Essex () is a
county
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposes Chambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
in the East of
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
. One of the
home counties
The home counties are the counties of England that surround London. The counties are not precisely defined but Buckinghamshire and Surrey are usually included in definitions and Berkshire, Essex, Hertfordshire and Kent are also often included ...
, it borders
Suffolk and
Cambridgeshire
Cambridgeshire (abbreviated Cambs.) is a county in the East of England, bordering Lincolnshire to the north, Norfolk to the north-east, Suffolk to the east, Essex and Hertfordshire to the south, and Bedfordshire and Northamptonshire to the ...
to the north, the
North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea, epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the ...
to the east,
Hertfordshire to the west,
Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces ...
across the estuary of the
River Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the second-longest in the United Kingdom, after the R ...
to the south, and
Greater London to the south and south-west. There are three cities in Essex: Southend, Colchester and Chelmsford, in order of population. For the purposes of government statistics, Essex is placed in the
East of England region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics ( physical geography), human impact characteristics ( human geography), and the interaction of humanity an ...
. There are four definitions of the extent of Essex, the widest being the
ancient county. Next, the largest is the former
postal county, followed by the
ceremonial county, with the smallest being the administrative county—the area administered by the
County Council
A county council is the elected administrative body governing an area known as a county. This term has slightly different meanings in different countries.
Ireland
The county councils created under British rule in 1899 continue to exist in Irel ...
, which excludes the two unitary
authorities of
Thurrock
Thurrock () is a unitary authority area with borough status and unparished area in the ceremonial county of Essex, England. It is part of the London commuter belt and an area of regeneration within the Thames Gateway redevelopment zone. The ...
and
Southend-on-Sea
Southend-on-Sea (), commonly referred to as Southend (), is a coastal city and unitary authority area with borough status in southeastern Essex, England. It lies on the north side of the Thames Estuary, east of central London. It is bordered ...
. The ceremonial county occupies the eastern part of what was, during the
Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
, the
Anglo-Saxon Kingdom of Essex
la, Regnum Orientalium Saxonum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of the East Saxons
, common_name = Essex
, era = Heptarchy
, status =
, status_text =
, government_type = Monarch ...
. As well as rural areas and urban areas, it forms part of the wider
Home Counties
The home counties are the counties of England that surround London. The counties are not precisely defined but Buckinghamshire and Surrey are usually included in definitions and Berkshire, Essex, Hertfordshire and Kent are also often included ...
of England.
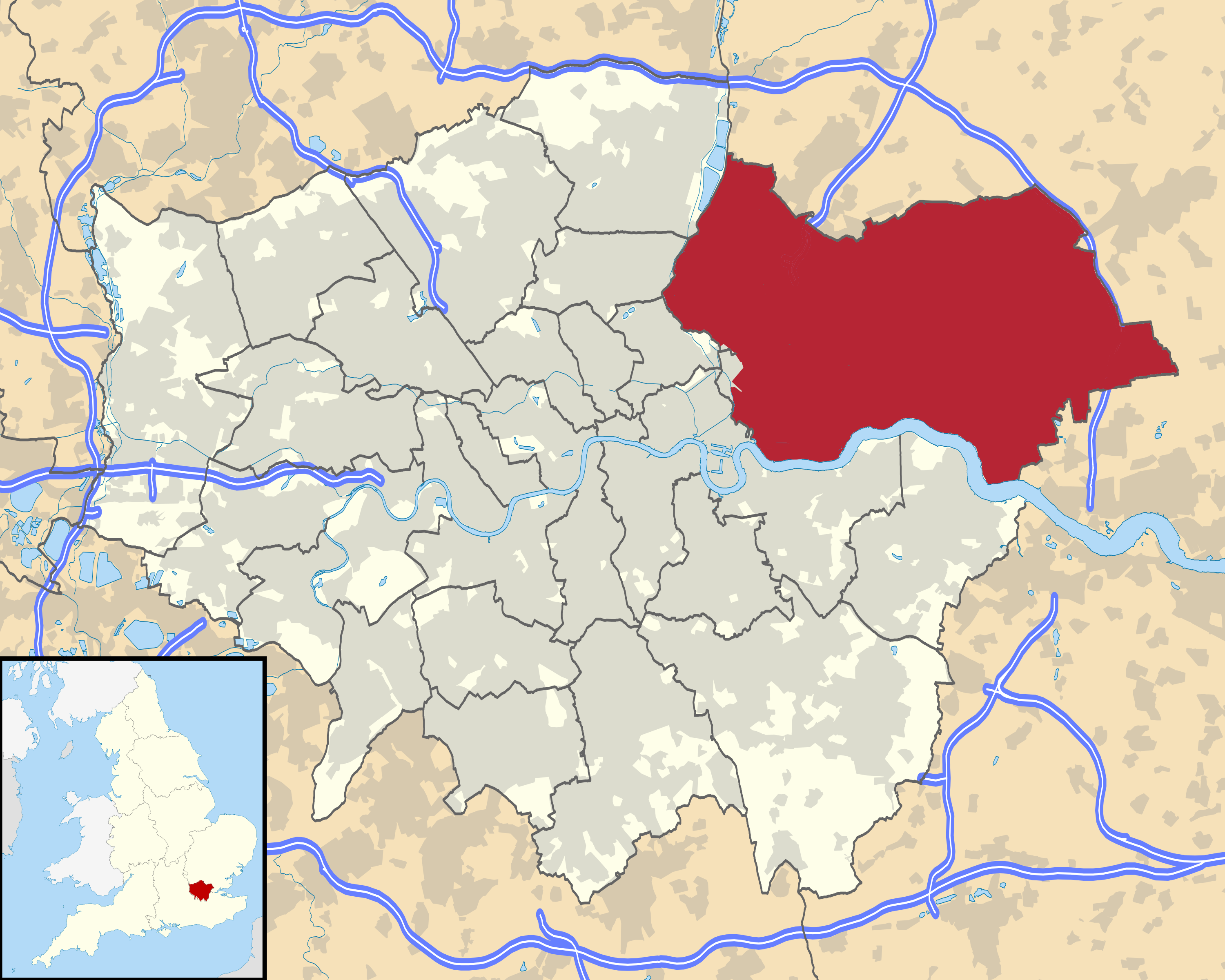
Physical geography and boundaries
The ceremonial county of Essex is bounded by
Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces ...
, south of the
Thames Estuary
The Thames Estuary is where the River Thames meets the waters of the North Sea, in the south-east of Great Britain.
Limits
An estuary can be defined according to different criteria (e.g. tidal, geographical, navigational or in terms of salini ...
;
Greater London to the south-west;
Hertfordshire, broadly west of the
River Lea and the
Stort
The River Stort is a river in Essex and Hertfordshire, England. It is 24 miles (38 km) long and flows from just south of the village of Langley to the River Lea at Hoddesdon.
The river's name is a back-formation; the town of Bishop's Stor ...
;
Cambridgeshire
Cambridgeshire (abbreviated Cambs.) is a county in the East of England, bordering Lincolnshire to the north, Norfolk to the north-east, Suffolk to the east, Essex and Hertfordshire to the south, and Bedfordshire and Northamptonshire to the ...
to the northwest;
Suffolk broadly north of the
River Stour; with the
North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea, epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the ...
to the east.
Definitions
The county of Essex has four definitions: the ancient, ceremonial, administrative and postal counties.


Ancient county
The
ancient county of Essex consists of the entire territory of the county of Essex, as established in the late Anglo-Saxon period, some time after the larger former
Kingdom of the East Saxons had lost its independence. It includes areas such as the three north-western parishes transferred to the
administrative county
An administrative county was a first-level administrative division in England and Wales from 1888 to 1974, and in Ireland from 1899 until either 1973 (in Northern Ireland) or 2002 (in the Republic of Ireland). They are now abolished, although mos ...
of Cambridgeshire in 1889, and the five
boroughs
A borough is an administrative division in various English-speaking countries. In principle, the term ''borough'' designates a self-governing walled town, although in practice, official use of the term varies widely.
History
In the Middle A ...
of
Greater London east of the
River Lea.
The ancient county also includes
Thurrock
Thurrock () is a unitary authority area with borough status and unparished area in the ceremonial county of Essex, England. It is part of the London commuter belt and an area of regeneration within the Thames Gateway redevelopment zone. The ...
and
Southend-on-sea
Southend-on-Sea (), commonly referred to as Southend (), is a coastal city and unitary authority area with borough status in southeastern Essex, England. It lies on the north side of the Thames Estuary, east of central London. It is bordered ...
, which became
unitary authorities
A unitary authority is a local authority responsible for all local government functions within its area or performing additional functions that elsewhere are usually performed by a higher level of sub-national government or the national governme ...
in 1998.
Ceremonial county
The
ceremonial county is the area represented by the
Lord Lieutenant of Essex
This is a list of people who have served as Lord Lieutenant of Essex. Since 1688, all the Lord Lieutenants have also been Custos Rotulorum of Essex.
*John Petre, 1st Baron Petre
* John de Vere, 16th Earl of Oxford 1558–?
* Robert Dudley, 1st E ...
. It excludes the areas transferred out in 1889 and 1965, but includes the unitary authorities of Thurrock and Southend which separated from the administrative county in 1998.
Administrative county
The administrative county is the area for which
Essex County Council
Essex County Council is the county council that governs the non-metropolitan county of Essex in England. It has 75 councillors, elected from 70 divisions, and is currently controlled by the Conservative Party. The council meets at County Hall ...
has responsibility. The administrative county was formed in 1889, and has reduced in size since that time. The administrative county excludes Thurrock, Southend, areas in Greater London, and the much smaller areas transferred in 1889.
Postal county
The
postal county of Essex was a term in use by the
Royal Mail until 1996,
intended to facilitate the sorting of mail by assisting the differentiation of similar
post town
A post town is a required part of all postal addresses in the United Kingdom and Ireland, and a basic unit of the postal delivery system.Royal Mail, ''Address Management Guide'', (2004) Including the correct post town in the address increases ...
s.
The postal county was a collection of post towns approximating to the Ancient and Ceremonial County areas. There were two main distinctions: the first that the postal county of Hertfordshire extended deep into west Essex, with Stansted isolated as an exclave of postal Essex. Postal counties were abolished in 1996, although they are still commonly used in postal addressing.
Metropolitan Essex
Metropolitan Essex refers to places in Essex that form part of the
conurbation and/or the
metropolitan area of
London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
, including the five
boroughs
A borough is an administrative division in various English-speaking countries. In principle, the term ''borough'' designates a self-governing walled town, although in practice, official use of the term varies widely.
History
In the Middle A ...
of
Greater London east of the
Lea
Lea or LEA may refer to:
Places Australia
* Lea River, Tasmania, Australia
* Lake Lea, Tasmania, from which the Lea River flows
* RAAF Base Learmonth, IATA airport code "LEA"
England
* Lea, Cheshire, a civil parish
* Lea, Derbyshire, a set ...
, which were created in the
London Government Act 1963
The London Government Act 1963 (c. 33) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, which created Greater London and a new local government structure within it. The Act significantly reduced the number of local government districts in the ...
from former
municipal borough
Municipal boroughs were a type of local government district which existed in England and Wales between 1835 and 1974, in Northern Ireland from 1840 to 1973 and in the Republic of Ireland from 1840 to 2002. Broadly similar structures existed in S ...
s,
county borough
County borough is a term introduced in 1889 in the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, to refer to a borough or a city independent of county council control, similar to the unitary authorities created since the 1990s. An equivalent te ...
s and
urban districts within administrative Essex. Greater London is a ceremonial county created for administrative purposes by the act, which aimed to place more of London within a single administrative district, replacing the
County of London
The County of London was a county of England from 1889 to 1965, corresponding to the area known today as Inner London. It was created as part of the general introduction of elected county government in England, by way of the Local Government A ...
, which solely covered the inner part of the conurbation. Metropolitan Essex does not have a precise, formal definition.
Coast
The deep estuaries on the east coast give Essex, by some measures, the longest coast of any county. These estuaries mean the county's
North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea, epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the ...
coast is characterised by three major peninsulas, each named after the
Hundred
100 or one hundred (Roman numeral: C) is the natural number following 99 and preceding 101.
In medieval contexts, it may be described as the short hundred or five score in order to differentiate the English and Germanic use of "hundred" to des ...
based on the peninsula:
*
Tendring
Tendring is a village and civil parish in Essex. It gives its name to the Tendring District and before that the Tendring Hundred. Its name was given to the larger groupings because it was at the centre, not because it was larger than the other ...
between the
Stour and the
Colne
Colne () is a market town and civil parish in the Borough of Pendle in Lancashire, England. Located northeast of Nelson, north-east of Burnley, east of Preston and west of Leeds.
The town should not be confused with the unrelated Colne Val ...
.
*
Dengie
Dengie is a village and civil parish in the Maldon district of Essex, England, with a population of 119 at the 2011 census.
It gives its name to the Dengie peninsula and hundred and to the Dengie Special Protection Area.
The place-name 'Dengi ...
between the
Blackwater and the
Crouch
*
Rochford between the Crouch and the
Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the second-longest in the United Kingdom, after the R ...
A consequence of these features is that the broad estuaries defining them have been a factor in preventing any transport infrastructure linking them to neighbouring areas on the other side of the river estuaries, to the north and south.
Highest point
The highest point of the county of Essex is
Chrishall Common near the village of
Langley Langley may refer to:
People
* Langley (surname), a common English surname, including a list of notable people with the name
* Dawn Langley Simmons (1922–2000), English author and biographer
* Elizabeth Langley (born 1933), Canadian perfor ...
, close to the
Hertfordshire border, which reaches .
Human and economic geography
The county's infrastructure is shaped by its physical geography and proximity to London. Together, these influences both stimulate and constrain the Essex economy.
Economy
A high proportion of the population, especially in the south, work outside the county, commuting to London and elsewhere by rail and by road. These London-based jobs are often well paid and complement the contribution made by the employers based within Essex.
Industry is largely limited to the south of the county, with the majority of the land elsewhere being given over to agriculture. Harlow is a centre for electronics, science and
pharmaceutical
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field an ...
companies. Chelmsford has been an important location for
electronics
The field of electronics is a branch of physics and electrical engineering that deals with the emission, behaviour and effects of electrons using electronic devices. Electronics uses active devices to control electron flow by amplification ...
companies, such as the
Marconi Company
The Marconi Company was a British telecommunications and engineering company that did business under that name from 1963 to 1987. Its roots were in the Wireless Telegraph & Signal Company founded by Italian inventor Guglielmo Marconi in 189 ...
, since the industry was born; it is also the location for a number of insurance and financial services organisations and, until 2015, was the home of the soft drinks producer
Britvic
Britvic plc is a British producer of soft drinks based in Hemel Hempstead, England. It is listed on the London Stock Exchange and is a constituent of the FTSE 250 Index. It produces soft drinks under its own name, and several other brands.
Hist ...
.
Basildon
Basildon ( ) is the largest town in the borough of Basildon, within the county of Essex, England. It has a population of 107,123. In 1931 the parish had a population of 1159.
It lies east of Central London, south of the city of Chelmsford and ...
is home to
New Holland Agriculture's European headquarters as well as the
Ford Motor Company
Ford Motor Company (commonly known as Ford) is an American multinational automobile manufacturer headquartered in Dearborn, Michigan, United States. It was founded by Henry Ford and incorporated on June 16, 1903. The company sells automobi ...
's British HQ.
Debden, in
Loughton
Loughton () is a town and civil parish in the Epping Forest District of Essex. Part of the metropolitan and urban area of London, the town borders Chingford, Waltham Abbey, Theydon Bois, Chigwell and Buckhurst Hill, and is northeast of Chari ...
, is home to a production facility for British and foreign
banknotes
A banknote—also called a bill (North American English), paper money, or simply a note—is a type of negotiable promissory note, made by a bank or other licensed authority, payable to the bearer on demand.
Banknotes were originally issued ...
.
Other businesses in the county are dominated by mechanical engineering, including but not limited to
metalworking
Metalworking is the process of shaping and reshaping metals to create useful objects, parts, assemblies, and large scale structures. As a term it covers a wide and diverse range of processes, skills, and tools for producing objects on every scal ...
,
glassmaking
Glass production involves two main methods – the float glass process that produces sheet glass, and glassblowing that produces bottles and other containers. It has been done in a variety of ways during the history of glass.
Glass container ...
and plastics and the
service sector. Colchester is a
garrison town and the local economy is helped by the
Army
An army (from Old French ''armee'', itself derived from the Latin verb ''armāre'', meaning "to arm", and related to the Latin noun ''arma'', meaning "arms" or "weapons"), ground force or land force is a fighting force that fights primarily on ...
's personnel
living there. Basildon is the location of
State Street Corporation
State Street Corporation is an American financial services and bank holding company headquartered at One Lincoln Street in Boston with operations worldwide. It is the second-oldest continually operating United States bank; its predecessor, Un ...
's United Kingdom HQ International Financial Data Services and remains heavily dependent on London for employment, due to its proximity and direct transport routes. Southend-on-Sea is home to the
Adventure Island theme park and is one of the few still growing British
seaside resort
A seaside resort is a town, village, or hotel that serves as a vacation resort and is located on a coast. Sometimes the concept includes an aspect of official accreditation based on the satisfaction of certain requirements, such as in the Germ ...
s, benefiting from modern and direct rail links from
Fenchurch Street railway station
Fenchurch Street railway station, also known as London Fenchurch Street, is a central London railway terminus in the southeastern corner of the City of London. It takes its name from its proximity to Fenchurch Street, a key thoroughfare in th ...
and
Liverpool Street station (so that housing is in high demand, especially for financial services commuters), which maintains the town's commercial and general economy.
Parts of eastern Essex suffer from high levels of deprivation; one of the most highly deprived wards is in the seaside town of
Clacton. In the
Indices of deprivation 2007 The Indices of deprivation 2007 (ID 2007) is a deprivation index at the small area level, created by the British Department for Communities and Local Government (DCLG) and released on 12 June 2007. It follows the Indices of deprivation 2004 (ID200 ...
,
Jaywick
Jaywick is a coastal village in the Tendring district of Essex, England, west of Clacton-on-Sea. It lies on the North Sea coast of England, from London and from Colchester. It was constructed in the 1930s as a holiday resort for Londoners, ...
was identified as the most deprived Lower Super Output Area in Southern England. Unemployment was estimated at 44% and many homes were found to lack very basic amenities. The Brooklands and Grasslands area of Jaywick was found to be the third-most deprived area in England; two areas in
Liverpool
Liverpool is a city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. With a population of in 2019, it is the 10th largest English district by population and its metropolitan area is the fifth largest in the United Kingdom, with a populat ...
and
Manchester
Manchester () is a city in Greater Manchester, England. It had a population of 552,000 in 2021. It is bordered by the Cheshire Plain to the south, the Pennines to the north and east, and the neighbouring city of Salford to the west. The t ...
were rated more deprived. In contrast, mid, west and south-west Essex is one of the most affluent parts of eastern England, forming part of the
London commuter belt
The London metropolitan area is the metropolitan area of London, England. It has several definitions, including the London Travel to Work Area, and usually consists of the London urban area, settlements that share London's infrastructure, and ...
. There is a large middle class here and the area is widely known for its private schools. In 2008, ''
The Daily Telegraph
''The Daily Telegraph'', known online and elsewhere as ''The Telegraph'', is a national British daily broadsheet newspaper published in London by Telegraph Media Group and distributed across the United Kingdom and internationally.
It was f ...
'' found
Ingatestone
Ingatestone is a village and former civil parish in Essex, England, with a population of 5,365 inhabitants according to the 2011 census. Just north lies the village of Fryerning, the two forming now the parish of Ingatestone and Fryerning. In ...
and Brentwood to be the 14th- and 19th-richest towns in the UK respectively.
Settlement patterns
The pattern of settlement in the county is diverse. The areas closest to London are the most densely settled, though the
Metropolitan Green Belt
The Metropolitan Green Belt is a statutory green belt around London, England. It comprises parts of Greater London, Berkshire, Buckinghamshire, Essex, Hertfordshire, Kent and Surrey, parts of two of the three districts of Bedfordshire and a s ...
has prevented the further sprawl of London into the county. The Green Belt was initially a narrow band of land, but subsequent expansions meant it was able to limit the further expansion of many of the commuter towns close to the capital. The Green Belt zone close to London includes many prosperous commuter towns, as well as the
new towns of
Basildon
Basildon ( ) is the largest town in the borough of Basildon, within the county of Essex, England. It has a population of 107,123. In 1931 the parish had a population of 1159.
It lies east of Central London, south of the city of Chelmsford and ...
and
Harlow, originally developed to resettle Londoners after the destruction of London housing in the
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
; they have since been significantly developed and expanded.
Epping Forest
Epping Forest is a area of ancient woodland, and other established habitats, which straddles the border between Greater London and Essex. The main body of the forest stretches from Epping in the north, to Chingford on the edge of the London ...
also prevents the further spread of the
Greater London Urban Area
The Greater London Built-up Area, or Greater London Urban Area, is a conurbation in south-east England that constitutes the continuous urban sprawl of London, and includes surrounding adjacent urban towns as defined by the Office for National Sta ...
. As it is not far from London, with its economic magnetism, many of Essex's settlements, particularly those near or within short driving distance of railway stations, function as
dormitory town
A commuter town is a populated area that is primarily residential rather than commercial or industrial. Routine travel from home to work and back is called commuting, which is where the term comes from. A commuter town may be called by many o ...
s or villages where London workers raise their families. In these areas a high proportion of the population commute to London, and the wages earned in the capital are typically significantly higher than more local jobs. Many parts of Essex therefore, especially those closest to London, have a major economic dependence on London and the transport links that take people to work there.

Part of the south-east of the county, already containing the major population centres of
Basildon
Basildon ( ) is the largest town in the borough of Basildon, within the county of Essex, England. It has a population of 107,123. In 1931 the parish had a population of 1159.
It lies east of Central London, south of the city of Chelmsford and ...
,
Southend
Southend-on-Sea (), commonly referred to as Southend (), is a coastal city and unitary authority area with borough status in southeastern Essex, England. It lies on the north side of the Thames Estuary, east of central London. It is bordered ...
and
Thurrock
Thurrock () is a unitary authority area with borough status and unparished area in the ceremonial county of Essex, England. It is part of the London commuter belt and an area of regeneration within the Thames Gateway redevelopment zone. The ...
, is within the
Thames Gateway
Thames Gateway is a term applied to an area around the Thames Estuary in the context of discourse around regeneration and further urbanisation. The term was first coined by the UK government and applies to an area of land stretching east from ...
and designated for further development. Parts of the south-west of the county, such as
Buckhurst Hill
Buckhurst Hill is an affluent suburban town in the Epping Forest district of Essex, England. It is part of the Greater London Urban Area and adjacent to the northern boundary of the London Borough of Redbridge. The area developed following the o ...
and
Chigwell
Chigwell is a town and civil parish in the Epping Forest District of Essex, England. It is part of the urban and metropolitan area of London, and is adjacent to the northern boundary of Greater London. It is on the Central line of the Lond ...
, are contiguous with
Greater London neighbourhoods and therefore form part of the
Greater London Urban Area
The Greater London Built-up Area, or Greater London Urban Area, is a conurbation in south-east England that constitutes the continuous urban sprawl of London, and includes surrounding adjacent urban towns as defined by the Office for National Sta ...
.
A small part of the south-west of the county,
Sewardstone
Sewardstone is a hamlet and district of southern Waltham Abbey, in the Epping Forest District of Essex, England, lying between Epping Forest and the built-up areas of Waltham Abbey, Chingford and Enfield. It is 11.6 miles north-northeast of Cent ...
, is the only settlement outside Greater London to be covered by a postcode district of the
London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
post town (). Besides the cities of
Colchester
Colchester ( ) is a city in Essex, in the East of England. It had a population of 122,000 in 2011. The demonym is Colcestrian.
Colchester occupies the site of Camulodunum, the first major city in Roman Britain and its first capital. Colch ...
,
Chelmsford
Chelmsford () is a City status in the United Kingdom, city in the City of Chelmsford district in the county of Essex, England. It is the county town of Essex and one of three cities in the county, along with Southend-on-Sea and Colchester. It ...
and
Southend-on-Sea
Southend-on-Sea (), commonly referred to as Southend (), is a coastal city and unitary authority area with borough status in southeastern Essex, England. It lies on the north side of the Thames Estuary, east of central London. It is bordered ...
, the county is rural, with many small towns, villages and hamlets largely built in the traditional materials of timber and brick, with clay tile or thatched roofs.
Transport
Much of Essex lies within the
London commuter belt
The London metropolitan area is the metropolitan area of London, England. It has several definitions, including the London Travel to Work Area, and usually consists of the London urban area, settlements that share London's infrastructure, and ...
, with radial transport links to the capital an important part of the area's economy. There are nationally or regionally important ports and airports and these also rely on the Essex infrastructure, causing an additional load on the local road and rail links.
Railway
Essex's railway routes to London are, running clockwise:
* The
West Anglia Main Line
The West Anglia Main Line is one of the two main lines that operate out of , the other being the Great Eastern Main Line, which operates services to Ipswich and Norwich via Colchester. It runs generally north through Cheshunt, Broxbourne, Har ...
from
Liverpool Street to
Harlow,
Stansted Airport
London Stansted Airport is a tertiary international airport serving London, England, United Kingdom. It is located near Stansted Mountfitchet, Essex, England, northeast of Central London.
London Stansted serves over 160 destinations acro ...
and onward to
Cambridgeshire
Cambridgeshire (abbreviated Cambs.) is a county in the East of England, bordering Lincolnshire to the north, Norfolk to the north-east, Suffolk to the east, Essex and Hertfordshire to the south, and Bedfordshire and Northamptonshire to the ...
.
* The southern part of
Epping Forest
Epping Forest is a area of ancient woodland, and other established habitats, which straddles the border between Greater London and Essex. The main body of the forest stretches from Epping in the north, to Chingford on the edge of the London ...
district is served by the
London Underground
The London Underground (also known simply as the Underground or by its nickname the Tube) is a rapid transit system serving Greater London and some parts of the adjacent counties of Buckinghamshire, Essex and Hertfordshire in England.
The ...
Central line.
* The
Great Eastern Main Line from Liverpool Street to
Shenfield
Shenfield is a commuter suburb of Brentwood, in the borough of Brentwood, Essex, England. In 2020, the suburb was estimated to have a population of 5,396.
History
The old village (now town), by the church and Green Dragon pub, lies along the ...
,
Chelmsford
Chelmsford () is a City status in the United Kingdom, city in the City of Chelmsford district in the county of Essex, England. It is the county town of Essex and one of three cities in the county, along with Southend-on-Sea and Colchester. It ...
,
Colchester
Colchester ( ) is a city in Essex, in the East of England. It had a population of 122,000 in 2011. The demonym is Colcestrian.
Colchester occupies the site of Camulodunum, the first major city in Roman Britain and its first capital. Colch ...
and onto
East Anglia. The Great Eastern includes branch lines to:
#
Harwich and its port. The nearby port of Felixstowe in Suffolk is served by a separate branch.
# The
Sunshine Coast Line linking
Colchester
Colchester ( ) is a city in Essex, in the East of England. It had a population of 122,000 in 2011. The demonym is Colcestrian.
Colchester occupies the site of Camulodunum, the first major city in Roman Britain and its first capital. Colch ...
to the seaside resorts of
Clacton-on-Sea
Clacton-on-Sea is a seaside town in the Tendring District in the county of Essex, England. It is located on the Tendring Peninsula and is the largest settlement in the Tendring District with a population of 56,874 (2016). The town is situated ...
and
Walton-on-the-Naze
Walton-on-the-Naze is a seaside town on the North Sea coast and (as Walton le Soken) a former civil parish, now in the parish of Frinton and Walton, in the Tendring district in Essex, England. It is north of Clacton and south of the port of H ...
via the picturesque towns of
Wivenhoe
Wivenhoe ( ) is a town and civil parish in north-eastern Essex, England, approximately south-east of Colchester. Historically Wivenhoe village, on the banks of the River Colne, and Wivenhoe Cross, on the higher ground to the north, were two ...
and
Great Bentley
Great Bentley is a village, civil parish and electoral ward in the Tendring district of north Essex, England, located seven miles east of Colchester. The parish includes the hamlets of Aingers Green and South Heath. It is home to the second lar ...
.
#
Braintree.
# Branch from
Marks Tey
Marks Tey is a large village and electoral ward in Essex, England; it is located six miles west of Colchester.
Facilities
Marks Tey is one of a group of villages called the Teys, also including Great Tey and Little Tey. Its main features includ ...
to Sudbury (Suffolk) and villages in-between.
# In the densely populated south, there is a branch to
Southend Victoria
Southend Victoria railway station is the eastern terminus of the Shenfield to Southend Line in the East of England, a branch off the Great Eastern Main Line, and is one of the primary stations serving the resort city of Southend-on-Sea, Essex ...
, the Rochford Peninsula and several south Essex towns. This branch has a sub-branch – the
Crouch Valley Line – linking
Wickford
Wickford is a town and civil parish in the south of the English county of Essex, with a population of 33,486. Located approximately 30 miles (50 km) east of London, it is within the Borough of Basildon along with the original town of Basil ...
to the remote
Dengie Peninsula
__NOTOC__
Dengie is a peninsula in Essex, England, that once formed a hundred of the same name (sometimes spelled Dengy).
The peninsula is formed by the River Crouch to the south, the Blackwater to the north, both of which are tidal, and the N ...
, including
Burnham-on-Crouch and
Southminster
Southminster is a town and electoral ward on the Dengie Peninsula in the Maldon district of Essex in the East of England. It lies about north of Burnham-on-Crouch and south-east of Maldon; it is approximately east-north-east of London. To the ...
.
* Like the Southend Victoria branch, the
London, Tilbury & Southend Railway
The London, Tilbury and Southend Railway (LT&SR), was a British railway company, whose network connected Fenchurch Street station, in central London, with destinations in east London and Essex, including , , , Tilbury, Southend and . The company ...
also serves Southend (
Southend Central), the Rochford Peninsula and many towns in the densely populated south of the county. The London terminus is
Fenchurch Street
Fenchurch Street is a street in London linking Aldgate at its eastern end with Lombard Street and Gracechurch Street in the west. It is a well-known thoroughfare in the City of London financial district and is the site of many corporate office ...
and heading eastward from Barking, the line separates into three, which later merge back into one by the time the railway reaches
Pitsea
Pitsea is a small town and former civil parish, now in the unparished area of Basildon, in south Essex, England. It comprises five sub-districts: Eversley, Northlands Park Neighbourhood (previously known as Felmores), Chalvedon, Pitsea Mount and B ...
.
The
Essex Thameside
Essex Thameside is a railway franchise for the provision of passenger services on the London, Tilbury and Southend line in east London and south Essex. It was formed on 26 May 1996, following the privatisation of British Rail and the franchise wa ...
franchise is operated by
. The Greater Anglia routes (both the
West Anglia and
Great Eastern Main Line and their branches) are operated by
Greater Anglia.
Road

Essex has six main strategic routes, five of which reflect the powerful influence exerted by London.
The
M25 is London's orbital motorway which redistributes traffic across the London area. It includes the
Dartford Road Crossings, over the Thames Estuary, linking Essex to Kent.
There are four radial commuter routes into the capital:
*
M11 motorway, which also serves
Stansted Airport
London Stansted Airport is a tertiary international airport serving London, England, United Kingdom. It is located near Stansted Mountfitchet, Essex, England, northeast of Central London.
London Stansted serves over 160 destinations acro ...
and provides commuter links to
Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a College town, university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cam ...
.
*
A12, to
East Anglia via
Chelmsford
Chelmsford () is a City status in the United Kingdom, city in the City of Chelmsford district in the county of Essex, England. It is the county town of Essex and one of three cities in the county, along with Southend-on-Sea and Colchester. It ...
and
Colchester
Colchester ( ) is a city in Essex, in the East of England. It had a population of 122,000 in 2011. The demonym is Colcestrian.
Colchester occupies the site of Camulodunum, the first major city in Roman Britain and its first capital. Colch ...
. It also serves the ports of Harwich and Felixstowe (Suffolk).
*
A127
The A127, also known as the Southend Arterial Road, is a major road in Essex, England. It was constructed as a new arterial road project in the 1920s, linking Romford with Southend-on-Sea, replacing the older A13. Formerly classified as a tr ...
, to the Rochford Peninsula, including
Southend
Southend-on-Sea (), commonly referred to as Southend (), is a coastal city and unitary authority area with borough status in southeastern Essex, England. It lies on the north side of the Thames Estuary, east of central London. It is bordered ...
and
Southend Airport
Southend-on-Sea (), commonly referred to as Southend (), is a coastal city and unitary authority area with borough status in southeastern Essex, England. It lies on the north side of the Thames Estuary, east of central London. It is bordered ...
. This is no longer maintained as a trunk road.
*
A13, to the Rochford Peninsula, also including Southend. It also serves the expanding
Tilbury
Tilbury is a port town in the borough of Thurrock, Essex, England. The present town was established as separate settlement in the late 19th century, on land that was mainly part of Chadwell St Mary. It contains a 16th century fort and an ancie ...
and
London Gateway
DP World London Gateway is a port within the wider Port of London, United Kingdom. Opened in November 2013, the site is a fully integrated logistics facility, comprising a semi-automated deep-sea container terminal on the same site as the UK ...
ports.
The A120 is a major route heading west from the ports of Harwich and Felixstowe (Suffolk) and, like the A12, the route was in use during the Roman period and, in part at least, before then.
Ports and waterborne transport
The
Port of Tilbury
The Port of Tilbury is a port on the River Thames at Tilbury in Essex, England. It is the principal port for London, as well as being the main United Kingdom port for handling the importation of paper. There are extensive facilities for contai ...
is one of Britain's three major ports and has proposed a major extension onto the site of the former
Tilbury power stations
The Tilbury power stations were two thermal power stations on the north bank of the River Thames at Tilbury in Essex. The 360 MW dual coal- and oil-fired Tilbury A Power Station operated from 1956 until 1981 when it was mothballed, prior to dem ...
. The port of
Harwich has passenger and freight services to the
Hook of Holland
Hook of Holland ( nl, Hoek van Holland, ) is a town in the southwestern corner of Holland, hence the name; ''hoek'' means "corner" and was the word in use before the word ''kaap'' – "cape", from Portuguese ''cabo'' – became Dutch. The English t ...
and a freight service to
Europoort
Europoort (, en, Eurogate, also "Europort") is an area of the Port of Rotterdam and the adjoining industrial area in the Netherlands. Being situated at Southside of the mouth of the rivers Rhine and Meuse with the hinterland consisting of the ...
. A service to
Esbjerg, Denmark ceased in September 2014 and earlier a service to
Cuxhaven
Cuxhaven (; ) is an independent town and seat of the Cuxhaven district, in Lower Saxony, Germany. The town includes the northernmost point of Lower Saxony. It is situated on the shore of the North Sea at the mouth of the Elbe River. Cuxhaven has ...
in Germany was discontinued in December 2005.
The UK's largest container terminal
London Gateway
DP World London Gateway is a port within the wider Port of London, United Kingdom. Opened in November 2013, the site is a fully integrated logistics facility, comprising a semi-automated deep-sea container terminal on the same site as the UK ...
at
Shell Haven
Shell Haven was a port on the north bank of the Thames Estuary at the eastern end of Thurrock, Essex, England and then an oil refinery. The refinery closed in 1999 and the site was purchased by DP World who received planning consent in May 200 ...
in
Thurrock
Thurrock () is a unitary authority area with borough status and unparished area in the ceremonial county of Essex, England. It is part of the London commuter belt and an area of regeneration within the Thames Gateway redevelopment zone. The ...
partly opened in November 2013; final completion date is yet to be confirmed. The port was opposed by the local authority and environmental and wildlife organisations.
The ports have branch lines to connect them to the national rail network. These freight movements conflict with the needs of commuter passenger services, limiting their frequency and reliability.
East of the
Dartford Road Crossing to
Dartford in Kent, across the
Thames Estuary
The Thames Estuary is where the River Thames meets the waters of the North Sea, in the south-east of Great Britain.
Limits
An estuary can be defined according to different criteria (e.g. tidal, geographical, navigational or in terms of salini ...
, a pedestrian ferry to
Gravesend, Kent operates from
Tilbury
Tilbury is a port town in the borough of Thurrock, Essex, England. The present town was established as separate settlement in the late 19th century, on land that was mainly part of Chadwell St Mary. It contains a 16th century fort and an ancie ...
during limited daily hours; there are pedestrian ferries across some of Essex's rivers and estuaries in spring and summer.
Airports

The main airport in Essex is
Stansted Airport
London Stansted Airport is a tertiary international airport serving London, England, United Kingdom. It is located near Stansted Mountfitchet, Essex, England, northeast of Central London.
London Stansted serves over 160 destinations acro ...
, serving destinations in Europe, North Africa and Asia. The Conservative-Liberal Democrat coalition government, formed in May 2010, agreed not to allow a further runway until a set time period, so curtailing the operator's ambitions for expansion.
London Southend Airport
London Southend Airport is an international airport situated on the outskirts of Southend-on-Sea in Essex, England, approximately from the centre of London. The airport straddles the boundaries between the city of Southend-on-Sea and the R ...
, once one of Britain's busiest airports, opened a new runway extension, terminal building and railway station in March 2012. It has a station on the
Shenfield to Southend Line, with a direct link to London.
Southend Airport has scheduled flights to Ireland, the
Channel Islands
The Channel Islands ( nrf, Îles d'la Manche; french: îles Anglo-Normandes or ''îles de la Manche'') are an archipelago in the English Channel, off the French coast of Normandy. They include two Crown Dependencies: the Bailiwick of Jersey, ...
and multiple destinations in Europe. Essex has several smaller airfields, some of which owe their origins to military bases built during World War I or World War II, giving pleasure flights or flying lessons; these include
Clacton Airfield,
Earls Colne Airfield
Earls Colne Airfield is a general aviation aerodrome located south-east of the village of Earls Colne, Essex, England.
The site was previously RAF Earls Colne, a Royal Air Force station which was primilarly used by the United States Army Air For ...
and
Stapleford Aerodrome.
History
Essex evolved from the
Kingdom of the East Saxons, a polity which is likely to have its roots in the territory of the
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostl ...
Trinovantes
The Trinovantēs (Common Brittonic: *''Trinowantī'') or Trinobantes were one of the Celtic tribes of Pre-Roman Britain. Their territory was on the north side of the Thames estuary in current Essex, Hertfordshire and Suffolk, and included land ...
tribe.
Iron Age
Essex corresponds, fairly closely, to the territory of the
Trinovantes
The Trinovantēs (Common Brittonic: *''Trinowantī'') or Trinobantes were one of the Celtic tribes of Pre-Roman Britain. Their territory was on the north side of the Thames estuary in current Essex, Hertfordshire and Suffolk, and included land ...
tribe. Their production of their own coinage marks them out as one of the more advanced tribes on the island, this advantage (in common with other tribes in the south-east) is probably due to the
Belgic element within their elite. Their capital was the
oppidum (a type of town) of Colchester, Britain's oldest recorded town, which had its own mint.
The tribe were in extended conflict with their western neighbours, the
Catuvellauni
The Catuvellauni (Common Brittonic: *''Catu-wellaunī'', "war-chiefs") were a Celtic tribe or state of southeastern Britain before the Roman conquest, attested by inscriptions into the 4th century.
The fortunes of the Catuvellauni and their ...
, and steadily lost ground. By AD 10 they had come under the complete control of the Catuvellauni, who took Colchester as their own capital.
Roman
The
Roman invasion of AD 43 began with a landing on the south coast, probably in the
Richborough
Richborough () is a settlement north of Sandwich on the east coast of the county of Kent, England. Richborough lies close to the Isle of Thanet. The population of the settlement is included in the civil parish of Ash.
Although now some dist ...
area of
Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces ...
. After some initial successes against the Britons, they paused to await reinforcements, and the arrival of the Emperor
Claudius. The combined army then proceeded to the capital of the Catevellauni-Trinovantes at
Colchester
Colchester ( ) is a city in Essex, in the East of England. It had a population of 122,000 in 2011. The demonym is Colcestrian.
Colchester occupies the site of Camulodunum, the first major city in Roman Britain and its first capital. Colch ...
, and took it.
Claudius held a review of his invasion force on
Lexden
Lexden is a suburb of Colchester and former civil parish, now in the unparished area of Colchester, in the Colchester district, in the county of Essex, England. It was formerly a village, and has previously been called Lessendon, Lassendene and ...
Heath where the army formally proclaimed him
Imperator. The invasion force that assembled before him included four
legions, mounted auxiliaries and an elephant corps – a force of around 30,000 men. At Colchester, the kings of 11 British tribes surrendered to Claudius.
Colchester became a
Roman Colonia
A Roman (plural ) was originally a Roman outpost established in conquered territory to secure it. Eventually, however, the term came to denote the highest status of a Roman city. It is also the origin of the modern term ''colony''.
Characteri ...
, with the official name Colonia Claudia Victricensis ('the City of Claudius' Victory'). It was initially the most important city in Roman Britain and in it they
established a temple to the God-Emperor Claudius. This was the largest building of its kind in
Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the period in classical antiquity when large parts of the island of Great Britain were under occupation by the Roman Empire. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410. During that time, the territory conquered wa ...
.
The establishment of the Colonia is thought to have involved extensive appropriation of land from local people, this and other grievances led to the Trinovantes joining their northern neighbours, the
Iceni
The Iceni ( , ) or Eceni were a Brittonic tribe of eastern Britain during the Iron Age and early Roman era. Their territory included present-day Norfolk and parts of Suffolk and Cambridgeshire, and bordered the area of the Corieltauvi to the we ...
, in the
Boudiccan revolt. The rebels entered the city, and after a Roman last stand at the temple of Claudius, methodically destroyed it, massacring many thousands. A significant Roman force attempting to relieve Colchester was destroyed in pitched battle, known as the
Massacre of the Ninth Legion.
The rebels then proceeded to sack
London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
and
St Albans, with
Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
The surviving portions of his two major works—the ...
estimating that 70–80,000 people were killed in the destruction of the three cities. Boudicca was defeated in battle, somewhere in the west midlands, and the Romans are likely to have ravaged the lands of the rebel tribes, so Essex will have suffered greatly.
Despite this, the Trinovantes' identity persisted. Roman provinces were divided into ''civitas'' for local government purposes – with a civitas for the Trinovantes strongly implied by
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance ...
. Christianity is thought to have been flourishing among the Trinovantes in the fourth century, indications include the remains of a probable church at Colchester, the church dates from sometime after 320, shortly after the
Constantine the Great
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterran ...
granted freedom of worship to Christians in 313. Other archaeological evidence include a
chi-rho
The Chi Rho (☧, English pronunciation ; also known as ''chrismon'') is one of the earliest forms of Christogram, formed by superimposing the first two (capital) letters— chi and rho (ΧΡ)—of the Greek word ( Christos) in such a way tha ...
symbol etched on a tile at a site in
Wickford
Wickford is a town and civil parish in the south of the English county of Essex, with a population of 33,486. Located approximately 30 miles (50 km) east of London, it is within the Borough of Basildon along with the original town of Basil ...
, and a gold ring inscribed with a chi-rho monogram found at
Brentwood.
The late Roman period, and the period shortly after, was the setting for the
King Cole
Coel (Old Welsh: ''Coil''), also called ''Coel Hen'' (Coel the Old) and King Cole, is a figure prominent in Welsh literature and legend since the Middle Ages. Early Welsh tradition knew of a Coel Hen, a 4th-century leader in Roman or Sub-Roman ...
legends based around
Colchester
Colchester ( ) is a city in Essex, in the East of England. It had a population of 122,000 in 2011. The demonym is Colcestrian.
Colchester occupies the site of Camulodunum, the first major city in Roman Britain and its first capital. Colch ...
. One version of the legend concerns
St Helena, the mother of
Constantine the Great
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterran ...
. The legend makes her the daughter of Coel, Duke of the Britons (
King Cole
Coel (Old Welsh: ''Coil''), also called ''Coel Hen'' (Coel the Old) and King Cole, is a figure prominent in Welsh literature and legend since the Middle Ages. Early Welsh tradition knew of a Coel Hen, a 4th-century leader in Roman or Sub-Roman ...
) and in it she gives birth to Constantine in Colchester. This, and
related legends, are at variance with biographical details as they are now known, but it is likely that Constantine, and his father,
Constantius spent time in Colchester during their years in Britain. The presence of St Helena in the country is less certain.
Anglo-Saxon period

The name ''Essex'' originates in the
Anglo-Saxon period of the
Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
and has its root in the Anglo-Saxon (
Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th c ...
) name ''Ēastseaxe'' ("East Saxons"), the eastern kingdom of the
Saxons who had come from the continent and settled in Britain. Excavations at
Mucking
Mucking is a hamlet and former Church of England parish adjoining the Thames Estuary in southern Essex, England. It is located approximately south of the town of Stanford-le-Hope in what is now Thurrock unitary authority. In 1931 the parish had ...
have demonstrated the presence of Anglo-Saxon settlers in the early fifth century, however the way in which these settlers became ascendent in the territory of the Trinovantes is not known. Studies suggest a pattern of typically peaceful co-existence, with the structure of the Romano-British landscape being maintained, and with the Saxon settlers believed to have been in the minority.
The first known king of the East Saxons was
Sledd in 587, though there are less reliable sources giving an account of
Aescwine (other versions call him Erkenwine) founding the kingdom in 527. The early kings of the East Saxons were pagan and uniquely amongst the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms traced their lineage back to
Seaxnēat, god of the
Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
, rather than
Woden
Odin (; from non, Óðinn, ) is a widely revered god in Germanic paganism. Norse mythology, the source of most surviving information about him, associates him with wisdom, healing, death, royalty, the gallows, knowledge, war, battle, victory ...
. The
kings of Essex are notable for their S-nomenclature, nearly all of them begin with the letter S.
The
Kingdom of the East Saxons included not just the subsequent county of Essex, but also Middlesex (including the
City of London
The City of London is a city, ceremonial county and local government district that contains the historic centre and constitutes, alongside Canary Wharf, the primary central business district (CBD) of London. It constituted most of London f ...
), much of
Hertfordshire and at times also the
sub-Kingdom of Surrey. The Middlesex and Hertfordshire parts were known as the ''Province of the Middle Saxons'' since at least the early eighth century but it is not known if the province was previously an independent unit that came under East Saxon control. Charter evidence shows that the Kings of Essex appear to have had a greater control in the core area, east of the Lea and Stort, that would subsequently become the county of Essex. In the core area they granted charters freely, but further west they did so while also making reference to their
Mercia
la, Merciorum regnum
, conventional_long_name=Kingdom of Mercia
, common_name=Mercia
, status=Kingdom
, status_text=Independent kingdom (527–879) Client state of Wessex ()
, life_span=527–918
, era= Heptarchy
, event_start=
, date_start=
, ...
n overlords.
The early kings were pagan, together with much and perhaps by this time all of the population. Sledd's son
Sebert converted to Christianity around 604 and
St Pauls Cathedral in London was established. On Sebert's death in 616 his sons renounced Christianity and drove out
Mellitus
Saint Mellitus (died 24 April 624) was the first bishop of London in the Saxon period, the third Archbishop of Canterbury, and a member of the Gregorian mission sent to England to convert the Anglo-Saxons from their native paganism to Chris ...
, the
Bishop of London
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is ca ...
. The kingdom re-converted after
St Cedd, a monk from
Lindisfarne and now the patron saint of Essex, converted
Sigeberht II the Good around 653.
In AD 824,
Ecgberht, the King of the
Wessex
la, Regnum Occidentalium Saxonum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of the West Saxons
, common_name = Wessex
, image_map = Southern British Isles 9th century.svg
, map_caption = S ...
and grandfather of
Alfred the Great, defeated the Mercians at the
Battle of Ellandun in Wiltshire, fundamentally changing the balance of power in southern England. The small kingdoms of Essex,
Sussex and of
Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces ...
, previously independent albeit under Mercian overlordship, were subsequently fully absorbed into Wessex.
The later Anglo-Saxon period shows three major battles fought with the Norse recorded in Essex; the
Battle of Benfleet
The Battle of Benfleet was an 894 battle between the Vikings and the Anglo-Saxons commanded by Edward the Elder and Æthelred, Lord of the Mercians, the son and son-in-law of Alfred the Great respectively. The battle was part of a campaign start ...
in 894, the
Battle of Maldon
The Battle of Maldon took place on 11 August 991 AD near Maldon beside the River Blackwater in Essex, England, during the reign of Æthelred the Unready. Earl Byrhtnoth and his thegns led the English against a Viking invasion. The battl ...
in 991 and the
Battle of Assandun
The Battle of Assandun (or Essendune) was fought between Danish and English armies on 18 October 1016. There is disagreement whether Assandun may be Ashdon near Saffron Walden in north Essex, England, or, as long supposed and better evidenc ...
(probably at either
Ashingdon
Ashingdon is a village and civil parish in Essex, England. It is located about north of Rochford and is southeast from the county town of Chelmsford. The village lies within Rochford District and the parliamentary constituency of Rayleigh.
A ...
or
Ashdon
Ashdon, is a village and civil parish in Essex, England. It is about northeast of Saffron Walden and northwest from the county town of Chelmsford. The village is in the district of Uttlesford and the parliamentary constituency of Saffron Walde ...
) in 1016.
The county of Essex was formed from the core area, east of the
River Lea, of the former Kingdom of the East Saxons in the 9th or 10th centuries and divided into groupings called
Hundreds.
Before the
Norman conquest
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Norman, Breton, Flemish, and French troops, all led by the Duke of Normandy, later styled William the Con ...
the East Saxons were subsumed into the
Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England (, ) was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from 12 July 927, when it emerged from various History of Anglo-Saxon England, Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Kingdom of Scotland, ...
.
After the Norman Conquest
Having conquered England,
William the Conqueror
William I; ang, WillelmI (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), usually known as William the Conqueror and sometimes William the Bastard, was the first House of Normandy, Norman List of English monarchs#House of Norman ...
initially based himself at
Barking Abbey
Barking Abbey is a former royal monastery located in Barking, in the London Borough of Barking and Dagenham. It has been described as having been "one of the most important nunneries in the country".
Originally established in the 7th century, f ...
, an already ancient nunnery, for several months while a secure base, which eventually became the
Tower of London
The Tower of London, officially His Majesty's Royal Palace and Fortress of the Tower of London, is a historic castle on the north bank of the River Thames in central London. It lies within the London Borough of Tower Hamlets, which is sep ...
could be established in the city. While at Barking William received the submission of some of England's leading nobles. The invaders established a number of castles in the county, to help protect the new elites in a hostile country. There were castles at
Colchester
Colchester ( ) is a city in Essex, in the East of England. It had a population of 122,000 in 2011. The demonym is Colcestrian.
Colchester occupies the site of Camulodunum, the first major city in Roman Britain and its first capital. Colch ...
,
Castle Hedingham
Castle Hedingham is a village in northern Essex, England, located four miles west of Halstead and 3 miles southeast of Great Yeldham in the Colne Valley on the ancient road from Colchester, Essex, to Cambridge.
It developed around Hedingham ...
,
Rayleigh,
Pleshey
Pleshey is a historic village and civil parish in the Chelmsford district, in the county of Essex, England, north-west of Chelmsford. The Normans built a motte and bailey in the late 11th century; the motte is one of the largest of its kind in ...
and elsewhere.
Hadleigh Castle
Hadleigh Castle is a ruined fortification in the English county of Essex, overlooking the Thames Estuary from south of the town of Hadleigh. Built after 1215 during the reign of Henry III by Hubert de Burgh, the castle was surrounded by park ...
was developed much later, in the thirteenth century.

After the arrival of the
Normans
The Normans ( Norman: ''Normaunds''; french: Normands; la, Nortmanni/Normanni) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norse Viking settlers and indigenous West Franks and Gallo-Romans. ...
, the
Forest of Essex
The Forest of Essex was a royal forest that existed from around 1100 and was disestablished in the 13th century.
Forests were legal institutions introduced by the Normans to denote an area where the King or another magnate had the right to keep ...
was established as a
Royal forest
A royal forest, occasionally known as a kingswood (), is an area of land with different definitions in England, Wales, Scotland and Ireland. The term ''forest'' in the ordinary modern understanding refers to an area of wooded land; however, the ...
, however, it is important to note that at that time, the term was a legal term. There was a weak correlation between the area covered by the ''Forest of Essex'' (the large majority of the county) and the much smaller area covered by woodland. An analysis of
Domesday returns for Essex has shown that the ''Forest of Essex'' was mostly farmland, and that the county as a whole was 20% wooded in 1086.
After that point population growth caused the proportion of woodland to fall steadily until the arrival of the
Black Death, in 1348, killed between a third and a half of England's population, leading to a long term stabilisation of the extent of woodland. Similarly, various pressures led to areas being removed from the legal ''Forest of Essex'' and it ceased to exist as a legal entity after 1327, and after that time
Forest Law applied to smaller areas: the forests of
Writtle
The village and civil parish of Writtle lies west of Chelmsford, Essex, England. It has a traditional village green complete with duck pond and a Norman church, and was once described as "one of the loveliest villages in England, with a ravis ...
(near
Chelmsford
Chelmsford () is a City status in the United Kingdom, city in the City of Chelmsford district in the county of Essex, England. It is the county town of Essex and one of three cities in the county, along with Southend-on-Sea and Colchester. It ...
), long lost Kingswood (near Colchester),
, and
Waltham Forest
The London Borough of Waltham Forest () is a London borough in north-east London, England. Its population is estimated to be 276,983 in 2019. It borders five other London boroughs: Enfield to the north-west, Haringey to the west, Hackney to t ...
.
Waltham Forest had covered parts of the
Hundreds of
Waltham, Becontree and Ongar. It also included the physical woodland areas subsequently legally afforested (designated as a legal forest) and known as
Epping Forest
Epping Forest is a area of ancient woodland, and other established habitats, which straddles the border between Greater London and Essex. The main body of the forest stretches from Epping in the north, to Chingford on the edge of the London ...
and
Hainault Forest).
Peasants Revolt, 1381
The Black Death significantly reduced England's population, leading to a change in the balance of power between the working population on one hand, and their masters and employers on the other. Over a period of several decades, national government brought in legislation to reverse the situation, but it was only partially successful and led to simmering resentment.
By 1381, England's economic situation was very poor due to the
war with France, so a new
Poll Tax was levied with commissioners being sent round the country to interrogate local officials in an attempt to ensure tax evasion was reduced and more money extracted. This was hugely unpopular and the
Peasants' Revolt
The Peasants' Revolt, also named Wat Tyler's Rebellion or the Great Rising, was a major uprising across large parts of England in 1381. The revolt had various causes, including the socio-economic and political tensions generated by the Blac ...
broke out in
Brentwood on 1 June 1381.
Several thousand Essex rebels gathered at
Bocking on June 4, and then divided. Some heading to
Suffolk to raise rebellion there, with the rest heading to London, some directly – via
Bow Bridge and others may have gone via Kent. A large force of Kentish rebels also advanced on London while revolt also spread to a number of other parts of the country.
The rebels gained access to the walled
City of London
The City of London is a city, ceremonial county and local government district that contains the historic centre and constitutes, alongside Canary Wharf, the primary central business district (CBD) of London. It constituted most of London f ...
and gained control of the
Tower of London
The Tower of London, officially His Majesty's Royal Palace and Fortress of the Tower of London, is a historic castle on the north bank of the River Thames in central London. It lies within the London Borough of Tower Hamlets, which is sep ...
. They carried out extensive looting in the capital and executed a number of their enemies, but the revolt began to dissipate after the events at
West Smithfield on 15 June, when the Mayor of London,
William Walworth
Sir William Walworth (died 1385) was an English nobleman and politician who was twice Lord Mayor of London (1374–75 and 1380–81). He is best known for killing Wat Tyler during the Peasants' Revolt in 1381.
Political career
His family ca ...
, killed the rebel leader
Wat Tyler
Wat Tyler (c. 1320/4 January 1341 – 15 June 1381) was a leader of the 1381 Peasants' Revolt in England. He led a group of rebels from Canterbury to London to oppose the institution of a poll tax and to demand economic and social reforms. Wh ...
. The rebels prepared to fire arrows at the royal party but the 15 year old
King Richard II
Richard II (6 January 1367 – ), also known as Richard of Bordeaux, was King of England from 1377 until he was deposed in 1399. He was the son of Edward the Black Prince, Prince of Wales, and Joan, Countess of Kent. Richard's father d ...
rode toward the crowd and spoke to them, defusing the situation, in part by making a series of promises he did not subsequently keep.
Having bought himself time, Richard was able to receive reinforcements and then crush the rebellion in Essex and elsewhere. His forces defeated rebels in battle at
Billericay
Billericay ( ) is a town and civil parish in the Borough of Basildon, Essex, England. It lies within the London Basin and constitutes a commuter town east of Central London. The town has three secondary schools and a variety of open spaces. It i ...
on the 28th June, and there were mass executions; hangings and disembowelling at Chelmsford and Colchester.
Wars of the Roses
In 1471, during the
Wars of the Roses
The Wars of the Roses (1455–1487), known at the time and for more than a century after as the Civil Wars, were a series of civil wars fought over control of the English throne in the mid-to-late fifteenth century. These wars were fought bet ...
a force of around 2,000 Essex supporters of the
Lancastrian cause crossed
Bow Bridge to join with 3,000 Kentish Lancastrian supporters under the
Bastard of Fauconberg
Thomas Fauconberg or Thomas Neville, sometimes called Thomas the Bastard, or the Bastard of Fauconberg (1429 – 22 September 1471), was the natural son of William Neville, Lord Fauconberg, who was a leading commander in the Hundred Years' War ...
.
The Essex men joined with their allies in attempting to storm
Aldgate
Aldgate () was a gate in the former defensive wall around the City of London. It gives its name to Aldgate High Street, the first stretch of the A11 road, which included the site of the former gate.
The area of Aldgate, the most common use of ...
and
Bishopsgate during an assault known as the
Siege of London. The Lancastrians were defeated, and the Essex contingent retreated back over the
Lea
Lea or LEA may refer to:
Places Australia
* Lea River, Tasmania, Australia
* Lake Lea, Tasmania, from which the Lea River flows
* RAAF Base Learmonth, IATA airport code "LEA"
England
* Lea, Cheshire, a civil parish
* Lea, Derbyshire, a set ...
with heavy losses.
Armada
In 1588
Tilbury Fort
Tilbury Fort, also known historically as the Thermitage Bulwark and the West Tilbury Blockhouse, is an artillery fort on the north bank of the River Thames in England. The earliest version of the fort, comprising a small blockhouse with artil ...
was chosen as the focal point of the English defences against
King Philip II's Spanish Armada, and the large veteran army he had ordered to invade England. The English believed that the Spanish would land near the Fort, so
Queen Elizabeth's small and relatively poorly trained forces gathered at Tilbury, where the Queen made her
famous speech to the troops.
Civil War
Essex, London and the eastern counties backed Parliament in the
English Civil War
The English Civil War (1642–1651) was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Parliamentarians (" Roundheads") and Royalists led by Charles I ("Cavaliers"), mainly over the manner of England's governance and issues of re ...
, but by 1648, this loyalty was stretched. In June 1648 a force of 500 Kentish Royalists landed near the Isle of Dogs, linked up with a small Royalist cavalry force from Essex, fought a Bow Bridge (London), battle with local parliamentarians at Bow Bridge, then crossed the River Lea into Essex.
The combined force, bolstered by extra forces, marched towards Royalist held
Colchester
Colchester ( ) is a city in Essex, in the East of England. It had a population of 122,000 in 2011. The demonym is Colcestrian.
Colchester occupies the site of Camulodunum, the first major city in Roman Britain and its first capital. Colch ...
, but a Parliamentarian force caught up with them just as they were about to enter the city's medieval walls, and a bitter battle was fought but the Royalists were able to retire to the security of the walls. The Siege of Colchester followed, but ten weeks' starvation and news of Royalist defeats elsewhere led the Royalists to surrender.
Administrative history
Before the County Council
Before the creation of the county councils, county-level administration was limited in nature; lord-lieutenants replaced the sheriff#England, Wales and Northern Ireland, sheriffs from the time of Henry VIII of England, Henry VIII and took a primarily military role, responsible for the militia and the Volunteer Force that replaced it.
Most administration was carried out by justice of the peace, justices of the peace (JPs) appointed by the Lord-Lieutenant of Essex based upon their reputation. The JPs carried out judicial and administrative duties such as maintenance of roads and bridges, supervision of the poor laws, administration of county prisons and setting the County Rate. JPs carried out these responsibilities, mainly through quarter sessions, and did this on a voluntary basis.
At this time the county was sub-divided into units known as
Hundreds. At a very early but unknown date, small parts of the county on the east bank of the Stort, near Bishops Stortford and Sawbridgeworth were transferred to
Hertfordshire
County Councils
Essex County Council
Essex County Council is the county council that governs the non-metropolitan county of Essex in England. It has 75 councillors, elected from 70 divisions, and is currently controlled by the Conservative Party. The council meets at County Hall ...
was formed in 1889. However, County Boroughs of County Borough of West Ham, West Ham (1889–1965), County Borough of Southend-on-Sea, Southend-on-Sea (1914–1974) and County Borough of East Ham, East Ham (1915–1965) formed part of the county but were county boroughs (not under county council control, in a similar manner to unitary authorities today).
[Vision of Britain]
– Essex admin county
historic map
) 12 boroughs and districts provide more localised services such as rubbish and recycling collections, leisure and planning, as shown in the map on the right.
The north-west tip of Essex, the parishes of Great Chishill, Little Chishill and Heydon, Cambridgeshire, Heydon, were transferred to
Cambridgeshire
Cambridgeshire (abbreviated Cambs.) is a county in the East of England, bordering Lincolnshire to the north, Norfolk to the north-east, Suffolk to the east, Essex and Hertfordshire to the south, and Bedfordshire and Northamptonshire to the ...
when the County Councils were created in 1889. Parts of a number of other parishes were also transferred at that time, and since.
Greater London established
The boundary with
Greater London was established in 1965, when County Borough of East Ham, East Ham and County Borough of West Ham, West Ham county boroughs and the Municipal Borough of Barking, Barking, Municipal Borough of Chingford, Chingford, Municipal Borough of Dagenham, Dagenham, Hornchurch Urban District, Hornchurch, Municipal Borough of Ilford, Ilford, Municipal Borough of Leyton, Leyton, Municipal Borough of Romford, Romford, Municipal Borough of Walthamstow, Walthamstow and Municipal Borough of Wanstead and Woodford, Wanstead and Woodford districts as well as a part of Chigwell Urban District, Chigwell
[ were transferred to form the London boroughs of London Borough of Barking and Dagenham, Barking and Dagenham, London Borough of Havering, Havering, London Borough of Newham, Newham, London Borough of Redbridge, Redbridge and London Borough of Waltham Forest, Waltham Forest.
]
Two unitary authorities
In 1998, the borough status in the United Kingdom, boroughs of City of Southend-on-Sea, Southend-on-Sea and Thurrock
Thurrock () is a unitary authority area with borough status and unparished area in the ceremonial county of Essex, England. It is part of the London commuter belt and an area of regeneration within the Thames Gateway redevelopment zone. The ...
were separated from the administrative county of Essex after successful requests to become unitary authority, unitary authorities.
Administration and politics
Essex County Council
The county council governs the non-metropolitan county of Essex in England. It has 75 councillors, elected from 70 divisions, some of which elect more than one member, but before 1965, the number of councillors reached over 100. The council is currently controlled by the Conservative Party (UK), Conservative Party.Essex County Council#cite note-2, [2] The council meets at County Hall, Chelmsford, County Hall in the centre of Chelmsford
Chelmsford () is a City status in the United Kingdom, city in the City of Chelmsford district in the county of Essex, England. It is the county town of Essex and one of three cities in the county, along with Southend-on-Sea and Colchester. It ...
.
At the time of the 2011 census it served a population of 1,393,600, which makes it one of the largest local authorities in England. As a non-metropolitan county council, responsibilities are shared between districts (including Borough status in the United Kingdom, boroughs) and in many areas also between Civil parishes in England, civil parish (including town) councils. Births, marriages/civil partnerships and death registration, roads, libraries and archives, refuse disposal, most of state education, of social services and of transport are provided at the county level.Essex County Council#cite note-comp-3, [3]
The county council was formed in 1889, governing the administrative county
An administrative county was a first-level administrative division in England and Wales from 1888 to 1974, and in Ireland from 1899 until either 1973 (in Northern Ireland) or 2002 (in the Republic of Ireland). They are now abolished, although mos ...
of Essex. The county council was reconstituted in 1974 as a non-metropolitan county council, regaining jurisdiction in Southend-on-Sea; however, the non-metropolitan county was reduced in size in 1998 and the council passed responsibilities to Southend-on-Sea Borough Council and Thurrock Council in those districts. For certain services the three authorities co-operate through joint arrangements, such as the Essex fire authority.
 At the 2013 Essex County Council election, 2013 County Council elections the Conservative Party retained overall control of the council, but its majority fell from twenty-two to four councillors. UKIP, Labour and the Liberal Democrats (UK), Liberal Democrats each won nine seats. Out of those three parties, UKIP gained the largest share of the county-wide vote, more than 10% ahead of Labour.2013 Essex County Council election#cite note-change-3, [3] The Liberal Democrats remain as the official Opposition, despite winning fewer votes.2013 Essex County Council election#cite note-change-3, [3] The Green Party of England and Wales, Green Party gained two seats on the council, despite its overall share of the vote falling. The Independent Loughton Residents Association and the Canvey Island Independent Party both returned one member and an Independent (politician), Independent candidate was also elected.
The 2017 Essex County Council election, 2017 County Council elections saw a county-wide wipeout of UKIP. The Conservative Party profited most from this loss, regaining many of the seats it had lost at the previous election. Labour, despite a slight rise in its share of the vote, had fewer councillors elected. The Liberal Democrats also saw a notable revival, but were unable to translate this into seats. The Conservatives retained firm control of the council. The next election will be in 2021 Essex County Council election, 2021.
, -
! rowspan="2" colspan="2" style="text-align:left;" , Party
! colspan="4", Votes cast
! colspan="4", %
! colspan="4", Seats
, -
!2009
!2013
!2017
! ±
!2009
!2013
!2017
! ±
!2009
!2013
!2017
! ±
, -
, style="background:#0087dc;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Conservative Party (UK), Conservative
, 169,975
, 112,229
, 184,901
, 72,672
, 43.3
, 34.4
, 49.3
, 14.9
, 60
, 42
, 56
, 14
, -
, style="background:#dc241f;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Labour Party (UK), Labour
, 42,334
, 57,290
, 63,470
, 6,180
, 10.8
, 16.4
, 16.9
, 0.5
, 1
, 9
, 6
, 3
, -
, style="background:#fdbb30;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Liberal Democrats (UK), Liberal Democrat
, 79,085
, 35,651
, 51,524
, 15,873
, 20.1
, 11.6
, 13.7
, 2.1
, 12
, 9
, 7
, 2
, -
, style="background:#70147a;",
, style="text-align:left;" , UKIP
, 18,186
, 90,812
, 29,796
, 61,016
, 4.6
, 27.6
, 7.9
, 19.7
, 0
, 9
, 0
, 9
, -
, style="background:#6ab023;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Green Party of England and Wales, Green
, 26,547
, 15,187
, 15,187
,
, 6.8
, 4.8
, 4.3
, 0.5
, 0
, 2
, 1
, 1
, -
, style="background:#e9e9e9;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Independents
, 5,845
, 4,631
, 12,506
, 7,875
, 1.5
, 0.6
, 2.4
, 1.8
, 0
, 1
, 2
, 1
, -
, style="background-color:;" ,
, style="text-align:left;" , Residents for Uttlesford
, ''N/A''
, ''N/A''
, 5,231
,
, ''N/A''
, ''N/A''
, 1.4
,
, 0
, 0*(1)
, 0
, 1
, -
, style="background:black;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Canvey Island Independent Party, Canvey Island Independents
, 1,655
, 2,777
, 3,654
, 877
, 0.4
, 0.9
, 1.0
, 0.1
, 1
, 1
, 2
, 1
, -
, style="background:#008800;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Loughton Residents Association, Loughton Residents
, 2,764
, 3,286
, 2,824
, 462
, 0.7
, 1.1
, 0.8
, 0.3
, 1
, 1
, 1
,
, -
, style="background-color:;" ,
, style="text-align:left;" , Tendring First
, 5,866
, 4,093
, 1,332
, 2,761
, 1.5
, 1.4
, 0.4
, 1.0
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background-color:;" ,
, style="text-align:left;" , British National Party, BNP
, 35,037
, 909
, 847
, 62
, 8.9
, 0.3
, 0.2
, 0.1
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#915f6d;",
, style="text-align:left;" , English Democrats
, 5,212
, 835
, 58
, 164
, 1.3
, 0.3
, 0.0
, 0.3
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background-color:;" ,
, style="text-align:left;" , Trade Unionist and Socialist Coalition, TUSC
, ''N/A''
, 431
, ''N/A''
,
, ''N/A''
, 0.1
, ''N/A''
,
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background-color:;" ,
, style="text-align:left;" , National Front (UK), National Front
, ''N/A''
, 304
, ''N/A''
,
, ''N/A''
, 0.1
, ''N/A''
,
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
! colspan="2" style="text-align:left;" , Total
! 392,506
! 328,435
! 372,834
!
! 100%
! 100%
! 100%
!
! 75
! 75
! 75
!
At the 2013 Essex County Council election, 2013 County Council elections the Conservative Party retained overall control of the council, but its majority fell from twenty-two to four councillors. UKIP, Labour and the Liberal Democrats (UK), Liberal Democrats each won nine seats. Out of those three parties, UKIP gained the largest share of the county-wide vote, more than 10% ahead of Labour.2013 Essex County Council election#cite note-change-3, [3] The Liberal Democrats remain as the official Opposition, despite winning fewer votes.2013 Essex County Council election#cite note-change-3, [3] The Green Party of England and Wales, Green Party gained two seats on the council, despite its overall share of the vote falling. The Independent Loughton Residents Association and the Canvey Island Independent Party both returned one member and an Independent (politician), Independent candidate was also elected.
The 2017 Essex County Council election, 2017 County Council elections saw a county-wide wipeout of UKIP. The Conservative Party profited most from this loss, regaining many of the seats it had lost at the previous election. Labour, despite a slight rise in its share of the vote, had fewer councillors elected. The Liberal Democrats also saw a notable revival, but were unable to translate this into seats. The Conservatives retained firm control of the council. The next election will be in 2021 Essex County Council election, 2021.
, -
! rowspan="2" colspan="2" style="text-align:left;" , Party
! colspan="4", Votes cast
! colspan="4", %
! colspan="4", Seats
, -
!2009
!2013
!2017
! ±
!2009
!2013
!2017
! ±
!2009
!2013
!2017
! ±
, -
, style="background:#0087dc;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Conservative Party (UK), Conservative
, 169,975
, 112,229
, 184,901
, 72,672
, 43.3
, 34.4
, 49.3
, 14.9
, 60
, 42
, 56
, 14
, -
, style="background:#dc241f;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Labour Party (UK), Labour
, 42,334
, 57,290
, 63,470
, 6,180
, 10.8
, 16.4
, 16.9
, 0.5
, 1
, 9
, 6
, 3
, -
, style="background:#fdbb30;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Liberal Democrats (UK), Liberal Democrat
, 79,085
, 35,651
, 51,524
, 15,873
, 20.1
, 11.6
, 13.7
, 2.1
, 12
, 9
, 7
, 2
, -
, style="background:#70147a;",
, style="text-align:left;" , UKIP
, 18,186
, 90,812
, 29,796
, 61,016
, 4.6
, 27.6
, 7.9
, 19.7
, 0
, 9
, 0
, 9
, -
, style="background:#6ab023;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Green Party of England and Wales, Green
, 26,547
, 15,187
, 15,187
,
, 6.8
, 4.8
, 4.3
, 0.5
, 0
, 2
, 1
, 1
, -
, style="background:#e9e9e9;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Independents
, 5,845
, 4,631
, 12,506
, 7,875
, 1.5
, 0.6
, 2.4
, 1.8
, 0
, 1
, 2
, 1
, -
, style="background-color:;" ,
, style="text-align:left;" , Residents for Uttlesford
, ''N/A''
, ''N/A''
, 5,231
,
, ''N/A''
, ''N/A''
, 1.4
,
, 0
, 0*(1)
, 0
, 1
, -
, style="background:black;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Canvey Island Independent Party, Canvey Island Independents
, 1,655
, 2,777
, 3,654
, 877
, 0.4
, 0.9
, 1.0
, 0.1
, 1
, 1
, 2
, 1
, -
, style="background:#008800;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Loughton Residents Association, Loughton Residents
, 2,764
, 3,286
, 2,824
, 462
, 0.7
, 1.1
, 0.8
, 0.3
, 1
, 1
, 1
,
, -
, style="background-color:;" ,
, style="text-align:left;" , Tendring First
, 5,866
, 4,093
, 1,332
, 2,761
, 1.5
, 1.4
, 0.4
, 1.0
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background-color:;" ,
, style="text-align:left;" , British National Party, BNP
, 35,037
, 909
, 847
, 62
, 8.9
, 0.3
, 0.2
, 0.1
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#915f6d;",
, style="text-align:left;" , English Democrats
, 5,212
, 835
, 58
, 164
, 1.3
, 0.3
, 0.0
, 0.3
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background-color:;" ,
, style="text-align:left;" , Trade Unionist and Socialist Coalition, TUSC
, ''N/A''
, 431
, ''N/A''
,
, ''N/A''
, 0.1
, ''N/A''
,
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background-color:;" ,
, style="text-align:left;" , National Front (UK), National Front
, ''N/A''
, 304
, ''N/A''
,
, ''N/A''
, 0.1
, ''N/A''
,
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
! colspan="2" style="text-align:left;" , Total
! 392,506
! 328,435
! 372,834
!
! 100%
! 100%
! 100%
!
! 75
! 75
! 75
!
County Hall
The county council chamber and main headquarters is at the County Hall, Chelmsford, County Hall in Chelmsford
Chelmsford () is a City status in the United Kingdom, city in the City of Chelmsford district in the county of Essex, England. It is the county town of Essex and one of three cities in the county, along with Southend-on-Sea and Colchester. It ...
. Before 1938, the council regularly met in London near Moorgate railway station, Moorgate, which with significant parts of the county close to that point and the Railways in the United Kingdom, dominance of railway travel had been more convenient than any place in the county. The County Hall, made a listed building in 2007, dates largely from the mid-1930s and is decorated with fine artworks of that period, mostly the gift of the family who owned the textile firm Courtaulds.
English region
Essex became part of the East of England Regions of England, Government Office Region in 1994 and was statistically counted as part of that region from 1999, having previously been part of the South East England region.
Essex Police
Essex Police covers the administrative county and the two unitary authorities.
Youth councils
The Essex County Council also has a Youth Assembly, 75 members aged between 11 and 19 who aim to represent all young people in their districts across Essex. They decide on the priorities for young people and campaign to make a difference. With this, some district and unitary authorities may have their own youth councils, such as Epping Forest District, Epping Forest, Uttlesford and Harlow District Council elections, Harlow.
All these councillors are elected by their schools. The elections to the Young Essex Assembly occur in the respective schools in which the candidates are standing, likewise for the youth councils at a district and unitary level. These young people will then go on to represent their school and their parish/ward or (in the case of the Young Essex Assembly) their entire district.
The initiative seeks to engage younger people in the county and rely on the youth councillors of all status to work closely with schools and youth centres to improve youth services in Essex and help promote the opinions of Essex youth.
Local government
Borough and district level
The county of Essex is divided int
12 district and borough councils with 2 unitary authorities
(Southend-on-Sea City Council, Southend on Sea and Thurrock Council, Thurrock). The 12 councils manage housing, local planning, refuse collection, street cleaning, elections and meet in their respective civic offices. The local representatives are elected in parts in local elections, held every year.
Town and parish level
Town and Parish councils in England, parish councils vary in size from those with a population of around 200 to those with a population of over 30,000. Annual expenditure can vary greatly, depending on the circumstances of the individual council. Parish and town councils (local councils) have the same powers and duties, but a town council may elect a town mayor, rather than a chairman, each year in May.
There are just under 300 town and parish councils within Essex.
Westminster and the 2016 EU referendum
As of the 2019 United Kingdom general election, 2019 general election, all List of Parliamentary constituencies in Essex, 18 Essex seats are represented by Conservatives, all of them with absolute majorities (over 50% of the vote). There have previously been some Labour Party (UK), Labour MPs: most recently, Thurrock (UK Parliament constituency), Thurrock, Harlow (UK Parliament constituency), Harlow and Basildon (UK Parliament constituency), Basildon in Labour's 2005 election victory. The Liberal Democrats (UK), Liberal Democrats until 2015 had a sizeable following in Essex, gaining Colchester (UK Parliament constituency), Colchester in the 1997 United Kingdom general election, 1997 general election.  The 2015 United Kingdom general election, 2015 general election saw a large vote in Essex for the UK Independence Party (UKIP), with its only MP, Douglas Carswell, retaining the seat of Clacton that he had won in a 2014 Clacton by-election, 2014 by-election, and other strong performances, notably in Thurrock and Castle Point (UK Parliament constituency), Castle Point, but in the 2017 United Kingdom general election, 2017 general election, UKIP's vote share plummeted by 15.6% while both Conservative and Labour rose by 9%. This resulted in Labour regaining second place in Essex, increasing their vote share across the county and cutting some Conservative majorities in areas that had been unaffected by the 1997 United Kingdom general election, 1997 general election, namely Rochford and Southend East (UK Parliament constituency), Rochford and Southend East and Southend West (UK Parliament constituency), Southend West.
In 2015, Thurrock was a three-way marginal, with UKIP, Labour and the Conservatives gaining 30%, 31% and 32% respectively. In 2017, the Conservatives held Thurrock with an increased share of the vote, but a smaller margin of victory. It was the constituency in which UKIP performed best in 2017, with 20% of the vote, while all other areas had been reduced to low single-figure vote shares. Several new MPs were elected in the 2017 election, with Alex Burghart, Vicky Ford, Giles Watling and Kemi Badenoch all replacing senior Conservative politicians Eric Pickles, Sir Eric Pickles, Simon Burns, Sir Simon Burns, Douglas Carswell and Sir Alan Haselhurst, respectively.
At the 2019 general election, Castle Point constituency recorded the highest vote share for the Conservatives in the entire United Kingdom, with 76.7%. The most marginal constituency in the county is Colchester; however the Conservative Party still command a majority of over 9,400 votes.
In the 2016 United Kingdom European Union membership referendum, 2016 EU referendum, 62.3% of voters in Essex voted to Results of the 2016 United Kingdom European Union membership referendum, leave the EU, with all 14 District Council areas voting to leave, the smallest margin being in Uttlesford.
, -
! rowspan="2" colspan="2" style="text-align:left;" , Party
! colspan="4", Votes cast
! colspan="4", %
! colspan="4", Seats
, -
!2015
!2017
!2019
! ±
!2015
!2017
!2019
! ±
!2015
!2017
!2019
! ±
, -
, style="background:#0087dc;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Conservative Party (UK), Conservative
, 436,758
, 528,949
, 577,118
, 48,169
, 49.6
, 59.0
, 64.8
, 5.8
, 17
, 18
, 18
,
, -
, style="background:#dc241f;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Labour Party (UK), Labour
, 171,026
, 261,671
, 189,471
, 72,200
, 19.4
, 29.2
, 21.2
, 8.0
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#fdbb30;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Liberal Democrats (UK), Liberal Democrat
, 58,592
, 46,254
, 95,078
, 48,824
, 6.6
, 5.1
, 10.6
, 5.5
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#6ab023;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Green Party of England and Wales, Green
, 25,993
, 12,343
, 20,438
, 8,095
, 3.0
, 1.3
, 2.3
, 1.0
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#e9e9e9;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Independents
, 6,919
, 4,179
, 10,224
, 6,045
, 0.7
, 0.4
, 1.1
, 0.7
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#fff000;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Official Monster Raving Loony Party, Monster Raving Loony
, ''N/A''
, ''N/A''
, 804
, 804
, ''N/A''
, ''N/A''
, 0.09
, 0.09
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#915f6d;",
, style="text-align:left;" , English Democrats
, 453
, 289
, 532
, 243
, 0.05
, 0.03
, 0.06
, 0.03
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#D25469;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Social Democratic Party (UK, 1990–present), SDP
, ''N/A''
, ''N/A''
, 394
, 394
, ''N/A''
, ''N/A''
, 0.04
, 0.04
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#FF01FF;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Psychedelic Future
, ''N/A''
, ''N/A''
, 367
, 367
, ''N/A''
, ''N/A''
, 0.04
, 0.04
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#ff0;",
, style="text-align:left;" , YPP
, 80
, 110
, 170
, 60
, 0.00
, 0.01
, 0.02
, 0.01
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#70147a;",
, style="text-align:left;" , UKIP
, 177,756
, 41,478
, ''N/A''
, 41,478
, 20.2
, 4.6
, ''N/A''
, 4.6
, 1
, 0
, 0
,
, -
! colspan="2" style="text-align:left;" , Total
! 879,918
! 896,231
! 894,608
!
! 100%
! 100%
! 100%
!
! 18
! 18
! 18
!
The 2015 United Kingdom general election, 2015 general election saw a large vote in Essex for the UK Independence Party (UKIP), with its only MP, Douglas Carswell, retaining the seat of Clacton that he had won in a 2014 Clacton by-election, 2014 by-election, and other strong performances, notably in Thurrock and Castle Point (UK Parliament constituency), Castle Point, but in the 2017 United Kingdom general election, 2017 general election, UKIP's vote share plummeted by 15.6% while both Conservative and Labour rose by 9%. This resulted in Labour regaining second place in Essex, increasing their vote share across the county and cutting some Conservative majorities in areas that had been unaffected by the 1997 United Kingdom general election, 1997 general election, namely Rochford and Southend East (UK Parliament constituency), Rochford and Southend East and Southend West (UK Parliament constituency), Southend West.
In 2015, Thurrock was a three-way marginal, with UKIP, Labour and the Conservatives gaining 30%, 31% and 32% respectively. In 2017, the Conservatives held Thurrock with an increased share of the vote, but a smaller margin of victory. It was the constituency in which UKIP performed best in 2017, with 20% of the vote, while all other areas had been reduced to low single-figure vote shares. Several new MPs were elected in the 2017 election, with Alex Burghart, Vicky Ford, Giles Watling and Kemi Badenoch all replacing senior Conservative politicians Eric Pickles, Sir Eric Pickles, Simon Burns, Sir Simon Burns, Douglas Carswell and Sir Alan Haselhurst, respectively.
At the 2019 general election, Castle Point constituency recorded the highest vote share for the Conservatives in the entire United Kingdom, with 76.7%. The most marginal constituency in the county is Colchester; however the Conservative Party still command a majority of over 9,400 votes.
In the 2016 United Kingdom European Union membership referendum, 2016 EU referendum, 62.3% of voters in Essex voted to Results of the 2016 United Kingdom European Union membership referendum, leave the EU, with all 14 District Council areas voting to leave, the smallest margin being in Uttlesford.
, -
! rowspan="2" colspan="2" style="text-align:left;" , Party
! colspan="4", Votes cast
! colspan="4", %
! colspan="4", Seats
, -
!2015
!2017
!2019
! ±
!2015
!2017
!2019
! ±
!2015
!2017
!2019
! ±
, -
, style="background:#0087dc;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Conservative Party (UK), Conservative
, 436,758
, 528,949
, 577,118
, 48,169
, 49.6
, 59.0
, 64.8
, 5.8
, 17
, 18
, 18
,
, -
, style="background:#dc241f;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Labour Party (UK), Labour
, 171,026
, 261,671
, 189,471
, 72,200
, 19.4
, 29.2
, 21.2
, 8.0
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#fdbb30;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Liberal Democrats (UK), Liberal Democrat
, 58,592
, 46,254
, 95,078
, 48,824
, 6.6
, 5.1
, 10.6
, 5.5
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#6ab023;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Green Party of England and Wales, Green
, 25,993
, 12,343
, 20,438
, 8,095
, 3.0
, 1.3
, 2.3
, 1.0
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#e9e9e9;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Independents
, 6,919
, 4,179
, 10,224
, 6,045
, 0.7
, 0.4
, 1.1
, 0.7
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#fff000;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Official Monster Raving Loony Party, Monster Raving Loony
, ''N/A''
, ''N/A''
, 804
, 804
, ''N/A''
, ''N/A''
, 0.09
, 0.09
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#915f6d;",
, style="text-align:left;" , English Democrats
, 453
, 289
, 532
, 243
, 0.05
, 0.03
, 0.06
, 0.03
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#D25469;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Social Democratic Party (UK, 1990–present), SDP
, ''N/A''
, ''N/A''
, 394
, 394
, ''N/A''
, ''N/A''
, 0.04
, 0.04
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#FF01FF;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Psychedelic Future
, ''N/A''
, ''N/A''
, 367
, 367
, ''N/A''
, ''N/A''
, 0.04
, 0.04
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#ff0;",
, style="text-align:left;" , YPP
, 80
, 110
, 170
, 60
, 0.00
, 0.01
, 0.02
, 0.01
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#70147a;",
, style="text-align:left;" , UKIP
, 177,756
, 41,478
, ''N/A''
, 41,478
, 20.2
, 4.6
, ''N/A''
, 4.6
, 1
, 0
, 0
,
, -
! colspan="2" style="text-align:left;" , Total
! 879,918
! 896,231
! 894,608
!
! 100%
! 100%
! 100%
!
! 18
! 18
! 18
!
Culture and community
Flag and coat of arms
 Both the Flag of Essex and the county's coat of arms comprise three Saxon seax knives (although they look rather more like scimitars), mainly white and pointing to the right (from the point of view of the observer), arranged vertically one above another on a red background (''Gules three Seaxes fesswise in pale Argent pommels and hilts Or, points to the sinister and notches to the base''). The three-seax device is also used as the official logo of Essex County Council; this was granted in 1932.
Both the Flag of Essex and the county's coat of arms comprise three Saxon seax knives (although they look rather more like scimitars), mainly white and pointing to the right (from the point of view of the observer), arranged vertically one above another on a red background (''Gules three Seaxes fesswise in pale Argent pommels and hilts Or, points to the sinister and notches to the base''). The three-seax device is also used as the official logo of Essex County Council; this was granted in 1932.[Robert Young. (2009). Civic Heraldry of England and Wales]
Essex
. Retrieved 16 April 2009.
The emblem was attributed to Kingdom of Essex, Anglo-Saxon Essex in Early Modern historiography. The earliest reference to the arms of the East Saxon kings was by Richard Verstegan, the author of ''A Restitution of Decayed Intelligence'' (Antwerp, 1605), claiming that "Erkenwyne king of the East-Saxons did beare for his armes, three [seaxes] argent, in a field gules". There is no earlier evidence substantiating Verstegan's claim, which is an anachronism for the Anglo-Saxon period seeing that heraldry only evolved in the 12th century, well after the Norman Conquest.
John Speed in his ''Historie of Great Britaine'' (1611) follows Verstegan in his descriptions of the arms of Erkenwyne, but he qualifies the statement by adding "as some or our heralds have emblazed".
Patron saint
The East Saxon royal house had converted the Christianity around 604 AD, but subsequently apostasised. In the mid 7th century, a new Christian king, Sigeberht the Good, requested help from the monks of Lindisfarne in promoting Christianity among his people.
St Cedd, an Irish trained Northumbrian monk, sailed south and established a chapel, dedicated to Saint Peter, St Peter, on the site of the old Roman fort of Othona (modern Bradwell-on-Sea), a chapel which still stands. Cedd, who was well known for confronting political authority, filled Bishop of London#List of Bishops, the vacant position of Bishop of London – the Bishop of the East Saxons. The feast day of St Cedd, also known as ''Essex Day'', is marked on the 26th October.
County plant
The cowslip is the county plant of Essex.

Speech
The county has its own ''Essex dialect'', though this has lost ground to other forms so that it is now chiefly spoken in parts of the north and among older residents. It has been partially replaced by Received Pronunciation (RP) and Cockney, a form originally heavily influenced by the Essex dialect.
The prevalence of Cockney, particularly in the south, is the result of the large-scale migration of East Londoners to Essex, ''the Cockney Diaspora'', particularly after World War II. A blend of RP and Cockney is widely heard, and known as Estuary English.
Traditions
Essex is also home to the Great Dunmow, Dunmow Flitch Trials, a traditional ceremony that takes place every four years and consists of a test of a married couple's devotion to one another. A common claim of the origin of the Dunmow Flitch dates back to 1104 and the Augustinians, Augustinian Little Dunmow Priory, priory of Little Dunmow, founded by Lady Juga Baynard. Lord of the Manor Reginald Fitzwalter and his wife dressed themselves as humble folk and begged blessing of the Prior a year and a day after marriage. The prior, impressed by their devotion, bestowed upon them a flitch of bacon. Upon revealing his true identity, Fitzwalter gave his land to the priory on condition that a flitch should be awarded to any couple who could claim they were similarly devoted.
By the 14th century, the Dunmow Flitch Trials appear to have achieved a significant reputation outside the local area. The author William Langland, who lived on the Welsh borders, mentions it in his 1362 book ''The Vision of Piers Plowman'' in a manner that implies general knowledge of the custom among his readers.
Sport
Football
The ceremonial county is home to two professional sides, Southend United and Colchester United with ''Metropolitan Essex'' home to three more - West Ham United F.C., West Ham United, Leyton Orient F.C., Leyton Orient and Dagenham & Redbridge F.C., Dagenham & Redbridge.
Essex also has a number of other clubs which play below English football’s fifth tier. Billericay Town F.C., Billericay Town, Braintree Town F.C., Braintree Town, Chelmsford City F.C., Chelmsford City and Concord Rangers F.C., Concord Rangers all play in the National League South. The highest domestic trophy for non-league teams, the FA Trophy, has been won on three occasions by Essex teams: Colchester United (1992), Canvey Island (2001) and by Grays Athletic F.C., Grays Athletic in 2006. The FA Vase has been won three times by Billericay Town in 1976, 1977 and 1979, and by Stansted F.C., Stansted in 1984.
Cricket
Essex County Cricket Club became a First-class cricket, first-class county in 1894. The county has won eight County Championship league titles; six of these were won during the dominant period between 1979 and 1992, with a gap of 25 years before the county's next titles in 2017 and 2019.
Other sports
The county is also home to the Romford Raiders and Chelmsford Chieftains ice hockey teams and the Essex Leopards basketball team. It is home to the amateur rugby league football teams the Eastern Rhinos and Brentwood Eels (Essex Eels). Defunct teams include the Essex Pirates basketball team, as well as Motorcycle speedway, speedway teams the Lakeside Hammers (formerly Arena Essex Hammers), the Rayleigh Rockets and the Romford Bombers.
During the 2012 Summer Olympics, 2012 London Olympics, Hadleigh Farm played host to the mountain bike races. London Stadium, which was the host of the games, is located within the historical Essex boundaries.
Essex has one horse racing venue, Chelmsford City Racecourse at Great Leighs. Horse racing also took place at Chelmsford Racecourse in Galleywood until 1935. The county has one current greyhound racing track, Harlow Stadium. Rayleigh Weir Stadium and Southend Stadium are former greyhound venues.
Team Essex Volleyball Club is Chelmsford's national league volleyball club. It has four teams which play in Volleyball England's national volleyball league. Its men's 1st team currently competes in the top division in the country, the Super 8s, while the women's 1st team competes one tier below the men. The club has a strong junior programme and trains at The Boswells School in Chelmsford.
Sportspeople
Many famous sports stars have come from or trained in Essex. These have included swimmer Mark Foster (swimmer), Mark Foster; cricket stars Trevor Bailey, Nasser Hussain, Alastair Cook and Graham Gooch; footballers Peter Taylor (footballer, born 1953), Peter Taylor, James Tomkins (footballer), James Tomkins, Justin Edinburgh, Nigel Spink; tennis stars John Lloyd (tennis), John Lloyd and David Lloyd (tennis), David Lloyd; Olympic Gold-winning gymnast Max Whitlock; Olympic sailing champion Saskia Clark; World Champion snooker stars Stuart Bingham and Steve Davis; world champion boxers Terry Marsh (boxer), Terry Marsh, Nigel Benn and Frank Bruno; London Marathon winner Eamonn Martin; international rugby players Malcolm O'Kelly and Stuart Barnes; Formula 1 sports car drivers Johnny Herbert and Perry McCarthy.
Television
The county is served by BBC East and ITV Anglia, but southern parts of Essex are also served by BBC London and ITV London.
Education
Education in Essex is substantially provided by three authorities: Essex County Council
Essex County Council is the county council that governs the non-metropolitan county of Essex in England. It has 75 councillors, elected from 70 divisions, and is currently controlled by the Conservative Party. The council meets at County Hall ...
and the two unitary authorities, City of Southend-on-Sea, Southend-on-Sea and Thurrock
Thurrock () is a unitary authority area with borough status and unparished area in the ceremonial county of Essex, England. It is part of the London commuter belt and an area of regeneration within the Thames Gateway redevelopment zone. The ...
. In all there are some 90 state secondary schools provided by these authorities, the majority of which are comprehensive, although one in Uttlesford, two in Chelmsford
Chelmsford () is a City status in the United Kingdom, city in the City of Chelmsford district in the county of Essex, England. It is the county town of Essex and one of three cities in the county, along with Southend-on-Sea and Colchester. It ...
, two in Colchester
Colchester ( ) is a city in Essex, in the East of England. It had a population of 122,000 in 2011. The demonym is Colcestrian.
Colchester occupies the site of Camulodunum, the first major city in Roman Britain and its first capital. Colch ...
and four in Southend-on-Sea
Southend-on-Sea (), commonly referred to as Southend (), is a coastal city and unitary authority area with borough status in southeastern Essex, England. It lies on the north side of the Thames Estuary, east of central London. It is bordered ...
are selective grammar schools. There are also various independent schools particularly, as mentioned above, in rural parts and the west of the county.
The University of Essex, which was established in 1963, is located just outside Colchester, with two further campuses in Loughton
Loughton () is a town and civil parish in the Epping Forest District of Essex. Part of the metropolitan and urban area of London, the town borders Chingford, Waltham Abbey, Theydon Bois, Chigwell and Buckhurst Hill, and is northeast of Chari ...
and Southend-on-Sea.
Anglia Ruskin University has a campus in Chelmsford. Lord Ashcroft International Business School, Faculty of Medical Science, Faculty of Science and Technology, Anglia Law School, Faculty of Health, Social Care & Education and School of Medicine are located in the campus area.
Writtle University College, at Writtle, near Chelmsford, offers both higher and further education in land-management subjects.
Landmarks
Over 14,000 buildings have listed building, listed status in the county and around 1,000 of those are recognised as of Grade I or II* importance. The buildings range from the 7th century Saxon church of Church of St Peter-on-the-Wall, St Peter-on-the-Wall, to the Royal Corinthian Yacht Club which was the United Kingdom's entry in the 'International Exhibition of Modern Architecture' held at the Museum of Modern Art in New York City in 1932. Southend Pier is in the Guinness Book of Records as the longest pleasure pier in the world.
File:St Peter-on-the-Wall ext.jpg, Church of St Peter-on-the-Wall, Bradwell-on-Sea, The church of St Peter-on-the-Wall, Bradwell-on-Sea
File:The keep, Hedingham Castle in winter.jpg, The Grade I listed Hedingham Castle, with the best preserved Norman keep in the UK
File:Thaxted guildhall.JPG, Thaxted Guildhall, dating from around 1450
File:AudleyEndHouse.JPG, The 17th century Audley End House, Saffron Walden
File:Royal Corinthian Yacht Club Burnham-on-Crouch.jpg, Royal Corinthian Yacht Club, Burnham-on-Crouch
File:Colchester castle 800.jpg, Colchester Castle, Colchester
Colchester ( ) is a city in Essex, in the East of England. It had a population of 122,000 in 2011. The demonym is Colcestrian.
Colchester occupies the site of Camulodunum, the first major city in Roman Britain and its first capital. Colch ...
File:Hylands house.jpg, Hylands House, south of Writtle
The village and civil parish of Writtle lies west of Chelmsford, Essex, England. It has a traditional village green complete with duck pond and a Norman church, and was once described as "one of the loveliest villages in England, with a ravis ...
and south-west of Chelmsford
Chelmsford () is a City status in the United Kingdom, city in the City of Chelmsford district in the county of Essex, England. It is the county town of Essex and one of three cities in the county, along with Southend-on-Sea and Colchester. It ...
File:Southend from Southend Pier.jpg, Southend Pier, Southend-on-Sea
Southend-on-Sea (), commonly referred to as Southend (), is a coastal city and unitary authority area with borough status in southeastern Essex, England. It lies on the north side of the Thames Estuary, east of central London. It is bordered ...
Places of interest
 * Abberton Reservoir
* Anglia Ruskin University Chelmsford campus
*
* Abberton Reservoir
* Anglia Ruskin University Chelmsford campus
* Ashdon
Ashdon, is a village and civil parish in Essex, England. It is about northeast of Saffron Walden and northwest from the county town of Chelmsford. The village is in the district of Uttlesford and the parliamentary constituency of Saffron Walde ...
(The site of the ancient Bartlow Hills and also a claimant as the location of the Battle of Ashingdon)
* Ashingdon
Ashingdon is a village and civil parish in Essex, England. It is located about north of Rochford and is southeast from the county town of Chelmsford. The village lies within Rochford District and the parliamentary constituency of Rayleigh.
A ...
(The site of the Battle of Ashingdon in 1016), near Southend, with its isolated St Andrews Church and site of England's earliest aerodrome at South Fambridge
* Audley End House and Gardens, Saffron Walden
* Brentwood Cathedral
* Clacton-on-Sea
Clacton-on-Sea is a seaside town in the Tendring District in the county of Essex, England. It is located on the Tendring Peninsula and is the largest settlement in the Tendring District with a population of 56,874 (2016). The town is situated ...
* Chelmsford Cathedral
* Colchester Castle Epping Forest
Epping Forest is a area of ancient woodland, and other established habitats, which straddles the border between Greater London and Essex. The main body of the forest stretches from Epping in the north, to Chingford on the edge of the London ...
* Epping Ongar Railway
* Finchingfield (home of the author Dodie Smith)
* Frinton-on-Sea
* Great Bentley
Great Bentley is a village, civil parish and electoral ward in the Tendring district of north Essex, England, located seven miles east of Colchester. The parish includes the hamlets of Aingers Green and South Heath. It is home to the second lar ...
, which has the largest village green in England
* Hadleigh Castle
Hadleigh Castle is a ruined fortification in the English county of Essex, overlooking the Thames Estuary from south of the town of Hadleigh. Built after 1215 during the reign of Henry III by Hubert de Burgh, the castle was surrounded by park ...
* Harlow New Town
* Hedingham Castle, between Stansted and Colchester
Colchester ( ) is a city in Essex, in the East of England. It had a population of 122,000 in 2011. The demonym is Colcestrian.
Colchester occupies the site of Camulodunum, the first major city in Roman Britain and its first capital. Colch ...
, to the north of Braintree
* Ingatestone Hall, Ingatestone, between Brentwood and Chelmsford
* Kelvedon Hatch Secret Nuclear Bunker
* Lakeside Shopping Centre
* Loughton
Loughton () is a town and civil parish in the Epping Forest District of Essex. Part of the metropolitan and urban area of London, the town borders Chingford, Waltham Abbey, Theydon Bois, Chigwell and Buckhurst Hill, and is northeast of Chari ...
, near Epping Forest
Epping Forest is a area of ancient woodland, and other established habitats, which straddles the border between Greater London and Essex. The main body of the forest stretches from Epping in the north, to Chingford on the edge of the London ...
* Maldon, Essex, Maldon historic market town, close to Chelmsford and the North Sea, and site of the Battle of Maldon
The Battle of Maldon took place on 11 August 991 AD near Maldon beside the River Blackwater in Essex, England, during the reign of Æthelred the Unready. Earl Byrhtnoth and his thegns led the English against a Viking invasion. The battl ...
* Mangapps Railway Museum ( Burnham-on-Crouch)
* Marsh Farm Country Park (South Woodham Ferrers)
* Mersea Island, birdwatching and rambling resort with one settlement, West Mersea
* Mistley Towers, Manningtree, between Colchester and Ipswich, near Alton Water.
* Stansted Mountfitchet, Mountfitchet Castle , Stansted
* North Weald Airfield
* Northey Island
* Orsett Hall Hotel, Prince Charles Avenue, Orsett near Chadwell St Mary
* Real Circumstance Theatre Company
* Waltham Abbey Royal Gunpowder Mills, Royal Gunpowder Mills in Waltham Abbey
* St Peter-on-the-Wall
* Saffron Walden
* Southend Pier
* Thames Estuary
The Thames Estuary is where the River Thames meets the waters of the North Sea, in the south-east of Great Britain.
Limits
An estuary can be defined according to different criteria (e.g. tidal, geographical, navigational or in terms of salini ...
* Tilbury Fort
Tilbury Fort, also known historically as the Thermitage Bulwark and the West Tilbury Blockhouse, is an artillery fort on the north bank of the River Thames in England. The earliest version of the fort, comprising a small blockhouse with artil ...
* Thaxted, south of Saffron Walden
* Thurrock Thameside Nature Park
* University of Essex (Wivenhoe Park, Colchester and Loughton
Loughton () is a town and civil parish in the Epping Forest District of Essex. Part of the metropolitan and urban area of London, the town borders Chingford, Waltham Abbey, Theydon Bois, Chigwell and Buckhurst Hill, and is northeast of Chari ...
)
* Waltham Abbey Church
Notable people
Sister counties and regions
* Jiangsu, China
* Picardy, France
* Thuringia, Germany
* Henrico County, Virginia, Henrico County, Virginia, United States
* Accra, Ghana
See also
* Custos Rotulorum of Essex – Keepers of the Rolls
* Earl of Essex
* Essex (UK Parliament constituency)
* Essex Police and Crime Commissioner
* Healthcare in Essex
* High Sheriff of Essex
* List of civil parishes in England
* List of Sites of Special Scientific Interest in Essex
* Lord Lieutenant of Essex
This is a list of people who have served as Lord Lieutenant of Essex. Since 1688, all the Lord Lieutenants have also been Custos Rotulorum of Essex.
*John Petre, 1st Baron Petre
* John de Vere, 16th Earl of Oxford 1558–?
* Robert Dudley, 1st E ...
* Q Camp: WWII camp in Essex
* Essex girl
* University of Essex
* The Hundred Parishes
References
External links
*
Essex County Council
Seax – Essex Archives Online
Images of Essex
at the English Heritage Archive
{{Authority control
Essex,
Non-metropolitan counties
NUTS 2 statistical regions of the United Kingdom
English royal forests
Home counties
Counties of England established in antiquity


 Part of the south-east of the county, already containing the major population centres of
Part of the south-east of the county, already containing the major population centres of  The name ''Essex'' originates in the Anglo-Saxon period of the
The name ''Essex'' originates in the Anglo-Saxon period of the  After the arrival of the
After the arrival of the  The 2015 United Kingdom general election, 2015 general election saw a large vote in Essex for the UK Independence Party (UKIP), with its only MP, Douglas Carswell, retaining the seat of Clacton that he had won in a 2014 Clacton by-election, 2014 by-election, and other strong performances, notably in Thurrock and Castle Point (UK Parliament constituency), Castle Point, but in the 2017 United Kingdom general election, 2017 general election, UKIP's vote share plummeted by 15.6% while both Conservative and Labour rose by 9%. This resulted in Labour regaining second place in Essex, increasing their vote share across the county and cutting some Conservative majorities in areas that had been unaffected by the 1997 United Kingdom general election, 1997 general election, namely Rochford and Southend East (UK Parliament constituency), Rochford and Southend East and Southend West (UK Parliament constituency), Southend West.
In 2015, Thurrock was a three-way marginal, with UKIP, Labour and the Conservatives gaining 30%, 31% and 32% respectively. In 2017, the Conservatives held Thurrock with an increased share of the vote, but a smaller margin of victory. It was the constituency in which UKIP performed best in 2017, with 20% of the vote, while all other areas had been reduced to low single-figure vote shares. Several new MPs were elected in the 2017 election, with Alex Burghart, Vicky Ford, Giles Watling and Kemi Badenoch all replacing senior Conservative politicians Eric Pickles, Sir Eric Pickles, Simon Burns, Sir Simon Burns, Douglas Carswell and Sir Alan Haselhurst, respectively.
At the 2019 general election, Castle Point constituency recorded the highest vote share for the Conservatives in the entire United Kingdom, with 76.7%. The most marginal constituency in the county is Colchester; however the Conservative Party still command a majority of over 9,400 votes.
In the 2016 United Kingdom European Union membership referendum, 2016 EU referendum, 62.3% of voters in Essex voted to Results of the 2016 United Kingdom European Union membership referendum, leave the EU, with all 14 District Council areas voting to leave, the smallest margin being in Uttlesford.
, -
! rowspan="2" colspan="2" style="text-align:left;" , Party
! colspan="4", Votes cast
! colspan="4", %
! colspan="4", Seats
, -
!2015
!2017
!2019
! ±
!2015
!2017
!2019
! ±
!2015
!2017
!2019
! ±
, -
, style="background:#0087dc;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Conservative Party (UK), Conservative
, 436,758
, 528,949
, 577,118
, 48,169
, 49.6
, 59.0
, 64.8
, 5.8
, 17
, 18
, 18
,
, -
, style="background:#dc241f;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Labour Party (UK), Labour
, 171,026
, 261,671
, 189,471
, 72,200
, 19.4
, 29.2
, 21.2
, 8.0
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#fdbb30;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Liberal Democrats (UK), Liberal Democrat
, 58,592
, 46,254
, 95,078
, 48,824
, 6.6
, 5.1
, 10.6
, 5.5
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#6ab023;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Green Party of England and Wales, Green
, 25,993
, 12,343
, 20,438
, 8,095
, 3.0
, 1.3
, 2.3
, 1.0
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#e9e9e9;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Independents
, 6,919
, 4,179
, 10,224
, 6,045
, 0.7
, 0.4
, 1.1
, 0.7
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#fff000;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Official Monster Raving Loony Party, Monster Raving Loony
, ''N/A''
, ''N/A''
, 804
, 804
, ''N/A''
, ''N/A''
, 0.09
, 0.09
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#915f6d;",
, style="text-align:left;" , English Democrats
, 453
, 289
, 532
, 243
, 0.05
, 0.03
, 0.06
, 0.03
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#D25469;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Social Democratic Party (UK, 1990–present), SDP
, ''N/A''
, ''N/A''
, 394
, 394
, ''N/A''
, ''N/A''
, 0.04
, 0.04
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#FF01FF;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Psychedelic Future
, ''N/A''
, ''N/A''
, 367
, 367
, ''N/A''
, ''N/A''
, 0.04
, 0.04
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#ff0;",
, style="text-align:left;" , YPP
, 80
, 110
, 170
, 60
, 0.00
, 0.01
, 0.02
, 0.01
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#70147a;",
, style="text-align:left;" , UKIP
, 177,756
, 41,478
, ''N/A''
, 41,478
, 20.2
, 4.6
, ''N/A''
, 4.6
, 1
, 0
, 0
,
, -
! colspan="2" style="text-align:left;" , Total
! 879,918
! 896,231
! 894,608
!
! 100%
! 100%
! 100%
!
! 18
! 18
! 18
!
The 2015 United Kingdom general election, 2015 general election saw a large vote in Essex for the UK Independence Party (UKIP), with its only MP, Douglas Carswell, retaining the seat of Clacton that he had won in a 2014 Clacton by-election, 2014 by-election, and other strong performances, notably in Thurrock and Castle Point (UK Parliament constituency), Castle Point, but in the 2017 United Kingdom general election, 2017 general election, UKIP's vote share plummeted by 15.6% while both Conservative and Labour rose by 9%. This resulted in Labour regaining second place in Essex, increasing their vote share across the county and cutting some Conservative majorities in areas that had been unaffected by the 1997 United Kingdom general election, 1997 general election, namely Rochford and Southend East (UK Parliament constituency), Rochford and Southend East and Southend West (UK Parliament constituency), Southend West.
In 2015, Thurrock was a three-way marginal, with UKIP, Labour and the Conservatives gaining 30%, 31% and 32% respectively. In 2017, the Conservatives held Thurrock with an increased share of the vote, but a smaller margin of victory. It was the constituency in which UKIP performed best in 2017, with 20% of the vote, while all other areas had been reduced to low single-figure vote shares. Several new MPs were elected in the 2017 election, with Alex Burghart, Vicky Ford, Giles Watling and Kemi Badenoch all replacing senior Conservative politicians Eric Pickles, Sir Eric Pickles, Simon Burns, Sir Simon Burns, Douglas Carswell and Sir Alan Haselhurst, respectively.
At the 2019 general election, Castle Point constituency recorded the highest vote share for the Conservatives in the entire United Kingdom, with 76.7%. The most marginal constituency in the county is Colchester; however the Conservative Party still command a majority of over 9,400 votes.
In the 2016 United Kingdom European Union membership referendum, 2016 EU referendum, 62.3% of voters in Essex voted to Results of the 2016 United Kingdom European Union membership referendum, leave the EU, with all 14 District Council areas voting to leave, the smallest margin being in Uttlesford.
, -
! rowspan="2" colspan="2" style="text-align:left;" , Party
! colspan="4", Votes cast
! colspan="4", %
! colspan="4", Seats
, -
!2015
!2017
!2019
! ±
!2015
!2017
!2019
! ±
!2015
!2017
!2019
! ±
, -
, style="background:#0087dc;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Conservative Party (UK), Conservative
, 436,758
, 528,949
, 577,118
, 48,169
, 49.6
, 59.0
, 64.8
, 5.8
, 17
, 18
, 18
,
, -
, style="background:#dc241f;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Labour Party (UK), Labour
, 171,026
, 261,671
, 189,471
, 72,200
, 19.4
, 29.2
, 21.2
, 8.0
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#fdbb30;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Liberal Democrats (UK), Liberal Democrat
, 58,592
, 46,254
, 95,078
, 48,824
, 6.6
, 5.1
, 10.6
, 5.5
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#6ab023;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Green Party of England and Wales, Green
, 25,993
, 12,343
, 20,438
, 8,095
, 3.0
, 1.3
, 2.3
, 1.0
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#e9e9e9;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Independents
, 6,919
, 4,179
, 10,224
, 6,045
, 0.7
, 0.4
, 1.1
, 0.7
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#fff000;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Official Monster Raving Loony Party, Monster Raving Loony
, ''N/A''
, ''N/A''
, 804
, 804
, ''N/A''
, ''N/A''
, 0.09
, 0.09
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#915f6d;",
, style="text-align:left;" , English Democrats
, 453
, 289
, 532
, 243
, 0.05
, 0.03
, 0.06
, 0.03
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#D25469;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Social Democratic Party (UK, 1990–present), SDP
, ''N/A''
, ''N/A''
, 394
, 394
, ''N/A''
, ''N/A''
, 0.04
, 0.04
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#FF01FF;",
, style="text-align:left;" , Psychedelic Future
, ''N/A''
, ''N/A''
, 367
, 367
, ''N/A''
, ''N/A''
, 0.04
, 0.04
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#ff0;",
, style="text-align:left;" , YPP
, 80
, 110
, 170
, 60
, 0.00
, 0.01
, 0.02
, 0.01
, 0
, 0
, 0
,
, -
, style="background:#70147a;",
, style="text-align:left;" , UKIP
, 177,756
, 41,478
, ''N/A''
, 41,478
, 20.2
, 4.6
, ''N/A''
, 4.6
, 1
, 0
, 0
,
, -
! colspan="2" style="text-align:left;" , Total
! 879,918
! 896,231
! 894,608
!
! 100%
! 100%
! 100%
!
! 18
! 18
! 18
!

 * Abberton Reservoir
* Anglia Ruskin University Chelmsford campus
*
* Abberton Reservoir
* Anglia Ruskin University Chelmsford campus
*