Tingrith on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Tingrith is a small village and
Tingrith is a small village and
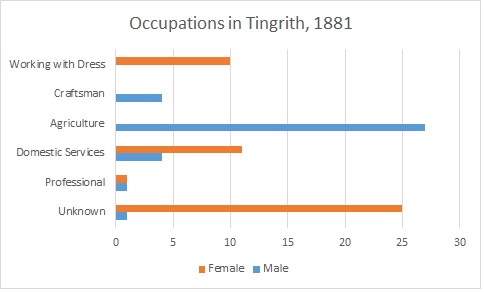
 As seen from the graphs above, today in Tingrith, the most common occupations for males are leading roles, such as managers, directors or senior officials. This is closely followed by jobs in skilled trade. This is very different to the most common occupation in 1881, which was agriculture; very little of this is seen in Tingrith today. The most common occupation among females is a working professional; this is closely followed by jobs in leading roles, such as managers, directors and senior officials. It is clear that far more women are working today than back in 1881, as far more of their occupations are recorded.
As seen from the graphs above, today in Tingrith, the most common occupations for males are leading roles, such as managers, directors or senior officials. This is closely followed by jobs in skilled trade. This is very different to the most common occupation in 1881, which was agriculture; very little of this is seen in Tingrith today. The most common occupation among females is a working professional; this is closely followed by jobs in leading roles, such as managers, directors and senior officials. It is clear that far more women are working today than back in 1881, as far more of their occupations are recorded.
 The area had a larger population around the 1870s of approximately 210 residents, the population then dipped to approximately 110 residents just less than 100 years later, around 1960. This then rose steadily to today's population of 153 residents.
Today the percentage of people over the age of 16, with 5 or more GCSE grades A-C is 20%; higher than the national average of 15.2%. Along with this, the percentage of unemployed in Tingrith is only 1.7%, which is lower than the national average of 4.4%
The area had a larger population around the 1870s of approximately 210 residents, the population then dipped to approximately 110 residents just less than 100 years later, around 1960. This then rose steadily to today's population of 153 residents.
Today the percentage of people over the age of 16, with 5 or more GCSE grades A-C is 20%; higher than the national average of 15.2%. Along with this, the percentage of unemployed in Tingrith is only 1.7%, which is lower than the national average of 4.4%

 Tingrith is a small village and
Tingrith is a small village and civil parish
In England, a civil parish is a type of administrative parish used for local government. It is a territorial designation which is the lowest tier of local government below districts and counties, or their combined form, the unitary authorit ...
in Bedfordshire
Bedfordshire (; abbreviated Beds) is a ceremonial county in the East of England. The county has been administered by three unitary authorities, Borough of Bedford, Central Bedfordshire and Borough of Luton, since Bedfordshire County Council ...
, England. It is located adjacent to the M1 motorway
The M1 motorway connects London to Leeds, where it joins the A1(M) near Aberford, to connect to Newcastle. It was the first inter-urban motorway to be completed in the UK; the first motorway in the country was the Preston By-pass, which ...
near the large village of Toddington. The nearest major town is Luton
Luton () is a town and unitary authority with borough status, in Bedfordshire, England. At the 2011 census, the Luton built-up area subdivision had a population of 211,228 and its built-up area, including the adjacent towns of Dunstable a ...
, located about to the southeast. The parish church of St Nicholas dates back to the 13th century and has Tingrith's only cemetery. The church can seat up to 200 people.
Tingrith has a population of 153 people – a ratio of 78:75 males to females, according to the 2011 census.
Tingrith is mentioned in the Domesday Book
Domesday Book () – the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book" – is a manuscript record of the "Great Survey" of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 by order of King William I, known as William the Conqueror. The manus ...
; the entry states ''Tingrei: Thorgils from Nigel d'Aubigny
Nigel d'Aubigny (''Neel d'Aubigny'' or ''Nigel de Albini'', died 1129), was a Norman Lord and English baron who was the son of Roger d'Aubigny and Amice or Avice de Mowbray. His paternal uncle William was lord of Aubigny, while his father was an ...
''
History
In the 1870s, Tingrith was described as:A parish in Woburn district, Beds; 4 miles E of Woburn, and 4½ SE of Ridgmount r. station. Real property, £1,450. Pop., 226. Houses, 38. The living is a rectory in the diocese of Ely. Value, £240.* Patrons, Misses Trevor. The church is chiefly later English.In the past, the most common occupation for males over the age of 20 in Tingrith was agricultural labour; in 1831 70% of males over the age of 20 were working in agriculture. Other popular occupations during this time were: farmers employing labourers, retail, professionals and servants. In 1881 agricultural work was still very popular in the Tingrith area, with 64% of males working in agriculture. Although information for male occupations was well recorded, 50% of female occupations were unknown in 1881. Of the female occupations that were recorded in 1881, the most common were for women to work in the domestic services or offices or working with dress. As 84% of the occupations were labourers or servants in 1831, it can interpreted that Tingrith at this time was a lower class area. Along with this, in 1831 only 11% of the population were employers or professionals.

 As seen from the graphs above, today in Tingrith, the most common occupations for males are leading roles, such as managers, directors or senior officials. This is closely followed by jobs in skilled trade. This is very different to the most common occupation in 1881, which was agriculture; very little of this is seen in Tingrith today. The most common occupation among females is a working professional; this is closely followed by jobs in leading roles, such as managers, directors and senior officials. It is clear that far more women are working today than back in 1881, as far more of their occupations are recorded.
As seen from the graphs above, today in Tingrith, the most common occupations for males are leading roles, such as managers, directors or senior officials. This is closely followed by jobs in skilled trade. This is very different to the most common occupation in 1881, which was agriculture; very little of this is seen in Tingrith today. The most common occupation among females is a working professional; this is closely followed by jobs in leading roles, such as managers, directors and senior officials. It is clear that far more women are working today than back in 1881, as far more of their occupations are recorded.
Demography
According to the 2011 census, 71.3% of the population of Tingrith are over the age of 30. The ethnic make up of the area is predominantly white; 89.5% of the population in this area are White (English, Welsh, Scottish or Northern Irish). The rest of the population are White Irish (3.3%), White Other (2.6%), Mixed Ethnic Group- White and Black Caribbean (1.3%), Mixed ethnic group- other (0.7%), Asian/Asian British- Indian (2%) and Black British- Caribbean (0.7%). The area had a larger population around the 1870s of approximately 210 residents, the population then dipped to approximately 110 residents just less than 100 years later, around 1960. This then rose steadily to today's population of 153 residents.
Today the percentage of people over the age of 16, with 5 or more GCSE grades A-C is 20%; higher than the national average of 15.2%. Along with this, the percentage of unemployed in Tingrith is only 1.7%, which is lower than the national average of 4.4%
The area had a larger population around the 1870s of approximately 210 residents, the population then dipped to approximately 110 residents just less than 100 years later, around 1960. This then rose steadily to today's population of 153 residents.
Today the percentage of people over the age of 16, with 5 or more GCSE grades A-C is 20%; higher than the national average of 15.2%. Along with this, the percentage of unemployed in Tingrith is only 1.7%, which is lower than the national average of 4.4%
Housing and transport
The number of houses in Tingrith has steadily grown from 1831. In 1831 there were 27 houses in Tingrith but this rose to 46 houses in 1951 and then dropped to 42 houses ten years later, in 1961. Today there are 59 houses in Tingrith civil parish According to the 2011 census, 49.2% of the Tingrith population own their homes outright; this is almost 20 percentage points higher than the national average. House prices in Tingrith range from approximately £120,000 up to £765,000. The closest rail stations are Flitwick and Harlington, which are within a 2-mile radius of Tingrith. The closest airports are Cranfield (8 miles) and Luton (16 miles).Notable residents
Sandra Kynes, the Pagan author, lived in Tingrith during her time in the United Kingdom. Charles Tanqueray, the founder and distiller ofTanqueray
Tanqueray is an English brand of gin produced by Diageo plc. It originated in London. In 2016 it displaced Beefeater as the number one global seller. While it does not command a sizable market share in its native market, its largest market i ...
Gin in 1830 lived at Tanqueray House.
References
External links
{{authority control Villages in Bedfordshire Civil parishes in Bedfordshire Central Bedfordshire District