Trigonal bipyramid on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 In
In
 The ''triangular bipyramid'' can be constructed by augmentation of smaller ones, specifically two stacked regular
The ''triangular bipyramid'' can be constructed by augmentation of smaller ones, specifically two stacked regular 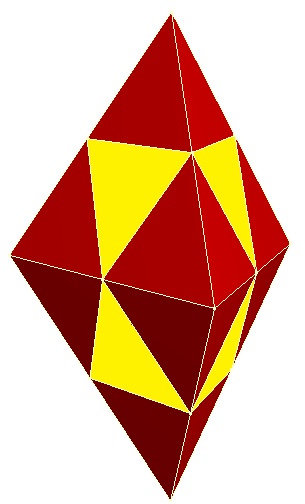 The triangular bipyramid can form a
The triangular bipyramid can form a
Conway Notation for Polyhedra
Try: dP3 {{Johnson solids navigator Johnson solids Deltahedra Pyramids and bipyramids Molecular geometry
 In
In geometry
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is ...
, the triangular bipyramid (or dipyramid) is a type of hexahedron
A hexahedron (plural: hexahedra or hexahedrons) or sexahedron (plural: sexahedra or sexahedrons) is any polyhedron with six faces. A cube, for example, is a regular hexahedron with all its faces square, and three squares around each vertex.
Ther ...
, being the first in the infinite set of face-transitive
In geometry, a tessellation of dimension (a plane tiling) or higher, or a polytope of dimension (a polyhedron) or higher, is isohedral or face-transitive if all its faces are the same. More specifically, all faces must be not merely congrue ...
bipyramids. It is the dual of the triangular prism
In geometry, a triangular prism is a three-sided prism; it is a polyhedron made of a triangular base, a translated copy, and 3 faces joining corresponding sides. A right triangular prism has rectangular sides, otherwise it is ''oblique''. A ...
with 6 isosceles triangle faces.
As the name suggests, it can be constructed by joining two tetrahedra
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the o ...
along one face. Although all its faces are congruent
Congruence may refer to:
Mathematics
* Congruence (geometry), being the same size and shape
* Congruence or congruence relation, in abstract algebra, an equivalence relation on an algebraic structure that is compatible with the structure
* In mod ...
and the solid is face-transitive
In geometry, a tessellation of dimension (a plane tiling) or higher, or a polytope of dimension (a polyhedron) or higher, is isohedral or face-transitive if all its faces are the same. More specifically, all faces must be not merely congrue ...
, it is not a Platonic solid
In geometry, a Platonic solid is a convex, regular polyhedron in three-dimensional Euclidean space. Being a regular polyhedron means that the faces are congruent (identical in shape and size) regular polygons (all angles congruent and all e ...
because some vertices adjoin three faces and others adjoin four.
The bipyramid whose six faces are all equilateral triangle
In geometry, an equilateral triangle is a triangle in which all three sides have the same length. In the familiar Euclidean geometry, an equilateral triangle is also equiangular; that is, all three internal angles are also congruent to each oth ...
s is one of the Johnson solids, (). As a Johnson solid with all faces equilateral triangles, it is also a deltahedron
In geometry, a deltahedron (plural ''deltahedra'') is a polyhedron whose faces are all equilateral triangles. The name is taken from the Greek upper case delta (Δ), which has the shape of an equilateral triangle. There are infinitely many d ...
.
Formulae
The following formulae for theheight
Height is measure of vertical distance, either vertical extent (how "tall" something or someone is) or vertical position (how "high" a point is).
For example, "The height of that building is 50 m" or "The height of an airplane in-flight is ab ...
(), surface area () and volume
Volume is a measure of occupied three-dimensional space. It is often quantified numerically using SI derived units (such as the cubic metre and litre) or by various imperial or US customary units (such as the gallon, quart, cubic inch). Th ...
() can be used if all faces are regular, with edge length :
:
:
:
Dual polyhedron
The dual polyhedron of the triangular bipyramid is thetriangular prism
In geometry, a triangular prism is a three-sided prism; it is a polyhedron made of a triangular base, a translated copy, and 3 faces joining corresponding sides. A right triangular prism has rectangular sides, otherwise it is ''oblique''. A ...
, with five faces: two parallel equilateral triangles linked by a chain of three rectangles.
Although the triangular prism has a form that is a uniform polyhedron (with square faces), the dual of the Johnson solid form of the bipyramid has rectangular rather than square faces, and is not uniform.
Related polyhedra and honeycombs
The ''triangular bipyramid'', dt, can be in sequence rectified, rdt, truncated, and alternated ( snubbed), : : The ''triangular bipyramid'' can be constructed by augmentation of smaller ones, specifically two stacked regular
The ''triangular bipyramid'' can be constructed by augmentation of smaller ones, specifically two stacked regular octahedra
In geometry, an octahedron (plural: octahedra, octahedrons) is a polyhedron with eight faces. The term is most commonly used to refer to the regular octahedron, a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet a ...
with 3 triangular bipyramids added around the sides, and 1 tetrahedron above and below. This polyhedron has 24 equilateral triangle
In geometry, an equilateral triangle is a triangle in which all three sides have the same length. In the familiar Euclidean geometry, an equilateral triangle is also equiangular; that is, all three internal angles are also congruent to each oth ...
faces, but it is not a Johnson solid because it has coplanar faces. It is a coplanar 24-triangle deltahedron
In geometry, a deltahedron (plural ''deltahedra'') is a polyhedron whose faces are all equilateral triangles. The name is taken from the Greek upper case delta (Δ), which has the shape of an equilateral triangle. There are infinitely many d ...
. This polyhedron exists as the augmentation of cells in a gyrated alternated cubic honeycomb. Larger triangular polyhedra can be generated similarly, like 9, 16 or 25 triangles per larger triangle face, seen as a section of a triangular tiling
In geometry, the triangular tiling or triangular tessellation is one of the three regular tilings of the Euclidean plane, and is the only such tiling where the constituent shapes are not parallelogons. Because the internal angle of the equilate ...
.
: The triangular bipyramid can form a
The triangular bipyramid can form a tessellation of space
In geometry, a honeycomb is a ''space filling'' or '' close packing'' of polyhedral or higher-dimensional ''cells'', so that there are no gaps. It is an example of the more general mathematical ''tiling'' or ''tessellation'' in any number of dim ...
with octahedra
In geometry, an octahedron (plural: octahedra, octahedrons) is a polyhedron with eight faces. The term is most commonly used to refer to the regular octahedron, a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet a ...
or with truncated tetrahedra
In geometry, the truncated tetrahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 4 regular hexagonal faces, 4 equilateral triangle faces, 12 vertices and 18 edges (of two types). It can be constructed by truncating all 4 vertices of a regular tetrahedron ...
.
When projected onto a sphere, it resembles a compound of a trigonal hosohedron and trigonal dihedron. It is part of an infinite series of dual pair compounds of regular polyhedra projected onto spheres. The triangular bipyramid can be referred to as a deltoidal hexahedron for consistency with the other solids in the series, although the "deltoids" are triangles instead of kites in this case, as the angle from the dihedron is 180 degrees.
See also
*Trigonal bipyramidal molecular geometry
In chemistry, a trigonal bipyramid formation is a molecular geometry with one atom at the center and 5 more atoms at the corners of a triangular bipyramid. This is one geometry for which the bond angles surrounding the central atom are not iden ...
* Boerdijk–Coxeter helix
The Boerdijk–Coxeter helix, named after H. S. M. Coxeter and A. H. Boerdijk, is a linear stacking of regular tetrahedra, arranged so that the edges of the complex that belong to only one tetrahedron form three intertwined helices. There are ...
, an extension of the triangular bipyramid by adding more tetrahedrons
References
External links
*Conway Notation for Polyhedra
Try: dP3 {{Johnson solids navigator Johnson solids Deltahedra Pyramids and bipyramids Molecular geometry