Gullah topics on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Gullah () are an
African American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
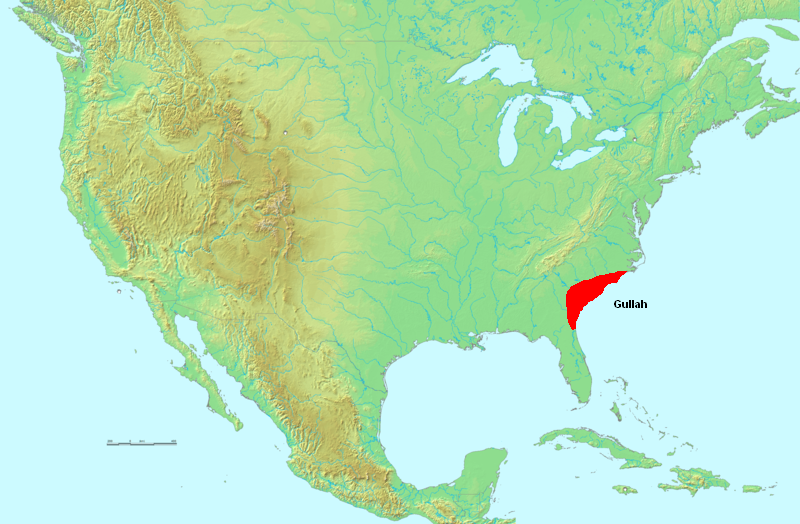
ethnic group who predominantly live in the Lowcountry
The Lowcountry (sometimes Low Country or just low country) is a geographic and cultural region along South Carolina's coast, including the Sea Islands. The region includes significant salt marshes and other coastal waterways, making it an impor ...
region of the U.S. states of Georgia, Florida, South Carolina, and North Carolina, within the coastal plain and the Sea Islands
The Sea Islands are a chain of tidal and barrier islands on the Atlantic Ocean coast of the Southeastern United States. Numbering over 100, they are located between the mouths of the Santee and St. Johns Rivers along the coast of South Caroli ...
. Their language and culture have preserved a significant influence of Africanisms
Africanisms refers to characteristics of African culture that can be traced through societal practices and institutions of the African diaspora. Throughout history, the dispersed descendants of Africans have retained many forms of their ancestr ...
as a result of their historical geographic isolation and the community's relation to their shared history and identity.
Historically, the Gullah region extended from the Cape Fear area on North Carolina's coast south to the vicinity of Jacksonville
Jacksonville is a city located on the Atlantic coast of northeast Florida, the most populous city proper in the state and is the List of United States cities by area, largest city by area in the contiguous United States as of 2020. It is the co ...
on Florida's coast. The Gullah people and their language are also called Geechee, which may be derived from the name of the Ogeechee River
The Ogeechee River is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed April 26, 2011 blackwater river in the U.S. state of Georgia. It heads at the confluence of its North and Sout ...
near Savannah, Georgia
Savannah ( ) is the oldest city in the U.S. state of Georgia and is the county seat of Chatham County. Established in 1733 on the Savannah River, the city of Savannah became the British colonial capital of the Province of Georgia and later t ...
. ''Gullah'' is a term that was originally used to designate the creole dialect of English spoken by Gullah and Geechee people. Over time, its speakers have used this term to formally refer to their creole language and distinctive ethnic identity as a people. The Georgia communities are distinguished by identifying as either "Freshwater Geechee" or "Saltwater Geechee", depending on whether they live on the mainland or the Sea Islands.
Because of a period of relative isolation from whites while working on large plantations
A plantation is an agricultural estate, generally centered on a plantation house, meant for farming that specializes in cash crops, usually mainly planted with a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. Th ...
in rural areas, the Africans, enslaved from a variety of Central and West African ethnic groups, developed a creole culture that has preserved much of their African linguistic and cultural heritage from various peoples; in addition, they absorbed new influences from the region. The Gullah people speak an English-based creole language
An English-based creole language (often shortened to English creole) is a creole language for which English was the '' lexifier'', meaning that at the time of its formation the vocabulary of English served as the basis for the majority of the cre ...
containing many African loanwords and influenced by African languages
The languages of Africa are divided into several major language families:
* Niger–Congo or perhaps Atlantic–Congo languages (includes Bantu and non-Bantu, and possibly Mande and others) are spoken in West, Central, Southeast and Souther ...
in grammar and sentence structure. Sometimes referred to as "Sea Island Creole" by linguists and scholars, the Gullah language is sometimes considered as being similar to Bahamian Creole
Bahamianese, also described as the Bahamian dialect, is spoken by both Black and white Bahamians, although in slightly different forms. Bahamian dialect also tends to be more prevalent in certain areas of the Bahamas. Islands that were settl ...
, Barbadian Creole
Bajan , or Bajan Dialect, is an English-based creole language with African and British influences spoken on the Caribbean island of Barbados. Bajan is primarily a spoken language, meaning that in general, standard English is used in print, in ...
, Guyanese Creole
Guyanese English Creole (''Creolese'' by its speakers or simply Guyanese) is an English-based creole language spoken by the Guyanese people. Linguistically, it is similar to other English dialects of the Caribbean region, based on 19th-century ...
, Belizean Creole, Jamaican Patois
Jamaican Patois (; locally rendered Patwah and called Jamaican Creole by linguists) is an English-based creole language with West African influences, spoken primarily in Jamaica and among the Jamaican diaspora. A majority of the non-English ...
and the Sierra Leone Krio language of West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, M ...
. Gullah crafts, farming and fishing traditions, folk beliefs, music, rice-based cuisine and story-telling traditions all exhibit strong influences from Central and West African cultures.
Etymology
The origin of the word "Gullah" can be traced to the KiKongo language, spoken around theCongo River
The Congo River ( kg, Nzâdi Kôngo, french: Fleuve Congo, pt, Rio Congo), formerly also known as the Zaire River, is the second longest river in Africa, shorter only than the Nile, as well as the second largest river in the world by discharge ...
's mouth from which the Gullah language
Gullah (also called Gullah-English, Sea Island Creole English, and Geechee) is a creole language spoken by the Gullah people (also called "Geechees" within the community), an African-American population living in coastal regions of South Car ...
dialects spoken by black Americans today come. Some scholars suggest that it may be cognate with the name ''Kongo'', where the ancestors of some of the Gullah people likely originated. They created a new culture synthesized from that of the various African peoples brought into Charleston and other parts of South Carolina. Some scholars have suggested that it may come from the name of the Gola, an ethnic group living in the border area between present-day Sierra Leone and Liberia in West Africa, another area of enslaved ancestors of the Gullah people. British planters in the Caribbean and the Southern colonies of North America referred to this area as the "Grain Coast" or "Rice Coast"; many of the tribes are of Mandé or Manding origins. The name "Geechee", another common name for the Gullah people, may derive from the name of the Kissi people
The Kissi people, are a West African ethnolinguistic group. They are the fourth largest ethnic group in Guinea, making up 6.2% of the population. Kissi people are also found in Liberia and Sierra Leone. They speak the Kissi language, which bel ...
, an ethnic group living in the border area between Sierra Leone, Guinea, and Liberia.
Still another possible linguistic source for "Gullah" are the Dyula ethnic group of West Africa, from whom the American Gullah might be partially descended. The Dyula civilization had a large territory that stretched from Senegal through Mali to Burkina Faso and the rest of what was French West Africa. These were vast savanna lands with lower population densities. Slave raiding was easier and more common here than in forested areas with natural forms of physical defenses. The word " Dyula" is pronounced "Gwullah" among members of the Akan Akan may refer to:
People and languages
*Akan people, an ethnic group in Ghana and Côte d'Ivoire
*Akan language, a language spoken by the Akan people
*Kwa languages, a language group which includes Akan
* Central Tano languages, a language group ...
ethnic group in Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and To ...
and Côte d'Ivoire. The primary land route through which captured Dyula people
The Dyula (Dioula or Juula) are a Mande ethnic group inhabiting several West African countries, including Mali, Cote d'Ivoire, Ghana, and Burkina Faso.
Characterized as a highly successful merchant caste, ''Dyula'' migrants began establishin ...
then came into contact with European slavers was the "Grain Coast" and "Rice Coast" (present-day Liberia, Sierra Leone, Senegambia, and Guinea). The story of Gullah Jack
Gullah Jack (died July 12, 1822), also known as Couter Jack and sometimes referred to as "Gullah" Jack Pritchard, was a Methodist, an African conjurer, and a slave to Paul Pritchard in Charleston, South Carolina.
Background
Little was known a ...
(an African slave trafficked from Angola to the United States) may indicate that the word ''Gullah'' originated in Angola, as some commentators believe the word is a shortened version of the country's name. Gullah Jack's other name was Jack Pritchard because he was sold to a white man with the last name Pritchard.
Some scholars have also suggested indigenous American origins for these words. The Spanish named the South Carolina and Georgia coastal region as ''Guale
Guale was a historic Native American chiefdom of Mississippian culture peoples located along the coast of present-day Georgia and the Sea Islands. Spanish Florida established its Roman Catholic missionary system in the chiefdom in the late 16t ...
'', after a Native American tribe. The name of the Ogeechee River
The Ogeechee River is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed April 26, 2011 blackwater river in the U.S. state of Georgia. It heads at the confluence of its North and Sout ...
, a prominent geographical feature in coastal Georgia and central to Guale territory, may have been derived from a Creek Indian
The Muscogee, also known as the Mvskoke, Muscogee Creek, and the Muscogee Creek Confederacy ( in the Muscogee language), are a group of related indigenous (Native American) peoples of the Southeastern WoodlandsMuskogee language) word.
 According to Port of Charleston records, African slaves shipped to the port came from the following areas:
According to Port of Charleston records, African slaves shipped to the port came from the following areas:  Two British trading companies based in England operated the slave castle at
Two British trading companies based in England operated the slave castle at
 The Gullah people have been able to preserve much of their African cultural heritage because of climate, geography, cultural pride, and patterns of importation of enslaved Africans. Enslaved persons from the Central Western region of Africa, originating primarily from the Mende populations of what is today
The Gullah people have been able to preserve much of their African cultural heritage because of climate, geography, cultural pride, and patterns of importation of enslaved Africans. Enslaved persons from the Central Western region of Africa, originating primarily from the Mende populations of what is today  The planters left their European or African "rice drivers", or overseers, in charge of Rice production in the United States#Early history, the rice plantations. These had hundreds of laborers, with African traditions reinforced by new imports from the same regions. Over time, the Gullah people developed a creole culture in which elements of African languages, cultures, and community life were preserved to a high degree. Their culture developed in a distinct way, different from that of the enslaved African Americans in states such as North Carolina, Virginia, and Maryland, where the enslaved lived in smaller groups, and had more sustained and frequent interactions with whites and British American culture.
The planters left their European or African "rice drivers", or overseers, in charge of Rice production in the United States#Early history, the rice plantations. These had hundreds of laborers, with African traditions reinforced by new imports from the same regions. Over time, the Gullah people developed a creole culture in which elements of African languages, cultures, and community life were preserved to a high degree. Their culture developed in a distinct way, different from that of the enslaved African Americans in states such as North Carolina, Virginia, and Maryland, where the enslaved lived in smaller groups, and had more sustained and frequent interactions with whites and British American culture.
 In the 20th century, some plantations were redeveloped as resort or hunting destinations by wealthy whites. Gradually more visitors went to the islands to enjoy their beaches and mild climate. Since the late 20th century, the Gullah people—led by Penn Center and other determined community groups—have been fighting to keep control of their traditional lands. Since the 1960s, resort development on the Sea Islands has greatly increased property values, threatening to push the Gullah off family lands which they have owned since Emancipation Proclamation, emancipation. They have fought back against uncontrolled development on the islands through community action, the courts, and the political process.
In the 20th century, some plantations were redeveloped as resort or hunting destinations by wealthy whites. Gradually more visitors went to the islands to enjoy their beaches and mild climate. Since the late 20th century, the Gullah people—led by Penn Center and other determined community groups—have been fighting to keep control of their traditional lands. Since the 1960s, resort development on the Sea Islands has greatly increased property values, threatening to push the Gullah off family lands which they have owned since Emancipation Proclamation, emancipation. They have fought back against uncontrolled development on the islands through community action, the courts, and the political process.
 The Gullah have also struggled to preserve their traditional culture in the face of much more contact with modern culture and media. In 1979, a translation of the New Testament into the Gullah language was begun. The American Bible Society published ''De Nyew Testament'' in 2005. In November 2011, ''Healin fa de Soul'', a five-CD collection of readings from the Gullah Bible, was released. This collection includes ''Scipcha Wa De Bring Healing'' ("Scripture That Heals") and the Gospel of John (''De Good Nyews Bout Jedus Christ Wa John Write''). This was also the most extensive collection of Gullah recordings, surpassing those of Lorenzo Dow Turner. The recordings have helped people develop an interest in the culture, because they get to hear the language and learn how to pronounce some words.
The Gullah have also struggled to preserve their traditional culture in the face of much more contact with modern culture and media. In 1979, a translation of the New Testament into the Gullah language was begun. The American Bible Society published ''De Nyew Testament'' in 2005. In November 2011, ''Healin fa de Soul'', a five-CD collection of readings from the Gullah Bible, was released. This collection includes ''Scipcha Wa De Bring Healing'' ("Scripture That Heals") and the Gospel of John (''De Good Nyews Bout Jedus Christ Wa John Write''). This was also the most extensive collection of Gullah recordings, surpassing those of Lorenzo Dow Turner. The recordings have helped people develop an interest in the culture, because they get to hear the language and learn how to pronounce some words.
 The Gullah achieved another victory in 2006 when the U.S. Congress passed the "Gullah/Geechee Cultural Heritage Corridor, Gullah/Geechee Cultural Heritage Corridor Act"; it provided $10 million over 10 years for the preservation and interpretation of historic sites in the Low Country relating to Gullah culture. The National Heritage Area, Heritage Corridor will extend from southern North Carolina to northern Florida. The project will be administered by the US National Park Service, with extensive consultation with the Gullah community.
The Gullah achieved another victory in 2006 when the U.S. Congress passed the "Gullah/Geechee Cultural Heritage Corridor, Gullah/Geechee Cultural Heritage Corridor Act"; it provided $10 million over 10 years for the preservation and interpretation of historic sites in the Low Country relating to Gullah culture. The National Heritage Area, Heritage Corridor will extend from southern North Carolina to northern Florida. The project will be administered by the US National Park Service, with extensive consultation with the Gullah community.
 The Gullah have also reached out to
The Gullah have also reached out to


 The Gullah have preserved many of their west African food ways growing and eating crops such as Sea Island red pea, Sea island red peas, Carolina Gold, Carolina Gold rice
The Gullah have preserved many of their west African food ways growing and eating crops such as Sea Island red pea, Sea island red peas, Carolina Gold, Carolina Gold rice
Sea Island BenneSea island Okra
Sorghum bicolor, sorghum, and watermelon all of which were brought with them from
 Gullah people now organize cultural festivals every year in towns up and down the Lowcountry. Hilton Head Island, South Carolina, Hilton Head Island, for instance, hosts a "Gullah Celebration" in February. It includes "De Aarts ob We People" show; the "Ol’ Fashioned Gullah Breakfast"; "National Freedom Day," the "Gullah Film Fest", "A Taste of Gullah" food and entertainment, a "Celebration of Lowcountry Authors and Books," an "Arts, Crafts & Food Expo," and "De Gullah Playhouse". Beaufort, South Carolina, Beaufort hosts the oldest and the largest celebration, "The Original Gullah Festival" in May. The nearby Penn Center on St. Helena Island, South Carolina, St. Helena Island holds "Heritage Days" in November. Other Gullah festivals are celebrated on James Island, South Carolina and Sapelo Island, Sapelo Island, Georgia.
Gullah people now organize cultural festivals every year in towns up and down the Lowcountry. Hilton Head Island, South Carolina, Hilton Head Island, for instance, hosts a "Gullah Celebration" in February. It includes "De Aarts ob We People" show; the "Ol’ Fashioned Gullah Breakfast"; "National Freedom Day," the "Gullah Film Fest", "A Taste of Gullah" food and entertainment, a "Celebration of Lowcountry Authors and Books," an "Arts, Crafts & Food Expo," and "De Gullah Playhouse". Beaufort, South Carolina, Beaufort hosts the oldest and the largest celebration, "The Original Gullah Festival" in May. The nearby Penn Center on St. Helena Island, South Carolina, St. Helena Island holds "Heritage Days" in November. Other Gullah festivals are celebrated on James Island, South Carolina and Sapelo Island, Sapelo Island, Georgia.
 Gullah culture is also being celebrated elsewhere in the United States. The High Art Museum in Atlanta has presented exhibits about Gullah culture. The Black Cultural Center at Purdue University in West Lafayette, Indiana conducted a research tour, cultural arts festival, and other related events to showcase the Gullah culture. The Black Cultural Center Library maintains a bibliography of Gullah books and materials, as well. Metro State College in Denver, Colorado recently hosted a conference on Gullah culture, called ''The Water Brought Us: Gullah History and Culture,'' which featured a panel of Gullah scholars and cultural activists. These events in Indiana and Colorado are typical of the attention Gullah culture regularly receives throughout the United States.
Gullah culture is also being celebrated elsewhere in the United States. The High Art Museum in Atlanta has presented exhibits about Gullah culture. The Black Cultural Center at Purdue University in West Lafayette, Indiana conducted a research tour, cultural arts festival, and other related events to showcase the Gullah culture. The Black Cultural Center Library maintains a bibliography of Gullah books and materials, as well. Metro State College in Denver, Colorado recently hosted a conference on Gullah culture, called ''The Water Brought Us: Gullah History and Culture,'' which featured a panel of Gullah scholars and cultural activists. These events in Indiana and Colorado are typical of the attention Gullah culture regularly receives throughout the United States.
 The Gullah custom of painting porch ceilings haint blue to deter haints, or ghosts, survives in the American South. Having also been adopted by White Southerners, it has lost some of its spiritual significance.
The Gullah custom of painting porch ceilings haint blue to deter haints, or ghosts, survives in the American South. Having also been adopted by White Southerners, it has lost some of its spiritual significance.
Sapelo Island
Sapelo Island is a state-protected barrier island located in McIntosh County, Georgia. The island is accessible only by aircraft or boat; the primary ferry comes from the Sapelo Island Visitors Center in McIntosh County, Georgia, a seven-mil ...
, the site of the last Gullah community of Hog Hammock, was also principal place of refuge for Guale people who also fled slavery on the mainland.
The Gullah people have several West African words in their language that survived despite hundreds of years of slavery when African Americans were forced to speak English.
History
African roots
 According to Port of Charleston records, African slaves shipped to the port came from the following areas:
According to Port of Charleston records, African slaves shipped to the port came from the following areas: Angola
, national_anthem = " Angola Avante"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capital = Luanda
, religion =
, religion_year = 2020
, religion_ref =
, coordina ...
(39%), Senegambia (20%), the Windward Coast
The Windward Coast was used to describe an area of West Africa located on the coast between Cape Mount and Assini, i.e. the coastlines of the modern states of Liberia and Ivory Coast, to the west of what was called the Gold Coast. A related re ...
(17%), the Gold Coast
Gold Coast may refer to:
Places Africa
* Gold Coast (region), in West Africa, which was made up of the following colonies, before being established as the independent nation of Ghana:
** Portuguese Gold Coast (Portuguese, 1482–1642)
** Dutch G ...
(13%), Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone,)]. officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered by Liberia to the southeast and Guinea surrounds the northern half of the nation. Covering a total area of , Sierr ...
(6%), and Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
, Mozambique
Mozambique (), officially the Republic of Mozambique ( pt, Moçambique or , ; ny, Mozambiki; sw, Msumbiji; ts, Muzambhiki), is a country located in southeastern Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi ...
, and the two Bights (viz., Benin
Benin ( , ; french: Bénin , ff, Benen), officially the Republic of Benin (french: République du Bénin), and formerly Dahomey, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east, Burkina Faso to the nort ...
and Biafra
Biafra, officially the Republic of Biafra, was a partially recognised secessionist state in West Africa that declared independence from Nigeria and existed from 1967 until 1970. Its territory consisted of the predominantly Igbo-populated form ...
) (5% combined) (Pollitzer, 1999:43). The term "Windward Coast" often referred to Sierra Leone, so the total figure of slaves from that region is higher than 6%.
Particularly along the western coast, the local peoples had cultivated African rice
''Oryza glaberrima'', commonly known as African rice, is one of the two domesticated rice species. It was first domesticated and grown in West Africa around 3,000 years ago. In agriculture, it has largely been replaced by higher-yielding Asian ri ...
for what is estimated to approach 3,000 years. African rice is a species related to, yet distinct from, Asian rice
''Oryza sativa'', commonly known as Asian rice or indica rice, is the plant species most commonly referred to in English as ''rice''. It is the type of farmed rice whose cultivars are most common globally, and was first domesticated in the Yan ...
. It was originally domesticated in the inland delta of the Upper Niger River
The Niger River ( ; ) is the main river of West Africa, extending about . Its drainage basin is in area. Its source is in the Guinea Highlands in south-eastern Guinea near the Sierra Leone border. It runs in a crescent shape through ...
. Once Carolinian and Georgian planters in the American South discovered that African rice would grow in that region, they often sought enslaved Africans from rice-growing regions because they had the skills and knowledge needed to develop and build irrigation, dams and earthworks.
 Two British trading companies based in England operated the slave castle at
Two British trading companies based in England operated the slave castle at Bunce Island
Bunce Island (also spelled "Bence," "Bense," or "Bance" at different periods) is an island in the Sierra Leone River. It is situated in Freetown Harbour, the estuary of the Rokel River and Port Loko Creek, about upriver from Sierra Leone's capi ...
(formerly called Bance Island), located in the Sierra Leone River
The Sierra Leone River is a river estuary on the Atlantic Ocean in Western Sierra Leone. It is formed by the Bankasoka River and Rokel River and is between 4 and 10 miles wide (6–16 km) and 25 miles (40 km) long. It holds the major port ...
. Henry Laurens
Henry Laurens (December 8, 1792) was an American Founding Father, merchant, slave trader, and rice planter from South Carolina who became a political leader during the Revolutionary War. A delegate to the Second Continental Congress, Laure ...
was their main contact in Charleston and was a planter and slave trader. His counterpart in Britain was the Scottish merchant and slave trader Richard Oswald. Many of the enslaved Africans taken in West Africa were processed through Bunce Island. It was a prime export site for slaves to South Carolina and Georgia. Slave castles in Ghana, by contrast, shipped many of the people they handled to ports and markets in the Caribbean islands.
After Freetown, Sierra Leone, was founded in the late 18th century by the British as a colony for poor blacks from London and black Loyalists from Nova Scotia resettled after the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
, the British did not allow slaves to be taken from Sierra Leone, protecting the people from kidnappers. In 1808 both Great Britain and the United States prohibited the African slave trade
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
. After that date, the British, whose navy patrolled to intercept slave ships off Africa, sometimes resettled Africans liberated from slave trader ships in Sierra Leone. Similarly, Americans sometimes settled freed slaves at Liberia, a similar colony established in the early 19th century by the American Colonization Society
The American Colonization Society (ACS), initially the Society for the Colonization of Free People of Color of America until 1837, was an American organization founded in 1816 by Robert Finley to encourage and support the migration of freebor ...
. As it was a place for freed slaves and free blacks from the United States, some free blacks emigrated there voluntarily, for the chance to create their own society.
Origin of Gullah culture
Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone,)]. officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered by Liberia to the southeast and Guinea surrounds the northern half of the nation. Covering a total area of , Sierr ...
, and transported to some areas of Brazil (including Bahia
Bahia ( , , ; meaning "bay") is one of the 26 states of Brazil, located in the Northeast Region of the country. It is the fourth-largest Brazilian state by population (after São Paulo, Minas Gerais, and Rio de Janeiro) and the 5th-largest b ...
), the enslaved Gullah-Gheechee people were traded in what was then Charlestowne, South Carolina. According to British historian P.E.H. Hair, Gullah culture developed as a creole culture in the colonies and United States from the peoples of many different African cultures who came together there. These included the Baga, Fula
Fula may refer to:
*Fula people (or Fulani, Fulɓe)
*Fula language (or Pulaar, Fulfulde, Fulani)
**The Fula variety known as the Pulaar language
**The Fula variety known as the Pular language
**The Fula variety known as Maasina Fulfulde
*Al-Fula ...
, Kissi, Kpelle, Limba, Mandinka, Mende, Susu, Temne, Vai, and Wolof people, Wolof of the Rice Coast, and many from Angola
, national_anthem = " Angola Avante"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capital = Luanda
, religion =
, religion_year = 2020
, religion_ref =
, coordina ...
, Yoruba people, Yoruba, Igbo people, Igbo, Calabar, Congo Basin, Congo and the Gold Coast
Gold Coast may refer to:
Places Africa
* Gold Coast (region), in West Africa, which was made up of the following colonies, before being established as the independent nation of Ghana:
** Portuguese Gold Coast (Portuguese, 1482–1642)
** Dutch G ...
.
By the middle of the 18th century, thousands of acres in the Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia and South Carolina Lowcountry, and the Sea Islands were developed as African rice
''Oryza glaberrima'', commonly known as African rice, is one of the two domesticated rice species. It was first domesticated and grown in West Africa around 3,000 years ago. In agriculture, it has largely been replaced by higher-yielding Asian ri ...
fields. African farmers from the "Rice Coast" brought the skills for cultivation and tidal irrigation that made rice farming one of the most successful industries in early America.
The subtropical climate encouraged the spread of malaria and yellow fever, which were both carried and transmitted by mosquitoes. These tropical diseases were Endemic (epidemiology), endemic in Africa and might have been carried by enslaved Africans to the colonies. Mosquitoes in the swamps and inundated rice fields of the Lowcountry picked up and spread the diseases to European settlers, as well. Malaria and yellow fever soon became endemic in the region.
Because they had acquired some immunity (medical), immunity in their homeland, Africans were more resistant to these tropical fevers than were the Europeans. As the rice industry was developed, planters continued to import enslaved Africans. By about 1708, South Carolina had a black majority. Golden Isles of Georgia, Coastal Georgia developed a black majority after rice cultivation expanded there in the mid-18th century. Malaria and yellow fever became endemic. Fearing these diseases, many white planters and their families left the Lowcountry during the rainy spring and summer months when fevers ran rampant. Others lived mostly in cities such as Charleston rather than on the isolated plantations, especially those on the Sea Islands.
 The planters left their European or African "rice drivers", or overseers, in charge of Rice production in the United States#Early history, the rice plantations. These had hundreds of laborers, with African traditions reinforced by new imports from the same regions. Over time, the Gullah people developed a creole culture in which elements of African languages, cultures, and community life were preserved to a high degree. Their culture developed in a distinct way, different from that of the enslaved African Americans in states such as North Carolina, Virginia, and Maryland, where the enslaved lived in smaller groups, and had more sustained and frequent interactions with whites and British American culture.
The planters left their European or African "rice drivers", or overseers, in charge of Rice production in the United States#Early history, the rice plantations. These had hundreds of laborers, with African traditions reinforced by new imports from the same regions. Over time, the Gullah people developed a creole culture in which elements of African languages, cultures, and community life were preserved to a high degree. Their culture developed in a distinct way, different from that of the enslaved African Americans in states such as North Carolina, Virginia, and Maryland, where the enslaved lived in smaller groups, and had more sustained and frequent interactions with whites and British American culture.
Civil War period
When the American Civil War, U.S. Civil War began, the Union rushed to blockade Confederate States of America, Confederate shipping. White planters on the Sea Islands, fearing an invasion by the US naval forces, abandoned their plantations and fled to the mainland. When Union forces arrived on the Sea Islands in 1861, they found the Gullah people eager for their freedom, and eager as well to defend it. Many Gullah served with distinction in the Union Army's First South Carolina Volunteers. The Sea Islands were the first place in the South where slaves were freed. Long before the War ended, American Unitarian Association, Unitarian missionaries from Pennsylvania came to start schools on the islands for the newly freed slaves. Penn Center (Saint Helena Island, South Carolina), Penn Center, now a Gullah community organization on Saint Helena Island, South Carolina, Saint Helena Island, South Carolina, was founded as the first school for freed slaves. After the Civil War ended, the Gullahs' isolation from the outside world increased in some respects. The rice planters on the mainland gradually abandoned their plantations and moved away from the area because of labor issues and hurricane damage to crops. Free blacks were unwilling to work in the dangerous and disease-ridden rice fields. A series of 1893 Sea Islands Hurricane, hurricanes devastated the crops in the 1890s. Left alone in remote rural areas of the Lowcountry, the Gullah continued to practice their traditional culture with little influence from the outside world well into the 20th century.Recent history
 The Gullah have also struggled to preserve their traditional culture in the face of much more contact with modern culture and media. In 1979, a translation of the New Testament into the Gullah language was begun. The American Bible Society published ''De Nyew Testament'' in 2005. In November 2011, ''Healin fa de Soul'', a five-CD collection of readings from the Gullah Bible, was released. This collection includes ''Scipcha Wa De Bring Healing'' ("Scripture That Heals") and the Gospel of John (''De Good Nyews Bout Jedus Christ Wa John Write''). This was also the most extensive collection of Gullah recordings, surpassing those of Lorenzo Dow Turner. The recordings have helped people develop an interest in the culture, because they get to hear the language and learn how to pronounce some words.
The Gullah have also struggled to preserve their traditional culture in the face of much more contact with modern culture and media. In 1979, a translation of the New Testament into the Gullah language was begun. The American Bible Society published ''De Nyew Testament'' in 2005. In November 2011, ''Healin fa de Soul'', a five-CD collection of readings from the Gullah Bible, was released. This collection includes ''Scipcha Wa De Bring Healing'' ("Scripture That Heals") and the Gospel of John (''De Good Nyews Bout Jedus Christ Wa John Write''). This was also the most extensive collection of Gullah recordings, surpassing those of Lorenzo Dow Turner. The recordings have helped people develop an interest in the culture, because they get to hear the language and learn how to pronounce some words.
 The Gullah achieved another victory in 2006 when the U.S. Congress passed the "Gullah/Geechee Cultural Heritage Corridor, Gullah/Geechee Cultural Heritage Corridor Act"; it provided $10 million over 10 years for the preservation and interpretation of historic sites in the Low Country relating to Gullah culture. The National Heritage Area, Heritage Corridor will extend from southern North Carolina to northern Florida. The project will be administered by the US National Park Service, with extensive consultation with the Gullah community.
The Gullah achieved another victory in 2006 when the U.S. Congress passed the "Gullah/Geechee Cultural Heritage Corridor, Gullah/Geechee Cultural Heritage Corridor Act"; it provided $10 million over 10 years for the preservation and interpretation of historic sites in the Low Country relating to Gullah culture. The National Heritage Area, Heritage Corridor will extend from southern North Carolina to northern Florida. The project will be administered by the US National Park Service, with extensive consultation with the Gullah community.
 The Gullah have also reached out to
The Gullah have also reached out to West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, M ...
. Gullah groups made three celebrated "homecomings" to Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone,)]. officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered by Liberia to the southeast and Guinea surrounds the northern half of the nation. Covering a total area of , Sierr ...
in 1989, 1997, and 2005. Sierra Leone is at the heart of the traditional rice-growing region of West Africa where many of the Gullahs' ancestors originated. Bunce Island
Bunce Island (also spelled "Bence," "Bense," or "Bance" at different periods) is an island in the Sierra Leone River. It is situated in Freetown Harbour, the estuary of the Rokel River and Port Loko Creek, about upriver from Sierra Leone's capi ...
, the British slave castle in Sierra Leone, sent many African captives to Charleston and Savannah during the mid- and late 18th century. These dramatic homecomings were the subject of three documentary films—''Family Across the Sea'' (1990), ''The Language You Cry In'' (1998), and ''Priscilla's Homecoming'' (in production).
Customs and traditions


African influences
*The Gullah word ''guba'' for peanut derives from the Kongo Language, Kikongo and Kimbundu word ''N'guba''. *Gullah rice dishes called "red rice" and "okra soup" are similar to West African "jollof rice" and "okra soup" and hog maws. Jollof rice is a traditional style of rice preparation brought by the Wolof people, Wolof people of West Africa. *The Gullah version of "gumbo" has its roots in African cooking. "Gumbo" is derived from a word in the ''Umbundu'' language of Angola, meaning okra, one of the dish's main ingredients. *Gullah rice farmers once made and used mortar and pestles and winnowing fanners similar in style to tools used by West African rice farmers. *Gullah beliefs about "Boo Hag, hags" and "haunts" are similar to African beliefs about malevolent ancestors, witchcraft, witches, and "devils" (forest spirits). *Gullah "Hoodoo (folk magic), root doctors" protect their clients against dangerous spiritual forces by using ritual objects similar to those employed by African witch doctor, traditional healers. *Gullah herbalism, herbal medicines are similar to traditional African remedies. *The Gullah "seekin" ritual is similar to coming of age ceremonies in West African secret societies, such as the Poro and Sande society, Sande. *The Gullah ring shout is similar to ecstatic religious rituals performed in West and Central Africa. *Gullah stories about "Br'er Rabbit" are similar to West and Central African trickster tales about the figures of the clever and conniving rabbit, spider, and tortoise. *Gullah spirituals, shouts, and other musical forms employ the "call and response" method commonly used in African music. *Gullah "sweetgrass baskets" are coil straw baskets made by the descendants of enslaved peoples in the South Carolina Lowcountry. They are nearly identical to traditional coil baskets made by the Wolof people in Senegal. *Gullah "strip quilts" mimic the design of cloth woven with the traditional strip loom used throughout West Africa. Kente cloth from the Ashanti people, Ashanti and the Ewe people, Ewe peoples, as well as Akwete cloth from the Igbo people are woven on the strip loom. * An African song, preserved by a Gullah family in coastal Georgia, was identified in the 1940s by linguist Lorenzo Turner and found to be a Mende song from Sierra Leone. It is probably the longest text in an African language to survive the transatlantic crossing of enslaved Africans to the present-day United States. Later, in the 1990s, researchers Joseph Opala, Cynthia Schmidt, and Taziff Koroma located a remote village in Sierra Leone where the song is still sung today, and determined it is a funeral hymn. This research and the resulting reunion between a Gullah family and a Mende family that have both retained versions of the song is recounted in the documentary ''The Language You Cry In'' (1998). * Some words coming from other African languages such as Yoruba language, Yoruba, Fon language, Fon, Ewe language, Ewe, Twi, Ga language, Ga, Mende language, Mende, and Edo people, Bini are still used by Gullah people. *The Gullahs’ English-based creole language is strikingly similar to Sierra Leone Krio of West Africa and contains such identical expressions as ''bigyai'' ("greedy"), ''pantap'' ("on top of"), ''ohltu'' ("both"), ''tif'' ("theft, steal"), ''yeys'' ("ear"), and ''swit'' ("delicious").Cuisine
 The Gullah have preserved many of their west African food ways growing and eating crops such as Sea Island red pea, Sea island red peas, Carolina Gold, Carolina Gold rice
The Gullah have preserved many of their west African food ways growing and eating crops such as Sea Island red pea, Sea island red peas, Carolina Gold, Carolina Gold riceSea Island Benne
Sorghum bicolor, sorghum, and watermelon all of which were brought with them from
West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, M ...
. Rice is a staple food in Gullah communities and continues to be cultivated in abundance in the coastal regions of Georgia and South Carolina. Rice is also an important food in West African cultures. As descendants of enslaved Africans, the Gullah continued the traditional food and food techniques of their ancestors, demonstrating another link to traditional African cultures.
Rice is a core commodity of the Gullah food system: a meal was not considered complete without rice. There are strict rituals surrounding the preparation of rice in the Gullah communities. First, individuals would remove the darker grains from the rice, and then hand wash the rice numerous times before it was ready for cooking. The Gullah people would add enough water for the rice to steam on its own, but not so much that one would have to stir or drain it. These traditional techniques were passed down during the period of slavery and are still an important part of rice preparation by Gullah people.
The first high-profile book on Gullah cooking was published in 2022 by Emily Meggett, an 89-year-old Gullah cook.
Celebrating Gullah culture
Over the years, the Gullah have attracted study by many historians, linguists, folklorists, and anthropologists interested in their rich cultural heritage. Many academic books on that subject have been published. The Gullah have also become a symbol of cultural pride for blacks throughout the United States and a subject of general interest in the media. Numerous newspaper and magazine articles, documentary films, and children's books on Gullah culture, have been produced, in addition to popular novels set in the Gullah region. In 1991 Julie Dash wrote and directed ''Daughters of the Dust'', the first feature film about the Gullah, set at the turn of the 20th century on St. Helena Island. Born into a Gullah family, she was the first African-American woman director to produce a feature film. Gullah people now organize cultural festivals every year in towns up and down the Lowcountry. Hilton Head Island, South Carolina, Hilton Head Island, for instance, hosts a "Gullah Celebration" in February. It includes "De Aarts ob We People" show; the "Ol’ Fashioned Gullah Breakfast"; "National Freedom Day," the "Gullah Film Fest", "A Taste of Gullah" food and entertainment, a "Celebration of Lowcountry Authors and Books," an "Arts, Crafts & Food Expo," and "De Gullah Playhouse". Beaufort, South Carolina, Beaufort hosts the oldest and the largest celebration, "The Original Gullah Festival" in May. The nearby Penn Center on St. Helena Island, South Carolina, St. Helena Island holds "Heritage Days" in November. Other Gullah festivals are celebrated on James Island, South Carolina and Sapelo Island, Sapelo Island, Georgia.
Gullah people now organize cultural festivals every year in towns up and down the Lowcountry. Hilton Head Island, South Carolina, Hilton Head Island, for instance, hosts a "Gullah Celebration" in February. It includes "De Aarts ob We People" show; the "Ol’ Fashioned Gullah Breakfast"; "National Freedom Day," the "Gullah Film Fest", "A Taste of Gullah" food and entertainment, a "Celebration of Lowcountry Authors and Books," an "Arts, Crafts & Food Expo," and "De Gullah Playhouse". Beaufort, South Carolina, Beaufort hosts the oldest and the largest celebration, "The Original Gullah Festival" in May. The nearby Penn Center on St. Helena Island, South Carolina, St. Helena Island holds "Heritage Days" in November. Other Gullah festivals are celebrated on James Island, South Carolina and Sapelo Island, Sapelo Island, Georgia.
 Gullah culture is also being celebrated elsewhere in the United States. The High Art Museum in Atlanta has presented exhibits about Gullah culture. The Black Cultural Center at Purdue University in West Lafayette, Indiana conducted a research tour, cultural arts festival, and other related events to showcase the Gullah culture. The Black Cultural Center Library maintains a bibliography of Gullah books and materials, as well. Metro State College in Denver, Colorado recently hosted a conference on Gullah culture, called ''The Water Brought Us: Gullah History and Culture,'' which featured a panel of Gullah scholars and cultural activists. These events in Indiana and Colorado are typical of the attention Gullah culture regularly receives throughout the United States.
Gullah culture is also being celebrated elsewhere in the United States. The High Art Museum in Atlanta has presented exhibits about Gullah culture. The Black Cultural Center at Purdue University in West Lafayette, Indiana conducted a research tour, cultural arts festival, and other related events to showcase the Gullah culture. The Black Cultural Center Library maintains a bibliography of Gullah books and materials, as well. Metro State College in Denver, Colorado recently hosted a conference on Gullah culture, called ''The Water Brought Us: Gullah History and Culture,'' which featured a panel of Gullah scholars and cultural activists. These events in Indiana and Colorado are typical of the attention Gullah culture regularly receives throughout the United States.
Cultural survival
Gullah culture has proven to be particularly resilient. Gullah traditions are strong in the rural areas of the Lowcountry mainland and on the Sea Islands, and among their people in urban areas such as Charleston and Savannah. Gullah people who have left the Lowcountry and moved far away have also preserved traditions; for instance, many Gullah in New York, who went North in the Great Migration (African American), Great Migration of the first half of the 20th century, have established their own neighborhood churches in Harlem, Brooklyn, and Queens. Typically they send their children back to rural communities in South Carolina and Georgia during the summer months to live with grandparents, uncles, and aunts. Gullah people living in New York frequently return to the Lowcountry to retire. Second- and third-generation Gullah in New York often maintain many of their traditional customs and many still speak the Gullah language. The Gullah custom of painting porch ceilings haint blue to deter haints, or ghosts, survives in the American South. Having also been adopted by White Southerners, it has lost some of its spiritual significance.
The Gullah custom of painting porch ceilings haint blue to deter haints, or ghosts, survives in the American South. Having also been adopted by White Southerners, it has lost some of its spiritual significance.
Representation in art, entertainment, and media
Notable Americans with Gullah roots
*E.B Riv *Dr Edward A. CoatesSee also
* Atlantic Creole * Bilali Document * Black Seminoles * Bristol slave trade * Coastwise slave trade * Colonial South and the Chesapeake * First Africans in Virginia * Virginia Mixson Geraty * Ambrose E. Gonzales * Great Dismal Swamp maroons * Igbo Landing * Joseph Opala * Port Royal Experiment * Slavery in the colonial history of the United States * Stono Rebellion * Peter H. Wood *Gullah language
Gullah (also called Gullah-English, Sea Island Creole English, and Geechee) is a creole language spoken by the Gullah people (also called "Geechees" within the community), an African-American population living in coastal regions of South Car ...
References
{{Authority control Gullah, African-American society Articles containing video clips