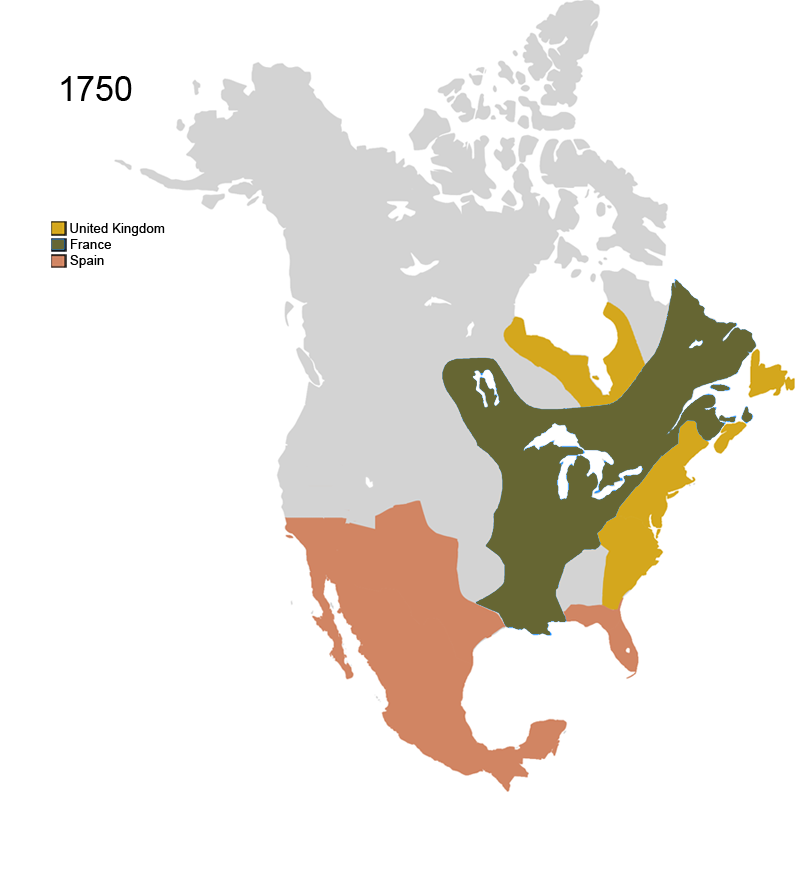
Territorial evolution of North America prior to 1763 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Before contact with Europeans, the natives of North America were divided into many different
Before contact with Europeans, the natives of North America were divided into many different

 The Popham Colony colonists abandoned their colony leaving on the 30-ton ship, a
The Popham Colony colonists abandoned their colony leaving on the 30-ton ship, a
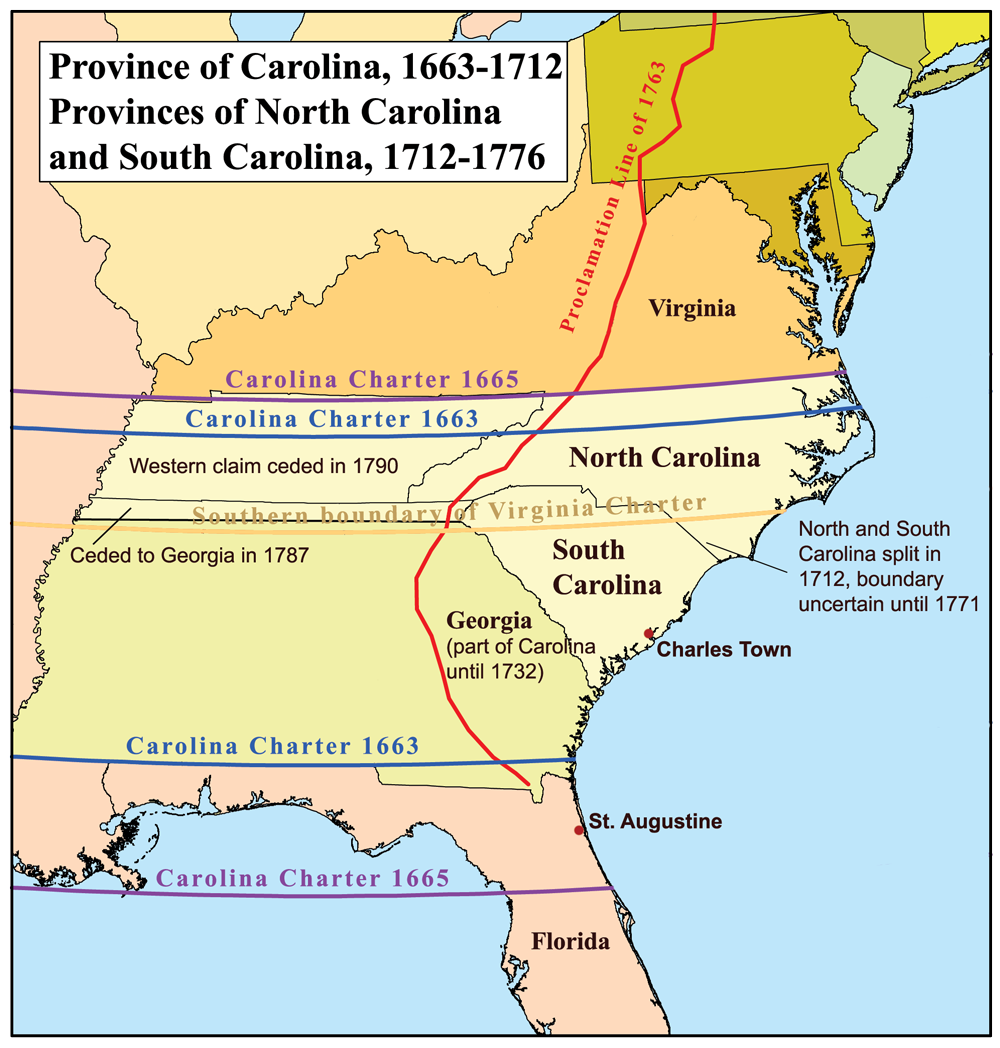 The 1663 Province of Carolina charter granted the Lords Proprietor title to all of the land from the southern border of the
The 1663 Province of Carolina charter granted the Lords Proprietor title to all of the land from the southern border of the
 *In the 1667 Treaty of Breda ending the
*In the 1667 Treaty of Breda ending the
 Before contact with Europeans, the natives of North America were divided into many different
Before contact with Europeans, the natives of North America were divided into many different polities
A polity is an identifiable political entity – a group of people with a collective identity, who are organized by some form of institutionalized social relations, and have a capacity to mobilize resources. A polity can be any other group of p ...
, from small bands of a few families to large empire
An empire is a "political unit" made up of several territories and peoples, "usually created by conquest, and divided between a dominant center and subordinate peripheries". The center of the empire (sometimes referred to as the metropole) ex ...
s. Modern anthropology assigns some larger divisions into various "culture area
In anthropology and geography, a cultural region, cultural sphere, cultural area or culture area refers to a geography with one relatively homogeneous human activity or complex of activities (culture). Such activities are often associated ...
s", regions within which a particular set of cultural, political, subsistence
A subsistence economy is an economy directed to basic subsistence (the provision of food, clothing, shelter) rather than to the market. Henceforth, "subsistence" is understood as supporting oneself at a minimum level. Often, the subsistence econo ...
and/or linguistic traits predominated. These pre-Columbian American culture areas may also roughly correspond to particular geographic and biological zones of the continent. During the thousands of years of native inhabitation on the continent, cultures changed and shifted. One of the oldest cultures yet found is that of the Clovis peoples. Upon the arrival of the Europeans in the "New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. ...
", Native American population declined substantially, primarily due to the introduction of European diseases to which the Native Americans lacked immunity.
There was limited contact between North American people and the outside world before 1492. Several theoretical contacts have been proposed, but the earliest physical evidence comes from the Norse or Vikings
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and ...
. Norse captain Leif Ericson
Leif Erikson, Leiv Eiriksson, or Leif Ericson, ; Modern Icelandic: ; Norwegian: ''Leiv Eiriksson'' also known as Leif the Lucky (), was a Norse explorer who is thought to have been the first European to have set foot on continental Nort ...
is believed to have reached the Island of Newfoundland circa 1000 AD. In 1492 Columbus reached land in the Bahamas
The Bahamas (), officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the West Indies in the North Atlantic. It takes up 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and is home to 88% of the ar ...
. Almost 500 years after the Norse, John Cabot explored the east coast of what would become Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
in 1497. Giovanni da Verrazzano
Giovanni da Verrazzano ( , , often misspelled Verrazano in English; 1485–1528) was an Italian ( Florentine) explorer of North America, in the service of King Francis I of France.
He is renowned as the first European to explore the Atlanti ...
explored the East Coast of North America from Florida to presumably Newfoundland in 1524. Jacques Cartier made a series of voyages on behalf of the French crown in 1534 and penetrated the St. Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (french: Fleuve Saint-Laurent, ) is a large river in the middle latitudes of North America. Its headwaters begin flowing from Lake Ontario in a (roughly) northeasterly direction, into the Gulf of St. Lawrence, connecting ...
. These powers slowly replaced the native nations of the North American east coast and then spread into the interior. The main powers in North America frequently fought over territory. One of the biggest wars was the French and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the ...
that ended in France leaving the continent and giving up its claims in the Treaty of Paris Treaty of Paris may refer to one of many treaties signed in Paris, France:
Treaties
1200s and 1300s
* Treaty of Paris (1229), which ended the Albigensian Crusade
* Treaty of Paris (1259), between Henry III of England and Louis IX of France
* Trea ...
. After 1763 a new power emerged, the independent United States of America.
c. 1003
Norse captainLeif Erikson
Leif Erikson, Leiv Eiriksson, or Leif Ericson, ; Modern Icelandic: ; Norwegian: ''Leiv Eiriksson'' also known as Leif the Lucky (), was a Norse explorer who is thought to have been the first European to have set foot on continental Nort ...
is believed to have reached the Island of Newfoundland 1000 AD. They established a colony on 1003 at L'Anse aux Meadows
L'Anse aux Meadows ( lit. Meadows Cove) is an archaeological site, first excavated in the 1960s, of a Norse settlement dating to approximately 1,000 years ago. The site is located on the northernmost tip of the island of Newfoundland in the ...
and later abandoned the site.

1494
The Treaty of Tordesillas was signed on June 7, 1494 and ratified by Spain and Portugal on July 2 and September 5, 1494, respectively. The Treaty divided the "newly discovered" lands outsideEurope
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
between Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
and Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
along a meridian 370 leagues west of the Cape Verde islands off the west coast of Africa. There was great confusion around the implementation of the Treaty.
1513
The Spanish claims on the Pacific coast, based on a 1493 papal bull which had granted Spain the rights to colonize the western coast of North America, allowedVasco Núñez de Balboa
Vasco Núñez de Balboa (; c. 1475around January 12–21, 1519) was a Spanish explorer, governor, and conquistador. He is best known for having crossed the Isthmus of Panama to the Pacific Ocean in 1513, becoming the first European to lead an ...
to claim all of the "South Sea" (the Pacific Ocean) and the lands adjoining the Pacific Ocean for the Spanish Crown.
August 13, 1521
The Aztec Triple Alliance fell into Spanish hands after the long Siege of Tenochtitlan when Tenochtitlan and Tlatelolco fell on August 13, 1521 after the last Aztec emperor,Cuauhtémoc
Cuauhtémoc (, ), also known as Cuauhtemotzín, Guatimozín, or Guatémoc, was the Aztec ruler ('' tlatoani'') of Tenochtitlan from 1520 to 1521, making him the last Aztec Emperor. The name Cuauhtemōc means "one who has descended like an eagle ...
, surrendered to Cortés.
1546
The Spanish completed their conquest of Yucatán with the help of their Xiu allies in 1546, although various Maya peoples were never completely conquered and would revolt throughout Spanish rule.1559
In 1559Tristán de Luna y Arellano
Tristán de Luna y Arellano (1510 – September 16, 1573) was a Spanish explorer and Conquistador of the 16th century.Herbert Ingram Priestley, Tristan de Luna: Conquistador of the Old South: A Study of Spanish Imperial Strategy (1936). http://palm ...
established a brief settlement in Pensacola.
1561
A hurricane struck Florida and forced the abandonment of the Pensacola settlement in 1561.1564
René Goulaine de Laudonnière
Rene Goulaine de Laudonnière (c. 1529–1574) was a French Huguenot explorer and the founder of the French colony of Fort Caroline in what is now Jacksonville, Florida. Admiral Gaspard de Coligny, a Huguenot, sent Jean Ribault and Laudonnière ...
founded Fort Caroline
Fort Caroline was an attempted French colonial settlement in Florida, located on the banks of the St. Johns River in present-day Duval County. It was established under the leadership of René Goulaine de Laudonnière on 22 June, 1564, follow ...
in what is now Jacksonville
Jacksonville is a city located on the Atlantic coast of northeast Florida, the most populous city proper in the state and is the List of United States cities by area, largest city by area in the contiguous United States as of 2020. It is the co ...
in 1564 as a haven for the Huguenot
The Huguenots ( , also , ) were a religious group of French Protestants who held to the Reformed, or Calvinist, tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, the Genevan burgomaster Be ...
s. Rowland-Moore-Rogers 1996, p. 26.
1565
;September 20, 1565 Menéndez de Avilés attacked Fort Caroline, killing all the French Huguenot soldiers defending it (sparing only a fewCatholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
s), and renamed the fort San Mateo. Rowland-Moore-Rogers 1996, p. 28.
;1565
Further down the coast in Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
, the Spanish founded in 1565 by Pedro Menéndez de Avilés, San Agustín ( St. Augustine) Rowland-Moore-Rogers 1996, p. 27. became the oldest continuously-inhabited European settlement in any State of the United States. This is the second oldest settlement, following only San Juan, Puerto Rico
San Juan (, , ; Spanish for "Saint John") is the capital city and most populous municipality in the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, an unincorporated territory of the United States. As of the 2020 census, it is the 57th-largest city under the juri ...
, in the current territory and possessions of the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
. From this base of operation, Spanish missionaries began building Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
missions in Florida.
1585
Under the supervision of Sir Walter Raleigh in 1585, a colonizing expedition composed solely of men, many of them veteran soldiers who had fought to establish the British rule in Ireland, was sent to establish a colony inVirginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
. With about 75 men, Raleigh decided to establish the English colony at the northern end of Roanoke Island. The British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
ships disembarked on August 17, 1585, leaving the isolated men to form a colony.
1590
The initial colony was abandoned but a second attempt led by John White, an artist and friend of Sir Walter Raleigh who had accompanied the previous expeditions to Roanoke, was sent out. After problems with the colony mounted they sent White back to England for help due to the continuing war withSpain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
( Anglo-Spanish War (1585)
Anglo-Spanish War may refer to:
* Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604), including the Spanish Armada and the English Armada
* Anglo-Spanish War (1625–1630), part of the Thirty Years' War
* Anglo-Spanish War (1654–1660), part of the Franco-Spanish ...
), White was not able to mount another resupply attempt for three more years. He finally gained passage on a privateer
A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or deleg ...
ing expedition that agreed to stop off at Roanoke on the way back from the Caribbean. White landed on August 18, 1590, on his granddaughter's third birthday, but found the settlement deserted. His men could not find any trace of the ninety men, seventeen women, and eleven children, nor was there any sign of a struggle or battle. The only clue was the word "Croatoan" carved into a post of the fort and "Cro" carved into a nearby tree.
June 26, 1604
The French settled at a site in the Baie Francis (present day Bay of Fundy), at the mouth of the Saint Croix River which separates present dayNew Brunswick
New Brunswick (french: Nouveau-Brunswick, , locally ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. It is the only province with both English and ...
and Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and ...
, on a small island named Saint Croix
Saint Croix; nl, Sint-Kruis; french: link=no, Sainte-Croix; Danish and no, Sankt Croix, Taino: ''Ay Ay'' ( ) is an island in the Caribbean Sea, and a county and constituent district of the United States Virgin Islands (USVI), an unincor ...
. Litalien-Roth-Vaugeois 2004, p. 347.
1607
;May 14, 1607 Jamestown was the first successfulEnglish
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
settlement on the mainland of North America. Named for King James I of England
James VI and I (James Charles Stuart; 19 June 1566 – 27 March 1625) was King of Scotland as James VI from 24 July 1567 and King of England and Ireland as James I from the union of the Scottish and English crowns on 24 March 1603 until ...
, Jamestown was founded in the Virginia Colony
The Colony of Virginia, chartered in 1606 and settled in 1607, was the first enduring English colony in North America, following failed attempts at settlement on Newfoundland by Sir Humphrey GilbertGilbert (Saunders Family), Sir Humphrey" (histor ...
on May 14, 1607
;August 1607
Arriving in August 1607, these British Plymouth Company colonists established their settlement, known as the Popham Colony
The Popham Colony—also known as the Sagadahoc Colony—was a short-lived English colonial settlement in North America. It was established in 1607 by the proprietary Plymouth Company and was located in the present-day town of Phippsburg, Ma ...
, in the present-day town of Phippsburg, Maine
Phippsburg is a town in Sagadahoc County, Maine, United States, on the west side of the mouth of the Kennebec River. The population was 2,155 at the 2020 census. It is within the Portland– South Portland– Biddeford, Maine, metro ...
near the mouth of the Kennebec River.
1608
 The Popham Colony colonists abandoned their colony leaving on the 30-ton ship, a
The Popham Colony colonists abandoned their colony leaving on the 30-ton ship, a pinnace
Pinnace may refer to:
* Pinnace (ship's boat), a small vessel used as a tender to larger vessels among other things
* Full-rigged pinnace
The full-rigged pinnace was the larger of two types of vessel called a pinnace in use from the sixteenth c ...
they named ''Virginia''. It was the first ship built in America by Europeans, and was meant to show that the colony could be used for shipbuilding
Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other floating vessels. It normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces its roots to befo ...
. The short-lived colony had lasted about a year.
1613
The earliest Dutch settlement was built around 1613, and consisted of a number of small huts built by the crew of the "''Tijger''" (''Tiger''), a Dutch ship under the command of CaptainAdriaen Block
Adriaen (Arjan) Block (c. 1567 – buried April 27, 1627) was a Dutch private trader, privateer, and ship's captain who is best known for exploring the coastal and river valley areas between present-day New Jersey and Massachusetts during four v ...
which had caught fire while sailing on the Hudson. Soon after, the first of two Fort Nassaus was built and small ''factorijen'', or trading posts, where commerce could be conducted with Algonquian and Iroquois
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of First Nations peoples in northeast North America/ Turtle Island. They were known during the colonial years to ...
population, went up (possibly at Schenectady
Schenectady () is a city in Schenectady County, New York, United States, of which it is the county seat. As of the 2020 census, the city's population of 67,047 made it the state's ninth-largest city by population. The city is in eastern New Y ...
, Schoharie, Esopus, Quinnipiac
Quinnipiac is the English name for the Eansketambawg (meaning "original people"; ''cf.'' Ojibwe: '' Anishinaabeg'' and Blackfoot: ''Niitsítapi''), a Quiripi-speaking Native American nation of the Algonquian family who inhabited the ''Wamp ...
, Communipaw
Communipaw is a neighborhood in Jersey City in Hudson County, New Jersey, United States. It is located west of Liberty State Park and east of Bergen Hill, and the site of one of the earliest European settlements in North America. It gives its nam ...
and elsewhere).
1620
Pilgrim separatists landed atPlymouth Rock
Plymouth Rock is the traditional site of disembarkation of William Bradford and the ''Mayflower'' Pilgrims who founded Plymouth Colony in December 1620. The Pilgrims did not refer to Plymouth Rock in any of their writings; the first known writt ...
and formed the Plymouth Colony
Plymouth Colony (sometimes Plimouth) was, from 1620 to 1691, the first permanent English colony in New England and the second permanent English colony in North America, after the Jamestown Colony. It was first settled by the passengers on the ...
. Aided by Squanto
Tisquantum (; 1585 (±10 years?) – late November 1622 O.S.), more commonly known as Squanto Sam (), was a member of the Patuxet tribe best known for being an early liaison between the Native American population in Southern New England and ...
, a Native American of the Patuxet people, the colony was able to establish a treaty with Chief Massasoit which helped to ensure the colony's success. The colony played a central role in King Philip's War
King Philip's War (sometimes called the First Indian War, Metacom's War, Metacomet's War, Pometacomet's Rebellion, or Metacom's Rebellion) was an armed conflict in 1675–1676 between indigenous inhabitants of New England and New England coloni ...
, one of the earliest and bloodiest of the Indian Wars
The American Indian Wars, also known as the American Frontier Wars, and the Indian Wars, were fought by European governments and colonists in North America, and later by the United States and Canadian governments and American and Canadian settle ...
. Ultimately, the colony was annexed by the Massachusetts Bay Colony in 1691.
1629
In 1629, the first Scottish settlement at Port Royal in the Bay of Fundy was established.1631
In 1631, underCharles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
, the Scots were forced to abandon their Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
colony in its infancy.
March 29, 1638
The Swedish ships ''Fogel Grip
''Fogel Grip'' (''Bird Griffin'', Swedish: ''Fågel Grip'') was a Swedish sailing ship originally built in the Netherlands in the early 17th century. She was used on the first Swedish expedition in 1638 together with '' Kalmar Nyckel'' to establi ...
'' and ''Kalmar Nyckel
''Kalmar Nyckel'' (''Key of Kalmar'') was a Swedish ship built by the Dutch famed for carrying Swedish settlers to North America in 1638, to establish the colony of New Sweden. The name Kalmar Nyckel comes from the Swedish city of Kalmar and nyc ...
'', sailed into Delaware Bay
Delaware Bay is the estuary outlet of the Delaware River on the northeast seaboard of the United States. It is approximately in area, the bay's freshwater mixes for many miles with the saltwater of the Atlantic Ocean.
The bay is bordered inland ...
, which lay within the territory claimed by the Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
, passing Cape May
Cape May consists of a peninsula and barrier island system in the U.S. state of New Jersey. It is roughly coterminous with Cape May County and runs southwards from the New Jersey mainland, separating Delaware Bay from the Atlantic Ocean. The so ...
and Cape Henlopen
Cape Henlopen is the southern cape of the Delaware Bay along the Atlantic coast of the United States. It lies in the state of Delaware, near the town of Lewes, where the Delaware Bay meets the Atlantic Ocean. Off the coast on the bay side are t ...
in late March 1638, and anchored at a rocky point on the Minquas Kill that is known today as Swedes' Landing
Swedes' Landing is the warehouse road found along the Minquas Kill in Wilmington, Delaware that is close to the Delaware River. This was the site where the initial Swedish landing took place and marks the spot where the New Sweden colony began. ...
on March 29, 1638. They built a fort on the present site of the city of Wilmington, which they named Fort Christina, after Queen Christina of Sweden
Christina ( sv, Kristina, 18 December ( New Style) 1626 – 19 April 1689), a member of the House of Vasa, was Queen of Sweden in her own right from 1632 until her abdication in 1654. She succeeded her father Gustavus Adolphus upon his death ...
. Thorne-Long 1993, p. 005.
1654
In 1654, war between France and England broke out. Led by Major Robert Sedgwick, a flotilla from Boston, under orders fromOliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell (25 April 15993 September 1658) was an English politician and military officer who is widely regarded as one of the most important statesmen in English history. He came to prominence during the 1639 to 1651 Wars of the Three K ...
, arrived in Acadia to chase the French out. The flotilla seized La Tour’s fort, then Port-Royal.
September 15, 1655
In May 1654, the DutchFort Casimir
Fort Casimir or Fort Trinity was a Dutch fort in the seventeenth-century colony of New Netherland. It was located on a no-longer existing barrier island at the end of Chestnut Street in what is now New Castle, Delaware.
Background
The Dutch c ...
was captured by soldiers from the colony of New Sweden
New Sweden ( sv, Nya Sverige) was a Swedish colony along the lower reaches of the Delaware River in what is now the United States from 1638 to 1655, established during the Thirty Years' War when Sweden was a great military power. New Sweden f ...
, led by Governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
Johan Risingh
Johan Classon Risingh (1617 in Risinge – 1672) was the last governor of the Swedish colony of New Sweden.
Biography
Risingh was born in 1617 in Risinge, Östergötland, Sweden. After gymnasium at Linköping, he attended the University of Upp ...
. The fort was taken without a fight because its garrison did not have any gunpowder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, carbon (in the form of charcoal) and potassium nitrate (saltpeter). Th ...
, and the fort was renamed Fort Trinity (in Swedish, ''Trefaldigheten'').
As reprisal, the Dutch — led by Governor Peter Stuyvesant — moved an army to the Delaware River in the late summer of 1655, leading to the immediate surrender of Fort Trinity and Fort Christina. Thus the settlement was absorbed into the Dutch New Netherlands
New Netherland ( nl, Nieuw Nederland; la, Novum Belgium or ) was a 17th-century colonial province of the Dutch Republic that was located on the east coast of what is now the United States. The claimed territories extended from the Delmarva P ...
on September 15, 1655.
1663
 The 1663 Province of Carolina charter granted the Lords Proprietor title to all of the land from the southern border of the
The 1663 Province of Carolina charter granted the Lords Proprietor title to all of the land from the southern border of the Virginia Colony
The Colony of Virginia, chartered in 1606 and settled in 1607, was the first enduring English colony in North America, following failed attempts at settlement on Newfoundland by Sir Humphrey GilbertGilbert (Saunders Family), Sir Humphrey" (histor ...
at 36 degrees north to 31 degrees north (along the coast of present-day Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
). In 1665, the charter was revised slightly, with the northerly boundary extended to 36 degrees 30 minutes north to include the lands of settlers along the Albemarle Sound
Albemarle Sound () is a large estuary on the coast of North Carolina in the United States located at the confluence of a group of rivers, including the Chowan and Roanoke. It is separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Currituck Banks, a bar ...
who had left the Virginia Colony
The Colony of Virginia, chartered in 1606 and settled in 1607, was the first enduring English colony in North America, following failed attempts at settlement on Newfoundland by Sir Humphrey GilbertGilbert (Saunders Family), Sir Humphrey" (histor ...
. Likewise, the southern boundary was moved south to 29 degrees north, just south of present-day Daytona Beach, Florida, which had the effect of including the existing Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
settlement at St. Augustine. The charter also granted all the land, between these northerly and southerly bounds, from the Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe an ...
, westward to the shores of the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contin ...
.
July 31, 1667
Second Anglo-Dutch War
The Second Anglo-Dutch War or the Second Dutch War (4 March 1665 – 31 July 1667; nl, Tweede Engelse Oorlog "Second English War") was a conflict between England and the Dutch Republic partly for control over the seas and trade routes, whe ...
when the Dutch exchanged their claims on their North American colony of New Netherland
New Netherland ( nl, Nieuw Nederland; la, Novum Belgium or ) was a 17th-century colonial province of the Dutch Republic that was located on the east coast of what is now the United States. The claimed territories extended from the Delmarva P ...
s for the ''status quo'', with the Dutch occupying Suriname and the nutmeg
Nutmeg is the seed or ground spice of several species of the genus ''Myristica''. ''Myristica fragrans'' (fragrant nutmeg or true nutmeg) is a dark-leaved evergreen tree cultivated for two spices derived from its fruit: nutmeg, from its seed, an ...
island of Run Island. Page-Sonnenburg 1973, p. 177.
*Acadia returned to France via the Treaty of Breda, signed July 31, 1667. However, it took three years before the officials of the French Empire to take control of this land.
1673
In August 1673, the Dutch recapturedNew Netherlands
New Netherland ( nl, Nieuw Nederland; la, Novum Belgium or ) was a 17th-century colonial province of the Dutch Republic that was located on the east coast of what is now the United States. The claimed territories extended from the Delmarva P ...
with a fleet of 21 warship
A warship or combatant ship is a naval ship that is built and primarily intended for naval warfare. Usually they belong to the armed forces of a state. As well as being armed, warships are designed to withstand damage and are usually faster ...
s, the largest fleet that had ever been seen off the North American coast.
1674
In November 1674, the Treaty of Westminster concluded the war and ceded New Netherland to the English.1683
The first settlement inBaja California
Baja California (; 'Lower California'), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Baja California), is a state in Mexico. It is the northernmost and westernmost of the 32 federal entities of Mex ...
, named San Bruno, was founded but it lasted only about two years before being abandoned.
1697
In 1697, the first "permanent" mission in Baja California was established at Loreto, about 20 miles away from San Bruno, also on the east coast of the peninsula. Brown-Brown-Stevenson 2006, p. 175.April 11, 1713
TheTreaty of Utrecht
The Peace of Utrecht was a series of peace treaties signed by the belligerents in the War of the Spanish Succession, in the Dutch city of Utrecht between April 1713 and February 1715. The war involved three contenders for the vacant throne ...
was actually a group of documents. The treaties were among several European states, including France, Spain, Great Britain, Savoy, and the Dutch Republic, and they helped end the War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Phil ...
. In North America, France ceded to Great Britain its claims to the Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC; french: Compagnie de la Baie d'Hudson) is a Canadian retail business group. A fur trading business for much of its existence, HBC now owns and operates retail stores in Canada. The company's namesake business di ...
territories in Rupert's Land
Rupert's Land (french: Terre de Rupert), or Prince Rupert's Land (french: Terre du Prince Rupert, link=no), was a territory in British North America which comprised the Hudson Bay drainage basin; this was further extended from Rupert's Land t ...
, Newfoundland and Acadia
Acadia (french: link=no, Acadie) was a colony of New France in northeastern North America which included parts of what are now the The Maritimes, Maritime provinces, the Gaspé Peninsula and Maine to the Kennebec River. During much of the 17t ...
. Hansen-Brebner 1970, p. 23. France retained its other pre-war North American possessions, including Île-Saint-Jean (now Prince Edward Island
Prince Edward Island (PEI; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is the smallest province in terms of land area and population, but the most densely populated. The island has several nicknames: "Garden of the Gulf", ...
) as well as Île Royale (now Cape Breton Island), on which it erected the Fortress of Louisbourg
The Fortress of Louisbourg (french: Forteresse de Louisbourg) is a National Historic Site and the location of a one-quarter partial reconstruction of an 18th-century French fortress at Louisbourg on Cape Breton Island, Nova Scotia. Its two siege ...
.
1719
In 1719, the French captured the Spanish settlement atPensacola
Pensacola () is the westernmost city in the Florida Panhandle, and the county seat and only incorporated city of Escambia County, Florida, United States. As of the 2020 United States census, the population was 54,312. Pensacola is the principal ci ...
, but the Spanish were able to retake the town. Then the Spanish lost it again later in the same year.
1722
The French turned over the settlement of Pensacola to the Spanish in the Treaty of 1722.1759
Russians began to live inUnalaska
Unalaska ( ale, Iluulux̂; russian: Уналашка) is the chief center of population in the Aleutian Islands. The city is in the Aleutians West Census Area, a regional component of the Unorganized Borough in the U.S. state of Alaska. Unalaska ...
on the Aleutian islands.
See also
* Territorial evolution of the United States *Territorial evolution of Canada
The history of post-confederation Canada began on July 1, 1867, when the British North American colonies of Canada, New Brunswick, and Nova Scotia were united to form a single Dominion within the British Empire. Upon Confederation, the United Pro ...
*Territorial evolution of Mexico
Mexico has experienced many changes in territorial organization during its history as an independent state. The territorial boundaries of Mexico were affected by presidential and imperial decrees. One such decree was ''the Law of Bases for the ...
* Animated map of the Canada provinces evolution version 1
* Animated map of the Canada provinces evolution version 2
* Animated map of US states by date of statehood
* Animated map of Mexico
Bibliography
;Notes ;Reference * - Total pages: 251 * - Total pages: 294 * - Total pages: 407 * - Total pages: 340 * - Total pages: 274 * - Total pages: 372 * - Total pages: 230 * - Total pages: 351 * - Total pages: 266 * - Total pages: 397 * - Total pages: 236 * - Total pages: 292 * - Total pages: 242 * - Total pages: 1208 * - Total pages: 297 * - Total pages: 521 * - Total pages: 892 * - Total pages: 326 * - Total pages: 514 {{Territorial evolution of the world History of North America North America