Tennis elbow on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Tennis elbow, also known as lateral epicondylitis or enthesopathy of the extensor carpi radialis origin, is a condition in which the outer part of the elbow becomes painful and tender. The pain may also extend into the back of the
 Enthesopathy of the extensor carpi radialis brevis origin is idiopathic, meaning that it has no known cause.
Tennis players generally believe tennis elbow is caused by the repetitive nature of hitting thousands of tennis balls, which leads to tiny tears in the forearm tendon attachment at the elbow. Traditionally, people have speculated that tennis elbow is a type of
Enthesopathy of the extensor carpi radialis brevis origin is idiopathic, meaning that it has no known cause.
Tennis players generally believe tennis elbow is caused by the repetitive nature of hitting thousands of tennis balls, which leads to tiny tears in the forearm tendon attachment at the elbow. Traditionally, people have speculated that tennis elbow is a type of 

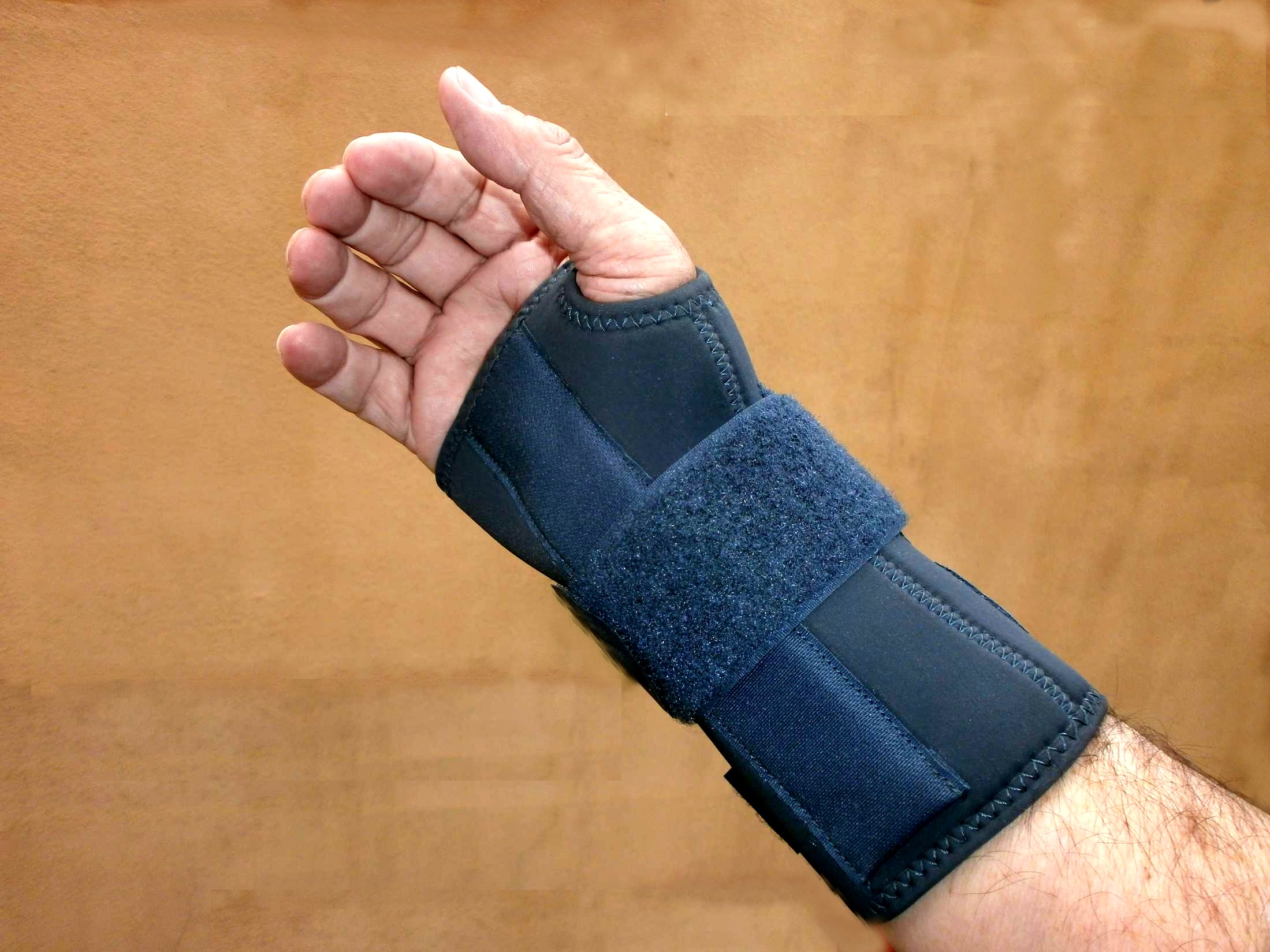 Orthosis is a device externally used on the limb to improve the function or reduce the pain. Orthotics may be useful in tennis elbow, however long-term effects are unknown. There are two main types of orthoses prescribed for this problem: counterforce elbow orthoses and wrist extension orthoses. Counterforce orthosis has a circumferential structure surrounding the arm. This orthosis usually has a strap which applies a binding force over the origin of the wrist extensors. The applied force by orthosis reduces the elongation within the musculotendinous fibers. Wrist extensor orthosis maintains the wrist in the slight extension.
Orthosis is a device externally used on the limb to improve the function or reduce the pain. Orthotics may be useful in tennis elbow, however long-term effects are unknown. There are two main types of orthoses prescribed for this problem: counterforce elbow orthoses and wrist extension orthoses. Counterforce orthosis has a circumferential structure surrounding the arm. This orthosis usually has a strap which applies a binding force over the origin of the wrist extensors. The applied force by orthosis reduces the elongation within the musculotendinous fibers. Wrist extensor orthosis maintains the wrist in the slight extension.
forearm
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is most often used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in ...
. Onset of symptoms is generally gradual although they can seem sudden and be misinterpreted as an injury. Golfer's elbow is a similar condition that affects the inside of the elbow.
Enthesopathies are idiopathic, meaning science has not yet determined the cause. Enthesopathies are most common in middle age (ages 35 to 60).
It is often stated that the condition is caused by excessive use of the muscles of the back of the forearm, but this is not supported by experimental evidence and is a common misinterpretation or unhelpful thought about symptoms. It may be associated with work or sports, classically racquet sports
Racket sports are games in which players use a racket or paddle to hit a ball or other object. Rackets consist of a handled frame with an open hoop that supports a network of tightly stretched strings. Paddles have a solid face rather than a netw ...
, but most people with the condition are not exposed to these activities. The diagnosis is based on the symptoms and examination. Medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to re ...
is not particularly useful. Signs consistent with the diagnosis include pain when a subject tries to bend back the wrist when the wrist is against resistance.
The natural history of untreated enthesopathy is resolution over a period of 1-2 years. Palliative (symptoms alleviating) treatment may include pain medications such as NSAIDS or acetaminophen (paracetamol), a wrist brace or strap over the upper forearm. The role of corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are inv ...
injections is debated. Recent evidence suggests corticosteroid injections may delay symptom resolution.
Signs and symptoms
* Pain on the outer part of the elbow ( lateral epicondyle) * Point tenderness over the lateral epicondyle—a prominent part of the bone on the outside of the elbow * Pain with resisted wrist extension or passive wrist flexion Symptoms associated with tennis elbow include, but are not limited to, pain from the outside of the elbow to theforearm
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is most often used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in ...
and wrist and pain during extension of wrist.
Terminology
The term "tennis elbow" is widely used (although informal), but the condition should be understood as not limited to tennis players. Historically, the medical term "lateral epicondylitis" was most commonly used for the condition, but "itis" implies inflammation and the condition is not inflammatory. Since histological findings reveal noninflammatory tissue, the terms “lateral elbow tendinopathy" and " tendinosis” are suggested. In 2019, a group of international experts suggested that "lateral elbow tendinopathy" was the most appropriate terminology. But a disease of an attachment point (or enthesia) is most accurately referred to as an "enthesopathy."Causes
 Enthesopathy of the extensor carpi radialis brevis origin is idiopathic, meaning that it has no known cause.
Tennis players generally believe tennis elbow is caused by the repetitive nature of hitting thousands of tennis balls, which leads to tiny tears in the forearm tendon attachment at the elbow. Traditionally, people have speculated that tennis elbow is a type of
Enthesopathy of the extensor carpi radialis brevis origin is idiopathic, meaning that it has no known cause.
Tennis players generally believe tennis elbow is caused by the repetitive nature of hitting thousands of tennis balls, which leads to tiny tears in the forearm tendon attachment at the elbow. Traditionally, people have speculated that tennis elbow is a type of repetitive strain injury
A repetitive strain injury (RSI) is an injury to part of the musculoskeletal or nervous system caused by repetitive use, vibrations, compression or long periods in a fixed position. Other common names include repetitive stress disorders, cumula ...
resulting from tendon overuse and failed healing of the tendon, but there is no evidence of injury or repair on histopathology, and misinterpretation of painful activities as a source of damage is common.
Other speculative risk factors for lateral epicondylitis include taking up tennis later in life, unaccustomed strenuous activity, decreased mental chronometry
Mental chronometry is the scientific study of processing speed or reaction time on cognitive tasks to infer the content, duration, and temporal sequencing of mental operations. Reaction time (RT; sometimes referred to as "response time") is meas ...
and speed and repetitive eccentric contraction of muscle (controlled lengthening of a muscle group).
Pathophysiology
Histological findings are of mucoid degeneration: disorganized collagen, increased extracellular matrix, and chondroid metaplasia. There is no evidence of inflammation or repair. Therefore, the disorder is more appropriately referred to as ''tendinosis'' or ''tendinopathy—more accurately an enthesopathy—''rather than '' tendinitis.''Diagnosis
Physical examination
Diagnosis is based on symptoms and clinical signs that are discrete and characteristic. For example, extension of the elbow and flexion of the wrist cause outer elbow pain. There is point tenderness at the origin of the extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle from the lateral epicondyle (extensor carpi radialis brevis origin). There is also pain with resisted wristextension
Extension, extend or extended may refer to:
Mathematics
Logic or set theory
* Axiom of extensionality
* Extensible cardinal
* Extension (model theory)
* Extension (predicate logic), the set of tuples of values that satisfy the predicate
* Ext ...
( Cozen's test).
Medical imaging
Medical imaging is not necessary or helpful. X-rays can confirm and distinguish possibilities of existing causes of pain that are unrelated to tennis elbow, such asfracture
Fracture is the separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacement discontinuity surfaces within the solid. If a displ ...
or arthritis. Rarely, calcification can be found where the extensor muscles attach to the lateral epicondyle. Medical ultrasonography
Medical ultrasound includes diagnostic techniques (mainly imaging techniques) using ultrasound, as well as therapeutic applications of ultrasound. In diagnosis, it is used to create an image of internal body structures such as tendons, mus ...
and magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio wave ...
(MRI) are other valuable tools for diagnosis but are frequently avoided due to the high cost.
Longitudinal sonogram of the lateral elbow displays thickening and heterogeneity of the common extensor tendon that is consistent with tendinosis, as the ultrasound reveals calcifications, intrasubstance tears, and marked irregularity of the lateral epicondyle. Although the term “epicondylitis” is frequently used to describe this disorder, most histopathologic findings of studies have displayed no evidence of an acute, or a chronic inflammatory process. Histologic studies have demonstrated that this condition is the result of tendon degeneration, which replaces normal tissue with a disorganized arrangement of collagen.
Treatment
The natural history of untreated enthesopathy is resolution over a period of 1-2 years. Palliative (symptoms alleviating) treatment may include pain medications such as NSAIDS or acetaminophen (paracetamol), a wrist brace or strap over the upper forearm.Exercises
Stretching and isometric strengthening are the most common recommended exercises. The muscle is stretched with the elbow straight and the wrist passively flexed. Isometric strengthening can be done by pushing the top of the hand up against the undersurface of a table and holding the wrist straight.Orthotic devices

 Orthosis is a device externally used on the limb to improve the function or reduce the pain. Orthotics may be useful in tennis elbow, however long-term effects are unknown. There are two main types of orthoses prescribed for this problem: counterforce elbow orthoses and wrist extension orthoses. Counterforce orthosis has a circumferential structure surrounding the arm. This orthosis usually has a strap which applies a binding force over the origin of the wrist extensors. The applied force by orthosis reduces the elongation within the musculotendinous fibers. Wrist extensor orthosis maintains the wrist in the slight extension.
Orthosis is a device externally used on the limb to improve the function or reduce the pain. Orthotics may be useful in tennis elbow, however long-term effects are unknown. There are two main types of orthoses prescribed for this problem: counterforce elbow orthoses and wrist extension orthoses. Counterforce orthosis has a circumferential structure surrounding the arm. This orthosis usually has a strap which applies a binding force over the origin of the wrist extensors. The applied force by orthosis reduces the elongation within the musculotendinous fibers. Wrist extensor orthosis maintains the wrist in the slight extension.
Speculative treatments
Other approaches that are not experimentally tested include eccentric exercise using a rubber bar, joint manipulation directed at the elbow and wrist,spinal manipulation
Spinal manipulation is an intervention performed on spinal articulations, synovial joints, which is asserted to be therapeutic. These articulations in the spine that are amenable to spinal manipulative therapy include the z-joints, the atlanto ...
directed at the cervical and thoracic spinal regions, low level laser therapy, and extracorporeal shockwave therapy.
Medication
Although anti-inflammatories are a commonly prescribed treatment for tennis elbow, the evidence for their effect is usually anecdotal with only limited studies showing a benefit. A systematic review found that topical non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may improve pain in the short term (up to 4 weeks) but was unable to draw firm conclusions due to methodological issues. Evidence for oral NSAIDs is mixed. Evidence is poor for long term improvement from injections of any type, whethercorticosteroids
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invol ...
, botulinum toxin
Botulinum toxin, or botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT), is a neurotoxic protein produced by the bacterium ''Clostridium botulinum'' and related species. It prevents the release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine from axon endings at the neurom ...
, prolotherapy or other substances. Corticosteroid injection may be effective in the short term however are of little benefit after a year, compared to a wait-and-see approach. A randomized control trial comparing the effect of corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are inv ...
injection, physiotherapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is one of the allied health professions. It is provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through physical examination, diagnosis, management, prognosis, patie ...
, or a combination of corticosteroid injection and physiotherapy found that patients treated with corticosteroid injection versus placebo had lower complete recovery or improvement at 1 year (Relative risk
The relative risk (RR) or risk ratio is the ratio of the probability of an outcome in an exposed group to the probability of an outcome in an unexposed group. Together with risk difference and odds ratio, relative risk measures the association be ...
0.86). Patients that received corticosteroid injection also had a higher recurrence rate at 1 year versus placebo (54% versus 12%, relative risk 0.23).
Complications from repeated steroid injections include skin problems such as hypopigmentation and fat atrophy leading to indentation of the skin around the injection site. Steroid injections against appear to be more effective than shock wave therapy. Botulinum toxin
Botulinum toxin, or botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT), is a neurotoxic protein produced by the bacterium ''Clostridium botulinum'' and related species. It prevents the release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine from axon endings at the neurom ...
type A to paralyze the forearm extensor muscles in those with chronic tennis elbow that has not improved with conservative measures may be viable.
Surgery
Surgery
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pa ...
is an option. Surgical methods include:
* Lengthening, release, debridement, or repair of the origin of the extrinsic extensor muscles of the hand at the lateral epicondyle
Surgical techniques for lateral epicondylitis can be done by open surgery, percutaneous surgery or arthroscopic surgery, with no high-quality evidence that any particular type is better or worse than another. Side effects include infection, damage to nerves and inability to straighten the arm. A review of the evidence related to surgery found that published studies were of low quality and did not show that surgery was any more effective than other treatments. A subsequent research trial showed that surgery was no more effective than sham surgery, where patients only received a skin incision, although the trial was limited by a small number of patients.
Prognosis
According to a review and metanalysis from 2022 about 90% of tennis elbow achieve resolution within one year Depending upon severity and quantity of multiple tendon injuries that have built up, the extensor carpi radialis brevis may not be fully healed by conservative treatment. Nirschl defines four stages of lateral epicondylitis, showing the introduction of permanent damage beginning at Stage 2. # Inflammatory changes that are reversible # Nonreversible pathologic changes to origin of the extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle # Rupture of ECRB muscle origin # Secondary changes such as fibrosis or calcification.Epidemiology
Enthesopathy of the ECRB origin
Evidence from imaging studies suggests that about 1 in 5 humans have detectable enthesopathy of the extensor carpi radialis brevis origin in their lifetime. Symptoms likely vary and are self-limited. The signal changes on MRI seem permanent. There is no evidence that specific occupations or activities are associated with enthesopathy.Symptoms of lateral epicondylitis
Symptoms suggestive of lateral epicondylitis are present in about 1% of the adult population, and is most common between ages 40 and 60. The prevalence varies somewhat between studies, likely as a result of varied diagnostic criteria and limited reliability between different observers. The data regarding symptoms of lateral epicondylitis in relation to occupations and sports are inconsistent and inconclusive. The shortcomings of the evidence that addresses the relationship between symptoms and occupation/sport include: variation in diagnostic criteria, limited reliability of diagnosis, confounding association of psychosocial factors, selection bias due to a high non-response rate, and the fact that exposures are usually by subjective patient report and symptomatic patient might perceive greater exposure.History
German physician F. Runge is usually credited for the first description of the condition, calling it "writer's cramp" (''Schreibekrampf'') in 1873. Later, it was called "washer women's elbow". British surgeon Henry Morris published an article in ''The Lancet
''The Lancet'' is a weekly peer-reviewed general medical journal and one of the oldest of its kind. It is also the world's highest-impact academic journal. It was founded in England in 1823.
The journal publishes original research articles ...
'' describing "lawn tennis arm" in 1883. The popular term "tennis elbow" first appeared the same year in a paper by H. P. Major, described as "lawn-tennis elbow".
See also
* Olecranon bursitis * Radial tunnel syndrome *Repetitive strain injury
A repetitive strain injury (RSI) is an injury to part of the musculoskeletal or nervous system caused by repetitive use, vibrations, compression or long periods in a fixed position. Other common names include repetitive stress disorders, cumula ...
References
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Tennis Elbow Inflammations Overuse injuries Tennis terminology Sports injuries Soft tissue disorders Tennis culture Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate