
The territorial evolution of Germany include all of changes on the territorial borders of
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
. Modern Germany was formed in 1871 when
Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918. Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. ...
unified most of the German states, with the notable exception of
Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, into the
German Empire.
[Timeline: Germany - BBC News](_blank)
/ref> After the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, Germany lost about 10% of its territory to its neighbours and the Weimar Republic
The Weimar Republic (german: link=no, Weimarer Republik ), officially named the German Reich, was the government of Germany from 1918 to 1933, during which it was a constitutional federal republic for the first time in history; hence it is ...
was formed. This republic included territories to the east of today's German borders.
The period of Nazi
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in ...
rule from the early 1930s through the end of the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
brought significant territorial losses for the country. Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
initially expanded the country's territory dramatically and conquered most of Europe, though not all areas were added to Germany officially. The Nazis' fortunes changed after the failure of the invasion of Soviet Union. The Nazi regime eventually collapsed, and the Allies occupied Germany.
The former eastern territories of Germany
The former eastern territories of Germany (german: Ehemalige deutsche Ostgebiete) refer in present-day Germany to those territories east of the current eastern border of Germany i.e. Oder–Neisse line which historically had been considered Ger ...
were ceded to Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
and the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
and the Oder and Neisse Rivers became Germany's new eastern boundary. This territory became Poland's so-called "Recovered Territories
The Recovered Territories or Regained Lands ( pl, Ziemie Odzyskane), also known as Western Borderlands ( pl, Kresy Zachodnie), and previously as Western and Northern Territories ( pl, Ziemie Zachodnie i Północne), Postulated Territories ( pl, Z ...
", while approximately one-third of East Prussia became the Russian Federation
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
's Kaliningrad Oblast
Kaliningrad Oblast (russian: Калинингра́дская о́бласть, translit=Kaliningradskaya oblast') is the westernmost federal subject of Russia. It is a semi-exclave situated on the Baltic Sea. The largest city and admin ...
; virtually the entire German population in these areas was expelled or fled. In the west, the Saar area formed a French-controlled protectorate with limited autonomy, but its own citizenship laws, fact that it was separated from German interior by France as protectorate made Saarland's status unclear.
With the onset of the Cold War, the western part of Germany was unified as the Trizone, becoming the Federal Republic of Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated between ...
in May 1949 ("West Germany"). Western-occupied West Berlin
West Berlin (german: Berlin (West) or , ) was a political enclave which comprised the western part of Berlin during the years of the Cold War. Although West Berlin was de jure not part of West Germany, lacked any sovereignty, and was under mi ...
declared its accession to the Federal Republic of Germany in 1949 but was denied by the occupying powers. The Soviet zone, including the Soviet sector of Berlin, became the communist German Democratic Republic
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**G ...
("East Germany") in October the same year.Grundgesetz
The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany (german: Grundgesetz für die Bundesrepublik Deutschland) is the constitution of the Federal Republic of Germany.
The West German Constitution was approved in Bonn on 8 May 1949 and came in ...
(constitution) article no. 23 (" Little Reunification"). Following the end of the Cold War, East Germany, including East Berlin, and West Berlin used the same West German constitutional clause and declared their accession to the Federal Republic of Germany effective 3 October 1990 – an event referred to as German reunification.
Background
German settlement in Central and Eastern Europe
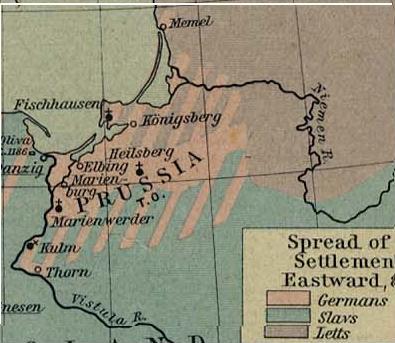 Part of the motivation behind the territorial changes is based on historical events in Germany and
Part of the motivation behind the territorial changes is based on historical events in Germany and Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
. Migrations that took place over more than a millennium led to pockets of Germans living throughout Central and Eastern Europe as far east as Russia. The existence of these enclaves was sometimes used by German nationalists, such as the Nazis, to justify territorial claims.
The rise of European nationalism
The territorial changes of Germany after World War II can be interpreted in the context of the evolution of global nationalism and European nationalism.
The latter half of the 19th century and the first half of the 20th century saw the rise of nationalism
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a group of people), Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: The ...
in Europe. Previously, a country consisted largely of whatever peoples lived on the land that was under the dominion of a particular ruler. As principalities and kingdoms grew through conquest and marriage, a ruler could wind up with many different ethnicities under his dominion.
The concept of nationalism was based on the idea of a "people" who shared a common bond through race, religion, language and culture. Furthermore, nationalism asserted that each "people" had a right to its own state. Thus, much of European history in the latter half of the 19th century and the first half of the 20th century can be understood as efforts to realign national boundaries with this concept of "one people, one state". Many interior conflicts were a result of more or less pressurising citizens of alternative ethnicities and/or other native languages to assimilate to the ethnicity dominant in the state. Switzerland was the exception, lacking a common native language.
Much conflict would arise when one nation asserted territorial rights to land outside its borders on the basis of an ethnic bond with the people living on the land. Another source of conflict arose when a group of people who constituted a minority in one nation would seek to secede from the nation either to form an independent nation or join another nation with whom they felt stronger ties. Yet another source of conflict was the desire of some nations to expel people from territory within its borders because people did not share a common bond with the majority of people of that nation.
Formation of the German Empire

Prussia
Following the capture of Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. Silesia is split ...
in 1742 by Frederick the Great
Frederick II (german: Friedrich II.; 24 January 171217 August 1786) was King in Prussia from 1740 until 1772, and King of Prussia from 1772 until his death in 1786. His most significant accomplishments include his military successes in the S ...
during the Silesian Wars
The Silesian Wars (german: Schlesische Kriege, links=no) were three wars fought in the mid-18th century between Prussia (under King Frederick the Great) and Habsburg Austria (under Archduchess Maria Theresa) for control of the Central European ...
with the Habsburg monarchy, the territorial expansion of the Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918. Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. ...
continued with the annexation of lands belonging to the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi- confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Poland and Lithuania ru ...
. During the Partitions of Poland between 1772 and 1795, Prussia seized 141,400 km2 (54,600 sq mi) of the Commonwealth's western territory, including the regions of Greater Poland, Pomorze
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to ...
, Mazovia
Mazovia or Masovia ( pl, Mazowsze) is a historical region in mid-north-eastern Poland. It spans the North European Plain, roughly between Łódź and Białystok, with Warsaw being the unofficial capital and largest city. Throughout the centurie ...
and the Duchy of Siewierz
The Duchy of Siewierz was a Silesian duchy with its capital in Siewierz. The area was part of the original Duchy of Silesia established after the death of Duke Bolesław III Wrymouth in 1138 during the times of the fragmentation of Poland.
S ...
. Subsequently, renaming them as South Prussia, West Prussia, New East Prussia and New Silesia. After the annexation of the Polish territories, Frederick the Great
Frederick II (german: Friedrich II.; 24 January 171217 August 1786) was King in Prussia from 1740 until 1772, and King of Prussia from 1772 until his death in 1786. His most significant accomplishments include his military successes in the S ...
immediately sent 57,475 German families to the newly conquered lands in order to solidify his new acquisitions, and abolished the use of the Polish language.
North German Confederation
Following the Napoleonic wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
and the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
the North German Confederation
The North German Confederation (german: Norddeutscher Bund) was initially a German military alliance established in August 1866 under the leadership of the Kingdom of Prussia, which was transformed in the subsequent year into a confederated st ...
, led by Prussia, was combined with the southern states of Baden
Baden (; ) is a historical territory in South Germany, in earlier times on both sides of the Upper Rhine but since the Napoleonic Wars only East of the Rhine.
History
The margraves of Baden originated from the House of Zähringen. Baden i ...
, Württemberg
Württemberg ( ; ) is a historical German territory roughly corresponding to the cultural and linguistic region of Swabia. The main town of the region is Stuttgart.
Together with Baden and Hohenzollern, two other historical territories, Württ ...
, Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total lan ...
and Hesse
Hesse (, , ) or Hessia (, ; german: Hessen ), officially the State of Hessen (german: links=no, Land Hessen), is a state in Germany. Its capital city is Wiesbaden, and the largest urban area is Frankfurt. Two other major historic cities are Dar ...
and the formerly French newly annexed Alsace-Lorraine to form the German Empire in 1871. In some areas of Prussia's eastern provinces
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
, such as the Province of Posen, the majority of the population was Polish. Many Lorrainians were by native language French. Many Alsatians and Lorrainians of German language clung to France (see ), despite their native languages.
Heligoland
Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
ceded Heligoland
Heligoland (; german: Helgoland, ; Heligolandic Frisian: , , Mooring Frisian: , da, Helgoland) is a small archipelago in the North Sea. A part of the German state of Schleswig-Holstein since 1890, the islands were historically possessions ...
to Germany in 1890 in accordance with the terms of the Heligoland–Zanzibar Treaty
The Heligoland–Zanzibar Treaty (german: Helgoland-Sansibar-Vertrag; also known as the Anglo-German Agreement of 1890) was an agreement signed on 1 July 1890 between the German Empire and the United Kingdom.
The accord gave Germany control of ...
. The Heligolanders, then still prevailingly fluent in their Heligolandic dialect of North Frisian, adopted German citizenship, like many other Frisians of Germany along the North Sea coast.
World War I
Brest-Litovsk
As part of the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (also known as the Treaty of Brest in Russia) was a separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Russia and the Central Powers (Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire), that ended Russia's ...
, Russia's new Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
( communist) government renounced all claims to Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
, and Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
.
Most of these territories were in effect ceded to the German Empire, intended to become economically dependent on and politically closely tied to that empire under different German king
King is the title given to a male monarch in a variety of contexts. The female equivalent is queen, which title is also given to the consort of a king.
*In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contemporary indigenous peoples, the tit ...
s and duke
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, grand dukes, and sovereign princes. As royalty or nobility, they are rank ...
s.
Regarding the ceded territories, the treaty stated that "Germany and Austria-Hungary intend to determine the future fate of these territories in agreement with their population" with few other effects than the appointment of German rulers to the new thrones of Finland, Latvia, Lithuania, and Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
.
Territorial changes after World War I
Treaty of Versailles
The provisions of the Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June ...
at the end of World War I obliged Germany to cede some territory to other countries. Besides the loss of the German colonial empire the territories Germany lost were:
* Alsace-Lorraine, which were part of Germany for 48 years, in accordance with the Preliminaries of Peace signed at Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; french: Château de Versailles ) is a former royal residence built by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, about west of Paris, France. The palace is owned by the French Republic and since 1995 has been managed, ...
on 26 February 1871, and the Treaty of Frankfurt of 10 May 1871, returned under French sovereignty without a plebiscite
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of ...
as a precondition to armistice (i.e. and therefore not as a clause of the Treaty of Versailles) with effect from the date of the armistice (11 November 1918), (, 1,815,000 inhabitants (1905)).
* Northern Schleswig
South Jutland County ( Danish: ''Sønderjyllands Amt'') is a former county ( Danish: ''amt'') on the south-central portion of the Jutland Peninsula in southern Denmark.
The county was formed on 1 April 1970, comprising the former counties of A ...
including the German-dominated towns of Tondern (Tønder
Tønder (; german: Tondern ) is a town in the Region of Southern Denmark. With a population of 7,505 (as of 1 January 2022), it is the main town and the administrative seat of the Tønder Municipality.
History
The first mention of Tønder might ...
), Apenrade (Aabenraa
Aabenraa (; , ; Sønderjysk: ''Affenråe'') is a town in Southern Denmark, at the head of the Aabenraa Fjord, an arm of the Little Belt, north of the Denmark–Germany border and north of German town of Flensburg. It was the seat of Sønderjyl ...
) and Sonderburg (Sønderborg
(; german: Sonderburg ) is a Danish town in the Region of Southern Denmark. It is the main town and the administrative seat of Sønderborg Municipality (Kommune). The town has a population of 27,766 (1 January 2022),[Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; da, Slesvig-Holsten; nds, Sleswig-Holsteen; frr, Slaswik-Holstiinj) is the northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Sc ...]
, after the Schleswig Plebiscite, to Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
(, 163,600 inhabitants (1920)).
* The Prussian provinces Posen and West Prussia
The Province of West Prussia (german: Provinz Westpreußen; csb, Zôpadné Prësë; pl, Prusy Zachodnie) was a province of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and 1878 to 1920. West Prussia was established as a province of the Kingdom of Prussia in 177 ...
, which Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
had annexed in Partitions of Poland (1772–1795), were given to the new country of Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
. Most of this territory had already been liberated by local Polish population during the Greater Poland Uprising of 1918-1919 (, 4,224,000 inhabitants (1931), including and 26,000 inhabitants from Upper Silesia). Minor areas of both the provinces remained in Germany and were combined to become the new Prussian province of Grenzmark Posen-West Prussia. In these territories ceded to Poland, a sizeable German population remained.
* The Hlučín Region
Hlučín Region ( cs, Hlučínsko, german: Hultschiner Ländchen, pl, Ziemia hulczyńska) is a historically significant part of Czech Silesia, now part of the Moravian-Silesian Region in the Czech Republic. It is named after its largest town, Hlu ...
(Hlučínsko around Hultschin) of Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( pl, Górny Śląsk; szl, Gůrny Ślůnsk, Gōrny Ślōnsk; cs, Horní Slezsko; german: Oberschlesien; Silesian German: ; la, Silesia Superior) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, locate ...
to Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
(area 316 or 333 km², 49,000 inhabitants).
* East Upper Silesia East Upper Silesia (german: Ostoberschlesien) is the easternmost extremity of Silesia, the eastern part of the Upper Silesian region around the city of Katowice (german: Kattowitz).Isabel Heinemann, ''"Rasse, Siedlung, deutsches Blut": das Rasse- u ...
, to Poland (area out of - around 30% with 965,000 inhabitants ), after Upper Silesia plebiscite in which 60% had voted in favor of remaining German and 40% wanted whole Upper Silesia to become Polish. The vote was designed to provide guidance on how to divide the area, and most of the areas voting for Poland were separated from Germany.
* The area of Eupen-Malmedy
Eupen-Malmedy is a small, predominantly German-speaking region in eastern Belgium. It consists of three administrative cantons around the towns of Eupen, Malmedy, and Sankt Vith which encompass some . Elsewhere in Belgium, the region is common ...
to Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
, along with the Vennbahn
The (, "Fen Railway") is a former railway line that was built partly across what was then German territory by the Prussian state railways. It is now entirely in Belgium, because the trackbed of the line, as well as the stations and other instal ...
railway trackbed (which created six German enclaves within Belgian territory).
* The northern part of East Prussia as '' Memelland'' under control of France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, Japan and the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, later transferred to Lithuania without a vote.
* The area of Soldau in East Prussia (a railway station on the Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officia ...
- Danzig route) to Poland (area ).
* From the eastern part of West Prussia and the southern part of East Prussia Warmia
Warmia ( pl, Warmia; Latin: ''Varmia'', ''Warmia''; ; Warmian: ''Warńija''; lt, Varmė; Old Prussian: ''Wārmi'') is both a historical and an ethnographic region in northern Poland, forming part of historical Prussia. Its historic capital ...
and Masuria
Masuria (, german: Masuren, Masurian: ''Mazurÿ'') is a ethnographic and geographic region in northern and northeastern Poland, known for its 2,000 lakes. Masuria occupies much of the Masurian Lake District. Administratively, it is part of the ...
, an area to Poland (see East Prussian plebiscite); contrary what nationalists claim, that ethnicity should determine national identity, the majority of the Slavonic Masurians
The Masurians or Mazurs ( pl, Mazurzy; german: Masuren; Masurian: ''Mazurÿ''), historically also known as Prussian Masurians ( Polish: ''Mazurzy pruscy''), is an ethnographic group of Polish people, that originate from the region of Masuri ...
voted to remain part of Germany.
* The Saar area to be under the control of the League of Nations for 15 years, after that a vote between France and Germany, to decide to which country it would belong. During this time the coal was given to France.
* The port of Danzig (now Gdańsk, Poland) with the delta of Vistula river at the Baltic Sea was made the '' Free City of Danzig'' (Freie Stadt Danzig) under the League of Nations (area , 408,000 inhabitants (1929)), 90% Germans.
* Germany acknowledges and will respect strictly the independence of Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
.
Sudetenland
The Sudeten Germans had attempted to prevent the German language border areas of former Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
from becoming part of Czechoslovakia in 1918. Once part of Bohemia, they had proclaimed the German-Austrian province of Sudetenland in October 1918, voting instead to join the newly declared Republic of German Austria
The Republic of German-Austria (german: Republik Deutschösterreich or ) was an unrecognised state that was created following World War I as an initial rump state for areas with a predominantly German-speaking and ethnic German population ...
in November 1918. However, this had been forbidden by the victorious allied powers of the First World War (the Treaty of Saint-Germain
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal pers ...
) and by the Czechoslovak government, partly with force of arms in 1919. Many Sudeten Germans rejected an affiliation to Czechoslovakia, since they had been refused the right to self-determination promised by US president Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was an American politician and academic who served as the 28th president of the United States from 1913 to 1921. A member of the Democratic Party, Wilson served as the president of ...
in his Fourteen Points
U.S. President Woodrow Wilson
The Fourteen Points was a statement of principles for peace that was to be used for peace negotiations in order to end World War I. The principles were outlined in a January 8, 1918 speech on war aims and peace terms ...
of January 1918.
Silesian uprisings
The Silesian Uprisings
The Silesian Uprisings (german: Aufstände in Oberschlesien, Polenaufstände, links=no; pl, Powstania śląskie, links=no) were a series of three uprisings from August 1919 to July 1921 in Upper Silesia, which was part of the Weimar Republic ...
( pl, Powstania śląskie) were a series of three armed uprisings (1919–1921) of Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in C ...
in the Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( pl, Górny Śląsk; szl, Gůrny Ślůnsk, Gōrny Ślōnsk; cs, Horní Slezsko; german: Oberschlesien; Silesian German: ; la, Silesia Superior) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, locate ...
region against Weimar Republic
The Weimar Republic (german: link=no, Weimarer Republik ), officially named the German Reich, was the government of Germany from 1918 to 1933, during which it was a constitutional federal republic for the first time in history; hence it is ...
in order to separate the region (where in some parts Poles constituted a majority) from Germany and join it with the Second Polish Republic.
Interbellum
Territorial claims of German nationalists
By World War I, there were isolated groups of Germans or so-called Schwaben
Swabia ; german: Schwaben , colloquially ''Schwabenland'' or ''Ländle''; archaic English also Suabia or Svebia is a cultural, historic and linguistic region in southwestern Germany.
The name is ultimately derived from the medieval Duchy of ...
as far southeast as the Bosphorus (Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
), Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
, and Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of t ...
. After the war, Germany's and Austria-Hungary's loss of territory and the rise of communism in the Soviet Union meant that more Germans than ever constituted sizable minorities in various countries.
German nationalists used the existence of large German minorities in other countries as a basis for territorial claims. Many of the propaganda themes of the Nazi regime against Czechoslovakia and Poland claimed that the ethnic Germans (''Volksdeutsche
In Nazi German terminology, ''Volksdeutsche'' () were "people whose language and culture had German origins but who did not hold German citizenship". The term is the nominalised plural of '' volksdeutsch'', with ''Volksdeutsche'' denoting a sin ...
'') in those territories were persecuted.
The Nazis negotiated a number of population transfers with Joseph Stalin and others with Benito Mussolini so that both Germany and the other country would increase their ethnic homogeneity. However, these population transfers were not sufficient to appease the demands of the Nazis. The '' Heim ins Reich'' rhetoric of the Nazis over the continued disjoint status of enclaves such as Danzig and East Prussia was an agitating factor in the politics leading up to World War II, and is considered by many to be among the major causes of Nazi aggressiveness and thus the war. Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
used these issues as a pretext for waging wars of aggression against Czechoslovakia and Poland.
Rhineland
On 7 March 1936, Hitler sent a small expeditionary force into the demilitarized Rhineland. This was a clear violation of the Treaty of Versailles (1919, official end of World War I), and as such, France and Britain were within their rights, via the Treaty, to oust the German forces. British public opinion blocked any use of military force, thus preventing French action, as they were internally divided and would not act without British support.
Saar region
In 1933, a considerable number of anti-Nazi
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in ...
Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
fled to the Saar, as it was the only part of Germany left outside the Third Reich
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
's control. As a result, anti-Nazi groups campaigned heavily for the Saarland to remain under control of League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference that ...
as long as Adolf Hitler ruled Germany. However, long-held sentiments against France remained entrenched, with very few sympathizing openly with France. When the 15-year-term was over, a plebiscite
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of ...
was held in the territory on 13 January 1935: 90.3% of those voting wished to join Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
.
On 17 January 1935, the territory's re-union with Germany was approved by the League Council. On 1 March, Nazi Germany took over the region and appointed Josef Bürckel as ''Reichskommissar
(, rendered as "Commissioner of the Empire", "Reich Commissioner" or "Imperial Commissioner"), in German history, was an official gubernatorial title used for various public offices during the period of the German Empire and Nazi Germany.
Ger ...
für die Rückgliederung des Saarlandes'', "Realm Commissioner for the re-union of Saarland
The Saarland (, ; french: Sarre ) is a state of Germany in the south west of the country. With an area of and population of 990,509 in 2018, it is the smallest German state in area apart from the city-states of Berlin, Bremen, and Hamburg, and ...
".
As the new Gau was extended to the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
, including the historic Palatinate, the region's name was changed again on 8 April 1940 to Gau Saarpfalz (Saar-Palatinate). After the Battle of France, the French département
In the administrative divisions of France, the department (french: département, ) is one of the three levels of government under the national level (" territorial collectivities"), between the administrative regions and the communes. Ninety ...
of Moselle was incorporated in the Reichsgau.
Anschluss
The Allies were, on paper, committed to upholding the terms of the Treaty of Versailles, which specifically prohibited the union of Austria and Germany. This notwithstanding, the Anschluss was among the first major steps in the Austrian-born Adolf Hitler's long-desired creation of an empire including German-speaking lands and territories Germany had lost after World War I.
The events of 12 March 1938, marked the culmination of historical cross-national pressures to unify the German populations of Austria and Germany under one nation. However, the 1938 Anschluss, regardless of its popularity, was enacted by Germany. Earlier, Hitler's Germany had provided support for the Austrian National Socialist Party
Austrian Nazism or Austrian National Socialism was a German nationalism in Austria, pan-German movement that was formed at the beginning of the 20th century. The movement took a concrete form on 15 November 1903 when the German Workers' Party (A ...
(Austrian Nazi Party) in its bid to seize power from Austria's Austrofascist leadership. Fully devoted to remaining independent but amidst growing pressures, the chancellor of Austria, Kurt Schuschnigg
Kurt Alois Josef Johann von Schuschnigg (; 14 December 1897 – 18 November 1977) was an Austrian Fatherland Front politician who was the Chancellor of the Federal State of Austria from the 1934 assassination of his predecessor Engelbert Doll ...
, tried to hold a plebiscite
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of ...
.
Although Schuschnigg expected Austria to vote in favour of maintaining autonomy, a well-planned coup d'état
A coup d'état (; French for 'stroke of state'), also known as a coup or overthrow, is a seizure and removal of a government and its powers. Typically, it is an illegal seizure of power by a political faction, politician, cult, rebel group, m ...
by the Austrian Nazi Party of Austria's state institutions in Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
took place on 11 March, prior to the vote. With power quickly transferred over to Germany, the Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the '' Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previo ...
troops entered Austria to enforce the Anschluss. The Nazis held a plebiscite
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of ...
within the following month, where they received 99.73% of the vote. No fighting ever took place and the strongest voices against the annexation, particularly Fascist Italy, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
and the United Kingdom (parties to the Stresa Front), were powerless or, in the case of Italy, appeased.
Czechoslovakia
Sudetenland
On 29 September 1938, Adolf Hitler, Neville Chamberlain, Benito Mussolini and Édouard Daladier
Édouard Daladier (; 18 June 1884 – 10 October 1970) was a French Radical-Socialist (centre-left) politician, and the Prime Minister of France who signed the Munich Agreement before the outbreak of World War II.
Daladier was born in Carpe ...
signed the Munich Agreement
The Munich Agreement ( cs, Mnichovská dohoda; sk, Mníchovská dohoda; german: Münchner Abkommen) was an agreement concluded at Munich on 30 September 1938, by Germany, the United Kingdom, France, and Italy. It provided "cession to Germany ...
. The Czechoslovak government capitulated on September 30 and reluctantly agreed to abide by the agreement. The settlement gave Germany the Sudetenland starting October 10, and de facto control over the rest of Czechoslovakia as long as Hitler promised to go no further.
Hitler and Chamberlain signed an additional resolution determining to resolve all future disputes between Germany and the United Kingdom through peaceful means. This is often confused with the Four-Power Munich Agreement itself, not least because most photographs of Chamberlain's return show him waving the paper containing the resolution, not the Munich Agreement itself.
Without fortification
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere' ...
which was built in Sudetenland, Czechoslovakia was now defenseless. On 5 October, Edvard Beneš
Edvard Beneš (; 28 May 1884 – 3 September 1948) was a Czech politician and statesman who served as the president of Czechoslovakia from 1935 to 1938, and again from 1945 to 1948. He also led the Czechoslovak government-in-exile 1939 to 194 ...
resigned as President of Czechoslovakia, realising that the fall of Czechoslovakia was '' fait accompli''. Following the outbreak of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, he would form a Czechoslovak government-in-exile
The Czechoslovak government-in-exile, sometimes styled officially as the Provisional Government of Czechoslovakia ( cz, Prozatímní vláda Československa, sk, Dočasná vláda Československa), was an informal title conferred upon the Czechos ...
in London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
.
Invasion of the rest of Czechoslovakia
 On 13 March 1939, Nazi armies entered
On 13 March 1939, Nazi armies entered Prague
Prague ( ; cs, Praha ; german: Prag, ; la, Praga) is the capital and List of cities in the Czech Republic, largest city in the Czech Republic, and the historical capital of Bohemia. On the Vltava river, Prague is home to about 1.3 milli ...
and proceeded to occupy the remainder of Bohemia and Moravia
Moravia ( , also , ; cs, Morava ; german: link=yes, Mähren ; pl, Morawy ; szl, Morawa; la, Moravia) is a historical region in the east of the Czech Republic and one of three historical Czech lands, with Bohemia and Czech Silesia.
The m ...
, which was transformed into a protectorate of the Reich. The eastern half of the country, Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the s ...
, became a separate pro-Nazi state, the Slovak Republic.
Prime Minister Chamberlain felt betrayed by the Nazi seizure of Czechoslovakia, realising his policy of appeasement towards Hitler had failed, and immediately began to mobilize the British Empire's armed forces on a war footing. France did the same. Though no immediate action followed, Hitler's move on Poland in September started World War II in Europe.
Memel Territory
By late 1938, Lithuania had lost control over the situation in the Memel Territory
Memel, a name derived from the Couronian-Latvian ''memelis, mimelis, mēms'' for "mute, silent", may refer to:
*Memel, East Prussia, Germany, now Klaipėda, Lithuania
**Memelburg, ( Klaipėda Castle), the ''Ordensburg'' in Memel, a castle built in ...
. In the early hours of 23 March 1939, after a political ultimatum had made a Lithuanian delegation travel to Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and List of cities in Germany by population, largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European Union by population within ci ...
, the Lithuanian Minister of Foreign Affairs Juozas Urbšys and his German counterpart Joachim von Ribbentrop signed the ''Treaty of the Cession of the Memel Territory to Germany'' in exchange for a Lithuanian Free Zone in the port of Memel, using the facilities erected in previous years.
World War II

Poland
After invading Poland in 1939, Germany annexed the lands it was forced to give to a reformed Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
in 1919–1922 by the Treaty of Versailles, including the "Polish Corridor
The Polish Corridor (german: Polnischer Korridor; pl, Pomorze, Polski Korytarz), also known as the Danzig Corridor, Corridor to the Sea or Gdańsk Corridor, was a territory located in the region of Pomerelia (Pomeranian Voivodeship, easter ...
", West Prussia, the Province of Posen, and East Upper Silesia East Upper Silesia (german: Ostoberschlesien) is the easternmost extremity of Silesia, the eastern part of the Upper Silesian region around the city of Katowice (german: Kattowitz).Isabel Heinemann, ''"Rasse, Siedlung, deutsches Blut": das Rasse- u ...
. The Volkstag
The Volkstag (English: ''People's Diet'') was the parliament of the Free City of Danzig between 1919 and 1939.
After World War I Danzig (Gdańsk) became a Free City under the protection of the League of Nations. The first elections to a const ...
of the Free City of Danzig voted to become a part of Germany again, although Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in C ...
and Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
were deprived of their voting rights and all non-Nazi
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in ...
political parties were banned. Parts of Poland that had not been part of Wilhelmine Germany were also incorporated into the Reich
''Reich'' (; ) is a German noun whose meaning is analogous to the meaning of the English word "realm"; this is not to be confused with the German adjective "reich" which means "rich". The terms ' (literally the "realm of an emperor") and ' (lit ...
.
 Two decrees by Adolf Hitler (8 October and 12 October 1939) provided for the division of the annexed areas of Poland into the following administrative units:
*
Two decrees by Adolf Hitler (8 October and 12 October 1939) provided for the division of the annexed areas of Poland into the following administrative units:
* Reichsgau Wartheland
The ''Reichsgau Wartheland'' (initially ''Reichsgau Posen'', also: ''Warthegau'') was a Nazi German ''Reichsgau'' formed from parts of Polish territory annexed in 1939 during World War II. It comprised the region of Greater Poland and adjacent ...
(initially Reichsgau Posen), which included the entire Poznań Voivodeship
Poznań Voivodeship was the name of several former administrative regions (''województwo'', rendered as ''voivodeship'' and usually translated as "province") in Poland, centered on the city of Poznań, although the exact boundaries changed over t ...
, most of the Łódź Voivodeship
Łódź Voivodeship (also known as Lodz Province, or by its Polish name ''Województwo łódzkie'' ) is a province- voivodeship in central Poland. It was created on 1 January 1999 out of the former Łódź Voivodeship (1975–1999) and the Sier ...
, five counties of the Pomeranian Voivodeship, and the Działdowo/Soldau County of the Warsaw Voivodeship;
* Reichsgau Danzig-West Prussia (initially Reichsgau West Prussia), which consisted of the remaining area of the Pomeranian Voivodeship and the Free City of Danzig;
* Ciechanów
Ciechanów is a city in north-central Poland. From 1975 to 1998, it was the capital of the Ciechanów Voivodeship. Since 1999, it has been situated in the Masovian Voivodeship. As of December 2021, it has a population of 43,495.
History
The ...
District (Regierungsbezirk
A ' () means "governmental district" and is a type of administrative division in Germany. Four of sixteen ' ( states of Germany) are split into '. Beneath these are rural and urban districts.
Saxony has ' (directorate districts) with more res ...
Zichenau), consisting of the five northern counties of Warsaw Voivodeship (Płock
Płock (pronounced ) is a city in central Poland, on the Vistula river, in the Masovian Voivodeship. According to the data provided by GUS on 31 December 2021, there were 116,962 inhabitants in the city. Its full ceremonial name, according to th ...
, Płońsk
Płońsk (; yi, פּלאָנסק, Plonsk) is a town in central Poland with 22,500 inhabitants (2010).
Situated at the Płonka river in the historic region of Mazovia, it is the seat of Płońsk County in the Masovian Voivodeship.
History
Ac ...
, Sierpc
Sierpc ( Polish: ) is a town in north-central Poland, in the north-west part of the Masovian Voivodeship, about 125 km northwest of Warsaw. It is the capital of Sierpc County. Its population is 18,791 (2006). It is located near the national ...
, Ciechanów
Ciechanów is a city in north-central Poland. From 1975 to 1998, it was the capital of the Ciechanów Voivodeship. Since 1999, it has been situated in the Masovian Voivodeship. As of December 2021, it has a population of 43,495.
History
The ...
, and Mława
Mława (; yi, מלאווע ''Mlave'') is a town in north-east Poland with 30,403 inhabitants in 2020. It is the capital of Mława County. It is situated in the Masovian Voivodeship.
During the invasion of Poland in 1939, the battle of Mława was ...
), which became a part of East Prussia;
* Katowice District (Regierungsbezirk Kattowitz), or unofficially East Upper Silesia East Upper Silesia (german: Ostoberschlesien) is the easternmost extremity of Silesia, the eastern part of the Upper Silesian region around the city of Katowice (german: Kattowitz).Isabel Heinemann, ''"Rasse, Siedlung, deutsches Blut": das Rasse- u ...
(Ost-Oberschlesien), which included Sosnowiec, Będzin
Będzin (; also ''Bendzin'' in English; german: Bendzin; yi, בענדין, Bendin) is a city in the Dąbrowa Basin, in southern Poland. It lies in the Silesian Highlands, on the Czarna Przemsza River (a tributary of the Vistula). Even though pa ...
, Chrzanów
Chrzanów () is a town in southern Poland with 35,651 inhabitants as of December 2021. It is situated in the Lesser Poland Voivodeship (since 1999) and is the seat of Chrzanów County.
History
History to 1809
It is impossible to establish ...
, and Zawiercie
Zawiercie is a city in the south of Poland located in the Silesian Voivodeship with 49,334 inhabitants (2019). It is situated in the Kraków-Częstochowa Upland near the source of the Warta River. The town lies near the historical region of Sile ...
Counties, and parts of Olkusz
Olkusz ( yi, עלקיש ''Elkish'', german: 1941-45 Ilkenau) is a town in southern Poland with 36,607 inhabitants (2014). Situated in the Lesser Poland Voivodeship (since 1999), previously in Katowice Voivodeship (1975–1998), it is the capita ...
and Żywiec
Żywiec () (german: Saybusch) is a town in southern Poland with 31,194 inhabitants (2019). Between 1975 and 1998, it was located within the Bielsko-Biała Voivodeship, but has since become part of the Silesian Voivodeship.It is the capital of Ż ...
Counties.
These territories had an area of and a population of 10,000,000 people. The remainder of the Polish territory was annexed by the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
(c. 52%; see Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact
The Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact was a non-aggression pact between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union that enabled those powers to partition Poland between them. The pact was signed in Moscow on 23 August 1939 by German Foreign Minister Joachim von Ri ...
) or made into the German-controlled General Government occupation zone.
After the German attack on the Soviet Union
Operation Barbarossa (german: link=no, Unternehmen Barbarossa; ) was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and many of its Axis allies, starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during the Second World War. The operation, code-named after ...
in June 1941, the Białystok Voivodeship, which included the Białystok, Bielsk Podlaski, Grajewo, Łomża
Łomża (), in English known as Lomza, is a city in north-eastern Poland, approximately 150 kilometers (90 miles) to the north-east of Warsaw and west of Białystok. It is situated alongside the Narew river as part of the Podlaskie Voivodeship ...
, Sokółka
Sokółka (; lt, Sokulka, Sakalinė, be, Саку́лка, yi, סאקאלקע, Sokolke) is a town in northeastern Poland, seat of the Sokółka County in Podlaskie Voivodeship. It is a busy rail junction located on the international Warsaw–B ...
, Volkovysk
Vawkavysk ( be, Ваўкавы́ск, ; russian: Волковы́ск; pl, Wołkowysk; lt, Valkaviskas; yi, וואלקאוויסק; names in other languages) is one of the oldest towns in southwestern Belarus and the capital of the Vawkavysk ...
, and Grodno Counties, was "attached to" (not incorporated into) East Prussia, while East Galicia was added to the General Government.
Alsace-Lorraine
After the invasion of France in 1940, Germany annexed the départements of Bas-Rhin
Bas-Rhin (; Alsatian: ''Unterelsàss'', ' or '; traditional german: links=no, Niederrhein; en, Lower Rhine) is a department in Alsace which is a part of the Grand Est super-region of France. The name means 'Lower Rhine', referring to its low ...
, Haut-Rhin
Haut-Rhin (, ; Alsatian: ''Owerelsàss'' or '; german: Oberelsass, ) is a department in the Grand Est region of France, bordering both Germany and Switzerland. It is named after the river Rhine. Its name means ''Upper Rhine''. Haut-Rhin is th ...
and Moselle (Alsace-Lorraine). The German government never negotiated or declared a formal annexation, however, in order to preserve the possibility of an agreement with the West.
Eupen and Malmedy
See Eupen-Malmedy
Eupen-Malmedy is a small, predominantly German-speaking region in eastern Belgium. It consists of three administrative cantons around the towns of Eupen, Malmedy, and Sankt Vith which encompass some . Elsewhere in Belgium, the region is common ...
Luxembourg
Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small lan ...
was invaded and occupied by German Forces in June 1940. It was formally annexed to Germany in August 1942.
Parts of Yugoslavia
From: History of Slovenia
The history of Slovenia chronicles the period of the Slovenian territory from the 5th century BC to the present. In the Early Bronze Age, Proto- Illyrian tribes settled an area stretching from present-day Albania to the city of Trieste. The Slov ...
"After Yugoslavia fell, Germany, Italy, and Hungary each annexed parts of Slovenia, the largest part being Lower Styria
Styria ( sl, Štajerska), also Slovenian Styria (''Slovenska Štajerska'') or Lower Styria (''Spodnja Štajerska''; german: Untersteiermark), is a traditional region in northeastern Slovenia, comprising the southern third of the former Duchy o ...
which was annexed to the "Ostmark" (Nazi German Austria)."
South Tyrol
See Annexation of South Tyrol to Nazi Germany and Italian Social Republic.
Recognition
All areas that were incorporated into Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
between 1937 and 8 May 1945 were ''de facto'' repudiated at the Yalta
Yalta (: Я́лта) is a resort city on the south coast of the Crimean Peninsula surrounded by the Black Sea. It serves as the administrative center of Yalta Municipality, one of the regions within Crimea. Yalta, along with the rest of Cri ...
and Potsdam Conference
The Potsdam Conference (german: Potsdamer Konferenz) was held at Potsdam in the Soviet occupation zone from July 17 to August 2, 1945, to allow the three leading Allies to plan the postwar peace, while avoiding the mistakes of the Paris P ...
s, and were therefore non-issues in the post-war division of Nazi Germany. One exception was Memelland, the incorporation of which at the end of March 1939 was recognised by the UK and France, but not by the US.
Territorial changes after World War II
 As it became evident that the Allies were going to defeat Nazi Germany decisively, the question arose as to how to redraw the borders of Central and Eastern European countries after the war. In the context of those decisions, the problem arose of what to do about ethnic minorities within the redrawn borders. The territorial changes at the end of World War II were part of negotiated agreements between the victorious Allies to redraw national borders and arrange for deportation of all Germans that were east of the Oder–Neisse line. The Allies occupied Germany, but the Western allies and Soviet Union formed separate governments covering specific parts of Germany. On 7 October 1949, the two German countries appeared with the establishment of the German Democratic Republic; however the two German countries were unified to form present-day Germany on 3 October 1990.
As it became evident that the Allies were going to defeat Nazi Germany decisively, the question arose as to how to redraw the borders of Central and Eastern European countries after the war. In the context of those decisions, the problem arose of what to do about ethnic minorities within the redrawn borders. The territorial changes at the end of World War II were part of negotiated agreements between the victorious Allies to redraw national borders and arrange for deportation of all Germans that were east of the Oder–Neisse line. The Allies occupied Germany, but the Western allies and Soviet Union formed separate governments covering specific parts of Germany. On 7 October 1949, the two German countries appeared with the establishment of the German Democratic Republic; however the two German countries were unified to form present-day Germany on 3 October 1990.
The Yalta Conference
The final decision to move Poland's boundary westward was made by the US, Britain and the Soviets at the Yalta Conference
The Yalta Conference (codenamed Argonaut), also known as the Crimea Conference, held 4–11 February 1945, was the World War II meeting of the heads of government of the United States, the United Kingdom, and the Soviet Union to discuss the post ...
, shortly before the end of the war. The precise location of the border was left open; the western Allies also accepted in general the principle of the Oder River as the future western border of Poland and of population transfer as the way to prevent future border disputes. The open question was whether the border should follow the eastern or western Neisse rivers, and whether Stettin, the traditional seaport of Berlin, should remain German or be included in Poland.
Originally, Germany was to retain Stettin while the Poles were to annex East Prussia with Königsberg
Königsberg (, ) was the historic Prussian city that is now Kaliningrad, Russia. Königsberg was founded in 1255 on the site of the ancient Old Prussian settlement ''Twangste'' by the Teutonic Knights during the Northern Crusades, and was name ...
Eventually, however, Stalin decided that he wanted Königsberg as a year-round warm water port for the Soviet Navy and argued that the Poles should receive Stettin instead. The wartime Polish government in exile had little to say in these decision
Key points of the meeting that are relevant to the territorial changes of Germany are as follows:
*There was an agreement that the priority would be the unconditional surrender
An unconditional surrender is a surrender in which no guarantees are given to the surrendering party. It is often demanded with the threat of complete destruction, extermination or annihilation.
In modern times, unconditional surrenders most ofte ...
of Nazi Germany. After the war, Germany would be split into four occupied zones, with a quadripartite occupation of Berlin as well, prior to unification of Germany.
*Stalin agreed to let France have the fourth occupation zone in Germany and Austria, carved out from the British and American zones. France would also be granted a seat in the Allied Control Council.
*Germany would undergo demilitarization
Demilitarisation or demilitarization may mean the reduction of state armed forces; it is the opposite of militarisation in many respects. For instance, the demilitarisation of Northern Ireland entailed the reduction of British security and military ...
and denazification.
*The status of Poland was discussed, but was complicated by the fact that Poland was at this time under the control of the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army ( Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, afte ...
. It was agreed to reorganize the Provisionary Polish Government that had been set up by the Red Army through the inclusion of other groups such as the Polish Provisional Government of National Unity and to have democratic elections. This effectively excluded the Polish government-in-exile
The Polish government-in-exile, officially known as the Government of the Republic of Poland in exile ( pl, Rząd Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej na uchodźstwie), was the government in exile of Poland formed in the aftermath of the Invasion of Pola ...
that had evacuated in 1939.
*The Polish eastern border would follow the Curzon Line
The Curzon Line was a proposed demarcation line between the Second Polish Republic and the Soviet Union, two new states emerging after World War I. It was first proposed by The 1st Earl Curzon of Kedleston, the British Foreign Secretary, to ...
, and Poland would receive substantial territorial compensation in the west from Germany, although the exact border was to be determined at a later time.
*A "Committee on Dismemberment of Germany" was to be set up. The purpose was to decide whether Germany was to be divided into several nations, and if so, what borders and inter-relationships the new German states were to have.
The Potsdam Conference
At the Potsdam Conference
The Potsdam Conference (german: Potsdamer Konferenz) was held at Potsdam in the Soviet occupation zone from July 17 to August 2, 1945, to allow the three leading Allies to plan the postwar peace, while avoiding the mistakes of the Paris P ...
the United States, the United Kingdom, and the Soviet Union placed the German territories within the 1937 Nazi Germany borders east of the Oder–Neisse line
The Oder–Neisse line (german: Oder-Neiße-Grenze, pl, granica na Odrze i Nysie Łużyckiej) is the basis of most of the international border between Germany and Poland from 1990. It runs mainly along the Oder and Lusatian Neisse rivers a ...
, and with the exception of parts of East Prussia, as formally under Polish administrative control (These were referred to by the Polish communist government as the "Western Territories" or "Regained Territories
The Recovered Territories or Regained Lands ( pl, Ziemie Odzyskane), also known as Western Borderlands ( pl, Kresy Zachodnie), and previously as Western and Northern Territories ( pl, Ziemie Zachodnie i Północne), Postulated Territories ( pl, Z ...
"). It was anticipated that a final peace treaty
A peace treaty is an agreement between two or more hostile parties, usually countries or governments, which formally ends a state of war between the parties. It is different from an armistice
An armistice is a formal agreement of warring ...
would follow shortly and either confirm this border or determine whatever alterations might be agreed upon. Northern East Prussia and Memelland were placed under Soviet administrative control. The 1919 Versailles Treaty created Free City of Danzig was also placed under Polish administration. The German population east of the Oder–Neisse line was forcibly expelled.
At the end of the conference, the Three Heads of Government agreed on the following actions:
* Issuance of a statement of aims of the occupation of Germany by the Allies: demilitarization
Demilitarisation or demilitarization may mean the reduction of state armed forces; it is the opposite of militarisation in many respects. For instance, the demilitarisation of Northern Ireland entailed the reduction of British security and military ...
, denazification, democratization and decartelization. (''see also: The industrial plans for Germany'')
* Division of Germany and Austria respectively into four occupation zones (earlier agreed in principle at Yalta
Yalta (: Я́лта) is a resort city on the south coast of the Crimean Peninsula surrounded by the Black Sea. It serves as the administrative center of Yalta Municipality, one of the regions within Crimea. Yalta, along with the rest of Cri ...
), and the similar division of each's capital, Berlin and Vienna, into four and five sectors (one quadripartite sector), respectively.
* Reversion of all German annexations in Europe after 1937, among these were Sudetenland, Alsace-Lorraine, Austria, the westmost parts of Poland, and others.
* Germany's eastern border was to be shifted westwards to the Oder–Neisse line
The Oder–Neisse line (german: Oder-Neiße-Grenze, pl, granica na Odrze i Nysie Łużyckiej) is the basis of most of the international border between Germany and Poland from 1990. It runs mainly along the Oder and Lusatian Neisse rivers a ...
, effectively reducing Germany in size by approximately 25% compared to its 1937 borders. The territories east of the new border comprised East Prussia, all of Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. Silesia is split ...
(except for its westernmost part around the city of Görlitz), the eastern part of Brandenburg, and most of Pomerania
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to ...
(including former Grenzmark Posen-West Prussia). These areas included large urban centres such as Stettin, Breslau, Landsberg an der Warthe
Landsberg may refer to:
* Landsberg (surname)
* Margraviate of Landsberg, a march of the Holy Roman Empire
* Palatinate-Landsberg, a state of the Holy Roman Empire
Places
* Landsberg (district), Bavaria, Germany
* Landsberg, Saxony-Anhalt, German ...
and so on.
* Expulsion of the German populations remaining beyond the new eastern borders of Germany, and ethnically German denaturalised citizens of other states such Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
, Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the ...
, Poland, Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
, and Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
. France, which had not participated in the Potsdam conference, took its liberties to dismiss this point and therefore refused to absorb any expellees in its zone of occupation.
Finalization of the Polish-German border
The problem with the status of these territories was that the concluding document of the Potsdam Conference
The Potsdam Conference (german: Potsdamer Konferenz) was held at Potsdam in the Soviet occupation zone from July 17 to August 2, 1945, to allow the three leading Allies to plan the postwar peace, while avoiding the mistakes of the Paris P ...
in 1945 was not a legally binding treaty
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal pe ...
, but a memorandum
A memorandum ( : memoranda; abbr: memo; from the Latin ''memorandum'', "(that) which is to be remembered") is a written message that is typically used in a professional setting. Commonly abbreviated "memo," these messages are usually brief and ...
between the USSR, the US and the UK. It regulated the issue of the eastern German border, which was to be the Oder–Neisse line, but the final article of the memorandum said that the final decisions concerning Germany were to be subject to a separate peace treaty.
The SED
sed ("stream editor") is a Unix utility that parses and transforms text, using a simple, compact programming language. It was developed from 1973 to 1974 by Lee E. McMahon of Bell Labs,
and is available today for most operating systems.
sed w ...
, the German party in East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
, initially opposed this but was later forced to sign a treaty recognizing a new border with Poland under pressure from the Soviet Union in 1950.
Based upon the interpretation of the Potsdam Agreement, the CDU controlled German government maintained that the Oder–Neisse line
The Oder–Neisse line (german: Oder-Neiße-Grenze, pl, granica na Odrze i Nysie Łużyckiej) is the basis of most of the international border between Germany and Poland from 1990. It runs mainly along the Oder and Lusatian Neisse rivers a ...
was completely unacceptable and subject to negotiation. Also the Social Democrats of the SPD initially refused to accept the Oder–Neisse line. Thus, the official German government position on the status of areas vacated by settled German communities east of the Oder–Neisse rivers was that the areas were "temporarily under Polish (or oviet administration."
Between 1970 and 1990, the West German political establishment gradually recognised the "facts on the ground
Facts on the ground is a diplomatic and geopolitical term that means the situation in reality as opposed to in the abstract.
The term was popularised in the 1970s in discussions of the Israeli–Palestinian conflict to refer to Israeli settlement ...
" and accepted clauses in the Treaty on the Final Settlement, whereby Germany renounced all claims to territory east of the Oder–Neisse line.
In the Treaty of Warsaw (1970; ratified in 1972) West Germany
West Germany is the colloquial term used to indicate the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG; german: Bundesrepublik Deutschland , BRD) between its formation on 23 May 1949 and the German reunification through the accession of East Germany on 3 O ...
recognized the Oder–Neisse line as Poland's western border and renounced any present and future territorial claims; this was reaffirmed by both German states in the 1990 as a pre-condition for re-union. The treaty was ratified in 1991 by the united Germany. United Germany and Poland then finally settled the issue of the Oder–Neisse border by the German–Polish Border Treaty
The German–Polish Border Treaty of 1990; pl, Traktat między Rzeczpospolitą Polską a Republiką Federalną Niemiec o potwierdzeniu istniejącej między nimi granicy) finally settled the issue of the Polish–German border, which in terms ...
in November 1990. This ended the legal limbo which meant that for 45 years, people on both sides of the border could not be sure whether the status quo reached in 1945 might be changed at some future date.
Belgium
The "Working Party on Provisional Adjustments to the Western Frontiers of Germany" approved in 1949 the provisional transfer of containing 500 inhabitants to Belgium:
# Bildchen (returned in 1956)
# Lichtenbusch (returned in 1956)
# Fringshaus — roads between Roetgen
Roetgen () is a municipality in the district of Aachen, in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany.
Geography
Roetgen is located approximately 16 km (10 mi) south-east of Aachen, near the border with Belgium. It is in the north of the High Fe ...
and Fringshaus, Fringshaus and Lammersdorf, Fringshaus and Konzen (first two returned in 1956)
# Leykoul (eastern part returned in 1956)
# Elsenborn
# Losheim (only the village returned in 1956)
# Hemmeres (returned in 1956)
As part of the 1956 treaty, in exchange for the territory ceded by Germany, Belgium ceded to Germany its territory north of the Fringshaus roads and bounded by the Vennbahn
The (, "Fen Railway") is a former railway line that was built partly across what was then German territory by the Prussian state railways. It is now entirely in Belgium, because the trackbed of the line, as well as the stations and other instal ...
. The detached territory, in 1956 containing 704 inhabitants including refugees, was, prior to its 1956 dissolution and partition between West Germany and Belgium, ruled as an independent territory by Belgian Army Major General Paul Bolle, who enjoyed dictatorial powers.
Netherlands
Despite the more extensive annexation proposals of the Bakker-Schut Plan, only a few border modifications were implemented. On 23 April 1949, Dutch troops occupied an area of , the largest parts of which were Elten (near Emmerich am Rhein
Emmerich am Rhein ( Low Rhenish and nl, Emmerik) is a city and municipality in the northwest of the German federal state of North Rhine-Westphalia. The city has a harbour and a quay at the Rhine. In terms of local government organization, it i ...
) and Selfkant
Selfkant (; nl, Selfkant or ''Zelfkant'' ; Limburgish: ) is a municipality in the Heinsberg district, in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is the most westerly municipality in Germany.
Geography
Isenbruch in Selfkant is the most westerly po ...
. Many other small border changes were executed, mostly in the vicinity of Arnhem
Arnhem ( or ; german: Arnheim; South Guelderish: ''Èrnem'') is a city and municipality situated in the eastern part of the Netherlands about 55 km south east of Utrecht. It is the capital of the province of Gelderland, located on both ban ...
and Dinxperlo
Dinxperlo (; Dutch Low Saxon: ) is a town and former municipality in the eastern Netherlands (Achterhoek region), situated directly at the Germany-Netherlands border.
Since 1 January 2005, Dinxperlo has been part of the municipality of Aalten. ...
. At that time, these areas were inhabited by a total of almost 10,000 people.
Starting in March 1957, West Germany negotiated with the Netherlands for the return of these areas. The negotiations led to an agreement (german: Vertrag vom 8. April 1960 zwischen der Bundesrepublik Deutschland und dem Königreich der Niederlande zur Regelung von Grenzfragen und anderen zwischen beiden Ländern bestehenden Problemen; short: Ausgleichsvertrag, i.e. treaty of settlement[Cf. Bundesgesetzblatt (Federal Law Gazette), part III, no. 181-1.]) made in The Hague on 8 April 1960, in which Germany agreed to pay DEM
DEM was the ISO 4217 currency code for the Deutsche Mark, former currency of Germany
Computing
* Digital elevation model, a digital representation of ground-surface topography or terrain
** .dem, a common extension for USGS DEM files
* Discret ...
280 million for the return of Elten, Selfkant, and Suderwick, as ''Wiedergutmachung
The German word ''Wiedergutmachung'' after World War II refers to the reparations that the German government agreed to pay in 1953 to the direct survivors of the Holocaust, and to those who were made to work at forced labour camps or who othe ...
''.
The territory was returned to Germany on 1 August 1963, except for one small hill (about ) near Wyler village, called Duivelsberg/Wylerberg which was annexed by the Netherlands.
France
Starting on 16 February 1946 France disentangled the Saar area and established the separate Saar Protectorate
The Saar Protectorate (german: Saarprotektorat ; french: Protectorat de la Sarre) officially Saarland (french: Sarre) was a French protectorate separated from Germany; which was later opposed by the Soviet Union, one side occupying Germany lik ...
, further attaching parts of the Prussian Rhine Province and the Bavarian Palatinate (Saarpfalz
Saarpfalz (''Saar-Palatinate'') is a Kreis (district) in the south-east of the Saarland, Germany. Neighboring districts are (from west clockwise) Saarbrücken, Neunkirchen, Kusel, Kaiserslautern, Südwestpfalz, district-free Zweibrücken, and the ...
). Like the former eastern territories of Germany
The former eastern territories of Germany (german: Ehemalige deutsche Ostgebiete) refer in present-day Germany to those territories east of the current eastern border of Germany i.e. Oder–Neisse line which historically had been considered Ger ...
the Saar area was out of the jurisdiction of the Allied Control Council for Germany and thus not a part of Allied-occupied Germany
Germany was already de facto occupied by the Allies from the real fall of Nazi Germany in World War II on 8 May 1945 to the establishment of the East Germany on 7 October 1949. The Allies (United States, United Kingdom, Soviet Union, and Franc ...
. However, unlike the eastern territories, the domestic Saar population was not expelled by the controlling French; moreover, it is not fully incorporated into France nor is it a country. With the effect of 1 January 1957, the Saar Protectorate declared its accession to the Federal Republic of Germany, as provided by its Grundgesetz
The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany (german: Grundgesetz für die Bundesrepublik Deutschland) is the constitution of the Federal Republic of Germany.
The West German Constitution was approved in Bonn on 8 May 1949 and came in ...
(constitution) art. 23 (Little Reunification), thus becoming the new federal state of Saarland
The Saarland (, ; french: Sarre ) is a state of Germany in the south west of the country. With an area of and population of 990,509 in 2018, it is the smallest German state in area apart from the city-states of Berlin, Bremen, and Hamburg, and ...
.
Maps about territorial evolution of Germany



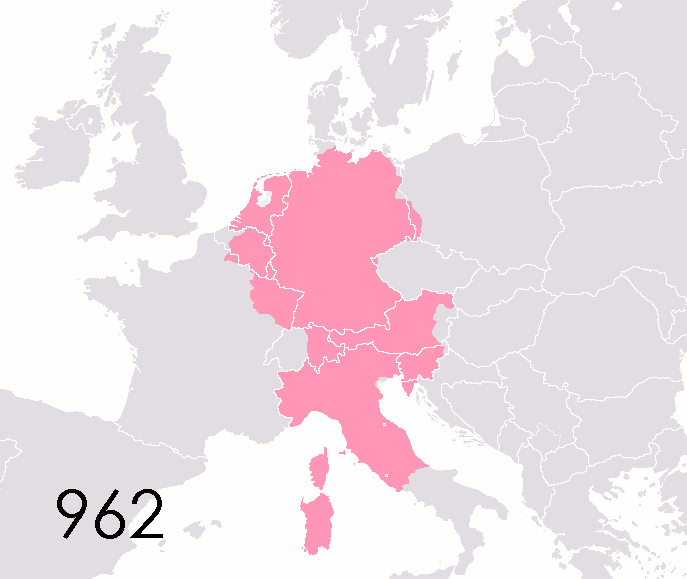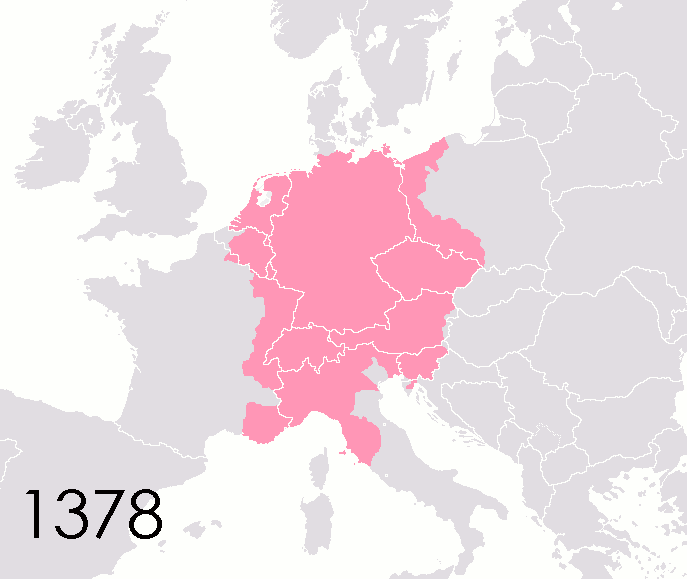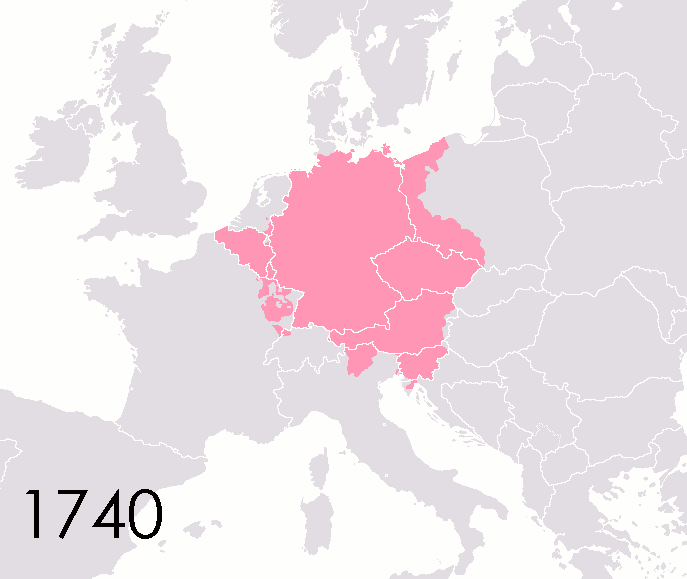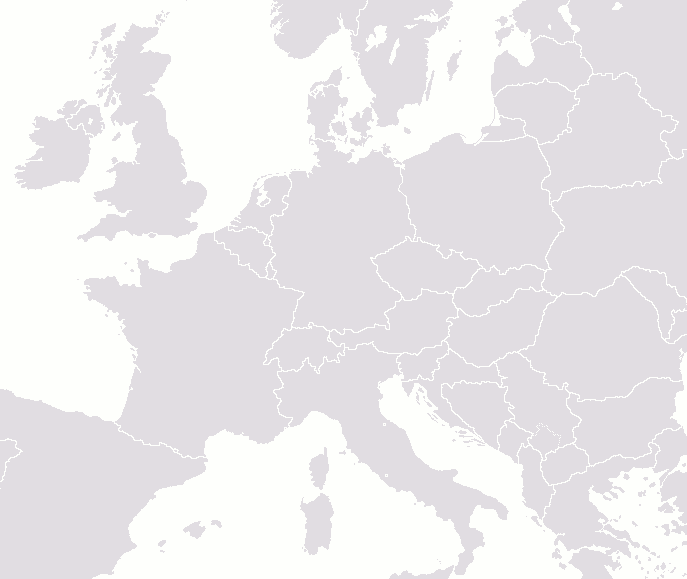







See also
* History of Germany
*Administrative divisions of Nazi Germany
The ''Gaue'' (Singular: ''Gau'') were the main administrative divisions of Nazi Germany from 1934 to 1945.
The ''Gaue'' were formed in 1926 as Nazi Party regional districts in Weimar Germany based on the territorial changes after the First ...
*Areas annexed by Nazi Germany
There were many areas annexed by Germany both immediately before and throughout the course of World War II. Territories that were part of Germany before the annexations were known as the "Altreich" (Old Reich).
Fully annexed territories
Ac ...
References
External links
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Germany
Geographic history of Germany
Aftermath of World War I in Germany
Aftermath of World War II in Germany
German diaspora in Europe
Foreign relations of Germany

 On 13 March 1939, Nazi armies entered
On 13 March 1939, Nazi armies entered 
 Two decrees by Adolf Hitler (8 October and 12 October 1939) provided for the division of the annexed areas of Poland into the following administrative units:
*
Two decrees by Adolf Hitler (8 October and 12 October 1939) provided for the division of the annexed areas of Poland into the following administrative units:
* 



