Treaty of Tsarskoye Selo on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Treaty of Tsarskoye Selo was a territorial and dynastic
 In 1460, upon his election as
In 1460, upon his election as
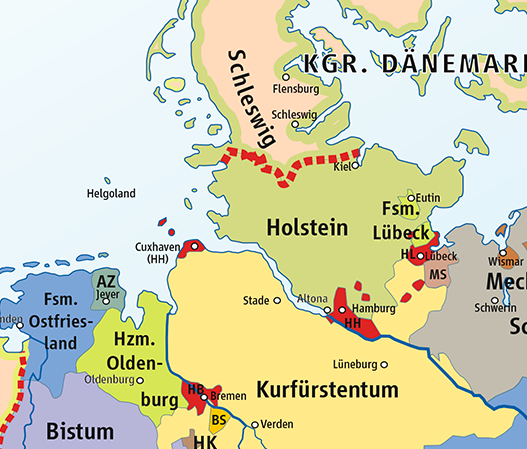 This territorial exchange placed the duchies of Schleswig and Holstein under a single sovereign, the Danish King, and ended the political and dynastic conflicts that had divided the region since its partition two centuries earlier. The political unification of Schleswig–Holstein made possible the development of the
This territorial exchange placed the duchies of Schleswig and Holstein under a single sovereign, the Danish King, and ended the political and dynastic conflicts that had divided the region since its partition two centuries earlier. The political unification of Schleswig–Holstein made possible the development of the
treaty
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal per ...
between the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
and Denmark–Norway
Denmark–Norway ( Danish and Norwegian: ) was an early modern multi-national and multi-lingual real unionFeldbæk 1998:11 consisting of the Kingdom of Denmark, the Kingdom of Norway (including the then Norwegian overseas possessions: the Faroe ...
. Signed on 1 June 1773, it transferred control of ducal Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; da, Slesvig-Holsten; nds, Sleswig-Holsteen; frr, Slaswik-Holstiinj) is the northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Sc ...
to the Danish crown in return for Russian control of the County of Oldenburg
The County of Oldenburg was a county of the Holy Roman Empire.
In 1448 Christian I of Denmark (of the House of Oldenburg), Count of Oldenburg became King of Denmark, and later King of Norway and King of Sweden. One of his grandsons, Adolf, Duk ...
and adjacent lands within the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
. The treaty reduced the fragmentation of Danish territory and led to an alliance between Denmark–Norway and Russia that lasted into the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fre ...
. It also made possible the construction of the Eider Canal
The Eider Canal (also called the Schleswig-Holstein Canal) was an artificial waterway in southern Denmark (later northern Germany) which connected the North Sea with the Baltic Sea by way of the rivers Eider and Levensau. Constructed between 1 ...
, parts of which were later incorporated into the Kiel Canal
The Kiel Canal (german: Nord-Ostsee-Kanal, literally "North- oEast alticSea canal", formerly known as the ) is a long freshwater canal in the German state of Schleswig-Holstein. The canal was finished in 1895, but later widened, and links the N ...
.
Historical background
Oldenburg and Delmenhorst
In 1448 the Count of Oldenburg was electedKing of Denmark
The monarchy of Denmark is a constitutional institution and a historic office of the Kingdom of Denmark. The Kingdom includes Denmark proper and the autonomous territories of the Faroe Islands and Greenland. The Kingdom of Denmark was alre ...
and took the throne as Christian I
Christian I (February 1426 – 21 May 1481) was a Scandinavian monarch under the Kalmar Union. He was king of Denmark (1448–1481), Norway (1450–1481) and Sweden (1457–1464). From 1460 to 1481, he was also duke of Schleswig (within ...
. He assigned Oldenburg to his brother, Gerhard, in 1454, and Gerhard's descendants in the House of Oldenburg
The House of Oldenburg is a German dynasty with links to Denmark since the 15th century. It has branches that rule or have ruled in Denmark, Iceland, Greece, Norway, Russia, Sweden, the United Kingdom, Schleswig, Holstein, and Oldenburg. The cu ...
continued to rule the county for the next two centuries. In 1547 Emperor Charles V
Charles V, french: Charles Quint, it, Carlo V, nl, Karel V, ca, Carles V, la, Carolus V (24 February 1500 – 21 September 1558) was Holy Roman Emperor and Archduke of Austria from 1519 to 1556, King of Spain ( Castile and Aragon) fr ...
also gave the counts of Oldenburg control of the town of Delmenhorst
Delmenhorst (; Northern Low Saxon: ''Demost'') is an urban district ('' Kreisfreie Stadt'') in Lower Saxony, Germany. It has a population of 74,500 and is located west of downtown Bremen with which it forms a contiguous urban area, whereas the ...
, which adjoins Oldenburg on the left bank of the Weser
The Weser () is a river of Lower Saxony in north-west Germany. It begins at Hannoversch Münden through the confluence of the Werra and Fulda. It passes through the Hanseatic city of Bremen. Its mouth is further north against the ports o ...
, in return for Oldenburg's support in the Schmalkaldic War
The Schmalkaldic War (german: link=no, Schmalkaldischer Krieg) was the short period of violence from 1546 until 1547 between the forces of Emperor Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles V of the Holy Roman Empire (simultaneously King Charles I ...
. When the last count of Oldenburg, Anthony Günther, died childless in 1667, these territories reverted to the kings of Denmark, who began to rule them in personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interli ...
.
Schleswig-Holstein
 In 1460, upon his election as
In 1460, upon his election as Duke of Holstein
The Duchy of Holstein (german: Herzogtum Holstein, da, Hertugdømmet Holsten) was the northernmost state of the Holy Roman Empire, located in the present German state of Schleswig-Holstein. It originated when King Christian I of Denmark had h ...
, King Christian I promulgated the Treaty of Ribe, affirming that Schleswig
The Duchy of Schleswig ( da, Hertugdømmet Slesvig; german: Herzogtum Schleswig; nds, Hartogdom Sleswig; frr, Härtochduum Slaswik) was a duchy in Southern Jutland () covering the area between about 60 km (35 miles) north and 70 km ...
(a Danish fief) and Holstein
Holstein (; nds, label=Northern Low Saxon, Holsteen; da, Holsten; Latin and historical en, Holsatia, italic=yes) is the region between the rivers Elbe and Eider. It is the southern half of Schleswig-Holstein, the northernmost state of German ...
(part of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
) were to remain "forever undivided" in return for his recognition by the region's noble estates as the rightful ruler of Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; da, Slesvig-Holsten; nds, Sleswig-Holsteen; frr, Slaswik-Holstiinj) is the northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Sc ...
. From that time forward, Denmark and Schleswig-Holstein were ruled in personal union by the Danish kings for nearly a century. Then, in 1544 King Christian III of Denmark
Christian III (12 August 1503 – 1 January 1559) reigned as King of Denmark from 1534 and King of Norway from 1537 until his death in 1559. During his reign, Christian formed close ties between the church and the crown. He established ...
partitioned the two duchies between himself and his two half-brothers, John
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Secon ...
and Adolf
Adolf (also spelt Adolph or Adolphe, Adolfo and when Latinised Adolphus) is a given name used in German-speaking countries, Scandinavia, the Netherlands and Flanders, France, Italy, Spain, Portugal, Latin America and to a lesser extent in vari ...
, in an unusual way that would shape Danish politics for centuries.
Schleswig-Holstein's noble estates remained opposed to the actual division of the region, so the revenues of the duchies were divided into three equal shares by assigning the revenues of particular areas and landed estates to particular brothers. The piecemeal assignment of the estates left Holstein and Schleswig with a patchwork of political boundaries, precluding any future separation of the regions, as intended by the estates. The rule in the duchies thus became a condominium
A condominium (or condo for short) is an ownership structure whereby a building is divided into several units that are each separately owned, surrounded by common areas that are jointly owned. The term can be applied to the building or complex ...
of the king and the two dukes. Duke John died childless, and his share in the region was divided between his brothers' lines, but Duke Adolf's descendants in the House of Holstein-Gottorp
Holstein-Gottorp or Schleswig-Holstein-Gottorp () is the Historiography, historiographical name, as well as contemporary shorthand name, for the parts of the duchies of Duchy of Schleswig, Schleswig and Duchy of Holstein, Holstein, also known as ...
, who ruled not only the ducal share of Schleswig-Holstein but also the Prince-Bishopric of Lübeck, became rivals to the Danish kings.
Gottorp Question
By the mid-17th century the so-called "Gottorp Question" of Holstein's relationship with the crown threatened the stability of the Danish kingdom, as the dukes of Holstein-Gottorp allied themselves withSweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic countries, Nordic c ...
and other foreign powers against Denmark–Norway
Denmark–Norway ( Danish and Norwegian: ) was an early modern multi-national and multi-lingual real unionFeldbæk 1998:11 consisting of the Kingdom of Denmark, the Kingdom of Norway (including the then Norwegian overseas possessions: the Faroe ...
. During the minority of Duke Charles Frederick, Schleswig-Holstein's government affairs were entrusted to Minister Georg Heinrich von Görtz
Georg Heinrich von Görtz, Baron of Schlitz (1668 – 19 February 1719), diplomat in Swedish service, was born in Holstein and educated at Jena.
Career
He entered the Holstein-Gottorp service, and after the death of the duchess Hedwig Sophia, C ...
, who supported Sweden in the Great Northern War
The Great Northern War (1700–1721) was a conflict in which a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in Northern, Central and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the anti-Swe ...
; in that war's aftermath, Denmark–Norway seized the duke's territory in Schleswig and ended Sweden's patronage of Holstein-Gottorp with the 1720 Treaty of Frederiksborg
The Treaty of Frederiksborg ( da, Frederiksborgfreden) was a treaty signed at Frederiksborg Castle, Zealand, on 3 July 1720Heitz (1995), p.244 (14 July 1720 according to the Gregorian calendar), ending the Great Northern War between Denmark-No ...
.
Duke Charles Frederick sought support for the recovery of Schleswig in Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
, and in 1725 he married Russian Princess Anna Petrovna
Grand Duchess Anna Petrovna of Russia (russian: А́нна Петро́вна; 27 January 1708 – 4 March 1728) was the eldest daughter of Emperor Peter I of Russia and his wife Empress Catherine I. Her younger sister, Empress Elizabeth, ...
, the daughter of Emperor Peter the Great
Peter I ( – ), most commonly known as Peter the Great,) or Pyotr Alekséyevich ( rus, Пётр Алексе́евич, p=ˈpʲɵtr ɐlʲɪˈksʲejɪvʲɪtɕ, , group=pron was a Russian monarch who ruled the Tsardom of Russia from t ...
and sister of the future Empress Elizabeth
Elizabeth or Elisabeth may refer to:
People
* Elizabeth (given name), a female given name (including people with that name)
* Elizabeth (biblical figure), mother of John the Baptist
Ships
* HMS ''Elizabeth'', several ships
* ''Elisabeth'' (sch ...
. In 1742 the childless Elizabeth appointed her nephew, Charles Peter Ulrich (Charles Frederick and Anna's son), to be her successor in Russia. After her death in 1762, this Duke of Holstein ascended the throne as Peter III of Russia
Peter may refer to:
People
* List of people named Peter, a list of people and fictional characters with the given name
* Peter (given name)
** Saint Peter (died 60s), apostle of Jesus, leader of the early Christian Church
* Peter (surname), a s ...
; Ducal Holstein was now ruled in personal union by the Emperor of Russia. With the resources of Russia now backing his claims, Peter dispatched his minister Caspar von Saldern
Caspar is a masculine given name. It may refer to:
People
* Caspar (magus), a name traditionally given to one of the Three Magi in the Bible who brought the baby Jesus gifts
* Caspar Austa (born 1982), Estonian cyclist
*Caspar Badrutt (1848–1904 ...
to the Danish court to demand the recovery of his former ducal territory in Schleswig, as well as the concession of the royal portion of Holstein, under threat of war.
Negotiations
At the time of Peter's accession Russia was already fighting in theThird Silesian War
The Third Silesian War () was a war between Prussia and Austria (together with its allies) that lasted from 1756 to 1763 and confirmed Prussia's control of the region of Silesia (now in south-western Poland). The war was fought mainly in Silesi ...
theatre of the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754 ...
, but he quickly made peace with Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an e ...
and directed troops into Pomerania
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to ...
to press his claims against Denmark–Norway. The Danish government under Johann Hartwig Ernst von Bernstorff
Count Johann Hartwig Ernst von Bernstorff (german: Johann Hartwig Ernst Graf von Bernstorff; 13 May 1712 – 18 February 1772) was a German-Danish statesman and a member of the Bernstorff noble family of Mecklenburg. He was the son of Joachi ...
refused to relinquish Schleswig, and Russian and Danish troops came face to face in Mecklenburg
Mecklenburg (; nds, label= Low German, Mękel(n)borg ) is a historical region in northern Germany comprising the western and larger part of the federal-state Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania. The largest cities of the region are Rostock, Schweri ...
; but, on 9 July 1762, before fighting began or any agreement could be reached, Peter was overthrown by his wife, who took control of Russia as Empress Catherine II
, en, Catherine Alexeievna Romanova, link=yes
, house =
, father = Christian August, Prince of Anhalt-Zerbst
, mother = Joanna Elisabeth of Holstein-Gottorp
, birth_date =
, birth_name = Princess Sophie of Anhal ...
.
Catherine reversed Russia's stance, withdrawing her husband's ultimatum and even entering a non-aggression pact with Denmark–Norway on 11 March 1765. She transferred the Duchy of Holstein to her minor son, Grand Duke Paul (later Emperor Paul I of Russia
Paul I (russian: Па́вел I Петро́вич ; – ) was Emperor of Russia from 1796 until his assassination. Officially, he was the only son of Peter III and Catherine the Great, although Catherine hinted that he was fathered by her l ...
), and instructed her representative, von Saldern, to negotiate a peaceful solution to the Schleswig-Holstein conflict with his Danish counterpart, Foreign Minister Andreas Peter Bernstorff
Andreas Peter Bernstorff (28 August 173521 June 1797), also known as Andreas Peter Graf von Bernstorff, was a Danish diplomat and Foreign Minister. He was a guardian of civil and political liberty.
Background and early career
Bernstorff was bo ...
. The negotiators reached a provisional agreement in 1767.
Grand Duke Paul would renounce the House of Romanov
The House of Romanov (also transcribed Romanoff; rus, Романовы, Románovy, rɐˈmanəvɨ) was the reigning dynasty, imperial house of Russia from 1613 to 1917. They achieved prominence after the Tsarina, Anastacia of Russia, Anastasi ...
's claims in Schleswig-Holstein and transfer the ducal lands in Holstein to King Christian VII of Denmark–Norway, ending the Duchy of Holstein-Gottorp; in return, Denmark would reaffirm its alliance with Russia, pay a sizeable indemnity
In contract law, an indemnity is a contractual obligation of one Party (law), party (the ''indemnitor'') to Financial compensation, compensate the loss incurred by another party (the ''indemnitee'') due to the relevant acts of the indemnitor or ...
, and give Paul control of the County of Oldenburg and other hereditary Oldenburg lands in the Holy Roman Empire. The agreement was accepted by Catherine in 1767; after he came of age, Grand Duke Paul ratified the treaty on 1 June 1773 at the Russian imperial family's residence in Tsarskoye Selo
Tsarskoye Selo ( rus, Ца́рское Село́, p=ˈtsarskəɪ sʲɪˈlo, a=Ru_Tsarskoye_Selo.ogg, "Tsar's Village") was the town containing a former residence of the Russian imperial family and visiting nobility, located south from the c ...
, south of Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
, together with Danish King Christian VII
Christian VII (29 January 1749 – 13 March 1808) was a monarch of the House of Oldenburg who was King of Denmark–Norway and Duke of Duchy of Schleswig, Schleswig and Duchy of Holstein, Holstein from 1766 until his death in 1808. For his motto ...
. On 12 August Russia and Denmark signed a further treaty of alliance against Sweden, and the bargain was complete.
Results
 This territorial exchange placed the duchies of Schleswig and Holstein under a single sovereign, the Danish King, and ended the political and dynastic conflicts that had divided the region since its partition two centuries earlier. The political unification of Schleswig–Holstein made possible the development of the
This territorial exchange placed the duchies of Schleswig and Holstein under a single sovereign, the Danish King, and ended the political and dynastic conflicts that had divided the region since its partition two centuries earlier. The political unification of Schleswig–Holstein made possible the development of the Eider Canal
The Eider Canal (also called the Schleswig-Holstein Canal) was an artificial waterway in southern Denmark (later northern Germany) which connected the North Sea with the Baltic Sea by way of the rivers Eider and Levensau. Constructed between 1 ...
, whose construction began the following year.
The establishment of full, direct control over this strategically significant borderland strengthened Denmark's geopolitical position considerably and marked a major step toward Denmark's emergence as a centralised, unitary state
A unitary state is a sovereign state governed as a single entity in which the central government is the supreme authority. The central government may create (or abolish) administrative divisions (sub-national units). Such units exercise only th ...
. The alliance which shortly followed (contemporaneously called the "Eternal Alliance" ( da, Den Evige Alliance)) tied Denmark's foreign policy to Russia's and led directly to Danish-Norwegian involvement in the Theatre War
{{Campaignbox Dano-Swedish Wars
The Theatre War ( sv, Teaterkriget), Cowberry War, Cranberry War or Lingonberry War ( no, Tyttebærkrigen, da, Tyttebærkrigen), was a brief war between Denmark–Norway and Sweden, starting on 24 September 1788 ...
of 1788–1789 and the Dano-Swedish War of 1808–09.
On the Russian side, the exchange allowed Catherine to turn Denmark–Norway from an enemy into an ally, furthering Nikita Ivanovich Panin
Count Nikita Ivanovich Panin (russian: Ники́та Ива́нович Па́нин) () was an influential Russian statesman and political mentor to Catherine II of Russia, Catherine the Great for the first 18 years of her reign (1762-1780). In ...
's policy of building a Northern Accord
The Russo-Prussian alliance signed by the Kingdom of Prussia and the Russian Empire on 11 April 1764. It was pivotal to the people of Prussia and Russia, and it followed the end of the Seven Years' War. The alliance agreement expanded on the Tr ...
to balance the power of Bourbon France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
; a stronger Denmark would also help to contain Sweden (Russia's chief rival in the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
region). In 1774, Grand Duke Paul (at the urging of his mother) transferred the German lands obtained from the exchange to his great-uncle, Frederick August, and in 1777 they were united within a newly declared Duchy of Oldenburg
The Duchy of Oldenburg (german: Herzogtum Oldenburg)—named after its capital, the town of Oldenburg—was a state in the north-west of present-day Germany. The counts of Oldenburg died out in 1667, after which it became a duchy until 1810, w ...
. The Duchy of Oldenburg would remain connected to the Russian Empire until its annexation by Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
's French Empire in 1810.
See also
*Denmark–Russia relations
Denmark–Russia relations (alternatively: ''Dano-Russian relations'') are the relations between the two countries of Denmark and Russia. The Kings of Denmark and the Russian Tsars interacted from the 15th century onwards - subsequently De ...
* History of Schleswig-Holstein
References
{{Reflist, 30em 1773 in Denmark 1773 in the Russian Empire 1773 treaties History of Schleswig-Holstein Treaties involving territorial changes Treaties of Denmark–Norway Treaties of the Russian Empire Bilateral treaties of Russia