North Malabar on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
North Malabar refers to the geographic area of southwest
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
covering the state of
Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South ...
's present day
Kasaragod,
Kannur
Kannur (), formerly known in English as Cannanore, is a city and a municipal corporation in the state of Kerala, India. It is the administrative headquarters of the Kannur district and situated north of the major port city and commercial hu ...
, and
Wayanad
Wayanad () is a district in the north-east of Indian state Kerala with administrative headquarters at the municipality of Kalpetta. It is the only plateau in Kerala. The Wayanad Plateau forms a continuation of the Mysore Plateau, the southern ...
districts, and the taluks of
Vatakara
Vatakara, also spelled Vadakara (formerly Badagara), , french: Bargaret, is a Municipality in the state of Kerala, India. Vatakara is located between Kannur and Kozhikode. The municipality of Vatakara covers an area of and is bordered by ...
,
Koyilandy
A Survey of Kerala History, A. Shreedhara Menon ar, Fundriya pt, Pandarani
, settlement_type = MunicipalityTaluk
, image_skyline = KadaloorPointLight 01.jpg
, image_alt =
, image_caption ...
, and
Thamarassery
Thamarassery, formerly known as Thazhmalachery, it is one of the taluk in Kozhikode district and major hill town in the Kozhikode district of Kerala, India, 30 km north-east of Kozhikode (Calicut) City and 29 km east of Koyilandy. It li ...
in the
Kozhikode District
Kozhikode (), or Calicut district, is one of the 14 districts in the Indian state of Kerala, along its Southwestern Malabar Coast. The city of Kozhikode, also known as Calicut, is the district headquarters. The district is 67.15% urbanised.
...
of Kerala and the entire
Mahé Sub-Division of the
Union Territory of Puducherry. Traditionally North Malabar is defined as the northern portion of erstwhile
Malabar District
Malabar District, also known as Malayalam District, was an administrative district on the southwestern Malabar Coast of Bombay Presidency (1792-1800) and Madras Presidency (1800-1947) in British India, and independent India's Madras State (19 ...
which lies between
Chandragiri River and
Korapuzha River.
The region between
Netravathi River and
Chandragiri River, which included the portions between
Mangalore
Mangalore (), officially known as Mangaluru, is a major port city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It is located between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats about west of Bangalore, the state capital, 20 km north of Karnataka–Ke ...
and
Kasaragod, are also often included in the term North Malabar, as the
Kumbla
Kumbla is a small town in Kasaragod district of Kerala state in India. It is located 12 km north of Kasaragod town.
History
The original name "Kanvapura" was derived from the name of Maharshi Kanva. Since then the name has morphed into ...
dynasty in the southernmost region of
Tulu Nadu
Tulunad or Tulu Nadu, also called Bermere sristi or Parashurama Srishti, is a region and a proposed state on the southwestern coast of India. The Tulu people, known as 'Tuluva' (plural 'Tuluver'), speakers of Tulu, a Dravidian language, ar ...
(between
Mangalore
Mangalore (), officially known as Mangaluru, is a major port city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It is located between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats about west of Bangalore, the state capital, 20 km north of Karnataka–Ke ...
and
Kasaragod), had a mixed lineage of
Malayali
The Malayali people () (also spelt Malayalee and also known by the demonym Keralite) are a Dravidian ethnolinguistic group originating from the present-day state of Kerala in India, occupying its southwestern Malabar coast. They are predomin ...
Nair
The Nair , also known as Nayar, are a group of Indian Hindu castes, described by anthropologist Kathleen Gough as "not a unitary group but a named category of castes". The Nair include several castes and many subdivisions, not all of whom histo ...
s and
Tuluva Brahmins.
The North Malabar region is bounded by
Dakshina Kannada (
Mangalore
Mangalore (), officially known as Mangaluru, is a major port city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It is located between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats about west of Bangalore, the state capital, 20 km north of Karnataka–Ke ...
) to north, the hilly regions of
Kodagu
Kodagu (also known by its former name Coorg) is an administrative district in the Karnataka state of India. Before 1956, it was an administratively separate Coorg State, at which point it was merged into an enlarged Mysore State.
It occupies ...
and
Mysore Plateau to east,
South Malabar
South Malabar refers to a geographical area of the southwestern coast of India covering some parts of the present-day Kerala. South Malabar covers the regions included in present-day Kozhikode taluk of Kozhikode district, the whole area of Malap ...
(
Korapuzha) to south, and
Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea ( ar, اَلْبَحرْ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Bahr al-ˁArabī) is a region of the northern Indian Ocean bounded on the north by Pakistan, Iran and the Gulf of Oman, on the west by the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channel ...
to west. The greater part of North Malabar (except Mahé) remained as one of the two administrative divisions of the
Malabar District
Malabar District, also known as Malayalam District, was an administrative district on the southwestern Malabar Coast of Bombay Presidency (1792-1800) and Madras Presidency (1800-1947) in British India, and independent India's Madras State (19 ...
(an administrative district of
British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
under the
Madras Presidency) until 1947 and later became part of India's
Madras State
Madras State was a state of India during the mid-20th century. At the time of its formation in 1950, it included the whole of present-day Tamil Nadu (except Kanyakumari district), Coastal Andhra, Rayalaseema, the Malabar region of North and ...
until 1956. Mahé remained under
French jurisdiction until 13June 1954. On 1November 1956, the state of Kerala was formed by the
States Reorganisation Act, which merged the
Malabar District
Malabar District, also known as Malayalam District, was an administrative district on the southwestern Malabar Coast of Bombay Presidency (1792-1800) and Madras Presidency (1800-1947) in British India, and independent India's Madras State (19 ...
with
Travancore
The Kingdom of Travancore ( /ˈtrævənkɔːr/), also known as the Kingdom of Thiruvithamkoor, was an Indian kingdom from c. 1729 until 1949. It was ruled by the Travancore Royal Family from Padmanabhapuram, and later Thiruvananthapuram. At ...
-
Cochin
Kochi (), also known as Cochin ( ) ( the official name until 1996) is a major port city on the Malabar Coast of India bordering the Laccadive Sea, which is a part of the Arabian Sea. It is part of the district of Ernakulam in the state of K ...
apart from the four southern taluks, which were merged with
Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is a state in southern India. It is the tenth largest Indian state by area and the sixth largest by population. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. Tamil Nadu is the home of the Tamil people, whose Tamil language ...
, and the
Kasaragod taluk of
South Kanara
South Canara was a district of the Madras Presidency of British India, located at . It comprised the towns of Kassergode and Udipi and adjacent villages, with the capital in Mangalore city. South Canara was one of the most heterogeneous areas o ...
District. During
British rule
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent;
*
* it is also called Crown rule in India,
*
*
*
*
or Direct rule in India,
* Quote: "Mill, who was hims ...
, North Malabar's chief importance laid in producing
Thalassery
Thalassery (), formerly Tellicherry, is a municipality, Commercial City on the Malabar Coast in Kannur district, in the state of Kerala, India, bordered by the List of districts of India, districts of Mahé, India, Mahé (Pondicherry), Kozhikode ...
pepper and
Coconuts.
North Malabar begins at
Korapuzha in the south and ends at
Manjeshwaram in the north of Kerala and traditionally comprises the erstwhile princely principalities and chiefdoms of
Kolathu Nadu,
Kingdom of Kottayam
Kottayam (Cotiote) is a former vassal feudal city-state in the erstwhile province of Malabar in present-day Kerala, in the Indian subcontinent. Kottayam (Cotiote) is famed for Pazhassi Raja, one of the principal leaders of the Wayanad Insurre ...
,
Kadathanadu
Kadathanadu (Vatakara) was a former feudatory (of Kolathunad) city-state in present-day Kerala, on the Malabar Coast. The region is most known for being the area where the events of the ''Vadakkan Pattukal,'' a set of warrior ballads from Kerala, ...
and southern part of
Tulu Nadu
Tulunad or Tulu Nadu, also called Bermere sristi or Parashurama Srishti, is a region and a proposed state on the southwestern coast of India. The Tulu people, known as 'Tuluva' (plural 'Tuluver'), speakers of Tulu, a Dravidian language, ar ...
.
Wayanad
Wayanad () is a district in the north-east of Indian state Kerala with administrative headquarters at the municipality of Kalpetta. It is the only plateau in Kerala. The Wayanad Plateau forms a continuation of the Mysore Plateau, the southern ...
, which forms a continuation of
Mysore Plateau, was the only
Plateau
In geology and physical geography, a plateau (; ; ), also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. Often one or more sides ...
in North Malabar as well as Kerala.
Indian Naval Academy
The Indian Naval Academy (INA or INA Ezhimala) is the defence service training establishment for officer cadre of the Indian Naval Service and the Indian Coast Guard, located in Ezhimala, Kannur district, Kerala. Situated between Ezhimala h ...
at
Ezhimala
Ezhimala, a hill reaching a height of , is located near Payyanur, in Kannur district of Kerala, south India. It is a part of a conspicuous and isolated cluster of hills, forming a promontory, north of Kannur (Cannanore). The Indian Naval Acad ...
is the Asia's largest, and the world's third-largest, naval academy.
Muzhappilangad beach
Muzhappilangad Drive-in Beach (3.8 Kms length) is a beach on the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in southwestern India. It is considered as the longest drive-in beach in Asia and is featured among the top 6 best beaches for driving in t ...
is the longest Drive-In Beach in Asia and is featured among the top 6 best beaches for driving in the world in
BBC #REDIRECT BBC #REDIRECT BBC
Here i going to introduce about the best teacher of my life b BALAJI sir. He is the precious gift that I got befor 2yrs . How has helped and thought all the concept and made my success in the 10th board exam. ...
...
article for Autos. North Malabar is home to several forts which include
Arikady fort
Arikadi fort is a fort located in the Kasaragod district of Kerala, India. It is also known as Kumbla fort. The fort is located at a distance of 2 km from Kumbla on the NH 66 National Highway between kumbala River and shiriya River There is a ...
,
Bekal Fort
Bekal Fort is a medieval fort built by Shivappa Nayaka of Keladi in 1650 AD, at Bekal. It is the largest fort in Kerala, spreading over .
Structure
The fort appears to emerge from the sea. Almost three-quarters of its exterior is in con ...
,
Chandragiri Fort,
Hosdurg Fort,
St. Angelo Fort, and
Tellicherry Fort.
Bekal Fort
Bekal Fort is a medieval fort built by Shivappa Nayaka of Keladi in 1650 AD, at Bekal. It is the largest fort in Kerala, spreading over .
Structure
The fort appears to emerge from the sea. Almost three-quarters of its exterior is in con ...
is the largest fort in Kerala.
Etymology
Until the arrival of
British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
, the term ''Malabar'' was used in foreign trade circles as a general name for
Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South ...
.
Earlier, the term ''Malabar'' had also been used to denote
Tulu Nadu
Tulunad or Tulu Nadu, also called Bermere sristi or Parashurama Srishti, is a region and a proposed state on the southwestern coast of India. The Tulu people, known as 'Tuluva' (plural 'Tuluver'), speakers of Tulu, a Dravidian language, ar ...
and
Kanyakumari
Kanniyakumari (; , referring to Devi Kanya Kumari), also known as Cape Comorin, is a city in Kanniyakumari district in the state of Tamil Nadu, India. It is the southern tip of the Indian subcontinent and the southernmost city in mainland Ind ...
which lie contiguous to Kerala in the southwestern coast of India, in addition to the modern state of Kerala. The people of Malabar were known as ''
Malabars''. Still the term
Malabar is often used to denote the entire southwestern coast of India. From the time of
Cosmas Indicopleustes
Cosmas Indicopleustes ( grc-x-koine, Κοσμᾶς Ἰνδικοπλεύστης, lit=Cosmas who sailed to India; also known as Cosmas the Monk) was a Greek merchant and later hermit from Alexandria of Egypt. He was a 6th-century traveller who ma ...
(6th century CE) itself, the
Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
sailors used to call Kerala as ''Male''. The first element of the name, however, is attested already in the ''Topography'' written by
Cosmas Indicopleustes
Cosmas Indicopleustes ( grc-x-koine, Κοσμᾶς Ἰνδικοπλεύστης, lit=Cosmas who sailed to India; also known as Cosmas the Monk) was a Greek merchant and later hermit from Alexandria of Egypt. He was a 6th-century traveller who ma ...
. This mentions a pepper emporium called ''Male'', which clearly gave its name to Malabar ('the country of Male'). The name ''Male'' is thought to come from the
Malayalam
Malayalam (; , ) is a Dravidian languages, Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry (union territory), Puducherry (Mahé district) by the Malayali people. It is one of 2 ...
word ''Mala'' ('hill').
Al-Biruni
Abu Rayhan Muhammad ibn Ahmad al-Biruni (973 – after 1050) commonly known as al-Biruni, was a Khwarazmian Iranian in scholar and polymath during the Islamic Golden Age. He has been called variously the "founder of Indology", "Father of Co ...
(AD 973 - 1048) must have been the first writer to call this state ''Malabar''.
Authors such as
Ibn Khordadbeh and
Al-Baladhuri
ʾAḥmad ibn Yaḥyā ibn Jābir al-Balādhurī ( ar, أحمد بن يحيى بن جابر البلاذري) was a 9th-century Muslim historian. One of the eminent Middle Eastern historians of his age, he spent most of his life in Baghdad and e ...
mention Malabar ports in their works.
[Mohammad, K.M. "Arab relations with Malabar Coast from 9th to 16th centuries" Proceedings of the Indian History Congress. Vol. 60 (1999), pp. 226–34.] The Arab writers had called this place ''Malibar'', ''Manibar'', ''Mulibar'', and ''Munibar''. ''Malabar'' is reminiscent of the word ''Malanad'' which means ''the land of hills''. According to
William Logan, the word ''Malabar'' comes from a combination of the
Malayalam
Malayalam (; , ) is a Dravidian languages, Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry (union territory), Puducherry (Mahé district) by the Malayali people. It is one of 2 ...
word ''Mala'' (hill) and the
Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
/
Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
word ''Barr'' (country/continent).
History
Ezhimala kingdom

The ancient port of ''Naura'', which is mentioned in the ''
Periplus of the Erythraean Sea
The ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' ( grc, Περίπλους τῆς Ἐρυθρᾶς Θαλάσσης, ', modern Greek '), also known by its Latin name as the , is a Greco-Roman periplus written in Koine Greek that describes navigation and ...
'' as a port somewhere north of
Muziris is identified with Kannur.
Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ' ...
(1st century CE) states that the port of ''
Tyndis'' was located at the northwestern border of ''Keprobotos'' (
Chera dynasty).
[Gurukkal, R., & Whittaker, D. (2001). In search of Muziris. ''Journal of Roman Archaeology,'' ''14'', 334-350.] The North Malabar region, which lies north of the port at ''
Tyndis'', was ruled by the kingdom of
Ezhimala
Ezhimala, a hill reaching a height of , is located near Payyanur, in Kannur district of Kerala, south India. It is a part of a conspicuous and isolated cluster of hills, forming a promontory, north of Kannur (Cannanore). The Indian Naval Acad ...
during
Sangam period
The Sangam period or age (, ), particularly referring to the third Sangam period, is the period of the history of ancient Tamil Nadu, Kerala and parts of Sri Lanka (then known as Tamilakam) spanning from c. 6th century BCE to c. 3rd century CE. ...
.
[A. Shreedhara Menon, A Survey of Kerala History] According to the ''
Periplus of the Erythraean Sea
The ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' ( grc, Περίπλους τῆς Ἐρυθρᾶς Θαλάσσης, ', modern Greek '), also known by its Latin name as the , is a Greco-Roman periplus written in Koine Greek that describes navigation and ...
'', a region known as ''
Limyrike
Limyrikê is a historical region of present-day India, mentioned in the ancient Greco-Roman texts. It generally corresponds to the present-day Malabar Coast of Kerala.
Extent
According to the ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' (53:17:15-27), ...
'' began at ''
Naura'' and ''
Tyndis''. However the
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance ...
mentions only ''
Tyndis'' as the ''
Limyrike
Limyrikê is a historical region of present-day India, mentioned in the ancient Greco-Roman texts. It generally corresponds to the present-day Malabar Coast of Kerala.
Extent
According to the ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' (53:17:15-27), ...
s starting point. The region probably ended at
Kanyakumari
Kanniyakumari (; , referring to Devi Kanya Kumari), also known as Cape Comorin, is a city in Kanniyakumari district in the state of Tamil Nadu, India. It is the southern tip of the Indian subcontinent and the southernmost city in mainland Ind ...
; it thus roughly corresponds to the present-day
Malabar Coast
The Malabar Coast is the southwestern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Geographically, it comprises the wettest regions of southern India, as the Western Ghats intercept the moisture-laden monsoon rains, especially on their westward-facing m ...
. The value of Rome's annual trade with the region was estimated at around 50,000,000
sesterces.
Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ' ...
mentioned that ''
Limyrike
Limyrikê is a historical region of present-day India, mentioned in the ancient Greco-Roman texts. It generally corresponds to the present-day Malabar Coast of Kerala.
Extent
According to the ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' (53:17:15-27), ...
'' was prone by pirates. The
Cosmas Indicopleustes
Cosmas Indicopleustes ( grc-x-koine, Κοσμᾶς Ἰνδικοπλεύστης, lit=Cosmas who sailed to India; also known as Cosmas the Monk) was a Greek merchant and later hermit from Alexandria of Egypt. He was a 6th-century traveller who ma ...
mentioned that the ''
Limyrike
Limyrikê is a historical region of present-day India, mentioned in the ancient Greco-Roman texts. It generally corresponds to the present-day Malabar Coast of Kerala.
Extent
According to the ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' (53:17:15-27), ...
'' was a source of peppers.
The Ezhimala dynasty had jurisdiction over two ''Nadu''s - The coastal ''Poozhinadu'' and the hilly eastern ''Karkanadu''. According to the works of
Sangam literature
The Sangam literature (Tamil: சங்க இலக்கியம், ''caṅka ilakkiyam'';) historically known as 'the poetry of the noble ones' (Tamil: சான்றோர் செய்யுள், ''Cāṉṟōr ceyyuḷ'') connotes ...
, ''Poozhinadu'' consisted much of the coastal belt between
Mangalore
Mangalore (), officially known as Mangaluru, is a major port city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It is located between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats about west of Bangalore, the state capital, 20 km north of Karnataka–Ke ...
and
Kozhikode
Kozhikode (), also known in English as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. It has a corporation limit population of 609,224 and a metropolitan population of more than 2 million, making it the second l ...
.
''Karkanadu'' consisted of
Wayanad
Wayanad () is a district in the north-east of Indian state Kerala with administrative headquarters at the municipality of Kalpetta. It is the only plateau in Kerala. The Wayanad Plateau forms a continuation of the Mysore Plateau, the southern ...
-
Gudalur hilly region with parts of
Kodagu
Kodagu (also known by its former name Coorg) is an administrative district in the Karnataka state of India. Before 1956, it was an administratively separate Coorg State, at which point it was merged into an enlarged Mysore State.
It occupies ...
(Coorg).
It is said that Nannan, the most renowned ruler of Ezhimala dynasty, took refuge at Wayanad hills in the 5th century CE when he was lost to
Cheras, just before his execution in a battle, according to the
Sangam works.
Ezhimala kingdom was succeeded by
Mushika dynasty
Mushika dynasty, also spelled Mushaka, was a minor dynastic power that held sway over the region in and around Mount Ezhi (Ezhimala (hill, Kannur), Ezhimala) in present-day North Malabar, Kerala, India. The country of the Mushikas, ruled by an a ...
in the early medieval period, most possibly due to the migration of
Tuluva Brahmins from
Tulu Nadu
Tulunad or Tulu Nadu, also called Bermere sristi or Parashurama Srishti, is a region and a proposed state on the southwestern coast of India. The Tulu people, known as 'Tuluva' (plural 'Tuluver'), speakers of Tulu, a Dravidian language, ar ...
. The Kolathunadu (
Kannur
Kannur (), formerly known in English as Cannanore, is a city and a municipal corporation in the state of Kerala, India. It is the administrative headquarters of the Kannur district and situated north of the major port city and commercial hu ...
) Kingdom at the peak of its power, reportedly extended from
Netravati River
The Netravati River or Netravathi Nadi has its origins at Bangrabalige valley, Yelaneeru Ghat in Kudremukh in Chikkamagaluru district of Karnataka, India. This river flows through the famous pilgrimage place Dharmasthala and is considered one ...
(
Mangalore
Mangalore (), officially known as Mangaluru, is a major port city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It is located between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats about west of Bangalore, the state capital, 20 km north of Karnataka–Ke ...
) in the north to
Korapuzha (
Kozhikode
Kozhikode (), also known in English as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. It has a corporation limit population of 609,224 and a metropolitan population of more than 2 million, making it the second l ...
) in the south with
Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea ( ar, اَلْبَحرْ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Bahr al-ˁArabī) is a region of the northern Indian Ocean bounded on the north by Pakistan, Iran and the Gulf of Oman, on the west by the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channel ...
on the west and
Kodagu
Kodagu (also known by its former name Coorg) is an administrative district in the Karnataka state of India. Before 1956, it was an administratively separate Coorg State, at which point it was merged into an enlarged Mysore State.
It occupies ...
hills on the eastern boundary, also including the isolated islands of
Lakshadweep
Lakshadweep (), also known as Laccadives (), is a union territory of India. It is an archipelago of 36 islands in the Arabian sea, located off the Malabar Coast.
The name ''Lakshadweep'' means "one lakh islands" in Sanskrit, though the Lac ...
in the
Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea ( ar, اَلْبَحرْ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Bahr al-ˁArabī) is a region of the northern Indian Ocean bounded on the north by Pakistan, Iran and the Gulf of Oman, on the west by the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channel ...
.
North Malabar was a hub of
Indian Ocean trade
Indian Ocean trade has been a key factor in East–West exchanges throughout history. Long-distance trade in dhows and proas made it a dynamic zone of interaction between peoples, cultures, and civilizations stretching from Southeast Asia to Ea ...
during the era. According to
Kerala Muslim tradition, the kingdom of Ezhimala was home to several
oldest mosques in the
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
. According to the
Legend of Cheraman Perumals
The legend of Cheraman Perumals is the medieval tradition associated with the Cheraman Perumals (Chera kings) of Kerala.Narayanan, M. G. S. ''Perumāḷs of Kerala.'' Thrissur (Kerala): CosmoBooks, 2013. 31-32. The sources of the legend include p ...
, the first Indian mosque was built in 624 AD at Kodungallur with the mandate of the last the ruler (the Cheraman Perumal) of
Chera dynasty, who left from
Dharmadom to
Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow ...
and converted to
Islam during the lifetime of
Prophet Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the monoth ...
(c. 570–632).
According to ''
Qissat Shakarwati Farmad
''Qissat Shakarwati Farmad'' (alternatively ''Qissat Shakruti Firmad'', literally ''"Tale of the Great Chera Ruler"'') is an Arabic manuscript of anonymous authorship, apparently written in Malabar Coast, south India.O. Loth, ''Arabic Manuscripts ...
'', the
''Masjids'' at Kodungallur,
Kollam,
Madayi
Madayi (a.k.a. Madai). is a Census Town and Grama panchayat in Kannur district of Kerala state, India. Bhagavathy shrine, Madayi Kavu (Thiruvar Kadu Bhagavathi Temple) where devotees worship Bhadrakali, is located here. The Goddess is on ...
,
Barkur
Barkur (also spelt Barcoor) is an area in the Brahmavara taluk, Udupi district of Karnataka state in India, comprising three villages, Hosala, Hanehalli, and Kachoor. The area is located on the bank of River Seetha. It is also referred to ...
,
Mangalore
Mangalore (), officially known as Mangaluru, is a major port city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It is located between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats about west of Bangalore, the state capital, 20 km north of Karnataka–Ke ...
,
Kasaragod,
Kannur
Kannur (), formerly known in English as Cannanore, is a city and a municipal corporation in the state of Kerala, India. It is the administrative headquarters of the Kannur district and situated north of the major port city and commercial hu ...
,
Dharmadam
Dharmadom or Dharmadam is a census town in Thalassery taluk of Kannur district in the state of Kerala, India. This town is located in between Anjarakandi River and Ummanchira river, and Palayad town and Arabian sea. It is known for the 100-yea ...
,
Panthalayani, and
Chaliyam
Chaliyam is a village situated at the estuary of Chaliyar (River Beypore) in Kozhikode district of Kerala, India. Chaliyam forms an island, bounded by the Chaliyar in the north, and River Kadalundi in south, and the Conolly Canal in the east. ...
, were built during the era of
Malik Dinar
Malik Dinar ( ar-at, مالك دينار, Mālik b. Dīnār, Malayalam: മാലിക് ദീനാര്) (died 748 CE)Al-Hujwiri, "Kashf al-Mahjoob", 89 was a Muslim scholar and traveller. He was one of the first known Muslims to have co ...
, and they are among the oldest ''Masjid''s in the
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
. It is believed that
Malik Dinar
Malik Dinar ( ar-at, مالك دينار, Mālik b. Dīnār, Malayalam: മാലിക് ദീനാര്) (died 748 CE)Al-Hujwiri, "Kashf al-Mahjoob", 89 was a Muslim scholar and traveller. He was one of the first known Muslims to have co ...
died at
Thalangara
Thalangara is a part of Kasaragod Town, the district headquarters of the Kasaragod district in the South Indian state of Kerala. Malik Deenar Jama Masjid and Dargah is located here. Its economy is dependent on remittance from expatriate workers ...
in
Kasaragod town.
[Pg 58, Cultural heritage of ]Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South ...
: an introduction, A. Sreedhara Menon, East-West Publications, 1978 Most of them lies in the erstwhile region of Ezhimala kingdom. The Koyilandy Jumu'ah Mosque contains an
Old Malayalam inscription written in a mixture of ''
Vatteluttu
''Vatteluttu,'' popularly romanised as ''Vattezhuthu'' ( ta, வட்டெழுத்து, ' and ml, വട്ടെഴുത്ത്, ', ), was a syllabic alphabet of south India (Tamil Nadu and Kerala) and Sri Lanka used for writing t ...
'' and
Grantha script
The Grantha script ( ta, கிரந்த எழுத்து, Granta eḻuttu; ml, ഗ്രന്ഥലിപി, granthalipi) is a South Indian script, found particularly in Tamil Nadu and Kerala. Originating from the Pallava script, th ...
s which dates back to the 10th century CE.
[Aiyer, K. V. Subrahmanya (ed.), ''South Indian Inscriptions.'' VIII, no. 162, Madras: Govt of India, Central Publication Branch, Calcutta, 1932. p. 69.] It is a rare surviving document recording patronage by a
Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
king (Bhaskara Ravi) to the
Muslims of Kerala.
Mushika dynasty

Between the 9th and 12th centuries, a dynasty called "Mushaka" controlled the Chirakkal areas of northern Malabar (the Wynad-Tellichery area was part of the Second Chera Kingdom). The Mushakas were probably the descendants of the ancient royal family of Nannan of Ezhi mala and were perhaps a vassal of the Cheras. The Kolla-desam (or the Mushika-rajya) came under the influence of the
Chera/Perumals kingdom during eleventh century AD.
[Ganesh, K. N. (2009). ''Historical Geography of Natu in South India with Special Reference to Kerala.'' Indian Historical Review, 36(1), 3–21.] The
Chola references to several kings in medieval Kerala confirms that the power of the
Chera/Perumal was restricted to the country around capital
Kodungallur
Kodungallur (; also Cranganore, Portuguese: Cranganor; formerly known as Mahodayapuram, Shingly, Vanchi, Muchiri, Muyirikkode, and Muziris) is a historically significant town situated on the banks of river Periyar on the Malabar Coast in Th ...
. The Perumal kingship remained nominal compared with the power that local rulers (such as that of the Mushika in the north and Venatu in the south) exercised politically and militarily. Medieval Kolla-desam stretched on the banks of Kavvai, Koppam and Valappattanam rivers.
An
Old Malayalam inscription (
Ramanthali inscriptions
Ramanthali inscriptions, also known as Ezhimala-Narayankannur inscriptions, are two medieval stone epigraphs from Ramanthali, near Ezhimala in Kannur district, Kerala. The first inscription, mentioning Mushika (Malayalam: Ezhimala) Validhara Vikr ...
), dated to 1075 CE, mentioning king Kunda Alupa, the ruler of
Alupa dynasty
The Alupa dynasty (ಅಳುಪೆರ್, ಆಳ್ವೆರ್) (circa 2nd century C.E to 15th century C.E) was an ancient ruling dynasty of India. The kingdom they ruled was known as ''Alvakheda Arusasira'' and its territory spanned the coa ...
of
Mangalore
Mangalore (), officially known as Mangaluru, is a major port city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It is located between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats about west of Bangalore, the state capital, 20 km north of Karnataka–Ke ...
, can be found at
Ezhimala
Ezhimala, a hill reaching a height of , is located near Payyanur, in Kannur district of Kerala, south India. It is a part of a conspicuous and isolated cluster of hills, forming a promontory, north of Kannur (Cannanore). The Indian Naval Acad ...
(the former headquarters of
Mushika dynasty
Mushika dynasty, also spelled Mushaka, was a minor dynastic power that held sway over the region in and around Mount Ezhi (Ezhimala (hill, Kannur), Ezhimala) in present-day North Malabar, Kerala, India. The country of the Mushikas, ruled by an a ...
) near
Cannanore
Kannur (), formerly known in English as Cannanore, is a Cities in India, city and a municipal corporation in the state of Kerala, India. It is the administrative headquarters of the Kannur district and situated north of the major port city a ...
, Kerala.
The
Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
inscription on a copper slab within the
Madayi Mosque in
Kannur
Kannur (), formerly known in English as Cannanore, is a city and a municipal corporation in the state of Kerala, India. It is the administrative headquarters of the Kannur district and situated north of the major port city and commercial hu ...
records its foundation year as 1124 CE.
In his book on travels (''
Il Milione''),
Marco Polo recounts his visit to the area in the mid 1290s. Other visitors included
Faxian
Faxian (法顯 ; 337 CE – c. 422 CE), also referred to as Fa-Hien, Fa-hsien and Sehi, was a Chinese Buddhist monk and translator who traveled by foot from China to India to acquire Buddhist texts. Starting his arduous journey about age 60, h ...
, the Buddhist pilgrim and
Ibn Batuta
Abu Abdullah Muhammad ibn Battutah (, ; 24 February 13041368/1369),; fully: ; Arabic: commonly known as Ibn Battuta, was a Berber Maghrebi scholar and explorer who travelled extensively in the lands of Afro-Eurasia, largely in the Muslim wo ...
, writer and historian of
Tangiers
Tangier ( ; ; ar, طنجة, Ṭanja) is a city in northwestern Morocco. It is on the Moroccan coast at the western entrance to the Strait of Gibraltar, where the Mediterranean Sea meets the Atlantic Ocean off Cape Spartel. The town is the capi ...
. The ''
Mushika-vamsha Mahakavya'', written by
Athula
Athula (IAST: Atula) was a Sanskrit-language poet from the Mushika Kingdom in present-day Kerala, India. He composed the '' Mushika-vamsa'', a mahakavya Mahākāvya (lit. great kāvya, court epic), also known as ''sargabandha'', is a genre of India ...
in the 11th century, throws light on the recorded past of the
Mushika Royal Family up until that point.
Old Malayalam inscriptions related to Mushika dynasty
*Validhara Vikkirama Rama (c. 929 AD) - mentioned in the
Ezhimala-Narayankannur inscription.[Narayanan, M. G. S. ''Perumāḷs of Kerala.'' Thrissur (Kerala): CosmoBooks, 2013. 180-181.]
* Kantan Karivarman ''alias'' Iramakuta Muvar (c. 1020 AD)
- mentioned in an Eramam inscription of
Chera/Perumal Bhaskara Ravi Manukuladitya (962–1021 AD).
*''Mushikesvara'' Chemani/Jayamani (c. 1020 AD) - Tiruvadur inscription.
[Narayanan, M. G. S. ''Perumāḷs of Kerala.'' Thrissur (Kerala): CosmoBooks, 2013. 480-81.]
* Ramakuta Muvar (as a donor to the
Tiruvalla temple in
Tiruvalla Copper Plates/Huzur Treasury Plates).
[Narayanan, M. G. S. ''Perumāḷs of Kerala.'' Thrissur (Kerala): CosmoBooks, 2013. 197.]
* Utaiya-varma ''alias Ramakuta Muvar'' (early 12th century AD) - mentioned in the Kannapuram inscription.
[Narayanan, M. G. S. ''Perumāḷs of Kerala.'' Thrissur (Kerala): CosmoBooks, 2013. 483.]
Kolathunadu

Kolathunadu
Kolattunādu (Kola Swarupam, as Kingdom of Cannanore in foreign accounts, Chirakkal (Chericul) in later times) was one of the four most powerful kingdoms on the Malabar Coast during the arrival of the Portuguese Armadas in India, along with ...
(Kingdom of
Kannur
Kannur (), formerly known in English as Cannanore, is a city and a municipal corporation in the state of Kerala, India. It is the administrative headquarters of the Kannur district and situated north of the major port city and commercial hu ...
) was one of the 4 most powerful
kingdom
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
s on the
Malabar Coast
The Malabar Coast is the southwestern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Geographically, it comprises the wettest regions of southern India, as the Western Ghats intercept the moisture-laden monsoon rains, especially on their westward-facing m ...
during the arrival of
Portuguese Armadas to
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, the others being
Zamorin
The Samoothiri (Anglicised as Zamorin; Malayalam: , Arabic: ''Sāmuri'', Portuguese: ''Samorim'', Dutch: ''Samorijn'', Chinese: ''Shamitihsi''Ma Huan's Ying-yai Sheng-lan: 'The Overall Survey of the Ocean's Shores' 433 Translated and Edited b ...
,
Kingdom of Cochin
The Kingdom of Cochin, named after its capital in the city of Kochi (Cochin), was a kingdom in the central part of present-day Kerala state. It commenced at the early part of the 12th century and continued to rule until 1949, when monarchy wa ...
and
Quilon
Kollam (), also known by its former name Quilon , is an ancient seaport and city on the Malabar Coast of India bordering the Laccadive Sea, which is a part of the Arabian Sea. It is north of the state capital Thiruvananthapuram. The city ...
. Kolattunādu had its capital at
Ezhimala
Ezhimala, a hill reaching a height of , is located near Payyanur, in Kannur district of Kerala, south India. It is a part of a conspicuous and isolated cluster of hills, forming a promontory, north of Kannur (Cannanore). The Indian Naval Acad ...
and was ruled by
Kolattiri Royal Family and roughly comprised the North Malabar region of
Kerala state in
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
. Traditionally, Kolattunādu is described as the land lying between
Perumba river in the north and Putupattanam river in the south.
[Keralolpatti Granthavari: The Kolattunad Traditions (Malayalam) (Kozhikode: Calicut University, 1984) M. R. Raghava Varier (ed.)] The ruling house of Kolathunādu, also known as the
Kolathiri
Kolathiri or Kolathiri Rājā (King of KolathunāduA. Shreedhara Menon (2007), ''A brief History of Kerala'', DC Books, Kottayam or King of Cannanore in foreign accounts) was the title by which the senior-most male along the matrilineal line of ...
s, were descendants of the
Mushaka Royal Family, (which was an ancient dynasty of kerala)and rose to become one of the major political powers in the Kerala region, after the disappearance of the
Cheras of Mahodayapuram and the
Pandyan Dynasty in the 12th century AD.
[Perumal of Kerala by M. G. S. Narayanan (Kozhikode: Private Circulation, 1996)] The Kolathiris trace their ancestry back to the ancient
Mushika kingdom
Mushika dynasty, also spelled Mushaka, was a minor dynastic power that held sway over the region in and around Mount Ezhi (Ezhimala) in present-day North Malabar, Kerala, India. The country of the Mushikas, ruled by an ancient lineage of the Heh ...
(Ezhimala kingdom, Eli-nadu) of the
Tamil Sangam
The Tamil Sangams (Tamil: சங்கம் ''caṅkam'', Old Tamil 𑀘𑀗𑁆𑀓𑀫𑁆, from Sanskrit ''saṅgha'') were assemblies of Tamil scholars and poets that, according to traditional Tamil accounts, occurred in the remote past. ...
Age. The Indian anthropologist
Ayinapalli Aiyappan states that a powerful and warlike clan of the
Bunt community of
Tulu Nadu
Tulunad or Tulu Nadu, also called Bermere sristi or Parashurama Srishti, is a region and a proposed state on the southwestern coast of India. The Tulu people, known as 'Tuluva' (plural 'Tuluver'), speakers of Tulu, a Dravidian language, ar ...
was called ''Kola Bari'' and the Kolathiri Raja of Kolathunadu was a descendant of this clan.

Until the 16th century CE, Kasargod town was known by the name ''Kanhirakode'' (may be by the meaning, 'The land of ''Kanhira'' Trees') in
Malayalam
Malayalam (; , ) is a Dravidian languages, Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry (union territory), Puducherry (Mahé district) by the Malayali people. It is one of 2 ...
.
The
Kumbla
Kumbla is a small town in Kasaragod district of Kerala state in India. It is located 12 km north of Kasaragod town.
History
The original name "Kanvapura" was derived from the name of Maharshi Kanva. Since then the name has morphed into ...
dynasty, who swayed over the land of southern
Tulu Nadu
Tulunad or Tulu Nadu, also called Bermere sristi or Parashurama Srishti, is a region and a proposed state on the southwestern coast of India. The Tulu people, known as 'Tuluva' (plural 'Tuluver'), speakers of Tulu, a Dravidian language, ar ...
wedged between
Chandragiri River and
Netravati River
The Netravati River or Netravathi Nadi has its origins at Bangrabalige valley, Yelaneeru Ghat in Kudremukh in Chikkamagaluru district of Karnataka, India. This river flows through the famous pilgrimage place Dharmasthala and is considered one ...
(including present-day Taluks of
Manjeshwar
Manjeshwar is a town and a minor port in Kasaragod district at the northern tip of Kerala. It is situated at a distance of from the state capital Thiruvananthapuram, north of district HQ Kasaragod and south of Mangalore city in neighbour ...
and
Kasaragod) from ''Maipady Palace'' at
Kumbla
Kumbla is a small town in Kasaragod district of Kerala state in India. It is located 12 km north of Kasaragod town.
History
The original name "Kanvapura" was derived from the name of Maharshi Kanva. Since then the name has morphed into ...
, had also been vassals to the
Kolathunadu
Kolattunādu (Kola Swarupam, as Kingdom of Cannanore in foreign accounts, Chirakkal (Chericul) in later times) was one of the four most powerful kingdoms on the Malabar Coast during the arrival of the Portuguese Armadas in India, along with ...
, before the
Carnatic conquests of
Vijayanagara Empire
The Vijayanagara Empire, also called the Karnata Kingdom, was a Hindu empire based in the region of South India, which consisted the modern states of Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Goa and some parts of Telangana and Mahar ...
. The Kumbla dynasty had a mixed lineage of
Malayali
The Malayali people () (also spelt Malayalee and also known by the demonym Keralite) are a Dravidian ethnolinguistic group originating from the present-day state of Kerala in India, occupying its southwestern Malabar coast. They are predomin ...
Nair
The Nair , also known as Nayar, are a group of Indian Hindu castes, described by anthropologist Kathleen Gough as "not a unitary group but a named category of castes". The Nair include several castes and many subdivisions, not all of whom histo ...
s and
Tuluva Brahmins.
They also claimed their origin from
Cheraman Perumals of Kerala.
states that the customs of Kumbla dynasty were similar to those of the contemporary
Malayali
The Malayali people () (also spelt Malayalee and also known by the demonym Keralite) are a Dravidian ethnolinguistic group originating from the present-day state of Kerala in India, occupying its southwestern Malabar coast. They are predomin ...
kings, though Kumbla was considered as the southernmost region of
Tulu Nadu
Tulunad or Tulu Nadu, also called Bermere sristi or Parashurama Srishti, is a region and a proposed state on the southwestern coast of India. The Tulu people, known as 'Tuluva' (plural 'Tuluver'), speakers of Tulu, a Dravidian language, ar ...
.
The
Zamorin
The Samoothiri (Anglicised as Zamorin; Malayalam: , Arabic: ''Sāmuri'', Portuguese: ''Samorim'', Dutch: ''Samorijn'', Chinese: ''Shamitihsi''Ma Huan's Ying-yai Sheng-lan: 'The Overall Survey of the Ocean's Shores' 433 Translated and Edited b ...
of
Calicut
Kozhikode (), also known in English as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. It has a corporation limit population of 609,224 and a metropolitan population of more than 2 million, making it the second l ...
, who was actually the ruler of
South Malabar
South Malabar refers to a geographical area of the southwestern coast of India covering some parts of the present-day Kerala. South Malabar covers the regions included in present-day Kozhikode taluk of Kozhikode district, the whole area of Malap ...
and became the most powerful ruler on
Malabar Coast
The Malabar Coast is the southwestern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Geographically, it comprises the wettest regions of southern India, as the Western Ghats intercept the moisture-laden monsoon rains, especially on their westward-facing m ...
, conquerred many regions of North Malabar including
Koyilandy
A Survey of Kerala History, A. Shreedhara Menon ar, Fundriya pt, Pandarani
, settlement_type = MunicipalityTaluk
, image_skyline = KadaloorPointLight 01.jpg
, image_alt =
, image_caption ...
(Panthalayini Kollam). By the 15th century CE,
Kolathiri
Kolathiri or Kolathiri Rājā (King of KolathunāduA. Shreedhara Menon (2007), ''A brief History of Kerala'', DC Books, Kottayam or King of Cannanore in foreign accounts) was the title by which the senior-most male along the matrilineal line of ...
Rajas came under the influence of Zamorin just like the other kingdoms of Kerala. The
Kolathiri
Kolathiri or Kolathiri Rājā (King of KolathunāduA. Shreedhara Menon (2007), ''A brief History of Kerala'', DC Books, Kottayam or King of Cannanore in foreign accounts) was the title by which the senior-most male along the matrilineal line of ...
Dominion emerged into independent 10 principalities i.e.,
Kadathanadu
Kadathanadu (Vatakara) was a former feudatory (of Kolathunad) city-state in present-day Kerala, on the Malabar Coast. The region is most known for being the area where the events of the ''Vadakkan Pattukal,'' a set of warrior ballads from Kerala, ...
(
Vadakara
Vatakara, also spelled Vadakara (formerly Badagara), , french: Bargaret, is a Municipality in the state of Kerala, India. Vatakara is located between Kannur and Kozhikode. The municipality of Vatakara covers an area of and is bordered by Ma ...
),
Randathara or Poyanad (
Dharmadom),
Kottayam
Kottayam () is a municipal town in the Indian state of Kerala. Flanked by the Western Ghats on the east and the Vembanad Lake and paddy fields of Kuttanad on the west. It is the district headquarters of Kottayam district, located in south- ...
(
Thalassery
Thalassery (), formerly Tellicherry, is a municipality, Commercial City on the Malabar Coast in Kannur district, in the state of Kerala, India, bordered by the List of districts of India, districts of Mahé, India, Mahé (Pondicherry), Kozhikode ...
),
Nileshwaram
Nileshwaram or Nileshwar or Neeleswaram is a municipality and a major town in Kasaragod District, state of Kerala, India. It is one of the three municipalities in Kasaragod district; the others are Kasaragod and Kanhangad. Nileshwaram is locat ...
, Iruvazhinadu (
Panoor),
Kurumbranad
Kurumbranad (Kurumbuzhai Nadu or Kurumbiathiri Swaroopam) was a kingdom, located in present-day Kerala state, South India, on the Malabar Coast. Once a powerful kingdom, it had important commercial centres such as Mapayil, Puthuppanam and Vatakara ...
etc., under separate royal chieftains due to the outcome of internal dissensions.
The
Nileshwaram
Nileshwaram or Nileshwar or Neeleswaram is a municipality and a major town in Kasaragod District, state of Kerala, India. It is one of the three municipalities in Kasaragod district; the others are Kasaragod and Kanhangad. Nileshwaram is locat ...
dynasty on the northernmost part of
Kolathiri
Kolathiri or Kolathiri Rājā (King of KolathunāduA. Shreedhara Menon (2007), ''A brief History of Kerala'', DC Books, Kottayam or King of Cannanore in foreign accounts) was the title by which the senior-most male along the matrilineal line of ...
dominion, were relatives to both
Kolathunadu
Kolattunādu (Kola Swarupam, as Kingdom of Cannanore in foreign accounts, Chirakkal (Chericul) in later times) was one of the four most powerful kingdoms on the Malabar Coast during the arrival of the Portuguese Armadas in India, along with ...
as well as
Zamorin
The Samoothiri (Anglicised as Zamorin; Malayalam: , Arabic: ''Sāmuri'', Portuguese: ''Samorim'', Dutch: ''Samorijn'', Chinese: ''Shamitihsi''Ma Huan's Ying-yai Sheng-lan: 'The Overall Survey of the Ocean's Shores' 433 Translated and Edited b ...
of
Calicut
Kozhikode (), also known in English as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. It has a corporation limit population of 609,224 and a metropolitan population of more than 2 million, making it the second l ...
, in the early medieval period.
The Portuguese arrived at
Kappad
Kappad, or Kappakadavu locally, is a beach and village near Koyilandy, in the district Kozhikode, Kerala, India.
A stone monument installed by government commemorates the "landing" by Vasco da Gama with the inscription, Vasco da Gama landed he ...
Kozhikode
Kozhikode (), also known in English as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. It has a corporation limit population of 609,224 and a metropolitan population of more than 2 million, making it the second l ...
in 1498 during the
Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (or the Age of Exploration), also known as the early modern period, was a period largely overlapping with the Age of Sail, approximately from the 15th century to the 17th century in European history, during which seafarin ...
, thus opening a direct sea route from
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
to
South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth descr ...
. The
St. Angelo Fort at Kannur was built in 1505 by Dom
Francisco de Almeida
Dom Francisco de Almeida (), also known as the Great Dom Francisco (c. 1450 – 1 March 1510), was a Portuguese nobleman, soldier and explorer. He distinguished himself as a counsellor to King John II of Portugal and later in the wars against ...
, the first Portuguese Viceroy of India. The Dutch captured the fort from the Portuguese in 1663. They modernized the fort and built the bastions Hollandia, Zeelandia, and Frieslandia that are the major features of the present structure. The original Portuguese fort was pulled down later. A painting of this fort and the fishing ferry behind it can be seen in the Rijksmuseum Amsterdam. The Dutch sold the fort to king Ali Raja of Arakkal in 1772.
During the 17th century, Kannur was the capital city of the only
Muslim Sultanate in Kerala, known as
Arakkal, who also ruled the
Laccadive Islands in addition to Kannur.
[Arakkal royal family]
The island of
Dharmadom near Kannur, along with
Thalassery
Thalassery (), formerly Tellicherry, is a municipality, Commercial City on the Malabar Coast in Kannur district, in the state of Kerala, India, bordered by the List of districts of India, districts of Mahé, India, Mahé (Pondicherry), Kozhikode ...
, was ceded to the
East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and South ...
as early as 1734, which were claimed by all of the
''Kolattu Rajas'',
''Kottayam Rajas'', and
'' Arakkal Bibi'' in the late medieval period, where the British initiated a factory and English settlement following the
cession
The act of cession is the assignment of property to another entity. In international law it commonly refers to land transferred by treaty. Ballentine's Law Dictionary defines cession as "a surrender; a giving up; a relinquishment of jurisdictio ...
.
Colonial era




In 1761, the British captured
Mahé, and the settlement was handed over to the ruler of
Kadathanadu
Kadathanadu (Vatakara) was a former feudatory (of Kolathunad) city-state in present-day Kerala, on the Malabar Coast. The region is most known for being the area where the events of the ''Vadakkan Pattukal,'' a set of warrior ballads from Kerala, ...
.
The British restored
Mahé to the French as a part of the 1763 Treaty of Paris.
In 1779, the Anglo-French war broke out, resulting in the French loss of
Mahé.
In 1783, the British agreed to restore to the French their settlements in India, and
Mahé was handed over to the French in 1785.
The northern parts of
Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South ...
was unified under
Tipu Sultan
Tipu Sultan (born Sultan Fateh Ali Sahab Tipu, 1 December 1751 – 4 May 1799), also known as the Tiger of Mysore, was the ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore based in South India. He was a pioneer of rocket artillery.Dalrymple, p. 243 He i ...
during the last decades of eighteenth century CE. When he was defeated by the
East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and South ...
through
Third Anglo-Mysore War
The Third Anglo-Mysore War (1790–1792) was a conflict in South India between the Kingdom of Mysore and the British East India Company, the Kingdom of Travancore, the Maratha Empire, and the Nizam of Hyderabad. It was the third of four Angl ...
, the
Treaty of Seringapatam
The Treaty of Seringapatam (also called Srirangapatinam or Srirangapatna), signed 18 March 1792, ended the Third Anglo-Mysore War. Its signatories included Lord Cornwallis on behalf of the British East India Company, representatives of the Niz ...
was agreed and the regions included in Tipu's kingdom was annexed with the East India Company. After the Anglo-Mysore wars, the parts of
Malabar Coast
The Malabar Coast is the southwestern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Geographically, it comprises the wettest regions of southern India, as the Western Ghats intercept the moisture-laden monsoon rains, especially on their westward-facing m ...
, those became British colonies, were organized into a district of
British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
. They divided it into North Malabar and
South Malabar
South Malabar refers to a geographical area of the southwestern coast of India covering some parts of the present-day Kerala. South Malabar covers the regions included in present-day Kozhikode taluk of Kozhikode district, the whole area of Malap ...
on 30 March 1793 for administrative convenience. Though the general administrative headquarters of Malabar was at
Calicut
Kozhikode (), also known in English as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. It has a corporation limit population of 609,224 and a metropolitan population of more than 2 million, making it the second l ...
in South Malabar, the special headquarters of South Malabar was decided to be at
Cherpulassery, which was then replaced to
Ottapalam
Ottapalam, (also spelled Ottappalam) is a town, taluk and municipality in the Palakkad District, Kerala, India. It is the administrative headquarters of the Ottapalam taluk. Ottapalam is located about 36 km from district headquarters Palakkad. ...
. South Malabar was the centre of the
Malabar Rebellion in 1921. On 1 November 1956, this region was annexed with the Indian state of
Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South ...
.
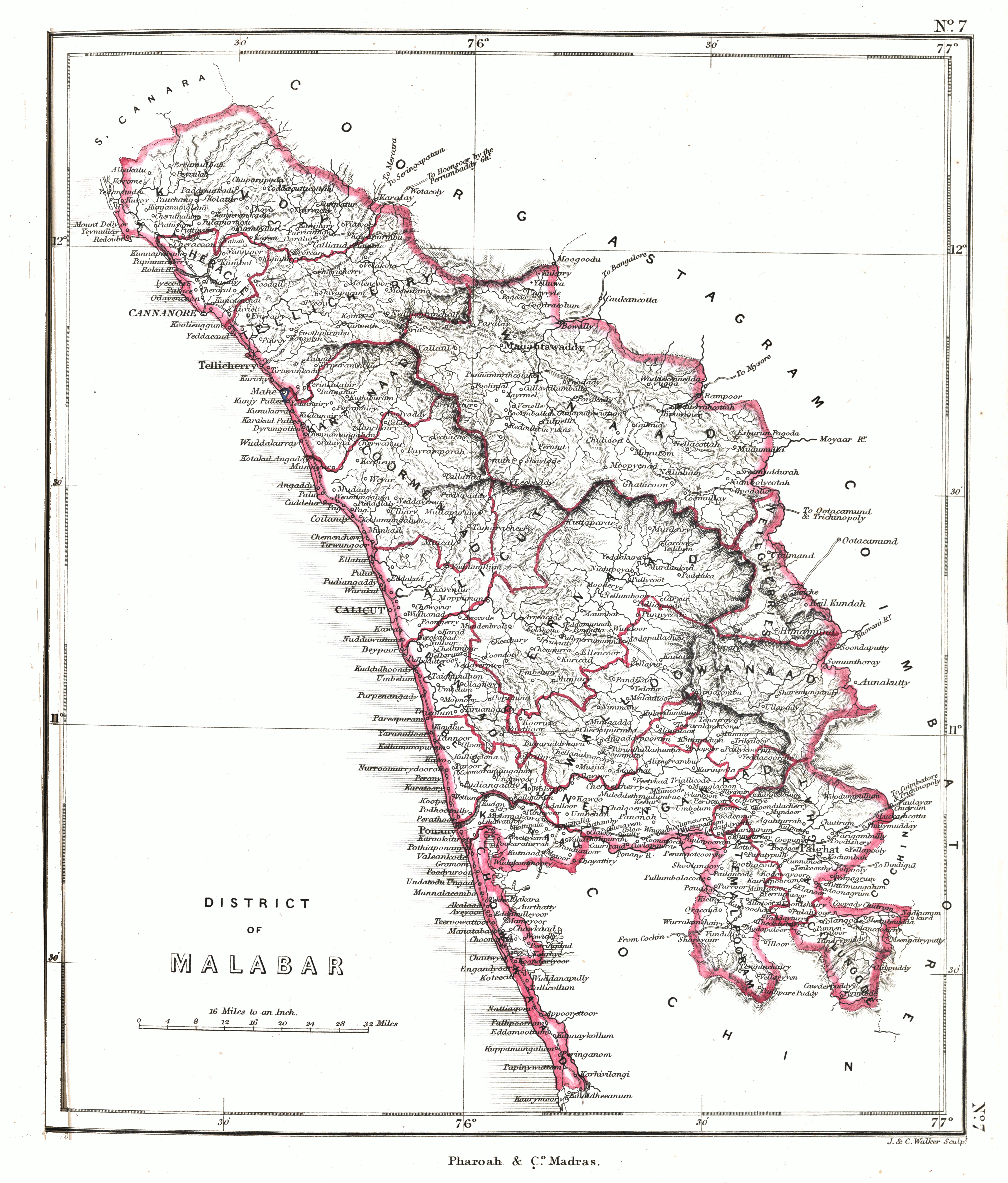
The East India Company
captured the fort Kannur in 1790 and used it as one of their major military stations on the
Malabar Coast
The Malabar Coast is the southwestern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Geographically, it comprises the wettest regions of southern India, as the Western Ghats intercept the moisture-laden monsoon rains, especially on their westward-facing m ...
. Initially the Malabar was placed under
Bombay Presidency. Later in 1799-1800 year, Malabar along with
South Canara was transferred to
Madras Presidency. During the period of
British colonial rule, Kannur was part of the
Madras province in the
Malabar District. The municipalities of
Kannur
Kannur (), formerly known in English as Cannanore, is a city and a municipal corporation in the state of Kerala, India. It is the administrative headquarters of the Kannur district and situated north of the major port city and commercial hu ...
and
Thalassery
Thalassery (), formerly Tellicherry, is a municipality, Commercial City on the Malabar Coast in Kannur district, in the state of Kerala, India, bordered by the List of districts of India, districts of Mahé, India, Mahé (Pondicherry), Kozhikode ...
were formed on 1 November 1866 according to the Madras Act 10 of 1865 (Amendment of the Improvements in Towns act 1850)
of the
British Indian Empire
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent;
*
* it is also called Crown rule in India,
*
*
*
*
or Direct rule in India,
* Quote: "Mill, who was himse ...
, along with the municipalities of
Kozhikode
Kozhikode (), also known in English as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. It has a corporation limit population of 609,224 and a metropolitan population of more than 2 million, making it the second l ...
,
Palakkad
Palakkad (), formerly known as Palghat, historically known as Palakkattussery is a city and municipality in the Indian state of Kerala. It is the administrative headquarters of the Palakkad District. Palakkad is most densely populated municipal ...
, and
Fort Kochi, making them the first modern municipalities in the modern state of Kerala.
Initially the British had to suffer local resistance against their rule under the leadership of
Kerala Varma Pazhassi Raja
Pazhassi Raja () (3 January 1753 – 30 November 1805) was known as Kerala Varma and was also known as Cotiote Rajah and Pychy Rajah. He was a warrior Hindu prince and de facto head of the kingdom of Kottayam, otherwise known as Cotiote, in ...
, who had popular support in
Thalassery
Thalassery (), formerly Tellicherry, is a municipality, Commercial City on the Malabar Coast in Kannur district, in the state of Kerala, India, bordered by the List of districts of India, districts of Mahé, India, Mahé (Pondicherry), Kozhikode ...
-
Wayanad
Wayanad () is a district in the north-east of Indian state Kerala with administrative headquarters at the municipality of Kalpetta. It is the only plateau in Kerala. The Wayanad Plateau forms a continuation of the Mysore Plateau, the southern ...
region.
The guerrilla war launched by
Pazhassi Raja
Pazhassi Raja () (3 January 1753 – 30 November 1805) was known as Kerala Varma and was also known as Cotiote Rajah and Pychy Rajah. He was a warrior Hindu prince and de facto head of the kingdom of Kottayam, otherwise known as Cotiote, in ...
, the ruler of Kottayam province, against the East India Company had a huge impact on the history of Kannur. Changes in the socio-economic and political sectors in Kerala during the initial decades of the 20th century created conditions congenial for the growth of the Communist Party. Extension of English education initiated by Christian missionaries in 1906 and later carried forward by government, rebellion for wearing a cloth to cover upper parts of body, installing an idol at Aruvippuram in 1888, Malayali Memorial in 1891, establishment of SNDP Yogam in 1903, activities, struggles etc. became factors helpful to accelerate changes in Kerala society during a short time. These movements eventually coalesced into the
Indian independence movement
The Indian independence movement was a series of historic events with the ultimate aim of ending British Raj, British rule in India. It lasted from 1857 to 1947.
The first nationalistic revolutionary movement for Indian independence emerged ...
.
Culture and people

The socio-cultural background and geography of this area has some distinctions compared to the rest of Kerala.
[Eleanor Kathleen Gough (1900), Nayar: North Kerala, University of California Press, (Berkeley, Los Angeles)][Eric J. Miller (1954), Caste and Territory in Malabar, American Anthropological Association][Praveena Kodoth (1998), Women and Property Rights: A Study of Land Relations and Personal Law in Malabar, 1880–1940' Unpublished PhD Dissertation, Department of Economics, University of Hyderabad][Ravindran Gopinath, 'Garden and Paddy Fields: Historical Implications of Agricultural Production Regimes in Colonial Malabar' in Mushirul Hasan and Narayani Gupta (eds.)][India's Colonial Encounters: Essays in Memory of Eric Stokes, Delhi: Monohar Publishers, 1993][M. Jayarajan, Sacred Groves of North Malabar, Discussion Paper No. 92](_blank)
[Praveena Kodoth (2002), FRAMING CUSTOM, DIRECTING PRACTICES: AUTHORITY, PROPERTY AND MATRILINY UNDER COLONIAL LAW IN NINETEENTH CENTURY MALABA]
/ref> The population consists of native Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
s, native Mappila
Mappila Muslim, often shortened to Mappila, formerly anglicized as Moplah/Mopla and historically known as Jonaka/Chonaka Mappila or Moors Mopulars/Mouros da Terra and Mouros Malabares, in general, is a member of the Muslim community of same n ...
-Muslims, native Jain
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle being ...
s and migrant- Christian communities and is characterized by distinct socio-cultural customs and behavior. The people of North Malabar have striven to preserve their distinct and unique identity and heritage since ancient times, through colonial times into modern political India. From the seventeenth century onward, until the early twentieth century, there were cultural taboos among certain communities from North Malabar, which forbade their women marrying people of the same respective communities, from the southern territories.[Fawcett (1901), Nayars of Malabar, AES Reprint 1985](_blank)
/ref>[https://books.google.com/books?hl=de&lr=&id=D27KRLsFNnAC&oi=fnd&pg=PP14&dq=Malabar+and+its+Folk+&ots=EDC3tVAOUl&sig=e6oL4t51asPD4q23Bu2B6CxCtko#v=onepage&q&f=false T.K.G. Panikkar (1900), Malabar and its Folk, AES Reprint 1995] Even in modern times it is not uncommon to see "alliances from Malabar region preferred" in newspaper matrimonial announcements placed by native North Malabar families, irrespective of their ethno-religious background. Traditionally North Malabar has remained the source of an erstwhile aristocracy for many of the southern territories of Kerala through displacement and adoptions including the Travancore Royal Family. Northern Malabar identity and pride is often possessively guarded by its natives of all ethnic and religious backgrounds.



Kottiyoor Utsavam
Kottiyoor Vysakha Mahotsavam is a 27-day yearly pilgrimage commemorating the mythology of Daksha Yaga, which attracts thousands of Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
pilgrims from the Malabar region.
Social, cultural and historical features
 In the pre-democratic era, Marumakkathayam- matriliniality was widely prevalent among the natives of North Malabar and included both the Muslim and Nambudiri communities of
In the pre-democratic era, Marumakkathayam- matriliniality was widely prevalent among the natives of North Malabar and included both the Muslim and Nambudiri communities of Payyanur
Payyanur, , is a municipal town and a taluk, a sub-district administrative unit, in the Kannur district of Kerala, India. On 10 March 2018, Kerala Chief Minister Pinarayi Vijayan inaugurated Payyanur as the fifth taluk in the district. Payyan ...
, in addition to other traditional matrilineal communities such as the Nair
The Nair , also known as Nayar, are a group of Indian Hindu castes, described by anthropologist Kathleen Gough as "not a unitary group but a named category of castes". The Nair include several castes and many subdivisions, not all of whom histo ...
and Thiyyas. Marumakkathayam was also practiced by the Nair
The Nair , also known as Nayar, are a group of Indian Hindu castes, described by anthropologist Kathleen Gough as "not a unitary group but a named category of castes". The Nair include several castes and many subdivisions, not all of whom histo ...
, Nambudiri
The Nambudiri (), also transliterated as Nampoothiri, Nambūdiri, Namboodiri, Nampoothiri, and Nampūtiri, are a Malayali Brahmin caste, native to what is now the state of Kerala, India, where they constituted part of the traditional feudal el ...
, and Mappila
Mappila Muslim, often shortened to Mappila, formerly anglicized as Moplah/Mopla and historically known as Jonaka/Chonaka Mappila or Moors Mopulars/Mouros da Terra and Mouros Malabares, in general, is a member of the Muslim community of same n ...
communities in the Ponnani region of South Malabar
South Malabar refers to a geographical area of the southwestern coast of India covering some parts of the present-day Kerala. South Malabar covers the regions included in present-day Kozhikode taluk of Kozhikode district, the whole area of Malap ...
.The practice of matrilineality was distinctly different and was predominantly virilocal with married couples residing with or near the husband's parents. Unlike other parts of erstwhile matrilineal-Kerala, polyandry was a strict taboo in North Malabar and exceptional customs such as ''Putravakaasham'' (purse/estate grants to children of male members) were occasionally allowed.
Landlords in Malabar during colonial and pre-colonial times were the largest landlords of Kerala and during this time political authority remained decentralized in contrast to that of the southern principalities. The royal position of Kolathiri
Kolathiri or Kolathiri Rājā (King of KolathunāduA. Shreedhara Menon (2007), ''A brief History of Kerala'', DC Books, Kottayam or King of Cannanore in foreign accounts) was the title by which the senior-most male along the matrilineal line of ...
, although immensely respected, was politically titular. In North Malabar, the Kolathiri Kings had the ritualistic status of Perumaal such that their official designates or ''sthanis'' retained their jurisdiction all over Kerala except for the Rajarajashwara Temple at Taliparamba.
The major festival observed by Hindus in this region is Vishu
Vishu (Malayalam: വിഷു), the traditional Malayali New Year, is a Hindu festival celebrated in the Indian state of Kerala, Tulu Nadu region of Karnataka, and Mahe district. The festival marks the first day of Medam, the first month of ...
rather than Onam
Onam ( ) is an annual Indian harvest festival celebrated predominantly by the Hindus of Kerala. A major annual event for Keralites, it is the official festival of the state and includes a spectrum of cultural events.
Onam commemorates Vamana ...
, which remains the major celebration for Hindus in the remainder of Kerala. In North Malabar, Vishu is celebrated as New Year. Because, the Kollavarsham month Medam - which is parallel to first Tamil month Chithirai - is the first month of the year for natives of North Malabar. The Vishu festival is spread over two days and comprises the ''Cheriya'' or small Vishu and the ''Valiya'', or main Vishu. Unlike in the rest of Kerala it is not uncommon to see Hindu natives of this region cook and eat non-vegetarian food during their festivals including Vishu and Onam and sometimes even in marriage households.
People from all religions participate in major festivals at temples, mosques and churches. Some examples include: Nadapuram Mosque, Mahe Church, Moonnu Pettumma Palli Pappinisseri
Pappinisseri is a census town and grama panchayat in Kannur district in the Indian state of Kerala. Pappinissery have consistently won the Swaraj Trophy for best Grama Panchayat from 2017-2018 to 2021. Pappinisseri Panchayat also bagged the thir ...
and Theyyam ritual art.
Unlike Travancore
The Kingdom of Travancore ( /ˈtrævənkɔːr/), also known as the Kingdom of Thiruvithamkoor, was an Indian kingdom from c. 1729 until 1949. It was ruled by the Travancore Royal Family from Padmanabhapuram, and later Thiruvananthapuram. At ...
, but like in rest of Malabar and Cochin
Kochi (), also known as Cochin ( ) ( the official name until 1996) is a major port city on the Malabar Coast of India bordering the Laccadive Sea, which is a part of the Arabian Sea. It is part of the district of Ernakulam in the state of K ...
, natives of North Malabar mix coconut paste with sambar, the most common dish of South India
South India, also known as Dakshina Bharata or Peninsular India, consists of the peninsular southern part of India. It encompasses the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana, as well as the union territ ...
.
North Malabar cuisine is noted for its variety of dishes including chutneys, pancakes, steamed cakes and various dishes such as '' kalathappam'', '' kinnathappam'', '' uruttu chammanthi'', '' poduthol'', '' pathiri'', '' chatti pathiri'' and ''moodakadamban''. Bakery-cuisine is well developed in the area and has led to large numbers of natives operating popular bakeries in Chennai
Chennai (, ), formerly known as Madras ( the official name until 1996), is the capital city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost Indian state. The largest city of the state in area and population, Chennai is located on the Coromandel Coast of th ...
, Bangalore
Bangalore (), List of renamed places in India, officially Bengaluru (), is the Capital city, capital and largest city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It has a population of more than and a metropolitan area, metropolitan population of a ...
, Mumbai
Mumbai (, ; also known as Bombay — List of renamed Indian cities and states#Maharashtra, the official name until 1995) is the capital city of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of Maharashtra and the ''de facto'' fin ...
, Coimbatore, Mysore
Mysore (), officially Mysuru (), is a city in the southern part of the state of Karnataka, India. Mysore city is geographically located between 12° 18′ 26″ north latitude and 76° 38′ 59″ east longitude. It is located at an altitude of ...
, Pune
Pune (; ; also known as Poona, ( the official name from 1818 until 1978) is one of the most important industrial and educational hubs of India, with an estimated population of 7.4 million As of 2021, Pune Metropolitan Region is the largest i ...
and Southern Kerala.
People from this area are characterized by a stronger sense of socio-political aspirations often leading to large outbreaks of political violence.
Textiles, beedi
A beedi (also spelled bidi or biri) is a thin cigarette or mini-cigar filled with tobacco flake and commonly wrapped in a tendu (''Diospyros melanoxylon'') or ''Piliostigma racemosum'' leaf tied with a string or adhesive at one end. It origi ...
, hand-weaving, plywood and coir
Coir (), also called coconut fibre, is a natural fibre extracted from the outer husk of coconut and used in products such as floor mats, doormats, brushes, and mattresses. Coir is the fibrous material found between the hard, internal shell an ...
represent important industries while cashew, cinnamon (North Malabar is home to Asia's largest cinnamon farm) and pepper
Pepper or peppers may refer to:
Food and spice
* Piperaceae or the pepper family, a large family of flowering plant
** Black pepper
* ''Capsicum'' or pepper, a genus of flowering plants in the nightshade family Solanaceae
** Bell pepper
** Chili ...
are important cash crops.
North Malabar represents one of the earliest and largest pockets of exposure to other cultures in Kerala through Chalukyas, Hoysala
The Hoysala Empire was a Kannadiga power originating from the Indian subcontinent that ruled most of what is now Karnataka between the 10th and the 14th centuries. The capital of the Hoysalas was initially located at Belur, but was later moved ...
s, Tuluva
The Tulu people or Tuluvas are an ethno-linguistic group from Southern India. They are native speakers of the Tulu language and the region they traditionally inhabit is known as Tulu Nadu. This region comprises the districts of Dakshina Kannada ...
s, Rashtrakutas, Kodavas, Tulus, Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
s, Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.
...
, Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
, Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
, French, British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
, and through early employment and migrations in government and military services from the time of its incorporation into the Madras Presidency. Nevertheless, its people are conservatively possessive of its identity preferring a "geographical endogamy" culture.

Calendar system
The version of the Malayalam calendar
The Malayalam Calendar is a sidereal solar calendar used in Kerala. The origin of the calendar has been dated to 825 CE, the beginning of the Kollam Era.
There are many theories regarding the origin of the era, but according to recent schola ...
or '' Kollavarsham '' used in central and south Kerala begins on August25, 825 AD. The year commences with ''Simha-raasi '' ( Leo) and not in ''Mesha-raasi'' ( Aries) as in other Indian calendars. However, in North Malabar and Kolathunadu the start of the Kollam era is reckoned from the month of ''Kanya-rasi'' (Virgo), which begins on 25 September. This variation has two accounts associated with it.[K.V Sarma (1996), Kollam era, Indian Journal of History of Science, 31 (1)]
'' Kerolopathi'', a traditional text dealing with the origins of Malabar, attributes the introduction of the Kollam era to Shankaracharya
Shankaracharya ( sa, शङ्कराचार्य, , " Shankara-''acharya''") is a religious title used by the heads of amnaya monasteries called mathas in the Advaita Vedanta tradition of Hinduism. The title derives from Adi Shankara; te ...
. Translation of the phrase ''Aa chaa rya vaa ga bhed ya'' (meaning Shankaracharya's word/law is unalterable) into numbers in the Katapayadi notation produces 0 6 1 4 3 4 1 and these written backwards give the age of the '' Kali Yuga'' in the first year of the Kollam era. ''Kali'', day 1,434,160, would work out to be September25, 825 AD, which corresponds to the beginning of the Kollam era in North Malabar, i.e. the first day of the month of ''Kanya-raasi'' (Virgo) .
Dialects
There are several dialects of the Malayalam language
Malayalam (; , ) is a Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry (Mahé district) by the Malayali people. It is one of 22 scheduled languages of India. Malayalam was d ...
prevalent in North Malabar. Loan words, excluding the significant number of words from Sanskrit, originated mostly due to centuries long interactions between the native population of North Malabar and the horse and spice traders of the world. These included trading contacts with Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plat ...
, Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
, China and European colonial powers for several centuries. Examples of these dialects include Kasaragod Malayalam and Mappila Malayalam. However, the majority of the young-adult Keralites from other provinces who are ignorant of the rich melting-pot culture of Malabar dialects are uncomfortable with these forms of Malayalam.
Image:Malik dinar mosque.jpg, Malik Deenar Mosque
Image:Big_hookah.jpg, The intricate work on a North Malabar Hookah
Image:PazhassiMemorial.JPG, Pazhassi Kudeeram in Mananthavadi
File:Ananteshwara Vinayaka Temple.jpg, Madhur Temple


Historic immigrations into North Malabar
Tulu Brahmin immigration
In 1617, the Kolathiri Raja Udayavarman, wished to attain the higher status of ''kshatriya
Kshatriya ( hi, क्षत्रिय) (from Sanskrit ''kṣatra'', "rule, authority") is one of the four varna (social orders) of Hindu society, associated with warrior aristocracy. The Sanskrit term ''kṣatriyaḥ'' is used in the con ...
'' by undergoing the Hiranyagarbham ritual in honour of Hiranyagarbha
Hiraṇyagarbha (Sanskrit: हिरण्यगर्भः ; literally the 'golden womb', poetically translated as 'universal womb') is the source of the creation of universe or the manifested cosmos in Vedic philosophy. It finds mention in on ...
, the creator of the universe. Since the Nambudiri Brahmins
The Nambudiri (), also transliterated as Nampoothiri, Nambūdiri, Namboodiri, Nampoothiri, and Nampūtiri, are a Malayali Brahmin caste, native to what is now the state of Kerala, India, where they constituted part of the traditional feudal el ...
were not prepared for the ceremony, Udayavarman brought 237 families of Shivalli Brahmins
The Shivalli Brahmins are a Hindu community in Karnataka. They are divided into two groups, the first of which follows the Dvaita philosophy founded by the Vaishnava saint Madhvacharya of Udupi are called Shivalli Madhva Brahmins, and the secon ...
from Gokarna in Coastal Karnataka and settled them in the five counties of Cheruthazham, Kunniriyam, Arathil, Kulappuram and Vararuchimangalam in North Malabar.[Chakrakshaalanapuram Brahmaswam Sabhaayogam Manual] The Sree Raghavapuram temple (Hanuman Kavu) at Pilathara was assigned to the 237 families for worship, and it became their village temple. The 93 Edukunchi families displaced as a result received the hereditary trusteeship of the Sreekrishnapuram temple in Cheruthazham, 62 Gunavantham families that of Arathil Sreebhadrapuram temple and the 82 Vilakkoor families that of Udayapurath Haripuram temple. These 237 families adopted the customs of local Nambudiri Brahmins and came to be referred to as Embranthiri
The Embrandiri (Malayalam: എമ്പ്രാന്തിരി), also transliterated as Embranthiri, are a Malayali Brahmin subcaste of Tulu origin.
Some sects of Embranthiris have adopted the Malayali Brahmin surnames "Namboothiri" and "Po ...
s.

Nasrani Migration
The Malabar Migration refers to the large-scale migration of Syrian Christians Syrian or Syriac Christians may refer to
* Adherents of Christianity in Syria
* Adherents of Syriac Christianity, various Christian bodies of Syriac traditions, especially:
** Syriac/Assyrian/Aramean people, Christian neo-Aramaic speakers through ...
(Nasranis) from the Travancore
The Kingdom of Travancore ( /ˈtrævənkɔːr/), also known as the Kingdom of Thiruvithamkoor, was an Indian kingdom from c. 1729 until 1949. It was ruled by the Travancore Royal Family from Padmanabhapuram, and later Thiruvananthapuram. At ...
region to the Malabar area of northern Kerala in the 20th century. The migration started in the decades of the 20th century and continued well into the 1970s and 1980s. This migration had a significant demographic and social impact as the Syrian Christian population of Malabar increased 15-fold from 31,191 in 1931 to in 1971.
Central Travancore had experienced a steep increase in population in the early 20th century while pressure on arable land increased. At the same time, people recognised the potential of the large uncultivated lands in the northern regions called Malabar, which was then part of the Madras Presidency under British Rule. Migration initially started in trickles with land bought from the local rulers. Huge tracts of uncultivated forest and waste land were later converted into farms and plantations. Against the odds, the community thrived, which attracted more migrants. This migration reached its peak in the 1950s.
These migrants came mostly from present day Kottayam
Kottayam () is a municipal town in the Indian state of Kerala. Flanked by the Western Ghats on the east and the Vembanad Lake and paddy fields of Kuttanad on the west. It is the district headquarters of Kottayam district, located in south- ...
, Idukki, Muvattupuzha
Muvattupuzha () is a town in the midlands directly to the east of Kochi in Ernakulam district, Kerala, India. It is located about from downtown Kochi, and is a growing urban centre in central Kerala. The town is also the starting po ...
and Kothamangalam
Kothamangalam, , is a municipality in Ernakulam district of Kerala, India. The town is in the foothills of the Western Ghats, and is a part of the Idukki Lok Sabha constituency.
The town serves as the headquarters of a taluk and a municipality ...
with migrations happening across the entire Malabar region (north Kerala) including into the following districts of present-day Kerala (some key migration centres are also mentioned):
*Kasaragod -Malom
Malom is a Hilly Town located on the slopes of Western Ghats in Maloth village Of vellarikundu in Kasaragod district of Kerala, India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of cou ...
, Kallar, Chittarikkal, Vellarikundu, Panathady, Panathur
Panathur is a major town in Vellarikundu Taluk of Kasaragod district in Kerala State, India. It belongs to Kanhangad legislative constituency. Its population is about 12,000. It lies 1 km away from Kerala - Karnataka border, 42 km awa ...
*Kannur - Alakkode, Chemperi, Cherupuzha, Kudianmala, Iritty
Iritty is a Municipality and a Taluk of Kannur district in Kerala State, India. The town is the main market place for the farmer communities in the surrounding regions. Iritty is known as The Coorg Valley in God's Own Country. Iritty is one of ...
, Peravoor, Payyavoor
Payyavoor is a village in Kannur district in the Indian state of Kerala. It's the headquarters of Payyavoor Grama Panchayat.
Demographics
As of 2011 Census, Payyavoor village had a population of 22,998 with 11,373 males and 11,625 females. ...
, Chempanthotty
*Calicut - Thiruvambady, Kuttiady
*Malapuram - Nilambur
Nilambur is a major town, a municipality and a Taluk in the Malappuram district of the Indian state of Kerala. It is located close to the Nilgiris range of the Western Ghats on the banks of the Chaliyar River. This place is also known as 'Teak ...
, Edakkara
Edakkara is a town located in Malappuram district of the Indian state of Kerala. It is an emerging commercial hub, and one of the busiest towns in Nilambur Taluk.
Location
Edakkara is located near Nilambur, Malappuram District, in the State of K ...
, Chungathara
Chungathara is a village panchayat in Nilambur Taluk in Malappuram district, Kerala, India. It is one of the smallest gramapnachayat in Kerala. It is surrounded by Western Ghats.
Geography
Two rivers, Chaliyar and Punnappuzha, pass throu ...
*Wayanad - Pulpally
Pulpally is a mid-sized town in Wayanad District of Kerala, India.Pulpally also known as 'The land of black gold'. Pulpally is also famous for its pure wild Wayanad honey. The only Seetha devi temple in Kerala is situated on Pulpally. Geographi ...
The Syro-Malabar Catholic Church gave significant support to the migration by providing churches, discipline, schools, hospitals and other infrastructure.
Overall, hundreds of thousands of people moved to North Kerala. The percentage of Christian residents in these districts was small before the migration but since 1950 this settler community has formed a significant part of the population in the hill areas of these districts.
Immigration of Knanaya Christians
 Historically, the North Malabar landlords were the largest land-holders in Kerala, but the introduction of the Kerala Land Reforms Bill in 1957 resulted in their panic selling of farm and forest land. This was followed by immigration of Christians from
Historically, the North Malabar landlords were the largest land-holders in Kerala, but the introduction of the Kerala Land Reforms Bill in 1957 resulted in their panic selling of farm and forest land. This was followed by immigration of Christians from Knanaya
The Knānāya, (from Syriac: ''Knā'nāya'' (Canaanite)) also known as the Southists or Tekkumbhagar, are an endogamous ethnic group found among the Saint Thomas Christian community of Kerala, India. They are differentiated from another part of ...
into the North Malabar Region in search of virgin land to cultivate and to seek relief from the poverty and financial strain caused by the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
. Under the direction of Prof. V.J. Joseph Kandoth and Bishop Mar Alexander Chulaparambil,[Fr. Jacob Vellian, Knanite Community, History and Culture][Kumbattu Varkey Joseph, Migration and economic development of Kerala] the Diocese of Kottayam bought of land in the Kasargod area in 1942. The new venture was announced in all the parishes of southern Kerala. Applications were invited and each family was allotted of land 1943. The emigrants from all southern Kerala parishes reached Cochin by boat and from there travelled by train to Shornur and Kanhangad
Kanhangad () is a town, located in the Kasaragod District, state of Kerala, India.
Location
The area contains villages around Kanhangad town with Kasaragod as the northern border, Nileshwar, popularly known as the 'cultural town' of Kasar ...
. A team of priests, especially of the O.S.H. Society and laymen were sent ahead to prepare the ground and to receive them on their arrival. The name of the local area was changed from Echikkol to Rajapuram. In the same way, the diocese organized another settlement at Madampam near Kannur
Kannur (), formerly known in English as Cannanore, is a city and a municipal corporation in the state of Kerala, India. It is the administrative headquarters of the Kannur district and situated north of the major port city and commercial hu ...
. The Diocese bought of land and 100 families migrated to the new area on 3 May 1943. The settlement was called Alexnagar after Bishop Mar Alexander Chulaparambil. Madathumala in Kasargod District
Kasaragod ( and Malayalam: , English: ''Kassergode'', Tulu: ''Kasrod'', Arabic: ''Harkwillia'') is one of the 14 districts in the southern Indian state of Kerala. Its northern border Thalappady is located just 10 km south to Ullal, whic ...
at its eastern border with the Karnataka
Karnataka (; ISO: , , also known as Karunāḍu) is a state in the southwestern region of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act. Originally known as Mysore State , it was renamed ''Karnat ...
state was the venue of a third settlement of 45 families. The land was purchased on 26September 1969 and the Ranipuram
Ranipuram (also known by its former name Madathumala) is a village and a major tourist attraction in the Kasaragod district of the Indian state of Kerala. It is located near Talakaveri Wildlife Sanctuary in Kerala-Karnataka border. Situated at a ...
settlement inaugurated on 2February 1970 dedicated to the Virgin Mary
Mary; arc, ܡܪܝܡ, translit=Mariam; ar, مريم, translit=Maryam; grc, Μαρία, translit=María; la, Maria; cop, Ⲙⲁⲣⲓⲁ, translit=Maria was a first-century Jewish woman of Nazareth, the wife of Joseph and the mother of ...
. Although there were initial difficulties due to wild animals, Ranipuram gradually prospered and today there is also a Government tourist center at Ranipuram. The Diocese of Kottayam made also arrangements with the Latin Ordinaries to have pastoral ministry and liturgical celebrations according to their own Syro-Malabar Rite. Presently, one third of the Knanaya Catholic population is in the Malabar area.
 In addition, taking advantage of the selling spree of landlords of Malabar in general and more particularly the larger landlords of North Malabar, several other
In addition, taking advantage of the selling spree of landlords of Malabar in general and more particularly the larger landlords of North Malabar, several other Travancore
The Kingdom of Travancore ( /ˈtrævənkɔːr/), also known as the Kingdom of Thiruvithamkoor, was an Indian kingdom from c. 1729 until 1949. It was ruled by the Travancore Royal Family from Padmanabhapuram, and later Thiruvananthapuram. At ...
Christian families immigrated into Malabar to pursue agriculture. These migrations peaked during 1960–71.
Immigration of teachers
The number of large land owning private- Tharavad-owned schools in North Malabar expanded in the first half of the twentieth century partly due to the availability of government grant-in-aid for such enterprises from 1939 onwards. Furthermore, corporate expansion of land owning Tharavads and a decrease in European engineered proletysing of the depressed classes also contributed to the growth pattern. These schools often had teaching staff from educated families.[Kerala Development Report by Government of India Planning Commission] In democratic Kerala however, many of these schools evolved as public and government enterprises, which led to the recruitment of teachers from the southern provinces and the subsequent immigration of teaching staff of all ethno-religious backgrounds, many of whom preferred to settle in the area permanently.
Historic emigrations to Southern Kerala
Historically significant emigration from North Malabar occurred in three phases.
Dispersement of the erstwhile ruling elite
From 1766 to 1792, during the era of Hyder Ali
Hyder Ali ( حیدر علی, ''Haidarālī''; 1720 – 7 December 1782) was the Sultan and ''de facto'' ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore in southern India. Born as Hyder Ali, he distinguished himself as a soldier, eventually drawing the at ...
and Tipu Sultan
Tipu Sultan (born Sultan Fateh Ali Sahab Tipu, 1 December 1751 – 4 May 1799), also known as the Tiger of Mysore, was the ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore based in South India. He was a pioneer of rocket artillery.Dalrymple, p. 243 He i ...
, multiple military invasions, plunder and systematic forcible religious conversions took place in both North and South Malabar.[ Malabar Manual by William Logan (Printed and published by Charitram Publications under the editorship of Dr. C.K, Kareem, Trivandrum)][Voyage to ]East Indies
The East Indies (or simply the Indies), is a term used in historical narratives of the Age of Discovery. The Indies refers to various lands in the East or the Eastern hemisphere, particularly the islands and mainlands found in and around ...
by Fra Bartolomaeo (Portuguese Traveller and Historian)[Historical Sketches by Col. Wilks, Vol. II.][A Journey from Madras through the counties of ]Mysore
Mysore (), officially Mysuru (), is a city in the southern part of the state of Karnataka, India. Mysore city is geographically located between 12° 18′ 26″ north latitude and 76° 38′ 59″ east longitude. It is located at an altitude of ...
, Canara
Kanara, also known as Karavali is the historically significant stretch of land situated by the southwestern coast of India, alongside the Arabian Sea in the present-day Indian state of Karnataka.
The region comprises three civil districts, ...
and Malabar by Dr. Francis Buchanan Hamilton, Vol. II.[Mysore History by Lewis Rice.][''Selected Letters of Tipu Sultan to various Functionaries'' by William Kirkpatrick, published in ]London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
, 1811.[History of Kerala by A. Sreedhara Menon.][History of Cochin State by K.P. Padmanabha Menon, ]Mathrubhumi
''Mathrubhumi'' is a Malayalam newspaper that is published from Kerala, India. It was founded by K. P. Kesava Menon, an active volunteer in the Indian freedom struggle against the British. The word "Mathrubhumi" translates to 'mother land'. ...
Publication, 1989.[''Cochin State Manual'' by C. Achuta Menon.][State Manual of Travancore by T.K. Velu Pillai.][Freedom Struggle in Kerala by Sardar K.M. Panicker.][Sakthan Thampuran by P. Raman Menon, Mathrubhoomi Publication, 1989.][Life of ]Raja Kesavadas
Kunnathur Kesavan Raman Pillai, also known as Raja Kesavadas (1745-1799; Sanskrit ') was the Dewan of Travancore during the reign of Dharma Raja Karthika Thirunal Rama Varma. He is well known for his military tactics and administrative acumen ...
by V.R. Parameswaran Pillai, N.B.S. Publications, Kottayam, 1973.[Chronicles and Reports originating from Trippunithura, Calicut, Palghat and other seats of Kerala Royal families and from Temples of Trichur and Carmichael Christian Mission, ]Varappuzha
Varappuzha, , (also known by its former name Verapoly) is a northern suburb of the city of Kochi. It is a census town in Paravur Taluk, Ernakulam district in the Indian state of Kerala. Situated around 15 km (9 mi) from the city centre ...
.[Bhasha Poshini of Chingam 10, 1099 (August 1923), Article on ]Tipu Sultan
Tipu Sultan (born Sultan Fateh Ali Sahab Tipu, 1 December 1751 – 4 May 1799), also known as the Tiger of Mysore, was the ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore based in South India. He was a pioneer of rocket artillery.Dalrymple, p. 243 He i ...
by Sardar
Sardar, also spelled as Sardaar/Sirdar ( fa, سردار, , 'commander', literally 'headmaster'), is a title of royalty and nobility that was originally used to denote princes, noblemen, chiefs, kings and other aristocrats. It has also been ...
K.M. Panicker.[Malabar Kalapam of 1921 by K. Madhavan Nair.][Travancore History by P. Sankrunni Menon.][Tipu Sultan X-rayed by Dr. I.M. Muthanna, Usha Press, Mysore 1980.][Articles, literary works etc. of ]Elamkulam Kunjan Pillai
Elamkulam P. N. Kunjan Pillai (8 November 1904 – 4 March 1973), known as Elamkulam, was an Indian historian, linguist and academic from southern Kerala, India. He was a pioneering scholar of southern Indian history, Kerala history, in partic ...
, Ulloor S. Parameswara Iyer, Vadakkumkoor Raja Raja Varma, and Shri Govinda Pillai.[''Zamorins in Kerala'' by K.V. Krishna Iyer.][Tipu Sultan by B.N. Jog.] Fearing forcible conversion, a significant number of Nair Chieftains and Brahmins from Malabar chose to take refuge in the erstwhile Kingdom of Travancore, as under the Treaty of Mangalore Travancore had an alliance with the English East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and South ...
according to which "aggression against Travancore would be viewed as equivalent to declaration of war against the English". Thus at various times between 1766 and 1792, all female members and many male members of the different royal families of North and South Malabar: Chirackal, Parappanad
Parappanad was a former feudal city-state in Malabar, India. The headquarters of Parappanad Royal family was at the town Parappanangadi in present-day Malappuram district. In 1425, the country divided into Northern Parappanad (Beypore kingdom) an ...
, and Calicut, and chieftains' families: Punnathoor, Nilambur
Nilambur is a major town, a municipality and a Taluk in the Malappuram district of the Indian state of Kerala. It is located close to the Nilgiris range of the Western Ghats on the banks of the Chaliyar River. This place is also known as 'Teak ...
, Kavalapara and Azhvanchery Thamprakkal
Azhvanchery Thamprakkal or Azhvanchery Samrāṭ is the title of the senior-most male member of the Brahmin (Namboothiri) feudal lords of Azhvanchery Mana in Athavanad, Tirur Taluk, present-day Malappuram district, Kerala state, South India. Th ...
(titular head of all Namboothiri Brahmins), sought asylum in Travancore and temporarily settled in different parts of the kingdom. Even after the fall of Tipu Sultan's regime in Srirangapatnam, some of the Malabar nobility, wholly or partly, preferred to remain in Travancore because of fear of atrocities if they returned home. The 17 prominent aristocratic lineages of southern Kerala that claim their origin from Malabar through displacement during this period are:
*Neerazhi Kovilakam
*Gramathil Kottaram
*Paliyakkara
*Nedumparampu
*Chempra Madham
*Ananthapuram Kottaram
*Ezhimatoor Palace
* Aranmula Kottaram
*Varanathu Kovilakam
*Mavelikkara
Mavelikkara is a taluk and municipality in the '' Onattukara'' region of Alappuzha district in the Indian state of Kerala. Located in the southern part of the district on the banks of the Achankovil River.
Etymology
The name Mavelikar ...
*Ennakkadu
*Murikkoyikkal Palace
*Mariappilly
*Koratti Swaroopam
*Kaippuzha Kovilakam
*Lakshmipuram Palace
* Kottapuram.

Adoptions by the erstwhile ruling elite
The Kolathiri
Kolathiri or Kolathiri Rājā (King of KolathunāduA. Shreedhara Menon (2007), ''A brief History of Kerala'', DC Books, Kottayam or King of Cannanore in foreign accounts) was the title by which the senior-most male along the matrilineal line of ...
s were a family descended from the Cheras and the Ay/Venad
Venad was a medieval kingdom lying between the Western Ghat mountains and the Arabian Sea on the south-western tip of India with its headquarters at the port city of Kollam/Quilon.Noburu Karashmia (ed.), A Concise History of South India: Is ...
/Travancore
The Kingdom of Travancore ( /ˈtrævənkɔːr/), also known as the Kingdom of Thiruvithamkoor, was an Indian kingdom from c. 1729 until 1949. It was ruled by the Travancore Royal Family from Padmanabhapuram, and later Thiruvananthapuram. At ...
Royal Family, that originated in the Thiruvananthapuram
Thiruvananthapuram (; ), also known by its former name Trivandrum (), is the capital of the Indian state of Kerala. It is the most populous city in Kerala with a population of 957,730 as of 2011. The encompassing urban agglomeration populati ...
area, and settled in the Kannur
Kannur (), formerly known in English as Cannanore, is a city and a municipal corporation in the state of Kerala, India. It is the administrative headquarters of the Kannur district and situated north of the major port city and commercial hu ...
region centuries ago. They had been a constant source of heirs for the Travancore royal family (and this practice of adoption was also reciprocal) by permitting some of its matrilineal branches of members to make settlements in Thiruvananthapuram and be adopted. The first adoption took place around 1310 whereby the two princesses of the Kolathiri family were installed as Senior and Junior Rānis of Attingal
Attingal is a municipality in Thiruvananthapuram metropolitan area in Thiruvananthapuram district of Kerala state, India. It was the location of the Attingal kingdom, under Travancore. It is the headquarters of Chirayinkeezhu Taluk, and the ...
, with the titles of Āttingal Mootha Thampurān and Āttingal Elaya Thampurān respectively. Adoptions into the Travancore Royal Family followed in 1684, 1688, 1718, 1748 and 1788 until the 19th century. The celebrated Mārthanda Varma the Great was a result of the 1688 adoption and his successor Dharmarājā, who fought and defeated Tipu Sultan of Mysore, was the result of the 1718 adoption. The weak Balarama Varma
Avittom Thirunal Bala Rama Varma (c. 17827 November 1810) was a ruler of the Indian princely state of Travancore from 1798 to 1810, succeeding his uncle Maharajah Dharma Raja on 12February 1798. His reign was a time of disturbances and inter ...
who ruled after Dharmarājā in the early 19th century belonged to the 1748 line. The noted Maharanis Gowri Lakshmi Bayi
Maharani Ayilyom Thirunal Gouri Lakshmi Bayi (1791–1815) was the Maharani of the Indian state of Travancore from 1810 till 1813 and Regent from 1813 till her death in 1815 for her son Swathi Thirunal Rama Varma. She was the only Queen of Travan ...
and Gowri Parvati Bayi
Uthrittathi Thirunal Gowri Parvathi Bayi (1802–1853) was the Regent of the Indian state of Travancore in 1815-1829. She succeeded her sister Maharani Gowri Lakshmi Bayi, till her regency was relinquished in favour of her nephew, Maharajah Sw ...
belonged to the 1788 line as did the Maharajahs Swāthi Thirunāl, Uthram Thirunāl, Āyilyam Thirunāl, Visākham Thirunāl and Moolam Thirunāl.
Economic migration in democratic India
In 1956, the State of Kerala was formed along linguistic lines, merging the Travancore, Cochin and Malabar regions. The first Kerala Legislative Assembly was formed on 1March 1957 and the following 50 years saw migration of lawyers, politicians, businessmen and government officials from North Malabar to the southern cities of Kerala especially Cochin
Kochi (), also known as Cochin ( ) ( the official name until 1996) is a major port city on the Malabar Coast of India bordering the Laccadive Sea, which is a part of the Arabian Sea. It is part of the district of Ernakulam in the state of K ...
and Trivandrum
Thiruvananthapuram (; ), also known by its former name Trivandrum (), is the capital of the Indian state of Kerala. It is the most populous city in Kerala with a population of 957,730 as of 2011. The encompassing urban agglomeration populatio ...
. However many of these families still retain their links to their native area through marriage association, partial retention of natal property and often a characteristic sacerdotal North Malabar self-identity.
Folk art
North Malabar has a rich history of folk-art, culture and tradition. The government of Kerala has encouraged promotion of these through the Kerala Folklore Academy
Kerala Folklore Academy is an autonomous center for cultural affairs constituted by the Government of Kerala and works under the Department of Cultural Affairs. It was established on 28 June 1995 to promote and project the traditional art forms ...
at Kannur. Among the notable examples are:
Theyyam
 Theyyam, an ancient ritual performance art of the region in which a man is dressed symbolically as god. In the Kadathanadan area, it is known as kaliyattam. There are around 400 types of Theyyam, which are conducted on a stage and use elaborate costumes and body-painting. Each type has a distinguishing head-dress and costume made from natural materials, such as coconut leaves and bark. Musical accompaniments are provided by the '' chenda'', ''elathalam'' and ''kuzhal'' (horn).
Theyyam, an ancient ritual performance art of the region in which a man is dressed symbolically as god. In the Kadathanadan area, it is known as kaliyattam. There are around 400 types of Theyyam, which are conducted on a stage and use elaborate costumes and body-painting. Each type has a distinguishing head-dress and costume made from natural materials, such as coconut leaves and bark. Musical accompaniments are provided by the '' chenda'', ''elathalam'' and ''kuzhal'' (horn).
Thottam Pattu
Thottam Pattu is ballad sung just before performance of the Theyyam ritual.
Kalaripayattu
Kalaripayattu is a martial art
Martial arts are codified systems and traditions of combat practiced for a number of reasons such as self-defense; military and law enforcement applications; competition; physical, mental, and spiritual development; entertainment; and the preserv ...
that originated in North Malabar and was developed between the 9th and 12th centuries.
Vadakkan Pattukal
The Vadakkan Pattukal are ballads that extol the adventures of the brave men and women of North Malabar. Set against a feudal medieval background, the stories celebrate the valour and skills of their characters. The ballads reflect the peak of Kerala folk-poetry and are associated with Kadathanadu. The movie ''Oru Vadakkan Veeragatha
''Oru Vadakkan Veeragatha'' () is a 1989 Indian Malayalam-language epic historical drama film directed by Hariharan, written by M. T. Vasudevan Nair, and starring Mammootty, Suresh Gopi, Balan K. Nair, Captain Raju and Madhavi. The film won ...
'' capitalised on the popularity of these stories.
Thidambu Nritham
Thidambu Nritham (dance with the replica of the deity) is a ritual dance performed in temples. It is mainly performed by Nambudiri
The Nambudiri (), also transliterated as Nampoothiri, Nambūdiri, Namboodiri, Nampoothiri, and Nampūtiri, are a Malayali Brahmin caste, native to what is now the state of Kerala, India, where they constituted part of the traditional feudal el ...
Brahmins and occasionally by other Brahmin communities.
Poorakkali
Poorakkali
Poorakkali (meaning Festival Performance) is a traditional dance ritual performed by men during the nine-day Pooram festival in Bhagavathy temples across North Malabar in Kerala State of south India.
The Pooram festival begins with the Kart ...
is a traditional art form performed by a group of men who dance and chant holy verses from the ''Ramayana
The ''Rāmāyana'' (; sa, रामायणम्, ) is a Sanskrit literature, Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epic composed over a period of nearly a millennium, with scholars' estimates for the earliest stage of the text ranging from the 8th ...
'' or '' Bhagavata''. It is performed during the nine-day Pooram festival in Bhagavathy temples. Payyannur, Trikaripur
Thrikaripur a small town located in south part of Kasaragod District in the state of Kerala, India. Its southernmost end Olavara touches Payyannur, Kannur District.
Demographics
The 2001 Census of India determined that the population of Trika ...
and nearby places like Vengara, Ramanthali, Karivellur, are well known for this art form.
Kolkali
Kolkali
Kolkali is a folk art performed in Malabar region of Kerala, India. The dance performers move in a circle, striking small sticks and keeping rhythm with special steps. The circle expands and contracts as the dance progress. The accompanying musi ...
is an art form involving both men and women which is also seen in South Malabar
South Malabar refers to a geographical area of the southwestern coast of India covering some parts of the present-day Kerala. South Malabar covers the regions included in present-day Kozhikode taluk of Kozhikode district, the whole area of Malap ...
too. It is the only folk art that is performed by both Hindus and Muslims, although there are slight differences in how the two do it. Muslims perform it as a form of entertainment during social gatherings and marriages, whereas the Hindus perform it at temple festivals. It involves rapid limb movements and simultaneous chanting of folksong, with the performers moving in pairs, hitting their batons (koles) against each other in a methodical way in tune with folksongs. It is played according to Vaithari or Thalam by the Gurukkal (Teacher).
The typical Kolkali group will contain between sixteen and twenty members. One among them will sing the folksong and it will be chorused by rest. Harmonizing with generational changes, Kolkali like all other folk-art of North Malabar, has also changed its look and style over time. The noted Kolkali groups are found in the Kasaragod District
Kasaragod ( and Malayalam: , English: ''Kassergode'', Tulu: ''Kasrod'', Arabic: ''Harkwillia'') is one of the 14 districts in the southern Indian state of Kerala. Its northern border Thalappady is located just 10 km south to Ullal, whi ...
.
Mappila (Muslim) folklore
Mappila folklore has deep roots in the region. The major Mappila arts of Malabar region
The Malabar Coast is the southwestern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Geographically, it comprises the wettest regions of southern India, as the Western Ghats intercept the moisture-laden monsoon rains, especially on their westward-facing m ...
(both North and South Malabar) are :
* Oppana
Oppana ( ml, ഒപ്പന) is a popular form of social entertainment among the Mappila (Kerala Muslims) community of Kerala, South India, prevalent throughout Kerala, especially in Malabar. The Term Oppana is believed to be originated from the ...
* Duff Muttu
Duffmuttu (also: Dubhmuttu) is an art form prevalent in the Malabar region of the states of Kerala and Karnataka in south India. It derives its name from the duff, a percussion instrument made of wood and ox skin. The word duff is of Arabic or ...
* Mappila Paattu
Mappila songs (or ''Mappila Paattu'') are a folklore Muslim song genre rendered to lyrics, within a melodic framework ( Ishal), in Arabi Malayalam by the Mappilas of the Malabar region in Kerala, India. Mappila songs have a distinct cultural i ...
Malabar Cuisine
The Malabar cuisine depicts it culture and heritage. Malabar cuisine is a blend of traditional Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South ...
, Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
, Yemenese and Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
food culture.mussels
Mussel () is the common name used for members of several families of bivalve molluscs, from saltwater and freshwater habitats. These groups have in common a shell whose outline is elongated and asymmetrical compared with other edible clams, which ...
) curry
A curry is a dish with a sauce seasoned with spices, mainly associated with South Asian cuisine. In southern India, leaves from the curry tree may be included.
There are many varieties of curry. The choice of spices for each dish in trad ...
, ''irachi puttu'' (''irachi'' meaning meat), ''parottas'' (soft flatbread),black pepper
Black pepper (''Piper nigrum'') is a flowering vine in the family Piperaceae, cultivated for its fruit, known as a peppercorn, which is usually dried and used as a spice and seasoning. The fruit is a drupe (stonefruit) which is about in dia ...
, cardamom
Cardamom (), sometimes cardamon or cardamum, is a spice made from the seeds of several plants in the genera ''Elettaria'' and ''Amomum'' in the family Zingiberaceae. Both genera are native to the Indian subcontinent and Indonesia. They are r ...
and clove are used profusely.
The Malabar version of ''biryani
Biryani () is a mixed rice dish originating among the Muslims of the Indian subcontinent. It is made with Indian spices, rice, and usually some type of meat ( chicken, beef, goat, lamb, prawn, fish) or in some cases without any meat, ...
'', popularly known as ''kuzhi mandi'' in Malayalam
Malayalam (; , ) is a Dravidian languages, Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry (union territory), Puducherry (Mahé district) by the Malayali people. It is one of 2 ...
is another popular item, which has an influence from Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
. Various varieties of ''biriyanis'' like Thalassery ''biriyani'', and Kannur ''biriyani'', are prepared in North Malabar.raisins
A raisin is a dried grape. Raisins are produced in many regions of the world and may be eaten raw or used in cooking, baking, and brewing. In the United Kingdom, Ireland, New Zealand, and Australia, the word ''raisin'' is reserved for the dar ...
and sugar),eggs
Humans and human ancestors have scavenged and eaten animal eggs for millions of years. Humans in Southeast Asia had domesticated chickens and harvested their eggs for food by 1,500 BCE. The most widely consumed eggs are those of fowl, especial ...
,
Notable individuals
* Kerala Varma Pazhassi (c. 1753 - c. 1805) popularly known as the Lion of Kerala, he was a prince from the royal dynasty of Kottayam (Malabar) which now belongs to the Kannur District of Kerala State. He waged war against Mysore and the British for 27 years.
* K. Kelappan - was the founder President of the Nair Service Society who later became the principal of a school run by the society. He fought for social reforms on the one hand and against the British on the other. He was a great revolutionary, social reformer and crusader for justice to the backward classes. He was called Kerala Gandhi.
* P. T. Usha- The first Indian sprinter to reach the Olympics. Winner of several gold medals in the Asian Games.
* Lt Gen Satish Nambiar
Lieutenant General Chenicheri Satish Nambiar is a retired Indian general. He was the first Force Commander and Head of Mission of UNPROFOR, the United Nations Protection Force in the former Yugoslavia during 1992-93. He is the elder brother of f ...
- recipient of a Vir Chakra
Vir Chakra (pronunciation: ʋ iː ɾ a tʃ a kɾa) is an Indian wartime military bravery award presented for acts of conspicuous gallantry in the presence of the enemy on the battlefield and is third in precedence in wartime gallantry awards a ...
and Force Commander of UNPROFOR
The United Nations Protection Force (UNPROFOR; also known by its French acronym FORPRONU: ''Force de Protection des Nations Unies'') was the first United Nations peacekeeping force in Croatia and in Bosnia and Herzegovina during the Yugoslav War ...
.
* E. K. Nayanar - (December 1918 - May 2004) born in Kalliasseri, Kannur was a prominent Indian political leader of the Communist Party of India (Marxist). He held the post of Chief Minister of Kerala three times. He was the longest-serving Chief Minister of Kerala, serving a total of 4009 days.
* K. Karunakaran - (July 1918 - December 2010) was an Indian politician from Chirakkal in the Kannur District. He held the post of Chief Minister of Kerala four times, making him the person who became the Chief Minister for the most number of times, and was also the second longest-serving Chief Minister of Kerala after Nayanar.
* Pinarayi Vijayan
Pinarayi Vijayan (; born 24 May 1945) is an Indian Communist politician who is the current Chief Minister of Kerala, serving since 25 May 2016. A member of the Politburo of the Communist Party of India (Marxist), he is the longest-serving sec ...
- veteran Communist leader, former State secretary of Communist Party of India (Marxist) and current Chief Minister of Kerala.
* Vijay K. Nambiar
Chenicheri Vijay Nambiar (born August 1943) is a retired Indian diplomat and served as the UN Secretary General's Special Advisor on Myanmar. He was Chef de Cabinet (Chief of Staff) under UN Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon from 1 January 2007 to F ...
- Former ambassador to China and Pakistan and former Chef de Cabinet
In several French-speaking countries and international organisations, a (French; literally 'head of office') is a senior civil servant or official who acts as an aide or private secretary to a high-ranking government figure, typically a minist ...
(Chief of Staff) under UN Secretary-General Ban Ki-Moon.
* Gireesh Puthenchery
Girish Puthenchery (1961–2010) was a noted Malayalam Lyricist, Poet, Scriptwriter and Screenwriter. He was always referred to as the aristocratic lyricist of Malayalam who had a distinctive writing style of his own. He also served as the dire ...
- Well known lyricist and screenwriter in the Malayalam film industry.
* T. V. Chandran - Well known director in the Malayalam film industry.
* Mavila Vishwanathan Nair - Banker.
* Vineeth
Vineeth Radhakrishnan (born 23 August 1969) is an Indian actor, classical dancer, voice artist and choreographer who primarily works in Malayalam, Tamil and Telugu language films. He has also starred in a few Kannada and Bollywood films. He h ...
- born on 23August 1969, a South Indian film actor and classical dancer.
* M. N. Nambiar - (1919—2008) film actor in Tamil cinema who spent more than 50 years in the film industry.
* Vengayil Kunhiraman Nayanar - (1861–1914) was a Malayali journalist, essay writer, critic and short story writer born into the chieftain family of "Vengayil", Chirakkal Taluk and was a close friend of Dr. Hermann Gundert
Hermann Gundert (Stuttgart, 4 February 1814 – 25 April 1893 in Calw, Germany) was a German missionary, scholar, and linguist, as well as the maternal grandfather of German novelist and Nobel laureate Hermann Hesse. Gundert is chiefly know ...
and William Logan, researchers on the history, language, culture of Kerala.
* Kannavath Sankaran Nambiar - Minister of Pazhassi Raja who was active in resistance to Mysorean and British invaders.
* Sreenivasan
Sreenivasan (born 6 April 1956) is an Indian actor, screenwriter, director, dubbing artist and producer who predominantly works in Malayalam cinema. Sreenivasan has starred in over 225 films. Sreenivasan wrote the screenplays of films such as ...
- Noted Malayalam actor and director.
* Samvrutha Sunil
Samvritha Sunil (born 31 October 1986) is an Indian actress who appears in Malayalam films. She made her debut in 2004 through the film ''Rasikan'' directed by Lal Jose before which she had also appeared as a junior artist in the film '' Ayal ...
- Noted Malayalam film heroine.
* Kavya Madhavan
Kavya Madhavan (born 19 September 1984) is a former Indian actress, who appeared predominantly in Malayalam films. She made her debut in 1991 as a child artist in '' Pookkalam Varavayi''. Her debut role as a lead actress was in Lal Jose's '' ...
- Popular Malayalam film actress.
* O. M. Nambiar - Renowned as an Indian athletics coach.
* M Kunjikannan - Kunjikannan Master, journalist, Gandhian, educational and social activist.
* Kodiyeri Balakrishnan - Home Minister
The Minister of Home Affairs (or simply, the Home Minister, short-form HM) is the head of the Ministry of Home Affairs of the Government of India. One of the senior-most officers in the Union Cabinet, the chief responsibility of the Home Minist ...
in the V.S. Achuthanandan ministry from 2006 to 2011, and current State secretary of Communist Party of India (Marxist).
* Kanayi Kunhiraman - Sculptor.
* M. Mukundan - Novelist and diplomat.
* K. Raghavan - Veteran Malayalam music director.
* Abu Salim (actor)
Abu Salim (born 1956) is an Indian actor in Malayalam movies, in which he has played villains roles and other characters. He has also acted in a few Tamil, Hindi, Kannada and Telugu films.
Early life and background
Abu Salim was born as the ...
- Popular film actor and Mr India Title winner in 1984 and 1992.
* C. P. Krishnan Nair - Internationally known businessman from the Leela Group of Hotels.
* Sanusha
Sanusha Santhosh is an Indian actress who works predominantly in Malayalam cinema.
Early life
She is from Pallikunnu, Kannur District, Kerala, she has studied at Sreepuram School, pallikunnu Kannur. After her graduation in B.Com. from S. N. ...
- Noted film actress.
* Anaswara Rajan - Noted film actress.
See also
* Malabar pepper
* Kolathiri
Kolathiri or Kolathiri Rājā (King of KolathunāduA. Shreedhara Menon (2007), ''A brief History of Kerala'', DC Books, Kottayam or King of Cannanore in foreign accounts) was the title by which the senior-most male along the matrilineal line of ...
* South Malabar
South Malabar refers to a geographical area of the southwestern coast of India covering some parts of the present-day Kerala. South Malabar covers the regions included in present-day Kozhikode taluk of Kozhikode district, the whole area of Malap ...
* North Malabar Gramin Bank
References
Further reading
General
* (The English translation of '' Tuhfat Ul Mujahideen'')
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Kasaragod region
*
*
*
*
*
{{Kerala topics
Regions of Kerala
Malabar Coast
 Between the 9th and 12th centuries, a dynasty called "Mushaka" controlled the Chirakkal areas of northern Malabar (the Wynad-Tellichery area was part of the Second Chera Kingdom). The Mushakas were probably the descendants of the ancient royal family of Nannan of Ezhi mala and were perhaps a vassal of the Cheras. The Kolla-desam (or the Mushika-rajya) came under the influence of the Chera/Perumals kingdom during eleventh century AD.Ganesh, K. N. (2009). ''Historical Geography of Natu in South India with Special Reference to Kerala.'' Indian Historical Review, 36(1), 3–21. The Chola references to several kings in medieval Kerala confirms that the power of the Chera/Perumal was restricted to the country around capital
Between the 9th and 12th centuries, a dynasty called "Mushaka" controlled the Chirakkal areas of northern Malabar (the Wynad-Tellichery area was part of the Second Chera Kingdom). The Mushakas were probably the descendants of the ancient royal family of Nannan of Ezhi mala and were perhaps a vassal of the Cheras. The Kolla-desam (or the Mushika-rajya) came under the influence of the Chera/Perumals kingdom during eleventh century AD.Ganesh, K. N. (2009). ''Historical Geography of Natu in South India with Special Reference to Kerala.'' Indian Historical Review, 36(1), 3–21. The Chola references to several kings in medieval Kerala confirms that the power of the Chera/Perumal was restricted to the country around capital 
 Until the 16th century CE, Kasargod town was known by the name ''Kanhirakode'' (may be by the meaning, 'The land of ''Kanhira'' Trees') in
Until the 16th century CE, Kasargod town was known by the name ''Kanhirakode'' (may be by the meaning, 'The land of ''Kanhira'' Trees') in 

 In 1761, the British captured Mahé, and the settlement was handed over to the ruler of
In 1761, the British captured Mahé, and the settlement was handed over to the ruler of  The East India Company captured the fort Kannur in 1790 and used it as one of their major military stations on the
The East India Company captured the fort Kannur in 1790 and used it as one of their major military stations on the  The socio-cultural background and geography of this area has some distinctions compared to the rest of Kerala.Eleanor Kathleen Gough (1900), Nayar: North Kerala, University of California Press, (Berkeley, Los Angeles)Eric J. Miller (1954), Caste and Territory in Malabar, American Anthropological AssociationPraveena Kodoth (1998), Women and Property Rights: A Study of Land Relations and Personal Law in Malabar, 1880–1940' Unpublished PhD Dissertation, Department of Economics, University of HyderabadRavindran Gopinath, 'Garden and Paddy Fields: Historical Implications of Agricultural Production Regimes in Colonial Malabar' in Mushirul Hasan and Narayani Gupta (eds.)India's Colonial Encounters: Essays in Memory of Eric Stokes, Delhi: Monohar Publishers, 1993M. Jayarajan, Sacred Groves of North Malabar, Discussion Paper No. 92
The socio-cultural background and geography of this area has some distinctions compared to the rest of Kerala.Eleanor Kathleen Gough (1900), Nayar: North Kerala, University of California Press, (Berkeley, Los Angeles)Eric J. Miller (1954), Caste and Territory in Malabar, American Anthropological AssociationPraveena Kodoth (1998), Women and Property Rights: A Study of Land Relations and Personal Law in Malabar, 1880–1940' Unpublished PhD Dissertation, Department of Economics, University of HyderabadRavindran Gopinath, 'Garden and Paddy Fields: Historical Implications of Agricultural Production Regimes in Colonial Malabar' in Mushirul Hasan and Narayani Gupta (eds.)India's Colonial Encounters: Essays in Memory of Eric Stokes, Delhi: Monohar Publishers, 1993M. Jayarajan, Sacred Groves of North Malabar, Discussion Paper No. 92


 In the pre-democratic era, Marumakkathayam- matriliniality was widely prevalent among the natives of North Malabar and included both the Muslim and Nambudiri communities of
In the pre-democratic era, Marumakkathayam- matriliniality was widely prevalent among the natives of North Malabar and included both the Muslim and Nambudiri communities of 

 Historically, the North Malabar landlords were the largest land-holders in Kerala, but the introduction of the Kerala Land Reforms Bill in 1957 resulted in their panic selling of farm and forest land. This was followed by immigration of Christians from
Historically, the North Malabar landlords were the largest land-holders in Kerala, but the introduction of the Kerala Land Reforms Bill in 1957 resulted in their panic selling of farm and forest land. This was followed by immigration of Christians from  Theyyam, an ancient ritual performance art of the region in which a man is dressed symbolically as god. In the Kadathanadan area, it is known as kaliyattam. There are around 400 types of Theyyam, which are conducted on a stage and use elaborate costumes and body-painting. Each type has a distinguishing head-dress and costume made from natural materials, such as coconut leaves and bark. Musical accompaniments are provided by the '' chenda'', ''elathalam'' and ''kuzhal'' (horn).
Theyyam, an ancient ritual performance art of the region in which a man is dressed symbolically as god. In the Kadathanadan area, it is known as kaliyattam. There are around 400 types of Theyyam, which are conducted on a stage and use elaborate costumes and body-painting. Each type has a distinguishing head-dress and costume made from natural materials, such as coconut leaves and bark. Musical accompaniments are provided by the '' chenda'', ''elathalam'' and ''kuzhal'' (horn).
