Titanocene Y on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
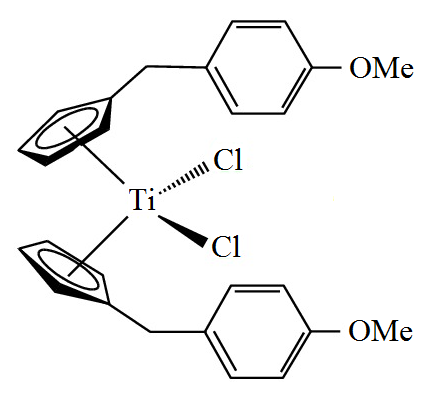 Titanocene Y also known as bis ''p''-methoxybenzyl)cyclopentadienylitanium(IV) dichloride or dichloridobis(η5-(''p''-methoxybenzyl)cyclopentadienyl)titanium is an
Titanocene Y also known as bis ''p''-methoxybenzyl)cyclopentadienylitanium(IV) dichloride or dichloridobis(η5-(''p''-methoxybenzyl)cyclopentadienyl)titanium is an
 Titanocene Y also known as bis ''p''-methoxybenzyl)cyclopentadienylitanium(IV) dichloride or dichloridobis(η5-(''p''-methoxybenzyl)cyclopentadienyl)titanium is an
Titanocene Y also known as bis ''p''-methoxybenzyl)cyclopentadienylitanium(IV) dichloride or dichloridobis(η5-(''p''-methoxybenzyl)cyclopentadienyl)titanium is an organotitanium compound
Organotitanium chemistry is the science of organotitanium compounds describing their physical properties, synthesis, and reactions. Organotitanium compounds in organometallic chemistry contain carbon-titanium chemical bonds. They are reagents in o ...
that has been investigated for use as an anticancer drug.
Discovery
Titanocene dichloride
Titanocene dichloride is the organotitanium compound with the formula ( ''η''5-C5H5)2TiCl2, commonly abbreviated as Cp2TiCl2. This metallocene is a common reagent in organometallic and organic synthesis. It exists as a bright red solid that slowl ...
is known to be a potential anticancer drug since the late 1970s. After initial clinical trials against breast and renal-cell cancer were performed with this compound, the search for improved derivatives started. Particularly, lipophilic titanocene dichloride derivatives derived from fulvene
Fulvene (pentafulvene) is a hydrocarbon with the formula (CH=CH)2C=CH2. It is a prototype of a cross-conjugated hydrocarbon. Fulvene is rarely encountered, but substituted derivatives (fulvenes) are numerous. They are mainly of interest as ligand ...
s were synthesised in structural diversity and this led to the development of bis ''p''-methoxybenzyl)cyclopentadienylitanium(IV) dichloride, which became better known in the literature under its trivial name of Titanocene Y.
Mechanism of action
Titanocene Y is a cytotoxic apoptosis-inducing and anti-angiogenic drug candidate targeting renal-cell cancer and other solid tumors. The compound is transported via serum albumin selectively into cancer cells and targets their DNA by coordinating strongly to phosphate groups. Additionally, Titanocene Y is able to induce apoptosis via the FAS receptor pathway. Very encouraging is the fact that Titanocene Y is breaking platinum-resistance in human colon and human lung cancer cells, which might make it attractive as a cytotoxic component of future 2nd or 3rd line cancer treatments.Animal testing
Titanocene Y was tested extensively ''in vivo''; it showed promising results against xenografted human epidermoid carcinoma and prostate cancer, while best results are reached against breast and renal-cell cancer. Titanocene Y can be given in the mouse in high dosages and it shows generally mild toxicity in the form of diarrhea. Titanocene Y is not patent protected and would therefore benefit from non-commercial sponsoring to develop it into a cytotoxic drug candidate for the treatment of advanced renal-cell cancer – an area in need of better therapies.References
External links
* {{Titanium compounds Titanocenes Chloro complexes Titanium(IV) compounds