Tie (cavity wall) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The tie in a
The tie in a

 Due to its materiality of the tie, its corrosion is related to the extent of the exposure at acidic substances. The major factors of the corrosion are:
* Acidic black ash mortar
* Exposure (coastal or general)
* Coastal areas (
Due to its materiality of the tie, its corrosion is related to the extent of the exposure at acidic substances. The major factors of the corrosion are:
* Acidic black ash mortar
* Exposure (coastal or general)
* Coastal areas (
Holland, Malcolm. ''Practical Guide to Diagnosing Structural Movement In Buildings.'' Hoboken: Wiley, 2012.Whittemore, Herbert L. ''Structural Properties of a Brick Cavity-Wall Construction Sponsored by the Brick Manufacturers Association of New York, Inc..'' Washington, D.C.: U.S. Dept. of Commerce, National Bureau of Standards, 1939.What is Wall Tie?, ''Ancon Building products company Homepage''What are Wall Ties?
by Adrian Dawson, Certified surveyors of remedial treatments C.S.R.T. {{DEFAULTSORT:Tie (Cavity Wall) Building engineering

 The tie in a
The tie in a cavity wall
A cavity wall is a type of wall that has a hollow center. They can be described as consisting of two "skins" separated by a hollow space (cavity). The skins typically are masonry, such as brick or cinder block. Masonry is an absorbent material ...
is a component used to tie the internal and external walls (or leaves)—constructed of bricks
A brick is a type of block used to build walls, pavements and other elements in masonry construction. Properly, the term ''brick'' denotes a block composed of dried clay, but is now also used informally to denote other chemically cured cons ...
or cement blocks—together, making the two parts to act as a homogeneous unit. It is placed in the cavity wall during construction and spans the cavity. The ends of the tie are designed to lock into the mortar. Also incorporated into the design of the tie is means of preventing water transfer from the outer to the inner leaves. In flat ties, this can be a twist. In wire ties, this can be corrugations formed in the wire or again a twist.
Background
Cavity walls often haveinsulation
Insulation may refer to:
Thermal
* Thermal insulation, use of materials to reduce rates of heat transfer
** List of insulation materials
** Building insulation, thermal insulation added to buildings for comfort and energy efficiency
*** Insulated ...
in the cavity which may either partially or fully fill the cavity. Partial fill insulation systems require specialized ties or clips to keep the insulation in position. A vapour barrier
A vapor barrier (or vapour barrier) is any material used for damp proofing, typically a plastic or foil sheet, that resists diffusion of moisture through the wall, floor, ceiling, or roof assemblies of buildings and of packaging to prevent inter ...
may be necessary on the inner wall to prevent interstitial condensation
Interstitial condensation is a type of condensation that may occur within an enclosed wall, roof or floor cavity structure, which can create dampening.
When moisture-laden air at dew point temperature penetrates inside a cavity of the structur ...
. This is often incorporated into the cavity wall insulation
A cavity wall is a type of wall that has a hollow center. They can be described as consisting of two "skins" separated by a hollow space (cavity). The skins typically are masonry, such as brick or cinder block. Masonry is an absorbent material ...
system. The spacing of ties is laid down in building regulations, though there may be variations with specialised blocks. Additional ties are used around window and door openings. Improper installation may lead to water damage or fungus
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from t ...
formation within the cavity, leading to structural and health hazards.
Ties are exposed to water and chemical attack from cement
A cement is a binder, a chemical substance used for construction that sets, hardens, and adheres to other materials to bind them together. Cement is seldom used on its own, but rather to bind sand and gravel ( aggregate) together. Cement mi ...
. They were traditionally made of galvanized steel
Galvanization or galvanizing ( also spelled galvanisation or galvanising) is the process of applying a protective zinc coating to steel or iron, to prevent rusting. The most common method is hot-dip galvanizing, in which the parts are submerg ...
, the fishtail tie being the most common. On high quality work, ties were occasionally made of bronze. In the mid-twentieth century, wire ties were widely used, again made from galvanized steel wire. As time has passed, many galvanized steel ties have deteriorated due to moisture in the outer leaf of brickwork. The corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engi ...
may force apart the cement joints and even result in the collapse of walls if no remedial action is taken. Any cracks appearing in cavity walls dating from the twentieth century need to be investigated before irremediable damage ensues. Horizontal cracking is especially suspect. Failed ties have to be isolated and substitute specialist ties installed by drilling through inner and outer leaves from outside the building. The replacement ties may be fixed mechanically or with special adhesives.
Galvanized steel ties are no longer in use for this reason. For a brief period, plastic ties were used but were not satisfactory. Modern practice is to use stainless steel ties.
Cavity walls were traditionally spaced 2"(50mm) apart. Due to the need for thicker insulation in exterior walls these days, a range of longer ties are now available so that cavities of up to 6"(150mm) can be constructed.
Types of ties
Ties in a cavity wall are typically made of iron, steel, or plastic; though figures are various. Basically, a tie has ring to fasten with mortar on both end like a bow. Ties would be selected by type ofmasonry
Masonry is the building of structures from individual units, which are often laid in and bound together by mortar; the term ''masonry'' can also refer to the units themselves. The common materials of masonry construction are bricks, building ...
, the cavity width, and so on.
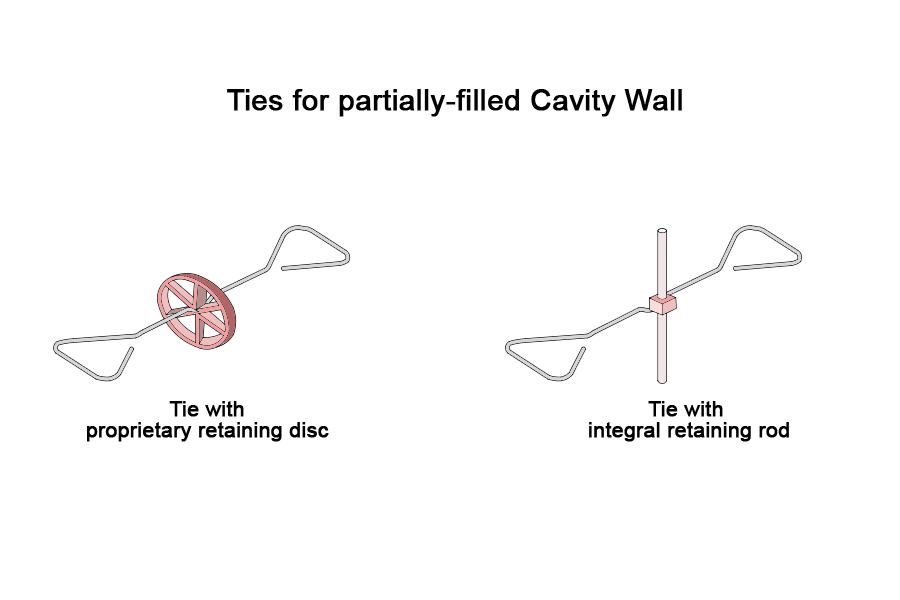
Typically, ties in a cavity wall are double triangular shape (like a bow), though, depending on the existence of another layer (e.g. insulation sheet) at the cavity, which fills the cavity partially, ties include retaining discs or rods.
Tie failure
Failure of ties is an increasing problem with cavity wall ties made from galvanized steel. It arises when the galvanizing is not of sufficient quality and the outer leaf of thecavity wall
A cavity wall is a type of wall that has a hollow center. They can be described as consisting of two "skins" separated by a hollow space (cavity). The skins typically are masonry, such as brick or cinder block. Masonry is an absorbent material ...
allows water penetration, usually due to porous
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void (i.e. "empty") spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0 and 1, or as a percentage between 0% and 100%. Strictly speaking, some tests measure ...
brick/blockwork. If the tie rusts, the swelling effect may cause horizontal, external cracks to appear in the wall. Frost action can swiftly enlarge these cracks to cause damage.
Tie corrosion
Since ties in a cavity wall are typically made of metal (iron or steel), they are prone tocorrode
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engin ...
over time. When metal corrodes, it expands its size, causing ties to lift up from the brickwork
Brickwork is masonry produced by a bricklayer, using bricks and mortar. Typically, rows of bricks called ''courses'' are laid on top of one another to build up a structure such as a brick wall.
Bricks may be differentiated from blocks by si ...
. Cracks caused by vertical loads leave parts of buildings vulnerable to corrosion, such as eaves and gable
A gable is the generally triangular portion of a wall between the edges of intersecting roof pitches. The shape of the gable and how it is detailed depends on the structural system used, which reflects climate, material availability, and aesth ...
walls above purlin
A purlin (or historically purline, purloyne, purling, perling) is a longitudinal, horizontal, structural member in a roof. In traditional timber framing there are three basic types of purlin: purlin plate, principal purlin, and common purlin.
Pu ...
positions, or placed directly beneath openings, where the weight on brickwork is light. Over the time, cracks appear from the top of the wall and extend downward.
Cracks due to tie corrosion at the cavity wall are horizontal and tend to occur at the location of wall ties, normally 6 courses apart. The corrosion causes the walls to detach and tilt, resulting in the outer wall snapping outward. The inner wall is held in place by the added support of floor joists. At the gable
A gable is the generally triangular portion of a wall between the edges of intersecting roof pitches. The shape of the gable and how it is detailed depends on the structural system used, which reflects climate, material availability, and aesth ...
wall, inner walls without these supporting joists, bow inwards. By avoiding several factors accelerating corrosion, it will last more than 60 years.
Acceleration factors of tie corrosion
 Due to its materiality of the tie, its corrosion is related to the extent of the exposure at acidic substances. The major factors of the corrosion are:
* Acidic black ash mortar
* Exposure (coastal or general)
* Coastal areas (
Due to its materiality of the tie, its corrosion is related to the extent of the exposure at acidic substances. The major factors of the corrosion are:
* Acidic black ash mortar
* Exposure (coastal or general)
* Coastal areas (salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quant ...
in the atmosphere)
* Industrial areas ( acid rain)
* Cavity wall insulation
Insulation may refer to:
Thermal
* Thermal insulation, use of materials to reduce rates of heat transfer
** List of insulation materials
** Building insulation, thermal insulation added to buildings for comfort and energy efficiency
*** Insulated ...
Cement
A cement is a binder, a chemical substance used for construction that sets, hardens, and adheres to other materials to bind them together. Cement is seldom used on its own, but rather to bind sand and gravel ( aggregate) together. Cement mi ...
-based mortar, giving an alkaline environment for cavity wall ties, has been used since the Second World War. Alkaline environment is beneficial for ties protecting from acid and procrastinating the corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engi ...
process. Before cement-based mortar, lime
Lime commonly refers to:
* Lime (fruit), a green citrus fruit
* Lime (material), inorganic materials containing calcium, usually calcium oxide or calcium hydroxide
* Lime (color), a color between yellow and green
Lime may also refer to:
Botany ...
-based one was used, which does not present an alkaline environment. Therefore, the majority buildings with wall tie corrosion are built before the Second World War. An alkaline degree gets weaker while exposed at acidic rain over the time.
Moreover, metal corrosion is a chemical reaction that the reaction rate is triggered by water and heat. Thus, some say that cavity wall insulation enhance the ability to grab water longer, so that the environment of the ties damper. Accordingly, the South or South West elevations warmed by the sunlight are warmer, letting ties more at risk for this type of corrosion.
See also
*Anchor plate
An anchor plate, floor plate or wall washer is a large plate or washer connected to a tie rod or bolt. Anchor plates are used on exterior walls of masonry buildings, for structural reinforcement against lateral bowing. Anchor plates are made of ...
* Cavity wall
A cavity wall is a type of wall that has a hollow center. They can be described as consisting of two "skins" separated by a hollow space (cavity). The skins typically are masonry, such as brick or cinder block. Masonry is an absorbent material ...
External links
Holland, Malcolm. ''Practical Guide to Diagnosing Structural Movement In Buildings.'' Hoboken: Wiley, 2012.
by Adrian Dawson, Certified surveyors of remedial treatments C.S.R.T. {{DEFAULTSORT:Tie (Cavity Wall) Building engineering