Political party strength in U.S. states on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Political party strength in U.S. states is the level of representation of the various
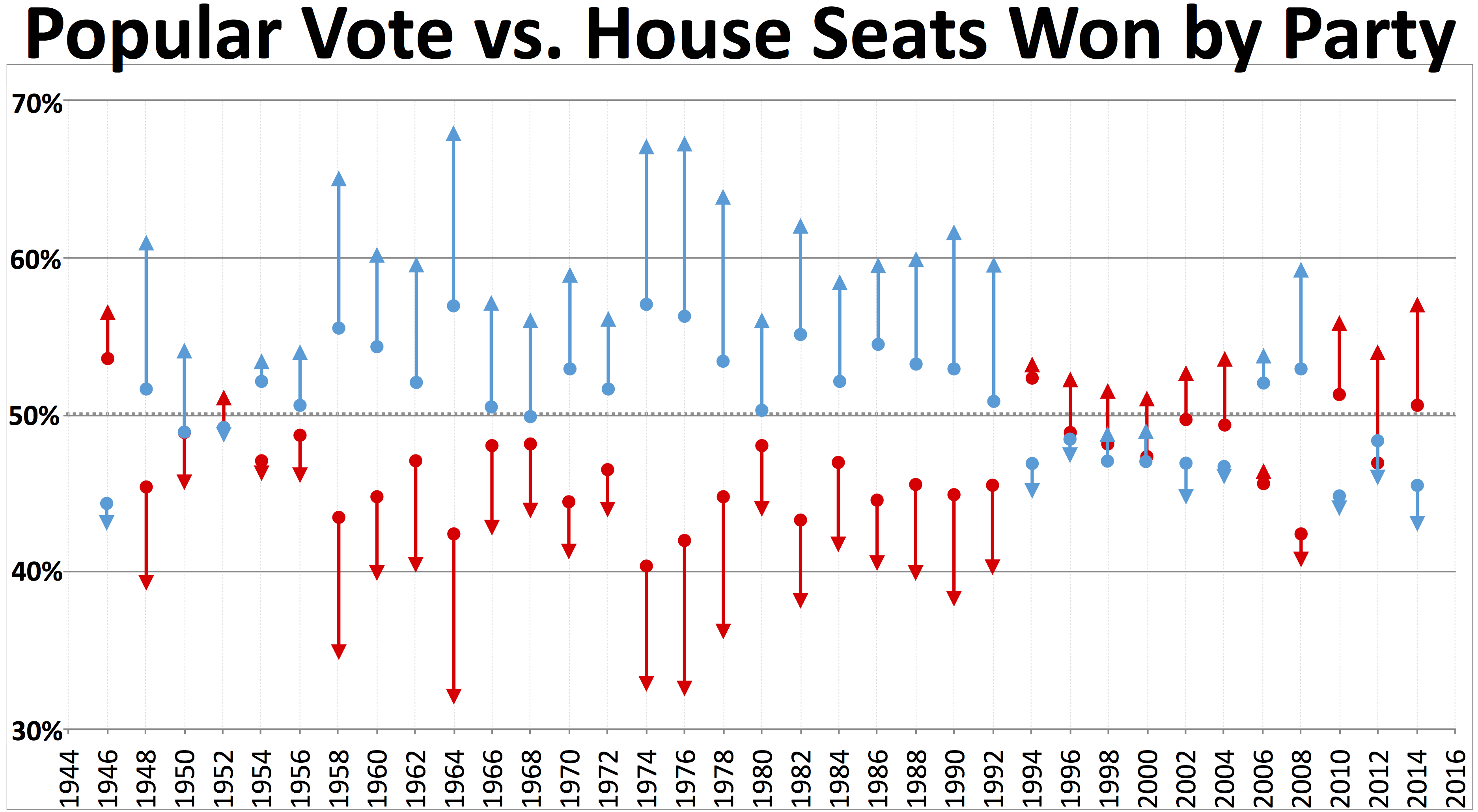 Throughout most of the 20th century, although the Republican and Democratic parties alternated in power at a national level, some states were so overwhelmingly dominated by one party that nomination was usually
Throughout most of the 20th century, although the Republican and Democratic parties alternated in power at a national level, some states were so overwhelmingly dominated by one party that nomination was usually
 Another metric measuring party preference is the
Another metric measuring party preference is the
political parties in the United States
American electoral politics have been dominated by two major political parties since shortly after the founding of the republic of the United States of America. Since the 1850s, the two have been the Democratic Party and the Republican Party‚ ...
in each statewide elective office providing legislators to the state and to the U.S. Congress and electing the executives at the state ( U.S. state governor) and national ( U.S. President) level.
History
 Throughout most of the 20th century, although the Republican and Democratic parties alternated in power at a national level, some states were so overwhelmingly dominated by one party that nomination was usually
Throughout most of the 20th century, although the Republican and Democratic parties alternated in power at a national level, some states were so overwhelmingly dominated by one party that nomination was usually tantamount to election
A safe seat is an electoral district (constituency) in a legislative body (e.g. Congress, Parliament, City Council) which is regarded as fully secure, for either a certain political party, or the incumbent representative personally or a combinati ...
. This was especially true in the Solid South
The Solid South or Southern bloc was the electoral voting bloc of the states of the Southern United States for issues that were regarded as particularly important to the interests of Democrats in those states. The Southern bloc existed especial ...
, where the Democratic Party was dominant for the better part of a century, from the end of Reconstruction
Reconstruction may refer to:
Politics, history, and sociology
* Reconstruction (law), the transfer of a company's (or several companies') business to a new company
*''Perestroika'' (Russian for "reconstruction"), a late 20th century Soviet Unio ...
in the late 1870s, through the period of Jim Crow Laws into the 1960s. Conversely, the New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
states of Vermont
Vermont () is a U.S. state, state in the northeast New England region of the United States. Vermont is bordered by the states of Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, and New York (state), New York to the west, and the Provin ...
, Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and nor ...
, and New Hampshire
New Hampshire is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the northeastern United States. It is bordered by Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec t ...
were dominated by the Republican Party, as were some Midwestern states like Iowa
Iowa () is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States, bordered by the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west. It is bordered by six states: Wiscon ...
and North Dakota
North Dakota () is a U.S. state in the Upper Midwest, named after the indigenous Dakota Sioux. North Dakota is bordered by the Canadian provinces of Saskatchewan and Manitoba to the north and by the U.S. states of Minnesota to the east, ...
.
However, in the 1970s and 1980s the increasingly conservative
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy that seeks to promote and to preserve traditional institutions, practices, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civilization in ...
Republican Party gradually overtook the Democrats in the southeast. The Democrats' support in the formerly Solid South had been eroded during the vast cultural, political and economic upheaval that surrounded the 1960s. By the 1990s, the Republican Party had completed the transition into the southeast's dominant political party, despite typically having fewer members due to the prevalence of Republican voting generational Democrats. In New England, the opposite trend occurred; the former Republican strongholds of Maine and Vermont became solidly Democratic, as did formerly Republican areas of New Jersey, New York, and Connecticut.
, the majority of the overall number of seats held in the state legislatures has been switching between the two parties every few years. In the U.S. state legislative elections of 2010, the Republican Party held an outright majority of 3,890 seats (53% of total) compared to the Democratic party's 3,450 (47% of total) seats elected on a partisan ballot. Of the 7,382 seats in all of the state legislatures combined, independents and third parties account for only 16 members, not counting the 49 members of the Nebraska Legislature
The Nebraska Legislature (also called the Unicameral) is the legislature of the U.S. state of Nebraska. The Legislature meets at the Nebraska State Capitol in Lincoln. With 49 members, known as "senators", the Nebraska Legislature is the sm ...
, which is the only legislature in the nation to hold non-partisan elections to determine its members. As a result of the 2010 elections, Republicans took control of an additional 19 state legislative chambers, giving them majority control of both chambers in 25 states versus the Democrats' majority control of both chambers in only 16 states, with 8 states having split or inconclusive control of both chambers (not including Nebraska); previous to the 2010 elections, it was Democrats who controlled both chambers in 27 states versus the Republican party having total control in only 14 states, with eight states divided and Nebraska being nonpartisan.
Current party strength
Gallup
On December 17, 2020,Gallup
Gallup may refer to:
* Gallup, Inc., a firm founded by George Gallup, well known for its opinion poll
* Gallup (surname), a surname
*Gallup, New Mexico, a city in New Mexico, United States
** Gallup station, an Amtrak train in downtown Gallup, New ...
polling found that 31% of Americans identified as Democrats, 25% identified as Republican, and 41% as Independent. Additionally, polling showed that 50% are either "Democrats or Democratic leaners" and 39% are either "Republicans or Republican leaners" when Independents are asked "do you lean more to the Democratic Party or the Republican Party?"
In 2018, the number of competitive states according to opinion polling dropped down to 10, the lowest number since 2008. From 2017 to 2018, New Hampshire, Nevada, and Pennsylvania moved from competitive to lean Democratic, while West Virginia, Louisiana, and Indiana moved from competitive to lean Republican, and Nebraska moved from lean Republican to competitive.
As of 2018, Massachusetts was the most Democratic state, with 56% of residents identifying as Democrat, while only 27% of residents identified as Republican. It is important to note, however, that Washington D.C. (while not a state) has 3 electoral votes and 76% of residents identify as Democrats, while 6% identify as Republicans. Wyoming was the most Republican state, with 59% of residents identifying as Republican, and only 25% of residents identifying as Democratic.
Cook Partisan Voting Index (PVI)
Cook Partisan Voting Index
The Cook Partisan Voting Index, abbreviated Cook PVI, CPVI, or PVI, is a measurement of how strongly a United States congressional district or U.S. state leans toward the Democratic or Republican Party, compared to the nation as a whole, based ...
(PVI). Cook PVIs are calculated by comparing a state's average Democratic Party or Republican Party share of the two-party presidential vote in the past two presidential elections to the nation's average share of the same. PVIs for the states over time can be used to show the trends of U.S. states towards, or away from, one party or the other.
Voter registration and state political control
The state Democratic or Republican Party controls the governorship, the state legislative houses, and U.S. Senate representation. Nebraska's legislature isunicameral
Unicameralism (from ''uni''- "one" + Latin ''camera'' "chamber") is a type of legislature, which consists of one house or assembly, that legislates and votes as one.
Unicameral legislatures exist when there is no widely perceived need for multi ...
(i.e., it has only one legislative house) and is officially non-partisan, though party affiliation still has an unofficial influence on the legislative process.
The simplest measure of party strength in a state voting population is the affiliation totals from voter registration
In electoral systems, voter registration (or enrollment) is the requirement that a person otherwise eligible to vote must register (or enroll) on an electoral roll, which is usually a prerequisite for being entitled or permitted to vote.
The r ...
(from the websites of the Secretaries of State or state Boards of Elections) for the 30 states and the District of Columbia
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle (Washington, D.C.), Logan Circle, Jefferson Memoria ...
that allow registered voters to indicate a party preference when registering to vote. 20 states do not include party preference with voter registration. The party affiliations in the party control table are obtained from state party registration figures where indicated.For example, for earlier 2014 registration figures, see: . Only Wyoming
Wyoming () is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is bordered by Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Idaho to the west, Utah to the southwest, and Colorado to t ...
has a majority of registered voters identifying themselves as Republicans; only one state has a majority of registered voters identifying themselves as Democrats: Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware and the Atlantic Ocean t ...
(since 2010, Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is bord ...
and Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
have seen their Democratic majority slip to pluralities, while Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virginia ...
and West Virginia
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian, Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States.The Census Bureau and the Association of American Geographers classify West Virginia as part of the Southern United States while the ...
now have Republican pluralities).
For those states that do not allow for registration by party, Gallup's annual polling of voter party identification by state is the next best metric of party strength in the U.S. states. The partisan figures in the table for the 20 states that don't register voters by party come from Gallup's poll.
U.S. state party control as of January 2023
Party strength by region
Local and regional political circumstances often influence party strength.State government
Presidential election results and congressional delegations
Results of the2020 Presidential election
This national electoral calendar for 2020 lists the national/ federal elections held in 2020 in all sovereign states and their dependent territories. By-elections are excluded, though national referendums are included.
January
*5 January:
** ...
:
Current standings in the U.S. Senate and in the U.S. House as of the 117th Congress
The 117th United States Congress is the current meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It convened in Washington, D.C., on ...
:
Historical party strength
Number of state legislatures controlled by each party. State governorships controlled by each party. State government full or split control, by party. ;Graphical summaryReferences
{{Political party strength in U.S. states