Energy in the United States on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Energy in the United States came mostly from
Energy in the United States came mostly from
(MS Excel format) As of 2006, the country's energy consumption had increased more rapidly than domestic energy production over the last 50 years in the nation (when they were roughly equal). This difference was largely met through imports.Ristinen, Robert, A. Energy and the Environment. Malloy, 2006. Print. Not included is the significant amount of energy used overseas in the production of retail and industrial goods consumed in the United States. According to the
 From its founding until the late 19th century, the United States was a largely agrarian country with abundant forests. During this period, energy consumption overwhelmingly focused on readily available
From its founding until the late 19th century, the United States was a largely agrarian country with abundant forests. During this period, energy consumption overwhelmingly focused on readily available
Energy in the United States: 1635–2000
Oil's unique qualities for transportation fuels in terms of energy content, cost of production, and speed of refueling all contributed to it being used over other fuels.
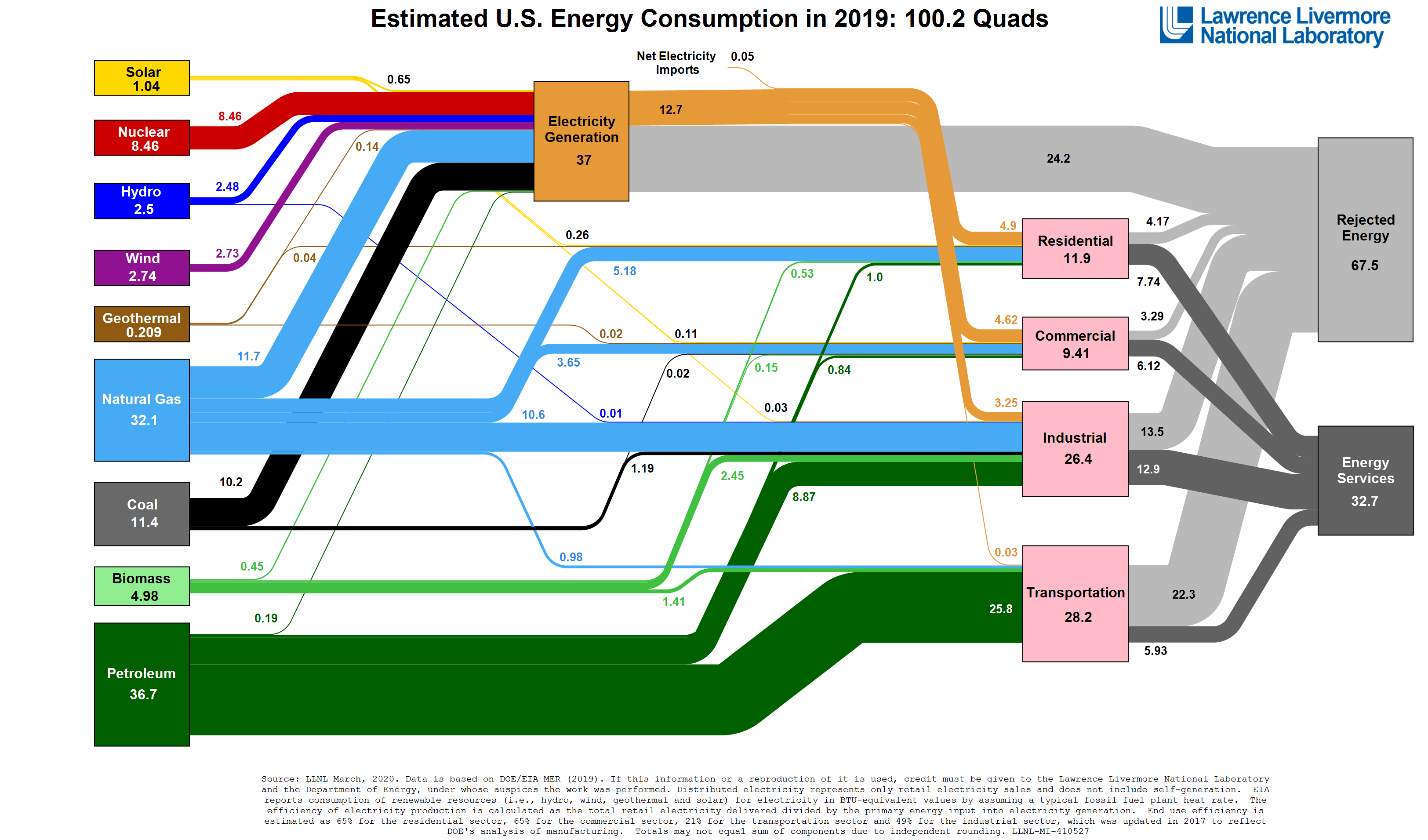 Primary energy use in the United States was or about per person in 2009. Primary energy use was less in the United States than in China in 2009. The share of energy import was 26% of the primary energy use. The energy import declined about 22% and the annual emissions about 10% in 2009 compared to 2004. In 2020, the U.S as a whole produced 87.79 exajoules of energy.
Primary energy use in the United States was or about per person in 2009. Primary energy use was less in the United States than in China in 2009. The share of energy import was 26% of the primary energy use. The energy import declined about 22% and the annual emissions about 10% in 2009 compared to 2004. In 2020, the U.S as a whole produced 87.79 exajoules of energy.
Annual Energy Report
(2010), Energy Flow diagram There are five main types/forms of wood resources that can be converted into fuel energy, the five are
 As
As


 Household energy use varies significantly across the United States. An average home in the Pacific region (consisting of
Household energy use varies significantly across the United States. An average home in the Pacific region (consisting of
 The United States is the world's second largest producer and consumer of electricity. It consumes about 20% of the world's electricity supply. This section provides a summary of the
The United States is the world's second largest producer and consumer of electricity. It consumes about 20% of the world's electricity supply. This section provides a summary of the
retrieved 2020-6-14 In 2018 the total U.S. consumption of electricity was 4,222.5
File:US Electric Energy Consumption by User Community 2009-20018.jpg, Ten-year consumption by user community, 20092018
File:2018 Electric Energy Consumption Profile 2018.jpg, 2018 electric energy consumption profile
File:Electric Customers 2008-2018.jpg, Residential, commercial and industrial U.S. customers
File:Average Residential Costs per kWh for US and selected States 2008-2018.jpg, U.S. Average Residential Costs per kWh
File:2018 Per Capita kWh Consumption by State.jpg, 2018 per capita Electric Energy consumption by state
A profile of the electric energy consumption for 2018 is shown in one of the above graphs. The April minimum of to the July peak of shows the monthly range of consumption variations.
In addition to consumption from the electrical grid, the U.S. consumers consumed an estimated additional 35.04 TWh from small scale solar systems. This will be included in the per capita data below.

 The United States has an installed summer electricity generation capacity of 1115.68 GW in 2020, up 16.5 GW from 2019. The U.S. electricity generation was 4,007.14TWh (14,429.7 PJ because 1TWh=3.6 PJ) in 2020 and down 120.7TWh (2.9%) from 2019 (pre-pandemic).
The United States has an installed summer electricity generation capacity of 1115.68 GW in 2020, up 16.5 GW from 2019. The U.S. electricity generation was 4,007.14TWh (14,429.7 PJ because 1TWh=3.6 PJ) in 2020 and down 120.7TWh (2.9%) from 2019 (pre-pandemic).
Eia.gov, retrieved 2022-6-01 The U.S. also imported; 61.45 TWh and exported 14.13 TWh, for a total of 4,054.45 TWh of electrical grid energy use in the U.S. This was down 112.5 TWh (2.7%) from 2019. Electrical energy generated from coal was 773.39 TWh (19.48%); natural and other gases, 1,635.985 TWh (40.35%); nuclear, 789.879 TWh (19.11%); hydro, 285.274 TWh (7.04%); Renewables (other than hydro), 497.729 TWh (12.28%); imports less exports, 47.314 TWh (1.17%) petroleum, 17.341 TWh (0.43%); and miscellaneous (including pumped storage), 7.534 TWh (0.19%). The United States' renewable sources (hydro reported separately) are wind, 337.938 TWh (8.33%); wood, 36.21 TWh (0.89%); other biomass, 18.493 TWh (0.46%); geothermal, 15.89 TWh (0.39%) and solar, 89.199 TWh (2.20%). Small-scale solar is estimated to have produced an additional 41.522 TWh . Natural gas electricity generation exceeded generation from coal for the first time in 2016 and continued its expansion. Wind exceeded Hydro in 2019 for the first time. Nuclear exceeded coal for the first time in 2020. The following tables summarize the electrical energy generated by fuel source for the United States. Electric Power Annual for 2020 data and preliminary data from Electric Power Monthly for the 2021 data[ was used throughout the rest of this section. Note: Biomass includes wood and wood derived fuel, landfill gas, biogenic municipal solid waste and other waste biomass.
File:Profile of US Electric Generation by Coal 2020-2018.jpg, Profile of U.S. Electric Generation by Coal 2020-2018
File:Profile of US Electric Generation by Natural Gas 2020-2018.jpg, Profile of U.S. Electric Generation by Natural Gas 2020-2018
File:Profile of US Electric Generation by Nuclear 2020-2018.jpg, Profile of U.S. Electric Generation by Nuclear 2020-2018
File:Profile of US Electric Generation by Nuclear 2020-2018.jpg, Profile of U.S. Electric Generation by Hydro 2020-2018
File:Profile of US Electric Generation for Utility Solar 2020-2018.jpg, Profile of U.S. Electric Generation by Wind 2020-2018
File:Profile of US Electric Generation for Utility Solar 2020-2018.jpg, Profile of U.S. Electric Generation for Utility Solar 2020-2018
File:2018 Electric Generation by Source.jpg, 2018 States Electric Generation by Source (%)
File:2018 Electric Generation by State.jpg, 2018 Total State Electric Energy Generation
File:2018 Top Ten States Coal.jpg, 2018 Top Ten States for Generation of Electricity by Coal
File:2018 Top Ten States Petroleum.jpg, 2018 Top Ten States for Generation of Electricity by Petroleum
File:2018 Top Ten States Gas.jpg, 2018 Top Ten States for Generation of Electricity by Natural and other Gases
File:2018 Top Ten States Nuclear.jpg, 2018 Top Ten States for Generation of Electricity by Nuclear
File:2018 Top Ten States Hydro.jpg, 2018 Top Ten States for Generation of Electricity by Hydro
File:2018 Top Ten States Solar.jpg, 2018 Top Ten States for Generation of Electricity by Solar
File:2018 Top Ten States Wind.jpg, 2018 Top Ten States for Generation of Electricity by Wind
File:2018 Top Ten States Biomass.jpg, 2018 Top Ten States for Generation of Electricity by Biomass
 The following table, derived from data mined from Electric Power Annual, identifies those states which must import electrical energy from neighboring states to meet their consumption needs. Each state's total electric generation for 2018 is compared with the state's consumption, and its share of the system loss and the difference between the generated electric energy and its total consumption (including its share of the system loss) is the amount of energy it imports. For Hawaii, total consumption equals generated energy. For the other states, multiplying their direct consumption by 1.082712997 (4168280574/3849848100), results in the United States' supply (including net imports) being equal to its total consumption.
The following table, derived from data mined from Electric Power Annual, identifies those states which must import electrical energy from neighboring states to meet their consumption needs. Each state's total electric generation for 2018 is compared with the state's consumption, and its share of the system loss and the difference between the generated electric energy and its total consumption (including its share of the system loss) is the amount of energy it imports. For Hawaii, total consumption equals generated energy. For the other states, multiplying their direct consumption by 1.082712997 (4168280574/3849848100), results in the United States' supply (including net imports) being equal to its total consumption.

File:2018 Profile of US Electric Energy from all Renewables.jpg, 2018 profile of renewables
File:2018 & 2017 Profile of US Electric Energy Generation from Hydro.jpg, Hydro
File:2018 & 2017 Profile of US Electric Energy Generation from Wind.jpg, Wind
File:2018 & 2017 Profile of US Electric Energy Generation from Utility Solar.jpg, Solar
File:2018 & 2017 Profile of US Electric Energy Generation from Biomass.jpg, Biomass
File:2018 & 2017 Profile of US Electric Energy Generation from Geothermal.jpg, Geothermal
 Renewable energy in the United States accounted for 13.2% of the domestically produced electricity in 2014, and 11.2% of total energy generation. As of 2014, more than 143,000 people work in the solar industry and 43 states deploy net metering, where energy utilities buy back excess energy generated by solar arrays.
Renewable energy reached a major milestone in the first quarter of 2011, when it contributed 11.7% of total U.S. energy production ( of energy), surpassing nuclear energy production (). 2011 was the first year since 1997 that renewables exceeded nuclear in total U.S. energy production.
Renewable energy in the United States accounted for 13.2% of the domestically produced electricity in 2014, and 11.2% of total energy generation. As of 2014, more than 143,000 people work in the solar industry and 43 states deploy net metering, where energy utilities buy back excess energy generated by solar arrays.
Renewable energy reached a major milestone in the first quarter of 2011, when it contributed 11.7% of total U.S. energy production ( of energy), surpassing nuclear energy production (). 2011 was the first year since 1997 that renewables exceeded nuclear in total U.S. energy production.
Annual U.S. wind power rankings track industry's rapid growth
The United States has some of the largest solar farms in the world.
 From the beginning of the United States until 1973, total energy (including electrical) use increased by about 3% per year, while population increased an average of 2.2% per year. Per-capita energy use from 1730 to 1870 was about per person. In the 20th century this increased to around ( per person per year in 1981).
A concentrating solar array (CSP) with thermal storage has a practical capacity factor of 33% and could provide power 24 hours a day. Prior to 2012, in six southwestern states (Arizona, California, Colorado, Nevada, New Mexico, and Utah) the U.S.
From the beginning of the United States until 1973, total energy (including electrical) use increased by about 3% per year, while population increased an average of 2.2% per year. Per-capita energy use from 1730 to 1870 was about per person. In the 20th century this increased to around ( per person per year in 1981).
A concentrating solar array (CSP) with thermal storage has a practical capacity factor of 33% and could provide power 24 hours a day. Prior to 2012, in six southwestern states (Arizona, California, Colorado, Nevada, New Mexico, and Utah) the U.S.
Energy: Sources, Utilization, Legislation, Sustainability, Illinois as Model State
World Sci. Pub. Co.,
Tough Love for Renewable Energy; Making Wind and Solar Power Affordable
May/June 2012
Energy Information Administration
– Official Energy Statistics from the U.S. government's
Biomass Energy Data Book
Buildings Energy Data Book
Power Technologies Energy Data Book (complete)
*
Transportation Energy Data Book
Interactive United States Energy Comparisons
Renewable Energy Tops 10% of U.S. Energy Production
U.S. Energy System Factsheet
by the
fossil fuel
A fossil fuel is a hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the remains of dead plants and animals that is extracted and burned as a fuel. The main fossil fuels are coal, oil, and natural gas. Fossil fuels m ...
s in 2021 as 36% of the nation's energy originated from petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crud ...
, 32% from natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
, and 11% from coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when dea ...
. Nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced b ...
supplied 8% and renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...
supplied 12%, which includes hydroelectric dam
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined an ...
s, biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms bi ...
, wind
Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few hou ...
, geothermal, and solar.
The United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
was the second-largest energy consumer in 2010 after China. The country is ranked seventh in energy consumption per capita after Canada and several small nations.World Per Capita Total Primary Energy Consumption, 1980–2005(MS Excel format) As of 2006, the country's energy consumption had increased more rapidly than domestic energy production over the last 50 years in the nation (when they were roughly equal). This difference was largely met through imports.Ristinen, Robert, A. Energy and the Environment. Malloy, 2006. Print. Not included is the significant amount of energy used overseas in the production of retail and industrial goods consumed in the United States. According to the
Energy Information Administration
The U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System responsible for collecting, analyzing, and disseminating energy information to promote sound policymaking, efficient markets, and publ ...
's statistics, the annual per-capita energy consumption in the U.S. has been somewhat consistent from the 1970s to the present time. The average was about per person from 1980 to 2010. One explanation suggested that the energy required to increase the nation's consumption of manufactured equipment, cars, and other goods has been shifted to other countries producing and transporting those goods to the U.S. with a corresponding shift of green house gases and pollution. Meanwhile any gains made by increasing energy efficiency were at least partially consumed by the rebound effect
The rebound effect, or rebound phenomenon, is the emergence or re-emergence of symptoms that were either absent or controlled while taking a medication, but appear when that same medication is discontinued, or reduced in dosage. In the case of re ...
. In comparison, the world average increased from per person per year between 1980 and 2008.
The United States has an installed summer electricity generation capacity of 1115.68 GW in 2020, up 16.5 GW from 2019.
History
firewood
Firewood is any wooden material that is gathered and used for fuel. Generally, firewood is not highly processed and is in some sort of recognizable log or branch form, compared to other forms of wood fuel like pellets or chips. Firewood can ...
. Rapid industrialization of the economy, urbanization, and the growth of railroads led to increased use of coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when dea ...
, and by 1885 it had eclipsed wood as the nation's primary energy
Primary energy (PE) is an energy form found in nature that has not been subjected to any human engineered conversion process. It is energy contained in raw fuels, and other forms of energy, including waste, received as input to a system. Pr ...
source.
Coal remained dominant for the next seven decades, but by 1950, it was surpassed in turn by both petroleum and natural gas. The 1973 oil embargo precipitated an energy crisis in the United States. In 2007, coal consumption was the highest it has ever been, with it mostly being used to generate electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described ...
. Natural gas has replaced coal as the preferred source of heating in homes, businesses, and industrial furnaces, which burns cleaner and is easier to transport.
Although total energy use increased by approximately a factor of 50 between 1850 and 2000, energy use per capita increased only by a factor of four.
As of 2009, United States per-capita energy use had declined to , 12% less than 2000, and in 2010, to levels not seen since the 1960s.
At the beginning of the 20th century, petroleum was a minor resource used to manufacture lubricants and fuel for kerosene
Kerosene, paraffin, or lamp oil is a combustible hydrocarbon liquid which is derived from petroleum. It is widely used as a fuel in aviation as well as households. Its name derives from el, κηρός (''keros'') meaning "wax", and was regi ...
and oil lamp
An oil lamp is a lamp used to produce light continuously for a period of time using an oil-based fuel source. The use of oil lamps began thousands of years ago and continues to this day, although their use is less common in modern times. Th ...
s.
One hundred years later it had become the preeminent energy source for the United States and the rest of the world.
This rise closely paralleled the emergence of the automobile
A car or automobile is a motor vehicle with Wheel, wheels. Most definitions of ''cars'' say that they run primarily on roads, Car seat, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport private transport#Personal transport, pe ...
as a major force in American culture and the economy.
While petroleum is also used as a source for plastics and other chemicals
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., wit ...
, and powers various industrial processes, today two-thirds of oil consumption in the U.S. is in the form of its derived transportation fuels.U.S. Dept. of Energy,Energy in the United States: 1635–2000
Oil's unique qualities for transportation fuels in terms of energy content, cost of production, and speed of refueling all contributed to it being used over other fuels.
Summary
Note: Sum of components may not equal 100% due to independent rounding.Primary energy consumption
 Primary energy use in the United States was or about per person in 2009. Primary energy use was less in the United States than in China in 2009. The share of energy import was 26% of the primary energy use. The energy import declined about 22% and the annual emissions about 10% in 2009 compared to 2004. In 2020, the U.S as a whole produced 87.79 exajoules of energy.
Primary energy use in the United States was or about per person in 2009. Primary energy use was less in the United States than in China in 2009. The share of energy import was 26% of the primary energy use. The energy import declined about 22% and the annual emissions about 10% in 2009 compared to 2004. In 2020, the U.S as a whole produced 87.79 exajoules of energy.
Energy consumption by source
Wood
Woodenergy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat a ...
is created by the incineration
Incineration is a waste treatment process that involves the combustion of substances contained in waste materials. Industrial plants for waste incineration are commonly referred to as waste-to-energy facilities. Incineration and other high ...
of rigid cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall ...
material found in trees and woody bushes captures Among the most significant renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...
sources is wood energy.See #Fossil-fuel equivalency – these figures are actually closer to 2.8% each. When examining the Renewable Energy as a Share of Total Primary Energy Consumption in 2011, wood consumption is 22%U.S. Dept. of Energy,Annual Energy Report
(2010), Energy Flow diagram There are five main types/forms of wood resources that can be converted into fuel energy, the five are
biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms bi ...
, woody biomass, wood pellets
Pellet fuels (or pellets) are biofuels made from compressed organic matter or biomass. Pellets can be made from any one of five general categories of biomass: industrial waste and co-products, food waste, agricultural residues, energy crops, and ...
, wood chips
Woodchips are small- to medium-sized pieces of wood formed by cutting or chipping larger pieces of wood such as trees, branches, logging residues, stumps, roots, and wood waste.
Woodchips may be used as a biomass solid fuel and are raw materia ...
, and cordwood.
Biomass has been used since cavemen and hunter and gatherer societies. Biomass is organic, indicating it is constructed up of elements obtained from living organisms such as animals and plants. The most prevalent biomass sources used for energy are plants, wood, and waste. Biomass fuel
A fuel is any material that can be made to react with other substances so that it releases energy as thermal energy or to be used for work. The concept was originally applied solely to those materials capable of releasing chemical energy but ...
sources are how they're referred to. Biomass energy is a nonrenewable energy source
Energy development is the field of activities focused on obtaining sources of energy from natural resources. These activities include production of renewable, nuclear, and fossil fuel derived sources of energy, and for the recovery and reuse ...
.
Woody biomass, which encompasses trees and other woody plants, is defined as a result of maintenance, regenerating, and hazardous
A hazard is a potential source of harm. Substances, events, or circumstances can constitute hazards when their nature would allow them, even just theoretically, to cause damage to health, life, property, or any other interest of value. The probabi ...
fuel reduction initiatives, as well as natural disaster
A natural disaster is "the negative impact following an actual occurrence of natural hazard in the event that it significantly harms a community". A natural disaster can cause loss of life or damage property, and typically leaves some econ ...
s.
The average American family until the 1800s was most likely to use wood as the main source of energy consumption. Wood would be considered the predominant renewable energy source used until the mid to late 1800s. The consumption of wood continues to be a significant aspect of fuel in various different countries, for numerous reasons including cooking and heating, as well as lighting their houses. As mentioned, the second largest source of wood consumption was in the United States. Wood was used within homes as wood-burning appliances, wood in fireplaces, as well as pellets in pellet stoves. Ranging from 1776 up until 2012, the use of wood as an energy source has been steady, there has been a minuscule increase from 1836 to 1926, with a peak in the late 1880s.
Petroleum
Oil is one of the largest sources of energy in the United States. The United States influences world oil reserves for both growth and development. As the 20th century progressed,petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crud ...
gained increasing importance by providing heating and electricity to the commercial and industrial sectors. Oil was also used in transportation; first for railroads
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in Track (rail transport), tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the ...
and later for motor vehicles.
 As
As automobile
A car or automobile is a motor vehicle with Wheel, wheels. Most definitions of ''cars'' say that they run primarily on roads, Car seat, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport private transport#Personal transport, pe ...
s became more affordable, demand for oil quickly rose.
Since the rise of the automobile industry, oil price, demand, and production have all increased as well. Between 1900 and 1980, fuel was directly correlated with Gross National Product (GNP). Furthermore, oil shocks have often coincided with recession
In economics, a recession is a business cycle contraction when there is a general decline in economic activity. Recessions generally occur when there is a widespread drop in spending (an adverse demand shock). This may be triggered by various ...
s, and the government has responded to oil shocks in several ways. In the 1920s, oil prices were peaking and many commentators believed that oil supplies were running out. Congress was confronted by requests to augment supplies, so a generous depletion allowance was enacted for producers in 1926, which increased investment returns substantially. This change induced additional exploration activity, and subsequently the discovery of large new oil reservoirs.
In the next decade the situation was reversed with prices low and dropping. This resulted in demands for more "orderly" competition and set minimum oil prices. Rather than repealing the previous policies enacted in the 1920s, Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of a ...
enacted a price-support system. Similar cycles have occurred in the 1950s and 1970s.
Gas


Natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
was the largest source of energy production in the United States in 2016, representing 33% of all energy produced in the country.
Natural gas has been the largest source of electrical generation in the United States since July 2015.
The United States has been the world's largest producer of natural gas since 2009, when it surpassed Russia. U.S. natural gas production achieved new record highs for each year from 2011 through 2015. Marketed natural gas production in 2015 was , a 5.4% increase over 2014, and a 52% increase over the production of per day in 2005.
Because of the greater supply, consumer prices for natural gas are significantly lower in the United States than in Europe and Japan.
The low price of natural gas, together with its smaller carbon footprint compared to coal, has encouraged a rapid growth in electricity generated from natural gas.
Between 2005 and 2014, U.S. production of natural gas liquids
Natural-gas condensate, also called natural gas liquids, is a low-density mixture of hydrocarbon liquids that are present as gaseous components in the raw natural gas produced from many natural gas fields. Some gas species within the raw natur ...
(NGLs) increased 70%, from per day in 2005 to per day in 2014.
The U.S. has been the world's leading producer of natural gas liquids since 2010, when U.S. NGL production passed that of Saudi Arabia.
Although the United States leads the world in natural gas production, it is only fifth in proved reserves of natural gas, behind Russia, Iran, Qatar, and Turkmenistan.
Coal
Generation of electricity is the largest user of coal, although its use is in decline. About 50% of electric power was produced by coal in 2005, declining to 30% in 2016 and 23% in 2019. Electric utilities buy more than 90% of the coal consumed in the United States. The United States is a net exporter of coal. Coal exports, for which Europe is the largest customer, peaked in 2012 and have declined since. In 2015, the U.S. exported 7.0% of mined coal. Coal has been used to generate electricity in the United States since an Edison plant was built in New York City in 1882. The first AC power station was opened byGeneral Electric
General Electric Company (GE) is an American multinational conglomerate founded in 1892, and incorporated in New York state and headquartered in Boston. The company operated in sectors including healthcare, aviation, power, renewable energ ...
in Ehrenfeld, Pennsylvania
Ehrenfeld is a borough in Cambria County, Pennsylvania, United States. It is part of the Johnstown, Pennsylvania Metropolitan Statistical Area. The population was 228 at the 2010 census.
Geography
Ehrenfeld is located in south-central Cambria Cou ...
in 1902, servicing the Webster Coal and Coke Company.
By the mid-20th century, coal had become the leading fuel for generating electricity in the U.S.
The long, steady rise of coal-fired generation of electricity shifted to a decline after 2007.
The decline has been linked to the increased availability of natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
, decreased consumption, renewable electricity
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...
, and more stringent environmental regulations.
The Environmental Protection Agency
A biophysical environment is a biotic and abiotic surrounding of an organism or population, and consequently includes the factors that have an influence in their survival, development, and evolution. A biophysical environment can vary in scale f ...
has advanced restrictions on coal plants to counteract mercury pollution
Mercury is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is also known as quicksilver and was formerly named hydrargyrum ( ) from the Greek words, ''hydor'' (water) and ''argyros'' (silver). A heavy, silvery d-block element, m ...
, smog
Smog, or smoke fog, is a type of intense air pollution. The word "smog" was coined in the early 20th century, and is a portmanteau of the words ''smoke'' and '' fog'' to refer to smoky fog due to its opacity, and odor. The word was then inte ...
, and global warming
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to E ...
.
Hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is Electricity generation, electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other Renewabl ...
was considered one of the largest sources of electricity until 2019. Hydroelectricity was responsible for about 6.3% of the U.S. utility-scale electricity generation, as well as about 31.5% of total utility-scale renewable electricity generation in 2021. Hydroelectric energy, also known as hydroelectric power
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and ...
or hydroelectricity, is a type of energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat a ...
that generates electricity by utilizing the potential energy of water, such as water running over a waterfall. For centuries, individuals have exploited this energy.
In many cases, hydroelectric energy or hydroelectric power plants' process to produce electricity can be compared to coal-fired
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when dea ...
power plants. Hydropower presently accounts for 37% of total renewable electricity output and 7% of overall electricity generation in the United States. The angle of inclination
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a Plane of reference, reference plane and the orbital plane or Axis of rotation, axis of direction of the orbiting object ...
formed by a dam
A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use ...
or diversion construction allows water to flow in and out on one side, therefore, generating electricity.
The cost of hydropower can be considered very affordable, due to the fact that the source of electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described ...
and energy come from moving water, states within the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
that have more moving water such as Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
and Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
have more affordable electricity bills. There are many advantages of hydropower, since it is fueled by water it is considered a clean source of energy. As well as it is a domestic source of energy, making it easier to reply to each state's sources rather than being reliant on international sources. Hydropower
Hydropower (from el, ὕδωρ, "water"), also known as water power, is the use of falling or fast-running water to Electricity generation, produce electricity or to power machines. This is achieved by energy transformation, converting the Pot ...
accounted for 17% of global energy generation in 2020, making it the third largest generator following coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when dea ...
and natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
. Hydropower's overall production has grown by 70% internationally in the previous 20 years, but its percentage of overall generation has remained steady due to the rise of wind
Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few hou ...
, solar PV
A photovoltaic system, also PV system or solar power system, is an electric power system designed to supply usable solar power by means of photovoltaics. It consists of an arrangement of several components, including solar panels to absorb and co ...
, coal, and natural gas.
Hydroelectricity is mostly used for electricity production in the United States and in 2019 there were 1,460 utility scale hydropower facilities. These produced 274 billion kilowatt-hours. In 2019, it accounted for 6.6% of total electricity production and 38% of renewable electricity
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...
. The amount of electricity in the United States from hydropower has remained relatively the same since the 70's, however it's percentage has decreased due to more production from other sources. In 1950, 30% of total electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described ...
production came from hydropower despite only 101 billion kilowatt-hours being produced.
Hydropower has been used to produce electricity in the United States since 1880 when it was used to power the Wolverine Chair factory in Grand Rapids, Michigan
Grand Rapids is a city and county seat of Kent County, Michigan, Kent County in the U.S. state of Michigan. At the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the city had a population of 198,917 which ranks it as the List of municipalities in Mi ...
.
In 2019, the top five Hydroelectricity producing states produced 65% of the United States total hydroelectricity. This includes Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
state with 24%, California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
with 15%, New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
with 11%, Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
, with 11% and, Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = "Alabama (state song), Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery, Alabama, Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville, Alabama, Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County, Al ...
with 4%. The largest hydroelectric power plant in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
, which is also the largest overall power, is the Grand Coulee Dam
Grand Coulee Dam is a concrete gravity dam on the Columbia River in the U.S. state of Washington, built to produce hydroelectric power and provide irrigation water. Constructed between 1933 and 1942, Grand Coulee originally had two powerh ...
built in Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
state in 1942 with a generating capacity of 6,809 Megawatts
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer. The watt is named after James Wat ...
.
Nuclear
Other renewables
Final energy consumption
Consumption by sector
The U.S. Department of Energy tracks national energy consumption in four broad sectors: industrial, transportation, residential, and commercial. The industrial sector has long been the country's largest energy user, currently representing about 33% of the total. Next in importance is the transportation sector followed by the residential and commercial sectors.Regional variation
 Household energy use varies significantly across the United States. An average home in the Pacific region (consisting of
Household energy use varies significantly across the United States. An average home in the Pacific region (consisting of California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
, Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
, and Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
) consumes 35% less energy than a home in the South Central region. Some of the regional differences can be explained by climate. The heavily populated coastal areas of the Pacific states experience generally mild winters and summers, reducing the need for both home heating and air conditioning
Air conditioning, often abbreviated as A/C or AC, is the process of removing heat from an enclosed space to achieve a more comfortable interior environment (sometimes referred to as 'comfort cooling') and in some cases also strictly controlling ...
. The warm, humid climates of the South Central and South Atlantic regions lead to higher electricity usage, while the cold winters experienced in the Northeast and North Central regions result in much higher consumption of natural gas and heating oil
Heating oil is any petroleum product or other oil used for heating; a fuel oil. Most commonly, it refers to low viscosity grades of fuel oil used for furnaces or boilers use for home heating and in other buildings. Home heating oil is often a ...
. The state with the lowest per-capita energy use is New York, at per year, and the highest is Wyoming, at slightly over per year.
Other regional differences stem from energy efficiency measures taken at the local and state levels. California has some of the strictest environmental laws and building codes in the country, leading its per-household energy consumption to be lower than all other states except Hawaii.
The land-use decisions of cities and towns also explain some of the regional differences in energy use. Townhouses are more energy efficient than single-family homes because less heat, for example, is used per person. Similarly, areas with more homes in a compact neighborhood encourage walking, biking and transit, thereby reducing transportation energy use. A 2011 U.S. EPA study found that multi-family homes in urban neighborhoods, with well-insulated buildings and fuel-efficient cars, use less than two-thirds of the energy used by conventionally built single-family houses in suburban areas (with standard cars).
Electricity
 The United States is the world's second largest producer and consumer of electricity. It consumes about 20% of the world's electricity supply. This section provides a summary of the
The United States is the world's second largest producer and consumer of electricity. It consumes about 20% of the world's electricity supply. This section provides a summary of the consumption
Consumption may refer to:
*Resource consumption
*Tuberculosis, an infectious disease, historically
* Consumption (ecology), receipt of energy by consuming other organisms
* Consumption (economics), the purchasing of newly produced goods for curren ...
and generation
A generation refers to all of the people born and living at about the same time, regarded collectively. It can also be described as, "the average period, generally considered to be about 20–30 years, during which children are born and gr ...
of the nation's electric industry, based on data mined from U.S. DOE Energy Information Administration/Electric Power Annual 2018 files. Data was obtained from the most recent DOE Energy Information Agency (EIA) files. Consumption is detailed from the residential, commercial, industrial, and other user communities. Generation is detailed for the major fuel sources of coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when dea ...
, natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
, nuclear
Nuclear may refer to:
Physics
Relating to the nucleus of the atom:
* Nuclear engineering
*Nuclear physics
*Nuclear power
*Nuclear reactor
*Nuclear weapon
*Nuclear medicine
*Radiation therapy
*Nuclear warfare
Mathematics
*Nuclear space
*Nuclear ...
, petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crud ...
, hydro
Hydro from Ancient Greek word ὕδωρ (húdōr), meaning ''water''.
Hydro may also refer to:
Energy technologies
* Water-derived power or energy:
** Hydropower, derived from water
** Hydroelectricity, in electrical form
* "Hydro", AC mains ...
, and the other renewables
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...
of wind
Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few hou ...
, wood
Wood is a porous and fibrous structural tissue found in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulose fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin th ...
, other biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms bi ...
, geothermal, and solar. Changes to the electrical energy fuel mix and other trends are identified. Progress in wind
Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few hou ...
and solar contributing to the energy mix are addressed.
Consumption
Electricity consumption
Electric energy consumption is the form of energy consumption that uses electrical energy. Electric energy consumption is the actual energy demand made on existing electricity supply for transportation, residential, industrial, commercial, and ot ...
in this section is based upon data mined from U.S. DOE Energy Information Administration/Electric Power Annual 2018 files"Electric Power Annuaretrieved 2020-6-14 In 2018 the total U.S. consumption of electricity was 4,222.5
terawatt-hour
A kilowatt-hour (unit symbol: kW⋅h or kW h; commonly written as kWh) is a unit of energy: one kilowatt of power for one hour. In terms of SI derived units with special names, it equals 3.6 megajoules (MJ). Kilowatt-hours are a common bil ...
s (TWh) or 15201 PJ. Consumption was up from 2017, by 131.9 TWh (475 PJ) or +3.2%. This is broken down as:
* Residential customers (133.89 million) directly consumed 1,469.09 TWh (5289 PJ), or 34.74% of the total. This was up 90.5 TWh (326 PJ) or 6.5% from 2017. An average residential customer used 914 kWh (3290 MJ) per month and with the average U.S. residential cost of $0.1287/kWh ($0.03575/MJ) the average monthly electrical bill would be $117.67, up slightly from 2017.
* Commercial customers (18.605 million) directly consumed 1,381.76 TWh (4974 PJ) or 32.72% of the total. This was more (28.86 TWh or 104 PJ) than in 2017 with over 246K new customers. An average commercial customer used 6,189 kWh (22,280 MJ) per month and with the average U.S. commercial electric cost of $0.1067/kWh ($0.0296/MJ) the average monthly electrical bill would be $660.36.
* Industrial customers (840,321, flat with 2017) directly consumed 1000.7 TWh (3603 PJ) or 23.70% of the total. This was a little more (16.4 TWh or 59 PJ) than in 2017 (+1.6%).
* Transportation customers (83) directly consumed 7.665 TWh (27,594 MJ) or 0.18% of the total. This was a little higher (0.14 TWh or 1PJ) than in 2017.
* System loss throughout the total electrical grid infrastructure by direct use of the suppliers (144.1 TWh or 519 PJ) and for transmission and other system losses and for unaccounted for loads (219.2 TWh or 789 PJ) amounts to 363.3 TWh (1308 PJ)or 8.6% of the total which is down by 0.4% from 2017. Thus, the U.S. electric distribution system is 91.4% efficient and efficiency has improved slightly over the last year.
Electricity consumption
Electric energy consumption is the form of energy consumption that uses electrical energy. Electric energy consumption is the actual energy demand made on existing electricity supply for transportation, residential, industrial, commercial, and ot ...
per capita is based upon data mined from U.S. DOE Energy Information Administration/Electric Power Annual 2018 files Population data is from Demographics of the United States
The United States had an official estimated resident population of 333,287,557 on July 1, 2022, according to the U.S. Census Bureau. This figure includes the 50 states and the District of Columbia but excludes the population of five unincorpor ...
. Per-capita consumption in 2018 is . This is up from 2017, down 4.6% from a decade ago, and down 6.4% from its peak in 2007. The following table shows the yearly U.S. per-capita consumption from 2013 to 2019.
Generation

 The United States has an installed summer electricity generation capacity of 1115.68 GW in 2020, up 16.5 GW from 2019. The U.S. electricity generation was 4,007.14TWh (14,429.7 PJ because 1TWh=3.6 PJ) in 2020 and down 120.7TWh (2.9%) from 2019 (pre-pandemic).
The United States has an installed summer electricity generation capacity of 1115.68 GW in 2020, up 16.5 GW from 2019. The U.S. electricity generation was 4,007.14TWh (14,429.7 PJ because 1TWh=3.6 PJ) in 2020 and down 120.7TWh (2.9%) from 2019 (pre-pandemic).Eia.gov, retrieved 2022-6-01 The U.S. also imported; 61.45 TWh and exported 14.13 TWh, for a total of 4,054.45 TWh of electrical grid energy use in the U.S. This was down 112.5 TWh (2.7%) from 2019. Electrical energy generated from coal was 773.39 TWh (19.48%); natural and other gases, 1,635.985 TWh (40.35%); nuclear, 789.879 TWh (19.11%); hydro, 285.274 TWh (7.04%); Renewables (other than hydro), 497.729 TWh (12.28%); imports less exports, 47.314 TWh (1.17%) petroleum, 17.341 TWh (0.43%); and miscellaneous (including pumped storage), 7.534 TWh (0.19%). The United States' renewable sources (hydro reported separately) are wind, 337.938 TWh (8.33%); wood, 36.21 TWh (0.89%); other biomass, 18.493 TWh (0.46%); geothermal, 15.89 TWh (0.39%) and solar, 89.199 TWh (2.20%). Small-scale solar is estimated to have produced an additional 41.522 TWh . Natural gas electricity generation exceeded generation from coal for the first time in 2016 and continued its expansion. Wind exceeded Hydro in 2019 for the first time. Nuclear exceeded coal for the first time in 2020. The following tables summarize the electrical energy generated by fuel source for the United States. Electric Power Annual for 2020 data and preliminary data from Electric Power Monthly for the 2021 data[ was used throughout the rest of this section. Note: Biomass includes wood and wood derived fuel, landfill gas, biogenic municipal solid waste and other waste biomass.
Electricity generation by source
State electric characteristics
Individual states have very diverse electric generation systems, and their new initiatives to expand their generation base are equally diverse. Coupled with consumption disparages, it leads to a mix of "have" and "have not" electric energy states. Using the data from the U.S. DOE Energy Information Administration/Electric Power Annual 2017 files. Data was obtained from the most recent DOE Energy Information Agency (EIA) full year files. Full use of the excellent EIA data browser permits easy access to the plethora of data available.State electric generation
Top ten states by fuel source
Importing states
 The following table, derived from data mined from Electric Power Annual, identifies those states which must import electrical energy from neighboring states to meet their consumption needs. Each state's total electric generation for 2018 is compared with the state's consumption, and its share of the system loss and the difference between the generated electric energy and its total consumption (including its share of the system loss) is the amount of energy it imports. For Hawaii, total consumption equals generated energy. For the other states, multiplying their direct consumption by 1.082712997 (4168280574/3849848100), results in the United States' supply (including net imports) being equal to its total consumption.
The following table, derived from data mined from Electric Power Annual, identifies those states which must import electrical energy from neighboring states to meet their consumption needs. Each state's total electric generation for 2018 is compared with the state's consumption, and its share of the system loss and the difference between the generated electric energy and its total consumption (including its share of the system loss) is the amount of energy it imports. For Hawaii, total consumption equals generated energy. For the other states, multiplying their direct consumption by 1.082712997 (4168280574/3849848100), results in the United States' supply (including net imports) being equal to its total consumption.
Exporting states
The following table, derived from data mined from Electric Power Annual, identifies those states which generate more electrical energy than they need to meet their consumption needs. They supply those that need additional energy. Each state's total electric generation for 2018 is compared with the state's consumption, and its share of the system losses and the difference between the generated electric energy and its total consumption (including its share of the system losses) is the amount of energy it exports. For Hawaii, total consumption equals generated energy. For the other states, multiplying their direct consumption by 1.082712997 (4168280574/3849848100) results in the United States' supply (including net imports) being equal to its total consumption usage. A state's exported energy is determined by subtracting the state's total consumption from its generation.
Renewable energy
 Renewable energy in the United States accounted for 13.2% of the domestically produced electricity in 2014, and 11.2% of total energy generation. As of 2014, more than 143,000 people work in the solar industry and 43 states deploy net metering, where energy utilities buy back excess energy generated by solar arrays.
Renewable energy reached a major milestone in the first quarter of 2011, when it contributed 11.7% of total U.S. energy production ( of energy), surpassing nuclear energy production (). 2011 was the first year since 1997 that renewables exceeded nuclear in total U.S. energy production.
Renewable energy in the United States accounted for 13.2% of the domestically produced electricity in 2014, and 11.2% of total energy generation. As of 2014, more than 143,000 people work in the solar industry and 43 states deploy net metering, where energy utilities buy back excess energy generated by solar arrays.
Renewable energy reached a major milestone in the first quarter of 2011, when it contributed 11.7% of total U.S. energy production ( of energy), surpassing nuclear energy production (). 2011 was the first year since 1997 that renewables exceeded nuclear in total U.S. energy production.
Hydroelectric power
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and ...
is currently the largest producer of renewable energy in the U.S. It produced around 6.2% of the nation's total electricity in 2010 which was 60.2% of the total renewable energy in the U.S. The United States is the fourth largest producer of hydroelectricity in the world after China, Canada, and Brazil. The Grand Coulee Dam
Grand Coulee Dam is a concrete gravity dam on the Columbia River in the U.S. state of Washington, built to produce hydroelectric power and provide irrigation water. Constructed between 1933 and 1942, Grand Coulee originally had two powerh ...
is the 5th largest hydroelectric power station in the world.
U.S. wind power's installed capacity now exceeds 65,000 MW and supplies 4% of the nation's electric power. Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
is firmly established as the leader in wind power development followed by Iowa and California.American Wind Energy AssociationAnnual U.S. wind power rankings track industry's rapid growth
The United States has some of the largest solar farms in the world.
Solar Star
Solar Star is a 579-megawatt ( MWAC) photovoltaic power station near Rosamond, California, United States, that is operated and maintained by SunPower Services. When completed in June 2015, it was the world's largest solar farm in terms of instal ...
is a 579-megawatt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of Power (physics), power or radiant flux in the International System of Units, International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantification (science), ...
( MWAC) farm near Rosamond, California
Rosamond is a unincorporated community in Kern County, California, US, near the Los Angeles county line. Rosamond is part of Greater Los Angeles and is located in the Mojave Desert just north of Lancaster and Palmdale, two of the largest cities ...
. The Desert Sunlight Solar Farm
The Desert Sunlight Solar Farm is a 550 megawatt (MW AC) photovoltaic power station approximately six miles north of Desert Center, California, United States, in the Mojave Desert. It uses approximately 8.8 million cadmium telluride modul ...
is a 550-megawatt solar power
Solar power is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV) or indirectly using concentrated solar power. Photovoltaic cells convert light into an electric current using the photovoltaic e ...
plant in Riverside County, California
Riverside County is a County (United States), county located in the southern California, southern portion of the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 United States Census, 2020 census, the population was 2,418,185, making it the fourth-most ...
and the Topaz Solar Farm
Topaz Solar Farm is a 550 megawatt ( MWAC) photovoltaic power station in San Luis Obispo County, California, United States. Construction on the project began in November 2011 and ended in November 2014. It is one of the world's largest sola ...
, a 550 MW photovoltaic power plant, is in San Luis Obispo County, California
San Luis Obispo County (), officially the County of San Luis Obispo, is a County (United States), county on the Central Coast (California), Central Coast of California. As of the 2020 United States Census, 2020 census, the population was 282, ...
. The solar thermal
Solar thermal energy (STE) is a form of energy and a technology for harnessing solar energy to generate thermal energy for use in industry, and in the residential and commercial sectors.
Solar thermal collectors are classified by the United Sta ...
SEGS
Solar Energy Generating Systems (SEGS) is a concentrated solar power plant in California, United States. With the combined capacity from three separate locations at 354 megawatt (MW), it was once the world's second largest solar thermal energy g ...
group of plants in the Mojave Desert has a total generating capacity of 354 MW.SEGS I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII, VIII & IXRooftop solar
A rooftop solar power system, or rooftop PV system, is a photovoltaic (PV) system that has its electricity-generating solar panels mounted on the rooftop of a residential or commercial building or structure. The various components of such a syst ...
has also become a growing contributor to overall solar power generation, with overall generated capacity at 26 GW in 2022 (around 1% of total generation capacity), with the states of California, Texas, Florida experiencing the fastest growth.
The Geysers
The Geysers is the world's largest geothermal field, containing a complex of 18 geothermal power plants, drawing steam from more than 350 wells, located in the Mayacamas Mountains approximately north of San Francisco, California.
Geysers produce ...
in Northern California is the largest complex of geothermal energy
Geothermal energy is the thermal energy in the Earth's crust which originates from the formation of the planet and from radioactive decay of materials in currently uncertain but possibly roughly equal proportions. The high temperature and pres ...
production in the world.
The development of renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...
and efficient energy use
Efficient energy use, sometimes simply called energy efficiency, is the process of reducing the amount of energy required to provide products and services. For example, insulating a building allows it to use less heating and cooling energy to ...
marks "a new era of energy exploration" in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
, according to President Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the U ...
. Studies suggest that if there is enough political will, it is feasible to supply the whole United States with 100% renewable energy
100% renewable energy means getting all energy from renewable resources. The endeavor to use 100% renewable energy for electricity, heating, cooling and transport is motivated by climate change, pollution and other environmental issues, ...
by 2050.
Trends and projections
In 2015, electrical energy usage in the United States was 1.6% more than in 2005 and 1% less than the peak in 2007. Per-capita consumption has decreased about 7% since its peak in 2007 and every year since has shown a decrease in individual consumption. Conservation efforts are helping. At least, for the next decade, coal, natural gas, and nuclear will remain the top three fuels for electric energy generation in the United States. Coal will continuously decrease its contribution, with natural gas increasing its contribution. Nuclear will have some downs (decommissionings) and ups (new online plants) but probably remain about constant. Hydro will maintain. Petroleum will continue to decrease in importance. Wind and solar will continue to grow in importance; their combined generation was 5.29% of U.S. electric generation for 2015 or 5.20% of total U.S. consumption. From the beginning of the United States until 1973, total energy (including electrical) use increased by about 3% per year, while population increased an average of 2.2% per year. Per-capita energy use from 1730 to 1870 was about per person. In the 20th century this increased to around ( per person per year in 1981).
A concentrating solar array (CSP) with thermal storage has a practical capacity factor of 33% and could provide power 24 hours a day. Prior to 2012, in six southwestern states (Arizona, California, Colorado, Nevada, New Mexico, and Utah) the U.S.
From the beginning of the United States until 1973, total energy (including electrical) use increased by about 3% per year, while population increased an average of 2.2% per year. Per-capita energy use from 1730 to 1870 was about per person. In the 20th century this increased to around ( per person per year in 1981).
A concentrating solar array (CSP) with thermal storage has a practical capacity factor of 33% and could provide power 24 hours a day. Prior to 2012, in six southwestern states (Arizona, California, Colorado, Nevada, New Mexico, and Utah) the U.S. Bureau of Land Management
The Bureau of Land Management (BLM) is an agency within the United States Department of the Interior responsible for administering federal lands. Headquartered in Washington DC, and with oversight over , it governs one eighth of the country's la ...
(BLM) owned nearly (an area larger than the state of Montana) that was open to proposals for solar power installations. To streamline consideration of applications, the BLM produced a Programmatic Environmental Impact Statement (PEIS). By the subsequent Record of Decision in October 2012, the BLM withdrew 78% of its land from possible solar development, leaving still open to applications for solar installations, an area nearly as large as South Carolina. Of the area left open to solar proposals, the BLM has identified in highly favorable areas it calls Solar Energy Zones. In Spain, with natural gas backups, CSP has reached a capacity factor of 66%, with 75% being a theoretical maximum.
See also
*Carter Doctrine
The Carter Doctrine was a policy proclaimed by President of the United States Jimmy Carter in his State of the Union Address on January 23, 1980, which stated that the United States would use military force, if necessary, to defend its national i ...
* The Climate Registry
The Climate Registry (TCR) is a non-profit organization governed by U.S. states and Canadian provinces and territories. TCR designs and operates voluntary and compliance greenhouse gas (GHG) reporting programs globally, and assists organizations ...
* Efficient energy use
Efficient energy use, sometimes simply called energy efficiency, is the process of reducing the amount of energy required to provide products and services. For example, insulating a building allows it to use less heating and cooling energy to ...
* Energy conservation in the United States
The United States is the second-largest single consumer of energy in the world. The U.S. Department of Energy categorizes national energy use in four broad sectors: transportation, residential, commercial, and industrial.
Energy usage in transp ...
* Energy policy of the United States
The energy policy of the United States is determined by federal, state, and local entities. It addresses issues of energy production, distribution, consumption, and modes of use, such as building codes, mileage standards, and commuting polic ...
* World energy resources
World energy resources are the estimated maximum capacity for energy production given all available resources on Earth. They can be divided by type into fossil fuel, nuclear fuel and renewable resources.
Fossil fuel
Remaining reserves of ...
* World energy consumption
World energy supply and consumption is global production and preparation of fuel, generation of electricity, energy transport, and energy consumption. It is a basic part of economic activity. It includes heat, but not energy from food.
This art ...
* List of countries by energy consumption and production
This is a list of countries by total primary energy consumption and production.
: 1 quadrillion BTU = 293 T W·h = 1.055 E J
: 1 quadrillion BTU/yr = 1.055 EJ/yr = 293 TW·h/yr = 33.433 GW
The numbers below are for the total energy consumptio ...
* List of countries by energy consumption per capita
This is a list of countries by total energy consumption per capita. This is not the consumption of end-users but all energy needed as input to produce fuel and electricity for end-users. It is known as total primary energy supply (TPES), a ...
* List of U.S. states by electricity production from renewable sources
References
Further reading
*GA Mansoori, N Enayati, LB Agyarko (2016)Energy: Sources, Utilization, Legislation, Sustainability, Illinois as Model State
World Sci. Pub. Co.,
Tough Love for Renewable Energy; Making Wind and Solar Power Affordable
May/June 2012
Foreign Affairs
''Foreign Affairs'' is an American magazine of international relations and U.S. foreign policy published by the Council on Foreign Relations, a nonprofit, nonpartisan, membership organization and think tank specializing in U.S. foreign policy and ...
External links
Energy Information Administration
– Official Energy Statistics from the U.S. government's
Energy Information Administration
The U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System responsible for collecting, analyzing, and disseminating energy information to promote sound policymaking, efficient markets, and publ ...
Biomass Energy Data Book
Buildings Energy Data Book
Power Technologies Energy Data Book (complete)
*
Transportation Energy Data Book
Interactive United States Energy Comparisons
Renewable Energy Tops 10% of U.S. Energy Production
U.S. Energy System Factsheet
by the
University of Michigan
, mottoeng = "Arts, Knowledge, Truth"
, former_names = Catholepistemiad, or University of Michigania (1817–1821)
, budget = $10.3 billion (2021)
, endowment = $17 billion (2021)As o ...
's
__FORCETOC__
{{DEFAULTSORT:Energy In The United States
Energy policy of the United States
Energy in North America