Thích Quảng Đức on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Thích Quảng Đức (; vi-hantu, , 1897 – 11 June 1963; born Lâm Văn Túc) was a Vietnamese Mahayana Buddhist
 In a country where surveys of the religious composition at the time estimated the Buddhist majority to be between 70 and 90 percent, President Diệm was a member of the
In a country where surveys of the religious composition at the time estimated the Buddhist majority to be between 70 and 90 percent, President Diệm was a member of the

 On 10 June 1963, U.S. correspondents were informed that "something important" would happen the following morning on the road outside the Cambodian embassy in Saigon. Most of the reporters disregarded the message, since the Buddhist crisis had at that point been going on for more than a month, and the next day only a few journalists turned up, including David Halberstam of ''
On 10 June 1963, U.S. correspondents were informed that "something important" would happen the following morning on the road outside the Cambodian embassy in Saigon. Most of the reporters disregarded the message, since the Buddhist crisis had at that point been going on for more than a month, and the next day only a few journalists turned up, including David Halberstam of ''
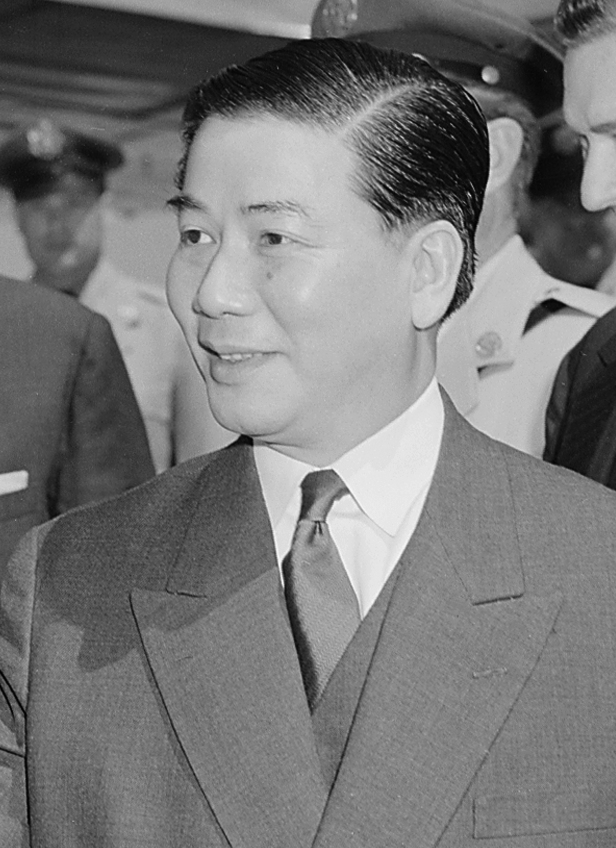 Diệm made a radio address at 19:00 on the day of Quảng Đức's death, asserting that he was profoundly troubled by the event. He appealed for "serenity and patriotism", and announced that stalled negotiations would resume with the Buddhists. He claimed that negotiations had been progressing well and in a time of religious tension emphasized the role of the Roman Catholic philosophy of personalism in his rule. He alleged that extremists had twisted the facts and he asserted that the Buddhists can "count on the Constitution, in other words, me."
The ARVN responded to the appeal, putting on a show of solidarity behind Diệm to isolate dissident officers. Thirty high-ranking officers headed by General Lê Văn Tỵ declared their resolve to carry out all missions entrusted to the army for the defense of the constitution and the Republic. The declaration was a veneer which masked a developing plot to oust Diệm. Some of the signatories were to become personally involved in Diệm's overthrow and death in November. Generals
Diệm made a radio address at 19:00 on the day of Quảng Đức's death, asserting that he was profoundly troubled by the event. He appealed for "serenity and patriotism", and announced that stalled negotiations would resume with the Buddhists. He claimed that negotiations had been progressing well and in a time of religious tension emphasized the role of the Roman Catholic philosophy of personalism in his rule. He alleged that extremists had twisted the facts and he asserted that the Buddhists can "count on the Constitution, in other words, me."
The ARVN responded to the appeal, putting on a show of solidarity behind Diệm to isolate dissident officers. Thirty high-ranking officers headed by General Lê Văn Tỵ declared their resolve to carry out all missions entrusted to the army for the defense of the constitution and the Republic. The declaration was a veneer which masked a developing plot to oust Diệm. Some of the signatories were to become personally involved in Diệm's overthrow and death in November. Generals
 President
President
 After Quảng Đức, five more Buddhist monks self-immolated up until late October 1963 as the Buddhist protests in Vietnam escalated. On 1 November, the ARVN overthrew Diệm in a coup. Diệm and Nhu were assassinated the next day. Monks have followed Quảng Đức's example since for other reasons.
The Americans in Saigon often found the self-immolations to be surreal and made puns about " bonze fires" and "hot cross bonzes", almost as an escape mechanism from the bewilderment. In one instance in 1963, the young son of an American officer based at the Saigon U.S. Embassy doused himself with gasoline and set himself on fire. He was seriously burned before the fire was extinguished and later could only offer the explanation that "I wanted to see what it was like.". Thich Quang Duc's actions were fatally copied in the United States in protest against the Vietnam War. On March 16, 1965, Alice Herz an 82-year-old peace activist immolated herself in front of the Federal Department Store in northwest Detroit.. Later that same year, Norman Morrison, a 31-year-old Quaker pacifist, poured
After Quảng Đức, five more Buddhist monks self-immolated up until late October 1963 as the Buddhist protests in Vietnam escalated. On 1 November, the ARVN overthrew Diệm in a coup. Diệm and Nhu were assassinated the next day. Monks have followed Quảng Đức's example since for other reasons.
The Americans in Saigon often found the self-immolations to be surreal and made puns about " bonze fires" and "hot cross bonzes", almost as an escape mechanism from the bewilderment. In one instance in 1963, the young son of an American officer based at the Saigon U.S. Embassy doused himself with gasoline and set himself on fire. He was seriously burned before the fire was extinguished and later could only offer the explanation that "I wanted to see what it was like.". Thich Quang Duc's actions were fatally copied in the United States in protest against the Vietnam War. On March 16, 1965, Alice Herz an 82-year-old peace activist immolated herself in front of the Federal Department Store in northwest Detroit.. Later that same year, Norman Morrison, a 31-year-old Quaker pacifist, poured
– Official Buddhist monastery dedicated to Thích Quảng Đức
{{DEFAULTSORT:Thich, Quang Duc Vietnamese Buddhists Buddhism in Vietnam 20th-century Buddhist monks 1897 births 1963 suicides Date of birth unknown People from Khánh Hòa Province Vietnamese Buddhist monks Buddhist crisis History of South Vietnam Suicides in Vietnam 1963 in Vietnam Filmed suicides Vietnamese people of the Vietnam War Self-immolations by Buddhists Articles containing video clips People notable for being the subject of a specific photograph Suicides by self-immolation Buddhist martyrs Photographs of protests
monk
A monk (, from el, μοναχός, ''monachos'', "single, solitary" via Latin ) is a person who practices religious asceticism by monastic living, either alone or with any number of other monks. A monk may be a person who decides to dedica ...
who burned himself to death at a busy Saigon road intersection on 11 June 1963. Quảng Đức was protesting the persecution of Buddhists by the South Vietnamese government led by Ngô Đình Diệm, a staunch Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
. Photographs of his self-immolation
The term self-immolation broadly refers to acts of altruistic suicide, otherwise the giving up of one's body in an act of sacrifice. However, it most often refers specifically to autocremation, the act of sacrificing oneself by setting oneself ...
circulated around the world, drawing attention to the policies of the Diệm government. John F. Kennedy
John Fitzgerald Kennedy (May 29, 1917 – November 22, 1963), often referred to by his initials JFK and the nickname Jack, was an American politician who served as the 35th president of the United States from 1961 until his assassination ...
said of one photograph, "No news picture in history has generated so much emotion around the world as that one." Malcolm Browne
Malcolm Wilde Browne (April 17, 1931August 27, 2012) was an American journalist and photographer, best known for his award-winning photograph of the self-immolation of Buddhist monk Thích Quảng Đức in 1963.
Early life and education
Brown ...
won the World Press Photo of the Year
The World Press Photo of the Year award is part of the World Press Photo Awards, organized by the Dutch foundation World Press Photo.
Considered one of the most prestigious and coveted awards in photojournalism, The World Press Photo of the Ye ...
for his photograph of the monk's death.
Quảng Đức's act increased international pressure on Diệm and led him to announce reforms with the intention of mollifying the Buddhists. However, the promised reforms were not implemented, leading to a deterioration in the dispute. As protests continued, the ARVN Special Forces loyal to Diệm's brother, Ngô Đình Nhu
Ngô Đình Nhu (; 7 October 19102 November 1963; baptismal name Jacob) was a Vietnamese archivist and politician. He was the younger brother and chief political advisor of South Vietnam's first president, Ngô Đình Diệm. Although he held n ...
, launched raids across South Vietnam on Buddhist pagoda
A pagoda is an Asian tiered tower with multiple eaves common to Nepal, India, China, Japan, Korea, Myanmar, Vietnam, and other parts of Asia. Most pagodas were built to have a religious function, most often Buddhist but sometimes Taoist, ...
s, seizing Quảng Đức's heart and causing deaths and widespread damage. Several Buddhist monks followed Quảng Đức's example, also immolating themselves. Eventually, a U.S.-backed coup toppled Diệm, who was assassinated on 2 November 1963.
Biography
Accounts of the life of Quảng Đức are derived from information disseminated by Buddhist organizations. He was born in the village of Hội Khánh, in Vạn Ninh District of Khánh Hòa Province in central Vietnam as Lâm Văn Túc, one of seven children of Lâm Hữu Ứng and his wife, Nguyễn Thị Nương. At the age of seven, he left to study Buddhism under Hòa thượng Thích Hoằng Thâm, who was his maternal uncle and spiritual master. Thích Hoằng Thâm raised him as a son and Lâm Văn Túc changed his name to Nguyễn Văn Khiết. At age 15, he took thesamanera
A sāmaṇera (Pali); sa, श्रामणेर (), is a novice male monastic in a Buddhist context. A female novice is a ''śrāmaṇerī'' or ''śrāmaṇerikā'' (Sanskrit; Pāli: ''sāmaṇerī'').
Etymology
The ''sāmaṇera'' is a ...
(novice
A novice is a person who has entered a religious order and is under probation, before taking vows. A ''novice'' can also refer to a person (or animal e.g. racehorse) who is entering a profession with no prior experience.
Religion Buddhism
...
) vows and was ordained as a monk
A monk (, from el, μοναχός, ''monachos'', "single, solitary" via Latin ) is a person who practices religious asceticism by monastic living, either alone or with any number of other monks. A monk may be a person who decides to dedica ...
at age 20 under the dharma name
A Dharma name or Dhamma name is a new name acquired during both lay and monastic Buddhist initiation rituals in Mahayana Buddhism and monastic ordination in Theravada Buddhism (where it is more proper to call it Dhamma or Sangha name). The nam ...
Thích Quảng Đức. The Vietnamese name
Traditional Vietnamese personal names generally consist of three parts, used in Eastern name order.
* A family name (normally patrilineal, The father’s family name may be combined with the mother's family name to form a compound family name) ...
''Thích'' ( 釋) is from "Thích Ca" or "Thích Già" ( 釋迦), means "of the Shakya
Shakya ( Pāḷi: ; sa, शाक्य, translit=Śākya) was an ancient eastern sub-Himalayan ethnicity and clan of north-eastern region of the Indian subcontinent, whose existence is attested during the Iron Age. The Shakyas were organised ...
clan." After ordination, he traveled to a mountain near Ninh Hòa, vowing to live the life of a solitary Buddhism-practicing hermit
A hermit, also known as an eremite (adjectival form: hermitic or eremitic) or solitary, is a person who lives in seclusion. Eremitism plays a role in a variety of religions.
Description
In Christianity, the term was originally applied to a Ch ...
for three years. He returned in later life to open the Thien Loc pagoda at his mountain retreat...
After his self-imposed isolation ended, he began to travel around central Vietnam expounding the dharma. After two years, he went into retreat at the Sac Tu Thien An pagoda near Nha Trang
Nha Trang ( or ; ) is a coastal city and capital of Khánh Hòa Province, on the South Central Coast of Vietnam. It is bounded on the north by Ninh Hoà town, on the south by Cam Ranh city and on the west by Diên Khánh District. The city ha ...
. In 1932, he was appointed an inspector for the Buddhist Association in Ninh Hòa before becoming the inspector of monks in his home province of Khánh Hòa. During this period in central Vietnam, he was responsible for the construction of 14 temples.. In 1934, he moved to southern Vietnam and traveled throughout the provinces spreading Buddhist teachings. During his time in southern Vietnam, he also spent two years in Cambodia
Cambodia (; also Kampuchea ; km, កម្ពុជា, UNGEGN: ), officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochinese Peninsula in Southeast Asia, spanning an area of , bordered by Thailan ...
studying the Theravada
''Theravāda'' () ( si, ථේරවාදය, my, ထေရဝါဒ, th, เถรวาท, km, ថេរវាទ, lo, ເຖຣະວາດ, pi, , ) is the most commonly accepted name of Buddhism's oldest existing school. The school' ...
Buddhist tradition.
Upon his return from Cambodia, he oversaw the construction of a further 17 new temples during his time in the south. The last of the 31 new temples that he was responsible for constructing was the Quan The Am pagoda in the Phú Nhuận District of Gia Định Province on the outskirts of Saigon. The street on which the temple stands was later renamed Quảng Đức Street in 1975. After the temple-building phase, Quảng Đức was appointed to serve as the Chairman of the Panel on Ceremonial Rites of the Congregation of Vietnamese Monks, and as abbot
Abbot is an ecclesiastical title given to the male head of a monastery in various Western religious traditions, including Christianity. The office may also be given as an honorary title to a clergyman who is not the head of a monastery. The ...
of the Phuoc Hoa pagoda, which was the initial location of the Association for Buddhist Studies of Vietnam (ABSV). When the office of the ABSV was relocated to the Xá Lợi Pagoda, the main pagoda of Saigon, Quảng Đức resigned.
Self-immolation
Religious background
Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
minority, and pursued discriminatory policies favoring Catholics for public service and military promotions, as well as in the allocation of land, business arrangements and tax concessions. Diệm once told a high-ranking officer, forgetting that the officer was from a Buddhist family, "Put your Catholic officers in sensitive places. They can be trusted." Many officers in the Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN) converted to Roman Catholicism as their military prospects depended on it. Additionally, the distribution of firearms to village self-defense militias saw weapons given only to Roman Catholics, with some Buddhists in the army being denied promotion if they refused to convert to Roman Catholicism.
Some Catholic priests ran their own private armies; there were forced conversion
Forced conversion is the adoption of a different religion or the adoption of irreligion under duress. Someone who has been forced to convert to a different religion or irreligion may continue, covertly, to adhere to the beliefs and practices which ...
s, looting, shelling, and demolition of pagodas in some areas, to which the government turned a blind eye. Some Buddhist villages converted ''en masse'' to receive aid or avoid being forcibly resettled by Diệm's regime. The "private" status that was imposed on Buddhism by the French, which required official permission to be obtained by those wishing to conduct public Buddhist activities, was not repealed by Diệm. Catholics were also ''de facto'' exempt from corvée
Corvée () is a form of unpaid, forced labour, that is intermittent in nature lasting for limited periods of time: typically for only a certain number of days' work each year.
Statute labour is a corvée imposed by a state for the purposes of ...
labor, which the government obliged all citizens to perform, and United States aid was distributed disproportionately to Catholic majority villages by Diệm's regime.
The Catholic Church was the largest landowner in the country and enjoyed special exemptions in property acquisition, and land owned by the Catholic Church was exempt from land reform. The white and gold Vatican flag was regularly flown at all major public events in South Vietnam, and Diệm dedicated his country to the Virgin Mary
Mary; arc, ܡܪܝܡ, translit=Mariam; ar, مريم, translit=Maryam; grc, Μαρία, translit=María; la, Maria; cop, Ⲙⲁⲣⲓⲁ, translit=Maria was a first-century Jewish woman of Nazareth, the wife of Joseph and the mother of ...
in 1959.
Buddhist discontent erupted following a ban in early May on flying the Buddhist flag
The Buddhist flag is a flag designed in the late 19th century as a universal symbol of Buddhism. It is used by Buddhists throughout the world.
History
The flag was originally designed in 1885 by the Colombo Committee, in Colombo, Ceylon (''no ...
in Huế
Huế () is the capital of Thừa Thiên Huế province in central Vietnam and was the capital of Đàng Trong from 1738 to 1775 and of Vietnam during the Nguyễn dynasty from 1802 to 1945. The city served as the old Imperial City and admi ...
on Vesak
Vesak (Pali: ''Vesākha''; sa, Vaiśākha), also known as Buddha Jayanti, Buddha Purnima and Buddha Day, is a holiday traditionally observed by Buddhists in South Asia and Southeast Asia as well as Tibet and Mongolia. The festival commemora ...
, the birthday of Gautama Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism.
According to Buddhist tradition, he was born in Lu ...
. Just days before, Catholics had been encouraged to fly the Vatican flag at a celebration for Archbishop Ngô Đình Thục
Pierre Martin Ngô Đình Thục () (6 October 1897 – 13 December 1984) was the Roman Catholic Archbishop of Huế, Vietnam, and later a sedevacantist bishop who was excommunicated by the Vatican and allegedly reconciled with the Vatican b ...
of Huế, Diệm's elder brother. A large crowd of Buddhists protested the ban, defying the government by flying Buddhist flags on the Buddhist holy day of Vesak and marching on the government broadcasting station. Government forces fired into the crowd of protesters, killing nine people. Diệm's refusal to take responsibility—he blamed the Viet Cong
,
, war = the Vietnam War
, image = FNL Flag.svg
, caption = The flag of the Viet Cong, adopted in 1960, is a variation on the flag of North Vietnam. Sometimes the lower stripe was green.
, active ...
for the deaths—led to further Buddhist protests and calls for religious equality. As Diem remained unwilling to comply with Buddhist demands, the frequency of protests increased.
Day of the act

The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid d ...
'' and Malcolm Browne
Malcolm Wilde Browne (April 17, 1931August 27, 2012) was an American journalist and photographer, best known for his award-winning photograph of the self-immolation of Buddhist monk Thích Quảng Đức in 1963.
Early life and education
Brown ...
, the Saigon bureau chief for the Associated Press
The Associated Press (AP) is an American non-profit news agency headquartered in New York City. Founded in 1846, it operates as a cooperative, unincorporated association. It produces news reports that are distributed to its members, U.S. ne ...
(AP). Quảng Đức arrived as part of a procession that had begun at a nearby pagoda. Around 350 monks and nuns marched in two phalanxes, preceded by an Austin Westminster sedan, carrying banners printed in both English and Vietnamese. They denounced the Diệm government and its policy towards Buddhists, demanding that it fulfill its promises of religious equality. Another monk offered himself, but Quảng Đức's seniority prevailed.
The act occurred at the intersection of Phan Đình Phùng Boulevard (now Nguyễn Đình Chiểu Street) and Lê Văn Duyệt Street (now Cách Mạng Tháng Tám Street) (), a few blocks southwest of the Presidential Palace (now the Reunification Palace). Quảng Đức emerged from the car along with two other monks. One placed a cushion on the road while the second opened the trunk and took out a five-gallon petrol can. As the marchers formed a circle around him, Quảng Đức calmly sat down in the traditional Buddhist meditative lotus position on the cushion. A colleague emptied the contents of the petrol container over Quảng Đức's head. Quảng Đức rotated a string of wooden prayer beads
Prayer beads are a form of beadwork used to count the repetitions of prayers, chants, or mantras by members of various religions such as Hinduism, Buddhism, Shinto, Umbanda, Islam, Sikhism, the Baháʼí Faith, and some Christian denominati ...
and recited the words ' ("Homage to Amitābha Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism.
According to Buddhist tradition, he was born in L ...
") before striking a match and dropping it on himself. Flames consumed his robes and flesh, and black oily smoke emanated from his burning body.
Quảng Đức's last words before his self-immolation
The term self-immolation broadly refers to acts of altruistic suicide, otherwise the giving up of one's body in an act of sacrifice. However, it most often refers specifically to autocremation, the act of sacrificing oneself by setting oneself ...
were documented in a letter he had left:
David Halberstam wrote:
The spectators were mostly stunned into silence, but some wailed and several began praying. Many of the monks and nuns, as well as some shocked passersby, prostrated themselves before the burning monk. Even some of the policemen, who had orders to control the gathered crowd, prostrated before him.
In English and Vietnamese
Vietnamese may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Vietnam, a country in Southeast Asia
** A citizen of Vietnam. See Demographics of Vietnam.
* Vietnamese people, or Kinh people, a Southeast Asian ethnic group native to Vietnam
** Overse ...
, a monk repeated into a microphone: "A Buddhist priest burns himself to death. A Buddhist priest becomes a martyr." After approximately 10 minutes, Quảng Đức's body was fully immolated and it eventually toppled backwards onto its back. Once the fire subsided, a group of monks covered the smoking corpse with yellow robes, picked it up and tried to fit it into a coffin, but the limbs could not be straightened and one of the arms protruded from the wooden box as he was carried to the nearby Xá Lợi Pagoda in central Saigon. Outside the pagoda, students unfurled bilingual banners which read: "A Buddhist priest burns himself for our five requests."
By 1:30p.m. (13:30), around 1,000 monks had congregated inside to hold a meeting, while outside a large crowd of pro-Buddhist students had formed a human barrier around it. The meeting soon ended and all but 100 monks slowly left the compound. Nearly 1,000 monks, accompanied by laypeople, returned to the cremation site. The police lingered nearby. At around 6:00p.m. (18:00), thirty nuns and six monks were arrested for holding a prayer meeting on the street outside Xá Lợi. The police encircled the pagoda, blocking public passage and giving observers the impression that an armed siege was imminent by donning riot gear.
Funeral and aftermath
After the self-immolation, the U.S. put more pressure on Diệm to re-open negotiations on the faltering agreement. Diệm had scheduled an emergency cabinet meeting at 11:30 on 11 June to discuss the Buddhist crisis which he believed to be winding down. Following Quảng Đức's death, Diệm canceled the meeting and met individually with his ministers. Acting U.S. Ambassador to South Vietnam William Trueheart warned Nguyễn Đình Thuận, Diệm's Secretary of State, of the desperate need for an agreement, saying that the situation was "dangerously near breaking point" and expected Diệm would meet the Buddhists' five-point manifesto.United States Secretary of State
The United States secretary of state is a member of the executive branch of the federal government of the United States and the head of the U.S. Department of State. The office holder is one of the highest ranking members of the president's Ca ...
Dean Rusk
David Dean Rusk (February 9, 1909December 20, 1994) was the United States Secretary of State from 1961 to 1969 under presidents John F. Kennedy and Lyndon B. Johnson, the second-longest serving Secretary of State after Cordell Hull from the F ...
warned the Saigon embassy that the White House
The White House is the official residence and workplace of the president of the United States. It is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue NW in Washington, D.C., and has been the residence of every U.S. president since John Adams in ...
would publicly announce that it would no longer "associate itself" with the regime if this did not occur. The Joint Communiqué and concessions to the Buddhists were signed on 16 June.
15 June was set as the date for the funeral, and on that day 4,000 people gathered outside the Xá Lợi pagoda, only for the ceremony to be postponed. On 19 June, his remains were carried out of Xá Lợi to a cemetery south of the city for a re-cremation and funeral ceremony. Following the signing of the Joint Communiqué, attendance was limited by agreement between Buddhist leaders and police to approximately 500 monks..
Intact heart and symbolism
The body was re-cremated during the funeral, but Quảng Đức's heart remained intact and did not burn. It was considered to be holy and placed in a glass chalice at Xá Lợi Pagoda. The intact heart relic is regarded as a symbol of compassion. Quảng Đức has subsequently been revered by Vietnamese Buddhists as a ''bodhisattva
In Buddhism, a bodhisattva ( ; sa, 𑀩𑁄𑀥𑀺𑀲𑀢𑁆𑀢𑁆𑀯 (Brahmī), translit=bodhisattva, label=Sanskrit) or bodhisatva is a person who is on the path towards bodhi ('awakening') or Buddhahood.
In the Early Buddhist schools ...
'' (''Bồ Tát''), and accordingly is often referred to in Vietnamese as Bồ Tát Thích Quảng Đức. On 21 August, the ARVN Special Forces of Nhu attacked Xá Lợi and other Buddhist pagodas across Vietnam. The secret police intended to confiscate Quảng Đức's ashes, but two monks had escaped with the urn, jumping over the back fence and finding safety at the U.S. Operations Mission next door. Nhu's men managed to confiscate Đức's charred heart.
The location chosen for the self-immolation, in front of the Cambodian embassy, raised questions as to whether it was coincidence or a symbolic choice. Trueheart and embassy official Charles Flowerree felt that the location was selected to show solidarity with the Cambodian government of Prince Norodom Sihanouk. South Vietnam and Cambodia had strained relations: in a speech on 22 May, Sihanouk had accused Diệm of mistreating Vietnamese and ethnic minority Khmer Buddhists. The pro-Diệm ''Times of Vietnam
The ''Times of Vietnam'' is a defunct English language newspaper that existed in South Vietnam under the rule of President Ngô Đình Diệm.
Regarded as the official mouthpiece of the Diệm regime, the ''Times'' was disbanded following the 1 ...
'' published an article on 9 June which claimed that Cambodian monks had been encouraging the Buddhist crisis, asserting it was part of a Cambodian plot to extend its neutralist foreign policy into South Vietnam. Flowerree noted that Diệm was "ready and eager to see a fine Cambodian hand in all the organized Buddhist actions".
Diệm reaction
 Diệm made a radio address at 19:00 on the day of Quảng Đức's death, asserting that he was profoundly troubled by the event. He appealed for "serenity and patriotism", and announced that stalled negotiations would resume with the Buddhists. He claimed that negotiations had been progressing well and in a time of religious tension emphasized the role of the Roman Catholic philosophy of personalism in his rule. He alleged that extremists had twisted the facts and he asserted that the Buddhists can "count on the Constitution, in other words, me."
The ARVN responded to the appeal, putting on a show of solidarity behind Diệm to isolate dissident officers. Thirty high-ranking officers headed by General Lê Văn Tỵ declared their resolve to carry out all missions entrusted to the army for the defense of the constitution and the Republic. The declaration was a veneer which masked a developing plot to oust Diệm. Some of the signatories were to become personally involved in Diệm's overthrow and death in November. Generals
Diệm made a radio address at 19:00 on the day of Quảng Đức's death, asserting that he was profoundly troubled by the event. He appealed for "serenity and patriotism", and announced that stalled negotiations would resume with the Buddhists. He claimed that negotiations had been progressing well and in a time of religious tension emphasized the role of the Roman Catholic philosophy of personalism in his rule. He alleged that extremists had twisted the facts and he asserted that the Buddhists can "count on the Constitution, in other words, me."
The ARVN responded to the appeal, putting on a show of solidarity behind Diệm to isolate dissident officers. Thirty high-ranking officers headed by General Lê Văn Tỵ declared their resolve to carry out all missions entrusted to the army for the defense of the constitution and the Republic. The declaration was a veneer which masked a developing plot to oust Diệm. Some of the signatories were to become personally involved in Diệm's overthrow and death in November. Generals Dương Văn Minh
Dương Văn Minh (; 16 February 19166 August 2001), popularly known as Big Minh, was a South Vietnamese politician and a senior general in the Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN) and a politician during the presidency of Ngô Đình Diệm ...
and Trần Văn Đôn, the presidential military advisor and the chief of the army who were to lead the coup, were overseas.
Madame Nhu (a Catholic convert from Buddhism and the wife of Diệm's younger brother and chief adviser Ngô Đình Nhu
Ngô Đình Nhu (; 7 October 19102 November 1963; baptismal name Jacob) was a Vietnamese archivist and politician. He was the younger brother and chief political advisor of South Vietnam's first president, Ngô Đình Diệm. Although he held n ...
), who was regarded as the First Lady of South Vietnam at the time (as Diệm was a bachelor), said she would "clap hands at seeing another monk barbecue show". Later that month, Diệm's government charged that Quảng Đức had been drugged before being forced to commit suicide. The regime also accused Browne of bribing Quảng Đức to burn himself.
Political and media impact
Photographs taken by Malcolm Browne of the self-immolation quickly spread across thewire service
A news agency is an organization that gathers news reports and sells them to subscribing news organizations, such as newspapers, magazines and radio and television broadcasters. A news agency may also be referred to as a wire service, newswire, ...
s and were featured on the front pages of newspapers worldwide. The self-immolation was later regarded as a turning point in the Buddhist crisis and a critical point in the collapse of the Diệm regime.
Historian Seth Jacobs asserted that Quảng Đức had "reduced America's Diệm experiment to ashes as well" and that "no amount of pleading could retrieve Diệm's reputation" once Browne's images had become ingrained into the psyche of the world public. Ellen Hammer
Ellen Joy Hammer (September 17, 1921 – January 28, 2001) was an American historian who specialized in 20th-century Vietnamese history.
Biography
Born in New York City, the daughter of David and Rea (Welt) Hammer, she received a bachelor's de ...
described the event as having "evoked dark images of persecution and horror corresponding to a profoundly Asian reality that passed the understanding of Westerners." John Mecklin, an official from the U.S. embassy, noted that the photograph "had a shock effect of incalculable value to the Buddhist cause, becoming a symbol of the state of things in Vietnam." William Colby
William Egan Colby (January 4, 1920 – May 6, 1996) was an American intelligence officer who served as Director of Central Intelligence (DCI) from September 1973 to January 1976.
During World War II Colby served with the Office of Strateg ...
, then chief of the Central Intelligence Agency
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gathering, processing, ...
's Far East Division, opined that Diệm "handled the Buddhist crisis fairly badly and allowed it to grow. But I really don't think there was much they could have done about it once that bonze burned himself."
 President
President John F. Kennedy
John Fitzgerald Kennedy (May 29, 1917 – November 22, 1963), often referred to by his initials JFK and the nickname Jack, was an American politician who served as the 35th president of the United States from 1961 until his assassination ...
, whose government was the main sponsor of Diệm's regime, learned of Quảng Đức's death when handed the morning newspapers while he was talking to his brother, Attorney General Robert F. Kennedy
Robert Francis Kennedy (November 20, 1925June 6, 1968), also known by his initials RFK and by the nickname Bobby, was an American lawyer and politician who served as the 64th United States Attorney General from January 1961 to September 1964, ...
, on the phone. Kennedy reportedly interrupted their conversation about segregation in Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = "Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County
, LargestMetro = Greater Birmingham
, area_total_km2 = 135,765 ...
by exclaiming "Jesus Christ!" He later remarked that "no news picture in history has generated so much emotion around the world as that one." U.S. Senator Frank Church (D-Idaho), a member of the Senate Foreign Relations Committee
The United States Senate Committee on Foreign Relations is a standing committee of the U.S. Senate charged with leading foreign-policy legislation and debate in the Senate. It is generally responsible for overseeing and funding foreign aid p ...
, claimed that "such grisly scenes have not been witnessed since the Christian martyrs
In Christianity, a martyr is a person considered to have died because of their testimony for Jesus or faith in Jesus. In years of the early church, stories depict this often occurring through death by sawing, stoning, crucifixion, burning at th ...
marched hand in hand into the Roman arenas."
In Europe, the photographs were sold on the streets as postcards during the 1960s, and communist China distributed Distribution may refer to:
Mathematics
*Distribution (mathematics), generalized functions used to formulate solutions of partial differential equations
*Probability distribution, the probability of a particular value or value range of a varia ...
millions of copies of the photograph throughout Asia and Africa as evidence of what it called US imperialism. One of Browne's photographs remains affixed to the sedan in which Quảng Đức was riding and is part of a tourist attraction in Huế
Huế () is the capital of Thừa Thiên Huế province in central Vietnam and was the capital of Đàng Trong from 1738 to 1775 and of Vietnam during the Nguyễn dynasty from 1802 to 1945. The city served as the old Imperial City and admi ...
..
For Browne and the AP, the pictures were a marketing success. Ray Herndon, the United Press International
United Press International (UPI) is an American international news agency whose newswires, photo, news film, and audio services provided news material to thousands of newspapers, magazines, radio and television stations for most of the 20t ...
(UPI) correspondent who had forgotten to take his camera on the day, was harshly criticized in private by his employer. UPI estimated that 5,000 readers in Sydney, then a city of around 1.5–2 million, had switched to AP news sources.
Diệm's English-language mouthpiece, the ''Times of Vietnam'', intensified its attacks on both journalists and Buddhists. Headlines such as "Xá Lợi politburo makes new threats" and "Monks plot murder" were printed. One article questioned the relationship between the monks and the press by posing the question as to why "so many young girls are buzzing in and out of Xá Lợi early n the day and then going on to allege that they were brought in for sexual purposes for the U.S. reporters.
Browne's photographs of Quảng Đức's death have been reproduced in popular media for decades, and the incident has been used as a touchstone reference in many films and television programs.
One of Browne's photographs was used for the cover of American rap metal
Rap metal is a subgenre of rap rock and alternative metal music which combines hip hop with heavy metal. It usually consists of heavy metal guitar riffs, funk metal elements, rapped vocals and sometimes turntables.
History Origins and earl ...
band Rage Against the Machine
Rage Against the Machine (often abbreviated as RATM or shortened to simply Rage) is an American rock band from Los Angeles, California. Formed in 1991, the group consists of vocalist Zack de la Rocha, bassist and backing vocalist Tim Commer ...
's debut album which came out in 1992, as well as the cover of their single "Killing in the Name
"Killing in the Name" is a protest song by American rock band Rage Against the Machine, and appears on their 1992 self-titled debut album. It was released as the lead single from the album in November 1992. It features heavy drop-D guitar riff ...
". Another was used for the cover of Canadian electronic act Delerium
Delerium is a Canadian new-age ambient electronic musical duo that formed in 1987, originally as a side project of the influential industrial music act Front Line Assembly. Throughout the band’s history, their musical style has encompassed a ...
's debut album '' Faces, Forms & Illusions'', which came out in 1989.
Precedents and influence
Despite the shock of the Western public, the practice of Vietnamese monks self-immolating was not unprecedented. Instances of self-immolations in Vietnam had been recorded for centuries, usually carried out to honor Gautama Buddha. The most recently recorded case had been in North Vietnam in 1950. TheFrench colonial
French colonial architecture includes several styles of architecture used by the French during colonization. Many former French colonies, especially those in Southeast Asia, have previously been reluctant to promote their colonial architectur ...
authorities had tried to eradicate the practice after their conquest of Vietnam in the nineteenth century, but had not been totally successful. They did manage to prevent one monk from setting fire to himself in Huế in the 1920s, but he managed to starve himself to death instead. During the 1920s and 1930s, Saigon newspapers reported multiple instances of self-immolations by monks in a matter-of-fact style. The practice had also been seen in the Chinese city of Harbin in 1948 when a monk seated down in the lotus position on a pile of sawdust
Sawdust (or wood dust) is a by-product or waste product of woodworking operations such as sawing, sanding, milling, planing, and routing. It is composed of small chippings of wood. These operations can be performed by woodworking machine ...
and soybean
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean, which has numerous uses.
Traditional unfermented food uses of soybeans include soy milk, from which tofu a ...
oil and set fire to himself in protest against the treatment of Buddhism by the anti-religious communists of Mao Zedong
Mao Zedong pronounced ; also romanised traditionally as Mao Tse-tung. (26 December 1893 – 9 September 1976), also known as Chairman Mao, was a Chinese communist revolutionary who was the founder of the People's Republic of China (PRC) ...
. His heart remained intact, as did that of Quảng Đức.
 After Quảng Đức, five more Buddhist monks self-immolated up until late October 1963 as the Buddhist protests in Vietnam escalated. On 1 November, the ARVN overthrew Diệm in a coup. Diệm and Nhu were assassinated the next day. Monks have followed Quảng Đức's example since for other reasons.
The Americans in Saigon often found the self-immolations to be surreal and made puns about " bonze fires" and "hot cross bonzes", almost as an escape mechanism from the bewilderment. In one instance in 1963, the young son of an American officer based at the Saigon U.S. Embassy doused himself with gasoline and set himself on fire. He was seriously burned before the fire was extinguished and later could only offer the explanation that "I wanted to see what it was like.". Thich Quang Duc's actions were fatally copied in the United States in protest against the Vietnam War. On March 16, 1965, Alice Herz an 82-year-old peace activist immolated herself in front of the Federal Department Store in northwest Detroit.. Later that same year, Norman Morrison, a 31-year-old Quaker pacifist, poured
After Quảng Đức, five more Buddhist monks self-immolated up until late October 1963 as the Buddhist protests in Vietnam escalated. On 1 November, the ARVN overthrew Diệm in a coup. Diệm and Nhu were assassinated the next day. Monks have followed Quảng Đức's example since for other reasons.
The Americans in Saigon often found the self-immolations to be surreal and made puns about " bonze fires" and "hot cross bonzes", almost as an escape mechanism from the bewilderment. In one instance in 1963, the young son of an American officer based at the Saigon U.S. Embassy doused himself with gasoline and set himself on fire. He was seriously burned before the fire was extinguished and later could only offer the explanation that "I wanted to see what it was like.". Thich Quang Duc's actions were fatally copied in the United States in protest against the Vietnam War. On March 16, 1965, Alice Herz an 82-year-old peace activist immolated herself in front of the Federal Department Store in northwest Detroit.. Later that same year, Norman Morrison, a 31-year-old Quaker pacifist, poured kerosene
Kerosene, paraffin, or lamp oil is a combustible hydrocarbon liquid which is derived from petroleum. It is widely used as a fuel in aviation as well as households. Its name derives from el, κηρός (''keros'') meaning "wax", and was regi ...
over himself and set light to himself below the third-floor window of Secretary of Defense Robert McNamara
Robert Strange McNamara (; June 9, 1916 – July 6, 2009) was an American business executive and the eighth United States Secretary of Defense, serving from 1961 to 1968 under Presidents John F. Kennedy and Lyndon B. Johnson. He remains the ...
at the Pentagon
The Pentagon is the headquarters building of the United States Department of Defense. It was constructed on an accelerated schedule during World War II. As a symbol of the U.S. military, the phrase ''The Pentagon'' is often used as a meton ...
on November 2, 1965. A week later, Roger Allen LaPorte did the same thing in front of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
in New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the Un ...
.
See also
*List of civil rights leaders
Civil rights leaders are influential figures in the promotion and implementation of political freedom and the expansion of personal civil liberties and rights. They work to protect individuals and groups from political repressio ...
* List of political self-immolations
This is a list of notable people who committed suicide by setting themselves on fire for political reasons. Non-political self-immolations are not included in the list.
List Before 1900
1940s
1950s
1960s
1970s
1980s ...
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
– Official Buddhist monastery dedicated to Thích Quảng Đức
{{DEFAULTSORT:Thich, Quang Duc Vietnamese Buddhists Buddhism in Vietnam 20th-century Buddhist monks 1897 births 1963 suicides Date of birth unknown People from Khánh Hòa Province Vietnamese Buddhist monks Buddhist crisis History of South Vietnam Suicides in Vietnam 1963 in Vietnam Filmed suicides Vietnamese people of the Vietnam War Self-immolations by Buddhists Articles containing video clips People notable for being the subject of a specific photograph Suicides by self-immolation Buddhist martyrs Photographs of protests