Trigonal bipyramidal geometry on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
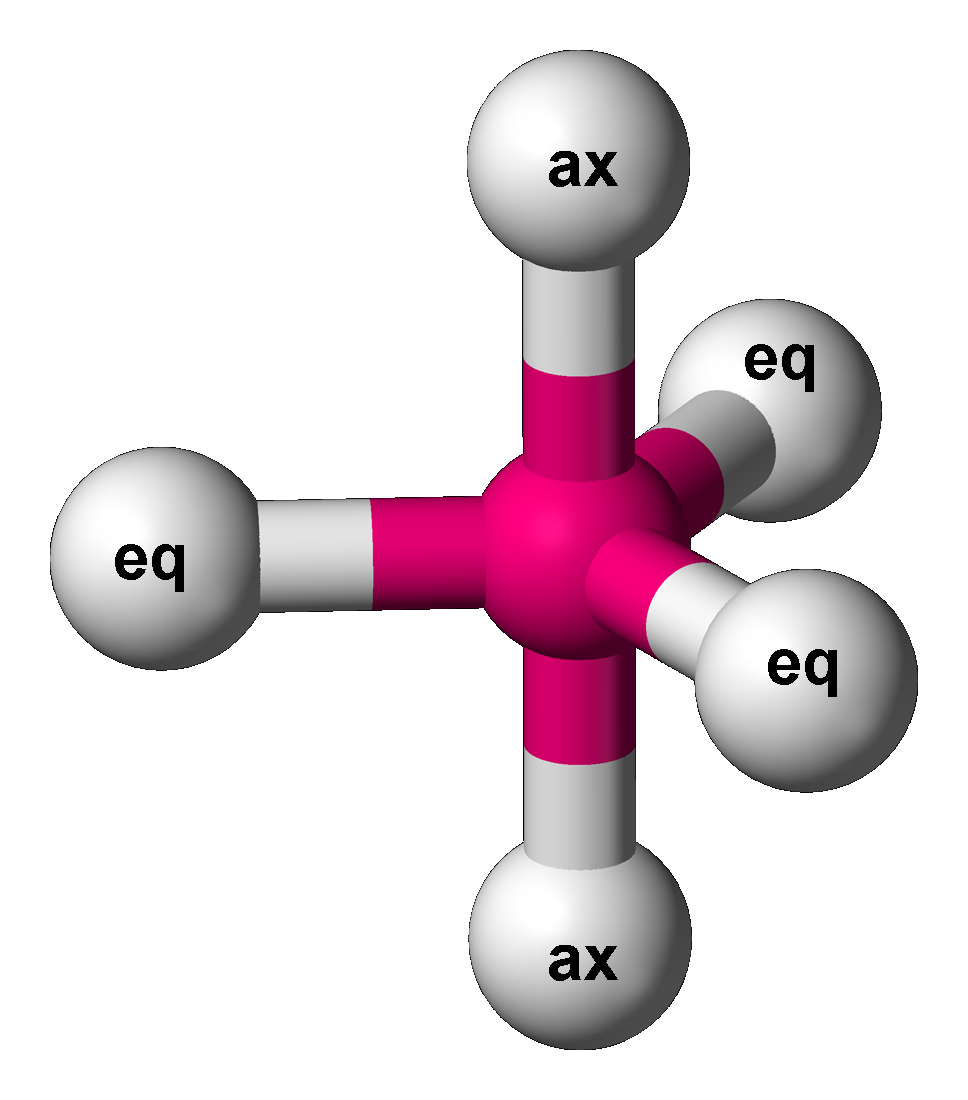 The five atoms bonded to the central atom are not all equivalent, and two different types of position are defined. For
The five atoms bonded to the central atom are not all equivalent, and two different types of position are defined. For
Indiana University Molecular Structure Center
{{MolecularGeometry Stereochemistry Molecular geometry
chemistry
Chemistry is the science, scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the Chemical element, elements that make up matter to the chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions ...
, a trigonal bipyramid formation is a molecular geometry with one atom at the center and 5 more atoms at the corners of a triangular bipyramid
In geometry, the triangular bipyramid (or dipyramid) is a type of hexahedron, being the first in the infinite set of face-transitive bipyramids. It is the dual of the triangular prism with 6 isosceles triangle faces.
As the name suggests, i ...
. This is one geometry for which the bond angles surrounding the central atom are not identical (see also pentagonal bipyramid
In geometry, the pentagonal bipyramid (or dipyramid) is third of the infinite set of face-transitive bipyramids, and the 13th Johnson solid (). Each bipyramid is the dual of a uniform prism.
Although it is face-transitive, it is not a Platoni ...
), because there is no geometrical arrangement with five terminal atoms in equivalent positions. Examples of this molecular geometry are phosphorus pentafluoride (), and phosphorus pentachloride
Phosphorus pentachloride is the chemical compound with the formula PCl5. It is one of the most important phosphorus chlorides, others being PCl3 and POCl3. PCl5 finds use as a chlorinating reagent. It is a colourless, water-sensitive and moist ...
() in the gas phase.
Axial (or apical) and equatorial positions
 The five atoms bonded to the central atom are not all equivalent, and two different types of position are defined. For
The five atoms bonded to the central atom are not all equivalent, and two different types of position are defined. For phosphorus pentachloride
Phosphorus pentachloride is the chemical compound with the formula PCl5. It is one of the most important phosphorus chlorides, others being PCl3 and POCl3. PCl5 finds use as a chlorinating reagent. It is a colourless, water-sensitive and moist ...
as an example, the phosphorus atom shares a plane with three chlorine atoms at 120° angles to each other in ''equatorial'' positions, and two more chlorine atoms above and below the plane (''axial'' or ''apical'' positions).
According to the VSEPR theory of molecular geometry, an axial position is more crowded because an axial atom has three neighboring equatorial atoms (on the same central atom) at a 90° bond angle, whereas an equatorial atom has only two neighboring axial atoms at a 90° bond angle. For molecules with five identical ligands, the axial bond lengths tend to be longer because the ligand atom cannot approach the central atom as closely. As examples, in PF5 the axial P−F bond length is 158 pm and the equatorial is 152 pm, and in PCl5 the axial and equatorial are 214 and 202 pm respectively.
In the mixed halide PF3Cl2 the chlorines occupy two of the equatorial positions, indicating that fluorine has a greater apicophilicity
Apicophilicity is the phenomenon in which electronegative substituents of trigonal bipyramidal pentacoordinate compounds prefer to occupy apical (axial) positions (Lap).
The term "apicophilicity" was first proposed by Earl L. Muetterties in 1963 ...
or tendency to occupy an axial position. In general ligand apicophilicity increases with electronegativity and also with pi-electron withdrawing ability, as in the sequence Cl < F < CN. Both factors decrease electron density in the bonding region near the central atom so that crowding in the axial position is less important.
Related geometries with lone pairs
The VSEPR theory also predicts that substitution of a ligand at a central atom by a lone pair of valence electrons leaves the general form of the electron arrangement unchanged with the lone pair now occupying one position. For molecules with five pairs of valence electrons including both bonding pairs and lone pairs, the electron pairs are still arranged in a trigonal bipyramid but one or more equatorial positions is not attached to a ligand atom so that the molecular geometry (for the nuclei only) is different. Theseesaw molecular geometry
Disphenoidal or seesaw (also known as sawhorse) is a type of molecular geometry where there are four bonds to a central atom with overall C2v molecular symmetry. The name "seesaw" comes from the observation that it looks like a playground seesaw ...
is found in sulfur tetrafluoride
Sulfur tetrafluoride is the chemical compound with the formula S F4. It is a colorless corrosive gas that releases dangerous HF upon exposure to water or moisture. Despite these unwelcome characteristics, this compound is a useful reagent for t ...
(SF4) with a central sulfur atom surrounded by four fluorine atoms occupying two axial and two equatorial positions, as well as one equatorial lone pair, corresponding to an AX4E molecule in the AXE notation. A T-shaped molecular geometry
In chemistry, T-shaped molecular geometry describes the structures of some molecules where a central atom has three ligands. Ordinarily, three-coordinated compounds adopt trigonal planar or pyramidal geometries. Examples of T-shaped molecules are ...
is found in chlorine trifluoride (ClF3), an AX3E2 molecule with fluorine atoms in two axial and one equatorial position, as well as two equatorial lone pairs. Finally, the triiodide ion () is also based upon a trigonal bipyramid, but the actual molecular geometry is linear
Linearity is the property of a mathematical relationship (''function'') that can be graphically represented as a straight line. Linearity is closely related to '' proportionality''. Examples in physics include rectilinear motion, the linear r ...
with terminal iodine atoms in the two axial positions only and the three equatorial positions occupied by lone pairs of electrons (AX2E3); another example of this geometry is provided by xenon difluoride
Xenon difluoride is a powerful fluorinating agent with the chemical formula , and one of the most stable xenon compounds. Like most covalent inorganic fluorides it is moisture-sensitive. It decomposes on contact with water vapor, but is otherwis ...
, XeF2.
Berry pseudorotation
Isomers with a trigonal bipyramidal geometry are able to interconvert through a process known as Berry pseudorotation. Pseudorotation is similar in concept to the movement of a conformational diastereomer, though no full revolutions are completed. In the process of pseudorotation, two equatorial ligands (both of which have a shorter bond length than the third) "shift" toward the molecule's axis, while the axial ligands simultaneously "shift" toward the equator, creating a constant cyclical movement. Pseudorotation is particularly notable in simple molecules such as phosphorus pentafluoride (PF5).See also
* AXE method * Molecular geometryReferences
External links
Indiana University Molecular Structure Center
{{MolecularGeometry Stereochemistry Molecular geometry