Tooth discoloration on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Tooth discoloration is abnormal

 The appearance and perception of a tooth is the result of a complex interaction of factors such as lighting conditions,
The appearance and perception of a tooth is the result of a complex interaction of factors such as lighting conditions,
 Extrinsic discolorations are common and have many different causes. The same range of factors are capable of staining the surface of restorations (e.g., composite fillings, porcelain crowns). Some extrinsic discolorations that are allowed to remain for a long time may become intrinsic.
*
Extrinsic discolorations are common and have many different causes. The same range of factors are capable of staining the surface of restorations (e.g., composite fillings, porcelain crowns). Some extrinsic discolorations that are allowed to remain for a long time may become intrinsic.
*

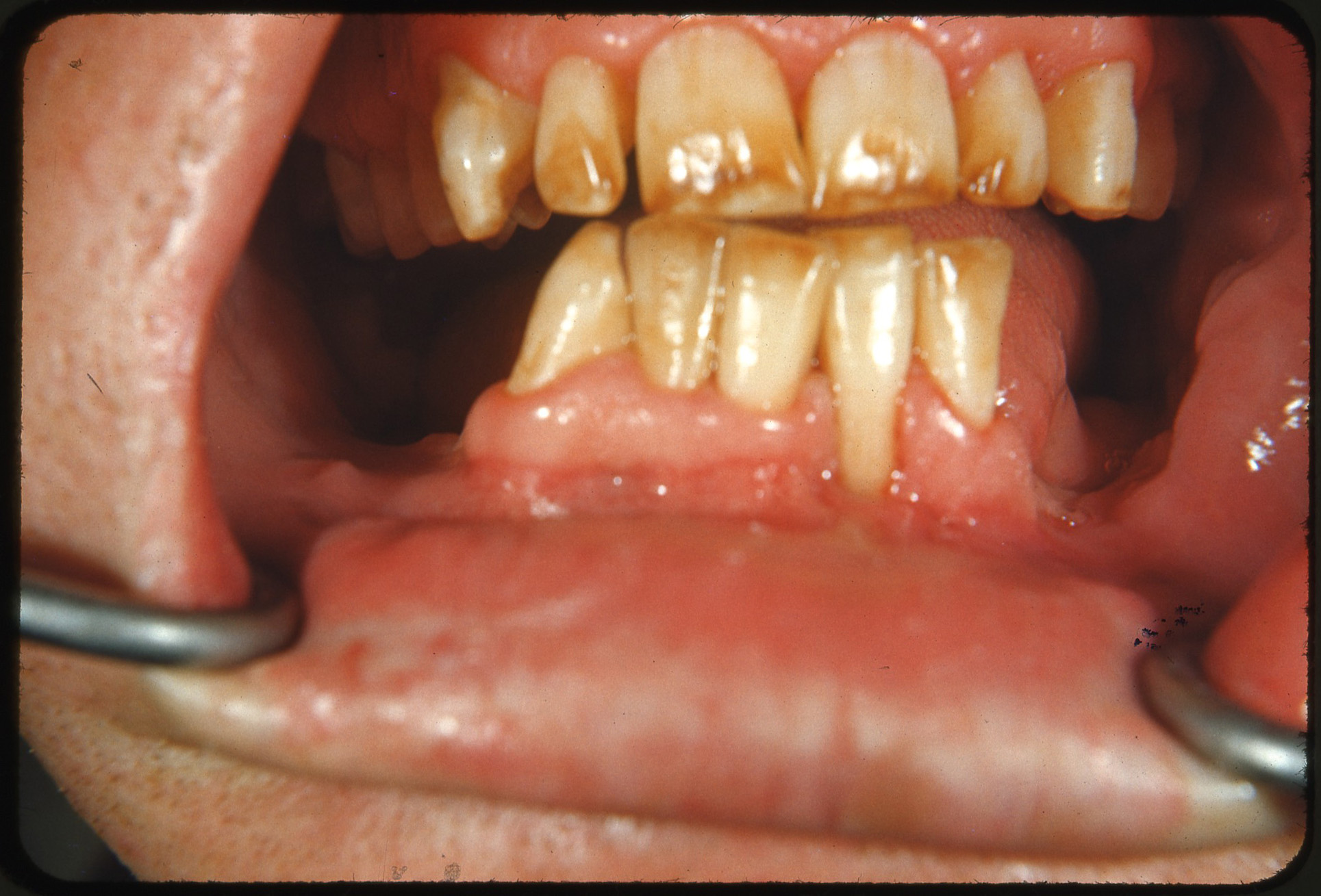 Fluorosis may occur when there is chronic and excessive exposure to fluoride during the years of tooth development. Fluoride is a naturally occurring mineral in water, although some regions have higher levels than others, and in some areas fluoride is added to water supplies in low levels to help prevent tooth decay. Exposure can also occur via bottled water and fluoride toothpaste. In its mildest form, fluorosis appears as small opaque white flecks on the enamel surface. More severe cases show severely hypoplastic patches of enamel, which are also prone to accumulation of surface stains. Chronological, fine white bands of fluorosis may be seen that correspond to the times of high exposure to fluoride.
Fluorosis may occur when there is chronic and excessive exposure to fluoride during the years of tooth development. Fluoride is a naturally occurring mineral in water, although some regions have higher levels than others, and in some areas fluoride is added to water supplies in low levels to help prevent tooth decay. Exposure can also occur via bottled water and fluoride toothpaste. In its mildest form, fluorosis appears as small opaque white flecks on the enamel surface. More severe cases show severely hypoplastic patches of enamel, which are also prone to accumulation of surface stains. Chronological, fine white bands of fluorosis may be seen that correspond to the times of high exposure to fluoride.

tooth
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tear ...
color, hue
In color theory, hue is one of the main properties (called Color appearance model#Color appearance parameters, color appearance parameters) of a color, defined technically in the CIECAM02 model as "the degree to which a Stimulus (physiology ...
or translucency. External discoloration is accumulation of stains on the tooth surface. Internal discoloration is due to absorption of pigment particles into tooth structure. Sometimes there are several different co-existent factors responsible for discoloration.
Normal tooth shade

 The appearance and perception of a tooth is the result of a complex interaction of factors such as lighting conditions,
The appearance and perception of a tooth is the result of a complex interaction of factors such as lighting conditions, translucency
In the field of optics, transparency (also called pellucidity or diaphaneity) is the physical property of allowing light to pass through the material without appreciable scattering of light. On a macroscopic scale (one in which the dimensions a ...
, opacity, light scattering
Scattering is a term used in physics to describe a wide range of physical processes where moving particles or radiation of some form, such as light or sound, are forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by localized non-uniformities (including ...
, gloss and the human eye and brain. Of these, the intrinsic pigmentation of a tooth is the most influential, which in turn is determined by genetic and natural factors. Light hitting a tooth undergoes reflection Reflection or reflexion may refer to:
Science and technology
* Reflection (physics), a common wave phenomenon
** Specular reflection, reflection from a smooth surface
*** Mirror image, a reflection in a mirror or in water
** Signal reflection, in ...
, absorption
Absorption may refer to:
Chemistry and biology
* Absorption (biology), digestion
**Absorption (small intestine)
*Absorption (chemistry), diffusion of particles of gas or liquid into liquid or solid materials
*Absorption (skin), a route by which ...
and transmission by varying degrees in each tissue layer of the tooth substance. Reflected light detected by the human eye determines the perceived appearance of a tooth.
Teeth have a thin enamel layer on the outer surface. The enamel layer is whiter and semitransparent, and contributes blue, pink green tints to the tooth color. The underlying dentin
Dentin () (American English) or dentine ( or ) (British English) ( la, substantia eburnea) is a calcified tissue of the body and, along with enamel, cementum, and pulp, is one of the four major components of teeth. It is usually covered by ena ...
layer is darker than enamel, yellow-brown in color, and less transparent. Dentin forms the bulk of the tooth substance, and contributes most to the overall tooth color. At the core of the tooth is soft connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tiss ...
termed the dental pulp
The pulp is the connective tissue, nerves, blood vessels, and odontoblasts that comprise the innermost layer of a tooth. The pulp's activity and signalling processes regulate its behaviour.
Anatomy
The pulp is the neurovascular bundle cent ...
. The pulp is pink/red due to its vascularity, but is rarely visible through the overlying enamel and dentin unless the thickness of these layers is reduced by tooth wear (or rarely internal resorption).
Public opinion of what is normal tooth shade tends to be distorted. Portrayals of cosmetically enhanced teeth are common in the media. In one report, the most common tooth shade in the general population ranged from A1 to A3 on the VITA
Vita or VITA (plural vitae) is Latin for "life", and may refer to:
* ''Vita'', the usual start to the title of a biography in Latin, by which (in a known context) the work is often referred to; frequently of a saint, then called hagiography
* Vit ...
classical A1-D4 shade guide.
Tooth color varies according to race, gender and geographic region. Females generally have slightly whiter teeth than males, partly because females' teeth are smaller, and therefore there is less bulk of dentin, partially visible through the enamel layer. For the same reason, larger teeth such as the molars and the canine (cuspid) teeth tend to be darker. Baby teeth (deciduous teeth
Deciduous teeth or primary teeth, also informally known as baby teeth, milk teeth, or temporary teeth,Illustrated Dental Embryology, Histology, and Anatomy, Bath-Balogh and Fehrenbach, Elsevier, 2011, page 255 are the first set of teeth in the ...
) are generally whiter than the adult teeth that follow, again due to differences in the ratio of enamel to dentin.
Causes
Extrinsic discoloration
 Extrinsic discolorations are common and have many different causes. The same range of factors are capable of staining the surface of restorations (e.g., composite fillings, porcelain crowns). Some extrinsic discolorations that are allowed to remain for a long time may become intrinsic.
*
Extrinsic discolorations are common and have many different causes. The same range of factors are capable of staining the surface of restorations (e.g., composite fillings, porcelain crowns). Some extrinsic discolorations that are allowed to remain for a long time may become intrinsic.
* Dental plaque
Dental plaque is a biofilm of microorganisms (mostly bacteria, but also fungi) that grows on surfaces within the mouth. It is a sticky colorless deposit at first, but when it forms tartar, it is often brown or pale yellow. It is commonly found bet ...
: Although usually virtually invisible on the tooth surface, plaque may become stained by chromogenic bacteria such as ''Actinomyces
''Actinomyces'' is a genus of the Actinomycetia class of bacteria. They all are gram-positive. ''Actinomyces'' species are facultatively anaerobic and they grow best under anaerobic conditions. ''Actinomyces'' species may form endospores, and ...
'' species.
* Calculus
Calculus, originally called infinitesimal calculus or "the calculus of infinitesimals", is the mathematical study of continuous change, in the same way that geometry is the study of shape, and algebra is the study of generalizations of arithm ...
: Neglected plaque eventually calcifies, and leads to formation of a hard deposit on the teeth, especially around the gumline. The color of calculus varies, and may be grey, yellow, black or brown.
* Tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
: Tar
Tar is a dark brown or black viscous liquid of hydrocarbons and free carbon, obtained from a wide variety of organic materials through destructive distillation. Tar can be produced from coal, wood, petroleum, or peat. "a dark brown or black bit ...
in smoke from tobacco products (and also smokeless tobacco
Smokeless tobacco is a tobacco products, tobacco product that is used by means other than smoking. Their use involves chewing, sniffing, or placing the product between gum and the cheek or lip. Smokeless tobacco products are produced in various f ...
products) tends to form a yellow-brown-black stain around the necks of the teeth above the gumline.
* Betel
The betel (''Piper betle'') is a vine of the family Piperaceae, which includes pepper and kava. The betel plant is native to Southeast Asia. It is an evergreen, dioecious perennial, with glossy heart-shaped leaves and white catkins. Betel plan ...
chewing.
* Certain foods and drinks. Foods, such as vegetables, that are rich with carotenoids
Carotenoids (), also called tetraterpenoids, are yellow, orange, and red organic pigments that are produced by plants and algae, as well as several bacteria, and fungi. Carotenoids give the characteristic color to pumpkins, carrots, parsnips, ...
or xanthonoids
A xanthonoid is a chemical natural phenolic compound formed from the xanthone backbone. Many members of the Clusiaceae contain xanthonoids.
Xanthonoid biosynthesis in cell cultures of ''Hypericum androsaemum'' involves the presence of a benzophe ...
can stain teeth. Ingesting colored liquids like sports drinks, cola, coffee, tea and red wine can discolor teeth.
* Certain topical medications.
**Chlorhexidine
Chlorhexidine (CHX) (commonly known by the salt forms chlorhexidine gluconate and chlorhexidine digluconate (CHG) or chlorhexidine acetate) is a disinfectant and antiseptic that is used for skin disinfection before surgery and to sterilize surg ...
(antiseptic
An antiseptic (from Greek ἀντί ''anti'', "against" and σηπτικός ''sēptikos'', "putrefactive") is an antimicrobial substance or compound that is applied to living tissue/skin to reduce the possibility of infection, sepsis, or putre ...
mouthwash
Mouthwash, mouth rinse, oral rinse, or mouth bath is a liquid which is held in the mouth passively or swilled around the mouth by contraction of the perioral muscles and/or movement of the head, and may be gargling, gargled, where the head is ti ...
) binds to tannin
Tannins (or tannoids) are a class of astringent, polyphenolic biomolecules that bind to and precipitate proteins and various other organic compounds including amino acids and alkaloids.
The term ''tannin'' (from Anglo-Norman ''tanner'', ...
s, meaning that prolonged use in persons who consume coffee, tea or red wine is associated with extrinsic staining (i.e., removable staining) of teeth.
**Cetylpyridinium chloride
Cetylpyridinium chloride (CPC) is a cationic quaternary ammonium compound used in some types of mouthwashes, toothpastes, lozenges, throat sprays, breath sprays, and nasal sprays. It is an antiseptic that kills bacteria and other microorganisms ...
, which is found in many antimicrobial
An antimicrobial is an agent that kills microorganisms or stops their growth. Antimicrobial medicines can be grouped according to the microorganisms they act primarily against. For example, antibiotics are used against bacteria, and antifungals ar ...
mouthwashes, can result in staining due to dead bacterial residue.
* Metallic compounds. Exposure to such metallic compounds may be in the form of medication or other environmental exposure. Examples include iron (black stain), iodine (black), copper (green), nickel (green) and cadmium (yellow-brown).
* Antibiotics. Tetracycline and its derivatives are capable of intrinsic discoloration (discussed below). However other antibiotics may form insoluble complexes with calcium, iron and other elements that cause extrinsic staining.
Intrinsic discoloration
Causes of intrinsic discoloration generally fall into those that occur during tooth development and those acquired later in life. The known causes of intrinsic staining are listed below, however some causes are unknown.Dental caries
Dental caries
Tooth decay, also known as cavities or caries, is the breakdown of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria. The cavities may be a number of different colors from yellow to black. Symptoms may include pain and difficulty with eating. Complicatio ...
(tooth decay) begins as an opaque white spot on the surface of the enamel. As demineralization progresses, the various lesion eventually cavitates and the underlying brown color becomes visible.
Fluorosis

 Fluorosis may occur when there is chronic and excessive exposure to fluoride during the years of tooth development. Fluoride is a naturally occurring mineral in water, although some regions have higher levels than others, and in some areas fluoride is added to water supplies in low levels to help prevent tooth decay. Exposure can also occur via bottled water and fluoride toothpaste. In its mildest form, fluorosis appears as small opaque white flecks on the enamel surface. More severe cases show severely hypoplastic patches of enamel, which are also prone to accumulation of surface stains. Chronological, fine white bands of fluorosis may be seen that correspond to the times of high exposure to fluoride.
Fluorosis may occur when there is chronic and excessive exposure to fluoride during the years of tooth development. Fluoride is a naturally occurring mineral in water, although some regions have higher levels than others, and in some areas fluoride is added to water supplies in low levels to help prevent tooth decay. Exposure can also occur via bottled water and fluoride toothpaste. In its mildest form, fluorosis appears as small opaque white flecks on the enamel surface. More severe cases show severely hypoplastic patches of enamel, which are also prone to accumulation of surface stains. Chronological, fine white bands of fluorosis may be seen that correspond to the times of high exposure to fluoride.
Trauma
Dental trauma may result in discolorations. Following luxation injuries red discoloration may develop almost instantly. This is due to severance of the venous microcirculation to a tooth, while the arteries continue to supply blood to the pulp. The blood is then decomposed gradually and a blue-brown discoloration develops. Teeth may turn grey following trauma-inducedpulp necrosis Pulp necrosis is a clinical diagnostic category indicating the death of the pulp and nerves of the pulp chamber and root canal of a tooth which may be due to bacterial sequelae, trauma and chemical or mechanical irritation. It is often the end resul ...
(death of the pulp). This discoloration typically develops weeks or months after the injury and is caused by incorporation of pigments released during the breakdown of the pulpal tissue and blood into the dentin.
Yellow discoloration may occur following pulp canal obliteration, i.e., the sealing up of the pulp. Trauma to a developing adult tooth (e.g., intrusion of a baby tooth into the bone) may affect the enamel layer of the adult tooth. This becomes apparent when the adult tooth erupts into the mouth.
Pulp necrosis
Teeth die mainly as a result of extensive tooth decay, however this may also occur following dental trauma or heavy drilling down of the tooth during tooth preparation prior to restoration.Internal resorption
Internal resorption may sometimes follow dental trauma (although in other cases it appears unrelated). This is where the dentin is resorbed and replaced instead byhyperplastic
Hyperplasia (from ancient Greek ὑπέρ ''huper'' 'over' + πλάσις ''plasis'' 'formation'), or hypergenesis, is an enlargement of an organ or tissue caused by an increase in the amount of organic tissue that results from cell proliferatio ...
, vascular pulp tissue. As this process starts to approach the external surface of the tooth, a pink hue of this replacement pulp tissue may become visible through the remaining overlying tooth substance. This appearance is sometimes termed "pink tooth of Mummery".
Root canal treatment
Internal staining is common followingroot canal treatment
Root canal treatment (also known as endodontic therapy, endodontic treatment, or root canal therapy) is a treatment sequence for the infected pulp of a tooth which is intended to result in the elimination of infection and the protection of ...
, however the exact causes for this are not completely understood. Failure to completely clean out the necrotic soft tissue of the pulp system may cause staining, and certain root canal materials (e.g., gutta percha
Gutta-percha is a tree of the genus ''Palaquium'' in the family Sapotaceae. The name also refers to the rigid, naturally biologically inert, resilient, electrically nonconductive, thermoplastic latex derived from the tree, particularly from ' ...
and root canal sealer cements) can also. Another possible factor is the lack of pulp pressure in dentinal tubules once the pulp is removed, leading to incorporation of dietary stains in dentin.
Amalgam fillings

Amalgam
Amalgam most commonly refers to:
* Amalgam (chemistry), mercury alloy
* Amalgam (dentistry), material of silver tooth fillings
** Bonded amalgam, used in dentistry
Amalgam may also refer to:
* Amalgam Comics, a publisher
* Amalgam Digital
...
fillings often stain the tooth they are placed in. This is most noticeable in very old fillings, as pigment slowly leaches out of the amalgam filling material and its associated corroded surfaces. In addition, metallic fillings cast a shadow that can be visible through the tooth and make it appear darker.
Tetracycline and tetracycline-derivatives
Tetracycline
Tetracycline, sold under various brand names, is an oral antibiotic in the tetracyclines family of medications, used to treat a number of infections, including Acne vulgaris, acne, cholera, brucellosis, plague (disease), plague, malaria, and sy ...
is a broad spectrum antibiotic, and its derivative minocycline
Minocycline, sold under the brand name Minocin among others, is a tetracycline antibiotic medication used to treat a number of bacterial infections such as pneumonia. It is generally less preferred than the tetracycline doxycycline. It is also ...
is common in the treatment of acne
Acne, also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term Cutaneous condition, skin condition that occurs when Keratinocyte, dead skin cells and Sebum, oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include comedo, black ...
. The drug is able to chelate calcium ions and is incorporated into teeth, cartilage and bone. Ingestion during the years of tooth development causes a yellow-green discoloration of dentin, which is visible through the enamel and fluorescent under ultraviolet light. Later, the tetracycline oxidizes and the staining becomes more brown and no longer fluoresces under UV light. Other drugs derived from tetracycline such as glycylcycline Glycylcyclines are a class of antibiotics derived from tetracycline. These tetracycline analogues are specifically designed to overcome two common mechanisms of Tetracycline#Mechanism and resistance, tetracycline resistance, namely resistance media ...
share this side effect. Because tetracyclines cross the placenta, a child may have tooth staining if the drugs are administered during the mother's pregnancy.
Genetic disorders
Several genetic disorders affect tooth development (odontogenesis
Tooth development or odontogenesis is the complex process by which teeth form from embryonic cells, grow, and erupt into the mouth. For human teeth to have a healthy oral environment, all parts of the tooth must develop during appropriate stage ...
), and lead to abnormal tooth appearance and structure. Enamel hypoplasia
Enamel hypoplasia is a defect of the teeth in which the enamel is deficient in quantity, caused by defective enamel matrix formation during enamel development, as a result of inherited and acquired systemic condition(s). It can be identified as m ...
and enamel hypocalcification
Enamel hypocalcification is a defect of tooth enamel in which normal amounts of enamel are produced but are hypomineralized. In this defect the enamel is softer than normal. Some areas in enamel are hypocalcified: enamel spindles, enamel tufts, an ...
are examples of defective enamel that potentially gives a discolored appearance to the tooth. Teeth affected in this way are also usually more susceptible to further staining acquired throughout life.
Amelogenesis imperfecta
Amelogenesis imperfecta (AI) is a congenital disorder which presents with a rare abnormal formation of the enamel or external layer of the crown of teeth, unrelated to any systemic or generalized conditions. Enamel is composed mostly of mineral, ...
is a rare condition that affects the formation of enamel (amelogenesis
Amelogenesis is the formation of enamel on teeth and begins when the crown is forming during the advanced bell stage of tooth development after dentinogenesis forms a first layer of dentin. Dentin must be present for enamel to be formed. Amelobla ...
). The enamel is fragile, the teeth appear yellow or brown, and surface stains build up more readily.
Dentinogenesis imperfecta
Dentinogenesis imperfecta (DI) is a genetic disorder of tooth development. It is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, as a result of mutations on chromosome 4q21, in the dentine sialophosphoprotein gene (DSPP). It is one of the most frequen ...
is a defect of dentin formation, and the teeth may be discolored yellow-brown, deep amber or blue-grey with increased translucency. Dentinal dysplasia is another disorder of dentin.
Congenital erythropoietic porphyria
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can r ...
(Gunther disease) is a rare congenital form of porphyria
Porphyria is a group of liver disorders in which substances called porphyrins build up in the body, negatively affecting the skin or nervous system. The types that affect the nervous system are also known as acute porphyria, as symptoms are ra ...
, and may be associated with red or brown discolored teeth.
Hyperbilirubinemia
Bilirubin (BR) (Latin for "red bile") is a red-orange compound that occurs in the normal catabolic pathway that breaks down heme in vertebrates. This catabolism is a necessary process in the body's clearance of waste products that arise from the ...
during the years of tooth formation may make bilirubin
Bilirubin (BR) (Latin for "red bile") is a red-orange compound that occurs in the normal catabolic pathway that breaks down heme in vertebrates. This catabolism is a necessary process in the body's clearance of waste products that arise from the ...
incorporate into the dental hard tissues, causing yellow-green or blue-green discoloration. One such condition is hemolytic disease of the newborn
Hemolytic disease of the newborn, also known as hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn, HDN, HDFN, or erythroblastosis foetalis, is an alloimmune condition that develops in a fetus at or around birth, when the IgG molecules (one of the five ...
(erythroblastosis fetalis).
Thalassemia
Thalassemias are inherited blood disorders characterized by decreased hemoglobin production. Symptoms depend on the type and can vary from none to severe. Often there is mild to severe anemia (low red blood cells or hemoglobin). Anemia can result ...
and sickle cell anemia
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a group of blood disorders typically inherited from a person's parents. The most common type is known as sickle cell anaemia. It results in an abnormality in the oxygen-carrying protein haemoglobin found in red blo ...
may be associated with blue, green or brown tooth discoloration.
A high proportion of children with cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a rare genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. Long-term issues include difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent lung infections. O ...
have discolored teeth. This is possibly the result of exposure to tetracycline during odontogenesis, however cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator
A cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct envelope and division compared with the nearby tissue. Hence, it is a cluster of cells that have grouped together to form a sac (like the manner in which water molecules group together to form a bubble) ...
has also been demonstrated to be involved in enamel formation, suggesting that the disease has some influence on tooth discoloration regardless of exposure to tetracyclines.
Aging
Intrinsic discoloration tends to accompany aging. Throughout life deposition of secondary dentin occurs along the internal walls of the pulp chamber. Secondary dentin is darker and more opaque than primary dentin. This gives the dentin an overall darker appearance. At the same time, the enamel layer is gradually thinned by tooth wear processes such as attrition and acid erosion, a degree of which is considered normal. Enamel also becomes less porous and phosphate deficient.Management
Discoloration of the front teeth is one of the most common reasons people seek dental care. However, many people with teeth of normal shade ask for them to be whitened. Management of tooth discoloration depends on the cause. Most discoloration is harmless and may or may not be of cosmetic concern to the individual. In other cases it may indicate underlying pathology such aspulp necrosis Pulp necrosis is a clinical diagnostic category indicating the death of the pulp and nerves of the pulp chamber and root canal of a tooth which may be due to bacterial sequelae, trauma and chemical or mechanical irritation. It is often the end resul ...
or rarely a systemic disorder.
Most extrinsic discoloration is readily removed by cleaning the teeth, whether with "whitening" (i.e., abrasive) toothpaste at home, or as treatment carried out by a professional (e.g., scaling
Scaling may refer to:
Science and technology
Mathematics and physics
* Scaling (geometry), a linear transformation that enlarges or diminishes objects
* Scale invariance, a feature of objects or laws that do not change if scales of length, energ ...
and/or polishing
Polishing is the process of creating a smooth and shiny surface by rubbing it or by applying a chemical treatment, leaving a clean surface with a significant specular reflection (still limited by the index of refraction of the material accordin ...
). To prevent future buildup of extrinsic stains, identification of the cause (e.g., smoking) is required.
Intrinsic discoloration generally requires one of the many types of tooth bleaching
Tooth whitening or tooth bleaching is the process of lightening the color of human teeth. Whitening is often desirable when teeth become yellowed over time for a number of reasons, and can be achieved by changing the intrinsic or extrinsic color o ...
. Alternatively the appearance of the tooth can be hidden with dental restorations (e.g., composite fillings, veneers, crowns).
References
External links
{{Authority control Tooth pathology