Transposition of great vessels on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Transposition of the great vessels (TGV) is a group of congenital congenital heart defect, heart defects involving an abnormal spatial arrangement of any of the great vessels: superior vena cava, superior and/or inferior vena cava, inferior venae cavae, pulmonary artery, pulmonary veins, and aorta. Congenital heart diseases involving only the primary artery, arteries (pulmonary artery and aorta) belong to a sub-group called transposition of the great arteries (TGA), which is considered the most common congenital heart lesion that presents in neonates.
 Transposition (birth defect), Transposed vessels can present with wikt:atriovenous, atriovenous, wikt:ventriculoarterial, ventriculoarterial and/or wikt: arteriovenous, arteriovenous wikt:discordant, discordance. The effects may range from a slight change in blood pressure to an interruption in circulatory system, circulation depending on the nature and degree of the misplacement, and on which specific vessels are involved.
Although "transposed" literally means "swapped", many types of TGV involve vessels that are in abnormal positions, while not actually being swapped with each other. The terms TGV and TGA are most commonly used in reference to dextro-Transposition of the great arteries, dextro-TGA – in which the two main arteries ''are'' in swapped positions; however, both terms are also commonly used, though to a slightly lesser extent, in reference to Levo-Transposition of the great arteries, levo-TGA – in which both the arteries and the ventricle (heart), ventricles are swapped; while other defects in this category are almost never referred to by either of these terms.
Transposition (birth defect), Transposed vessels can present with wikt:atriovenous, atriovenous, wikt:ventriculoarterial, ventriculoarterial and/or wikt: arteriovenous, arteriovenous wikt:discordant, discordance. The effects may range from a slight change in blood pressure to an interruption in circulatory system, circulation depending on the nature and degree of the misplacement, and on which specific vessels are involved.
Although "transposed" literally means "swapped", many types of TGV involve vessels that are in abnormal positions, while not actually being swapped with each other. The terms TGV and TGA are most commonly used in reference to dextro-Transposition of the great arteries, dextro-TGA – in which the two main arteries ''are'' in swapped positions; however, both terms are also commonly used, though to a slightly lesser extent, in reference to Levo-Transposition of the great arteries, levo-TGA – in which both the arteries and the ventricle (heart), ventricles are swapped; while other defects in this category are almost never referred to by either of these terms.
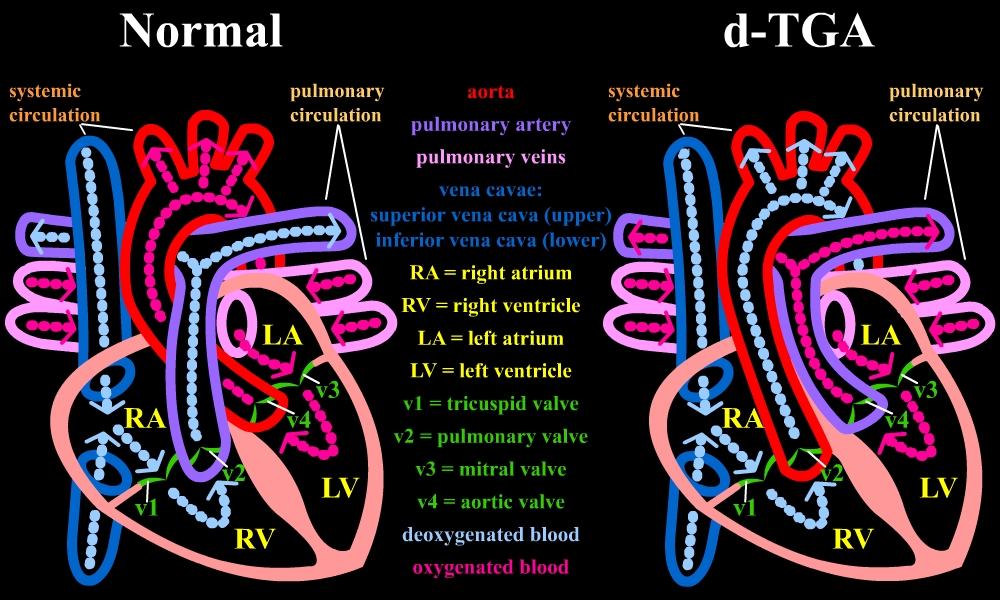

Types
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries (also known as dextro-TGA) is a cyanotic heart defect in which the aorta arises from the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery arises from the left ventricle. This switch causes deoxygenated blood from the right heart to be pumped immediately through the aorta and circulated throughout the body and the heart itself, bypassing the lungs altogether. In this same condition, the left heart continuously pumps oxygenated blood back into the lungs through the pulmonary artery, instead of out into the body's circulation as it normally would. In effect, two separate "parallel" circulatory systems are created. It is called a cyanotic heart defect, cyanotic congenital heart defect (CHD) because the newborn infant turns blue (cyanotic) from the lack of oxygen.Levo-Transposition of the great arteries
Levo-Transposition of the great arteries (also known as Levo-TGA, congenitally corrected TGA, double discordance, or ventricular inversion) is a rare, acyanotic heart defect in which the primary arteries are transposed, with the aorta anterior and to the left of the pulmonary artery, and the morphological left and right ventricles with their corresponding atrioventricular valves are also transposed. In other words, the right ventricle is on the left side of the heart and the left ventricle is on the right side of the heart. The systemic and the pulmonary circulation are connected in this condition. Complications can arise from the pressure change due to the fact that the right ventricle, which is adapted for pumping blood into the low-pressure pulmonary circulation, is being tasked with pumping blood at a much higher pressure against the high resistance of the systemic circulation, since it is now in the position of where the left ventricle is typically located.Simple and complex TGV
In many cases, TGV is accompanied by other heart defects, the most common type being wikt:intracardiac, intracardiac shunt (medical), shunts such as atrial septal defect including patent foramen ovale, ventricular septal defect, and patent ductus arteriosus. Stenosis, or other defects, of valves and/or Blood vessel, vessels may also be present. When no other heart defects are present it is called 'simple' TGV; when other defects are present it is called 'complex' TGV.Symptoms and signs
Symptoms may appear at birth or after birth. The severity of symptoms depends on the type of TGV, and the type and size of other heart defects that may be present (Ventricular septal defect, Atrial septal defect, or Patent ductus arteriosus). Most babies with TGA have blue skin color (cyanosis) in the first hours or days of their lives, since dextro-TGA is the more common type. Other symptoms include: •Fast breathing (tachypnea) •Difficulty breathing (dyspnea) •Fast heart rate (tachycardia) •Poor feedingRisk factors
Preexisting diabetes mellitus of a pregnant mother is a risk factor that has been described for the fetus having TGV.Diagnosis
•Electrocardiogram: An electrocardiogram (ECG) records the electrical activity of the heart through the use of electrodes that are placed on the body. The findings through this diagnostic method are not specific to only TGA. If TGA is present, rightward deviation of the QRS complex and right ventricular hypertrophy or biventricular hypertrophy may be noted. •Chest X-Ray: On chest X-ray (CXR), transposition of the great vessels typically shows a cardio-Mediastinum, mediastinal silhouette appearing as an "''egg on a string'' ", in which the Cardiomegaly, enlarged heart represents an egg on its side and the narrowed, Atrophy, atrophic thymus of the superior mediastinum represents the string. •Echocardiogram: An echocardiogram is an ultrasound of the heart that accurately assesses the heart’s structure and function, and can show the specific features of TGA, if present. This imaging modality allows for the definitive diagnosis of TGA to be made. •Cardiac catheterization: Catheterization is done if other diagnostic tests do not provide enough information to make a diagnosis, or if a neonate is unstable. During this procedure, a catheter is inserted in the artery or vein in the groin and makes its way up to the heart. Dye is used to visualize the heart’s structures on x-ray. It can also measure the pressures in the heart and lungs.Treatment
All infants with TGA will need surgery to correct the defect. Life expectancy is only a few months if corrective surgery is not performed. Before surgery: For newborns with transposition, prostaglandins can be given to keep the ductus arteriosus open which allows for the mixing of the otherwise isolated pulmonary and systemic circuits. Thus, oxygenated blood that recirculates back to the lungs can mix with blood that circulates throughout the body and can keep the body oxygenated until surgery can be performed. Atrial septostomy can also be performed, usually with a cardiac catheter instead of surgery, to enlarge a natural connection between the heart's upper chambers (atria). This will allow for the oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood to mix, resulting in improved oxygen delivery to the baby's body. Surgery: The Arterial switch operation is a surgery where the pulmonary artery and the aorta are moved to their normal positions. This is the most common surgery done to correct dextro-TGA, and is considered the definitive treatment. The Atrial switch operation is an alternative surgical option when the arterial switch is not feasible due to the particular coronary artery anatomy. This operation creates a tunnel (baffle) between the heart's two upper chambers (atria). After surgery: Lifelong follow-up care with a cardiologist is needed. Most infants who undergo surgery have their symptoms relieved and are able to live a normal life. Potential complications that can occur include coronary artery problems, heart valves problems or irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias).History
Transposition of the Great Vessels was first described in 1797 by Matthew Baillie.Additional images

See also
* Levo-Transposition of the great arteries * Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries * Mustard procedure, Mustard ProcedureReferences
External links
{{Congenital malformations and deformations of circulatory system Congenital heart defects Neonatology