United States Department of the Treasury on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Department of the Treasury (USDT) is the national treasury and finance department of the
 Congress transferred several agencies that had previously been under the aegis of the Treasury Department to other departments as a consequence of the
Congress transferred several agencies that had previously been under the aegis of the Treasury Department to other departments as a consequence of the

National Archives website, (Record Group 167), 1830–1987. After 1901, responsibility was assigned to the agency that subsequently became known as the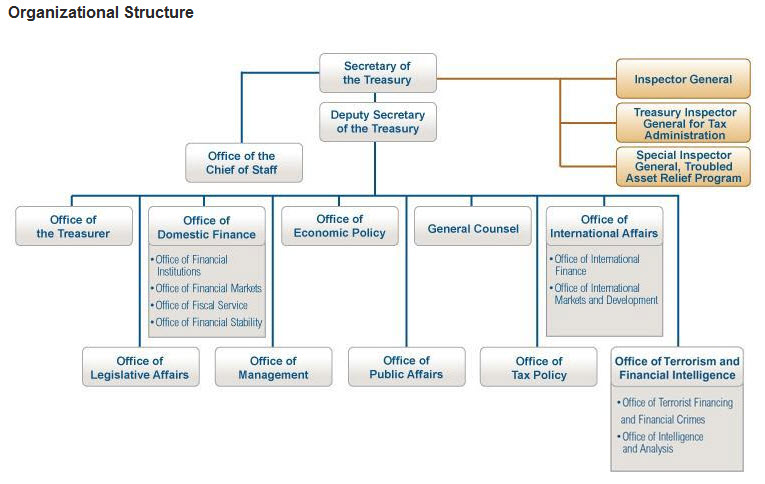

 * Secretary of the TreasuryTreasury Order 101-05
* Secretary of the TreasuryTreasury Order 101-05
U.S. Dept. of the Treasury. January 10, 2011. Updated April 26, 2011. Accessed November 11, 2012. ** Deputy Secretary of the Treasury *** Treasurer of the United States **** Bureau of Engraving and Printing ***** Bureau of Engraving and Printing Police **** United States Mint ***** United States Mint Police ***
"The Office of Domestic Finance". U.S. Dept. of the Treasury. October 2011. Accessed November 11, 2012. **** Assistant Secretary for Financial Institutions ***** Office of Financial Institutions **** Assistant Secretary for Financial Markets ***** Office of Financial Markets **** Fiscal Assistant Secretary ***** Office of Fiscal Service ***** Bureau of the Fiscal Service *** Under Secretary for International AffairsInternational Affairs
"About International Affairs". U.S. Dept. of the Treasury. February 14, 2012. Accessed November 11, 2012. **** Assistant Secretary for International Markets and Development **** Assistant Secretary for International Affairs **** Assistant Secretary of the Treasury for Investment Security **** Office of Environment and Energy *** Under Secretary for Terrorism and Financial Intelligence ( Office of Terrorism and Financial Intelligence)Terrorism and Financial Intelligence
"About Terrorism and Financial Intelligence". U.S. Dept. of the Treasury. July 2, 2012. Accessed November 11, 2012. **** Assistant Secretary for Terrorist Financing ***** Office of Terrorist Financing and Financial Crimes **** Assistant Secretary for Intelligence and Analysis ***** Office of Intelligence and Analysis **** Financial Crimes Enforcement Network **** Office of Foreign Assets Control **** Treasury Executive Office for Asset Forfeiture *** Assistant Secretary of the Treasury for Management / Chief Financial Officer / Performance Improvement Officer *** Assistant Secretary for Economic Policy *** Assistant Secretary for Legislative Affairs *** Assistant Secretary for Public Affairs/Director of policy planning *** Assistant Secretary for Tax Policy *** Climate Counselor ****
Making the Grade: Access to Information Scorecard 2015
', March 2015, 80 pages, Center for Effective Government, retrieved March 21, 2016
Department of the Treasury
on USAspending.gov
Department of the Treasury
in the '' Federal Register''
Map of Major Foreign Holders Of Treasury Securities 2009
Annual Reports of the Secretary of the Treasury on the State of Finances
– These annual reports also contain the reports of the many departments of the Treasury, including the Bureau of the Mint, Bureau of Engraving and Printing, Bureau of Customs, Office of the Comptroller of the Currency, Secret Service, and the Internal Revenue Service. *
Act to establish the Treasury Department. 1st Congress, 1st Session, Ch. 12, 1 Stat. 65
{{DEFAULTSORT:United States Department Of The Treasury Treasury 1789 establishments in the United States Finance ministries Financial regulatory authorities of the United States Ministries established in 1789 Robert Mills buildings
federal government of the United States
The federal government of the United States (U.S. federal government or U.S. government) is the national government of the United States, a federal republic located primarily in North America, composed of 50 states, a city within a fede ...
, where it serves as an executive department
The Executive, also referred as the Executive branch or Executive power, is the term commonly used to describe that part of government which enforces the law, and has overall responsibility for the governance of a state.
In political systems ba ...
. The department oversees the Bureau of Engraving and Printing and the U.S. Mint
The United States Mint is a bureau of the Department of the Treasury responsible for producing coinage for the United States to conduct its trade and commerce, as well as controlling the movement of bullion. It does not produce paper money; tha ...
. These two agencies are responsible for printing all paper currency and coins, while the treasury executes its circulation in the domestic fiscal system. The USDT collects all federal taxes through the Internal Revenue Service; manages U.S. government debt instruments; licenses and supervises banks and thrift institutions; and advises the legislative
A legislature is an assembly with the authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country or city. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial powers of government.
Laws enacted by legislatures are usually known ...
and executive branches on matters of fiscal policy
In economics and political science, fiscal policy is the use of government revenue collection ( taxes or tax cuts) and expenditure to influence a country's economy. The use of government revenue expenditures to influence macroeconomic variabl ...
. The department is administered by the secretary of the treasury, who is a member of the Cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filin ...
. The treasurer of the United States has limited statutory duties, but advises the Secretary on various matters such as coinage and currency production. Signatures of both officials appear on all Federal Reserve notes.
The department was established by an Act of Congress in 1789 to manage government revenue
In accounting, revenue is the total amount of income generated by the sale of goods and services related to the primary operations of the business.
Commercial revenue may also be referred to as sales or as turnover. Some companies receive rev ...
. The first secretary of the treasury was Alexander Hamilton, who was sworn into office on September 11, 1789. Hamilton was appointed by President George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Continental Congress as commander of ...
on the recommendation of Robert Morris, Washington's first choice for the position, who had declined the appointment. Hamilton established the nation's early financial system and for several years was a major presence in Washington's administration. The department is customarily referred to as "Treasury", solely, without any preceding article, as a remnant of the country's transition from British to American English
American English, sometimes called United States English or U.S. English, is the set of varieties of the English language native to the United States. English is the most widely spoken language in the United States and in most circumstances ...
during the late 18th century. Hamilton's portrait appears on the obverse of the ten-dollar bill, while the Treasury Department building is depicted on the reverse.
History
Revolutionary period
The history of the Department of the Treasury began in the turmoil of theAmerican Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revoluti ...
, when the Continental Congress at Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Since ...
deliberated the crucial issue of financing a war of independence against Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It ...
. The Congress had no power to levy and collect taxes, nor was there a tangible basis for securing funds from foreign investors or governments. The delegates resolved to issue paper money in the form of bills of credit, promising redemption in coin
A coin is a small, flat (usually depending on the country or value), round piece of metal or plastic used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in order ...
on faith in the revolutionary cause. On June 22, 1775—only a few days after the Battle of Bunker Hill—Congress issued $2 million in bills; on July 25, 28 citizens of Philadelphia were employed by Congress to sign and number the currency.
On July 29, 1775, the Second Continental Congress assigned the responsibility for the administration of the revolutionary government's finances to joint Continental treasurers George Clymer and Michael Hillegas. Congress stipulated that each of the colonies contribute to the Continental government's funds. To ensure proper and efficient handling of the growing national debt in the face of weak economic and political ties between the colonies, the Congress, on February 17, 1776, designated a committee of five to superintend the treasury, settle accounts, and report periodically to the Congress. On April 1, a Treasury Office of Accounts, consisting of an auditor general and clerks, was established to facilitate the settlement of claims and to keep the public accounts for the government of the United Colonies. With the signing of the Declaration of Independence on July 4, 1776, the newborn republic as a sovereign nation was able to secure loans from abroad.
Despite the infusion of foreign and domestic loans, the united colonies were unable to establish a well-organized agency for financial administration. Michael Hillegas was first called Treasurer of the United States on May 14, 1777. The Treasury Office was reorganized three times between 1778 and 1781. The $241.5 million in paper Continental bills devalued rapidly. By May 1781, the dollar collapsed at a rate of from 500 to 1000 to 1 against hard currency. Protests against the worthless money swept the colonies, giving rise to the expression " not worth a Continental". The office has, since the late 18th century, been customarily referred to as the singular “Treasury”, without any preceding article, as a remnant of the country's transition from British to American English
American English, sometimes called United States English or U.S. English, is the set of varieties of the English language native to the United States. English is the most widely spoken language in the United States and in most circumstances ...
. For example, the department notes its guiding purpose as "Treasury's mission" instead of "the Treasury's mission."
Robert Morris was designated Superintendent of Finance in 1781 and restored stability to the nation's finances. Morris, a wealthy colonial merchant, was nicknamed "the financier" because of his reputation for procuring funds or goods on a moment's notice. His staff included a comptroller, a treasurer, a register
Register or registration may refer to:
Arts entertainment, and media Music
* Register (music), the relative "height" or range of a note, melody, part, instrument, etc.
* ''Register'', a 2017 album by Travis Miller
* Registration (organ), th ...
, and auditors, who managed the country's finances through 1784, when Morris resigned because of ill health. The treasury board, consisting of three commissioners, continued to oversee the finances of the confederation of former colonies until September 1789.
Creation of the Treasury
The First Congress of the United States was called to convene in New York on March 4, 1789, marking the beginning of government under the Constitution. On September 2, 1789, Congress created a permanent institution for the management of government finances:Be it enacted by the Senate and House of Representatives of the United States of America in Congress assembled, That there shall be a Department of Treasury, in which shall be the following officers, namely: a Secretary of the Treasury, to be deemed head of the department; a Comptroller, an Auditor, a Treasurer, a Register, and an Assistant to the Secretary of the Treasury, which assistant shall be appointed by the said Secretary.Alexander Hamilton took the oath of office as the first secretary of the treasury on September 11, 1789. Hamilton had served as George Washington's '' aide-de-camp'' during the Revolution and was of great importance in the
ratification
Ratification is a principal's approval of an act of its agent that lacked the authority to bind the principal legally. Ratification defines the international act in which a state indicates its consent to be bound to a treaty if the parties inten ...
of the Constitution. Because of his financial and managerial acumen, Hamilton was a logical choice for solving the problem of the new nation's heavy war debt. Hamilton's first official act was to submit a report to Congress in which he laid the foundation for the nation's financial health.
To the surprise of many legislators, he insisted upon federal assumption and dollar-for-dollar repayment of the country's $75 million debt in order to revitalize the public credit: " e debt of the United States was the price of liberty. The faith of America has been repeatedly pledged for it, and with solemnities that give peculiar force to the obligation." Hamilton foresaw the development of industry and trade in the United States, suggesting that government revenues be based upon customs duties. His sound financial policies
The economy of governments covers the systems for setting levels of taxation, Government budget, government budgets, the money supply and interest rates as well as the labour market, state ownership, national ownership, and many other areas of go ...
also inspired investment in the Bank of the United States, which acted as the government's fiscal agent.
The treasury believes their seal was created by Francis Hopkinson
Francis Hopkinson (October 2,Hopkinson was born on September 21, 1737, according to the then-used Julian calendar (old style). In 1752, however, Great Britain and all its colonies adopted the Gregorian calendar (new style) which moved Hopkinso ...
, the treasurer of loans. He submitted bills to Congress in 1780 that authorized the design of department seals, including the seal for the Board of Treasury. While it is it not certain that Hopkinson designed the seal, it is very similar to others he's done.
2003 reorganization
 Congress transferred several agencies that had previously been under the aegis of the Treasury Department to other departments as a consequence of the
Congress transferred several agencies that had previously been under the aegis of the Treasury Department to other departments as a consequence of the September 11 attacks
The September 11 attacks, commonly known as 9/11, were four coordinated suicide terrorist attacks carried out by al-Qaeda against the United States on Tuesday, September 11, 2001. That morning, nineteen terrorists hijacked four commer ...
. Effective January 24, 2003, the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms
The Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (BATFE), commonly referred to as the ATF, is a domestic law enforcement agency within the United States Department of Justice. Its responsibilities include the investigation and prevent ...
(ATF), which had been a bureau of the department since 1972, was extensively reorganized under the provisions of the Homeland Security Act of 2002. The law enforcement
Law enforcement is the activity of some members of government who act in an organized manner to enforce the law by discovering, deterring, rehabilitating, or punishing people who violate the rules and norms governing that society. The term ...
functions of ATF, including the regulation of legitimate traffic in firearms and explosives, were transferred to the Department of Justice as the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives (BATFE). The regulatory and tax collection functions of ATF related to legitimate traffic in alcohol and tobacco remained with the treasury at its new Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau
The Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau, statutorily named the Tax and Trade Bureau and frequently shortened to TTB, is a bureau of the United States Department of the Treasury, which regulates and collects taxes on trade and imports of alcoh ...
(TTB).
Effective March 1, 2003, the Federal Law Enforcement Training Center, the United States Customs Service, and the United States Secret Service
The United States Secret Service (USSS or Secret Service) is a federal law enforcement agency under the Department of Homeland Security charged with conducting criminal investigations and protecting U.S. political leaders, their families, and ...
were transferred to the newly created Department of Homeland Security ("DHS").
2020 data breach
In 2020, the Treasury suffered a data breach following a cyberattack likely conducted by a nation state adversary, possibly Russia. This was in fact the first detected case of the much wider 2020 United States federal government data breach, which involved at least eight federal departments.Responsibilities

Basic functions
The basic functions of the Department of the Treasury mainly include: * Producing all currency and coinage of the U.S.; * Collecting taxes, duties and money paid to and due to the U.S.; * Paying all bills of the U.S.; * Managing the federal finances; * Managing government accounts and the United States public debt; * Supervising national banks and thrift institutions; * Advising on domestic and international financial,monetary
Money is any item or verifiable record that is generally accepted as payment for goods and services and repayment of debts, such as taxes, in a particular country or socio-economic context. The primary functions which distinguish money are ...
, economic
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with th ...
, trade and tax policy (fiscal policy
In economics and political science, fiscal policy is the use of government revenue collection ( taxes or tax cuts) and expenditure to influence a country's economy. The use of government revenue expenditures to influence macroeconomic variabl ...
being the sum of these);
* Enforcing federal finance and tax laws;
* Investigating and prosecuting tax evaders;
* Publishing statistical reports.
With respect to the estimation of revenues for the executive branch, Treasury serves a purpose parallel to that of the Office of Management and Budget
The Office of Management and Budget (OMB) is the largest office within the Executive Office of the President of the United States (EOP). OMB's most prominent function is to produce the president's budget, but it also examines agency programs, pol ...
for the estimation of spending for the executive branch, the Joint Committee on Taxation
The Joint Committee on Taxation (JCT) is a Committee of the U.S. Congress established under the Internal Revenue Code at .
Structure
The Joint Committee is composed of ten Members: five from the Senate Finance Committee and five from the House W ...
for the estimation of revenues for Congress, and the Congressional Budget Office for the estimation of spending for Congress.
From 1830 until 1901, responsibility for overseeing weights and measures
A unit of measurement is a definite magnitude of a quantity, defined and adopted by convention or by law, that is used as a standard for measurement of the same kind of quantity. Any other quantity of that kind can be expressed as a multip ...
was carried out by the Office of Standard Weights and Measures under the auspices of the Treasury Department.Records of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)National Archives website, (Record Group 167), 1830–1987. After 1901, responsibility was assigned to the agency that subsequently became known as the
National Institute of Standards and Technology
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into physical s ...
.

Organization
The Department of the Treasury is organized into two major components: the departmental offices and the operating bureaus. The departmental offices are primarily responsible for the formulation of policy and management of the department as a whole, while the operating bureaus carry out the specific operations assigned to the department.Structure
U.S. Dept. of the Treasury. January 10, 2011. Updated April 26, 2011. Accessed November 11, 2012. ** Deputy Secretary of the Treasury *** Treasurer of the United States **** Bureau of Engraving and Printing ***** Bureau of Engraving and Printing Police **** United States Mint ***** United States Mint Police ***
Under Secretary for Domestic Finance
The Under Secretary of the Treasury for Domestic Finance is a high-ranking position within United States Department of the Treasury that reports to, advises, and assists the Secretary of the Treasury and the Deputy Secretary of the Treasury. The u ...
DF Org Chart"The Office of Domestic Finance". U.S. Dept. of the Treasury. October 2011. Accessed November 11, 2012. **** Assistant Secretary for Financial Institutions ***** Office of Financial Institutions **** Assistant Secretary for Financial Markets ***** Office of Financial Markets **** Fiscal Assistant Secretary ***** Office of Fiscal Service ***** Bureau of the Fiscal Service *** Under Secretary for International AffairsInternational Affairs
"About International Affairs". U.S. Dept. of the Treasury. February 14, 2012. Accessed November 11, 2012. **** Assistant Secretary for International Markets and Development **** Assistant Secretary for International Affairs **** Assistant Secretary of the Treasury for Investment Security **** Office of Environment and Energy *** Under Secretary for Terrorism and Financial Intelligence ( Office of Terrorism and Financial Intelligence)Terrorism and Financial Intelligence
"About Terrorism and Financial Intelligence". U.S. Dept. of the Treasury. July 2, 2012. Accessed November 11, 2012. **** Assistant Secretary for Terrorist Financing ***** Office of Terrorist Financing and Financial Crimes **** Assistant Secretary for Intelligence and Analysis ***** Office of Intelligence and Analysis **** Financial Crimes Enforcement Network **** Office of Foreign Assets Control **** Treasury Executive Office for Asset Forfeiture *** Assistant Secretary of the Treasury for Management / Chief Financial Officer / Performance Improvement Officer *** Assistant Secretary for Economic Policy *** Assistant Secretary for Legislative Affairs *** Assistant Secretary for Public Affairs/Director of policy planning *** Assistant Secretary for Tax Policy *** Climate Counselor ****
Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau
The Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau, statutorily named the Tax and Trade Bureau and frequently shortened to TTB, is a bureau of the United States Department of the Treasury, which regulates and collects taxes on trade and imports of alcoh ...
*** Commissioner of Internal Revenue
**** Internal Revenue Service
*** Office of the Comptroller of the Currency
The Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC) is an independent bureau within the United States Department of the Treasury that was established by the National Currency Act of 1863 and serves to charter, regulate, and supervise all nat ...
*** Office of Financial Research
*** Office of the General Counsel
*** Office of the Inspector General
*** Treasury Inspector General for Tax Administration
The Treasury Inspector General for Tax Administration (TIGTA) is an office in the United States Federal government. It was established in January 1999 in accordance with the Internal Revenue Service Restructuring and Reform Act of 1998 (RRA 98) t ...
(TIGTA)
Bureaus
Budget and staffing
The Treasury Department has authorized a budget for Fiscal Year 2015 of $22.6 billion. The budget authorization is broken down as follows:Freedom of Information Act processing performance
In the latest Center for Effective Government analysis of the fifteen federal agencies that receive the mostFreedom of Information Act Freedom of Information Act may refer to the following legislations in different jurisdictions which mandate the national government to disclose certain data to the general public upon request:
* Freedom of Information Act 1982, the Australian act
* ...
FOIA requests, published in 2015 (using 2012 and 2013 data, the most recent years available), the treasury failed to earn a satisfactory overall grade.Making the Grade: Access to Information Scorecard 2015
', March 2015, 80 pages, Center for Effective Government, retrieved March 21, 2016
See also
*Federal Reserve System
The Federal Reserve System (often shortened to the Federal Reserve, or simply the Fed) is the central banking system of the United States of America. It was created on December 23, 1913, with the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act, after ...
* MicroLoan Program
* Title 12 of the Code of Federal Regulations
* Title 17 of the Code of Federal Regulations
* Title 19 of the Code of Federal Regulations
* Title 31 of the Code of Federal Regulations
* Treasury Enterprise Architecture Framework
* Treasury Information System Architecture Framework
Notes and references
External links
*Department of the Treasury
on USAspending.gov
Department of the Treasury
in the '' Federal Register''
Map of Major Foreign Holders Of Treasury Securities 2009
Annual Reports of the Secretary of the Treasury on the State of Finances
– These annual reports also contain the reports of the many departments of the Treasury, including the Bureau of the Mint, Bureau of Engraving and Printing, Bureau of Customs, Office of the Comptroller of the Currency, Secret Service, and the Internal Revenue Service. *
Act to establish the Treasury Department. 1st Congress, 1st Session, Ch. 12, 1 Stat. 65
{{DEFAULTSORT:United States Department Of The Treasury Treasury 1789 establishments in the United States Finance ministries Financial regulatory authorities of the United States Ministries established in 1789 Robert Mills buildings