Tetanus toxoid on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Tetanus vaccine, also known as tetanus toxoid (TT), is a
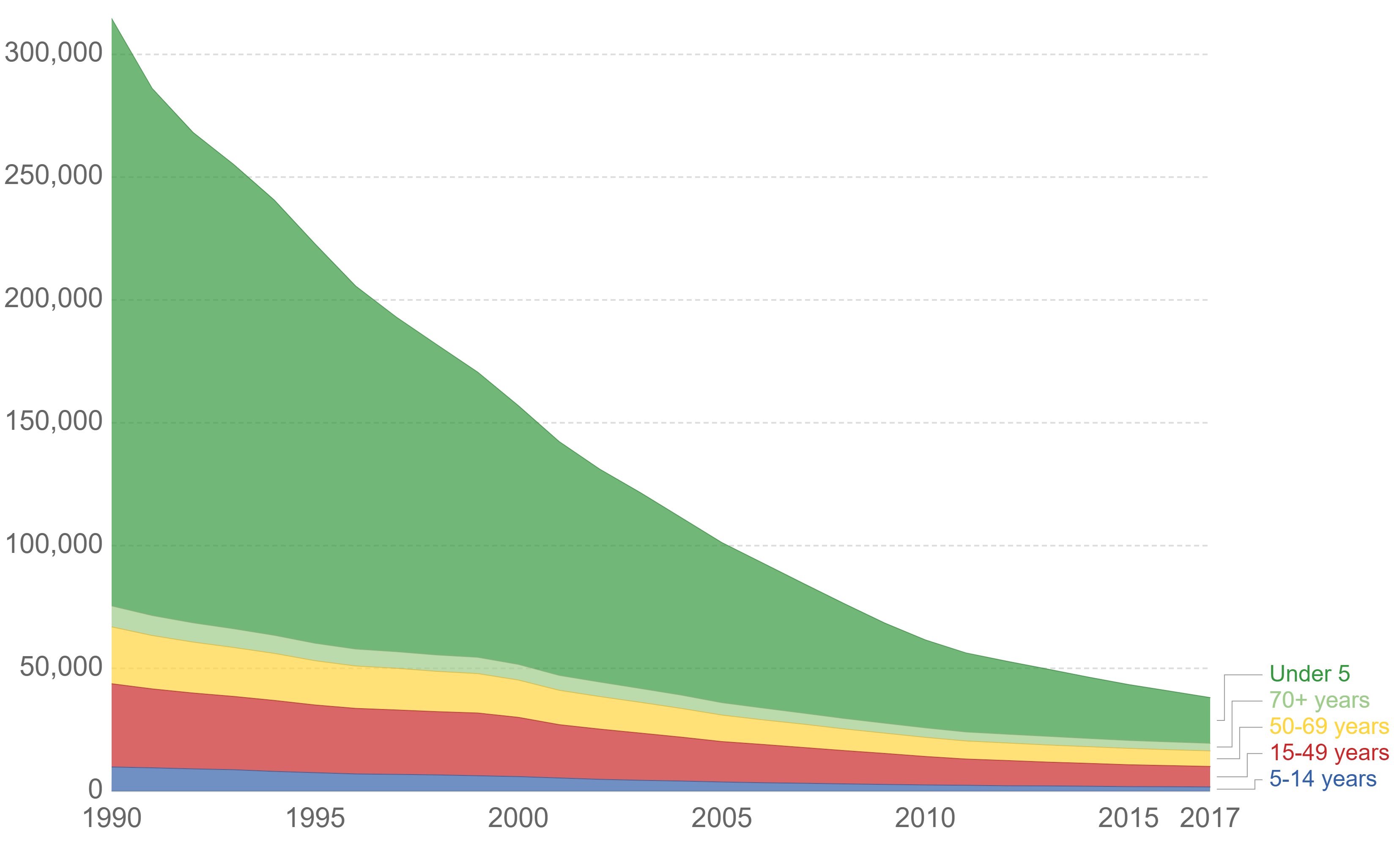 Following vaccination, 95% of people are protected from diphtheria, 80% to 85% from pertussis, and 100% from tetanus. Globally deaths from tetanus in newborns decreased from 787,000 in 1988 to 58,000 in 2010, and 34,000 deaths in 2015 (a 96% decrease from 1988).
In the 1940s, before the vaccine, there were about 550 cases of tetanus per year in the United States, which has decreased to about 30 cases per year in the 2000s. Nearly all cases are among those who have never received a vaccine, or adults who have not stayed up to date on their 10-year booster shots.
Following vaccination, 95% of people are protected from diphtheria, 80% to 85% from pertussis, and 100% from tetanus. Globally deaths from tetanus in newborns decreased from 787,000 in 1988 to 58,000 in 2010, and 34,000 deaths in 2015 (a 96% decrease from 1988).
In the 1940s, before the vaccine, there were about 550 cases of tetanus per year in the United States, which has decreased to about 30 cases per year in the 2000s. Nearly all cases are among those who have never received a vaccine, or adults who have not stayed up to date on their 10-year booster shots.
 Common side effects of the tetanus vaccine include fever, redness, and swelling with soreness or tenderness around the injection site (one of five people have redness or swelling). Body aches and tiredness have been reported following Tdap. Td / Tdap can cause painful swelling of the entire arm in one of 500 people.
Tetanus toxoid containing vaccines (DTaP, DTP, Tdap, Td, DT) may cause
Common side effects of the tetanus vaccine include fever, redness, and swelling with soreness or tenderness around the injection site (one of five people have redness or swelling). Body aches and tiredness have been reported following Tdap. Td / Tdap can cause painful swelling of the entire arm in one of 500 people.
Tetanus toxoid containing vaccines (DTaP, DTP, Tdap, Td, DT) may cause
toxoid
A toxoid is an inactivated toxin (usually an exotoxin) whose toxicity has been suppressed either by chemical (formalin) or heat treatment, while other properties, typically immunogenicity, are maintained. Toxins are secreted by bacteria, whereas ...
vaccine used to prevent tetanus
Tetanus, also known as lockjaw, is a bacterial infection caused by ''Clostridium tetani'', and is characterized by muscle spasms. In the most common type, the spasms begin in the jaw and then progress to the rest of the body. Each spasm usually ...
. During childhood, five doses are recommended, with a sixth given during adolescence.
After three doses, almost everyone is initially immune, but additional doses every ten years are recommended to maintain immunity. A booster shot should be given within 48 hours of an injury to people whose immunization is out of date. For people with high-risk injuries who are not fully immunized, tetanus antitoxin
An antitoxin is an antibody with the ability to neutralize a specific toxin. Antitoxins are produced by certain animals, plants, and bacteria in response to toxin exposure. Although they are most effective in neutralizing toxins, they can also ...
may also be recommended.
Confirming that pregnant women are up to date on tetanus immunization during each pregnancy can prevent both maternal and neonatal tetanus
Neonatal tetanus (''trismus nascentium'') is a form of generalised tetanus that occurs in newborns. Infants who have not acquired passive immunity from an immunized mother are at risk. It usually occurs through infection of the unhealed umbilical ...
.
The vaccine is very safe, including during pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops (gestation, gestates) inside a woman, woman's uterus (womb). A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occur ...
and in those with HIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual ...
.
Redness and pain at the site of injection occur in between 25% and 85% of people. Fever, feeling tired, and minor muscle pain occurs in less than 10% of people. Severe allergic reactions occur in less than one in 100,000 people.
A number of vaccine combinations include the tetanus vaccine, such as DTaP
The DPT vaccine or DTP vaccine is a class of combination vaccines against three infectious diseases in humans: diphtheria, pertussis (whooping cough), and tetanus. The vaccine components include diphtheria and tetanus toxoids and either kille ...
and Tdap, which contain diphtheria
Diphtheria is an infection caused by the bacterium '' Corynebacterium diphtheriae''. Most infections are asymptomatic or have a mild clinical course, but in some outbreaks more than 10% of those diagnosed with the disease may die. Signs and s ...
, tetanus, and pertussis vaccine
Pertussis vaccine is a vaccine that protects against whooping cough (pertussis). There are two main types: whole-cell vaccines and acellular vaccines. The whole-cell vaccine is about 78% effective while the acellular vaccine is 71–85% effectiv ...
s, and DT and Td, which contain diphtheria
Diphtheria is an infection caused by the bacterium '' Corynebacterium diphtheriae''. Most infections are asymptomatic or have a mild clinical course, but in some outbreaks more than 10% of those diagnosed with the disease may die. Signs and s ...
and tetanus vaccines. DTaP and DT are given to children less than seven years old, while Tdap and Td are given to those seven years old and older. The lowercase d and p denote lower strengths of diphtheria and pertussis vaccines.
Tetanus antiserum was developed in 1890, with its protective effects lasting a few weeks. The tetanus toxoid vaccine was developed in 1924, and came into common use for soldiers in World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
. Its use resulted in a 95% decrease in the rate of tetanus. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines
The WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (aka Essential Medicines List or EML), published by the World Health Organization (WHO), contains the medications considered to be most effective and safe to meet the most important needs in a health s ...
.
Medical uses
Effectiveness
 Following vaccination, 95% of people are protected from diphtheria, 80% to 85% from pertussis, and 100% from tetanus. Globally deaths from tetanus in newborns decreased from 787,000 in 1988 to 58,000 in 2010, and 34,000 deaths in 2015 (a 96% decrease from 1988).
In the 1940s, before the vaccine, there were about 550 cases of tetanus per year in the United States, which has decreased to about 30 cases per year in the 2000s. Nearly all cases are among those who have never received a vaccine, or adults who have not stayed up to date on their 10-year booster shots.
Following vaccination, 95% of people are protected from diphtheria, 80% to 85% from pertussis, and 100% from tetanus. Globally deaths from tetanus in newborns decreased from 787,000 in 1988 to 58,000 in 2010, and 34,000 deaths in 2015 (a 96% decrease from 1988).
In the 1940s, before the vaccine, there were about 550 cases of tetanus per year in the United States, which has decreased to about 30 cases per year in the 2000s. Nearly all cases are among those who have never received a vaccine, or adults who have not stayed up to date on their 10-year booster shots.
Pregnancy
Guidelines onprenatal care in the United States
Prenatal care in the United States is a health care preventive care protocol recommended to women with the goal to provide regular check-ups that allow obstetricians- gynecologists or midwives to detect, treat and prevent potential health proble ...
specify that women should receive a dose of the Tdap vaccine
The DPT vaccine or DTP vaccine is a class of combination vaccines against three infectious diseases in humans: diphtheria, pertussis (whooping cough), and tetanus. The vaccine components include diphtheria and tetanus toxoids and either kill ...
during each pregnancy, preferably between weeks 27 and 36, to allow antibody transfer to the fetus. All postpartum women who have not previously received the Tdap vaccine are recommended to get it prior to discharge after delivery. It is recommended for pregnant women who have never received the tetanus vaccine (i.e., neither DTP or DTaP, nor DT as a child or Td or TT as an adult) to receive a series of three Td vaccinations starting during pregnancy to ensure protection against maternal and neonatal tetanus
Neonatal tetanus (''trismus nascentium'') is a form of generalised tetanus that occurs in newborns. Infants who have not acquired passive immunity from an immunized mother are at risk. It usually occurs through infection of the unhealed umbilical ...
. In such cases, Tdap is recommended to be substituted for one dose of Td, again preferably between 27 and 36 weeks of gestation, and then the series completed with Td.
Specific types
The first vaccine is given in infancy. The baby is injected with theDTaP
The DPT vaccine or DTP vaccine is a class of combination vaccines against three infectious diseases in humans: diphtheria, pertussis (whooping cough), and tetanus. The vaccine components include diphtheria and tetanus toxoids and either kille ...
vaccine, which is three inactive toxins in one injection. DTaP protects against diphtheria
Diphtheria is an infection caused by the bacterium '' Corynebacterium diphtheriae''. Most infections are asymptomatic or have a mild clinical course, but in some outbreaks more than 10% of those diagnosed with the disease may die. Signs and s ...
, pertussis
Whooping cough, also known as pertussis or the 100-day cough, is a highly contagious bacterial disease. Initial symptoms are usually similar to those of the common cold with a runny nose, fever, and mild cough, but these are followed by two or t ...
, and tetanus. This vaccine is safer than the previously used DTP. Another option is DT, which is a combination of diphtheria and tetanus vaccines. This is given as an alternative to infants who have conflicts with the DTaP vaccine. Quadrivalent, pentavalent, and hexavalent formulations contain DTaP with one or more of the additional vaccines: inactivated polio
Poliomyelitis, commonly shortened to polio, is an infectious disease caused by the poliovirus. Approximately 70% of cases are asymptomatic; mild symptoms which can occur include sore throat and fever; in a proportion of cases more severe s ...
virus vaccine (IPV), Haemophilus influenzae type b
''Haemophilus influenzae'' (formerly called Pfeiffer's bacillus or ''Bacillus influenzae'') is a Gram-negative, non-motile, coccobacillary, facultatively anaerobic, capnophilic pathogenic bacterium of the family Pasteurellaceae. The bacter ...
conjugate, Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the '' Hepatitis B virus'' (HBV) that affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. It can cause both acute and chronic infection.
Many people have no symptoms during an initial infection. ...
, with the availability varying in different countries.
For the every ten-year booster Td or Tdap may be used, though Tdap is more expensive.
Schedule
Because DTaP and DT are administered to children less than a year old, the recommended location for injection is the anterolateral thigh muscle. However, these vaccines can be injected into thedeltoid muscle
The deltoid muscle is the muscle forming the rounded contour of the human shoulder. It is also known as the 'common shoulder muscle', particularly in other animals such as the domestic cat. Anatomically, the deltoid muscle appears to be made up o ...
if necessary.
The World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of ...
(WHO) recommends six doses in childhood starting at six weeks of age. Four doses of DTaP are to be given in early childhood. The first dose should be around two months of age, the second at four months, the third at six, and the fourth from fifteen to eighteen months of age. There is a recommended fifth dose to be administered to four- to six-year-olds.
Td and Tdap are for older children, adolescents, and adults and can be injected into the deltoid muscle. These are boosters and are recommended every ten years. It is safe to have shorter intervals between a single dose of Tdap and a dose of the Td booster.
Additional doses
Booster shots are important becauselymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include natural killer cells (which function in cell-mediated, cytotoxic innate immunity), T cells (for cell-mediated, cytotoxic ad ...
production (antibodies) is not at a constant high rate of activity. This is because after the introduction of the vaccine when lymphocyte production is high, the production activity of white blood cells
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from mult ...
will start to decline. The decline in activity of the T-helper cells means that there must be a booster to help keep the white blood cells active.
Td and Tdap are the booster shots given every ten years to maintain immunity for adults nineteen years of age to sixty-five years of age.
Tdap is given as a one-time, first-time-only dose that includes the tetanus, diphtheria, and acellular pertussis vaccinations. This should not be administered to those who are under the age of eleven or over the age of sixty-five.
Td is the booster shot given to people over the age of seven and includes the tetanus and diphtheria toxoid
A toxoid is an inactivated toxin (usually an exotoxin) whose toxicity has been suppressed either by chemical (formalin) or heat treatment, while other properties, typically immunogenicity, are maintained. Toxins are secreted by bacteria, whereas ...
s. However, Td has less of the diphtheria toxoid, which is why the "d" is lowercase and the "T" is capitalized.
In 2020, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency, under the Department of Health and Human Services, and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgi ...
(CDC) Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) is a committee within the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) that provides advice and guidance on effective control of vaccine-preventable diseases in the U.S. c ...
(ACIP) recommended that either tetanus and diphtheria toxoids (Td) vaccine or Tdap to be used for the decennial Td booster, tetanus prevention during wound management, and for additional required doses in the catch-up immunization schedule if a person has received at least one Tdap dose.
Side effects
 Common side effects of the tetanus vaccine include fever, redness, and swelling with soreness or tenderness around the injection site (one of five people have redness or swelling). Body aches and tiredness have been reported following Tdap. Td / Tdap can cause painful swelling of the entire arm in one of 500 people.
Tetanus toxoid containing vaccines (DTaP, DTP, Tdap, Td, DT) may cause
Common side effects of the tetanus vaccine include fever, redness, and swelling with soreness or tenderness around the injection site (one of five people have redness or swelling). Body aches and tiredness have been reported following Tdap. Td / Tdap can cause painful swelling of the entire arm in one of 500 people.
Tetanus toxoid containing vaccines (DTaP, DTP, Tdap, Td, DT) may cause brachial neuritis Brachial means "pertaining to the arm", and may refer to:
* Brachial artery, in anatomy
* Brachial fascia
* Brachial lymph nodes
* Brachial veins
* Brachial plexus, a network of nerves
* Brachial valve, the upper valve in Brachiopods
* Brachiali ...
at a rate of one out of every 100,000 to 200,000 doses.
Mechanism of action
The type of vaccination for this disease is called artificial active immunity. This type ofimmunity
Immunity may refer to:
Medicine
* Immunity (medical), resistance of an organism to infection or disease
* ''Immunity'' (journal), a scientific journal published by Cell Press
Biology
* Immune system
Engineering
* Radiofrequence immunity desc ...
is generated when a dead or weakened version of the disease enters the body, causing an immune response
An immune response is a reaction which occurs within an organism for the purpose of defending against foreign invaders. These invaders include a wide variety of different microorganisms including viruses, bacteria, parasites, and fungi which could ...
which includes the production of antibodies. This is beneficial because it means that if the disease is ever introduced into the body, the immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splint ...
will recognize the antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune respons ...
and produce antibodies more rapidly.
History
The first vaccine for passive immunology was discovered by a group of German scientists under the leadership ofEmil von Behring
Emil von Behring (; Emil Adolf von Behring), born Emil Adolf Behring (15 March 1854 – 31 March 1917), was a German physiologist who received the 1901 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, the first one awarded in that field, for his discovery ...
in 1890.
The first inactive tetanus toxoid was discovered and produced in 1924. A more effective adsorbed
Adsorption is the adhesion of atoms, ions or molecules from a gas, liquid or dissolved solid to a surface. This process creates a film of the ''adsorbate'' on the surface of the ''adsorbent''. This process differs from absorption, in which a ...
version of the vaccine, created in 1938, was proven to be successful when it was used to prevent tetanus in the military during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
. DTP (which is the combined vaccine for diphtheria
Diphtheria is an infection caused by the bacterium '' Corynebacterium diphtheriae''. Most infections are asymptomatic or have a mild clinical course, but in some outbreaks more than 10% of those diagnosed with the disease may die. Signs and s ...
, tetanus, and pertussis
Whooping cough, also known as pertussis or the 100-day cough, is a highly contagious bacterial disease. Initial symptoms are usually similar to those of the common cold with a runny nose, fever, and mild cough, but these are followed by two or t ...
) was first used in 1948, and was continued until 1991, when it was replaced with an acellular form of the pertussis vaccine due to safety concerns. Half of those who received the DTP vaccine had redness, swelling, and pain around the injection site, which convinced researchers to find a replacement vaccine.
Two new vaccines were launched in 1992. These combined tetanus and diphtheria with acellular pertussis (TDaP or DTaP), which could be given to adolescents and adults (as opposed to previously when the vaccine was only given to children).
References
Further reading
* * * * * *External links
* * * * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Tetanus Vaccine Tetanus 1924 in biology Toxoid vaccines Vaccines World Health Organization essential medicines (vaccines) Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate