Islands of the Clyde on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


 The Islands of the Firth of Clyde are the fifth largest of the major Scottish island groups after the Inner and Outer Hebrides, Orkney and Shetland. They are situated in the
The Islands of the Firth of Clyde are the fifth largest of the major Scottish island groups after the Inner and Outer Hebrides, Orkney and Shetland. They are situated in the
The Holy Isle Project. Retrieved 12 May 2012. Unlike the isles in the four larger Scottish archipelagos, none of the isles in this group are connected to one another or to the mainland by bridges. The
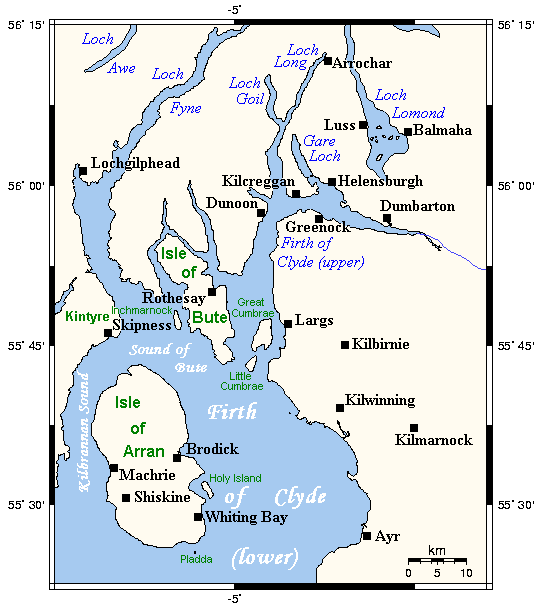 The
The
 The Firth of Clyde lies between 55 and 56 degrees north latitude. This is the same latitude as
The Firth of Clyde lies between 55 and 56 degrees north latitude. This is the same latitude as
Met Office. Retrieved 4 September 2009. Snow seldom lies at sea level, and frosts are generally less frequent than they are on the mainland. In common with most islands off the west coast of Scotland, the average annual rainfall is generally high: between on Bute, in the Cumbraes, and in the south of Arran, and in the north of Arran. The Arran mountains are even wetter: Their summits receive over of rain annually. May, June and July are the sunniest months: on average, there is a total of 200 hours of bright sunshine during that 3-month period each year. Southern Bute benefits from a particularly large number of sunny days.
 Mesolithic humans arrived in the area of the Firth of Clyde during the 4th millennium BC, probably from
Mesolithic humans arrived in the area of the Firth of Clyde during the 4th millennium BC, probably from
 Beginning in the 2nd century AD, Irish influence was at work in the region, and by the 6th century,
Beginning in the 2nd century AD, Irish influence was at work in the region, and by the 6th century,
 Beginning in the 9th century and into the 13th century, the Islands of the Clyde constituted a border zone between the Norse '' Suðreyjar'' and Scotland, and many of them were under Norse hegemony.
Beginning in the last half of the 12th century, and then into the early 1200s, the islands may well have served as the power base of Somhairle mac Giolla Brighde and his descendants. During this time, the islands seem to have come under the sway of the
Beginning in the 9th century and into the 13th century, the Islands of the Clyde constituted a border zone between the Norse '' Suðreyjar'' and Scotland, and many of them were under Norse hegemony.
Beginning in the last half of the 12th century, and then into the early 1200s, the islands may well have served as the power base of Somhairle mac Giolla Brighde and his descendants. During this time, the islands seem to have come under the sway of the
 Politically, from the conclusion of the
Politically, from the conclusion of the
 The islets that lie remote from the larger islands are described separately below.
There are two islets in Gare Loch: Green Island and Perch Rock. Gare Loch is small, but it hosts the
The islets that lie remote from the larger islands are described separately below.
There are two islets in Gare Loch: Green Island and Perch Rock. Gare Loch is small, but it hosts the
ladyisle.com. Quoting ''Geographical Collections relating to Scotland''. Vol.1, pages 412/3. Retrieved 14 October 2007. However, in June 1821, someone set fire to the "turf and pasture". Once the pasture had burned away, gales blew much of the island's soil into the sea. This permanently destroyed the island's ability to support grazing.
www.ladyisle.com. Retrieved 29 August 2010. There are no islands in Loch Goil or Loch Long, which are
 Around the Firth of Clyde, there are populations of
Around the Firth of Clyde, there are populations of
Arran Natural History Society. Retrieved 12 May 2012. Davaar is home to a population of wild
"Trees on Arran 'are a whole new species' "
Edinburgh. ''
(14 June 2007) BBC. Retrieved 18 January 2011.''New species of tree discovered on Arran''. Scottish Wildlife. November 2007, p. 9
 The
The
"Get-a-map"
Retrieved 1–31 August 2010. * Watson, W. J (1994) ''The Celtic Place-Names of Scotland''. Edinburgh. Birlinn. . First published 1926. {{Use dmy dates, date=August 2019

 The Islands of the Firth of Clyde are the fifth largest of the major Scottish island groups after the Inner and Outer Hebrides, Orkney and Shetland. They are situated in the
The Islands of the Firth of Clyde are the fifth largest of the major Scottish island groups after the Inner and Outer Hebrides, Orkney and Shetland. They are situated in the Firth of Clyde
The Firth of Clyde is the mouth of the River Clyde. It is located on the west coast of Scotland and constitutes the deepest coastal waters in the British Isles (it is 164 metres deep at its deepest). The firth is sheltered from the Atlantic ...
between Ayrshire and Argyll and Bute
Argyll and Bute ( sco, Argyll an Buit; gd, Earra-Ghàidheal agus Bòd, ) is one of 32 unitary authority council areas in Scotland and a lieutenancy area. The current lord-lieutenant for Argyll and Bute is Jane Margaret MacLeod (14 July 2020) ...
. There are about forty islands and skerries. Only four are inhabited, and only nine are larger than . The largest and most populous are Arran and Bute. They are served by dedicated ferry routes, as are Great Cumbrae
Great Cumbrae ( sco, Muckle Cumbrae; gd, Cumaradh Mòr; also known as Great Cumbrae Island, Cumbrae or the Isle of Cumbrae) is the larger of the two islands known as The Cumbraes in the lower Firth of Clyde in western Scotland. The island is ...
and Holy Island. "Destinations"Caledonian MacBrayne
Caledonian MacBrayne ( gd, Caledonian Mac a' Bhriuthainn), usually shortened to CalMac, is the major operator of passenger and vehicle ferries, and ferry services, between the mainland of Scotland and 22 of the major islands on Scotland's west ...
. Retrieved 22 January 2011."Getting Here"The Holy Isle Project. Retrieved 12 May 2012. Unlike the isles in the four larger Scottish archipelagos, none of the isles in this group are connected to one another or to the mainland by bridges. The
geology
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Ea ...
and geomorphology of the area is complex, and the islands and the surrounding sea lochs each have distinctive features. The influence of the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
and the North Atlantic Drift
The North Atlantic Current (NAC), also known as North Atlantic Drift and North Atlantic Sea Movement, is a powerful warm western boundary current within the Atlantic Ocean that extends the Gulf Stream northeastward.
The NAC originates from where ...
create a mild, damp oceanic climate. There is a diversity of wildlife, including three species of rare endemic trees.
The larger islands have been continuously inhabited since Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
times. The cultures of their inhabitants were influenced by the emergence of the kingdom of Dál Riata
Dál Riata or Dál Riada (also Dalriada) () was a Gaelic kingdom that encompassed the western seaboard of Scotland and north-eastern Ireland, on each side of the North Channel. At its height in the 6th and 7th centuries, it covered what is n ...
, beginning in 500 AD. The islands were then politically absorbed into the emerging kingdom of Alba
The Kingdom of Alba ( la, Scotia; sga, Alba) was the Kingdom of Scotland between the deaths of Donald II in 900 and of Alexander III in 1286. The latter's death led indirectly to an invasion of Scotland by Edward I of England in 1296 and the ...
, led by Kenneth MacAlpin
Kenneth MacAlpin ( mga, Cináed mac Ailpin, label= Medieval Gaelic, gd, Coinneach mac Ailpein, label=Modern Scottish Gaelic; 810 – 13 February 858) or Kenneth I was King of Dál Riada (841–850), King of the Picts (843–858), and the K ...
. During the early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
, the islands experienced Viking
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
incursions. In the 13th century, they became part of the Kingdom of Scotland
The Kingdom of Scotland (; , ) was a sovereign state in northwest Europe traditionally said to have been founded in 843. Its territories expanded and shrank, but it came to occupy the northern third of the island of Great Britain, sharing a l ...
.
Geology and geography
 The
The Highland Boundary Fault
The Highland Boundary Fault is a major fault zone that traverses Scotland from Arran and Helensburgh on the west coast to Stonehaven in the east. It separates two different geological terranes which give rise to two distinct physiographic terr ...
runs past Bute and through the northern part of Arran. Therefore, from a geological perspective, some of the islands are in the Highlands and some in the Central Lowlands
The Central Lowlands, sometimes called the Midland Valley or Central Valley, is a geologically defined area of relatively low-lying land in southern Scotland. It consists of a rift valley between the Highland Boundary Fault to the north and ...
. As a result of Arran's geological similarity to Scotland, it is sometimes referred to as "Scotland in miniature" and the island is a popular destination for geologist
A geologist is a scientist who studies the solid, liquid, and gaseous matter that constitutes Earth and other terrestrial planets, as well as the processes that shape them. Geologists usually study geology, earth science, or geophysics, althoug ...
s. They come to Arran to study its intrusive igneous landforms, such as sills and dykes, as well as its sedimentary
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles ...
and metasedimentary rocks, which range widely in age.McKirdy ''et al.'' (2007) pp. 297- 301 Visiting in 1787, the geologist James Hutton found his first example of an unconformity
An unconformity is a buried erosional or non-depositional surface separating two rock masses or strata of different ages, indicating that sediment deposition was not continuous. In general, the older layer was exposed to erosion for an interval ...
there. The spot where he discovered it is one of the most famous places in the history of the study of geology. The group of weakly metamorphosed rocks that form the Highland Border Complex lie discontinuously along the Highland Boundary Fault. One of the most prominent exposures is along Loch Fad on Bute. Ailsa Craig
Ailsa Craig (; sco, Ailsae Craig; gd, Creag Ealasaid) is an island of in the outer Firth of Clyde, west of mainland Scotland, upon which microgranite has long been quarried to make curling stones. The now-uninhabited island comprises the ...
, which lies some south of Arran, has been quarried for a rare type of micro-granite containing riebeckite
Riebeckite is a sodium-rich member of the amphibole group of silicate minerals, chemical formula Na2(Fe2+3Fe3+2)Si8O22(OH)2. It forms a solid solution series with magnesioriebeckite. It crystallizes in the monoclinic system, usually as long prisma ...
, known as "Ailsite". It is used by Kays of Scotland
Kays of Scotland is the only remaining UK manufacturer and supplier of curling stones. Founded in 1851, it retains exclusive rights to harvest granite from Ailsa Craig, granted by the Marquess of Ailsa. Kays of Scotland produces the only stone ...
to make curling
Curling is a sport in which players slide stones on a sheet of ice toward a target area which is segmented into four concentric circles. It is related to bowls, boules, and shuffleboard. Two teams, each with four players, take turns slidi ...
stones. (As of 2004, 60 to 70% of all curling stones in use globally were made from granite quarried on the island.)
Like the rest of Scotland, the Firth of Clyde was covered by ice sheets during the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in ...
ice ages
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and gree ...
, and the landscape has been much affected by glaciation
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate be ...
. Back then, Arran's highest peaks may have been nunataks. Sea-level changes and the isostatic rise of land after the last retreat of the ice created clifflines behind raised beach
A raised beach, coastal terrace,Pinter, N (2010): 'Coastal Terraces, Sealevel, and Active Tectonics' (educational exercise), from 2/04/2011/ref> or perched coastline is a relatively flat, horizontal or gently inclined surface of marine origin,P ...
es, which are a prominent feature of the entire coastline. The action of these forces has made charting the post glacial coastlines a complex task.
The various soil types on the islands reflect their diverse geology. Bute has the most productive land, and it has a pattern of deposits that is typical of the southwest of Scotland. In the eroded valleys, there is a mixture of boulder clay
Boulder clay is an unsorted agglomeration of clastic sediment that is unstratified and structureless and contains gravel of various sizes, shapes, and compositions distributed at random in a fine-grained matrix. The fine-grained matrix consists o ...
and other glacial deposits. Elsewhere, especially to the south and west, there are raised beach- and marine deposits, which in some places, such as Stravanan, result in a machair
A machair (; sometimes machar in English) is a fertile low-lying grassy plain found on part of the northwest coastlines of Ireland and Scotland, in particular the Outer Hebrides. The best examples are found on North and South Uist, Harri ...
landscape inland from the sandy bays.
The Firth of Clyde, in which these islands lie, is north of the Irish Sea and has numerous branching inlets. Some of those inlets, including Loch Goil, Loch Long
Loch Long is a body of water in Argyll and Bute, Scotland. The Sea Loch extends from the Firth of Clyde at its southwestern end. It measures approximately in length, with a width of between . The loch also has an arm, Loch Goil, on its west ...
, Gare Loch
The Gare Loch or Gareloch ( gd, An Gearr Loch) is an open sea loch in Argyll and Bute, Scotland and bears a similar name to the village of Gairloch in the north west Highlands.
The loch is well used for recreational boating, water sports and f ...
, Loch Fyne
Loch Fyne ( gd, Loch Fìne, ; meaning "Loch of the Vine/Wine"), is a sea loch off the Firth of Clyde and forms part of the coast of the Cowal peninsula. Located on the west coast of Argyll and Bute, Scotland. It extends inland from the Soun ...
, and the estuary of the River Clyde, have their own substantial features. In places, the effect of glaciation on the seabed is pronounced. For example, the Firth is deep between Arran and Bute, even though they are only apart. The islands all stand exposed to wind and tide. Various lighthouses, such as those on Ailsa Craig, Pladda, and Davaar, act as an aid to navigation.
Climate
 The Firth of Clyde lies between 55 and 56 degrees north latitude. This is the same latitude as
The Firth of Clyde lies between 55 and 56 degrees north latitude. This is the same latitude as Labrador
, nickname = "The Big Land"
, etymology =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Canada
, subdivision_type1 = Province
, subdivision_name1 ...
in Canada and north of the Aleutian Islands
The Aleutian Islands (; ; ale, Unangam Tanangin,”Land of the Aleuts", possibly from Chukchi ''aliat'', "island"), also called the Aleut Islands or Aleutic Islands and known before 1867 as the Catherine Archipelago, are a chain of 14 large v ...
. However, the influence of the North Atlantic Drift
The North Atlantic Current (NAC), also known as North Atlantic Drift and North Atlantic Sea Movement, is a powerful warm western boundary current within the Atlantic Ocean that extends the Gulf Stream northeastward.
The NAC originates from where ...
—the northern extension of the Gulf Stream—moderates the winter weather. As a result, the area enjoys a mild, damp oceanic climate. Temperatures are generally cool, averaging about in January and in July at sea level."Regional mapped climate averages"Met Office. Retrieved 4 September 2009. Snow seldom lies at sea level, and frosts are generally less frequent than they are on the mainland. In common with most islands off the west coast of Scotland, the average annual rainfall is generally high: between on Bute, in the Cumbraes, and in the south of Arran, and in the north of Arran. The Arran mountains are even wetter: Their summits receive over of rain annually. May, June and July are the sunniest months: on average, there is a total of 200 hours of bright sunshine during that 3-month period each year. Southern Bute benefits from a particularly large number of sunny days.
History
Prehistory
 Mesolithic humans arrived in the area of the Firth of Clyde during the 4th millennium BC, probably from
Mesolithic humans arrived in the area of the Firth of Clyde during the 4th millennium BC, probably from Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
. This initial arrival was followed by another wave of Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
peoples using the same route. In fact, there is some evidence that the Firth of Clyde was a significant route through which mainland Scotland was colonised during the Neolithic period. The inhabitants of Argyll, the Clyde estuary, and elsewhere in western Scotland at that time developed a distinctive style of megalithic structure that is known today as the Clyde cairns. About 100 of these structures have been found. They were used for interment of the dead. They are rectangular or trapezoidal, with a small enclosing chamber into which the person's body was placed. They are faced with large slabs of stone set on end (sometimes subdivided into smaller compartments). They also feature a forecourt area, which may have been used for displays or rituals associated with interment.Noble (2006) pp. 104–05 They are mostly found in Arran, Bute, and Kintyre. It is thought likely that the Clyde cairns were the earliest forms of Neolithic monument constructed by incoming settlers. However, only a few of the cairns have been radiocarbon dated
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon.
The method was dev ...
. A cairn at Monamore on Arran has been dated to 3160 BC, although other evidence suggests that it was almost certainly built earlier than that, possibly around 4000 BC.Murray (1973) pp. 113–131 The area also features numerous standing stones dating from prehistoric times, including six stone circles on Machrie Moor in Arran, and other examples on Great Cumbrae and Bute.Cowie, Trevor "The Bronze Age" in Omand (2006) pp. 27–30
Later, Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
settlers also constructed megaliths at various sites. Many of them date from the 2nd millennium BC. However, instead of chambered cairns, these peoples constructed burial cist
A cist ( or ; also kist ;
from grc-gre, κίστη, Middle Welsh ''Kist'' or Germanic ''Kiste'') is a small stone-built coffin-like box or ossuary used to hold the bodies of the dead. Examples can be found across Europe and in the Middle Ea ...
s, which can be found, for example, on Inchmarnock. Evidence of settlement during this period, especially the early part of it, is scant. However, one notable artifact has been found on Bute that dates from around 2000 BC. Known today as the “Queen of the Inch necklace,” it is an article of jewellery made of lignite (commonly called “jet”).
During the early Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostl ...
, the Brython
The Britons ( *''Pritanī'', la, Britanni), also known as Celtic Britons or Ancient Britons, were people of Celtic language and culture who inhabited Great Britain from at least the British Iron Age and into the Middle Ages, at which point the ...
ic culture held sway. There is no evidence that the Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
occupation of southern Scotland extended into these islands.
Early Scots rule
 Beginning in the 2nd century AD, Irish influence was at work in the region, and by the 6th century,
Beginning in the 2nd century AD, Irish influence was at work in the region, and by the 6th century, Gaels
The Gaels ( ; ga, Na Gaeil ; gd, Na Gàidheil ; gv, Ny Gaeil ) are an ethnolinguistic group native to Ireland, Scotland and the Isle of Man in the British Isles. They are associated with the Gaelic languages: a branch of the Celtic langu ...
had established the kingdom of Dál Riata
Dál Riata or Dál Riada (also Dalriada) () was a Gaelic kingdom that encompassed the western seaboard of Scotland and north-eastern Ireland, on each side of the North Channel. At its height in the 6th and 7th centuries, it covered what is n ...
there. Unlike earlier inhabitants, such as the P-Celtic
The Gallo-Brittonic languages, also known as the P-Celtic languages, are a subdivision of the Celtic languages of Ancient Gaul (both '' celtica'' and '' belgica'') and Celtic Britain, which share certain features. Besides common linguistic in ...
speaking Brythons, these Gaels spoke a form of Gaelic (a modern version of which is still spoken today in the Hebrides
The Hebrides (; gd, Innse Gall, ; non, Suðreyjar, "southern isles") are an archipelago off the west coast of the Scottish mainland. The islands fall into two main groups, based on their proximity to the mainland: the Inner and Outer Hebr ...
). During this period, through the efforts of Saint Ninian
Ninian is a Christian saint, first mentioned in the 8th century as being an early missionary among the Pictish peoples of what is now Scotland. For this reason he is known as the Apostle to the Southern Picts, and there are numerous dedicatio ...
and others, Christianity slowly supplanted Druidism. The kingdom of Dál Riata flourished from the rule of Fergus Mór
Fergus Mór mac Eirc ( gd, Fearghas Mòr Mac Earca; English: ''Fergus the Great'') was a possible king of Dál Riata. He was the son of Erc of Dalriada.
While his historicity may be debatable, his posthumous importance as the founder of Scotl ...
in the late 5th century until the Viking
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
incursions beginning in the late 8th century. Islands close to the shores of modern Ayrshire presumably remained part of the Kingdom of Strathclyde
Strathclyde (lit. " Strath of the River Clyde", and Strað-Clota in Old English), was a Brittonic successor state of the Roman Empire and one of the early medieval kingdoms of the Britons, located in the region the Welsh tribes referred to as ...
during this period, whilst the main islands became part of the emerging Kingdom of Alba
The Kingdom of Alba ( la, Scotia; sga, Alba) was the Kingdom of Scotland between the deaths of Donald II in 900 and of Alexander III in 1286. The latter's death led indirectly to an invasion of Scotland by Edward I of England in 1296 and the ...
founded by Kenneth MacAlpin (Cináed mac Ailpín).
Viking influence
 Beginning in the 9th century and into the 13th century, the Islands of the Clyde constituted a border zone between the Norse '' Suðreyjar'' and Scotland, and many of them were under Norse hegemony.
Beginning in the last half of the 12th century, and then into the early 1200s, the islands may well have served as the power base of Somhairle mac Giolla Brighde and his descendants. During this time, the islands seem to have come under the sway of the
Beginning in the 9th century and into the 13th century, the Islands of the Clyde constituted a border zone between the Norse '' Suðreyjar'' and Scotland, and many of them were under Norse hegemony.
Beginning in the last half of the 12th century, and then into the early 1200s, the islands may well have served as the power base of Somhairle mac Giolla Brighde and his descendants. During this time, the islands seem to have come under the sway of the Steward of Scotland
The title of High Steward or Great Steward is that of an officer who controls the domestic affairs of a royal household. In the 12th century King David I of Scotland gave the title to Walter fitz Alan, a nobleman from Brittany, whose descenda ...
’s authority and to have been taken over by the expanding Stewart lordship.
This western extension of Scottish authority appears to have been one of the factors motivating the Norwegian invasion of the region in 1230, during which the invaders seized Rothesay Castle
Rothesay Castle is a ruined castle in Rothesay, the principal town on the Isle of Bute, in western Scotland. Located at , the castle has been described as "one of the most remarkable in Scotland", for its long history dating back to the beginn ...
.
In 1263, Norwegian troops commanded by Haakon Haakonarson
Haakon IV Haakonsson ( – 16 December 1263; Old Norse: ''Hákon Hákonarson'' ; Norwegian: ''Håkon Håkonsson''), sometimes called Haakon the Old in contrast to his namesake son, was King of Norway from 1217 to 1263. His reign lasted for 46 y ...
repeated the feat, but the ensuing Battle of Largs between Scots and Norwegian forces, which took place on the shores of the Firth of Clyde, was inconclusive as a military contest.
This battle marked an ultimately fatal weakening of Norwegian power in Scotland. Haakon retreated to Orkney, where he died in December 1263, consoled on his death bed by recitations of the old sagas. Following his death, under the 1266 Treaty of Perth
The Treaty of Perth, signed 2 July 1266, ended military conflict between Magnus VI of Norway and Alexander III of Scotland over possession of the Hebrides and the Isle of Man. The text of the treaty.
The Hebrides and the Isle of Man had becom ...
, all rights that the Norwegian Crown "had of old therein" in relation to the islands were yielded to the Kingdom of Scotland.
Modern Scotland
 Politically, from the conclusion of the
Politically, from the conclusion of the Treaty of Perth
The Treaty of Perth, signed 2 July 1266, ended military conflict between Magnus VI of Norway and Alexander III of Scotland over possession of the Hebrides and the Isle of Man. The text of the treaty.
The Hebrides and the Isle of Man had becom ...
in 1266 to the present day, all of the islands of the Clyde have been part of Scotland.
Ecclesiastically, beginning in the early medieval period all of these isles were part of the Diocese of Sodor and Man
The Diocese of Sodor and Man is a diocese of the Church of England. Originally much larger, today it covers just the Isle of Man and its adjacent islets. Today, the bishop's office is in Douglas and the cathedral is in Peel. The diocese is ''not ...
, based at Peel, on the Isle of Man
)
, anthem = "O Land of Our Birth"
, image = Isle of Man by Sentinel-2.jpg
, image_map = Europe-Isle_of_Man.svg
, mapsize =
, map_alt = Location of the Isle of Man in Europe
, map_caption = Location of the Isle of Man (green)
in Europe ...
. After 1387, the seat of the Bishopric of the Isles was relocated to the north, first to Snizort on Skye and then to Iona. This arrangement continued until the Scottish Reformation
The Scottish Reformation was the process by which Scotland broke with the Papacy and developed a predominantly Calvinist national Kirk (church), which was strongly Presbyterian in its outlook. It was part of the wider European Protestant Refor ...
in the 16th century, when Scotland broke with the Catholic Church.
The mid-1700s marked the beginning of a century of significant change. New forms of transport, industry, and agriculture brought an end to ways of life that had endured for centuries. The Battle of Culloden in 1746 foreshadowed the end of the clan system. These changes improved living standards for some, but came at a cost for others.
In the late 18th and early 19th centuries, Alexander, the 10th Duke of Hamilton (1767–1852), and others implemented a controversial agricultural-reform programme called the Highland Clearances that had a devastating effect on many of Arran's inhabitants. Whole villages were emptied, and the Gaelic culture of the island was dealt a terminal blow. (A memorial to the tenant farmers evicted from the island by this programme was later erected on the shore at Lamlash, funded by a Canadian descendant of some of those evicted.)
From the 1850s to the late 20th century, cargo ships known as “Clyde Puffer
The Clyde puffer is a type of small coal-fired and single-masted cargo ship, built mainly on the Forth and Clyde canal, and which provided a vital supply link around the west coast and Hebrides of Scotland.
Built between 1856 and 1939, these stu ...
s” (made famous by an early-20th-century story collection called the ''Vital Spark
The ''Vital Spark'' is a fictional Clyde puffer, created by Scottish writer Neil Munro (writer), Neil Munro. As its captain, the redoubtable Para Handy, often says: "the smertest boat in the coastin' tred".
Background
Puffers seem to have been ...
''), were the workhorses of the islands, carrying a great deal of produce and a great variety of products to and from the islands. In May 1889, the Caledonian Steam Packet Company (CSP) was founded and began operating steamer services to and from Gourock for the Caledonian Railway
The Caledonian Railway (CR) was a major Scottish railway company. It was formed in the early 19th century with the objective of forming a link between English railways and Glasgow. It progressively extended its network and reached Edinburgh an ...
. The company soon expanded by taking over rival steamer operators. David MacBrayne
David MacBrayne is a limited company owned by the Scottish Government. Formed in 1851 as the private shipping company David Hutcheson & Co. with three partners, David Hutcheson, Alexander Hutcheson and David MacBrayne, it passed in 1878 to David ...
operated the Glasgow-to- Ardrishaig steamer service, as part of the so-called "Royal Route" to Oban. During the 20th century, many of the islands were developed as tourist resorts along the lines of mainland resorts such as Largs
Largs ( gd, An Leargaidh Ghallda) is a town on the Firth of Clyde in North Ayrshire, Scotland, about from Glasgow. The original name means "the slopes" (''An Leargaidh'') in Scottish Gaelic.
A popular seaside resort with a pier, the town mark ...
and Troon
Troon is a town in South Ayrshire, situated on the west coast of Ayrshire in Scotland, about north of Ayr and northwest of Glasgow Prestwick Airport.
Troon has a port with freight services and a yacht marina. Up until January 2016, P&O ope ...
, but catering for Glaswegians who preferred to holiday "Doon the Watter".
In 1973, CSP and MacBraynes combined their Clyde and West Highland operations under the new name of Caledonian MacBrayne
Caledonian MacBrayne ( gd, Caledonian Mac a' Bhriuthainn), usually shortened to CalMac, is the major operator of passenger and vehicle ferries, and ferry services, between the mainland of Scotland and 22 of the major islands on Scotland's west ...
. A government-owned corporation
A state-owned enterprise (SOE) is a government entity which is established or nationalised by the ''national government'' or ''provincial government'' by an executive order or an act of legislation in order to earn profit for the governmen ...
, they serve Great Cumbrae, Arran, and Bute, and also run mainland-to-mainland ferries across the firth. Private companies operate services from Arran to Holy Isle, and from McInroy's Point (Gourock) to Hunter's Quay on the Cowal peninsula.
Politically, from 1890 to 1975, most of the islands comprised the traditional County of Bute
The County of Bute ( gd, Siorrachd Bhòid), also known as Buteshire, is a historic county and registration county of Scotland.
The county comprises a number of islands in the Firth of Clyde, between the counties of Argyll and Ayrshire, the p ...
, and its inhabitants were represented by the county council. Since the 1975 reorganization, however, the islands have been split more or less equally between two modern council authorities: Argyll and Bute
Argyll and Bute ( sco, Argyll an Buit; gd, Earra-Ghàidheal agus Bòd, ) is one of 32 unitary authority council areas in Scotland and a lieutenancy area. The current lord-lieutenant for Argyll and Bute is Jane Margaret MacLeod (14 July 2020) ...
, and North Ayrshire. Only Ailsa Craig
Ailsa Craig (; sco, Ailsae Craig; gd, Creag Ealasaid) is an island of in the outer Firth of Clyde, west of mainland Scotland, upon which microgranite has long been quarried to make curling stones. The now-uninhabited island comprises the ...
and Lady Isle in South Ayrshire are not part of either of these two council areas
For local government purposes, Scotland is divided into 32 areas designated as "council areas" ( gd, comhairlean), which are all governed by single-tier authorities designated as "councils". They have the option under the Local Government (Ga ...
.
Islands
Below is a table listing the nine islands of the Firth of Clyde that have an area greater than 40 hectares (approximately 100 acres), showing their population and listing the smaller uninhabited islets adjacent to them (including tidal islets separated only when the tide is higher, and skerries exposed only when the tide is lower). As of 2001, six of the islands were inhabited, but that included one with only two residents ( Davaar), and one with only one resident ( Sanda).. At the 2011 census, there was no one usually resident on either of these islands.Outlying islands
 The islets that lie remote from the larger islands are described separately below.
There are two islets in Gare Loch: Green Island and Perch Rock. Gare Loch is small, but it hosts the
The islets that lie remote from the larger islands are described separately below.
There are two islets in Gare Loch: Green Island and Perch Rock. Gare Loch is small, but it hosts the Faslane Naval Base
His Majesty's Naval Base, Clyde (HMNB Clyde; also HMS ''Neptune''), primarily sited at Faslane on the Gare Loch, is one of three operating bases in the United Kingdom for the Royal Navy (the others being HMNB Devonport and HMNB Portsmouth). It ...
, where the UK's Trident nuclear submarines are located. At its southern end, the loch opens into the Firth of Clyde
The Firth of Clyde is the mouth of the River Clyde. It is located on the west coast of Scotland and constitutes the deepest coastal waters in the British Isles (it is 164 metres deep at its deepest). The firth is sheltered from the Atlantic ...
via the Rhu narrows.
There are also several islets in the Kilbrannan Sound
Kilbrannan Sound (Scottish Gaelic: ''An Caolas Branndanach'') is a marine water body that separates the Kintyre Peninsula of Scotland from the island of Arran. Kilbrannan Sound is the western arm of the Firth of Clyde.
See also
* Dippen Bay
D ...
, which lies between Arran and the Kintyre
Kintyre ( gd, Cinn Tìre, ) is a peninsula in western Scotland, in the southwest of Argyll and Bute. The peninsula stretches about , from the Mull of Kintyre in the south to East and West Loch Tarbert in the north. The region immediately nor ...
peninsula. They are: An Struthlag, Cour Island, Eilean Carrach ( Carradale), Eilean Carrach ( Skipness), Eilean Grianain, Eilean Sunadale, Gull Isle, Island Ross and Thorn Isle.
(The Norse sagas tell a story about the Kintyre peninsula. In the late 11th century, a king of Norway
The Norwegian monarch is the head of state of Norway, which is a constitutional and hereditary monarchy with a parliamentary system. The Norwegian monarchy can trace its line back to the reign of Harald Fairhair and the previous petty kingd ...
(Magnus Barefoot
Magnus Olafsson (Old Norse: ''Magnús Óláfsson'', Norwegian: ''Magnus Olavsson''; 1073 – 24 August 1103), better known as Magnus Barefoot (Old Norse: ''Magnús berfœttr'', Norwegian: ''Magnus Berrføtt''), was King of Norway (being Ma ...
) devised a plan to increase his territorial possessions. He persuaded a king of Scotland ( Malcolm III or Edgar) to agree that he could take possession of an area of land on the west coast of Scotland if a ship could sail around it. Magnus then arranged for one of his longship
Longships were a type of specialised Scandinavian warships that have a long history in Scandinavia, with their existence being archaeologically proven and documented from at least the fourth century BC. Originally invented and used by the Nors ...
s to be dragged across the -long isthmus at the northern tip of the Kintyre peninsula, which connects Kintyre to the mainland. (The isthmus lies between East Loch Tarbert and West Loch Tarbert
West Loch Tarbert ( gd, Loch A Siar) is a sea loch that separates the northern and southern parts of Harris in the Outer Hebrides of Scotland. A small isthmus joins these two areas, on which is to be found the village of Tarbert. The loch contai ...
). He took command of the ship's tiller himself. Then, declaring that Kintyre had "better land than the best of the Hebrides
The Hebrides (; gd, Innse Gall, ; non, Suðreyjar, "southern isles") are an archipelago off the west coast of the Scottish mainland. The islands fall into two main groups, based on their proximity to the mainland: the Inner and Outer Hebr ...
", he claimed that dragging his ship across the isthmus had been equivalent to “sailing around” the peninsula, and thus that the peninsula counted as “land around which a ship could sail.” As a result of this maneuver, he was able to claim possession of the peninsula, which remained under Norse rule for more than a dozen years.)
There are also several islets and skerries in Loch Fyne, which extends inland from the Sound of Bute, and is the longest of Scotland's sea lochs. They are: Duncuan Island, Eilean Ardgaddan, Eilean a' Bhuic, Eilean Aoghainn, Eilean a' Chomhraig, Eilean an Dúnain, Eilean Buidhe (Ardmarnock), Eilean Buidhe ( Portavadie), Eilean Fraoch, Eilean Math-ghamhna, Eilean Mór, Glas Eilean, Heather Island, Inverneil Island, Kilbride Island, and Liath Eilean.
There are several islets surrounding Horse Isle in North Ayrshire: Broad Rock, East Islet, Halftide Rock, High Rock and North Islet.
Lady Isle lies off the South Ayrshire coast near Troon
Troon is a town in South Ayrshire, situated on the west coast of Ayrshire in Scotland, about north of Ayr and northwest of Glasgow Prestwick Airport.
Troon has a port with freight services and a yacht marina. Up until January 2016, P&O ope ...
. At one time it housed "ane old chapell with an excellent spring of water"."History of Lady Isle"ladyisle.com. Quoting ''Geographical Collections relating to Scotland''. Vol.1, pages 412/3. Retrieved 14 October 2007. However, in June 1821, someone set fire to the "turf and pasture". Once the pasture had burned away, gales blew much of the island's soil into the sea. This permanently destroyed the island's ability to support grazing.
www.ladyisle.com. Retrieved 29 August 2010. There are no islands in Loch Goil or Loch Long, which are
fjord
In physical geography, a fjord or fiord () is a long, narrow inlet with steep sides or cliffs, created by a glacier. Fjords exist on the coasts of Alaska, Antarctica, British Columbia, Chile, Denmark, Förden and East Jutland Fjorde, Germany, ...
-like arms in the northern part of the firth.
Non-island areas with “island” in their name
Here is a list of places along that shores of the Firth of Clyde that are not islands, but have names that misleadingly suggest they are islands (''eilean'' being Gaelic for "island"): Eilean na Beithe, Portavadie; Eilean Beag,Cove
A cove is a small type of bay or coastal inlet. Coves usually have narrow, restricted entrances, are often circular or oval, and are often situated within a larger bay. Small, narrow, sheltered bays, inlets, creeks, or recesses in a coast are o ...
; Eilean Dubh, Dalchenna, Loch Fyne; Eilean nan Gabhar, Melldalloch, Kyles of Bute
The Kyles of Bute ( gd, Na Caoil Bhòdach) form a narrow sea channel that separates the northern end of the Isle of Bute from the Cowal peninsula in Argyll and Bute, on the Scottish mainland. The surrounding hillsides are roughly wooded, and ov ...
; Barmore Island, just north of Tarbert, Kintyre; Eilean Aoidh, south of Portavadie; Eilean Leathan, Kilbrannan Sound just south of Torrisdale Bay; Island Muller, Kilbrannan Sound north of Campbeltown.
Natural history
red deer
The red deer (''Cervus elaphus'') is one of the largest deer species. A male red deer is called a stag or hart, and a female is called a hind. The red deer inhabits most of Europe, the Caucasus Mountains region, Anatolia, Iran, and parts of we ...
, red squirrel, badger
Badgers are short-legged omnivores in the family Mustelidae (which also includes the otters, wolverines, martens, minks, polecats, weasels, and ferrets). Badgers are a polyphyletic rather than a natural taxonomic grouping, being united by ...
, otter, adder, and common lizard. In the Firth itself, there are harbour porpoise
The harbour porpoise (''Phocoena phocoena'') is one of eight extant species of porpoise. It is one of the smallest species of cetacean. As its name implies, it stays close to coastal areas or river estuaries, and as such, is the most familiar ...
s, basking shark
The basking shark (''Cetorhinus maximus'') is the second-largest living shark and fish, after the whale shark, and one of three plankton-eating shark species, along with the whale shark and megamouth shark. Adults typically reach in leng ...
s and various species of dolphin
A dolphin is an aquatic mammal within the infraorder Cetacea. Dolphin species belong to the families Delphinidae (the oceanic dolphins), Platanistidae (the Indian river dolphins), Iniidae (the New World river dolphins), Pontoporiidae (the ...
."Natural History"Arran Natural History Society. Retrieved 12 May 2012. Davaar is home to a population of wild
goat
The goat or domestic goat (''Capra hircus'') is a domesticated species of goat-antelope typically kept as livestock. It was domesticated from the wild goat (''C. aegagrus'') of Southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of the a ...
s.
Over 200 bird species have been recorded as sighted in the area, including the black guillemot, the eider
Eiders () are large seaducks in the genus ''Somateria''. The three extant species all breed in the cooler latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere.
The down feathers of eider ducks, and some other ducks and geese, are used to fill pillows and quil ...
, the peregrine falcon, and the golden eagle
The golden eagle (''Aquila chrysaetos'') is a bird of prey living in the Northern Hemisphere. It is the most widely distributed species of eagle. Like all eagles, it belongs to the family Accipitridae. They are one of the best-known birds of ...
. In 1981, there were 28 ptarmigan
''Lagopus'' is a small genus of birds in the grouse subfamily commonly known as ptarmigans (). The genus contains three living species with numerous described subspecies, all living in tundra or cold upland areas.
Taxonomy and etymology
The ge ...
s sighted on Arran, but in 2009 it was reported that extensive surveys had been unable to find any recorded ptarmigans sightings. Similarly, the red-billed chough
The red-billed chough, Cornish chough or simply chough ( ; ''Pyrrhocorax pyrrhocorax''), is a bird in the crow family, one of only two species in the genus '' Pyrrhocorax''. Its eight subspecies breed on mountains and coastal cliffs from the w ...
no longer breeds on the island.
Arran has three species of the rare endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found else ...
trees known as Arran Whitebeams:Johnston, Ian (15 June 2007"Trees on Arran 'are a whole new species' "
Edinburgh. ''
The Scotsman
''The Scotsman'' is a Scottish compact newspaper and daily news website headquartered in Edinburgh. First established as a radical political paper in 1817, it began daily publication in 1855 and remained a broadsheet until August 2004. Its pare ...
''. Retrieved 18 June 2007. the Scottish or Arran whitebeam; the cut-leaved whitebeam; and the Catacol whitebeam. All of them are found only in Gleann Diomhan, and they are amongst the most endangered tree species in the world. (Gleann Diomhan was formerly part of a designated national nature reserve—the designation was removed in 2011)- and it continues to be part of an area designated as a Site of Special Scientific Interest.) Only 283 Arran whitebeam and 236 cut-leaved whitebeam were recorded as mature trees in 1980, and it is thought that grazing pressures and insect damage are preventing regeneration of the woodland. The Catacol whitebeam was discovered in 2007, but only two specimens have been found, so steps have been taken to protect them."New species of tree discovered "(14 June 2007) BBC. Retrieved 18 January 2011.''New species of tree discovered on Arran''. Scottish Wildlife. November 2007, p. 9
Etymology
 The
The Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
historian Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
The surviving portions of his two major works—the ...
refers to the ''Clota'', meaning the Clyde. The derivation is not certain but is probably from the Brythonic ''Clouta'', which became ''Clut'' in Old Welsh. The name literally means "wash", probably referring to a river goddess who is seen as "the washer" or "the strongly flowing one". The derivation of the word “Bute” is also uncertain. The Norse name for it is ''Bót'' an Old Irish word for "fire", which might be a reference to signal fires. The etymology of “Arran” is no clearer. Haswell-Smith (2004) suggests that it derive from a Brythonic word meaning "high place",Haswell-Smith (2004) p. 11 although Watson (1926) suggests it may be pre-Celtic.Watson (1994) p. 97
See also
*Scottish island names
The modern names of Scottish islands stem from two main influences. There are many names that derive from the Scottish Gaelic language in the Hebrides and Firth of Clyde. In the Northern Isles most place names have a Norse origin. There are also ...
* Rathlin Island
* Sleeping Warrior
* Arran Single Malt
* Mount Stuart House
* Cathedral of the Isles
* Earl of Arran (Scotland)
Earl of Arran is a title in the Peerage of Scotland. It is not to be confused with the title Earl of Arran in the Peerage of Ireland. The two titles refer to different places: the Isle of Arran in Scotland, and the Aran Islands in Ireland. The ...
* Marquess of Bute
* Mull of Kintyre test
Film censorship in the United Kingdom began with early cinema exhibition becoming subject to the Disorderly Houses Act 1751. The Cinematograph Act 1909 was primarily concerned with introducing annual licensing of premises where films were shown, p ...
Notes
Footnotes
References
* Barrett, James H. "The Norse in Scotland" in Brink, Stefan (ed) (2008) ''The Viking World''. Abingdon. Routledge. * Coventry, Martin (2008) ''Castles of the Clans''. Musselburgh. Goblinshead. * * Gillen, Con (2003) ''Geology and landscapes of Scotland''. Harpenden. Terra. * * Hollander, Lee M (ed. & tr.) (1964) ''Heimskringla: History of the Kings of Norway.'' Austin. University of Texas Press. * Hunter, James (2000) ''Last of the Free: A History of the Highlands and Islands of Scotland''. Edinburgh. Mainstream. * Keay, J. & Keay, J. (1994) ''Collins Encyclopaedia of Scotland
''Collins Encyclopaedia of Scotland'' is a reference work published by HarperCollins, edited by the husband and wife team, John and Julia Keay.
History
Scots had provided the impetus for a number of well-known references works, ''Chambers Dic ...
''. London. HarperCollins
HarperCollins Publishers LLC is one of the Big Five English-language publishing companies, alongside Penguin Random House, Simon & Schuster, Hachette, and Macmillan. The company is headquartered in New York City and is a subsidiary of News ...
*
* McDonald, Dan (1977) ''The Clyde Puffer''. Newton Abbot. David & Charles
David & Charles Ltd is an English publishing company. It is the owner of the David & Charles imprint, which specialises in craft and lifestyle publishing.
David and Charles Ltd acts as distributor for all David and Charles Ltd books and cont ...
* McKirdy, Alan Gordon, John & Crofts, Roger (2007) ''Land of Mountain and Flood: The Geology and Landforms of Scotland''. Edinburgh. Birlinn.
* Murray, W.H (1973) ''The Islands of Western Scotland.'' London. Eyre Methuen.
* Murray, W.H. (1977) ''The Companion Guide to the West Highlands of Scotland.'' London. Collins.
* Noble, Gordon (2006) ''Neolithic Scotland: Timber, Stone, Earth and Fire.'' Edinburgh University Press.
* Omand, Donald (ed.) (2006) ''The Argyll Book''. Edinburgh. Birlinn.
* Ordnance Survey
Ordnance Survey (OS) is the national mapping agency for Great Britain. The agency's name indicates its original military purpose (see ordnance and surveying), which was to map Scotland in the wake of the Jacobite rising of 1745. There was a ...
(2009"Get-a-map"
Retrieved 1–31 August 2010. * Watson, W. J (1994) ''The Celtic Place-Names of Scotland''. Edinburgh. Birlinn. . First published 1926. {{Use dmy dates, date=August 2019
Clyde Clyde may refer to:
People
* Clyde (given name)
* Clyde (surname)
Places
For townships see also Clyde Township
Australia
* Clyde, New South Wales
* Clyde, Victoria
* Clyde River, New South Wales
Canada
* Clyde, Alberta
* Clyde, Ontario, a tow ...
Archipelagoes of Scotland
Archipelagoes of the Atlantic Ocean