The First Crusade on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
. Bohemond returned to Europe to fight the Byzantines from Italy but he was defeated in 1108 at Siege of Dyrrhachium (1107–1108)">Dyrrhachium. After Raymond's death, his heirs captured County of Tripoli#Capture by Christian forces">Tripoli in 1109 with Genoese support. Relations between the newly created Crusader states of the
The First Crusade (1096–1099) was the first of a series of religious wars, or
 On the Iberian Peninsula there was no significant Christian polity. The Christian realms of León,
On the Iberian Peninsula there was no significant Christian polity. The Christian realms of León,
 Since its founding, the Byzantine Empire was an historic center of wealth, culture and military power. Under
Since its founding, the Byzantine Empire was an historic center of wealth, culture and military power. Under
 The major ecclesiastical impetuses behind the First Crusade were the Council of Piacenza and subsequent
The major ecclesiastical impetuses behind the First Crusade were the Council of Piacenza and subsequent
Translations and reprints from the original sources of European history
Dept. of History, University of Pennsylvania. Volume 1, No. 2. pp. 2–12. According to one version of the speech, the enthusiastic crowd responded with cries of '' Deus lo volt!––''God wills it!.
 The great French nobles and their trained armies of knights were not the first to undertake the journey towards Jerusalem.Murray, Alan V. (2006)."People's Crusades (1096)". In ''The Crusades – An Encyclopedia''. pp. 939–941. Urban had planned the departure of the first crusade for 15 August 1096, the
The great French nobles and their trained armies of knights were not the first to undertake the journey towards Jerusalem.Murray, Alan V. (2006)."People's Crusades (1096)". In ''The Crusades – An Encyclopedia''. pp. 939–941. Urban had planned the departure of the first crusade for 15 August 1096, the 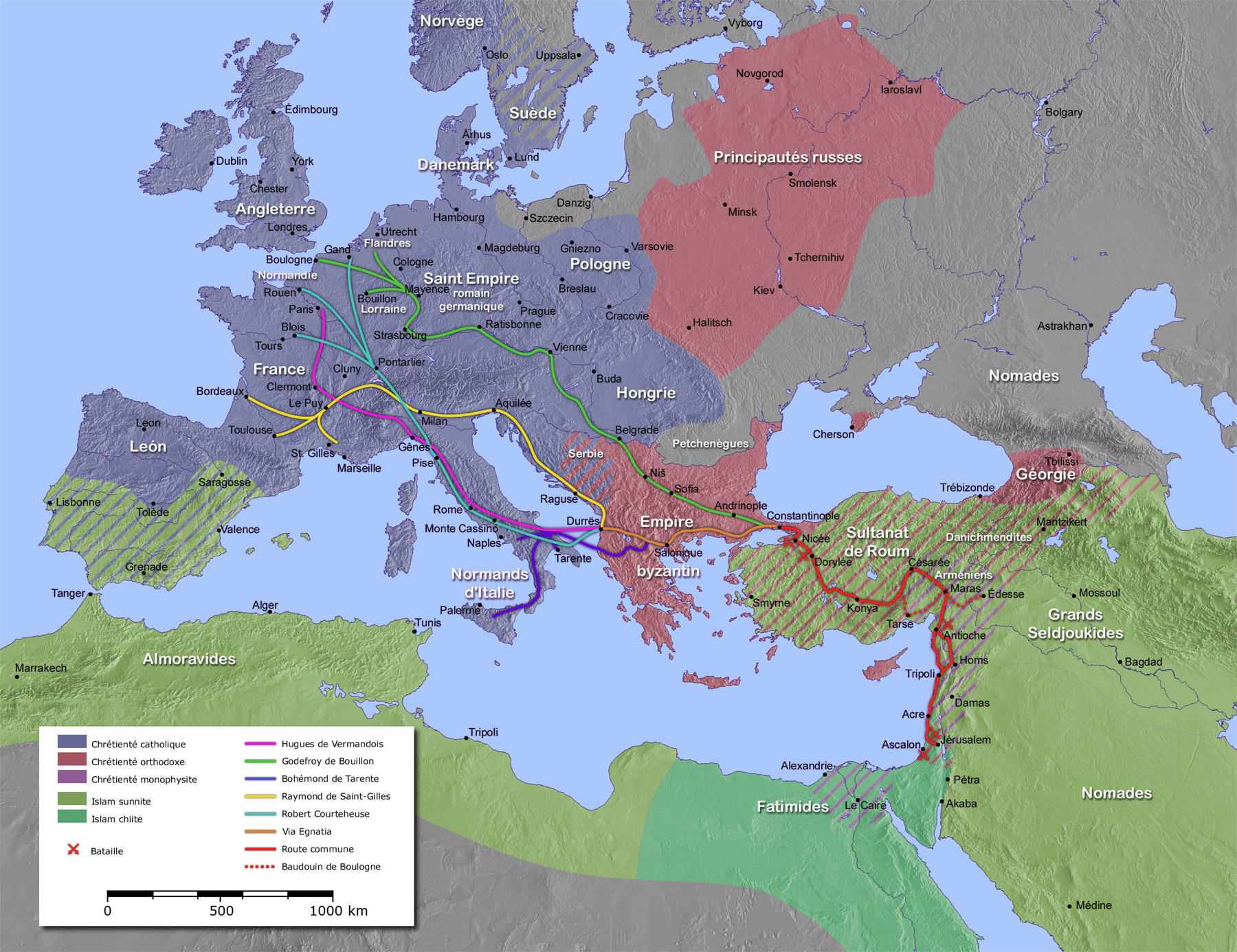 At a local level, the preaching of the First Crusade ignited the
At a local level, the preaching of the First Crusade ignited the
 Recruitment for such a large enterprise was continent-wide. Estimates as to the size of the crusader armies have been given as 70,000 to 80,000 on the number who left Western Europe in the year after Clermont, and more joined in the three-year duration. Estimates for the number of knights range from 7,000 to 10,000; 35,000 to 50,000 foot soldiers; and including non-combatants a total of 60,000 to 100,000. But Urban's speech had been well-planned. He had discussed the crusade with Adhemar of Le Puy and
Recruitment for such a large enterprise was continent-wide. Estimates as to the size of the crusader armies have been given as 70,000 to 80,000 on the number who left Western Europe in the year after Clermont, and more joined in the three-year duration. Estimates for the number of knights range from 7,000 to 10,000; 35,000 to 50,000 foot soldiers; and including non-combatants a total of 60,000 to 100,000. But Urban's speech had been well-planned. He had discussed the crusade with Adhemar of Le Puy and
The First Crusaders' Journey across the Balkan Peninsula
''Byzantion'', 19, 207–221. Raymond of Toulouse led the Provençals down the coast of The crusaders may have expected Alexios to become their leader, but he had no interest in joining them, and was mainly concerned with transporting them into Asia Minor as quickly as possible. In return for food and supplies, Alexios requested the leaders to swear fealty to him and promise to return to the Byzantine Empire any land recovered from the Turks. Godfrey was the first to take the oath, and almost all the other leaders followed him, although they did so only after warfare had almost broken out in the city between the citizens and the crusaders, who were eager to pillage for supplies. Raymond alone avoided swearing the oath, instead pledging that he would simply cause no harm to the empire. Before ensuring that the various armies were shuttled across the Bosporus, Alexios advised the leaders on how best to deal with the Seljuk armies that they would soon encounter.
The crusaders may have expected Alexios to become their leader, but he had no interest in joining them, and was mainly concerned with transporting them into Asia Minor as quickly as possible. In return for food and supplies, Alexios requested the leaders to swear fealty to him and promise to return to the Byzantine Empire any land recovered from the Turks. Godfrey was the first to take the oath, and almost all the other leaders followed him, although they did so only after warfare had almost broken out in the city between the citizens and the crusaders, who were eager to pillage for supplies. Raymond alone avoided swearing the oath, instead pledging that he would simply cause no harm to the empire. Before ensuring that the various armies were shuttled across the Bosporus, Alexios advised the leaders on how best to deal with the Seljuk armies that they would soon encounter.
Letters of the Crusaders
By Dana Carleton Munro (1902. Philadelphia, Pa. pp. 2–11. The fall of Nicaea is viewed as a rare product of close co-operation between the Crusaders and the Byzantines.
 After passing through the
After passing through the
 The crusader army, without Baldwin and Tancred, had marched on to
The crusader army, without Baldwin and Tancred, had marched on to
 The Crusaders' arrival at Jerusalem revealed an arid countryside, lacking in water or food supplies. Here there was no prospect of relief, even as they feared an imminent attack by the local Fatimid rulers. There was no hope of trying to blockade the city as they had at Antioch; the crusaders had insufficient troops, supplies, and time. Rather, they resolved to take the city by assault. They might have been left with little choice, as by the time the Crusader army reached Jerusalem, it has been estimated that only about 12,000 men including 1,500 cavalry remained.. Thus began the decisive Siege of Jerusalem. These contingents, composed of men with differing origins and varying allegiances, were also approaching another low ebb in their camaraderie. While Godfrey and Tancred made camp to the north of the city, Raymond made his to the south. In addition, the Provençal contingent did not take part in the initial assault on 13 June 1099. This first assault was perhaps more speculative than determined, and after scaling the outer wall the Crusaders were repulsed from the inner one.
After the failure of the initial assault, a meeting between the various leaders was organized in which it was agreed upon that a more concerted attack would be required in the future. On 17 June, a party of Genoese mariners under
The Crusaders' arrival at Jerusalem revealed an arid countryside, lacking in water or food supplies. Here there was no prospect of relief, even as they feared an imminent attack by the local Fatimid rulers. There was no hope of trying to blockade the city as they had at Antioch; the crusaders had insufficient troops, supplies, and time. Rather, they resolved to take the city by assault. They might have been left with little choice, as by the time the Crusader army reached Jerusalem, it has been estimated that only about 12,000 men including 1,500 cavalry remained.. Thus began the decisive Siege of Jerusalem. These contingents, composed of men with differing origins and varying allegiances, were also approaching another low ebb in their camaraderie. While Godfrey and Tancred made camp to the north of the city, Raymond made his to the south. In addition, the Provençal contingent did not take part in the initial assault on 13 June 1099. This first assault was perhaps more speculative than determined, and after scaling the outer wall the Crusaders were repulsed from the inner one.
After the failure of the initial assault, a meeting between the various leaders was organized in which it was agreed upon that a more concerted attack would be required in the future. On 17 June, a party of Genoese mariners under
 On 22 July, a council was held in the
On 22 July, a council was held in the
 The majority of crusaders now considered their pilgrimage complete and returned home. Only 300 knights and 2,000 infantry remained to defend Palestine. It was the support of the knights from Lorraine that enabled Godfrey to take leadership of Jerusalem, over the claims of Raymond. When he died a year later these same Lorrainers thwarted papal legate
The majority of crusaders now considered their pilgrimage complete and returned home. Only 300 knights and 2,000 infantry remained to defend Palestine. It was the support of the knights from Lorraine that enabled Godfrey to take leadership of Jerusalem, over the claims of Raymond. When he died a year later these same Lorrainers thwarted papal legate _
The_King_of_Jerusalem_was_the_supreme_ruler_of_the__Kingdom_of_Jerusalem,_a__Crusader_state_founded_in_Jerusalem_by_the_Latin_Catholic_leaders_of_the_First_Crusade,_when_the_city_was__conquered_in_1099.
_Godfrey_of_Bouillon,_the_first_ruler_of_...
._Bohemond_returned_to_Europe_to_fight_the_Byzantines_from_Italy_but_he_was_defeated_in_1108_at_Siege_of_Dyrrhachium_(1107–1108)">Dyrrhachium._After_Raymond's_death,_his_heirs_captured_County_of_Tripoli#Capture_by_Christian_forces.html" ;"title="List of kings of Jerusalem">king of Jerusalem
The King of Jerusalem was the supreme ruler of the Kingdom of Jerusalem, a Crusader state founded in Jerusalem by the Latin Catholic leaders of the First Crusade, when the city was conquered in 1099.
Godfrey of Bouillon, the first ruler of ...Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were ...
, initiated, supported and at times directed by the Latin Church
, native_name_lang = la
, image = San Giovanni in Laterano - Rome.jpg
, imagewidth = 250px
, alt = Façade of the Archbasilica of St. John in Lateran
, caption = Archbasilica of Saint Jo ...
in the medieval period
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
. The objective was the recovery of the Holy Land
The Holy Land; Arabic: or is an area roughly located between the Mediterranean Sea and the Eastern Bank of the Jordan River, traditionally synonymous both with the biblical Land of Israel and with the region of Palestine. The term "Holy ...
from Islamic rule. While Jerusalem had been under Muslim rule for hundreds of years, by the 11th century the Seljuk takeover of the region threatened local Christian populations, pilgrimages from the West, and the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
itself. The earliest initiative for the First Crusade began in 1095 when Byzantine emperor
This is a list of the Byzantine emperors from the foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD, which marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, to its fall to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as ...
Alexios I Komnenos
Alexios I Komnenos ( grc-gre, Ἀλέξιος Κομνηνός, 1057 – 15 August 1118; Latinized Alexius I Comnenus) was Byzantine emperor from 1081 to 1118. Although he was not the first emperor of the Komnenian dynasty, it was during ...
requested military support from the Council of Piacenza in the empire's conflict with the Seljuk-led Turks. This was followed later in the year by the Council of Clermont
The Council of Clermont was a mixed synod of ecclesiastics and laymen of the Catholic Church, called by Pope Urban II and held from 17 to 27 November 1095 at Clermont, Auvergne, at the time part of the Duchy of Aquitaine.
Pope Urban's speech ...
, during which Pope Urban II
Pope Urban II ( la, Urbanus II; – 29 July 1099), otherwise known as Odo of Châtillon or Otho de Lagery, was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 12 March 1088 to his death. He is best known for convening th ...
supported the Byzantine request for military assistance and also urged faithful Christians to undertake an armed pilgrimage to Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
.
This call was met with an enthusiastic popular response across all social classes in western Europe. Mobs of predominantly poor Christians numbering in the thousands, led by Peter the Hermit, a French priest, were the first to respond. What has become known as the People's Crusade passed through Germany and indulged in wide-ranging anti-Jewish activities, including the Rhineland massacres
The Rhineland massacres, also known as the German Crusade of 1096 or ''Gzerot Tatnó'' ( he, גזרות תתנ"ו, "Edicts of 4856"), were a series of mass murders of Jews perpetrated by mobs of French and German Christians of the People's Cru ...
. On leaving Byzantine-controlled territory in Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
, they were annihilated in a Turkish ambush led by the Seljuk Kilij Arslan at the Battle of Civetot in October 1096.
In what has become known as the Princes' Crusade, members of the high nobility and their followers embarked in late-summer 1096 and arrived at Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
between November and April the following year. This was a large feudal host led by notable Western European princes: southern French forces under Raymond IV of Toulouse
Raymond IV, Count of Toulouse ( 1041 – 28 February 1105), sometimes called Raymond of Saint-Gilles or Raymond I of Tripoli, was a powerful noble in southern France and one of the leaders of the First Crusade (1096–1099). He was the Count o ...
and Adhemar of Le Puy; men from Upper and Lower Lorraine
The Duchy of Lower Lotharingia, also called Northern Lotharingia, Lower Lorraine or Northern Lorraine (and also referred to as '' Lothier'' or '' Lottier''
led by Godfrey of Bouillon
Godfrey of Bouillon (, , , ; 18 September 1060 – 18 July 1100) was a French nobleman and pre-eminent leader of the First Crusade. First ruler of the Kingdom of Jerusalem from 1099 to 1100, he avoided the title of king, preferring that of princ ...
and his brother Baldwin of Boulogne; Italo-Norman forces led by Bohemond of Taranto
Bohemond I of Antioch (5 or 7 March 1111), also known as Bohemond of Taranto, was the prince of Taranto from 1089 to 1111 and the prince of Antioch from 1098 to 1111. He was a leader of the First Crusade, leading a contingent of Normans on the qu ...
and his nephew Tancred
Tancred or Tankred is a masculine given name of Germanic origin that comes from ''thank-'' (thought) and ''-rath'' (counsel), meaning "well-thought advice". It was used in the High Middle Ages mainly by the Normans (see French Tancrède) and espe ...
; as well as various contingents consisting of northern French and Flemish forces under Robert Curthose
Robert Curthose, or Robert II of Normandy ( 1051 – 3 February 1134, french: Robert Courteheuse / Robert II de Normandie), was the eldest son of William the Conqueror and succeeded his father as Duke of Normandy in 1087, reigning until 1106. ...
(Robert II of Normandy), Stephen of Blois
Stephen (1092 or 1096 – 25 October 1154), often referred to as Stephen of Blois, was King of England from 22 December 1135 to his death in 1154. He was Count of Boulogne ''jure uxoris'' from 1125 until 1147 and Duke of Normandy from 1135 unti ...
, Hugh of Vermandois, and Robert II of Flanders. In total and including non-combatants, the forces are estimated to have numbered as many as 100,000.
The crusader forces gradually arrived in Anatolia. With Kilij Arslan absent, a Frankish attack and Byzantine naval assault during the Siege of Nicaea
The siege of Nicaea was the first major battle of the First Crusade, taking place from 14 May to 19 June 1097. The city was under the control the Seljuk Turks who opted to surrender to the Byzantines in fear of the crusaders breaking into the ci ...
in June 1097 resulted in an initial crusader victory. In July, the crusaders won the Battle of Dorylaeum, fighting Turkish lightly-armoured mounted archers. After a difficult march through Anatolia, the crusaders began the Siege of Antioch
The siege of Antioch took place during the First Crusade in 1097 and 1098, on the crusaders' way to Jerusalem through Syria. Two sieges took place in succession. The first siege, by the crusaders against the city held by the Seljuk Empire, ...
, capturing the city in June 1098. Jerusalem was reached in June 1099 and the Siege of Jerusalem resulted in the city being taken by assault from 7 June to 15 July 1099, during which its defenders were ruthlessly massacred. A Fatimid counterattack was repulsed later that year at the Battle of Ascalon, ending the First Crusade. Afterwards the majority of the crusaders returned home.
Four Crusader states
The Crusader States, also known as Outremer, were four Catholic realms in the Middle East that lasted from 1098 to 1291. These feudal polities were created by the Latin Catholic leaders of the First Crusade through conquest and political i ...
were established in the Holy Land: the Kingdom of Jerusalem under Godfrey of Bouillon but not using the title king, the County of Edessa
The County of Edessa (Latin: ''Comitatus Edessanus'') was one of the Crusader states in the 12th century. Ferdinandi, Sergio (2017). La Contea Franca di Edessa. Fondazione e Profilo Storico del Primo Principato Crociato nel Levante (1098-115 ...
, the Principality of Antioch
The Principality of Antioch was one of the crusader states created during the First Crusade which included parts of modern-day Turkey and Syria. The principality was much smaller than the County of Edessa or the Kingdom of Jerusalem. It exte ...
, and the County of Tripoli
The County of Tripoli (1102–1289) was the last of the Crusader states. It was founded in the Levant in the modern-day region of Tripoli, northern Lebanon and parts of western Syria which supported an indigenous population of Christians, ...
. The Crusader presence remained in the region in some form until the loss of the last major Crusader stronghold in the Siege of Acre in 1291. After this loss of all Crusader territory in the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
, there were no further substantive attempts to recover the Holy Land.
Historical context
Christianity and Islam had been in conflict since the latter's founding in the 7th century. Less than a century passed from the death of the Islamic prophetMuhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the mon ...
in 632 until the Islamic occupation of Jerusalem and the Levant beginning in 638, and Muslim invaders landed in Spain. By the 11th century, Islamic control of Spain was gradually eroded by the ''Reconquista
The ' ( Spanish, Portuguese and Galician for "reconquest") is a historiographical construction describing the 781-year period in the history of the Iberian Peninsula between the Umayyad conquest of Hispania in 711 and the fall of the N ...
'', but the situation in the Holy Land had deteriorated. The Fatimid dynasty
The Fatimid dynasty () was an Isma'ili Shi'a dynasty of Arab descent that ruled an extensive empire, the Fatimid Caliphate, between 909 and 1171 CE. Claiming descent from Fatima and Ali, they also held the Isma'ili imamate, claiming to be the ...
ruled North Africa and swathes of Western Asia to include Jerusalem, Damascus and parts of the Mediterranean coastline from 969, but was at relative peace with the west. That all changed in 1071, with the defeat of Byzantium at the Battle of Manzikert
The Battle of Manzikert or Malazgirt was fought between the Byzantine Empire and the Seljuk Empire on 26 August 1071 near Manzikert, theme of Iberia (modern Malazgirt in Muş Province, Turkey). The decisive defeat of the Byzantine army and ...
and the loss of Jerusalem to the Seljuk dynasty
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; fa, سلجوقیان ''Saljuqian'', alternatively spelled as Seljuqs or Saljuqs), also known as Seljuk Turks, Seljuk Turkomans "The defeat in August 1071 of the Byzantine emperor Romanos Diogenes
by the Turk ...
two years later.
While the root causes are varied and continue to be debated, it is clear that the First Crusade came about from a combination of factors earlier in the 11thcentury in both Europe and the Near East. In Western Europe, Jerusalem was increasingly seen as worthy of penitential pilgrimages
A pilgrimage is a journey, often into an unknown or foreign place, where a person goes in search of new or expanded meaning about their self, others, nature, or a higher good, through the experience. It can lead to a personal transformation, aft ...
. While the Seljuk hold on Jerusalem was weak (the group later lost the city to the Fatimids), returning pilgrims reported difficulties and the oppression of Christians. The Byzantine need for military support coincided with an increase in the willingness of the western European warrior class to accept papal military command.
Situation in Europe
By the 11th century, the population of Europe had increased greatly as technological and agricultural innovations allowed trade to flourish. The Catholic Church had become a dominant influence on Western civilization. Society was organized bymanorialism
Manorialism, also known as the manor system or manorial system, was the method of land ownership (or " tenure") in parts of Europe, notably France and later England, during the Middle Ages. Its defining features included a large, sometimes for ...
and feudalism
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structu ...
, political structures whereby knights and other nobles owed military service to their overlords in return for the right to rent from lands and manors.
In the period from 1050 until 1080, the Gregorian Reform
The Gregorian Reforms were a series of reforms initiated by Pope Gregory VII and the circle he formed in the papal curia, c. 1050–80, which dealt with the moral integrity and independence of the clergy. The reforms are considered to be na ...
movement developed increasingly more assertive policies, eager to increase its power and influence. This prompted conflict with eastern Christians rooted in the doctrine of papal supremacy
Papal supremacy is the doctrine of the Catholic Church that the Pope, by reason of his office as Vicar of Christ, the visible source and foundation of the unity both of the bishops and of the whole company of the faithful, and as pastor of th ...
. The Eastern church viewed the pope as only one of the five patriarchs of the Church, alongside the Patriarchates of Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandri ...
, Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου, ''Antiókheia hē epì Oróntou'', Learned ; also Syrian Antioch) grc-koi, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου; or Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπ� ...
, Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
and Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
. In 1054 differences in custom, creed and practice spurred Pope Leo IX
Pope Leo IX (21 June 1002 – 19 April 1054), born Bruno von Egisheim-Dagsburg, was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 12 February 1049 to his death in 1054. Leo IX is considered to be one of the most historically ...
to send a legation to the Patriarch of Constantinople, which ended in mutual excommunication and an East–West Schism
The East–West Schism (also known as the Great Schism or Schism of 1054) is the ongoing break of communion between the Roman Catholic and Eastern Orthodox churches since 1054. It is estimated that, immediately after the schism occurred, a ...
.
Early Christians were used to the employment of violence for communal purposes. A Christian theology of war inevitably evolved from the point when Roman citizenship and Christianity became linked. Citizens were required to fight against the empire's enemies. Dating from the works of the 4th-century theologian Augustine of Hippo
Augustine of Hippo ( , ; la, Aurelius Augustinus Hipponensis; 13 November 354 – 28 August 430), also known as Saint Augustine, was a theologian and philosopher of Berber origin and the bishop of Hippo Regius in Numidia, Roman North Afr ...
a doctrine of holy war developed. Augustine wrote that an aggressive war was sinful, but war could be justified if proclaimed by a legitimate authority such as a king or bishop, it was defensive or for the recovery of lands, and it did not involve excessive violence. The breakdown of the Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–888) was a large Frankish-dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the L ...
in Western Europe created a warrior caste who now had little to do but fight amongst themselves. Violent acts were commonly used for dispute resolution, and the papacy attempted to mitigate it.
Pope Alexander II
Pope Alexander II (1010/1015 – 21 April 1073), born Anselm of Baggio, was the head of the Roman Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 1061 to his death in 1073. Born in Milan, Anselm was deeply involved in the Pataria reform ...
developed recruitment systems via oaths for military resourcing that Gregory VII further extended across Europe. These were deployed by the Church in the Christian conflicts with Muslims in the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, def ...
and for the Norman conquest of Sicily. Gregory VII went further in 1074, planning a display of military power to reinforce the principle of papal sovereignty in a holy war supporting Byzantium against the Seljuks, but was unable to build support for this. Theologian Anselm of Lucca
Anselm of Lucca ( la, Anselmus; it, Anselmo; 1036 – 18 March 1086), born Anselm of Baggio ('), was a medieval bishop of Lucca in Italy and a prominent figure in the Investiture Controversy amid the fighting in central Italy between Mat ...
took the decisive step towards an authentic crusader ideology, stating that fighting for legitimate purposes could result in the remission of sins.
Navarre
Navarre (; es, Navarra ; eu, Nafarroa ), officially the Chartered Community of Navarre ( es, Comunidad Foral de Navarra, links=no ; eu, Nafarroako Foru Komunitatea, links=no ), is a foral autonomous community and province in northern Spain, ...
and Catalonia
Catalonia (; ca, Catalunya ; Aranese Occitan: ''Catalonha'' ; es, Cataluña ) is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a '' nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy.
Most of the territory (except the Val d'Aran) lies on the no ...
lacked a common identity and shared history based on tribe or ethnicity so they frequently united and divided during the 11th and 12th centuries. Although small, all developed an aristocratic military technique and in 1031 the disintegration of the Caliphate of Córdoba in southern Spain created the opportunity for the territorial gains that later became known as the ''Reconquista
The ' ( Spanish, Portuguese and Galician for "reconquest") is a historiographical construction describing the 781-year period in the history of the Iberian Peninsula between the Umayyad conquest of Hispania in 711 and the fall of the N ...
''. In 1063, William VIII of Aquitaine led a combined force of French, Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and an, Aragón ; ca, Aragó ) is an autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces (from north to s ...
ese and Catalan
Catalan may refer to:
Catalonia
From, or related to Catalonia:
* Catalan language, a Romance language
* Catalans, an ethnic group formed by the people from, or with origins in, Northern or southern Catalonia
Places
* 13178 Catalan, asteroid #1 ...
knights to take the city of Barbastro that had been in Muslim hands since the year 711. This had the full support of Alexander II, and a truce was declared in Catalonia with indulgences granted to the participants. It was a holy war but differed from the First Crusade in that there was no pilgrimage, no vow, and no formal authorisation by the church. Shortly before the First Crusade, Urban II had encouraged the Iberian Christians to take Tarragona
Tarragona (, ; Phoenician: ''Tarqon''; la, Tarraco) is a port city located in northeast Spain on the Costa Daurada by the Mediterranean Sea. Founded before the fifth century BC, it is the capital of the Province of Tarragona, and part of Tarr ...
, using much of the same symbolism and rhetoric that was later used to preach the crusade to the people of Europe.
The Italo-Normans
The Italo-Normans ( it, Italo-Normanni), or Siculo-Normans (''Siculo-Normanni'') when referring to Sicily and Southern Italy, are the Italian-born descendants of the first Norman conquerors to travel to southern Italy in the first half of ...
were successful in seizing much of Southern Italy and Sicily from the Byzantines and North African Arabs in the decades before the First Crusade. This brought them into conflict with the Papacy leading to a campaign against them by Pope Leo IX
Pope Leo IX (21 June 1002 – 19 April 1054), born Bruno von Egisheim-Dagsburg, was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 12 February 1049 to his death in 1054. Leo IX is considered to be one of the most historically ...
who they defeated at Civitate, although when they invaded Muslim Sicily in 1059 they did so under a papal banner: the '' Invexillum sancti Petrior,'' or banner of St. Peter. Robert Guiscard
Robert Guiscard (; Modern ; – 17 July 1085) was a Norman adventurer remembered for the conquest of southern Italy and Sicily. Robert was born into the Hauteville family in Normandy, went on to become count and then duke of Apulia and Calab ...
captured the Byzantine city of Bari
Bari ( , ; nap, label= Barese, Bare ; lat, Barium) is the capital city of the Metropolitan City of Bari and of the Apulia region, on the Adriatic Sea, southern Italy. It is the second most important economic centre of mainland Southern Ital ...
in 1071 and campaigned along the Eastern Adriatic
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to the ...
coast around Dyrrachium in 1081 and 1085.
Situation in the East
Basil II
Basil II Porphyrogenitus ( gr, Βασίλειος Πορφυρογέννητος ;) and, most often, the Purple-born ( gr, ὁ πορφυρογέννητος, translit=ho porphyrogennetos).. 958 – 15 December 1025), nicknamed the Bulgar S ...
, the territorial recovery of the empire reached its furthest extent in 1025. The Empire's frontiers stretched east to Iran, Bulgaria and much of southern Italy were under control, and piracy in the Mediterranean Sea had been suppressed. Relations with the Empire's Islamic neighbours were no more quarrelsome than relations with the Slavs
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, main ...
or Western Christians. Normans
The Normans ( Norman: ''Normaunds''; french: Normands; la, Nortmanni/Normanni) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norse Viking settlers and indigenous West Franks and Gallo-Romans. ...
in Italy; Pechenegs
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks tr, Peçenek(ler), Middle Turkic: , ro, Pecenegi, russian: Печенег(и), uk, Печеніг(и), hu, Besenyő(k), gr, Πατζινάκοι, Πετσενέγοι, Πατζινακίται, ka, პა� ...
, Serbs
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are the most numerous South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to the Balkans in Southeastern Europe, who share a common Serbian Cultural heritage, ancestry, Culture of Serbia, culture, History of ...
and Cumans
The Cumans (or Kumans), also known as Polovtsians or Polovtsy (plural only, from the Russian exonym ), were a Turkic nomadic people comprising the western branch of the Cuman–Kipchak confederation. After the Mongol invasion (1237), many so ...
to the north; and Seljuk Turks in the east all competed with the Empire, and to meet these challenges the emperors recruited mercenaries, even on occasion from their enemies.
The Islamic world also experienced great success since its foundation in the 7th century, with major changes to come. The first waves of Turkic migration
The Turkic migrations were the spread of Turkic tribes and Turkic languages across Eurasia and between the 6th and 11th centuries. In the 6th century, the Göktürks overthrew the Rouran Khaganate in what is now Mongolia and expanded in all direct ...
into the Middle East enmeshed Arab and Turkic history from the 9thcentury. The status quo in Western Asia was challenged by later waves of Turkish migration, particularly the arrival of the Seljuk Turks
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; fa, سلجوقیان ''Saljuqian'', alternatively spelled as Seljuqs or Saljuqs), also known as Seljuk Turks, Seljuk Turkomans "The defeat in August 1071 of the Byzantine emperor Romanos Diogenes
by the Turk ...
in the 10thcentury. These were a minor ruling clan from Transoxania. They converted to Islam and migrated into Iran to seek their fortune. In the following two decades they conquered Iran, Iraq and the Near East. The Seljuks and their followers were Sunni Muslims, which led to conflict in Palestine and Syria with the Shi'ite Fatimid Caliphate
The Fatimid Caliphate was an Ismaili Shi'a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries AD. Spanning a large area of North Africa, it ranged from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Red Sea in the east. The Fatimids, a ...
. The Seljuks were nomads, Turkish speaking, and occasionally shamanistic, unlike their sedentary, Arabic-speaking subjects. This was a difference that weakened power structures when combined with the Seljuks' habitual governance of territory based on political preferment and competition between independent princes rather than geography. The Byzantine Emperor, Romanos IV Diogenes
Romanos IV Diogenes ( Greek: Ρωμανός Διογένης), Latinized as Romanus IV Diogenes, was a member of the Byzantine military aristocracy who, after his marriage to the widowed empress Eudokia Makrembolitissa, was crowned Byzantine E ...
, attempted to suppress the Seljuks' sporadic raiding, but was defeated at the Battle of Manzikert
The Battle of Manzikert or Malazgirt was fought between the Byzantine Empire and the Seljuk Empire on 26 August 1071 near Manzikert, theme of Iberia (modern Malazgirt in Muş Province, Turkey). The decisive defeat of the Byzantine army and ...
in 1071, the only time in history a Byzantine emperor became the prisoner of a Muslim commander. The result of this disastrous defeat was the loss of the Eastern Roman Empire's Anatolian heartland, and was one of the root causes of the First Crusade.
From 1092 the status quo in the Middle East disintegrated following the death of the vizier
A vizier (; ar, وزير, wazīr; fa, وزیر, vazīr), or wazir, is a high-ranking political advisor or minister in the near east. The Abbasid caliphs gave the title ''wazir'' to a minister formerly called '' katib'' (secretary), who was ...
and effective ruler of the Seljuk Empire, Nizam al-Mulk
Abu Ali Hasan ibn Ali Tusi (April 10, 1018 – October 14, 1092), better known by his honorific title of Nizam al-Mulk ( fa, , , Order of the Realm) was a Persian scholar, jurist, political philosopher and Vizier of the Seljuk Empire. Rising fr ...
. This was closely followed by the deaths of the Seljuk sultan Malik-Shah and the Fatimid caliph Al-Mustansir Billah
Abū Tamīm Maʿad al-Mustanṣir biʾllāh ( ar, أبو تميم معد المستنصر بالله; 2 July 1029 – 29 December 1094) was the eighth Fatimid Caliph from 1036 until 1094. He was one of the longest reigning Muslim rulers. ...
. Wracked by confusion and division, the Islamic world disregarded the world beyond, so that, when the First Crusade arrived, it came as a surprise. Malik-Shah was succeeded in the Anatolian Sultanate of Rûm
fa, سلجوقیان روم ()
, status =
, government_type = Hereditary monarchyTriarchy (1249–1254)Diarchy (1257–1262)
, year_start = 1077
, year_end = 1308
, p1 = B ...
by Kilij Arslan, and in Syria by his brother Tutush I
Abu Sa'id Taj al-Dawla Tutush (; died 25 February 1095) or Tutush I, was the Seljuk emir of Damascus from 1078 to 1092, and sultan of Damascus from 1092 to 1094.
Years under Malik Shah
Tutush was a brother of the Seljuk sultan Malik-Shah I. In 1 ...
. When Tutush died in 1095 his sons Ridwan and Duqaq Dukak or Duqaq may refer to:
* Tuqaq (died c. 924 AD), the father of Seljuq, eponymous founder of the Seljuk dynasty
* Duqaq (Seljuk ruler of Damascus)
Abu Nasr Shams al-Muluk Duqaq (died June 8, 1104) was the Seljuq ruler of Damascus from 1095 ...
inherited Aleppo
)), is an adjective which means "white-colored mixed with black".
, motto =
, image_map =
, mapsize =
, map_caption =
, image_map1 =
...
and Damascus
)), is an adjective which means "spacious".
, motto =
, image_flag = Flag of Damascus.svg
, image_seal = Emblem of Damascus.svg
, seal_type = Seal
, map_caption =
, ...
, respectively, further dividing Syria amongst emirs antagonistic towards each other, as well as Kerbogha
Qiwam al-Dawla Kerbogha ( tr, Kürboğa), known as Kerbogha or Karbughā, was atabeg of Mosul during the First Crusade and was renowned as a soldier.
Early life
Kerbogha was a Seljuk Turk who owed his success to his military talent. He supp ...
, the atabeg of Mosul. Egypt and much of Palestine were controlled by the Fatimids. The Fatimids, under the nominal rule of caliph al-Musta'li
Abu al-Qasim Ahmad ibn al-Mustansir ( ar, أبو القاسم أحمد بن المستنصر, Abū al-Qāsim Aḥmad ibn al-Mustanṣir; 15/16 September 1074 – 12 December 1101), better known by his regnal name al-Musta'li Billah ( ar, ال� ...
but actually controlled by their vizier al-Afdal Shahanshah
Al-Afdal Shahanshah ( ar, الأفضل شاهنشاه, al-Afḍal Shāhanshāh; la, Lavendalius/Elafdalio; 1066 – 11 December 1121), born Abu al-Qasim Shahanshah bin Badr al-Jamali was a vizier of the Fatimid caliphs of Egypt. According to a ...
, lost Jerusalem to the Seljuks in 1073 but succeeded in recapturing the city in 1098 from the Artuqids
The Artuqid dynasty (alternatively Artukid, Ortoqid, or Ortokid; , pl. ; ; ) was a Turkoman dynasty originated from tribe that ruled in eastern Anatolia, Northern Syria and Northern Iraq in the eleventh through thirteenth centuries. The Artuqi ...
, a smaller Turkish tribe associated with the Seljuks, just before the arrival of the crusaders.
Council of Clermont
 The major ecclesiastical impetuses behind the First Crusade were the Council of Piacenza and subsequent
The major ecclesiastical impetuses behind the First Crusade were the Council of Piacenza and subsequent Council of Clermont
The Council of Clermont was a mixed synod of ecclesiastics and laymen of the Catholic Church, called by Pope Urban II and held from 17 to 27 November 1095 at Clermont, Auvergne, at the time part of the Duchy of Aquitaine.
Pope Urban's speech ...
, both held in 1095 by Pope Urban II
Pope Urban II ( la, Urbanus II; – 29 July 1099), otherwise known as Odo of Châtillon or Otho de Lagery, was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 12 March 1088 to his death. He is best known for convening th ...
, and resulted in the mobilization of Western Europe to go to the Holy Land. Byzantine emperor Alexios I Komnenos
Alexios I Komnenos ( grc-gre, Ἀλέξιος Κομνηνός, 1057 – 15 August 1118; Latinized Alexius I Comnenus) was Byzantine emperor from 1081 to 1118. Although he was not the first emperor of the Komnenian dynasty, it was during ...
, worried about the advances of the Seljuks in the aftermath of the Battle of Manzikert
The Battle of Manzikert or Malazgirt was fought between the Byzantine Empire and the Seljuk Empire on 26 August 1071 near Manzikert, theme of Iberia (modern Malazgirt in Muş Province, Turkey). The decisive defeat of the Byzantine army and ...
of 1071 who had reached as far west as Nicaea
Nicaea, also known as Nicea or Nikaia (; ; grc-gre, Νίκαια, ) was an ancient Greek city in Bithynia, where located in northwestern Anatolia and is primarily known as the site of the First and Second Councils of Nicaea (the first and s ...
, sent envoys to the Council of Piacenza in March 1095 to ask Pope Urban II for aid against the invading Turks.
Urban responded favourably, perhaps hoping to heal the Great Schism of forty years earlier, and to reunite the Church under papal primacy
Papal primacy, also known as the primacy of the bishop of Rome, is a Roman Catholic ecclesiological doctrine concerning the respect and authority that is due to the pope from other bishops and their episcopal sees. The doctrine is accepted ...
by helping the Eastern churches in their time of need. Alexios and Urban had previously been in close contact in 1089 and after, and had discussed openly the prospect of the (re)union of the Christian church. There were signs of considerable co-operation between Rome and Constantinople in the years immediately before the crusade.
In July 1095, Urban turned to his homeland of France to recruit men for the expedition. His travels there culminated in the ten-day Council of Clermont, where on 27 November he gave an impassioned sermon to a large audience of French nobles and clergy. There are five versions of the speech recorded by people who may have been at the council (Baldric of Dol Baldric of Dol ( 10507 January 1130) was prior and then abbot of Bourgueil from 1077 to 1106, then made bishop of Dol-en-Bretagne in 1107 and archbishop in 1108 until his death. He fulfilled his monastic duties by travelling to attend Church counci ...
, Guibert of Nogent
Guibert de Nogent (c. 1055 – 1124) was a Benedictine historian, theologian and author of autobiographical memoirs. Guibert was relatively unknown in his own time, going virtually unmentioned by his contemporaries. He has only recently caught the ...
, Robert the Monk
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' ( non, Hróðr) "fame, glory, ho ...
, and Fulcher of Chartres Fulcher of Chartres (c. 1059 in or near Chartres – after 1128) was a priest who participated in the First Crusade. He served Baldwin I of Jerusalem for many years and wrote a Latin chronicle of the Crusade.
Life
Fulcher was born c. 1059. His app ...
) or who went on crusade (Fulcher and the anonymous author of the ''Gesta Francorum
The ''Gesta Francorum'' (Deeds of the Franks), or ''Gesta Francorum et aliorum Hierosolimitanorum'' (Deeds of the Franks and the other pilgrims to Jerusalem), is a Latin chronicle of the First Crusade by an anonymous author connected with Bohemon ...
''), as well as other versions found in the works of later historians (such as William of Malmesbury
William of Malmesbury ( la, Willelmus Malmesbiriensis; ) was the foremost English historian of the 12th century. He has been ranked among the most talented English historians since Bede. Modern historian C. Warren Hollister described him as " ...
and William of Tyre
William of Tyre ( la, Willelmus Tyrensis; 113029 September 1186) was a medieval prelate and chronicler. As archbishop of Tyre, he is sometimes known as William II to distinguish him from his predecessor, William I, the Englishman, a former ...
). All of these versions were written after Jerusalem had been captured. Thus it is difficult to know what was actually said and what was recreated in the aftermath of the successful crusade. The only contemporary records are a few letters written by Urban in 1095. It is also thought that Urban also may have preached the Crusade at Piacenza, but the only record of which is by Bernold of St. Blasien in his ''Chronicon''.
The five versions of the speech differ widely from one another in regard to particulars, but all versions except that in the ''Gesta Francorum'' agree that Urban talked about the violence of European society and the necessity of maintaining the Peace of God; about helping the Greeks, who had asked for assistance; about the crimes being committed against Christians in the east; and about a new kind of war, an armed pilgrimage, and of rewards in heaven, where remission of sins was offered to any who might die in the undertaking. They do not all specifically mention Jerusalem as the ultimate goal. However, it has been argued that Urban's subsequent preaching reveals that he expected the expedition to reach Jerusalem all along.''Urban and the Crusaders''. ITranslations and reprints from the original sources of European history
Dept. of History, University of Pennsylvania. Volume 1, No. 2. pp. 2–12. According to one version of the speech, the enthusiastic crowd responded with cries of '' Deus lo volt!––''God wills it!.
Peter the Hermit and the People's Crusade
 The great French nobles and their trained armies of knights were not the first to undertake the journey towards Jerusalem.Murray, Alan V. (2006)."People's Crusades (1096)". In ''The Crusades – An Encyclopedia''. pp. 939–941. Urban had planned the departure of the first crusade for 15 August 1096, the
The great French nobles and their trained armies of knights were not the first to undertake the journey towards Jerusalem.Murray, Alan V. (2006)."People's Crusades (1096)". In ''The Crusades – An Encyclopedia''. pp. 939–941. Urban had planned the departure of the first crusade for 15 August 1096, the Feast of the Assumption
The Assumption of Mary is one of the four Marian dogmas of the Catholic Church. Pope Pius XII defined it in 1950 in his apostolic constitution ''Munificentissimus Deus'' as follows:
We proclaim and define it to be a dogma revealed by Go ...
, but months before this, a number of unexpected armies of peasants and petty nobles set off for Jerusalem on their own, led by a charismatic priest called Peter the Hermit. Peter was the most successful of the preachers of Urban's message, and developed an almost hysterical enthusiasm among his followers, although he was probably not an "official" preacher sanctioned by Urban at Clermont. It is commonly believed that Peter's followers consisted entirely of a massive group of untrained and illiterate peasants who did not even know where Jerusalem was, but there were also many knights among the peasants, including Walter Sans Avoir, who was lieutenant to Peter and led a separate army.
Lacking military discipline, in what likely seemed to the participants a strange land (Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whi ...
), Peter's fledgling army quickly found itself in trouble despite the fact they were still in Christian territory. The army led by Walter fought with the Hungarians over food at Belgrade
Belgrade ( , ;, ; names in other languages) is the capital and largest city in Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers and the crossroads of the Pannonian Plain and the Balkan Peninsula. Nearly 1,166,763 mi ...
, but otherwise arrived in Constantinople unharmed. Meanwhile, the army led by Peter, which marched separately from Walter's army, also fought with the Hungarians, and may have captured Belgrade. At Niš
Niš (; sr-Cyrl, Ниш, ; names in other languages) is the third largest city in Serbia and the administrative center of the Nišava District. It is located in southern part of Serbia. , the city proper has a population of 183,164, whi ...
, the Byzantine governor tried to supply them, but Peter had little control over his followers and Byzantine troops were needed to quell their attacks. Peter arrived at Constantinople in August, where his army joined with the one led by Walter, which had already arrived, as well as separate bands of crusaders from France, Germany, and Italy. Another army of Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, Čechy ; ; hsb, Čěska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohem ...
ns and Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
did not make it past Hungary before splitting up.
Peter's and Walter's unruly mob began to pillage outside the city in search of supplies and food, prompting Alexios to hurriedly ferry the gathering across the Bosporus
The Bosporus Strait (; grc, Βόσπορος ; tr, İstanbul Boğazı 'Istanbul strait', colloquially ''Boğaz'') or Bosphorus Strait is a natural strait and an internationally significant waterway located in Istanbul in northwestern Tu ...
one week later. After crossing into Asia Minor, the crusaders split up and began to pillage the countryside, wandering into Seljuk territory around Nicaea. The far more-experienced Turks massacred most of this group. Some Italian and German crusaders were defeated at Xerigordon at the end of August. Meanwhile, Walter and Peter's followers, who, although for the most part untrained in battle but led by about 50 knights, fought the Turks at the Battle of Civetot in October 1096. The Turkish archers destroyed the crusader army, and Walter was among the dead. Peter, who was absent in Constantinople at the time, later joined the second wave of crusaders, along with the few survivors of Civetot.
 At a local level, the preaching of the First Crusade ignited the
At a local level, the preaching of the First Crusade ignited the Rhineland massacres
The Rhineland massacres, also known as the German Crusade of 1096 or ''Gzerot Tatnó'' ( he, גזרות תתנ"ו, "Edicts of 4856"), were a series of mass murders of Jews perpetrated by mobs of French and German Christians of the People's Cru ...
perpetrated against Jews. At the end of 1095 and beginning of 1096, months before the departure of the official crusade in August, there were attacks on Jewish communities in France and Germany. In May 1096, Emicho of Flonheim (sometimes incorrectly known as Emicho of Leiningen) attacked the Jews at Speyer and Worms. Other unofficial crusaders from Swabia, led by Hartmann of Dillingen, along with French, English, Lotharingian and Flemish volunteers, led by Drogo of Nesle
Drogo of Nesle, a relative of Ralph, Lord of Soissons, was a knight who joined the army of Emicho, Count of Flonheim. He was one of the knights that survived the violent dispersal of Emicho's People's Crusade army by Hungarian forces during the ...
and William the Carpenter
William the Carpenter (fl. 1087–1102), viscount of Melun, was a French nobleman who participated in the '' Reconquista'' in Spain and on the First Crusade. He was notorious for defecting from the army both in Spain and on the crusade, but he was ...
, as well as many locals, joined Emicho in the destruction of the Jewish community of Mainz at the end of May. In Mainz, one Jewish woman killed her children rather than let the crusaders kill them. Chief rabbi Kalonymus Ben Meshullam committed suicide in anticipation of being killed. Emicho's company then went on to Cologne, and others continued on to Trier, Metz, and other cities. Peter the Hermit also may have been involved in violence against the Jews, and an army led by a priest named Folkmar attacked Jews further east in Bohemia.
Coloman of Hungary had to deal with the problems that the armies of the First Crusade caused during their march across his country towards the Holy Land in 1096. He crushed two crusader hordes that had been pillaging the kingdom. Emicho's army eventually continued into Hungary but was also defeated by Coloman, at which point, Emicho's followers dispersed. Some eventually joined the main armies, although Emicho himself went home. Many of the attackers seem to have wanted to force the Jews to convert, although they were also interested in acquiring money from them. Physical violence against Jews was never part of the church hierarchy's official policy for crusading, and the Christian bishops, especially the Archbishop of Cologne, did their best to protect the Jews. A decade before, the Bishop of Speyer had taken the step of providing the Jews of that city with a walled ghetto to protect them from Christian violence and given their chief rabbis the control of judicial matters in the quarter. Nevertheless, some also took money in return for their protection. The attacks may have originated in the belief that Jews and Muslims were equally enemies of Christ, and enemies were to be fought or converted to Christianity.
From Clermont to Constantinople
The four main crusader armies left Europe around the appointed time in August 1096. They took different routes toConstantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
, some through Eastern Europe and the Balkans, some crossing the Adriatic Sea. Coloman of Hungary allowed Godfrey and his troops to cross Hungary only after his brother, Baldwin was offered as a hostage to guarantee his troops' good conduct. They gathered outside the Roman-era Walls of Constantinople
The Walls of Constantinople ( el, Τείχη της Κωνσταντινουπόλεως) are a series of defensive stone walls that have surrounded and protected the city of Constantinople (today Istanbul in Turkey) since its founding as the ...
between November 1096 and April 1097. Hugh of Vermandois arrived first, followed by Godfrey, Raymond, and Bohemond.
Recruitment
Raymond IV, Count of Toulouse
Raymond IV, Count of Toulouse ( 1041 – 28 February 1105), sometimes called Raymond of Saint-Gilles or Raymond I of Tripoli, was a powerful noble in southern France and one of the leaders of the First Crusade (1096–1099). He was the Count of ...
, and instantly the expedition had the support of two of southern France's most important leaders. Adhemar himself was present at the council and was the first to "take the cross". During the rest of 1095 and into 1096, Urban spread the message throughout France, and urged his bishops and legates to preach in their own dioceses elsewhere in France, Germany, and Italy as well. However, it is clear that the response to the speech was much greater than even the Pope, let alone Alexios, expected. On his tour of France, Urban tried to forbid certain people (including women, monks, and the sick) from joining the crusade, but found this nearly impossible. In the end, most who took up the call were not knights, but peasants who were not wealthy and had little in the way of fighting skills, in an outpouring of a new emotional and personal piety that was not easily harnessed by the ecclesiastical and lay aristocracy. Typically, preaching would conclude with every volunteer taking a vow to complete a pilgrimage to the Church of the Holy Sepulchre; they were also given a cross, usually sewn onto their clothes.
It is difficult to assess the motives of the thousands of participants for whom there is no historical record, or even those of important knights, whose stories were usually retold by monks or clerics. It is quite likely that personal piety was a major factor for many crusaders. Even with this popular enthusiasm, Urban was ensured that there would be an army of knights, drawn from the French aristocracy. Aside from Adhemar and Raymond, other leaders he recruited throughout 1096 included Bohemond of Taranto
Bohemond I of Antioch (5 or 7 March 1111), also known as Bohemond of Taranto, was the prince of Taranto from 1089 to 1111 and the prince of Antioch from 1098 to 1111. He was a leader of the First Crusade, leading a contingent of Normans on the qu ...
, a southern Italian ally of the reform popes; Bohemond's nephew Tancred
Tancred or Tankred is a masculine given name of Germanic origin that comes from ''thank-'' (thought) and ''-rath'' (counsel), meaning "well-thought advice". It was used in the High Middle Ages mainly by the Normans (see French Tancrède) and espe ...
; Godfrey of Bouillon
Godfrey of Bouillon (, , , ; 18 September 1060 – 18 July 1100) was a French nobleman and pre-eminent leader of the First Crusade. First ruler of the Kingdom of Jerusalem from 1099 to 1100, he avoided the title of king, preferring that of princ ...
, who had previously been an anti-reform ally of the Holy Roman Emperor; his brother Baldwin of Boulogne; Hugh I, Count of Vermandois
Hugh, Count of Vermandois (1057 – October 18, 1101), called the Great (french: Hugues le Grand, la, Hugo Magnus) was the first count of Vermandois from the House of Capet. He is known primarily for being one of the leaders of First Crusade. His ...
, brother of the excommunicated Philip I of France
Philip I (23 May 1052 – 29 July 1108), called the Amorous, was King of the Franks from 1060 to 1108. His reign, like that of most of the early Capetians, was extraordinarily long for the time. The monarchy began a modest recovery from the low i ...
; Robert Curthose
Robert Curthose, or Robert II of Normandy ( 1051 – 3 February 1134, french: Robert Courteheuse / Robert II de Normandie), was the eldest son of William the Conqueror and succeeded his father as Duke of Normandy in 1087, reigning until 1106. ...
, brother of William II of England
William II ( xno, Williame; – 2 August 1100) was King of England from 26 September 1087 until his death in 1100, with powers over Normandy and influence in Scotland. He was less successful in extending control into Wales. The third so ...
; and his relatives Stephen II, Count of Blois, and Robert II, Count of Flanders. The crusaders represented northern and southern France, Flanders, Germany, and southern Italy, and so were divided into four separate armies that were not always cooperative, though they were held together by their common ultimate goal.
The crusade was led by some of the most powerful nobles of France, many of whom left everything behind, and it was often the case that entire families went on crusade at their own great expense. For example, Robert of Normandy loaned the Duchy of Normandy
The Duchy of Normandy grew out of the 911 Treaty of Saint-Clair-sur-Epte between King Charles III of West Francia and the Viking leader Rollo. The duchy was named for its inhabitants, the Normans.
From 1066 until 1204, as a result of the Norman c ...
to his brother William II of England, and Godfrey sold or mortgaged his property to the church. Tancred was worried about the sinful nature of knightly warfare, and was excited to find a holy outlet for violence. Tancred and Bohemond, as well as Godfrey, Baldwin, and their older brother Eustace III, Count of Boulogne, are examples of families who crusaded together. Much of the enthusiasm for the crusade was based on family relations, as most of the French crusaders were distant relatives. Nevertheless, in at least some cases, personal advancement played a role in Crusaders' motives. For instance, Bohemond was motivated by the desire to carve himself out a territory in the east, and had previously campaigned against the Byzantines to try to achieve this. The crusade gave him a further opportunity, which he took after the Siege of Antioch
The siege of Antioch took place during the First Crusade in 1097 and 1098, on the crusaders' way to Jerusalem through Syria. Two sieges took place in succession. The first siege, by the crusaders against the city held by the Seljuk Empire, ...
, taking possession of the city and establishing the Principality of Antioch.
The road to Constantinople
The armies travelled to Constantinople by various routes, with Godfrey taking the land route through the Balkans.Runciman, S. (1949)The First Crusaders' Journey across the Balkan Peninsula
''Byzantion'', 19, 207–221. Raymond of Toulouse led the Provençals down the coast of
Illyria
In classical antiquity, Illyria (; grc, Ἰλλυρία, ''Illyría'' or , ''Illyrís''; la, Illyria, ''Illyricum'') was a region in the western part of the Balkan Peninsula inhabited by numerous tribes of people collectively known as the Illyr ...
, and then due east to Constantinople. Bohemund and Tancred led their Normans by sea to Durazzo, and thence by land to Constantinople. The armies arrived in Constantinople with little food and expected provisions and help from Alexios. Alexios was understandably suspicious after his experiences with the People's Crusade, and also because the knights included his old Norman enemy, Bohemond, who had invaded Byzantine territory on numerous occasions with his father and may have even attempted to organize an attack on Constantinople while encamped outside the city. This time, Alexios was more prepared for the crusaders and there were fewer incidents of violence along the way.
 The crusaders may have expected Alexios to become their leader, but he had no interest in joining them, and was mainly concerned with transporting them into Asia Minor as quickly as possible. In return for food and supplies, Alexios requested the leaders to swear fealty to him and promise to return to the Byzantine Empire any land recovered from the Turks. Godfrey was the first to take the oath, and almost all the other leaders followed him, although they did so only after warfare had almost broken out in the city between the citizens and the crusaders, who were eager to pillage for supplies. Raymond alone avoided swearing the oath, instead pledging that he would simply cause no harm to the empire. Before ensuring that the various armies were shuttled across the Bosporus, Alexios advised the leaders on how best to deal with the Seljuk armies that they would soon encounter.
The crusaders may have expected Alexios to become their leader, but he had no interest in joining them, and was mainly concerned with transporting them into Asia Minor as quickly as possible. In return for food and supplies, Alexios requested the leaders to swear fealty to him and promise to return to the Byzantine Empire any land recovered from the Turks. Godfrey was the first to take the oath, and almost all the other leaders followed him, although they did so only after warfare had almost broken out in the city between the citizens and the crusaders, who were eager to pillage for supplies. Raymond alone avoided swearing the oath, instead pledging that he would simply cause no harm to the empire. Before ensuring that the various armies were shuttled across the Bosporus, Alexios advised the leaders on how best to deal with the Seljuk armies that they would soon encounter.
Siege of Nicaea
The Crusader armies crossed over into Asia Minor during the first half of 1097, where they were joined by Peter the Hermit and the remainder of his relatively small army. In addition, Alexios also sent two of his own generals, Manuel Boutoumites and Tatikios, to assist the crusaders. The first objective of their campaign wasNicaea
Nicaea, also known as Nicea or Nikaia (; ; grc-gre, Νίκαια, ) was an ancient Greek city in Bithynia, where located in northwestern Anatolia and is primarily known as the site of the First and Second Councils of Nicaea (the first and s ...
, a city once under Byzantine rule, but which had become the capital of the Seljuk Sultanate of Rûm
fa, سلجوقیان روم ()
, status =
, government_type = Hereditary monarchyTriarchy (1249–1254)Diarchy (1257–1262)
, year_start = 1077
, year_end = 1308
, p1 = B ...
under Kilij Arslan. Arslan was away campaigning against the Danishmends
The Danishmendids or Danishmends ( fa, دودمان دانشمند; tr, Dânişmendliler) was a Turkish beylik that ruled in north-central and eastern Anatolia from 1071/1075 to 1178. The dynasty centered originally around Sivas, Tokat, and N ...
in central Anatolia at the time, and had left behind his treasury and his family, underestimating the strength of these new crusaders.
Subsequently, upon the Crusaders' arrival, the city was subjected to a lengthy siege, and when Arslan had word of it he rushed back to Nicaea and attacked the crusader army on 16 May. He was driven back by the unexpectedly large crusader force, with heavy losses being suffered on both sides in the ensuing battle. The siege continued, but the crusaders had little success as they found they could not blockade Lake İznik
Lake Iznik ( tr, İznik Gölü) is a lake in the Province of Bursa, Turkey. It is around 32 km in length and 10 km in width with a maximum depth of about 80 m. The town of Iznik (historically known as Nicaea) lies at its eastern e ...
, which the city was situated on, and from which it could be provisioned. To break the city, Alexios had the Crusaders' ships rolled over land on logs, and at the sight of them the Turkish garrison finally surrendered on 18 June.
There was some discontent amongst the Franks who were forbidden from looting the city. This was ameliorated by Alexius financially rewarding the crusaders. Later chronicles exaggerate tension between the Greeks and Franks but Stephen of Blois, in a letter to his wife Adela of Blois confirms goodwill and cooperation continued at this point.The First CrusadeLetters of the Crusaders
By Dana Carleton Munro (1902. Philadelphia, Pa. pp. 2–11. The fall of Nicaea is viewed as a rare product of close co-operation between the Crusaders and the Byzantines.
Battle of Dorylaeum
At the end of June, the crusaders marched on through Anatolia. They were accompanied by some Byzantine troops under Tatikios, and still harboured the hope that Alexios would send a full Byzantine army after them. They also divided the army into two more-easily managed groups—one contingent led by the Normans, the other by the French. The two groups intended to meet again atDorylaeum
Dorylaeum or Dorylaion ( el, Δορύλαιον; tr, Şarhöyük) was an ancient city in Anatolia. It is now an archaeological site located near the city of Eskişehir, Turkey.
Its original location was about 10 km southwest of Eskişehi ...
, but on 1 July the Normans, who had marched ahead of the French, were attacked by Kilij Arslan. Arslan had gathered a much larger army than he previously had after his defeat at Nicaea, and now surrounded the Normans with his fast-moving mounted archers. The Normans "deployed in a tight-knit defensive formation", surrounding all their equipment and the non-combatants who had followed them along the journey, and sent for help from the other group. When the French arrived, Godfrey broke through the Turkish lines and the legate Adhemar outflanked the Turks from the rear. The Turks, who had expected to destroy the Normans and did not anticipate the quick arrival of the French, fled rather than face the combined crusader army.
The crusaders' march through Anatolia was thereafter unopposed, but the journey was unpleasant, as Arslan had burned and destroyed everything he left behind in his army's flight. It was the middle of summer, and the crusaders had very little food and water; many men and horses died. Fellow Christians sometimes gave them gifts of food and money, but more often than not, the crusaders simply looted and pillaged whenever the opportunity presented itself. Individual leaders continued to dispute the overall leadership, although none of them were powerful enough to take command on their own, as Adhemar was always recognized as the spiritual leader.
The Armenian interlude
Cilician Gates
The Cilician Gates or Gülek Pass is a pass through the Taurus Mountains connecting the low plains of Cilicia to the Anatolian Plateau, by way of the narrow gorge of the Gökoluk River. Its highest elevation is about 1000m.
The Cilician Gates ha ...
, Baldwin and Tancred broke away from the main body of the army and set off towards the Armenian lands. Baldwin desired to create a fiefdom for himself in the Holy Land, and, in Armenia, he could count on the support of the locals, especially an adventurer named Bagrat
Bagrat ( hy, Բագրատ, in Western Armenian pronounced Pakrad, ka, ბაგრატ) is a male name popular in Georgia and Armenia. It is derived from the Old Persian ''Bagadāta'', "gift of God".
The names of the Armenian Bagratuni and ...
. Baldwin and Tancred led two separate contingents, departing Heraclea on 15 September. Tancred arrived first at Tarsus where he persuaded the Seljuk garrison to raise his flag on the citadel. Baldwin reached Tarsus the next day and, in a reversal, the Turks allowed Baldwin to take possession of two towers. Heavily outnumbered, Tancred decided not to fight for the town. Shortly thereafter, a group of Norman knights arrived, but Baldwin denied entry to them. The Turks slaughtered the Normans during the night, and Baldwin's men blamed him for their fate and massacred the remaining Seljuk garrison. Baldwin took shelter in a tower and convinced his soldiers of his innocence. A pirate captain, Guynemer of Boulogne Guynemer or Guinemerz was a Boulognese pirate who played a role in the First Crusade.
Biography
He assembled a fleet of Northern French, Danes, Frisians, and Flemings and set out from northern Europe for the eastern Mediterranean in Spring 1 ...
, sailed up the Berdan River to Tarsus and swore fealty to Baldwin, who hired Guynemer's men to garrison the city while he continued his campaign.
Tancred had meanwhile seized the town of Mamistra
Mopsuestia and Mopsuhestia ( grc, Μοψουεστία and Μόψου ἑστία, Mopsou(h)estia and Μόψου ''Mopsou'' and Μόψου πόλις and Μόψος; Byzantine Greek: ''Mamista'', ''Manistra'', ''Mampsista''; Arabic: ''al-Maṣṣ ...
. Baldwin reached the town on around 30 September. The Norman Richard of Salerno
Richard of Salerno ( 1060 – 1114), was a participant in the First Crusade and governor of the County of Edessa from 1104 to 1108. He was the cousin of Richard of Hauteville.
Biography
Richard was born around 1060, the third son of William of ...
wanted to take revenge for Tarsus, causing a skirmish between the soldiers of Baldwin and Tancred. Baldwin left Mamistra and joined the main army at Marash, but Bagrat persuaded him to launch a campaign across a region densely populated by Armenians and he left the main army on 17 October. The Armenians welcomed Baldwin, and the local population massacred the Seljuks, seizing the fortresses Ravendel and Turbessel Turbessel ( syr, Tel Bshir, ar, Tell Bāshir or , hy, Թլպաշար, translit=Tʿlpašar, tr, Tilbeşar or ) is a fortress and Bronze Age tumulus in south-eastern Turkey, near the village of Gündoğan in the district of Oğuzeli, within Gaz ...
before the end of 1097. Baldwin made Bagrat the governor of Ravendel.
The Armenian lord Thoros of Edessa Thoros, alternative transliteration T'oros, is the Armenian variant of the Greek name Theodoros (Theodore). It may refer to:
Historical figures
Chronologically:
* Thoros of Edessa (died 1098)
*Thoros of Marash, aka Thatoul (late 11th – early 12th ...
sent envoys to Baldwin in early 1098, seeking his assistance against the nearby Seljuks. Before departing for Edessa, Baldwin ordered the arrest of Bagrat, accused of collaboration with the Seljuks. Bagrat was tortured and forced to surrender Ravendel. Baldwin left for Edessa in early February, being harassed en-route by the forces of Balduk, emir of Samosata
Samsat ( ku, Samîsad), formerly Samosata ( grc, Σαμόσατα) is a small town in the Adıyaman Province of Turkey, situated on the upper Euphrates river. It is the seat of Samsat District.Crusader states
The Crusader States, also known as Outremer, were four Catholic realms in the Middle East that lasted from 1098 to 1291. These feudal polities were created by the Latin Catholic leaders of the First Crusade through conquest and political i ...
.
While the Byzantines had lost Edessa to the Seljuks in 1087, the emperor did not demand that Baldwin hand over the town. Moreover, the acquisition of Ravendel, Turbessel and Edessa strengthened the position of the main crusader army later at Antioch. The lands along the Euphrates secured a supply of food for the crusaders, and the fortresses hindered the movement of the Seljuk troops.
As his force was small, Baldwin had used diplomacy to secure his rule in Edessa. He married Arda of Armenia
Arda ( hy, Արդա; died after 1116) was the queen of Jerusalem as the 2nd spouse of King Baldwin I of Jerusalem. She was the first Queen consort of the Kingdom of Jerusalem, as Baldwin's brother and predecessor Godfrey of Bouillon was unmarried ...
, who later became queen consort of the Kingdom of Jerusalem
The Kingdom of Jerusalem ( la, Regnum Hierosolymitanum; fro, Roiaume de Jherusalem), officially known as the Latin Kingdom of Jerusalem or the Frankish Kingdom of Palestine,Example (title of works): was a Crusader state that was establish ...
, and encouraged his retainers to marry local women. The city's rich treasury enabled him to employ mercenaries and to buy Samosata from Balduk. The resultant treaty for the transfer of Samosata was the first friendly arrangement between a crusader leader and a Muslim ruler, who remained governor of the city.
An important figure in the kingdom in the 12th century was Belek Ghazi, grandson of the former Seljuk governor of Jerusalem, Artuk. Belek was to play a small role in this story who, as an Artuqid
The Artuqid dynasty (alternatively Artukid, Ortoqid, or Ortokid; , pl. ; ; ) was a Turkoman dynasty originated from tribe that ruled in eastern Anatolia, Northern Syria and Northern Iraq in the eleventh through thirteenth centuries. The Art ...
emir, had hired Baldwin to suppress a revolt in Saruj. When the Muslim leaders of the town approached Balduk to come to their rescue, Balduk hurried to Saruj, but it soon became apparent that his forces were not able to resist a siege and the defenders yielded to Baldwin. Baldwin demanded Balduk's wife and children as hostages, and upon his refusal, Baldwin had him captured and executed. With Saruj, Baldwin now had consolidated the county and ensured his communications with the main body of Crusaders. Kerbogha, ever on guard to defeat the Crusaders, gathered a large army to eliminate Baldwin. During his march towards Antioch, Kerbogha besieged the walls of Edessa for three weeks in May, but could not capture it. As discussed below, his delay played a crucial part in the Crusader victory at Antioch.
Siege of Antioch
 The crusader army, without Baldwin and Tancred, had marched on to
The crusader army, without Baldwin and Tancred, had marched on to Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου, ''Antiókheia hē epì Oróntou'', Learned ; also Syrian Antioch) grc-koi, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου; or Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπ� ...
, situated midway between Constantinople and Jerusalem. Described in a letter by Stephen of Blois as "a city very extensive, fortified with incredible strength and almost impregnable", the idea of taking the city by assault was a discouraging one to the crusaders. Hoping rather to force a capitulation, or find a traitor inside the city—a tactic that had previously seen Antioch change to the control of the Byzantines and then the Seljuk Turks—the crusader army began a siege on 20 October 1097. Antioch was so large that the crusaders did not have enough troops to fully surround it, and as a result it was able to stay partially supplied. The subsequent Siege of Antioch
The siege of Antioch took place during the First Crusade in 1097 and 1098, on the crusaders' way to Jerusalem through Syria. Two sieges took place in succession. The first siege, by the crusaders against the city held by the Seljuk Empire, ...
has been called the "most interesting siege in history."
By January the attritional eight-month siege led to hundreds, or possibly thousands, of crusaders dying of starvation. Adhemar believed this to have been caused by their sinful nature, and rituals of fasting, prayer, alms-giving and procession were undertaken. Women were expelled from the camp. Many deserted, including Stephen of Blois. Foraging systems eased the situation, as did supplies from Cicilia and Edessa, through the recently captured ports of Latakia
, coordinates =
, elevation_footnotes =
, elevation_m = 11
, elevation_ft =
, postal_code_type =
, postal_code =
, area_code = Country code: 963 City code: 41
, geocode ...
and St Symeon. In March a small English fleet arrived with supplies. The Franks benefited from disunity in the Muslim world and the possibility that they mistakenly believed the crusaders to be Byzantine mercenaries. The Seljuk brothers, Duqaq Dukak or Duqaq may refer to:
* Tuqaq (died c. 924 AD), the father of Seljuq, eponymous founder of the Seljuk dynasty
* Duqaq (Seljuk ruler of Damascus)
Abu Nasr Shams al-Muluk Duqaq (died June 8, 1104) was the Seljuq ruler of Damascus from 1095 ...
of Syria and Ridwan of Aleppo, dispatched separate relief armies in December and February that, had they been combined, would probably have been victorious.
After these failures, Kerbogha raised a coalition from southern Syria, northern Iraq and Anatolia with the ambition of extending his power from Syria to the Mediterranean. His coalition first stopped at Saruj as noted above, a decisive mistake. Bohemond persuaded the other leaders that, if Antioch fell, he would keep it for himself and that an Armenian commander of a section of the city's walls had agreed to allow the crusaders to enter. Stephen of Blois had deserted, and his message to Alexios that the cause was lost persuaded the Emperor to halt his advance through Anatolia at Philomelium before returning to Constantinople. Alexios' failure to reach the siege was used by Bohemond to rationalise his refusal to return the city to the Empire as promised. The Armenian Firouz
Firouz was a wealthy Armenian Christian convert to Islam and armor maker who held a high post in Yaghi-Siyan's Seljuk Turkish government during the Crusades. Notably, he also served as a spy for Bohemond during the Siege of Antioch. Bohemond ...
helped Bohemond and a small party enter the city on 2 June and open a gate, at which point horns were sounded, the city's Christian majority opened the other gates and the crusaders entered. In the sack they killed most of the Muslim inhabitants and many Christian Greeks, Syrians and Armenians in the confusion.
On 4 June the vanguard of Kerbogha's 40,000 strong army arrived surrounding the Franks. From 10 June for 4 days waves of Kerbogha's men assailed the city walls from dawn until dusk. Bohemond and Adhemar barred the city gates to prevent mass desertions and managed to hold out. Kerbogha then changed tactics to trying to starve the crusaders out. Morale inside the city was low and defeat looked imminent but a peasant visionary called Peter Bartholomew
Peter Bartholomew (, died 20 April 1099) was a French soldier and mystic who was part of the First Crusade as part of the army of Raymond of Saint-Gilles. Peter was initially a servant to William, Lord of Cunhlat.
Mysticism
In December 1097 du ...
claimed the apostle St, Andrew came to him to show the location of the Holy Lance
The Holy Lance, also known as the Lance of Longinus (named after Saint Longinus), the Spear of Destiny, or the Holy Spear, is the lance that pierced the side of Jesus as he hung on the cross during his crucifixion.
Biblical references
The l ...
that had pierced Christ on the cross. This supposedly encouraged the crusaders but the accounts are misleading as it was two weeks before the final battle for the city. On 24 June the Franks sought terms for surrender that were refused. On 28 June 1098 at dawn the Franks marched out of the city in four battle groups to engage the enemy. Kerbogha allowed them to deploy with the aim of destroying them in the open. However the discipline of the Muslim army did not hold and a disorderly attack was launched. Unable to overrun a bedraggled force they outnumbered two to one Muslims attacking the Bridge Gate fled through the advancing main body of the Muslim army. With very few casualties the Muslim army broke and fled the battle.
Stephen of Blois was in Alexandretta when he learned of the situation in Antioch. It seemed like their situation was hopeless so he left the Middle East, warning Alexios and his army on his way back to France. Because of what looked like a massive betrayal, the leaders at Antioch, most notably Bohemond, argued that Alexios had deserted the Crusade and thus invalidated all of their oaths to him. While Bohemond asserted his claim to Antioch, not everyone agreed (most notably Raymond of Toulouse), so the crusade was delayed for the rest of the year while the nobles argued amongst themselves. When discussing this period, a common historiographical viewpoint advanced by some scholars is that the Franks of northern France, the Provençals of southern France,At that time the terms "Provençal" or "Provence" were not limited to the present-day region of Provence
Provence (, , , , ; oc, Provença or ''Prouvènço'' , ) is a geographical region and historical province of southeastern France, which extends from the left bank of the lower Rhône to the west to the Italian border to the east; it is bo ...
, but encompassed the regions of southern France that spoke the Occitan language
Occitan (; oc, occitan, link=no ), also known as ''lenga d'òc'' (; french: langue d'oc) by its native speakers, and sometimes also referred to as ''Provençal'', is a Romance language spoken in Southern France, Monaco, Italy's Occitan Valle ...
. They were then equivalent to the terms "Occitan" or "Occitania
Occitania ( oc, Occitània , , or ) is the historical region in Western and Southern Europe where the Occitan language was historically spoken and where it is sometimes still used as a second language. This cultural area roughly encompasse ...
" which appeared later. and the Normans
The Normans ( Norman: ''Normaunds''; french: Normands; la, Nortmanni/Normanni) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norse Viking settlers and indigenous West Franks and Gallo-Romans. ...
of southern Italy considered themselves separate nations, creating turmoil as each tried to increase its individual status. Others argue that while this may have had something to do with the disputes, personal ambition among the Crusader leaders might be just as easily blamed.
Meanwhile, a plague broke out, killing many among the army, including the legate Adhemar, who died on 1 August.. There were now even fewer horses than before, and worse, the Muslim peasants in the area refused to supply the crusaders with food. Thus, in December, following the Siege of Ma'arrat al-Numan
The Siege of Ma'arra occurred in late 1098 in the city of Ma'arrat al-Numan, in what is modern-day Syria, during the First Crusade. It is infamous for the claims of widespread cannibalism displayed by the Crusaders.
Prologue
After the Crusade ...
, some historians described the first occurrence of cannibalism among the crusaders, even though this account does not appear in any contemporary Muslim chronicle. At the same time, the minor knights and soldiers had become increasingly restless and threatened to continue to Jerusalem without their squabbling leaders. Finally, at the beginning of 1099, the march restarted, leaving Bohemond behind as the first Prince of Antioch..
From Antioch to Jerusalem
Proceeding down the Mediterranean coast, the crusaders encountered little resistance, as local rulers preferred to make peace with them and furnish them with supplies rather than fight. Their forces were evolving, with Robert Curthose and Tancred agreed to become vassals of Raymond IV of Toulouse, who was wealthy enough to compensate them for their service. Godfrey of Bouillon, now supported by his brother's territories in Edessa, refused to do the same. In January, Raymond dismantled the walls of Ma'arrat al-Numan, and he began the march south to Jerusalem, barefoot and dressed as a pilgrim, followed by Robert and Tancred and their respective armies. Raymond planned to take Tripoli to set up a state equivalent to Antioch, but first initiated asiege of Arqa
Arqa ( ar, عرقا; akk, 𒅕𒋡𒋫, translit=Irqata) is a Lebanese village near Miniara in Akkar Governorate, Lebanon, 22 km northeast of Tripoli, near the coast.
The town was a notable city-state during the Iron Age. The city of '' ...
, a city in northern Lebanon, on 14 February 1099. Meanwhile, Godfrey, along with Robert II of Flanders, who had also refused vassalage to Raymond, joined with the remaining Crusaders at Latakia
, coordinates =
, elevation_footnotes =
, elevation_m = 11
, elevation_ft =
, postal_code_type =
, postal_code =
, area_code = Country code: 963 City code: 41
, geocode ...
and marched south in February. Bohemond had originally marched out with them but quickly returned to Antioch in order to consolidate his rule against the advancing Byzantines. Tancred left Raymond's service and joined with Godfrey. A separate force linked to Godfrey's was led by Gaston IV of Béarn
Gaston is a masculine given name of French origin and a surname. The name "Gaston" may refer to:
People
First name
*Gaston I, Count of Foix (1287–1315)
*Gaston II, Count of Foix (1308–1343)
*Gaston III, Count of Foix (1331–1391)
* Gaston ...
.
Godfrey, Robert, Tancred, and Gaston arrived at Arqa in March, but the siege continued. Pons of Balazun Pons of Balazun (died 1099) was an Occitan nobleman who participated in the First Crusade and in the creation of one of its earliest histories, the '' Book of the Franks Who Captured Jerusalem''.
Pons was in the army of Count Raymond IV of Toulous ...
died, struck by a stone missile. The situation was tense not only among the military leaders, but also among the clergy. Since Adhemar's death there had been no real leader of the crusade, and ever since the discovery of the Holy Lance
The Holy Lance, also known as the Lance of Longinus (named after Saint Longinus), the Spear of Destiny, or the Holy Spear, is the lance that pierced the side of Jesus as he hung on the cross during his crucifixion.
Biblical references
The l ...
, there had been accusations of fraud among the clerical factions. On 8 April, Arnulf of Chocques challenged Peter Bartholomew
Peter Bartholomew (, died 20 April 1099) was a French soldier and mystic who was part of the First Crusade as part of the army of Raymond of Saint-Gilles. Peter was initially a servant to William, Lord of Cunhlat.
Mysticism
In December 1097 du ...
to an ordeal by fire. Peter underwent the ordeal and died after days of agony from his wounds, which discredited the Holy Lance as a fake. This also undermined Raymond's authority over the Crusade, as he was the main proponent of its authenticity.
The siege of Arqa lasted until 13 May, when the Crusaders left having captured nothing. The Fatimids had recaptured Jerusalem from the Seljuks the year before and attempted to make a deal with the Crusaders, promising freedom of passage to any pilgrims to the Holy Land on the condition that the Crusaders not advance into their domains, but this was rejected. The Fatimid Iftikhar ad-Daula was governor of Jerusalem and well aware of the Crusaders' intentions. Therefore, he expelled all of Jerusalem's Christian inhabitants. He also poisoned most of the wells in the area. On 13 May, the Crusaders came to Tripoli, where the emir Jalal al-Mulk Abu'l Hasan provided the crusader army with horses and vowed to convert to Christianity if the Crusaders defeated the Fatimids. Continuing south along the coast, the Crusaders passed Beirut
Beirut, french: Beyrouth is the capital and largest city of Lebanon. , Greater Beirut has a population of 2.5 million, which makes it the third-largest city in the Levant region. The city is situated on a peninsula at the midpoint o ...
on 19 May and Tyre on 23 May. Turning inland at Jaffa
Jaffa, in Hebrew Yafo ( he, יָפוֹ, ) and in Arabic Yafa ( ar, يَافَا) and also called Japho or Joppa, the southern and oldest part of Tel Aviv-Yafo, is an ancient port city in Israel. Jaffa is known for its association with the b ...
, on 3 June they reached Ramla
Ramla or Ramle ( he, רַמְלָה, ''Ramlā''; ar, الرملة, ''ar-Ramleh'') is a city in the Central District of Israel. Today, Ramle is one of Israel's mixed cities, with both a significant Jewish and Arab populations.
The city was f ...
, which had been abandoned by its inhabitants. The bishopric of Ramla-Lydda was established there at the Church of St. George before they continued on to Jerusalem. On 6 June, Godfrey sent Tancred and Gaston to capture Bethlehem
Bethlehem (; ar, بيت لحم ; he, בֵּית לֶחֶם '' '') is a city in the central West Bank, Palestine, about south of Jerusalem. Its population is approximately 25,000,Amara, 1999p. 18.Brynen, 2000p. 202. and it is the capital ...
, where Tancred flew his banner over the Church of the Nativity
The Church of the Nativity, or Basilica of the Nativity,; ar, كَنِيسَةُ ٱلْمَهْد; el, Βασιλική της Γεννήσεως; hy, Սուրբ Ծննդեան տաճար; la, Basilica Nativitatis is a basilica located in B ...
. On 7 June, the Crusaders reached Jerusalem. Many Crusaders wept upon seeing the city they had journeyed so long to reach..
Siege of Jerusalem
 The Crusaders' arrival at Jerusalem revealed an arid countryside, lacking in water or food supplies. Here there was no prospect of relief, even as they feared an imminent attack by the local Fatimid rulers. There was no hope of trying to blockade the city as they had at Antioch; the crusaders had insufficient troops, supplies, and time. Rather, they resolved to take the city by assault. They might have been left with little choice, as by the time the Crusader army reached Jerusalem, it has been estimated that only about 12,000 men including 1,500 cavalry remained.. Thus began the decisive Siege of Jerusalem. These contingents, composed of men with differing origins and varying allegiances, were also approaching another low ebb in their camaraderie. While Godfrey and Tancred made camp to the north of the city, Raymond made his to the south. In addition, the Provençal contingent did not take part in the initial assault on 13 June 1099. This first assault was perhaps more speculative than determined, and after scaling the outer wall the Crusaders were repulsed from the inner one.
After the failure of the initial assault, a meeting between the various leaders was organized in which it was agreed upon that a more concerted attack would be required in the future. On 17 June, a party of Genoese mariners under
The Crusaders' arrival at Jerusalem revealed an arid countryside, lacking in water or food supplies. Here there was no prospect of relief, even as they feared an imminent attack by the local Fatimid rulers. There was no hope of trying to blockade the city as they had at Antioch; the crusaders had insufficient troops, supplies, and time. Rather, they resolved to take the city by assault. They might have been left with little choice, as by the time the Crusader army reached Jerusalem, it has been estimated that only about 12,000 men including 1,500 cavalry remained.. Thus began the decisive Siege of Jerusalem. These contingents, composed of men with differing origins and varying allegiances, were also approaching another low ebb in their camaraderie. While Godfrey and Tancred made camp to the north of the city, Raymond made his to the south. In addition, the Provençal contingent did not take part in the initial assault on 13 June 1099. This first assault was perhaps more speculative than determined, and after scaling the outer wall the Crusaders were repulsed from the inner one.
After the failure of the initial assault, a meeting between the various leaders was organized in which it was agreed upon that a more concerted attack would be required in the future. On 17 June, a party of Genoese mariners under Guglielmo Embriaco
Guglielmo Embriaco (Latin ''Guillermus Embriacus'', Genoese ''Ghigærmo de ri Embrieghi'', English ''William the Drunkard''; born c. 1040), was a Genoese merchant and military leader who came to the assistance of the Crusader States in the afterm ...
arrived at Jaffa
Jaffa, in Hebrew Yafo ( he, יָפוֹ, ) and in Arabic Yafa ( ar, يَافَا) and also called Japho or Joppa, the southern and oldest part of Tel Aviv-Yafo, is an ancient port city in Israel. Jaffa is known for its association with the b ...
, and provided the Crusaders with skilled engineers, and perhaps more critically, supplies of timber (stripped from the ships) to build siege engine
A siege engine is a device that is designed to break or circumvent heavy castle doors, thick city walls and other fortifications in siege warfare. Some are immobile, constructed in place to attack enemy fortifications from a distance, while oth ...
s. The Crusaders' morale was raised when the priest Peter Desiderius claimed to have had a divine vision of Adhemar of Le Puy, instructing them to fast and then march in a barefoot procession around the city walls, after which the city would fall, following the Biblical story of the battle of Jericho. After a three-day fast, on 8 July the Crusaders performed the procession as they had been instructed by Desiderius, ending on the Mount of Olives where Peter the Hermit preached to them, and shortly afterward the various bickering factions arrived at a public rapprochement. News arrived shortly after that a Fatimid relief army had set off from Egypt, giving the Crusaders a very strong incentive to make another assault on the city.
The final assault on Jerusalem began on 13 July. Raymond's troops attacked the south gate while the other contingents attacked the northern wall. Initially the Provençals at the southern gate made little headway, but the contingents at the northern wall fared better, with a slow but steady attrition of the defence. On 15 July, a final push was launched at both ends of the city, and eventually the inner rampart of the northern wall was captured. In the ensuing panic, the defenders abandoned the walls of the city at both ends, allowing the Crusaders to finally enter.
The massacre that followed the capture of Jerusalem has attained particular notoriety, as a "juxtaposition of extreme violence and anguished faith". The eyewitness accounts from the crusaders themselves leave little doubt that there was great slaughter in the aftermath of the siege. Nevertheless, some historians propose that the scale of the massacre has been exaggerated in later medieval sources.
After the successful assault on the northern wall, the defenders fled to the Temple Mount
The Temple Mount ( hbo, הַר הַבַּיִת, translit=Har haBayīt, label=Hebrew, lit=Mount of the House f the Holy}), also known as al-Ḥaram al-Sharīf (Arabic: الحرم الشريف, lit. 'The Noble Sanctuary'), al-Aqsa Mosque compou ...
, pursued by Tancred and his men. Arriving before the defenders could secure the area, Tancred's men assaulted the precinct, butchering many of the defenders, with the remainder taking refuge in the Al-Aqsa Mosque
Al-Aqsa Mosque (, ), also known as Jami' Al-Aqsa () or as the Qibli Mosque ( ar, المصلى القبلي, translit=al-Muṣallā al-Qiblī, label=none), and also is a congregational mosque located in the Old City of Jerusalem. It is situate ...
. Tancred then called a halt to the slaughter, offering those in the mosque his protection. When the defenders on the southern wall heard of the fall of the northern wall, they fled to the citadel, allowing Raymond and the Provençals to enter the city. Iftikhar al-Dawla, the commander of the garrison, struck a deal with Raymond, surrendering the citadel in return for being granted safe passage to Ascalon.
The slaughter continued for the rest of the day; Muslims were indiscriminately killed, and Jews who had taken refuge in their synagogue died when it was burnt down by the Crusaders. The following day, Tancred's prisoners in the mosque were slaughtered. Nevertheless, it is clear that some Muslims and Jews of the city survived the massacre, either escaping or being taken prisoner to be ransomed. The Letter of the Karaite elders of Ascalon
The Letter of the Karaite elders of Ascalon (c. 1100) was a communication written by six elders of the Karaite Jewish community of Ascalon and sent to their coreligionists in Alexandria nine months after the fall of Jerusalem during the First Cr ...
provides details of Ascalon Jews making great efforts to ransom such Jewish captives and send them to safety in Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandri ...
. The Eastern Christian population of the city had been expelled before the siege by the governor, and thus escaped the massacre.
Establishment of the Kingdom of Jerusalem
 On 22 July, a council was held in the
On 22 July, a council was held in the Church of the Holy Sepulchre
The Church of the Holy Sepulchre, hy, Սուրբ Հարության տաճար, la, Ecclesia Sancti Sepulchri, am, የቅዱስ መቃብር ቤተክርስቲያን, he, כנסיית הקבר, ar, كنيسة القيامة is a church i ...
to establish governance for Jerusalem. The death of the Greek Patriarch meant there was no obvious ecclesiastical candidate to establish a religious lordship, as a body of opinion maintained. Although Raymond of Toulouse could claim to be the pre-eminent crusade leader from 1098 his support had waned since his failed attempts to besiege Arqa
Arqa ( ar, عرقا; akk, 𒅕𒋡𒋫, translit=Irqata) is a Lebanese village near Miniara in Akkar Governorate, Lebanon, 22 km northeast of Tripoli, near the coast.
The town was a notable city-state during the Iron Age. The city of ...
and create his own realm. This may have been why he piously refused the crown on the grounds that it could only be worn by Christ. It may also have been an attempt to persuade others to reject the title, but Godfrey was already familiar with such a position. Probably more persuasive was the presence of the large army from Lorraine, led by him and his brothers, Eustace and Baldwin, vassals of the Ardennes–Bouillion dynasty. Godfrey was then elected leader, accepting the title '' Advocatus Sancti Sepulchri'' or ''Defender of the Holy Sepulchre''. Raymond, incensed at this development, attempted to seize the Tower of David
The Tower of David ( he, מגדל דוד, Migdál Davíd), also known as the Citadel ( ar, القلعة, al-Qala'a), is an ancient citadel located near the Jaffa Gate entrance to the Old City of Jerusalem.
The citadel that stands today dates ...
before leaving the city.
While the Kingdom of Jerusalem would remain until 1291, the city of Jerusalem would be lost to the Muslims under Saladin
Yusuf ibn Ayyub ibn Shadi () ( – 4 March 1193), commonly known by the epithet Saladin,, ; ku, سهلاحهدین, ; was the founder of the Ayyubid dynasty. Hailing from an ethnic Kurdish family, he was the first of both Egypt an ...
in 1187, a result of the decisive Battle of Hattin
The Battle of Hattin took place on 4 July 1187, between the Crusader states of the Levant and the forces of the Ayyubid sultan Saladin. It is also known as the Battle of the Horns of Hattin, due to the shape of the nearby extinct volcano of ...
. The history of Jerusalem
During its long history, Jerusalem has been attacked 52 times, captured and recaptured 44 times, besieged 23 times, and destroyed twice.. According to Eric H. Cline's tally in Jerusalem Besieged. The oldest part of the city was settled in the ...
would record Muslim rule for 40 years, returning finally to Christian control following a series of later Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were ...
..
Battle of Ascalon
In August 1099, Fatimid vizieral-Afdal Shahanshah
Al-Afdal Shahanshah ( ar, الأفضل شاهنشاه, al-Afḍal Shāhanshāh; la, Lavendalius/Elafdalio; 1066 – 11 December 1121), born Abu al-Qasim Shahanshah bin Badr al-Jamali was a vizier of the Fatimid caliphs of Egypt. According to a ...
landed a force of 20,000 North Africans at Ascalon. Geoffrey and Raymond marched out to meet this force on 9 August with a force of only 1,200 knights and 9,000 foot soldiers. Outnumbered two to one, the Franks launched a surprise dawn attack and routed the overconfident and unprepared Muslim force. The opportunity was wasted though, as squabbling between Raymond and Godfrey prevented an attempt by the city's garrison to surrender to the more trusted Raymond. The crusaders had won a decisive victory, but the city remained in Muslim hands and a military threat to the nascent kingdom.
Aftermath and legacy
Dagobert of Pisa
Dagobert (or Daibert or Daimbert) (died 1105) was the first Archbishop of Pisa_and_the_second_Latin_Patriarch_of_Jerusalem.html" ;"title="717, Pisan and on 31 July 1725
and his plans to make Jerusalem a theocracy and instead made Baldwin the first Latin king_of_Jerusalemking_of_Jerusalem_
The_King_of_Jerusalem_was_the_supreme_ruler_of_the__Kingdom_of_Jerusalem,_a__Crusader_state_founded_in_Jerusalem_by_the_Latin_Catholic_leaders_of_the_First_Crusade,_when_the_city_was__conquered_in_1099.
_Godfrey_of_Bouillon,_the_first_ruler_of_...
._Bohemond_returned_to_Europe_to_fight_the_Byzantines_from_Italy_but_he_was_defeated_in_1108_at_Siege_of_Dyrrhachium_(1107–1108).html" ;"title="List_of_kings_of_Jerusalem.html" "title="726, Pisan
A special assembly (''conventus'') was held in P ... and the seco ...County of Edessa
The County of Edessa (Latin: ''Comitatus Edessanus'') was one of the Crusader states in the 12th century. Ferdinandi, Sergio (2017). La Contea Franca di Edessa. Fondazione e Profilo Storico del Primo Principato Crociato nel Levante (1098-115 ...
and Principality of Antioch
The Principality of Antioch was one of the crusader states created during the First Crusade which included parts of modern-day Turkey and Syria. The principality was much smaller than the County of Edessa or the Kingdom of Jerusalem. It exte ...
were variable. They fought together in the crusader defeat at the Battle of Harran in 1104, but the Antiocheans claimed suzerainty and blocked the return of Baldwin II of Jerusalem after his capture at the battle. The Franks became fully engaged in Near East politics with the result that Muslims and Christians often fought each other. Antioch's territorial expansion ended in 1119 with a major defeat to the Turks at the Battle of Ager Sanguinis
In the Battle of ''Ager Sanguinis'', also known as the Battle of the Field of Blood, the Battle of Sarmada, or the Battle of Balat, Roger of Salerno's Crusader army of the Principality of Antioch was annihilated by the army of Ilghazi of Mardin ...
, the Field of Blood.
Stephen of Blois
Stephen (1092 or 1096 – 25 October 1154), often referred to as Stephen of Blois, was King of England from 22 December 1135 to his death in 1154. He was Count of Boulogne ''jure uxoris'' from 1125 until 1147 and Duke of Normandy from 1135 unti ...
, and Hugh of Vermandois, both of whom had returned home before reaching Jerusalem. This crusader force was almost annihilated in Asia Minor by the Seljuks, but the survivors helped to reinforce the kingdom upon their arrival in Jerusalem.
There is limited written evidence of the Islamic reaction dating from before 1160, but what there is indicates the crusade was barely noticed. This may be the result of a cultural misunderstanding in that the Turks and Arabs did not recognise the crusaders as religiously-motivated warriors seeking conquest and settlement, assuming that the crusaders were just the latest in a long line of Byzantine mercenaries. Also, the Islamic world remained divided among rival rulers in Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the largest urban agglomeration in Africa, the Arab world and the Middle East: The Greater Cairo metr ...
, Damascus
)), is an adjective which means "spacious".
, motto =
, image_flag = Flag of Damascus.svg
, image_seal = Emblem of Damascus.svg
, seal_type = Seal
, map_caption =
, ...
, Aleppo
)), is an adjective which means "white-colored mixed with black".
, motto =
, image_map =
, mapsize =
, map_caption =
, image_map1 =
...
, and Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon ...
. There was no pan-Islamic counter-attack, giving the crusaders the opportunity to consolidate.
Historiography
Latin Christendom was amazed by the success of the First Crusade for which the only credible explanation was divine providence. If the crusade had failed it is likely that the paradigm of crusading would have been abandoned. Instead, this form of religious warfare was popular for centuries and the crusade itself became one of the most written-about historic events of the medieval period.Bréhier, Louis René (1908). " Crusades (Sources and Bibliography)". In Herbermann, Charles (ed.). ''Catholic Encyclopedia''. 4. New York: Robert Appleton Company. Thehistoriography
Historiography is the study of the methods of historians in developing history as an academic discipline, and by extension is any body of historical work on a particular subject. The historiography of a specific topic covers how historians h ...
(history of the histories) of the First Crusade and the Crusades in general, as expected, show works that reflect the views of the authors and the times that they lived in. Critical analyses of these works can be found in studies by Jonathan Riley-Smith
Jonathan Simon Christopher Riley-Smith (27 June 1938 – 13 September 2016) was a historian of the Crusades, and, between 1994 and 2005, Dixie Professor of Ecclesiastical History at Cambridge. He was a Fellow of Emmanuel College, Cambridge.
P ...
and Christopher Tyerman
Christopher Tyerman (born 22 May 1953) is an academic historian focusing on the Crusades. In 2015, he was appointed Professor of History of the Crusades at the University of Oxford.
Life and career
He graduated from New College, Oxford, with a f ...
.
Original sources
The 19th-century French work ''Recueil des historiens des croisades {{italic title
The ''Recueil des historiens des croisades'' (trans: ''Collection of the Historians of the Crusades'') is a major collection of several thousand medieval documents written during the Crusades. The documents were collected and publis ...
'' (RHC) documents the original narrative sources of the First Crusade from Latin, Arabic, Greek, Armenian and Syriac authors. The documents are presented in their original language with French translations. The work built on the 17th century work ''Gesta Dei per Francos'', compiled by Jacques Bongars. Several Hebrew sources on the First Crusade also exist. A complete bibliography can be found in ''The Routledge Companion to the Crusades.'' See also Crusade Texts in Translation Crusade Texts in Translation is a book series of English translations of texts about the Crusades published initially by Ashgate in Farnham, Surrey and Burlington, Vermont, and currently by Routledge. Publication began in May 1996.
The editors of ...
and ''Selected Sources: The Crusades,'' in Fordham University's ''Internet Medieval Sourcebook
The Internet History Sourcebooks Project is located at the Fordham University History Department and Center for Middle Ages, Medieval Studies. It is a web site with modern, medieval and ancient primary source documents, maps, secondary sources, Bi ...
.''
The Latin narrative sources for the First Crusade are: (1) the anonymous ''Gesta Francorum
The ''Gesta Francorum'' (Deeds of the Franks), or ''Gesta Francorum et aliorum Hierosolimitanorum'' (Deeds of the Franks and the other pilgrims to Jerusalem), is a Latin chronicle of the First Crusade by an anonymous author connected with Bohemon ...
''; (2) Peter Tudebode's ''Historia de Hierosolymitano itinere''; (3) the Monte Cassino chronicle ''Historia belli sacri
The ''Historia belli sacri'', also called the ''Historia de via Hierosolymis''Jerzy Kaliszuk"Historia de via Hierosolymis" in Graeme Dunphy and Cristian Bratu (eds.), '' Encyclopedia of the Medieval Chronicle'' (Brill, online 2016), retrieved 12 ...
;'' (4) ''Historia Francorum qui ceperunt Iherusalem
The ''Historia Francorum qui ceperunt Iherusalem'' (; "History of the Franks who captured Jerusalem"), which has also been published under the simple title ''Liber'' ("Book"), is a Latin chronicle of the First Crusade written between 1098 and 1105, ...
'' by Raymond of Aguilers; (5) ''Gesta Francorum Iherusalem Perefrinantium'' by Fulcher of Chartres Fulcher of Chartres (c. 1059 in or near Chartres – after 1128) was a priest who participated in the First Crusade. He served Baldwin I of Jerusalem for many years and wrote a Latin chronicle of the Crusade.
Life
Fulcher was born c. 1059. His app ...
; (6) Albert of Aachen's ''Historia Hierosolymitanae expeditionis''; (7) Ekkehard of Aura's ''Hierosolymita''; (8) Robert the Monk's ''Historia Hierosolymitana''; (9) Baldric of Dol's ''Historiae Hierosolymitanae libri IV''; (10) Radulph of Caen's ''Gesta Tancredi in expeditione Hierosolymitana''; and (11) ''Dei gesta per Francos
''Dei gesta per Francos'' ("Deeds of God through the Franks") is a narrative of the First Crusade by Guibert of Nogent written between 1107 and 1108. Traditionally it has not been well received by scholars, but recent translators and editors (such ...
'' by Guibert of Nogent
Guibert de Nogent (c. 1055 – 1124) was a Benedictine historian, theologian and author of autobiographical memoirs. Guibert was relatively unknown in his own time, going virtually unmentioned by his contemporaries. He has only recently caught the ...
. These include multiple first-hand accounts of the Council of Clermont and the crusade itself.Edgington, Susan, and Murray, Alan V. (2006). "Western Sources". In ''The Crusades – An Encyclopedia''. pp. 1269–1276. American historian August Krey has created a narrative ''The First Crusade: The Accounts of Eyewitnesses and Participants,'' verbatim from the various chronologies and letters which offers considerable insight into the endeavor.
Important related works include the Greek perspective offered in the ''Alexiad
The ''Alexiad'' ( el, Ἀλεξιάς, Alexias) is a medieval historical and biographical text written around the year 1148, by the Byzantine princess Anna Komnene, daughter of Emperor Alexios I Komnenos. It was written in a form of artificial ...
'' by Byzantine princess Anna Komnene
Anna Komnene ( gr, Ἄννα Κομνηνή, Ánna Komnēnḗ; 1 December 1083 – 1153), commonly Latinized as Anna Comnena, was a Byzantine princess and author of the ''Alexiad'', an account of the reign of her father, the Byzantine emperor, ...
, daughter of the emperor. The view of the Crusades from the Islamic perspective is found in two major sources. The first, ''The Chronicle of Damascus'', is by Arab historian Ibn al-Qalanisi
Abū Yaʿlā Ḥamzah ibn al-Asad ibn al-Qalānisī ( ar, ابو يعلى حمزة ابن الاسد ابن القلانسي; c. 1071 – 18 March 1160) was an Arab politician and chronicler in 12th-century Damascus.
Biography
Abu Ya‘la ('fathe ...
. The second is The Complete History
''The Complete History'' (, ''al-Kāmil fit-Tārīkh)'', is a classic Islamic history book written by Ali ibn al-Athir. Composed in ca. 1231AD/628AH, it is one of the most important Islamic historical works. Ibn al-Athir was a contemporary and memb ...
(''Kamil fi at-Tarikh'') by the Arab (or Kurdish) historian Ali ibn al-Athir
Abū al-Ḥasan ʿAlī ibn Muḥammad ibn Muḥammad ash-Shaybānī, better known as ʿAlī ʿIzz ad-Dīn Ibn al-Athīr al-Jazarī ( ar, علي عز الدین بن الاثیر الجزري) lived 1160–1233) was an Arab or Kurdish historian ...
. Minor but important works from the Armenian and Syriac are Matthew of Edessa's ''Chronicle'' and the ''Chronicle'' of Michael the Syrian
Michael the Syrian ( ar, ميخائيل السرياني, Mīkhaʾēl el Sūryani:),( syc, ܡܺܝܟ݂ܳܐܝܶܠ ܣܽܘܪܝܳܝܳܐ, Mīkhoʾēl Sūryoyo), died 1199 AD, also known as Michael the Great ( syr, ܡܺܝܟ݂ܳܐܝܶܠ ܪܰܒ݁ܳܐ, ...
. The three Hebrew chronicles include the Solomon bar Simson Chronicle The ''Solomon bar Simson Chronicle'' is an anonymous Hebrew narrative history produced in the mid-12th century (1140). Like the '' Eliezer bar Nathan Chronicle'' and the ''Mainz Anonymous'', it is concerned with the persecutions of Jewish communiti ...
discussing the Rhineland massacres
The Rhineland massacres, also known as the German Crusade of 1096 or ''Gzerot Tatnó'' ( he, גזרות תתנ"ו, "Edicts of 4856"), were a series of mass murders of Jews perpetrated by mobs of French and German Christians of the People's Cru ...
. A complete description of sources of the First Crusade is found in Claude Cahen's ''La Syrie du nord à l'époque des croisades et la principauté franque d'Antioche''.
The anonymous author of the ''Gesta'', Fulcher of Chartres and Raymond of Aguilers were all participants in the Crusade, accompanied different contingents, and their works are regarded as foundational. Fulcher and Raymond both utilized ''Gesta'' to some extent, as did Peter Tudebode and the ''Historia Belli Sacri'', with some variations. The ''Gesta'' was reworked (some with other eyewitness accounts) by Guibert of Nogent, Baldric of Dol, and Robert the Monk, whose work was the most widely read. Albert's account appears to be written independently of the ''Gesta,'' relying on other eyewitness reports. Derivative accounts of the Crusade include Bartolf of Nangis' ''Gesta Francorum Iherusalem expugnatium'', Henry of Huntingdon's ''De Captione Antiochiae,'' Sigebert of Gembloux's ''Chronicon sive Chronographia,'' and Benedetto Accolti's ''De Bello a Christianis contra Barbaros.Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). " Accolti, Benedetto". ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. 1 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 121.''
 A 19th-century perspective of these works can be found in Heinrich von Sybel's ''History and Literature of the Crusades''.Sybel, H. von (1861). ''Literature of the Crusades''. In
A 19th-century perspective of these works can be found in Heinrich von Sybel's ''History and Literature of the Crusades''.Sybel, H. von (1861). ''Literature of the Crusades''. InThe history and literature of the crusades
London. pp. 99–272. Von Sybel also discusses some of the more important letters and correspondence from the First Crusade that provide some historical insight. See also the works ''Die Kreuzzugsbriefe aus den Jahren'', ''1088–1100,'' by Heinrich Hagenmeyer and ''Letters of the Crusaders,'' by Dana Carleton Munro. Hagenmeyer also prepared the ''Chronologie de la première croisade 1094–1100,'' a day-by-day account of the First Crusade, cross-referenced to original sources, with commentary.
Later works through the 18th century
The popularity of these works shaped how crusading was viewed in the medieval mind. Numerous poems and songs sprung from the First Crusade, including Gilo of Toucy's ''Historia de via Hierosolymitana
The ''Historia de via Hierosolymitana'' is a Latin epic verse history of the First Crusade. Originally composed before 1120 as a work in five books by Gilo of Toucy, it was expanded by the addition of four more by an anonymous poet known as "F ...
.'' The well-known ''chanson de geste,'' ''Chanson d'Antioche
The ''Chanson d'Antioche'' is a ''chanson de geste'' in 9000 lines of in stanzas called ''laisses'', now known in a version composed about 1180 for a courtly French audience and embedded in a quasi-historical cycle of epic poems inspired by th ...
'', describes the First Crusade from the original preaching through the taking of Antioch in 1098 and into 1099. Based on Robert's work, ''Chanson d'Antioche'' was a valuable resource in helping catalog participants in the early Crusades and shaped how crusading was viewed in the medieval mind. A later poem was Torquato Tasso
Torquato Tasso ( , also , ; 11 March 154425 April 1595) was an Italian poet of the 16th century, known for his 1591 poem ''Gerusalemme liberata'' ( Jerusalem Delivered), in which he depicts a highly imaginative version of the combats between ...
's 16th century ''Gerusalemme liberata
''Jerusalem Delivered'', also known as ''The Liberation of Jerusalem'' ( it, La Gerusalemme liberata ; ), is an epic poem by the Italian poet Torquato Tasso, first published in 1581, that tells a largely mythified version of the First Crusad ...
,'' was based on Accolti's work and popular for nearly two centuries. Tasso's work was converted into the biography ''Godfrey of Bulloigne, or, The recoverie of Jerusalem,'' by Edward Fairfax
Edward Fairfax (c. 1580 – 27 January 1635) was an English translator. He translated Torquato Tasso's '' Jerusalem Delivered''. He also wrote an original work on demonology.
Life
He was the natural son of Sir Thomas Fairfax the elder, of ...
.
Later histories include English chronicler Orderic Vitalis' ''Historia Ecclesiastica.'' The work was a general social history of medieval England that includes a section on the First Crusade based on Baldric's account, with added details from oral sources and biographical details. The ''Gesta'' and the more detailed account of Albert of Aachen were used as the basis of the work of William of Tyre
William of Tyre ( la, Willelmus Tyrensis; 113029 September 1186) was a medieval prelate and chronicler. As archbishop of Tyre, he is sometimes known as William II to distinguish him from his predecessor, William I, the Englishman, a former ...
, ''Historia rerum in partibus transmarinis gestarum'' and its extensions. The archbishop of Tyre's work was a major primary source for the history of the First Crusade and is regarded as their first analytical history. Later histories, through the 17th century, relied heavily on his writings. These histories used primary source materials, but they used them selectively to talk of Holy War (''bellum sacrum''), and their emphasis was upon prominent individuals and upon battles and the intrigues of high politics.''''
Other works included by Bongars are ''Historia Hierosolymitana'' written by theologian and historian Jacques de Vitry
Jacques de Vitry (''Jacobus de Vitriaco'', c. 1160/70 – 1 May 1240) was a French canon regular who was a noted theologian and chronicler of his era.
He was elected bishop of Acre in 1214 and made cardinal in 1229.
His ''Historia Orientali ...
, a participant in a later crusade; ''Historia'' by Byzantine emperor John VI Kantakouzenos
John VI Kantakouzenos or Cantacuzene ( el, , ''Iōánnēs Ángelos Palaiológos Kantakouzēnós''; la, Johannes Cantacuzenus; – 15 June 1383) was a Byzantine Greek nobleman, statesman, and general. He served as grand domestic under ...
, an account of Godfrey of Bouillon's arrival in Constantinople in 1096; and '' Liber Secretorum Fidelium Crucis'' by Venetian statesman and geographer Marino Sanuto, whose work on geography was invaluable to later historians. The first biography of Godfrey of Bouillon
Godfrey of Bouillon (, , , ; 18 September 1060 – 18 July 1100) was a French nobleman and pre-eminent leader of the First Crusade. First ruler of the Kingdom of Jerusalem from 1099 to 1100, he avoided the title of king, preferring that of princ ...
, ''Historia et Gesta Ducis Gotfridi'' ''seu historia de desidione Terræ sanctæ,'' was written by anonymous German authors in 1141, relying on the original narratives and later histories, and appears in the RHC.
The first use of the term ''crusades'' was by 17th century French Jesuit and historian Louis Maimbourg in his ''Histoire des Croisades pour la délivrance de la Terre Sainte'', a populist and royalist history of the Crusades from 1195 to 1220. An earlier work by Thomas Fuller
Thomas Fuller (baptised 19 June 1608 – 16 August 1661) was an English churchman and historian. He is now remembered for his writings, particularly his ''Worthies of England'', published in 1662, after his death. He was a prolific author, and ...
,Stephen, Leslie (1889). "Thomas Fuller
Thomas Fuller (baptised 19 June 1608 – 16 August 1661) was an English churchman and historian. He is now remembered for his writings, particularly his ''Worthies of England'', published in 1662, after his death. He was a prolific author, and ...
". In ''Dictionary of National Biography''. 20. London. pp. 315–320. ''The Historie of the Holy Warre'' refers to the entire enterprise as the ''Holy War'', with individual campaigns called ''voyages.'' Fuller's account was more anecdotal than historical, and was very popular until the Restoration. The work used original sources from ''Gesta Dei per Francos,'' and includes a chronology that is surprisingly complete for such an early work.
Notable works of the 18th century include ''Histoire des Croisades'', a history of the Crusades from the rise of the Seljuks until 1195 by French philosopher Voltaire
François-Marie Arouet (; 21 November 169430 May 1778) was a French Enlightenment writer, historian, and philosopher. Known by his '' nom de plume'' M. de Voltaire (; also ; ), he was famous for his wit, and his criticism of Christianity—e ...
. Scottish philosopher and historian David Hume
David Hume (; born David Home; 7 May 1711 NS (26 April 1711 OS) – 25 August 1776) Cranston, Maurice, and Thomas Edmund Jessop. 2020 999br>David Hume" '' Encyclopædia Britannica''. Retrieved 18 May 2020. was a Scottish Enlightenment ph ...
did not write directly of the First Crusade, but his The History of England described the Crusades as the "nadir of Western civilization." This view was continued by Edward Gibbon
Edward Gibbon (; 8 May 173716 January 1794) was an English historian, writer, and member of parliament. His most important work, '' The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire'', published in six volumes between 1776 and 1788, i ...
in his History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire
''The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire'' is a six-volume work by the English historian Edward Gibbon. It traces Western civilization (as well as the Islamic and Mongolian conquests) from the height of the Roman Empire to t ...
, excerpted as ''The Crusades, A.D. 1095–1261''.Gibbon, E., Kaye, J., Scott, W., Caoursin, G. (1870)The crusades
London. This edition also includes an essay on
chivalry
Chivalry, or the chivalric code, is an informal and varying code of conduct developed in Europe between 1170 and 1220. It was associated with the medieval Christian institution of knighthood; knights' and gentlemen's behaviours were governed b ...
by Sir Walter Scott
Sir Walter Scott, 1st Baronet (15 August 1771 – 21 September 1832), was a Scottish novelist, poet, playwright and historian. Many of his works remain classics of European and Scottish literature, notably the novels '' Ivanhoe'', '' Rob Roy ...
, whose works helped popularize the Crusades.
The 19th and 20th centuries
Early in the 19th century, the monumental ''Histoire des Croisades''Michaud, J. Fr. (Joseph Fr.). (1841)Histoire des croisades
6. éd. Paris. was published by the French historian
Joseph François Michaud
Joseph is a common male given name, derived from the Hebrew Yosef (יוֹסֵף). "Joseph" is used, along with "Josef", mostly in English, French and partially German languages. This spelling is also found as a variant in the languages of the mo ...
. under the editorship of Jean Poujoulat. This provided a major new narrative based on original sources and was translated into English as ''The History of the Crusades''.Michaud, J. Fr., Robson, W. (1881)The history of the crusades
New ed. London. The work covers the First Crusade and its causes, and the crusades through 1481. French historian Jean-François-Aimé Peyré expanded Michaud's work on the First Crusade with his ''Histoire de la Première Croisade'',' a 900-page, two-volume set with extensive sourcing. The English school of Crusader historians included Charles Mills who wrote ''
History of the Crusades for the Recovery and Possession of the Holy Land
''The History of the Crusades for the Recovery and Possession of the Holy Land'' was a two-volume work published in 1820 by Charles Mills.Mills, C. (1822)The history of the crusades for the recovery and possession of the Holy Land 3d ed. London. ...
'', a complete history of nine Crusades, disparaging Gibbon's work as superficial. Henry Stebbings wrote his ''History of Chivalry and the Crusades'', a discussion of chivalry and history of the first seven Crusades. Thomas Archer
Thomas Archer (1668–1743) was an English Baroque architect, whose work is somewhat overshadowed by that of his
contemporaries Sir John Vanbrugh and Nicholas Hawksmoor. His buildings are important as the only ones by an English Baroque archit ...
and Charles Kingsford wrote ''The Crusades: The Story of the Latin Kingdom of Jerusalem'',Archer, T. Andrew., Kingsford, C. Lethbridge., Kingsford, C. Lethbridge., Kingsford, C. Lethbridge (1904)The crusades: The story of the Latin kingdom of Jerusalem
New York.. rejecting the idea that the
Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid S ...
and the Albigensian Crusade
The Albigensian Crusade or the Cathar Crusade (; 1209–1229) was a military and ideological campaign initiated by Pope Innocent III to eliminate Catharism in Languedoc, southern France. The Crusade was prosecuted primarily by the French crow ...
should be designated as crusades.
The German school of Crusaders was led by Friederich Wilken, whose ''Geschichte der Kreuzzüge'' was a complete history of the Crusades, based on Western, Arabic, Greek and Armenian sources. Later, Heinrich von Sybel, who studied under Leopold von Ranke
Leopold von Ranke (; 21 December 1795 – 23 May 1886) was a German historian and a founder of modern source-based history. He was able to implement the seminar teaching method in his classroom and focused on archival research and the analysis ...
(the father of modern source-based history) challenged the work of William of Tyre as being secondary. His ''Geschichte des ersten Kreuzzuges'' was a history of the First Crusade and contains a full study of the authorities for the First Crusade, and was translated to ''History and Literature of the Crusades'' by English author Lucie, Lady Duff-Gordon
Lucie, Lady Duff-Gordon ( Austin; 24 June 1821 – 14 July 1869) was an English author and translator who wrote as Lucie Gordon. She is best known for her ''Letters from Egypt, 1863–1865'' (1865) and ''Last Letters from Egypt'' (1875), most ...
.
The greatest German historian of the Crusades was then Reinhold Röhricht. His histories of the First Crusade, ''Geschichte des ersten Kreuzzuges'', and of the kings of Jerusalem, ''Geschichte des Königreichs Jerusalem,'' laid the foundation of all modern crusade research.La Monte, J. (1940)Some Problems in Crusading Historiography
Speculum, 15(1), 57–75. His ''Bibliotheca geographica Palaestinae'' summarizes over 3500 books on the geography of the Holy Land, providing a valuable resource for historians. Röhricht's colleague
Heinrich Hagenmeyer Heinrich Hagenmeyer (1834–1915) was a German Protestant pastor and historian, specializing in writing and editing texts from the beginning of the Crusades. Closely associated with fellow German Reinhold Röhricht, their contribution to the histor ...
wrote ''Peter der Eremite,'' a critical contribution to the history of the First Crusade and the role of Peter the Hermit.
Two encyclopedia articles appeared in the early 20th century that are frequently called out by Crusader historians.'''' The first of these is ''Crusades'', by French historian Louis R. Bréhier, appearing in the Catholic Encyclopedia
The ''Catholic Encyclopedia: An International Work of Reference on the Constitution, Doctrine, Discipline, and History of the Catholic Church'' (also referred to as the ''Old Catholic Encyclopedia'' and the ''Original Catholic Encyclopedia'') i ...
, based on his ''L'Église et l'Orient au Moyen Âge: Les Croisades''. The second is ''The Crusades'',''Barker, Ernest (1911). "Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were ...
". In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. 7 (11th ed.), Cambridge University Press. pp. 524–552.'' by English historian Ernest Barker
Sir Ernest Barker (23 September 1874 – 17 February 1960) was an English political scientist who served as Principal of King's College London from 1920 to 1927.
Life and career
Ernest Barker was born in Woodley, Cheshire, and educated at ...
, in the Encyclopædia Britannica
The (Latin for "British Encyclopædia") is a general knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It is published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.; the company has existed since the 18th century, although it has changed ownership various t ...
(11th edition). Collectively, Bréhier and Barker wrote more than 50 articles for these two publications. Barker's work was later revised as ''The Crusades'' and Bréhier published ''Histoire anonyme de la première croisade''.' According to the ''Routledge Companion,'' these articles are evidence that "not all old things are useless."''''
According to the ''Routledge Companion,'' the three works that rank as being monumental by 20th century standards are: René Grousset's ''Histoire des croisades et du royaume franc de Jérusalem''; Steven Runciman
Sir James Cochran Stevenson Runciman ( – ), known as Steven Runciman, was an English historian best known for his three-volume '' A History of the Crusades'' (1951–54).
He was a strong admirer of the Byzantine Empire. His history's negativ ...
's 3-volume set of ''A History of the Crusades
''A History of the Crusades'' by Steven Runciman, published in three volumes during 1951–1954 (vol. I - ''The First Crusade and the Foundation of the Kingdom of Jerusalem''; vol. II - ''The Kingdom of Jerusalem and the Frankish East, 1100-1187' ...
,'' and the Wisconsin Collaborative History of the Crusades (Wisconsin History). Grousset's volume on the First Crusade was ''L'anarchie musulmane'', ''1095–1130,'' a standard reference in the mid-twentieth century. The next two are still enjoying widespread use today. Runciman's first volume ''The First Crusade and the Foundation of the Kingdom of Jerusalem'' has been criticized for being out-of-date and biased, but remains one of the most widely read accounts of the crusade. The first volume of the Wisconsin History, ''Volume 1: The First One Hundred Years,'' first appeared in 1969 and was edited by Marshall W. Baldwin. The chapters on the First Crusade were written by Runciman and Frederic Duncalf and again are dated, but still well-used references. Additional background chapters on related events of the 11th century are: Western Europe, by Sidney Painter; the Byzantine Empire, by Peter Charanis
Peter Charanis (1908 – 23 March 1985), born Panagiotis Charanis ( el, Παναγιώτης Χαρανής), was a Greek-born American scholar of Byzantium and the Voorhees Professor of History at Rutgers University. Charanis was long associate ...
; the Islamic world by H. A. B. Gibb; the Seljuk invasion, by Claude Cahen
Claude Cahen (26 February 1909 – 18 November 1991) was a 20th-century French Marxist orientalist and historian. He specialized in the studies of the Islamic Middle Ages, Muslim sources about the Crusades, and social history of the medieval Isla ...
; and the Assassins
An assassin is a person who commits targeted murder.
Assassin may also refer to:
Origin of term
* Someone belonging to the medieval Persian Ismaili order of Assassins
Animals and insects
* Assassin bugs, a genus in the family ''Reduviid ...
, by Bernard Lewis
Bernard Lewis, (31 May 1916 – 19 May 2018) was a British American historian specialized in Oriental studies. He was also known as a public intellectual and political commentator. Lewis was the Cleveland E. Dodge Professor Emeritus of Near ...
.
Bibliographies of works on the First Crusade through the 20th century include ones by French medievalist and Byzantinist Ferdinand Chalandon in his ''Histoire de la Première Croisade jusqu'à l'élection de Godefroi de Bouillon'' and the ''Select Bibliography on the Crusades,'' compiled by Hans E. Mayer and Joyce McLellan.
Modern histories of the First Crusade
Since the 1970s, the Crusades have attracted hundreds of scholars to their study, many of which are identified in the on-line database ''Historians of the Crusades,'' part of the ''Resources for Studying the Crusades'' created atQueen Mary University of London
, mottoeng = With united powers
, established = 1785 – The London Hospital Medical College1843 – St Bartholomew's Hospital Medical College1882 – Westfield College1887 – East London College/Queen Mary College
, type = Public researc ...
in 2007–2008. Some of the more notable historians of the First Crusade include Jonathan Riley-Smith
Jonathan Simon Christopher Riley-Smith (27 June 1938 – 13 September 2016) was a historian of the Crusades, and, between 1994 and 2005, Dixie Professor of Ecclesiastical History at Cambridge. He was a Fellow of Emmanuel College, Cambridge.
P ...
(1938–2016), the leading historian of the Crusades of his generation. His work includes ''The First Crusade and the Idea of Crusading'' (1993) and ''The First Crusaders, 1095–1131'' (1998). His doctoral students are among the most renowned in the world and he led the team that created the ''Database of Crusaders to the Holy Land, 1096–1149''. Carole Hillenbrand (born 1943) is an Islamic scholar whose work ''The Crusades: Islamic Perspectives'' (1999) discusses themes that highlight how Muslims reacted to the presence of the Crusaders in the heart of traditionally Islamic territory and is regarded as one of the most influential works on the First Crusade. Other current researchers include Christopher Tyerman
Christopher Tyerman (born 22 May 1953) is an academic historian focusing on the Crusades. In 2015, he was appointed Professor of History of the Crusades at the University of Oxford.
Life and career
He graduated from New College, Oxford, with a f ...
(born 1953) whose ''God's War: A New History of the Crusades'' (2006) is regarded as the definitive account of all the crusades. In his ''An Eyewitness History of the Crusades'' (2004), Tyerman provides the history of the crusades told from original eyewitness sources, both Christian and Muslim. Thomas Asbridge
Thomas Scott Asbridge (born 1969) is a historian at Queen Mary University of London, a position he has held since 1999. He is the author of ''The First Crusade: A New History'' (2004), a book which describes the background, events, and consequences ...
(born 1969) has written ''The First Crusade: A New History: The Roots of Conflict between Christianity and Islam'' (2004) and the more expansive ''The Crusades: The Authoritative History of the War for the Holy Land'' (2012). Thomas Madden (born 1960) has written ''The New Concise History of the Crusades'' (2005) and ''The Real History of the Crusades'' (2011). ''The Crusades—An Encyclopedia'' (2006) edited by historian Alan V. Murray provides comprehensive treatment of the Crusades with over 1000 entries written by 120 authors from 25 countries. The list of other historians is extensive and excellent bibliographies include that by Asbridge and in ''The Routledge Companion to the Crusades.''
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
* {{authority control 1090s conflicts 1090s in Asia 1090s in Europe 1090s in the Byzantine Empire 1090s in the Kingdom of Jerusalem 11th century in the Fatimid Caliphate 11th-century crusades History of Antioch Wars involving Armenia Wars involving France Wars involving the Byzantine Empire Wars involving the Fatimid Caliphate Wars involving the Holy Roman Empire Wars involving the Republic of Genoa Wars involving the Republic of Pisa