Waterways legend on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
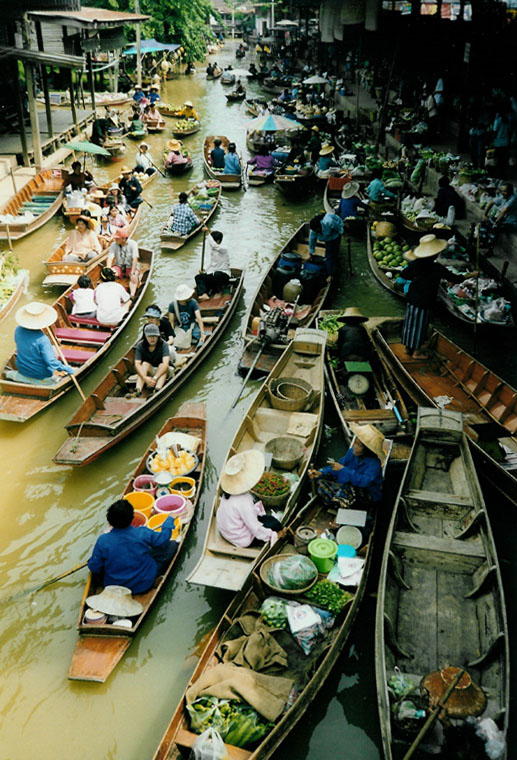 A waterway is any navigable body of water. Broad distinctions are useful to avoid ambiguity, and disambiguation will be of varying importance depending on the nuance of the equivalent word in other languages. A first distinction is necessary between maritime shipping routes and waterways used by inland water craft. Maritime shipping routes cross oceans and seas, and some lakes, where navigability is assumed, and no engineering is required, except to provide the draft for deep-sea shipping to approach seaports ( channels), or to provide a short cut across an isthmus; this is the function of ship canals. Dredged channels in the sea are not usually described as waterways. There is an exception to this initial distinction, essentially for legal purposes, see under international waters.
Where seaports are located inland, they are approached through a waterway that could be termed "inland" but in practice is generally referred to as a "maritime waterway" (examples Seine Maritime, Loire Maritime, Seeschiffahrtsstraße Elbe). The term "inland waterway" refers to navigable rivers and canals designed to be used by inland waterway craft only, implicitly of much smaller dimensions than seagoing ships.
In order for a waterway to be navigable, it must meet several criteria:
* it must be deep enough to accommodate
A waterway is any navigable body of water. Broad distinctions are useful to avoid ambiguity, and disambiguation will be of varying importance depending on the nuance of the equivalent word in other languages. A first distinction is necessary between maritime shipping routes and waterways used by inland water craft. Maritime shipping routes cross oceans and seas, and some lakes, where navigability is assumed, and no engineering is required, except to provide the draft for deep-sea shipping to approach seaports ( channels), or to provide a short cut across an isthmus; this is the function of ship canals. Dredged channels in the sea are not usually described as waterways. There is an exception to this initial distinction, essentially for legal purposes, see under international waters.
Where seaports are located inland, they are approached through a waterway that could be termed "inland" but in practice is generally referred to as a "maritime waterway" (examples Seine Maritime, Loire Maritime, Seeschiffahrtsstraße Elbe). The term "inland waterway" refers to navigable rivers and canals designed to be used by inland waterway craft only, implicitly of much smaller dimensions than seagoing ships.
In order for a waterway to be navigable, it must meet several criteria:
* it must be deep enough to accommodate
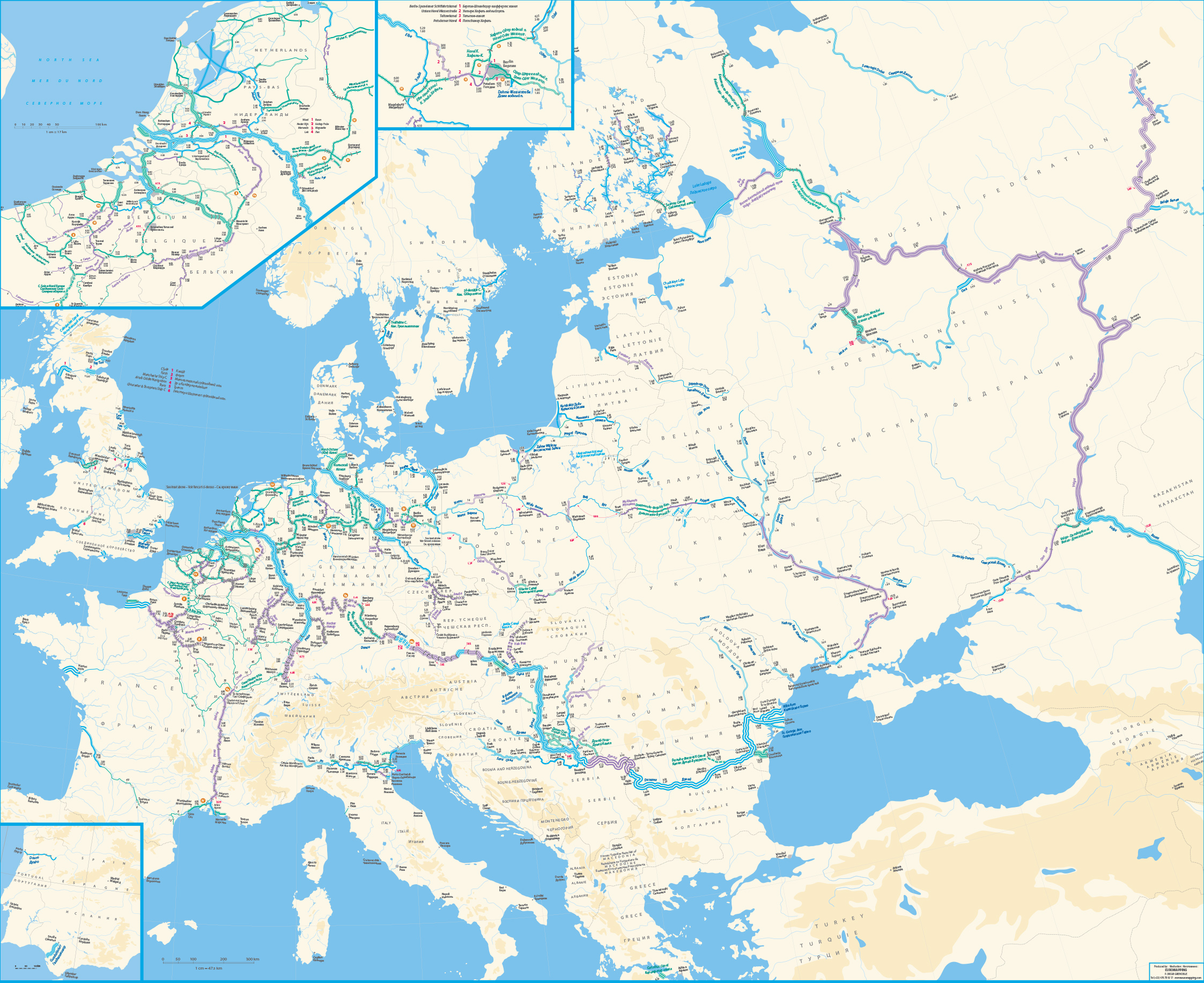
 The European Conference of Ministers of Transport established in 1953 a classification of waterways that was later expanded to take into account the development of push-towing. Europe is a continent with a great variety of waterway characteristics, which makes this classification valuable to appreciate the different classes in waterway. There is also a remarkable variety of waterway characteristics in many countries of Asia, but there has not been any equivalent international drive for uniformity. This classification is provided by the UN Economic Commission for Europe, Inland Transport Committee, Working Party on Inland Water Transport. A low resolution version of that map is shown here.
The European Conference of Ministers of Transport established in 1953 a classification of waterways that was later expanded to take into account the development of push-towing. Europe is a continent with a great variety of waterway characteristics, which makes this classification valuable to appreciate the different classes in waterway. There is also a remarkable variety of waterway characteristics in many countries of Asia, but there has not been any equivalent international drive for uniformity. This classification is provided by the UN Economic Commission for Europe, Inland Transport Committee, Working Party on Inland Water Transport. A low resolution version of that map is shown here.
 *
*
Blue Book on European inland waterways
- access to the Blue Book database.
Waterscape - Britain's official guide to canals, rivers and lakes
{{Authority control Bodies of water
 A waterway is any navigable body of water. Broad distinctions are useful to avoid ambiguity, and disambiguation will be of varying importance depending on the nuance of the equivalent word in other languages. A first distinction is necessary between maritime shipping routes and waterways used by inland water craft. Maritime shipping routes cross oceans and seas, and some lakes, where navigability is assumed, and no engineering is required, except to provide the draft for deep-sea shipping to approach seaports ( channels), or to provide a short cut across an isthmus; this is the function of ship canals. Dredged channels in the sea are not usually described as waterways. There is an exception to this initial distinction, essentially for legal purposes, see under international waters.
Where seaports are located inland, they are approached through a waterway that could be termed "inland" but in practice is generally referred to as a "maritime waterway" (examples Seine Maritime, Loire Maritime, Seeschiffahrtsstraße Elbe). The term "inland waterway" refers to navigable rivers and canals designed to be used by inland waterway craft only, implicitly of much smaller dimensions than seagoing ships.
In order for a waterway to be navigable, it must meet several criteria:
* it must be deep enough to accommodate
A waterway is any navigable body of water. Broad distinctions are useful to avoid ambiguity, and disambiguation will be of varying importance depending on the nuance of the equivalent word in other languages. A first distinction is necessary between maritime shipping routes and waterways used by inland water craft. Maritime shipping routes cross oceans and seas, and some lakes, where navigability is assumed, and no engineering is required, except to provide the draft for deep-sea shipping to approach seaports ( channels), or to provide a short cut across an isthmus; this is the function of ship canals. Dredged channels in the sea are not usually described as waterways. There is an exception to this initial distinction, essentially for legal purposes, see under international waters.
Where seaports are located inland, they are approached through a waterway that could be termed "inland" but in practice is generally referred to as a "maritime waterway" (examples Seine Maritime, Loire Maritime, Seeschiffahrtsstraße Elbe). The term "inland waterway" refers to navigable rivers and canals designed to be used by inland waterway craft only, implicitly of much smaller dimensions than seagoing ships.
In order for a waterway to be navigable, it must meet several criteria:
* it must be deep enough to accommodate vessels
Vessel(s) or The Vessel may refer to:
Biology
*Blood vessel, a part of the circulatory system and function to transport blood throughout the body
*Lymphatic vessel, a thin walled, valved structure that carries lymph
*Vessel element, a narrow wat ...
loading to the design draft;
* it must be wide enough to allow passage of the vessels with the design width or beam
Beam may refer to:
Streams of particles or energy
*Light beam, or beam of light, a directional projection of light energy
**Laser beam
*Particle beam, a stream of charged or neutral particles
**Charged particle beam, a spatially localized grou ...
;
* it must be free of obstacles to navigation such as waterfalls and rapids
Rapids are sections of a river where the river bed has a relatively steep gradient, causing an increase in water velocity and turbulence.
Rapids are hydrological features between a ''run'' (a smoothly flowing part of a stream) and a ''cascade''. ...
, or offer a way around them (such as canal lock
A lock is a device used for raising and lowering boats, ships and other watercraft between stretches of water of different levels on river and canal waterways. The distinguishing feature of a lock is a fixed chamber in which the water lev ...
s or boat lifts);
* its current must be mild enough to allow vessels to make headway upstream without undue difficulty;
* the wave height (on lakes) must not exceed the value for which the class of vessel is designed.
Vessels using waterways vary from small animal-drawn barges to immense ocean tanker
Tanker may refer to:
Transportation
* Tanker, a tank crewman (US)
* Tanker (ship), a ship designed to carry bulk liquids
** Chemical tanker, a type of tanker designed to transport chemicals in bulk
** Oil tanker, also known as a petroleum ta ...
s and ocean liner
An ocean liner is a passenger ship primarily used as a form of transportation across seas or oceans. Ocean liners may also carry cargo or mail, and may sometimes be used for other purposes (such as for pleasure cruises or as hospital ships).
Ca ...
s, such as cruise ships.
History
Waterways have been an important part of human activity since prehistoric times and navigability has allowed watercraft and canals to pass through every body of water. TheGrand Canal (China)
The Grand Canal, known to the Chinese as the Jing–Hang Grand Canal (, or more commonly, as the「大运河」("Grand Canal")), a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is the longest canal or artificial river in the world. Starting in Beijing, it passes ...
, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, the oldest known waterway system in the world, is considered to be one of the world's largest and most extensive project of engineering.
Example of classification of inland waterways
 The European Conference of Ministers of Transport established in 1953 a classification of waterways that was later expanded to take into account the development of push-towing. Europe is a continent with a great variety of waterway characteristics, which makes this classification valuable to appreciate the different classes in waterway. There is also a remarkable variety of waterway characteristics in many countries of Asia, but there has not been any equivalent international drive for uniformity. This classification is provided by the UN Economic Commission for Europe, Inland Transport Committee, Working Party on Inland Water Transport. A low resolution version of that map is shown here.
The European Conference of Ministers of Transport established in 1953 a classification of waterways that was later expanded to take into account the development of push-towing. Europe is a continent with a great variety of waterway characteristics, which makes this classification valuable to appreciate the different classes in waterway. There is also a remarkable variety of waterway characteristics in many countries of Asia, but there has not been any equivalent international drive for uniformity. This classification is provided by the UN Economic Commission for Europe, Inland Transport Committee, Working Party on Inland Water Transport. A low resolution version of that map is shown here.
Major waterways
 *
* Suez Canal
The Suez Canal ( arz, قَنَاةُ ٱلسُّوَيْسِ, ') is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia. The long canal is a popular ...
* Panama Canal
* Great Lakes Waterway
* Saint Lawrence Seaway
See also
* Air draft * Flume * Inland waterways of the United States * International waters * List of canals in France *List of countries by waterways length
This is a list of countries by total waterways length (km) mostly based on The World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a reference resource produced by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with alma ...
* List of waterways
* Mill race
* Salish Sea
*Strait of Magellan
The Strait of Magellan (), also called the Straits of Magellan, is a navigable sea route in southern Chile separating mainland South America to the north and Tierra del Fuego to the south. The strait is considered the most important natural pass ...
* Water trail
References
External links
*Blue Book on European inland waterways
- access to the Blue Book database.
Waterscape - Britain's official guide to canals, rivers and lakes
{{Authority control Bodies of water