Tree of life (Kabbalah) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Tree of Life ( Hebrew: ūóųĄūź ūŚųĘūÖų┤ų╝ūÖūØ ''╩┐─Æß╣Ż ßĖżayy─½m'') is a diagram used in
The Tree of Life ( Hebrew: ūóųĄūź ūŚųĘūÖų┤ų╝ūÖūØ ''╩┐─Æß╣Ż ßĖżayy─½m'') is a diagram used in

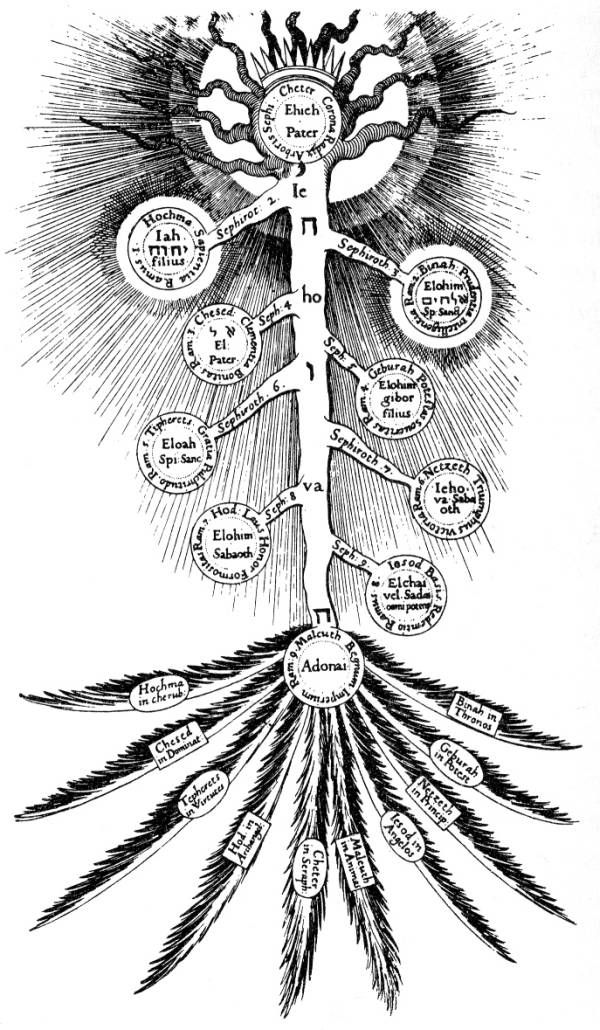 According to Chassidist Kabbalist scholars, the tree of life is to be interpreted in the following way:
* The tree represents a series of divine emanations of
According to Chassidist Kabbalist scholars, the tree of life is to be interpreted in the following way:
* The tree represents a series of divine emanations of
The Ilanot Project
ĆöA searchable descriptive catalogue of kabbalistic diagrams in manuscripts and books from Medieval Age to the 20th century Christian Kabbalah Hermetic Qabalah Jewish symbols Kabbalah Kabbalistic words and phrases Magic symbols Religious diagrams
 The Tree of Life ( Hebrew: ūóųĄūź ūŚųĘūÖų┤ų╝ūÖūØ ''╩┐─Æß╣Ż ßĖżayy─½m'') is a diagram used in
The Tree of Life ( Hebrew: ūóųĄūź ūŚųĘūÖų┤ų╝ūÖūØ ''╩┐─Æß╣Ż ßĖżayy─½m'') is a diagram used in Kabbalah
Kabbalah ( he, ū¦ųĘūæųĖų╝ū£ųĖūö ''Qabb─ül─ü'', literally "reception, tradition") is an esoteric method, discipline and school of thought in Jewish mysticism. A traditional Kabbalist is called a Mekubbal ( ''M╔Öq┼½bb─ül'' "receiver"). The defin ...
and various other mystical traditions. It usually consists of 10 or 11 node
In general, a node is a localized swelling (a "knot") or a point of intersection (a vertex).
Node may refer to:
In mathematics
* Vertex (graph theory), a vertex in a mathematical graph
*Vertex (geometry), a point where two or more curves, lines ...
s symbolizing different archetypes and 22 lines connecting the nodes. The nodes are often arranged into three columns
A column or pillar in architecture and structural engineering is a structural element that transmits, through compression, the weight of the structure above to other structural elements below. In other words, a column is a compression membe ...
to represent that they belong to a common category.
The nodes are usually represented as spheres
The Synchronized Position Hold Engage and Reorient Experimental Satellite (SPHERES) are a series of miniaturized satellites developed by MIT's Space Systems Laboratory for NASA and US Military, to be used as a low-risk, extensible test bed for the ...
and the lines are usually represented as paths. The nodes usually represent encompassing aspects of existence
Existence is the ability of an entity to interact with reality. In philosophy, it refers to the ontological property of being.
Etymology
The term ''existence'' comes from Old French ''existence'', from Medieval Latin ''existentia/exsistentia' ...
, God
In monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'', Oxford University Press, 1995. God is typically ...
, or the human psyche. The lines usually represent the relationship between the concepts ascribed to the spheres or a symbolic description of the requirements to go from one sphere to another. The nodes are also associated to deities, angels
In various theistic religious traditions an angel is a supernatural spiritual being who serves God.
Abrahamic religions often depict angels as benevolent celestial intermediaries between God (or Heaven) and humanity. Other roles incl ...
, celestial bodies, values
In ethics and social sciences, value denotes the degree of importance of something or action, with the aim of determining which actions are best to do or what way is best to live (normative ethics in ethics), or to describe the significance of di ...
, single color
Color (American English) or colour (British English) is the visual perceptual property deriving from the spectrum of light interacting with the photoreceptor cells of the eyes. Color categories and physical specifications of color are assoc ...
s or combinations of them, and specific numbers
A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The original examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. More universally, individual numbers can ...
. The columns are usually symbolized as pillars
A column or pillar in architecture and structural engineering is a structural element that transmits, through compression, the weight of the structure above to other structural elements below. In other words, a column is a compression member. ...
. These pillars
A column or pillar in architecture and structural engineering is a structural element that transmits, through compression, the weight of the structure above to other structural elements below. In other words, a column is a compression member. ...
usually represent different kinds of values
In ethics and social sciences, value denotes the degree of importance of something or action, with the aim of determining which actions are best to do or what way is best to live (normative ethics in ethics), or to describe the significance of di ...
, electric charges
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes charged matter to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. Electric charge can be ''positive'' or ''negative'' (commonly carried by protons and electrons respectiv ...
, or types of ceremonial magic
Ceremonial magic (ritual magic, high magic or learned magic) encompasses a wide variety of rituals of magic. The works included are characterized by ceremony and numerous requisite accessories to aid the practitioner. It can be seen as an ex ...
. It is usually referred to as the Kabbalistic tree of life in order to distinguish it from other concepts with the same name. In the Jewish Kabbalah, the nodes are called sephiroth. The diagram is also used by Christian Cabbala, Hermetic Qabalah and Theosophy.
Scholars believe that the concept of a tree of life with different spheres encompassing aspects of reality traces its origins back to Assyria
Assyria ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''m─üt A┼Ī┼Īur''; syc, ▄É▄¼▄ś▄¬, ╩Š─üthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the ...
in the 9th century BC. The Assyrians also assigned values
In ethics and social sciences, value denotes the degree of importance of something or action, with the aim of determining which actions are best to do or what way is best to live (normative ethics in ethics), or to describe the significance of di ...
and specific numbers
A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The original examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. More universally, individual numbers can ...
to their deities similar to those used by the later Jewish Kabbalah. The beginnings of the Jewish Kabbalah are traced back by scholars to the Medieval Age, originating in the ''Bahir
''Bahir'' or ''Sefer HaBahir'' ( he, ūĪųĄūżųČū© ūöųĘūæųĖų╝ūöų┤ūÖū©, ; "Book of Clarity" or "Book of Illumination") is an anonymous mystical work, attributed to a 1st-century rabbinic sage Nehunya ben HaKanah (a contemporary of Yochanan ben Zaka ...
'' and the '' Zohar''. However, the first historical instance of the modern diagram appeared centuries later in the cover of the Latin translation of ''Gates of Light'' in the year 1516. Scholars have traced the origin of the art in the ''Porta Lucis'' cover to Johann Reuchlin
Johann Reuchlin (; sometimes called Johannes; 29 January 1455 ŌĆō 30 June 1522) was a German Catholic humanist and a scholar of Greek and Hebrew, whose work also took him to modern-day Austria, Switzerland, and Italy and France. Most of Reuchlin' ...
.
Evolution
The first historical instance of the modern tree of life was designed byJohann Reuchlin
Johann Reuchlin (; sometimes called Johannes; 29 January 1455 ŌĆō 30 June 1522) was a German Catholic humanist and a scholar of Greek and Hebrew, whose work also took him to modern-day Austria, Switzerland, and Italy and France. Most of Reuchlin' ...
. Paolo Riccio
Paolo Riccio (1480 - 1541) was a German Jewish convert to Christianity in the first half of the sixteenth century. He became professor of philosophy in the University of Pavia; subsequently he was physician to Emperor Maximilian I.
Riccio was ...
's son, Hyeronomius, had actively exchanged letters and shared his father's work with Reuchlin before publication. Thus, in the year 1516, Reuchlin's diagram came to appear on the cover of the Paolo Riccio
Paolo Riccio (1480 - 1541) was a German Jewish convert to Christianity in the first half of the sixteenth century. He became professor of philosophy in the University of Pavia; subsequently he was physician to Emperor Maximilian I.
Riccio was ...
's Latin translation of Joseph Gikatilla
Joseph ben Abraham Gikatilla (1248 – after 1305) ( he, ūÖūĢūĪūŻ ūæū¤ ūÉūæū©ūöūØ ūÆ'ūÖū¦ūśūÖū£ūÖūö, es, Chiquitilla, "the very little one") was a Spanish kabbalist, student of Abraham Abulafia.
Biography
Born at Medinaceli, Old Castile, ...
's ''Gates of Light''. The diagram only had 17 paths and, at the time, the concepts of 10 spheres and 22 letters were still distinct in the literature. In 1573, a version sketched by Franciscus Zillettus appeared in ''Cesare Evoli, De divinis attributis''. This version introduced several innovations that would reappear in later versions: all the spheres were of the same size, the lines became wide paths, the spheres were aligned into 3 distinct columns, Malkuth was connected to three spheres, and astrological symbols for the known celestial bodies were used in conjunction with the Hebrew names to label the spheres. However, it also had only 17 paths, albeit distributed differently. Reuchlin's version was reprinted in Johann Pistorius' compilation of 1587. Finally, several versions from unknown artists introducing 21 and 22 paths appeared in the posthumous print editions of Moses Cordovero
Moses Cordovero was a physician who lived at Leghorn (Livorno), Tuscany
it, Toscano (man) it, Toscana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Citizenship ...
's ''Pardes Rimonim'' between 1592 and 1609. However, the diagrams with 22 paths lacked consistency with each other and none of them
had the 22 letters. Between 1652 and 1654, Athanasius Kircher
Athanasius Kircher (2 May 1602 ŌĆō 27 November 1680) was a German Jesuit scholar and polymath who published around 40 major works, most notably in the fields of comparative religion, geology, and medicine. Kircher has been compared to fe ...
published his own version of the tree in '' Oedipus Aegyptiacus''. Kircher might have designed his diagram in a syncretic
Syncretism () is the practice of combining different beliefs and various schools of thought. Syncretism involves the merging or assimilation of several originally discrete traditions, especially in the theology and mythology of religion, thu ...
attempt to reconcile several distinct ideas. This heavily annotated version, self-termed ''Sephirotic System'', introduced more innovations: abstract concepts, divine names, the 22 Hebrew letters for each path, and new astrological symbols. Between 1677 and 1684, Christian Knorr von Rosenroth
Christian Knorr von Rosenroth (15/16 July 1636 ŌĆō 4 May 1689) was a German Christian Hebraist and Christian Cabalist born at Alt-Raudten (today Stara Rudna) in Silesia. After having completed his studies in the universities of Wittenberg and Le ...
published ''Kabbala Denudat''. He designed several new versions of the tree of life, introduced the first version with 11 spheres, placed Daath between Kether and Tiphareth, and attempted to derive the tree of life from elemental geometry.
Consequently, to modern day, two versions are widely circulated: one where Malkuth has 1 path, owing to Reuchlin's original; and another where Malkuth has three paths, owing to several later versions; both having 22 paths in total, corresponding each to a Hebrew letter, owing to Kircher's syncretism. With the resurgence of occultism in the 19th century, many new versions appeared, but without major innovations. In the 20th century, Aleister Crowley
Aleister Crowley (; born Edward Alexander Crowley; 12 October 1875 ŌĆō 1 December 1947) was an English occultist, ceremonial magician, poet, painter, novelist, and mountaineer. He founded the religion of Thelema, identifying himself as the pr ...
might have resurfaced the idea of Daath as an 11th hidden sphere between Kether and Tiphareth in his book ''Liber 777'', syncretizing the concept with Kircher's symbols and von Rosenroth's diagrams. With the discovery of new planets, people might have tried to introduce more astrological symbols to their own versions of the diagram. As a result, there is no general agreement about the position of Uranus, Neptune and Pluto. However, in particular, it has been noted that Pluto bears resemblance with Daath: Pluto is a former planet, the last traditional celestial body to be discovered, and Daath is a hidden sphere, the last to be introduced. In the 21st century, enthusiasts might have rushed to attribute these collaborative works spanning centuries and involving several people through complex interactions to single authors. Thus, sometimes, the version where Malkuth has 3 paths is termed the ''Tree of Emanation'', and the version where Malkuth has 1 path is termed the ''Tree of Return''.
Interpretations
Chassidist

 According to Chassidist Kabbalist scholars, the tree of life is to be interpreted in the following way:
* The tree represents a series of divine emanations of
According to Chassidist Kabbalist scholars, the tree of life is to be interpreted in the following way:
* The tree represents a series of divine emanations of God
In monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'', Oxford University Press, 1995. God is typically ...
's creation itself ex nihilo, the nature of revealed divinity, the human soul, and the spiritual path of ascent by man. In this way, Kabbalists developed the symbol into a full model of reality, using the tree to depict a map of creation.
* The symbolic configuration is made of 10 spiritual principles, but 11 can be shown, since "Keter
Keter ( he-a, ūøųČų╝ū¬ųČū©, Keter.ogg, link=yes, ''Keß╣»er'', lit. "crown") also known as Kether, is the topmost of the sephirot of the Tree of Life in Kabbalah. Since its meaning is "crown", it is interpreted as both the "topmost" of the Sep ...
" and "Da'at
In the branch of Jewish mysticism known as Kabbalah, Da╩╗at or Da'ath (, in pausa: ', ) is the location (the mystical state) where all ten ''sefirot'' in the Tree of Life are united as one.
In Da╩╗at, all ''sefirot'' exist in their perfecte ...
" are interchangeable.
* The tree of knowledge of good and evil
In Judaism and Christianity, the tree of the knowledge of good and evil ( he, ūóųĄūź ūöųĘūōųĘų╝ūóųĘū¬ ūśūĢų╣ūæ ūĢųĖū©ųĖūó, ╩┐├¬ß╣Ż had-da╩┐aß╣» ß╣Ł┼ŹßĖć w─ü-r─ü╩┐, label=Tiberian Hebrew, ) is one of two specific trees in the story of the Garden ...
is equivalent to the 10 spheres seen from the last sphere of the diagram ("Malkuth
Modern: ''MalßĖĄ┼½t'' , Tiberian: ''MalßĖĄ┼½ß╣»'' , Ashkenazi: ''MalßĖĄ┼½s'' , 'kingdom'), Malkhut Malkhuth or Malchus is the tenth of the sephirot in the Kabbalistic Tree of Life. It sits at the bottom of the Tree, below Yesod. This sephira ...
"), and the original tree of life
The tree of life is a fundamental archetype in many of the world's mythological, religious, and philosophical traditions. It is closely related to the concept of the sacred tree.Giovino, Mariana (2007). ''The Assyrian Sacred Tree: A Hist ...
is equivalent to the 10 spheres seen from the middle sphere of the diagram ("Tiferet
Tiferet ( he, ū¬ų┤ų╝ūżų░ūÉųČū©ųČū¬ ''Tip╠ä╩Šereß╣»,'' in pausa: ū¬ų┤ų╝ūżų░ūÉųĖū©ųČū¬ ''Tip╠ä╩Š─üreß╣»'', lit. 'beauty, glory, adornment') alternatively Tifaret, Tiphareth, Tifereth or Tiphereth, is the sixth sefira in the kabbalistic Tree of ...
").
* Kabbalists believe the tree of life to be a diagrammatic representation of the process by which the universe came into being.
* On the tree of life, the beginning of the universe is placed in a space above the first sphere (named "Keter
Keter ( he-a, ūøųČų╝ū¬ųČū©, Keter.ogg, link=yes, ''Keß╣»er'', lit. "crown") also known as Kether, is the topmost of the sephirot of the Tree of Life in Kabbalah. Since its meaning is "crown", it is interpreted as both the "topmost" of the Sep ...
" or "crown" in English). It is not always pictured in reproductions of the tree of life, but is referred to universally as ''Ohr
''Ohr'' ("Light" he, ūÉūĢū©; plural: ''Ohros/Ohrot'' "Lights" ) is a central Kabbalistic term in the Jewish mystical tradition. The analogy of physical light is used as a way of describing metaphysical Divine emanations. ''Shefa'' ("Flow" an ...
Ein Sof'' (ūÉųĄūÖū¤ ūĪūĢų╣ūŻŌĆÄŌĆÄŌĆÄŌĆÄ ūÉūĢų╣ū©ŌĆÄ in Hebrew or "endless light" in English).
* To Kabbalists, it symbolizes that point beyond which our comprehension of the origins of being can't go. It is considered to be an infinite nothingness out of which the first "thing", usually understood among Kabbalists to be something approximating "energy", exploded to create a universe of multiple things.
* Kabbalists also don't envision time and space as pre-existing and place them at the next three stages on the tree of life.
* First is "Keter
Keter ( he-a, ūøųČų╝ū¬ųČū©, Keter.ogg, link=yes, ''Keß╣»er'', lit. "crown") also known as Kether, is the topmost of the sephirot of the Tree of Life in Kabbalah. Since its meaning is "crown", it is interpreted as both the "topmost" of the Sep ...
", which is thought of as the product of the contraction of "Ein Sof" into a singularity of infinite energy or limitless light. In the Kabbalah, it is the primordial energy out of which all things are created.
* The next stage is "Chokhmah
''Chokmah'' ( Hebrew: ūŚųĖūøų░ū×ųĖūö ) is the Biblical Hebrew word rendered as "wisdom" in English Bible versions (LXX '' sophia'', Vulgate ').'' Strong's Concordance'H2451
"from H2449 ŚųĖūøųĘūØ ''chakam'' "wise" wisdom (in a good sense):ŌĆö ...
" (or "wisdom" in English), which is considered to be a stage at which the infinitely hot and contracted singularity expanded forth into space and time. It is often thought of as pure dynamic energy of an infinite intensity forever propelled forth at a speed faster than light.
* Next comes " Binah" (or "understanding" in English), which is thought of as the primordial feminine energy, the supernal mother of the universe which receives the energy of "Chokhmah", cooling and nourishing it into the multitudinous forms present throughout the whole cosmos. It is also seen as the beginning of time itself.
* Numbers are very important to Kabbalists, and the Hebrew letters of the alphabet also have a numerical value. Each stage of the emanation of the universe on the tree of life is numbered meaningfully from one ("Keter
Keter ( he-a, ūøųČų╝ū¬ųČū©, Keter.ogg, link=yes, ''Keß╣»er'', lit. "crown") also known as Kether, is the topmost of the sephirot of the Tree of Life in Kabbalah. Since its meaning is "crown", it is interpreted as both the "topmost" of the Sep ...
") to ten ("Malkuth
Modern: ''MalßĖĄ┼½t'' , Tiberian: ''MalßĖĄ┼½ß╣»'' , Ashkenazi: ''MalßĖĄ┼½s'' , 'kingdom'), Malkhut Malkhuth or Malchus is the tenth of the sephirot in the Kabbalistic Tree of Life. It sits at the bottom of the Tree, below Yesod. This sephira ...
"). Each number is thought to express the nature of its sphere.
* The first three spheres, called the "supernal" spheres, are considered to be the primordial energies of the universe. The next stages of evolution on the tree of life are considered to exist beyond a space on the tree, called the "Abyss", between the "supernals" and the other spheres, because their levels of being are so distinct from each other that they appear to exist in two totally different realities. The "supernal" spheres exist on a plane of divine energy. This is why another correspondence for " Binah" is the idea of suffering because the "supernal" maternal energy gives birth to a world that is inherently excluded from that divine union.
* After " Binah", the universe gets down to the business of building the materials it will need to fulfill its evolution and be creating new combinations of those materials until it is so dense that, by the stage of "Malkuth
Modern: ''MalßĖĄ┼½t'' , Tiberian: ''MalßĖĄ┼½ß╣»'' , Ashkenazi: ''MalßĖĄ┼½s'' , 'kingdom'), Malkhut Malkhuth or Malchus is the tenth of the sephirot in the Kabbalistic Tree of Life. It sits at the bottom of the Tree, below Yesod. This sephira ...
", the initial pure limitless energy has solidified into the physical universe.
* Since its energies are the basis of all creation, the tree of life can potentially be applied to any area of life, especially the inner world of man, from the subconscious all the way to what Kabbalists call the higher self.
* But the tree of life does not only speak of the origins of the physical universe out of the unimaginable but also of man's place in the universe. Since man is invested with mind, consciousness in the Kabbalah is thought of as the fruit of the physical world, through whom the original infinite energy can experience and express itself as a finite entity.
* After the energy of creation has condensed into matter, it is thought to reverse its course back up the tree until it is once again united with its true nature: "Keter
Keter ( he-a, ūøųČų╝ū¬ųČū©, Keter.ogg, link=yes, ''Keß╣»er'', lit. "crown") also known as Kether, is the topmost of the sephirot of the Tree of Life in Kabbalah. Since its meaning is "crown", it is interpreted as both the "topmost" of the Sep ...
". Thus, the Kabbalist seeks to know himself and the universe as an expression of God and to make the journey of return by means of the stages charted by the spheres, until he has come to the realization he sought.
See also
*Atziluth
Atziluth or Atzilut (also ''Olam Atsiluth'', ūóūĢų╣ū£ųĖūØ ūÉų▓ū”ų┤ūÖū£ūĢų╝ū¬, literally "the World of Emanation") is the highest of four worlds in which exists the Kabbalistic Tree of Life. It is also known as "near to God."MEIJERS, L. D., and J. ...
* Flower of life
* Sephirot
Sefirot (; he, ūĪų░ūżų┤ūÖū©ūĢų╣ū¬, translit=S╔Öf─½r┼Źt, Tiberian: '), meaning '' emanations'', are the 10 attributes/emanations in Kabbalah, through which Ein Sof (The Infinite) reveals itself and continuously creates both the physical realm an ...
* Thelema
Thelema () is a Western esoteric and occult social or spiritual philosophy and new religious movement founded in the early 1900s by Aleister Crowley (1875–1947), an English writer, mystic, occultist, and ceremonial magician. The word ' ...
* The path of the flaming sword
* Tree of death (Kabbalah)
* Tree of life (biblical)
In Judaism and Christianity, the tree of life ( he, ūóųĄūź ūöųĘūŚųĘūÖų┤ų╝ūÖūØ, ŌĆś─ōß╣Ż haßĖźayy─½m) is first described in of the Book of Genesis as being "in the midst of the Garden of Eden" with the tree of the knowledge of good and evil ...
* Tree of life
The tree of life is a fundamental archetype in many of the world's mythological, religious, and philosophical traditions. It is closely related to the concept of the sacred tree.Giovino, Mariana (2007). ''The Assyrian Sacred Tree: A Hist ...
* Tree of the knowledge of good and evil
In Judaism and Christianity, the tree of the knowledge of good and evil ( he, ūóųĄūź ūöųĘūōųĘų╝ūóųĘū¬ ūśūĢų╣ūæ ūĢųĖū©ųĖūó, ╩┐├¬ß╣Ż had-da╩┐aß╣» ß╣Ł┼ŹßĖć w─ü-r─ü╩┐, label= Tiberian Hebrew, ) is one of two specific trees in the story of the Garden ...
References
External links
{{Commons category, Tree of life (Kabbalah)The Ilanot Project
ĆöA searchable descriptive catalogue of kabbalistic diagrams in manuscripts and books from Medieval Age to the 20th century Christian Kabbalah Hermetic Qabalah Jewish symbols Kabbalah Kabbalistic words and phrases Magic symbols Religious diagrams