a rectangle with two equal-length a ...
faces, 8 regular hexagon
In geometry, a hexagon (from Greek , , meaning "six", and , , meaning "corner, angle") is a six-sided polygon. The total of the internal angles of any simple (non-self-intersecting) hexagon is 720°.
Regular hexagon
A '' regular hexagon'' has ...
al faces, 6 regular octagonal faces, 48 vertices, and 72 edges. Since each of its faces has point symmetry (equivalently, 180° rotational symmetry), the truncated cuboctahedron is a 9-zonohedron
In geometry, a zonohedron is a convex polyhedron that is centrally symmetric, every face of which is a polygon that is centrally symmetric (a zonogon). Any zonohedron may equivalently be described as the Minkowski sum of a set of line segments i ...
. The truncated cuboctahedron can tessellate
A tessellation or tiling is the covering of a surface, often a plane, using one or more geometric shapes, called ''tiles'', with no overlaps and no gaps. In mathematics, tessellation can be generalized to higher dimensions and a variety of ...
with the octagonal prism
In geometry, the octagonal prism is the sixth in an infinite set of prisms, formed by rectangular sides and two regular octagon caps.
If faces are all regular, it is a semiregular polyhedron.
Symmetry
Images
The octagonal prism can also ...
.
Names
There is anonconvex uniform polyhedron
In geometry, a uniform star polyhedron is a self-intersecting uniform polyhedron. They are also sometimes called nonconvex polyhedra to imply self-intersecting. Each polyhedron can contain either star polygon faces, star polygon vertex figures, ...
with a similar name: the nonconvex great rhombicuboctahedron
In geometry, the nonconvex great rhombicuboctahedron is a nonconvex uniform polyhedron, indexed as U17. It has 26 faces (8 triangles and 18 squares), 48 edges, and 24 vertices. It is represented by the Schläfli symbol rr and Coxeter-Dynkin di ...
.
Cartesian coordinates
The Cartesian coordinates for the vertices of a truncated cuboctahedron having edge length 2 and centered at the origin are all the permutations of: :(±1, ±(1 + ), ±(1 + 2)).Area and volume
The area ''A'' and the volume ''V'' of the truncated cuboctahedron of edge length ''a'' are: :Dissection
The truncated cuboctahedron is the convex hull of arhombicuboctahedron
In geometry, the rhombicuboctahedron, or small rhombicuboctahedron, is a polyhedron with eight triangular, six square, and twelve rectangular faces. There are 24 identical vertices, with one triangle, one square, and two rectangles meeting at ea ...
with cubes above its 12 squares on 2-fold symmetry axes. The rest of its space can be dissected into 6 square cupola
In geometry, the square cupola, sometimes called lesser dome, is one of the Johnson solids (). It can be obtained as a slice of the rhombicuboctahedron. As in all cupolae, the base polygon has twice as many edges and vertices as the top; in t ...
s below the octagons, and 8 triangular cupola
In geometry, the triangular cupola is one of the Johnson solids (). It can be seen as half a cuboctahedron.
Formulae
The following formulae for the volume (V), the surface area (A) and the height (H) can be used if all faces are regular, ...
s below the hexagons.
A dissected truncated cuboctahedron can create a genus 5, 7, or 11 Stewart toroid
In geometry, a toroidal polyhedron is a polyhedron which is also a toroid (a -holed torus), having a topological genus () of 1 or greater. Notable examples include the Császár and Szilassi polyhedra.
Variations in definition
Toroidal polyhe ...
by removing the central rhombicuboctahedron, and either the 6 square cupolas, the 8 triangular cupolas, or the 12 cubes respectively. Many other lower symmetry toroids can also be constructed by removing the central rhombicuboctahedron, and a subset of the other dissection components. For example, removing 4 of the triangular cupolas creates a genus 3 toroid; if these cupolas are appropriately chosen, then this toroid has tetrahedral symmetry.
Uniform colorings
There is only oneuniform coloring
In geometry, a uniform coloring is a property of a uniform figure (uniform tiling or uniform polyhedron) that is colored to be vertex-transitive. Different symmetries can be expressed on the same geometric figure with the faces following differ ...
of the faces of this polyhedron, one color for each face type.
A 2-uniform coloring, with tetrahedral symmetry
150px, A regular tetrahedron, an example of a solid with full tetrahedral symmetry
A regular tetrahedron has 12 rotational (or orientation-preserving) symmetries, and a symmetry order of 24 including transformations that combine a reflection ...
, exists with alternately colored hexagons.
Orthogonal projections
The truncated cuboctahedron has two specialorthogonal projection
In linear algebra and functional analysis, a projection is a linear transformation P from a vector space to itself (an endomorphism) such that P\circ P=P. That is, whenever P is applied twice to any vector, it gives the same result as if it wer ...
s in the A2 and B2 Coxeter plane
In mathematics, the Coxeter number ''h'' is the order of a Coxeter element of an irreducible Coxeter group. It is named after H.S.M. Coxeter.
Definitions
Note that this article assumes a finite Coxeter group. For infinite Coxeter groups, there ar ...
s with and projective symmetry, and numerous symmetries can be constructed from various projected planes relative to the polyhedron elements.
Spherical tiling
The truncated cuboctahedron can also be represented as aspherical tiling
In geometry, a spherical polyhedron or spherical tiling is a tiling of the sphere in which the surface is divided or partitioned by great arcs into bounded regions called spherical polygons. Much of the theory of symmetrical polyhedra is most c ...
, and projected onto the plane via a stereographic projection. This projection is conformal, preserving angles but not areas or lengths. Straight lines on the sphere are projected as circular arcs on the plane.
Full octahedral group
 Like many other solids the truncated octahedron has full
Like many other solids the truncated octahedron has full octahedral symmetry
A regular octahedron has 24 rotational (or orientation-preserving) symmetries, and 48 symmetries altogether. These include transformations that combine a reflection and a rotation. A cube has the same set of symmetries, since it is the polyhedr ...
- but its relationship with the full octahedral group is closer than that: Its 48 vertices correspond to the elements of the group, and each face of its dual is a fundamental domain of the group.
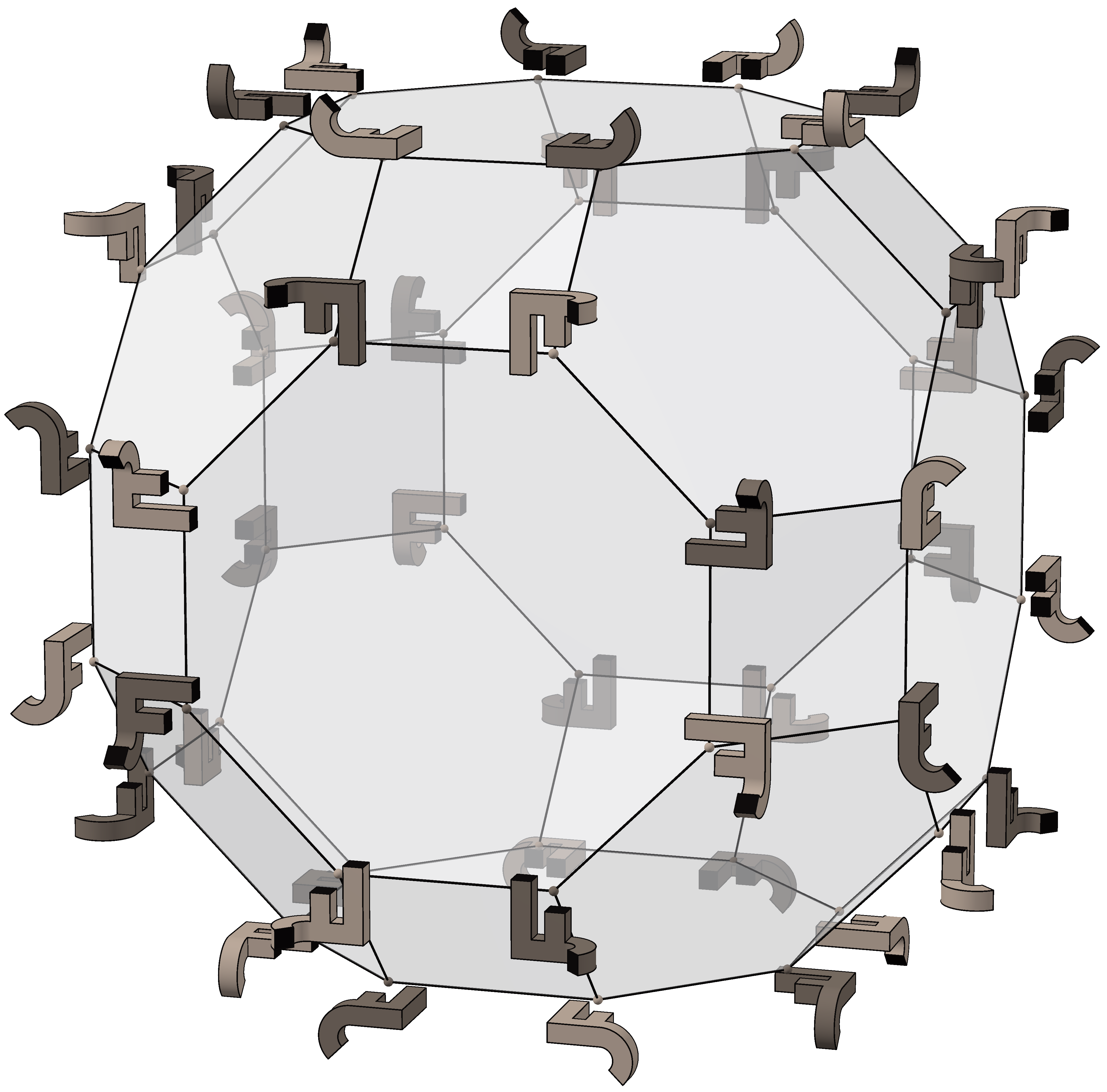
The image on the right shows the 48 permutations in the group applied to an example object (namely the light JF compound on the left). The 24 light elements are rotations, and the dark ones are their reflections.
The edges of the solid correspond to the 9 reflections in the group:
* Those between octagons and squares correspond to the 3 reflections between opposite octagons.
* Hexagon edges correspond to the 6 reflections between opposite squares.
* (There are no reflections between opposite hexagons.)
The subgroups correspond to solids that share the respective vertices of the truncated octahedron.E.g. the 3 subgroups with 24 elements correspond to a nonuniform
snub cube
In geometry, the snub cube, or snub cuboctahedron, is an Archimedean solid with 38 faces: 6 squares and 32 equilateral triangles. It has 60 edges and 24 vertices.
It is a chiral polyhedron; that is, it has two distinct forms, which are mirr ...
with chiral octahedral symmetry, a nonuniform rhombicuboctahedron
In geometry, the rhombicuboctahedron, or small rhombicuboctahedron, is a polyhedron with eight triangular, six square, and twelve rectangular faces. There are 24 identical vertices, with one triangle, one square, and two rectangles meeting at ea ...
with pyritohedral symmetry
image:tetrahedron.jpg, 150px, A regular tetrahedron, an example of a solid with full tetrahedral symmetry
A regular tetrahedron has 12 rotational (or orientation-preserving) symmetries, and a symmetry order of 24 including transformations that c ...
(the cantic snub octahedron) and a nonuniform truncated octahedron
In geometry, the truncated octahedron is the Archimedean solid that arises from a regular octahedron by removing six pyramids, one at each of the octahedron's vertices. The truncated octahedron has 14 faces (8 regular hexagons and 6 squares), 36 ...
with full tetrahedral symmetry. The unique subgroup with 12 elements is the alternating group
In mathematics, an alternating group is the group of even permutations of a finite set. The alternating group on a set of elements is called the alternating group of degree , or the alternating group on letters and denoted by or
Basic pr ...
A4. It corresponds to a nonuniform icosahedron with chiral tetrahedral symmetry.
Related polyhedra
The truncated cuboctahedron is one of a family of uniform polyhedra related to the cube and regular octahedron. This polyhedron can be considered a member of a sequence of uniform patterns withvertex configuration
In geometry, a vertex configurationCrystallography ...
(4.6.2''p'') and Coxeter-Dynkin diagram . For ''p'' < 6, the members of the sequence are omnitruncated polyhedra (zonohedron
In geometry, a zonohedron is a convex polyhedron that is centrally symmetric, every face of which is a polygon that is centrally symmetric (a zonogon). Any zonohedron may equivalently be described as the Minkowski sum of a set of line segments i ...
s), shown below as spherical tilings. For ''p'' < 6, they are tilings of the hyperbolic plane, starting with the truncated triheptagonal tiling.
It is first in a series of cantitruncated hypercubes:
Truncated cuboctahedral graph
In themathematical
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
field of graph theory
In mathematics, graph theory is the study of ''graphs'', which are mathematical structures used to model pairwise relations between objects. A graph in this context is made up of '' vertices'' (also called ''nodes'' or ''points'') which are conn ...
, a truncated cuboctahedral graph (or great rhombcuboctahedral graph) is the graph of vertices and edges of the truncated cuboctahedron, one of the Archimedean solids. It has 48 vertices and 72 edges, and is a zero-symmetric and cubic Archimedean graph.
See also
* Cube *Cuboctahedron
A cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with 8 triangular faces and 6 square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with 2 triangles and 2 squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such, it ...
*Octahedron
In geometry, an octahedron (plural: octahedra, octahedrons) is a polyhedron with eight faces. The term is most commonly used to refer to the regular octahedron, a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at ea ...
* Truncated icosidodecahedron
*Truncated octahedron
In geometry, the truncated octahedron is the Archimedean solid that arises from a regular octahedron by removing six pyramids, one at each of the octahedron's vertices. The truncated octahedron has 14 faces (8 regular hexagons and 6 squares), 36 ...
– truncated tetratetrahedron
*Snub cube
In geometry, the snub cube, or snub cuboctahedron, is an Archimedean solid with 38 faces: 6 squares and 32 equilateral triangles. It has 60 edges and 24 vertices.
It is a chiral polyhedron; that is, it has two distinct forms, which are mirr ...
References
*External links
* ** *Editable printable net of a truncated cuboctahedron with interactive 3D view
The Encyclopedia of Polyhedra
{{Polyhedron navigator Uniform polyhedra Archimedean solids Truncated tilings Zonohedra