Tonguing on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
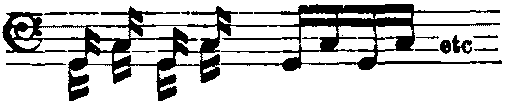 Tonguing is a technique used with
Tonguing is a technique used with
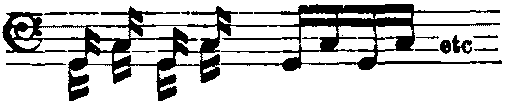 Tonguing is a technique used with
Tonguing is a technique used with wind instrument
A wind instrument is a musical instrument that contains some type of resonator (usually a tube) in which a column of air is set into vibration by the player blowing into (or over) a mouthpiece set at or near the end of the resonator. The pitc ...
s to enunciate notes using the tongue
The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for mastication and swallowing as part of the digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper surface (dorsum) is covered by taste ...
on the palate
The palate () is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity.
A similar structure is found in crocodilians, but in most other tetrapods, the oral and nasal cavities are not truly separ ...
or the reed
Reed or Reeds may refer to:
Science, technology, biology, and medicine
* Reed bird (disambiguation)
* Reed pen, writing implement in use since ancient times
* Reed (plant), one of several tall, grass-like wetland plants of the order Poales
* ...
or mouthpiece. A silent "tee" is made when the tongue strikes the reed or roof of the mouth causing a slight breach in the air flow through the instrument. If a more soft tone is desired, the syllable "da" (as in ''dou''ble) is preferred. The technique also works for whistling
Whistling without the use of an artificial whistle is achieved by creating a small opening with one's lips, usually after applying moisture (licking one's lips or placing water upon them) and then blowing or sucking air through the space. The a ...
. Tonguing also refers to articulation, which is how a musician begins the note (punchy, legato, or a breath attack) and how the note is released (air release, tongued release, etc.) For wind players, articulation is commonly spoken of in terms of tonguing because the tongue is used to stop and allow air to flow in the mouth. Tonguing does not apply to non wind instruments, but articulation does apply to all instruments.
An alteration called "double-tonguing" or "double-articulation" is used when the music being performed has many rapid notes in succession too fast for regular articulation. In this case, the tongue makes a silent "tee-kee".Arban's Complete Conservatory Method for Trumpet The Authentic Edition, p.153 (The actual tongue positioning varies slightly by instrument. Clarinetists may go "too-koo" but a bassoonist may actually say "taco".) Double-articulation allows the tongue to stop the airflow twice as fast when mastered. If the music specifies a ''pizzicato
Pizzicato (, ; translated as "pinched", and sometimes roughly as "plucked") is a playing technique that involves plucking the strings of a string instrument. The exact technique varies somewhat depending on the type of instrument :
* On bowe ...
'' sequence, the musician might perform this as a rapid sequence of the articulated note, thus: "tee-kee-tee-kee-tee-kee-..." etc., in ''staccato
Staccato (; Italian for "detached") is a form of musical articulation. In modern notation, it signifies a note of shortened duration, separated from the note that may follow by silence. It has been described by theorists and has appeared in music ...
''. When beginning with "da", the second syllable is "ga". Double tonguing is easiest on brass instruments, and it is more difficult for some woodwind instruments, primarily the clarinet and saxophone.
There is also "triple-tonguing", used in passages of triplets: "tee-tee-kee-tee-tee-kee", or less commonly "tee-kee-tee-tee-kee-tee". Cross-beat tonguing, used for dotted rhythms ( Notes inégales: louré or pointé): tu-ru, with ''ru'' falling on the longer note on the beat. Another method was made by Earl D. Irons, this method was a tee-kee-tee kee-tee-kee. This triple tonguing method is most likely the fastest if done correctly. The reason for this is that the tee and kee never repeat itself. Earl D. Irons is the author of 27 Groups Of Exercises, a book full of lip-slurs, double tonguing, and triple tonguing. Such as:
: - (=)
: tu-ru
There are different ways of tonguing for the flute. Some flutists tongue between the teeth; others do it between the lips as if spitting; others do it behind the teeth in the roof of the mouth as with trill consonant
In phonetics, a trill is a consonantal sound produced by vibrations between the active articulator and passive articulator. Standard Spanish as in , for example, is an alveolar trill.
A trill is made by the articulator being held in place ...
s. With this roof articulation the flutist thinks of the words dah-dah and for double tonguing it is dah-gah-dah-gah.
Tonguing is indicated in the score by the use of accent marks. The absence of slurs is usually understood to imply that each note should be tongued separately. When a group of notes is slurred together, the player is expected to tongue the first note of the group and not tongue any of the other notes, unless those notes have accent marks.
Trombone players must lightly tongue many slurs by tonguing "da"; otherwise, the result would be a glissando
In music, a glissando (; plural: ''glissandi'', abbreviated ''gliss.'') is a glide from one pitch to another (). It is an Italianized musical term derived from the French ''glisser'', "to glide". In some contexts, it is distinguished from the ...
. The bagpipes require finger articulations ("graces"), since direct tonguing is impossible.Kite-Powell, Jeffery (2007). ''A Performer's Guide to Renaissance Music'', p.98. Indiana University. .
See also
* Flutter-tonguing * ArticulationSources
{{Musical notation Articulations (music) Tongue