1876 United States presidential election on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The 1876 United States presidential election was the 23rd quadrennial
File:President Rutherford Hayes 1870 - 1880 Restored (cropped).jpg,
(declined to run) File:UlyssesGrant.jpg,
(declined in 1875)
It was widely assumed during the year 1875 that incumbent President
File:SamuelJonesTilden.jpg,
 The Democratic Party's failure to nominate its own ticket in the previous presidential election, in which they had instead endorsed the Liberal Republican candidacy of
The Democratic Party's failure to nominate its own ticket in the previous presidential election, in which they had instead endorsed the Liberal Republican candidacy of
Official proceedings of the National Democratic convention, held in St. Louis, Mo., June 27th, 28th and 29th, 1876
'. (September 3, 2012). Source:
Official proceedings of the National Democratic convention, held in St. Louis, Mo., June 27th, 28th and 29th, 1876
' (September 3, 2012).
File:Peter Cooper Photograph.jpg,
The Greenback Party had been organized by agricultural interests in
 Tilden, who had prosecuted machine politicians in New York and sent the legendary political boss William M. Tweed to jail, ran as a reform candidate against the background of the corruption of the
Tilden, who had prosecuted machine politicians in New York and sent the legendary political boss William M. Tweed to jail, ran as a reform candidate against the background of the corruption of the
HarpWeek Since all of the remaining available Justices were Republicans, they had already selected Justice Joseph P. Bradley, who was considered the most impartial remaining member of the court. That selection proved decisive.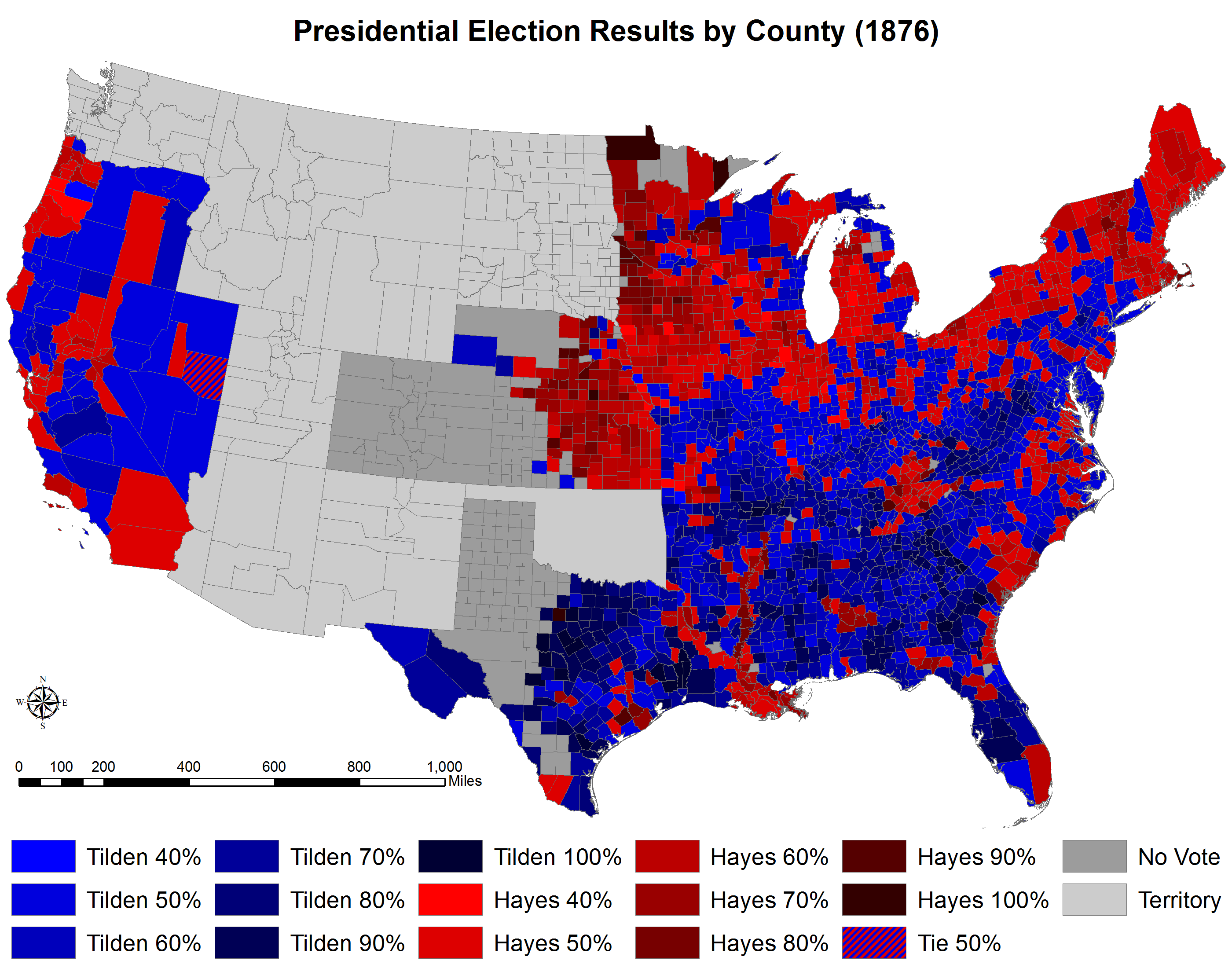 Since it was drawing perilously near to Inauguration Day, the commission met on January 31. Each of the disputed state election cases (Florida, Louisiana, Oregon, and South Carolina) was respectively submitted to the commission by Congress. Eminent counsel appeared for each side, and there were double sets of returns from every one of the states named.
The commission first decided not to question any returns that were ''
Since it was drawing perilously near to Inauguration Day, the commission met on January 31. Each of the disputed state election cases (Florida, Louisiana, Oregon, and South Carolina) was respectively submitted to the commission by Congress. Eminent counsel appeared for each side, and there were double sets of returns from every one of the states named.
The commission first decided not to question any returns that were ''
Image:1876 United States presidential election results map by county.svg, Results by county, shaded according to winning candidate's percentage of the vote
Image:PresidentialCounty1876Colorbrewer.gif, Map of presidential election results by county
Image:DemocraticPresidentialCounty1876Colorbrewer.gif, Map of Democratic presidential election results by county
Image:RepublicanPresidentialCounty1876Colorbrewer.gif, Map of Republican presidential election results by county
Image:OtherPresidentialCounty1876Colorbrewer.gif, Map of "other" presidential election results by county
Image:CartogramPresidentialCounty1876Colorbrewer.gif, Cartogram of presidential election results by county
Image:CartogramDemocraticPresidentialCounty1876Colorbrewer.gif, Cartogram of Democratic presidential election results by county
Image:CartogramRepublicanPresidentialCounty1876Colorbrewer.gif, Cartogram of Republican presidential election results by county
Image:CartogramOtherPresidentialCounty1876Colorbrewer.gif, Cartogram of "other" presidential election results by county
''Appleton's Annual Cyclopedia ...for 1876''
(1885), comprehensive world coverage * John Bigelow, Author, Edited by, Nikki Oldaker, ''The Life of Samuel J. Tilden.'' (2009 Revised edition-retype-set-new photos). 444 pages,
original 1895 edition
* Holt, Michael F. ''By One Vote: The Disputed Presidential Election of 1876.'' (2008). 304 pages, * * Foley, Edward. 2016. ''Ballot Battles: The History of Disputed Elections in the United States''. Oxford University Press. * * * * * , popular account * Summers, Mark Wahlgren.''The Press Gang: Newspapers and Politics, 1865-1878'' (1994) * Summers, Mark Wahlgren. ''The Era of Good Stealings'' (1993), covers corruption 1868-1877 *Richard White (historian), Richard White
"Corporations, Corruption, and the Modern Lobby: A Gilded Age Story of the West and the South in Washington, D.C."
''Southern Spaces'', April 16, 2009 *
online
* Porter, Kirk H. and Donald Bruce Johnson, eds. ''National party platforms, 1840-1964'' (1965
online 1840-1956
Hayes Presidential Library
with essays by historians
from the Library of Congress
Rutherford B. Hayes On The Election of 1876: Original Letter
Shapell Manuscript Foundation
* [http://www.countingthevotes.com/1876/ Election of 1876 in Counting the Votes] {{Authority control 1876 United States presidential election, 1876 United States presidential election Reconstruction Era Constitutional crises, United States Presidency of Rutherford B. Hayes Rutherford B. Hayes November 1876 events, United States United States election controversies
presidential election
A presidential election is the election of any head of state whose official title is President.
Elections by country
Albania
The president of Albania is elected by the Assembly of Albania who are elected by the Albanian public.
Chile
The p ...
, held on Tuesday, November 7, 1876, in which Republican nominee Rutherford B. Hayes faced Democrat Samuel J. Tilden. It was one of the most contentious presidential elections
A presidential election is the election of any head of state whose official title is President.
Elections by country
Albania
The president of Albania is elected by the Assembly of Albania who are elected by the Albanian public.
Chile
The pre ...
in American history. Its resolution involved negotiations between the Republicans and Democrats, resulting in the Compromise of 1877
The Compromise of 1877, also known as the Wormley Agreement or the Bargain of 1877, was an unwritten deal, informally arranged among members of the United States Congress, to settle the intensely disputed 1876 presidential election between Ruth ...
, and on March 2, 1877, the counting of electoral votes by the House and Senate occurred, confirming Hayes as President. It was the second of five U.S. presidential elections in which the winner did not win a plurality of the national popular vote. This is the only time both major party nominees were incumbent US governors.
After U.S. President Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant ; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was an American military officer and politician who served as the 18th president of the United States from 1869 to 1877. As Commanding General, he led the Union A ...
declined to seek a third term despite previously being expected to do so, U.S. Representative James G. Blaine
James Gillespie Blaine (January 31, 1830January 27, 1893) was an American statesman and Republican politician who represented Maine in the U.S. House of Representatives from 1863 to 1876, serving as Speaker of the U.S. House of Representati ...
emerged as the frontrunner for the Republican nomination. However, Blaine was unable to win a majority at the 1876 Republican National Convention
The 1876 Republican National Convention was a presidential nominating convention held at the Exposition Hall in Cincinnati, Ohio on June 14–16, 1876. President Ulysses S. Grant had considered seeking a third term, but with various scandals, a ...
, which settled on Governor Hayes of Ohio as a compromise candidate. The 1876 Democratic National Convention
The 1876 Democratic National Convention assembled in St. Louis just nine days after the conclusion of the Republican National Convention in Cincinnati.
This was the first political convention held west of the Mississippi River. St. Louis was noti ...
nominated Governor Tilden of New York on the second ballot.
The results of the election remain among the most disputed ever. Although it is not disputed that Tilden outpolled Hayes in the popular vote, there were wide allegations of electoral fraud, election violence, and other disfranchisement of predominantly Republican Black voters. After a first count of votes, Tilden had won 184 electoral votes to Hayes's 165, with 20 votes from four states unresolved. In Florida, Louisiana, and South Carolina, both parties reported their candidate to have won the state. In Oregon, one elector was replaced after being declared illegal for having been an "elected or appointed official." The question of who should have been awarded those electoral votes is the source of the continued controversy.
An informal, "back-room" deal was struck to resolve the votes: the Compromise of 1877
The Compromise of 1877, also known as the Wormley Agreement or the Bargain of 1877, was an unwritten deal, informally arranged among members of the United States Congress, to settle the intensely disputed 1876 presidential election between Ruth ...
. In the deal, the Democrats conceded the 20 contested electoral votes to Hayes, resulting in a 185-184 victory; in return, the Republicans agreed to withdraw federal troops from the South, marking the end of Reconstruction
Reconstruction may refer to:
Politics, history, and sociology
* Reconstruction (law), the transfer of a company's (or several companies') business to a new company
*''Perestroika'' (Russian for "reconstruction"), a late 20th century Soviet Unio ...
.
To date, it remains the election that yielded the highest voter turnout
In political science, voter turnout is the participation rate (often defined as those who cast a ballot) of a given election. This can be the percentage of registered voters, eligible voters, or all voting-age people. According to Stanford Univ ...
of the eligible voting-age population in American history, at 81.8%. Tilden's 50.9% is the largest share of the popular vote received by a candidate that was not elected to the presidency. This was the only presidential election in US history in which a candidate who received more than 50% of the popular vote did not win the election.
Nominations
Republican Party nomination
Governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
Rutherford B. Hayes of Ohio
Ohio () is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Of the List of states and territories of the United States, fifty U.S. states, it is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 34th-l ...
File:JamesGBlaine.png, Senator
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
James G. Blaine
James Gillespie Blaine (January 31, 1830January 27, 1893) was an American statesman and Republican politician who represented Maine in the U.S. House of Representatives from 1863 to 1876, serving as Speaker of the U.S. House of Representati ...
from Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and nor ...
File:Benjamin Helm Bristow Brady - Handy U.S. Secretary of Treasury.jpg, Secretary of the Treasury Benjamin Bristow
File:Oliver Hazard Perry Morton - Brady-Handy.jpg, Senator Oliver P. Morton from Indiana
Indiana () is a U.S. state in the Midwestern United States. It is the 38th-largest by area and the 17th-most populous of the 50 States. Its capital and largest city is Indianapolis. Indiana was admitted to the United States as the 19th ...
File:RConkling.jpg, Senator Roscoe Conkling
Roscoe Conkling (October 30, 1829April 18, 1888) was an American lawyer and Republican politician who represented New York in the United States House of Representatives and the United States Senate. He is remembered today as the leader of the ...
from New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
File:JohnFHartranft.jpg, Governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
John F. Hartranft
John Frederick Hartranft (December 16, 1830 – October 17, 1889) was the United States military officer who read the death warrant to the individuals who were executed on July 7, 1865 for conspiring to assassinate American President Abraham Li ...
of Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
File:Marshall Jewell - Brady-Handy.jpg, Postmaster General Marshall Jewell
Marshall Jewell (October 20, 1825February 10, 1883) was a manufacturer, pioneer telegrapher, telephone entrepreneur, world traveler, and political figure who served as 44th and 46th Governor of Connecticut, the US Minister to Russia, the 25th U ...
File:Elihu B. Washburne - Brady-Handy.jpg, Ambassador
An ambassador is an official envoy, especially a high-ranking diplomat who represents a state and is usually accredited to another sovereign state or to an international organization as the resident representative of their own government or s ...
Elihu B. Washburne
Elihu Benjamin Washburne (September 23, 1816 – October 22, 1887) was an American politician and diplomat. A member of the Washburn family, which played a prominent role in the early formation of the United States Republican Party, he served a ...
from Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolitan areas include, Peoria and Rock ...
File:VicePresident-WmAlWheeler.jpg, RepresentativeWilliam A. Wheeler
William Almon Wheeler (June 30, 1819June 4, 1887) was an American politician and attorney. He served as a United States representative from New York from 1861 to 1863 and 1869 to 1877, and the 19th vice president of the United States from 1877 t ...
from New York
File:Honorable_Hamilton_Fish_Brady-Handy.jpg, Secretary of StateHamilton Fish
Hamilton Fish (August 3, 1808September 7, 1893) was an American politician who served as the 16th Governor of New York from 1849 to 1850, a United States Senator from New York from 1851 to 1857 and the 26th United States Secretary of State fro ...
from New York(declined to run) File:UlyssesGrant.jpg,
President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
* President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ...
Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant ; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was an American military officer and politician who served as the 18th president of the United States from 1869 to 1877. As Commanding General, he led the Union A ...
(declined in 1875)
Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant ; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was an American military officer and politician who served as the 18th president of the United States from 1869 to 1877. As Commanding General, he led the Union A ...
would run for a third term as president despite the poor economic conditions, the numerous political scandals that had developed since he assumed office in 1869, and a longstanding tradition set by George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Continental Congress as commander of ...
not to stay in office for more than two terms. Grant's inner circle advised him to go for a third term and he almost did so, but on December 15, 1875, the House, by a sweeping 233-18 vote, passed a resolution declaring that the two-term tradition was to prevent a dictatorship. Later that year, Grant ruled himself out of running in 1876. He instead tried to persuade Secretary of State Hamilton Fish
Hamilton Fish (August 3, 1808September 7, 1893) was an American politician who served as the 16th Governor of New York from 1849 to 1850, a United States Senator from New York from 1851 to 1857 and the 26th United States Secretary of State fro ...
to run for the presidency, but the 67-year-old Fish declined since he believed himself too old for that role. Grant nonetheless sent a letter to the convention imploring them to nominate Fish, but the letter was misplaced and never read to the convention. Fish later confirmed that he would have declined the presidential nomination even if it had been offered to him.
When the Sixth Republican National Convention assembled in Cincinnati
Cincinnati ( ) is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Hamilton County. Settled in 1788, the city is located at the northern side of the confluence of the Licking and Ohio rivers, the latter of which marks the state line w ...
, Ohio, on June 14, 1876, James G. Blaine
James Gillespie Blaine (January 31, 1830January 27, 1893) was an American statesman and Republican politician who represented Maine in the U.S. House of Representatives from 1863 to 1876, serving as Speaker of the U.S. House of Representati ...
appeared to be the presidential nominee. On the first ballot, Blaine was just 100 votes short of a majority. His vote began to slide after the second ballot, however, as many Republicans feared that Blaine could not win the general election. Anti-Blaine delegates could not agree on a candidate until his total rose to 41% on the sixth ballot. Leaders of the reform Republicans met privately and considered alternatives. They chose the reforming Ohio Governor Rutherford B. Hayes, who had been gradually building support during the convention until he finished second on the sixth ballot. On the seventh ballot, Hayes was nominated for president with 384 votes, compared to 351 for Blaine and 21 for Benjamin Bristow. New York Representative William A. Wheeler
William Almon Wheeler (June 30, 1819June 4, 1887) was an American politician and attorney. He served as a United States representative from New York from 1861 to 1863 and 1869 to 1877, and the 19th vice president of the United States from 1877 t ...
was nominated for vice president by a much larger margin (366–89) over his chief rival, Frederick Theodore Frelinghuysen, who later served as a member of the Electoral Commission, which awarded the election to Hayes.
Democratic Party nomination
Democratic candidates: * Samuel J. Tilden, governor ofNew York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
* Thomas A. Hendricks
Thomas Andrews Hendricks (September 7, 1819November 25, 1885) was an American politician and lawyer from Indiana who served as the 16th governor of Indiana from 1873 to 1877 and the 21st vice president of the United States from March until his ...
, governor of Indiana
Indiana () is a U.S. state in the Midwestern United States. It is the 38th-largest by area and the 17th-most populous of the 50 States. Its capital and largest city is Indianapolis. Indiana was admitted to the United States as the 19th ...
* Winfield Scott Hancock, United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, ...
major general from Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
* William Allen, former governor of Ohio
Ohio () is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Of the List of states and territories of the United States, fifty U.S. states, it is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 34th-l ...
* Thomas F. Bayard
Thomas Francis Bayard (October 29, 1828 – September 28, 1898) was an American lawyer, politician and diplomat from Wilmington, Delaware. A Democrat, he served three terms as United States Senator from Delaware and made three unsuccessful bids ...
, U.S. senator from Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Maryland to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and New Jersey and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. The state takes its name from the adjacent ...
* Joel Parker, former governor of New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York; on the east, southeast, and south by the Atlantic Ocean; on the west by the Delawa ...
Governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
Samuel J. Tilden of New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
File:Thomas Andrews Hendricks.jpg, Governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
Thomas A. Hendricks
Thomas Andrews Hendricks (September 7, 1819November 25, 1885) was an American politician and lawyer from Indiana who served as the 16th governor of Indiana from 1873 to 1877 and the 21st vice president of the United States from March until his ...
of Indiana
Indiana () is a U.S. state in the Midwestern United States. It is the 38th-largest by area and the 17th-most populous of the 50 States. Its capital and largest city is Indianapolis. Indiana was admitted to the United States as the 19th ...
File:WinfieldScottHancock2.jpg, Major General
Major general (abbreviated MG, maj. gen. and similar) is a military rank used in many countries. It is derived from the older rank of sergeant major general. The disappearance of the "sergeant" in the title explains the apparent confusion of ...
Winfield Scott Hancock from Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
File:William Allen governor Brady-Handy-crop.jpg, William Allen from Ohio
Ohio () is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Of the List of states and territories of the United States, fifty U.S. states, it is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 34th-l ...
File:Thomas F. Bayard, Brady-Handy photo portrait, circa 1870-1880.jpg, Senator
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
Thomas F. Bayard
Thomas Francis Bayard (October 29, 1828 – September 28, 1898) was an American lawyer, politician and diplomat from Wilmington, Delaware. A Democrat, he served three terms as United States Senator from Delaware and made three unsuccessful bids ...
from Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Maryland to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and New Jersey and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. The state takes its name from the adjacent ...
File:JoelParker-small.png, Joel Parker from New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York; on the east, southeast, and south by the Atlantic Ocean; on the west by the Delawa ...
 The Democratic Party's failure to nominate its own ticket in the previous presidential election, in which they had instead endorsed the Liberal Republican candidacy of
The Democratic Party's failure to nominate its own ticket in the previous presidential election, in which they had instead endorsed the Liberal Republican candidacy of Horace Greeley
Horace Greeley (February 3, 1811 – November 29, 1872) was an American newspaper editor and publisher who was the founder and editor of the '' New-York Tribune''. Long active in politics, he served briefly as a congressman from New York ...
, had resulted in much debate about the party's viability. Any doubts about the party's future were dispelled firstly by the collapse of the Liberal Republicans in the aftermath of that election, and secondly by significant Democratic gains in the 1874 mid-term elections, which saw them take control of the House of Representatives for the first time in sixteen years.
The 12th Democratic National Convention assembled in St. Louis, Missouri, in June 1876, which was the first political convention ever held by one of the major American parties west of the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the List of longest rivers of the United States (by main stem), second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest Drainage system (geomorphology), drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson B ...
. There were 5000 people jammed the auditorium in St. Louis and hopes for the Democratic Party's first presidential victory in 20 years. The platform called for immediate and sweeping reforms in response to the scandals that had plagued the Grant administration. Tilden won more than 400 votes on the first ballot and the presidential nomination by a landslide on the second.
Tilden defeated Thomas A. Hendricks
Thomas Andrews Hendricks (September 7, 1819November 25, 1885) was an American politician and lawyer from Indiana who served as the 16th governor of Indiana from 1873 to 1877 and the 21st vice president of the United States from March until his ...
, Winfield Scott Hancock, William Allen, Thomas F. Bayard
Thomas Francis Bayard (October 29, 1828 – September 28, 1898) was an American lawyer, politician and diplomat from Wilmington, Delaware. A Democrat, he served three terms as United States Senator from Delaware and made three unsuccessful bids ...
, and Joel Parker for the presidential nomination. Tilden overcame strong opposition from "Honest John" Kelly, the leader of New York's Tammany Hall
Tammany Hall, also known as the Society of St. Tammany, the Sons of St. Tammany, or the Columbian Order, was a New York City political organization founded in 1786 and incorporated on May 12, 1789 as the Tammany Society. It became the main loc ...
, to obtain the presidential nomination. Thomas Hendricks was nominated for vice president since he was the only person to put forward for that position.
The Democratic platform pledged to replace the corruption of the Grant administration with honest, efficient government and to end "the rapacity of carpetbag tyrannies" in the South. It also called for treaty protection for naturalized United States citizens visiting their homelands, restrictions on Asian immigration, tariff reform, and opposition to land grants for railroads. It has been claimed that the voting Democrats received Tilden's presidential nomination with more enthusiasm than any leader since Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was an American lawyer, planter, general, and statesman who served as the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before being elected to the presidency, he gained fame as ...
.
Source: Official proceedings of the National Democratic convention, held in St. Louis, Mo., June 27th, 28th and 29th, 1876
'. (September 3, 2012). Source:
Official proceedings of the National Democratic convention, held in St. Louis, Mo., June 27th, 28th and 29th, 1876
' (September 3, 2012).
Greenback Party nomination
Greenback candidates: * Peter Cooper, U.S.philanthropist
Philanthropy is a form of altruism that consists of "private initiatives, for the public good, focusing on quality of life". Philanthropy contrasts with business initiatives, which are private initiatives for private good, focusing on material ...
from New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
* Andrew Curtin, former governor of Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
* William Allen, former governor of Ohio
Ohio () is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Of the List of states and territories of the United States, fifty U.S. states, it is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 34th-l ...
* Alexander Campbell, U.S. representative from Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolitan areas include, Peoria and Rock ...
Candidates gallery
Philanthropist
Philanthropy is a form of altruism that consists of "private initiatives, for the public good, focusing on quality of life". Philanthropy contrasts with business initiatives, which are private initiatives for private good, focusing on material ...
Peter Cooper from New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
File:Andrew Curtin2.jpg, Andrew Curtin from Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
File:William Allen governor Brady-Handy-crop.jpg, William Allen from Ohio
Ohio () is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Of the List of states and territories of the United States, fifty U.S. states, it is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 34th-l ...
File:AlexanderCampbell.png, Alexander Campbell from Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolitan areas include, Peoria and Rock ...
Indianapolis
Indianapolis (), colloquially known as Indy, is the state capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Indiana and the seat of Marion County. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the consolidated population of Indianapolis and Marion ...
, Indiana, in 1874 to urge the federal government to inflate the economy through the mass issuance of paper money called greenbacks. Its first national nominating convention was held in Indianapolis in the spring of 1876. Peter Cooper was nominated for president with 352 votes to 119 for three other contenders. The convention nominated Anti-Monopolist Senator Newton Booth
Newton Booth (December 30, 1825July 14, 1892) was an American entrepreneur and politician.
Early life
Born to Hannah (née Pitts) of North Carolina and Beebe Booth
of California for vice president. After Booth declined to run, the national committee chose Samuel Fenton Cary as his replacement on the ticket.
Prohibition Party nomination
TheProhibition Party
The Prohibition Party (PRO) is a political party in the United States known for its historic opposition to the sale or consumption of alcoholic beverages and as an integral part of the temperance movement. It is the oldest existing third party ...
, in its second national convention in Cleveland
Cleveland ( ), officially the City of Cleveland, is a city in the United States, U.S. U.S. state, state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County, Ohio, Cuyahoga County. Located in the northeastern part of the state, it is situated along ...
, nominated Green Clay Smith as its presidential candidate and Gideon T. Stewart
Gideon Tabor Stewart (August 7, 1824 – June 10, 1909) was an American lawyer and politician who served as the Prohibition Party's vice presidential nominee in 1876. He was elected three times as grand worthy chief templar of the Good Templars o ...
as its vice presidential candidate.
American National Party nomination
This small political party used several different names, often with different names in different states. It was a continuation of theAnti-Masonic Party
The Anti-Masonic Party was the earliest third party in the United States. Formally a single-issue party, it strongly opposed Freemasonry, but later aspired to become a major party by expanding its platform to take positions on other issues. After ...
that met in 1872 and nominated Charles Francis Adams, Sr., for president. When Adams declined to run, the party did not contest the 1872 election.
The convention was held from June 8 to 10, 1875 in Liberty Hall, Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, Allegheny County. It is the most populous city in both Allegheny County and Wester ...
, Pennsylvania. B.T. Roberts of New York served as chairman, and Jonathan Blanchard was the keynote speaker.
The platform supported the Reconstruction Amendments to the Constitution, international arbitration, the reading of the scriptures in public schools, specie payments, justice for Native Americans, abolition of the Electoral College, and prohibition of the sale of alcoholic beverages. It declared the first day of the week to be a day of rest for the United States. The platform opposed secret societies and monopolies.
The convention considered three potential presidential candidates: Charles F. Adams, Jonathan Blanchard, and James B. Walker. When Blanchard declined to run, Walker was unanimously nominated for president. The convention then nominated Donald Kirkpatrick of New York unanimously for vice president.
General election
Campaign
 Tilden, who had prosecuted machine politicians in New York and sent the legendary political boss William M. Tweed to jail, ran as a reform candidate against the background of the corruption of the
Tilden, who had prosecuted machine politicians in New York and sent the legendary political boss William M. Tweed to jail, ran as a reform candidate against the background of the corruption of the Grant administration
The presidency of Ulysses S. Grant began on March 4, 1869, when Ulysses S. Grant was inaugurated as the 18th president of the United States, and ended on March 4, 1877. The Reconstruction era took place during Grant's two terms of office. The K ...
. Both parties backed civil service reform. Both sides mounted mudslinging campaigns, with Democratic attacks on Republican corruption being countered by Republicans raising the Civil War issue, a tactic that was ridiculed by Democrats, who called it " waving the bloody shirt." Republicans chanted, "Not every Democrat was a rebel, but every rebel was a Democrat."
Hayes was a virtual unknown outside his home state of Ohio, where he had served two terms as a representative and then two terms as governor. Henry Adams
Henry Brooks Adams (February 16, 1838 – March 27, 1918) was an American historian and a member of the Adams political family, descended from two U.S. Presidents.
As a young Harvard graduate, he served as secretary to his father, Charles Fran ...
called Hayes "a third-rate nonentity whose only recommendations are that he is obnoxious to no one." Hayes had served in the Civil War with distinction as colonel of the 23rd Ohio Regiment and was wounded several times, which made him marketable to veterans. He had later been brevetted as a major-general. His most important asset was his help to the Republican ticket in carrying Ohio, a crucial swing state. On the other side, the newspaperman John D. Defrees described Tilden as "a very nice, prim, little, withered-up, fidgety old bachelor, about one-hundred and twenty-pounds avoirdupois, who never had a genuine impulse for many nor any affection for woman."
The Democratic strategy for victory in the South was highly reliant on paramilitary groups such as the Red Shirts and the White League
The White League, also known as the White Man's League, was a white paramilitary terrorist organization started in the Southern United States in 1874 to intimidate freedmen into not voting and prevent Republican Party political organizing. Its f ...
. Using the strategy of the Mississippi Plan
The Mississippi Plan of 1875 was developed by white Southern Democrats as part of the white insurgency during the Reconstruction Era in the Southern United States. It was devised by the Democratic Party in that state to overthrow the Republican Pa ...
, the groups actively suppressed both Black and White Republican voter turnouts by disrupting meetings and rallies and even using violence and intimidation. They saw themselves as the military wing of the Democratic Party.
Because it was considered improper for a candidate to pursue the presidency actively, neither Tilden nor Hayes actively stumped as part of the campaign and left that duty to their surrogates.
Colorado
Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of the ...
was admitted to the Union as the 38th state on August 1, 1876; this was the first presidential election in which the state sent electors. There was insufficient time or money to organize a presidential election in the new state. Therefore, Colorado's state legislature selected the state's three Electoral College electors. The Republican Party held a slim majority in the state legislature following a closely contested election on October 3, 1876. Many of the seats in that election had been decided by only a few hundred votes. On November 7, 1876, in a 50 to 24 vote, the state legislature chose Otto Mears, William Hadley, and Herman Beckurts to serve as the state's electors for president. All three of the state electors cast their votes for Hayes. This was the last election in which any state chose electors through its state legislature, rather than by popular vote.
Electoral disputes and Compromise of 1877
Florida (with 4 electoral votes), Louisiana (with 8), and South Carolina (with 7) reported returns that favored Tilden, but the elections in each state were marked by electoral fraud and threats of violence against Republican voters. The most extreme case was in South Carolina, where an impossible 101 percent of all eligible voters in the state had their votes counted, and an estimated 150 Black Republicans were murdered. One of the points of contention revolved around the design of ballots. At the time, parties would print ballots or "tickets" to enable voters to support them in the open ballots. To aid illiterate voters, the parties would print symbols on the tickets, and in this election, many Democratic ballots were printed with the Republican symbol ofAbraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation throu ...
on them. The Republican-dominated state electoral commissions subsequently rejected enough Democratic votes to award their electoral votes to Hayes.
In two Southern states, the governor recognized by the United States had signed the Republican certificates; the Democratic certificates from Florida were signed by the state attorney-general and the newly-elected Democratic governor. Those from Louisiana were signed by the Democratic gubernatorial candidate and those from South Carolina by no state official. The Tilden electors in South Carolina claimed that they had been chosen by the popular vote although they were rejected by the state election board.
Meanwhile, in Oregon, the vote of a single elector was disputed. The statewide result clearly favored Hayes, but the state's Democratic governor, La Fayette Grover, claimed that one of the Republican electors, Ex-Postmaster John Watts, was ineligible under Article II, Section 1, of the United States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, in 1789. Originally comprising seven articles, it delineates the natio ...
since he had been a "person holding an office of trust or profit under the United States." Grover substituted a Democratic elector in Watts's place.
The two Republican electors dismissed Grover's action and reported three votes for Hayes. However, the Democratic elector, C. A. Cronin, reported one vote for Tilden and two votes for Hayes. The two Republican electors presented a certificate signed by the secretary of state of Oregon, and Cronin and the two electors whom he appointed (Cronin voted for Tilden while his associates voted for Hayes) presented a certificate signed by the governor and attested by the secretary of state.
Ultimately, all three of Oregon's votes were awarded to Hayes, who had a majority of one in the Electoral College. The Democrats claimed fraud, and suppressed excitement pervaded the country. Threats were even muttered that Hayes would never be inaugurated. In Columbus, Ohio
Columbus () is the state capital and the most populous city in the U.S. state of Ohio. With a 2020 census population of 905,748, it is the 14th-most populous city in the U.S., the second-most populous city in the Midwest, after Chicago, an ...
, a shot was fired at Hayes's residence as he sat down to dinner. After supporters marched to his home to call for the President, Hayes urged the crowd that "it is impossible, at so early a time, to obtain the result."Morris, Roy, Jr. (2003). ''Fraud of the Century: Rutherford B. Hayes, Samuel Tilden and the Stolen Election of 1876''. New York: Simon and Schuster, pp. 168, 239. Grant quietly strengthened the military force in and around Washington.
The Constitution provides that "the President of the Senate shall, in presence of the Senate and House of Representatives, open all the lectoralcertificates, and the votes shall then be counted." The Republicans held that the power to count the votes lay with the President of the Senate, with the House and Senate being mere spectators. The Democrats objected to that construction, since the President Pro Tempore of the Senate, the Republican Thomas W. Ferry, could then count the votes of the disputed states for Hayes.
The Democrats insisted that Congress should continue the practice followed since 1865: no vote objected to should be counted except by the concurrence of both houses. Since the House had a solid Democratic majority, rejecting the vote of one state, however, would elect Tilden.
Facing an unprecedented constitutional crisis
In political science, a constitutional crisis is a problem or conflict in the function of a government that the political constitution or other fundamental governing law is perceived to be unable to resolve. There are several variations to this ...
, the Congress passed a law on January 29, 1877, to form a 15-member Electoral Commission, which would settle the result. Five members were selected from each house of Congress, and they were joined by five members of the United States Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. federal court cases, and over state court cases that involve a point o ...
, with William M. Evarts
William Maxwell Evarts (February 6, 1818February 28, 1901) was an American lawyer and statesman from New York who served as U.S. Secretary of State, U.S. Attorney General and U.S. Senator from New York. He was renowned for his skills as a litig ...
serving as counsel for the Republican Party.
The majority party in each house named three members and the minority party two members. As the Republicans controlled the Senate and the Democrats controlled the House of Representatives, that yielded five Democratic and five Republican members of the commission. Of the Supreme Court justices, two Republicans and two Democrats were chosen, with the fifth to be selected by those four.
The justices first selected the independent Justice David Davis. According to one historian, "No one, perhaps not even Davis himself, knew which presidential candidate he preferred." Just as the Electoral Commission Bill was passing Congress, the Illinois Legislature elected Davis to the Senate, and Democrats in the legislature believed that they had purchased Davis's support by voting for him. However, they had miscalculated, as Davis promptly excused himself from the commission and resigned as a Justice to take his Senate seat."Hayes v. Tilden: The Electoral College Controversy of 1876–1877."HarpWeek Since all of the remaining available Justices were Republicans, they had already selected Justice Joseph P. Bradley, who was considered the most impartial remaining member of the court. That selection proved decisive.
 Since it was drawing perilously near to Inauguration Day, the commission met on January 31. Each of the disputed state election cases (Florida, Louisiana, Oregon, and South Carolina) was respectively submitted to the commission by Congress. Eminent counsel appeared for each side, and there were double sets of returns from every one of the states named.
The commission first decided not to question any returns that were ''
Since it was drawing perilously near to Inauguration Day, the commission met on January 31. Each of the disputed state election cases (Florida, Louisiana, Oregon, and South Carolina) was respectively submitted to the commission by Congress. Eminent counsel appeared for each side, and there were double sets of returns from every one of the states named.
The commission first decided not to question any returns that were ''prima facie
''Prima facie'' (; ) is a Latin expression meaning ''at first sight'' or ''based on first impression''. The literal translation would be 'at first face' or 'at first appearance', from the feminine forms of ''primus'' ('first') and ''facies'' (' ...
'' lawful. Bradley then joined the other seven Republican committee members in a series of 8–7 votes that gave all 20 disputed electoral votes to Hayes, which gave Hayes a 185–184 electoral vote victory. The commission adjourned on March 2. Hayes privately took the oath of office the next day and was publicly sworn into office on March 5, 1877, and Hayes was inaugurated without disturbance.
The Compromise of 1877
The Compromise of 1877, also known as the Wormley Agreement or the Bargain of 1877, was an unwritten deal, informally arranged among members of the United States Congress, to settle the intensely disputed 1876 presidential election between Ruth ...
might be a reason for the Democrats accepting the Electoral Commission. During intense closed-door meetings, Democratic leaders agreed reluctantly to accept Hayes as President in return for the withdrawal of federal troops from the last two Southern states that were still occupied: South Carolina and Louisiana. Republican leaders in return agreed on a number of handouts and entitlements, including federal subsidies for a transcontinental railroad line through the South. Although some of the promises were not kept, particularly the railroad proposal, that was enough for the time being to avert a dangerous standoff.
The returns accepted by the Commission put Hayes's margin of victory in South Carolina at 889 votes, the second-closest popular vote margin in a decisive state in U.S. history, after the election of 2000, which was decided by 537 votes in Florida. In 2000, the margin of victory in the Electoral College for George W. Bush was five votes, as opposed to Hayes' one vote.
Upon his defeat, Tilden said, "I can retire to public life with the consciousness that I shall receive from posterity the credit of having been elected to the highest position in the gift of the people, without any of the cares and responsibilities of the office."
Congress would eventually enact the Electoral Count Act in 1887 to provide more detailed rules for the counting of electoral votes, especially in cases of multiple slates of electors being received from a single state.
Results
According to the commission's rulings, of the 2,249 counties and independent cities making returns, Tilden won in 1,301 (57.85%), and Hayes carried only 947 (42.11%). One county (0.04%) inNevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. N ...
split evenly between Tilden and Hayes.
The Greenback ticket did not have a major impact on the election's outcome by attracting slightly under one percent of the popular vote, Cooper nonetheless had the strongest performance of any third-party presidential candidate since John Bell in 1860
Events
January–March
* January 2 – The discovery of a hypothetical planet Vulcan is announced at a meeting of the French Academy of Sciences in Paris, France.
* January 10 – The Pemberton Mill in Lawrence, Massachusetts ...
. The Greenbacks' best showings were in Kansas, where Cooper earned just over six percent of the vote, and in Indiana, where he earned 17,207 votes, which far exceeded Tilden's margin of victory of roughly 5,500 votes over Hayes in that state.
The election of 1876 was the last one held before the end of the Reconstruction era, which sought to protect the rights of African Americans in the South, who usually voted for Republican presidential candidates. No antebellum slave state
In the United States before 1865, a slave state was a state in which slavery and the internal or domestic slave trade were legal, while a free state was one in which they were not. Between 1812 and 1850, it was considered by the slave states ...
would be carried by a Republican again until the 1896 realignment, which saw William McKinley
William McKinley (January 29, 1843September 14, 1901) was the 25th president of the United States, serving from 1897 until his assassination in 1901. As a politician he led a realignment that made his Republican Party largely dominant in t ...
carry Delaware, Maryland, West Virginia, and Kentucky.
No Republican presidential candidate until Warren G. Harding in 1920
Events January
* January 1
** Polish–Soviet War in 1920: The Russian Red Army increases its troops along the Polish border from 4 divisions to 20.
** Kauniainen, completely surrounded by the city of Espoo, secedes from Espoo as its own ma ...
would carry any states that seceded and joined the Confederacy. That year, he carried Tennessee, which had never experienced a long period of occupation by federal troops and had been completely "reconstructed" well before the first presidential election of the Reconstruction period ( 1868). None of the Southern states that experienced long periods of occupation by federal troops was carried by a Republican again until Herbert Hoover
Herbert Clark Hoover (August 10, 1874 – October 20, 1964) was an American politician who served as the 31st president of the United States from 1929 to 1933 and a member of the Republican Party, holding office during the onset of the Gre ...
in 1928
Events January
* January – British bacteriologist Frederick Griffith reports the results of Griffith's experiment, indirectly proving the existence of DNA.
* January 1 – Eastern Bloc emigration and defection: Boris Bazhano ...
, when he won Texas, Florida, North Carolina, and Virginia, and that proved the last election in which the Republican candidate won Louisiana until 1956
Events
January
* January 1 – The Anglo-Egyptian Condominium ends in Sudan.
* January 8 – Operation Auca: Five U.S. evangelical Christian missionaries, Nate Saint, Roger Youderian, Ed McCully, Jim Elliot and Pete Fleming, are kille ...
, when it was carried by Dwight D. Eisenhower, and the last in which the Republican candidate won South Carolina until 1964, when Barry Goldwater
Barry Morris Goldwater (January 2, 1909 – May 29, 1998) was an American politician and United States Air Force officer who was a five-term U.S. Senator from Arizona (1953–1965, 1969–1987) and the Republican Party nominee for president ...
did.
The next time those two states voted against the Democrats was their support of the "Dixiecrat
The States' Rights Democratic Party (whose members are often called the Dixiecrats) was a short-lived segregationist political party in the United States, active primarily in the South. It arose due to a Southern regional split in opposition ...
" candidate Strom Thurmond
James Strom Thurmond Sr. (December 5, 1902June 26, 2003) was an American politician who represented South Carolina in the United States Senate from 1954 to 2003. Prior to his 48 years as a senator, he served as the 103rd governor of South Car ...
in 1948
Events January
* January 1
** The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) is inaugurated.
** The Constitution of New Jersey (later subject to amendment) goes into effect.
** The railways of Britain are nationalized, to form British ...
.
Although 1876 marked the last competitive two-party election in the South before the Democratic dominance of the South until 1948 and that to of the Border States until 1896, it was also the last presidential election (as of 2020) in which the Democrats won the wartime Unionist Mitchell County, North Carolina
Mitchell County is a county located in the U.S. state of North Carolina. As of the 2020 census, the population was 14,903. Its county seat is Bakersville, population 439 (2022), elevation 2470 ft.
The county is home to the "Mineral Ci ...
; Wayne County, Tennessee
Wayne County is a county located in south central Tennessee, along the Alabama border. As of the 2010 census, the population was 17,021. Its county seat is Waynesboro. The county is named after General "Mad Anthony" Wayne, a prominent milita ...
; Henderson County, Tennessee; and Lewis County, Kentucky. Hayes was also the only Republican president ever to be elected who failed to carry Indiana.
Geography of results
Cartographic gallery
Results by state
Source: Data from Walter Dean Burnham, ''Presidential ballots, 1836–1892'' (Johns Hopkins University Press, 1955) pp 247–57.Close states
Margin of victory less than 1% (7 electoral votes): # ''South Carolina, 0.49% (889 votes) (tipping point state)'' Margin of victory less between 1% and 5% (164 electoral votes): #Ohio, 1.14% (7,516 votes) #Indiana, 1.26% (5,515 votes) #California, 1.80% (2,798 votes) #Florida, 1.97% (922 votes) #Pennsylvania, 2.37% (17,980 votes) #Connecticut, 2.37% (2,894 votes) #Wisconsin, 2.39% (6,141 votes) #New York, 3.22% (32,742 votes) #Louisiana, 3.30% (4,807 votes) #Oregon, 3.54% (1,057 votes) #Illinois, 3.54% (19,621 votes) #New Hampshire, 3.78% (3,030 votes) Margin of victory between 5% and 10% (33 electoral votes): #Nevada, 5.46% (1,075 votes) #New Jersey, 5.65% (12,445 votes) #North Carolina, 7.24% (16,943 votes) #Michigan, 7.92% (25,216 votes)Cultural references
*The presidential election of 1876 is a major theme of Gore Vidal's novel ''1876 (novel), 1876''.See also
* American election campaigns in the 19th century * History of the United States (1865–1918) * Inauguration of Rutherford B. Hayes * 1876 United States House of Representatives elections * 1876 and 1877 United States Senate elections * Third Party System * Contested elections in American historyReferences
Sources
''Appleton's Annual Cyclopedia ...for 1876''
(1885), comprehensive world coverage * John Bigelow, Author, Edited by, Nikki Oldaker, ''The Life of Samuel J. Tilden.'' (2009 Revised edition-retype-set-new photos). 444 pages,
original 1895 edition
* Holt, Michael F. ''By One Vote: The Disputed Presidential Election of 1876.'' (2008). 304 pages, * * Foley, Edward. 2016. ''Ballot Battles: The History of Disputed Elections in the United States''. Oxford University Press. * * * * * , popular account * Summers, Mark Wahlgren.''The Press Gang: Newspapers and Politics, 1865-1878'' (1994) * Summers, Mark Wahlgren. ''The Era of Good Stealings'' (1993), covers corruption 1868-1877 *Richard White (historian), Richard White
"Corporations, Corruption, and the Modern Lobby: A Gilded Age Story of the West and the South in Washington, D.C."
''Southern Spaces'', April 16, 2009 *
Primary sources
* * Chester, Edward W ''A guide to political platforms'' (1977online
* Porter, Kirk H. and Donald Bruce Johnson, eds. ''National party platforms, 1840-1964'' (1965
online 1840-1956
External links
*Hayes Presidential Library
with essays by historians
from the Library of Congress
Rutherford B. Hayes On The Election of 1876: Original Letter
Shapell Manuscript Foundation
* [http://www.countingthevotes.com/1876/ Election of 1876 in Counting the Votes] {{Authority control 1876 United States presidential election, 1876 United States presidential election Reconstruction Era Constitutional crises, United States Presidency of Rutherford B. Hayes Rutherford B. Hayes November 1876 events, United States United States election controversies