Trafalgar Square on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Trafalgar Square ( ) is a public square in the City of Westminster,
 Building work on the south side of the square in the late 1950s revealed deposits from the last interglacial period. Among the findings were the remains of cave lions,
Building work on the south side of the square in the late 1950s revealed deposits from the last interglacial period. Among the findings were the remains of cave lions,
 In 1826 the Commissioners of H.M. Woods, Forests and Land Revenues instructed John Nash to draw up plans for clearing a large area south of Kent's stable block, and as far east as St Martin's Lane. His plans left open the whole area of what became Trafalgar Square, except for a block in the centre, which he reserved for a new building for the Royal Academy. The plans included the demolition and redevelopment of buildings between St Martin's Lane and the Strand and the construction of a road (now called Duncannon Street) across the churchyard of St Martin-in-the-Fields. The Charing Cross Act was passed in 1826 and clearance started soon after. Nash died soon after construction started, impeding its progress. The square was to be named for William IV commemorating his ascent to the throne in 1830. Around 1835, it was decided that the square would be named after the
In 1826 the Commissioners of H.M. Woods, Forests and Land Revenues instructed John Nash to draw up plans for clearing a large area south of Kent's stable block, and as far east as St Martin's Lane. His plans left open the whole area of what became Trafalgar Square, except for a block in the centre, which he reserved for a new building for the Royal Academy. The plans included the demolition and redevelopment of buildings between St Martin's Lane and the Strand and the construction of a road (now called Duncannon Street) across the churchyard of St Martin-in-the-Fields. The Charing Cross Act was passed in 1826 and clearance started soon after. Nash died soon after construction started, impeding its progress. The square was to be named for William IV commemorating his ascent to the throne in 1830. Around 1835, it was decided that the square would be named after the  After the clearance, development progressed slowly. The National Gallery was built on the north side between 1832 and 1838 to a design by William Wilkins, and in 1837 the Treasury approved Wilkins' plan for the laying out of the square, but it was not put into effect. quoting the ' 'Observer' ' of 24 September 1837 In April 1840, following Wilkins' death, new plans by
After the clearance, development progressed slowly. The National Gallery was built on the north side between 1832 and 1838 to a design by William Wilkins, and in 1837 the Treasury approved Wilkins' plan for the laying out of the square, but it was not put into effect. quoting the ' 'Observer' ' of 24 September 1837 In April 1840, following Wilkins' death, new plans by
 Nelson's Column was planned independently of Barry's work. In 1838 a Nelson Memorial Committee had approached the government proposing that a monument to the victory of Trafalgar, funded by public subscription, should be erected in the square. A competition was held and won by the architect
Nelson's Column was planned independently of Barry's work. In 1838 a Nelson Memorial Committee had approached the government proposing that a monument to the victory of Trafalgar, funded by public subscription, should be erected in the square. A competition was held and won by the architect
 Barry's scheme provided two plinths for sculptures on the north side of the square. A bronze equestrian statue of
Barry's scheme provided two plinths for sculptures on the north side of the square. A bronze equestrian statue of
 In 1841, following suggestions from the local paving board, Barry agreed that two fountains should be installed to counteract the effects of reflected heat and glare from the asphalt surface. The First Commissioner of Woods and Forests welcomed the plan because the fountains reduced the open space available for public gatherings and reduced the risk of riotous assembly. The fountains were fed from two wells, one in front of the National Gallery and one behind it connected by a tunnel. Water was pumped to the fountains by a steam engine housed in a building behind the gallery.
In the late-1930s it was decided to replace the pump and the centrepieces of the fountains. The new centrepieces, designed by Sir Edwin Lutyens, were memorials to Lord Jellicoe and Lord Beatty, although busts of the admirals, initially intended to be placed in the fountain surrounds were placed against the northern retaining wall when the project was completed after the Second World War. The fountains cost almost ÂŁ50,000. The old ones were presented to the Canadian government and are now located in
In 1841, following suggestions from the local paving board, Barry agreed that two fountains should be installed to counteract the effects of reflected heat and glare from the asphalt surface. The First Commissioner of Woods and Forests welcomed the plan because the fountains reduced the open space available for public gatherings and reduced the risk of riotous assembly. The fountains were fed from two wells, one in front of the National Gallery and one behind it connected by a tunnel. Water was pumped to the fountains by a steam engine housed in a building behind the gallery.
In the late-1930s it was decided to replace the pump and the centrepieces of the fountains. The new centrepieces, designed by Sir Edwin Lutyens, were memorials to Lord Jellicoe and Lord Beatty, although busts of the admirals, initially intended to be placed in the fountain surrounds were placed against the northern retaining wall when the project was completed after the Second World War. The fountains cost almost ÂŁ50,000. The old ones were presented to the Canadian government and are now located in
 The square was once famous for
The square was once famous for
 A
A
 The square has become a social and political focus for visitors and Londoners, developing over its history from "an esplanade peopled with figures of national heroes, into the country's foremost ''place politique''", as historian Rodney Mace has written. Since its construction, it has been a venue for political demonstrations. The great Chartist rally in 1848, a campaign for social reform by the working class began in the square. A ban on political rallies remained in effect until the 1880s, when the emerging
The square has become a social and political focus for visitors and Londoners, developing over its history from "an esplanade peopled with figures of national heroes, into the country's foremost ''place politique''", as historian Rodney Mace has written. Since its construction, it has been a venue for political demonstrations. The great Chartist rally in 1848, a campaign for social reform by the working class began in the square. A ban on political rallies remained in effect until the 1880s, when the emerging  Throughout the 1980s, a continuous anti-
Throughout the 1980s, a continuous anti-
 The
The
 A Trafalgar Square in Stepney is recorded in ''
A Trafalgar Square in Stepney is recorded in ''
Official website of Trafalgar Square
on the Mayor of London's website
Trafalgar Square webcam
from Wxyz Webcams {{Authority control 1845 establishments in England Art gallery districts Battle of Trafalgar Cultural infrastructure completed in 1845 Fountains in the United Kingdom Horatio Nelson Monuments and memorials in London National squares Regency London Road junctions in London Tourist attractions in London Tourist attractions in the City of Westminster Works of Edwin Lutyens in England A4 road (England) Grade I listed parks and gardens in London Charles Barry buildings
Central London
Central London is the innermost part of London, in England, spanning several boroughs. Over time, a number of definitions have been used to define the scope of Central London for statistics, urban planning and local government. Its characteris ...
, laid out in the early 19th century around the area formerly known as Charing Cross. At its centre is a high column bearing a statue of Admiral Nelson commemorating the victory at the Battle of Trafalgar
The Battle of Trafalgar (21 October 1805) was a naval engagement between the British Royal Navy and the combined fleets of the French and Spanish Navies during the War of the Third Coalition (August–December 1805) of the Napoleonic Wars (1 ...
. The battle of 21 October 1805, established the British navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Fr ...
's dominance at sea in the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fre ...
over the fleets of France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
and Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
.
The site around Trafalgar Square had been a significant landmark since the 1200s. For centuries, distances measured from Charing Cross have served as location markers. The site of the present square formerly contained the elaborately designed, enclosed courtyard of the King's Mews. After George IV
George IV (George Augustus Frederick; 12 August 1762 – 26 June 1830) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and King of Hanover from the death of his father, King George III, on 29 January 1820, until his own death ten y ...
moved the mews to Buckingham Palace, the area was redeveloped by John Nash, but progress was slow after his death, and the square did not open until 1844. The Nelson's Column at its centre is guarded by four lion statues. A number of commemorative statues and sculptures occupy the square, but the Fourth Plinth, left empty since 1840, has been host to contemporary art since 1999. Prominent buildings facing the square include the National Gallery
The National Gallery is an art museum in Trafalgar Square in the City of Westminster, in Central London, England. Founded in 1824, it houses a collection of over 2,300 paintings dating from the mid-13th century to 1900. The current Director ...
, St Martin-in-the-Fields, Canada House
Canada House (french: Maison du Canada) is a Greek Revival building on Trafalgar Square in London. It has been a Grade II* Listed Building since 1970. It has served as the offices of the High Commission of Canada in the United Kingdom since ...
, and South Africa House
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunà ...
.
The square has been used for community gatherings and political demonstrations
Demonstration may refer to:
* Demonstration (acting), part of the Brechtian approach to acting
* Demonstration (military), an attack or show of force on a front where a decision is not sought
* Demonstration (political), a political rally or prote ...
, including Bloody Sunday
Bloody Sunday may refer to:
Historical events Canada
* Bloody Sunday (1923), a day of police violence during a steelworkers' strike for union recognition in Sydney, Cape Breton Island, Nova Scotia
* Bloody Sunday (1938), police violence aga ...
in 1887, the culmination of the first Aldermaston March
The Aldermaston marches were anti- nuclear weapons demonstrations in the 1950s and 1960s, taking place on Easter weekend between the Atomic Weapons Research Establishment at Aldermaston in Berkshire, England, and London, over a distance of fifty- ...
, anti-war protests, and campaigns against climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
. A Christmas tree has been donated to the square by Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of ...
since 1947 and is erected for twelve days before and after Christmas Day. The square is a centre of annual celebrations on New Year's Eve. It was well known for its feral pigeon
Feral pigeons (''Columba livia domestica'' or ''Columba livia forma urbana''), also called city doves, city pigeons, or street pigeons,Nagy, Kelsi, and Johnson, Phillip David. ''Trash animals: how we live with natures filthy, feral, invasive, an ...
s until their removal in the early 21st century.
Name
The square is named after theBattle of Trafalgar
The Battle of Trafalgar (21 October 1805) was a naval engagement between the British Royal Navy and the combined fleets of the French and Spanish Navies during the War of the Third Coalition (August–December 1805) of the Napoleonic Wars (1 ...
, a British naval victory in the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fre ...
with France and Spain that took place on 21 October 1805 off the coast of Cape Trafalgar
Cape Trafalgar (; es, Cabo Trafalgar ) is a headland in the Province of Cádiz in the southwest of Spain. The 1805 naval Battle of Trafalgar, in which the Royal Navy commanded by Admiral Horatio Nelson decisively defeated Napoleon's combined Sp ...
, southwest Spain, although it was not named as such until 1835.
The name "Trafalgar" is a Spanish word of Arabic origin, derived from either ''Taraf al-Ghar'' ( 'cape of the cave/laurel') or ''Taraf al-Gharb'' ( 'extremity of the west').
Geography
Trafalgar Square is owned by the King in Right of the Crown and managed by the Greater London Authority, while Westminster City Council owns the roads around the square, including the pedestrianised area of the North Terrace. The square contains a large central area with roadways on three sides and a terrace to the north, in front of theNational Gallery
The National Gallery is an art museum in Trafalgar Square in the City of Westminster, in Central London, England. Founded in 1824, it houses a collection of over 2,300 paintings dating from the mid-13th century to 1900. The current Director ...
. The roads around the square form part of the A4, a major road running west of the City of London. Originally having roadways on all four sides, traffic travelled in both directions around the square until a one-way clockwise gyratory system was introduced on 26 April 1926. Works completed in 2003 reduced the width of the roads and closed the northern side to traffic.
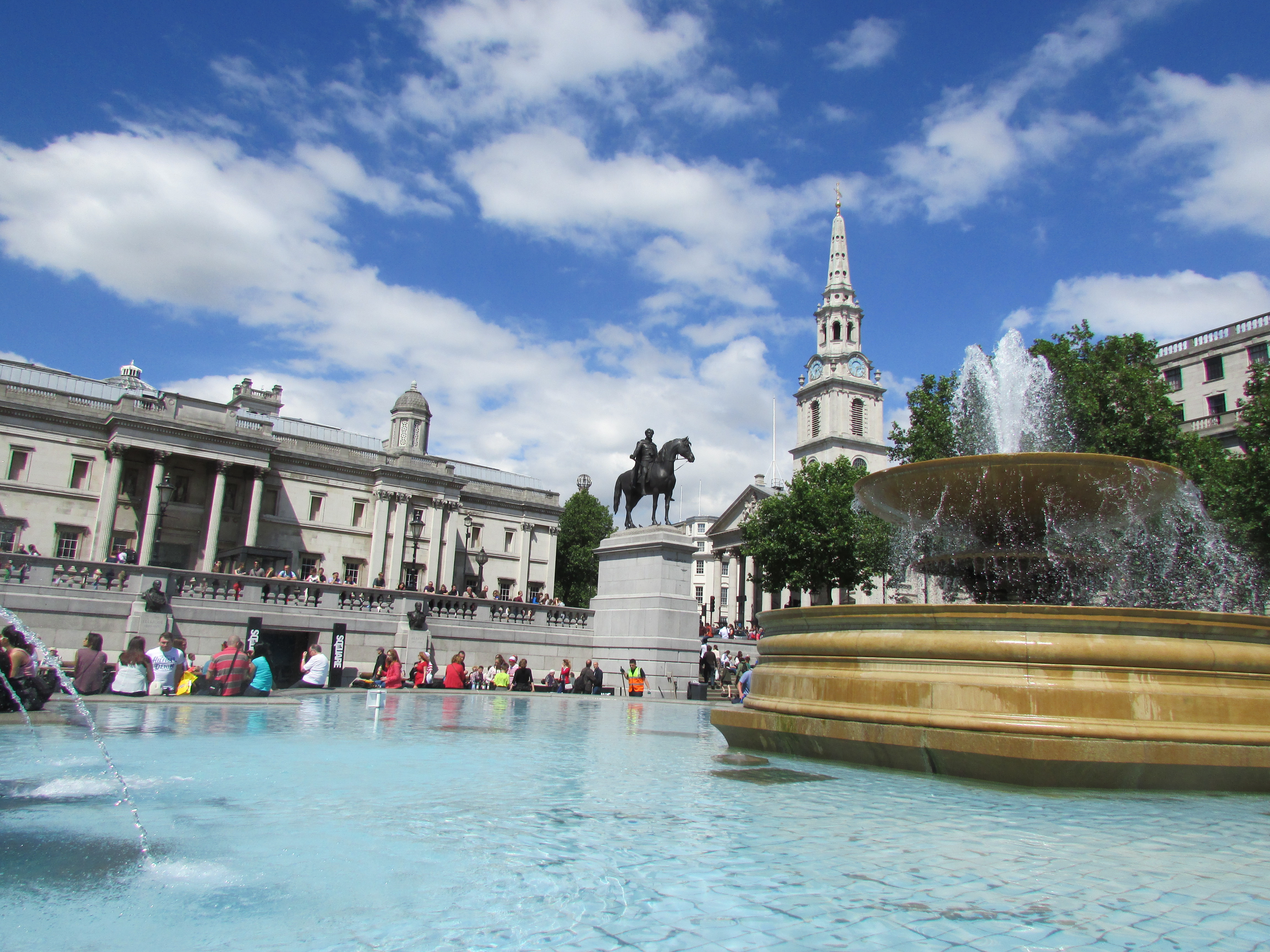
Nelson's Column is in the centre of the square, flanked by fountains designed by Sir Edwin Lutyens between 1937 and 1939 (replacements for two of Peterhead granite, now in Canada) and guarded by four monumental bronze lions sculpted by Sir Edwin Landseer. At the top of the column is a statue of Horatio Nelson, who commanded the British Navy at the Battle of Trafalgar
The Battle of Trafalgar (21 October 1805) was a naval engagement between the British Royal Navy and the combined fleets of the French and Spanish Navies during the War of the Third Coalition (August–December 1805) of the Napoleonic Wars (1 ...
.
Surrounding the square are the National Gallery on the north side and St Martin-in-the-Fields Church to the east. Also on the east is South Africa House
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunà ...
, and facing it across the square is Canada House
Canada House (french: Maison du Canada) is a Greek Revival building on Trafalgar Square in London. It has been a Grade II* Listed Building since 1970. It has served as the offices of the High Commission of Canada in the United Kingdom since ...
. To the south west is The Mall, which leads towards Buckingham Palace via Admiralty Arch, while Whitehall is to the south and the Strand to the east. Charing Cross Road passes between the National Gallery and the church.
London Underground
The London Underground (also known simply as the Underground or by its nickname the Tube) is a rapid transit system serving Greater London and some parts of the adjacent counties of Buckinghamshire, Essex and Hertfordshire in England.
The ...
's Charing Cross station on the Northern
Northern may refer to the following:
Geography
* North, a point in direction
* Northern Europe, the northern part or region of Europe
* Northern Highland, a region of Wisconsin, United States
* Northern Province, Sri Lanka
* Northern Range, a r ...
and Bakerloo
The Bakerloo line () is a London Underground line that goes from in suburban north-west London to in south London, via the West End. Printed in brown on the Tube map, it serves 25 stations, 15 of which are underground, over . It runs partl ...
lines has an exit in the square. The lines had separate stations, of which the Bakerloo line one was called Trafalgar Square until they were linked and renamed in 1979 as part of the construction of the Jubilee line, which was rerouted to Westminster
Westminster is an area of Central London, part of the wider City of Westminster.
The area, which extends from the River Thames to Oxford Street, has many visitor attractions and historic landmarks, including the Palace of Westminster, B ...
in 1999. Other nearby tube stations are Embankment
Embankment may refer to:
Geology and geography
* A levee, an artificial bank raised above the immediately surrounding land to redirect or prevent flooding by a river, lake or sea
* Embankment (earthworks), a raised bank to carry a road, railway ...
connecting the District
A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivision ...
, Circle
A circle is a shape consisting of all points in a plane that are at a given distance from a given point, the centre. Equivalently, it is the curve traced out by a point that moves in a plane so that its distance from a given point is cons ...
, Northern and Bakerloo lines, and Leicester Square on the Northern and Piccadilly lines.
London bus routes 3, 6, 9, 11, 12, 13, 15, 23, 24, 29, 53, 87, 88, 91, 139 139 may refer to:
* 139 (number), an integer
* AD 139, a year of the Julian calendar
* 139 BC, a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar
* 139 (New Jersey bus)
See also
* 139th (disambiguation) 139th may refer to:
* 139th (Northumberland) Battal ...
, 159, 176
Year 176 ( CLXXVI) was a leap year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Proculus and Aper (or, less frequently, year 929 ''Ab urbe condita''). ...
, 453 are only some among the bus routes that pass through Trafalgar Square.
A point in Trafalgar Square is regarded as the official centre of London in legislation and when measuring distances from the capital.
History
 Building work on the south side of the square in the late 1950s revealed deposits from the last interglacial period. Among the findings were the remains of cave lions,
Building work on the south side of the square in the late 1950s revealed deposits from the last interglacial period. Among the findings were the remains of cave lions, rhinoceroses
A rhinoceros (; ; ), commonly abbreviated to rhino, is a member of any of the five extant species (or numerous extinct species) of odd-toed ungulates in the family Rhinocerotidae. (It can also refer to a member of any of the extinct species ...
, straight-tusked elephants and hippopotami.
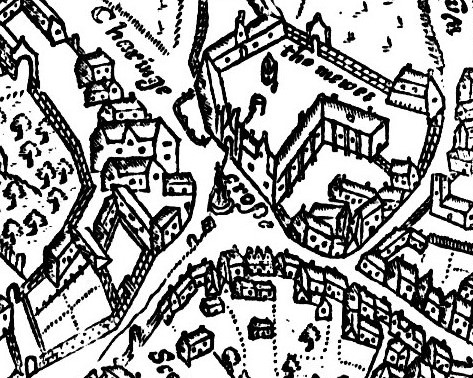
The site has been significant since the 13th century. During Edward I's reign it hosted the King's Mews, running north from the T-junction in the south, Charing Cross, where the Strand from the City meets Whitehall coming north from Westminster
Westminster is an area of Central London, part of the wider City of Westminster.
The area, which extends from the River Thames to Oxford Street, has many visitor attractions and historic landmarks, including the Palace of Westminster, B ...
. From the reign of Richard II to that of Henry VII, the mews was at the western end of the Strand. The name "Royal Mews" comes from the practice of keeping hawks here for moulting; "mew" is an old word for this. After a fire in 1534, the mews were rebuilt as stables, and remained here until George IV
George IV (George Augustus Frederick; 12 August 1762 – 26 June 1830) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and King of Hanover from the death of his father, King George III, on 29 January 1820, until his own death ten y ...
moved them to Buckingham Palace.
After 1732, the King's Mews were divided into the Great Mews and the smaller Green Mews to the north by the Crown Stables, a large block, built to the designs of William Kent. Its site is occupied by the National Gallery.
Clearance and development
 In 1826 the Commissioners of H.M. Woods, Forests and Land Revenues instructed John Nash to draw up plans for clearing a large area south of Kent's stable block, and as far east as St Martin's Lane. His plans left open the whole area of what became Trafalgar Square, except for a block in the centre, which he reserved for a new building for the Royal Academy. The plans included the demolition and redevelopment of buildings between St Martin's Lane and the Strand and the construction of a road (now called Duncannon Street) across the churchyard of St Martin-in-the-Fields. The Charing Cross Act was passed in 1826 and clearance started soon after. Nash died soon after construction started, impeding its progress. The square was to be named for William IV commemorating his ascent to the throne in 1830. Around 1835, it was decided that the square would be named after the
In 1826 the Commissioners of H.M. Woods, Forests and Land Revenues instructed John Nash to draw up plans for clearing a large area south of Kent's stable block, and as far east as St Martin's Lane. His plans left open the whole area of what became Trafalgar Square, except for a block in the centre, which he reserved for a new building for the Royal Academy. The plans included the demolition and redevelopment of buildings between St Martin's Lane and the Strand and the construction of a road (now called Duncannon Street) across the churchyard of St Martin-in-the-Fields. The Charing Cross Act was passed in 1826 and clearance started soon after. Nash died soon after construction started, impeding its progress. The square was to be named for William IV commemorating his ascent to the throne in 1830. Around 1835, it was decided that the square would be named after the Battle of Trafalgar
The Battle of Trafalgar (21 October 1805) was a naval engagement between the British Royal Navy and the combined fleets of the French and Spanish Navies during the War of the Third Coalition (August–December 1805) of the Napoleonic Wars (1 ...
as suggested by architect George Ledwell Taylor
George Ledwell Taylor (31 March 1788 – 1 May 1873) was an architect and landowner who lived in London.
Life
Taylor was born on 31 March 1788 and educated at Rawes's academy, Bromley. He became a pupil of the architect James Burton, and on ...
, commemorating Nelson's victory over the French and Spanish in 1805 during the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fre ...
.
 After the clearance, development progressed slowly. The National Gallery was built on the north side between 1832 and 1838 to a design by William Wilkins, and in 1837 the Treasury approved Wilkins' plan for the laying out of the square, but it was not put into effect. quoting the ' 'Observer' ' of 24 September 1837 In April 1840, following Wilkins' death, new plans by
After the clearance, development progressed slowly. The National Gallery was built on the north side between 1832 and 1838 to a design by William Wilkins, and in 1837 the Treasury approved Wilkins' plan for the laying out of the square, but it was not put into effect. quoting the ' 'Observer' ' of 24 September 1837 In April 1840, following Wilkins' death, new plans by Charles Barry
Sir Charles Barry (23 May 1795 – 12 May 1860) was a British architect, best known for his role in the rebuilding of the Palace of Westminster (also known as the Houses of Parliament) in London during the mid-19th century, but also respon ...
were accepted, and construction started within weeks. For Barry, as for Wilkins, a major consideration was increasing the visual impact of the National Gallery, which had been widely criticised for its lack of grandeur. He dealt with the complex sloping site by excavating the main area to the level of the footway between Cockspur Street and the Strand, and constructing a high balustraded terrace with a roadway on the north side, and steps at each end leading to the main level. Wilkins had proposed a similar solution with a central flight of steps. Plinths were provided for sculpture and pedestals for lighting. One of the original lanterns was hollowed out and converted into a police observation room, opening on 19 March 1928. All the stonework was of Aberdeen granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies un ...
.
In 1841 it was decided that two fountains should be included in the layout. The estimated budget, excluding paving and sculptures, was ÂŁ11,000. The earth removed was used to level Green Park. The square was originally surfaced with tarmacadam, which was replaced with stone in the 1920s.
Trafalgar Square was opened to the public on 1 May 1844.
Nelson's Column

William Railton
William Railton (1800–77) was an English architect, best known as the designer of Nelson's Column. He was based in London, with offices at 12 Regent Street for much of his career.
Life
He was born in Clapham (then in Surrey) on 14 May 1800, ...
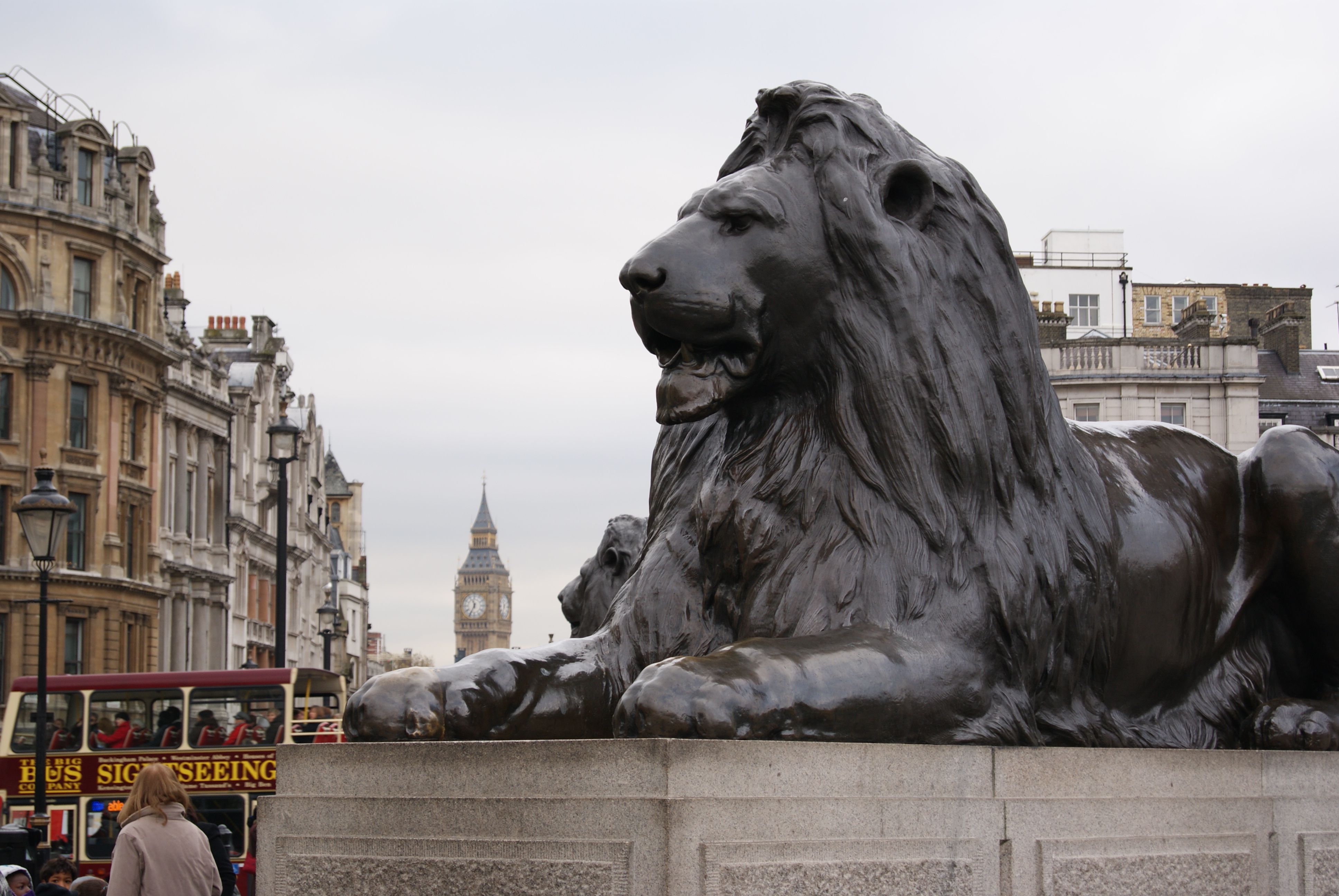
, who proposed a Corinthinan column topped by a statue of Nelson and guarded by four sculpted lions. The design was approved, but received widespread objections from the public. Construction went ahead beginning in 1840 but with the height reduced to . The column was completed and the statue raised in November 1843.
The last of the bronze reliefs on the column's pedestals was not completed until May 1854, and the four lions, although part of the original design, were only added in 1867. Each lion weighs seven tons. A hoarding remained around the base of Nelson's Column for some years and some of its upper scaffolding remained in place. Landseer, the sculptor, had asked for a lion that had died at the London Zoo to be brought to his studio. He took so long to complete sketches that its corpse began to decompose and some parts had to be improvised. The statues have paws that resemble cats more than lions.
Barry was unhappy about Nelson's Column being placed in the square. In July 1840, when its foundations had been laid, he told a parliamentary select committee that "it would in my opinion be desirable that the area should be wholly free from all insulated objects of art".
In 1940 the Nazi
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in ...
SS developed secret plans to transfer Nelson's Column to Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constitu ...
after an expected German invasion, as related by Norman Longmate in ''If Britain Had Fallen'' (1972).
The square has been Grade I listed on the Register of Historic Parks and Gardens since 1996.
Terrorist bombings
The square was the target of twosuffragette
A suffragette was a member of an activist women's organisation in the early 20th century who, under the banner "Votes for Women", fought for the right to vote in public elections in the United Kingdom. The term refers in particular to member ...
bombings in 1913 and 1914. This was as part of the suffragette bombing and arson campaign of 1912–1914, in which suffragettes carried out a series of politically-motivated bombing and arson attacks nationwide as part of their campaign for women's suffrage
Women's suffrage is the right of women to vote in elections. Beginning in the start of the 18th century, some people sought to change voting laws to allow women to vote. Liberal political parties would go on to grant women the right to vot ...
.
The first attack occurred on 15 May 1913. A bomb was planted in the public area outside the National Gallery
The National Gallery is an art museum in Trafalgar Square in the City of Westminster, in Central London, England. Founded in 1824, it houses a collection of over 2,300 paintings dating from the mid-13th century to 1900. The current Director ...
, but failed to explode. A second attack occurred at St Martin-in-the-Fields church at the north-east corner of the square one 4 April 1914. A bomb exploded inside the church, blowing out the windows and showering passers-by with broken glass. The bomb then started a fire. In the aftermath, a mass of people rushed to the scene, many of whom aggressively expressed their anger towards the suffragettes. Churches were a particular target during the campaign, as it was believed that the Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the established Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church recorded as existing in the Roman province of Brit ...
was complicit in reinforcing opposition to women's suffrage. Between 1913 and 1914, 32 churches were attacked nationwide. In the weeks after the bombing, there were also attacks on Westminster Abbey
Westminster Abbey, formally titled the Collegiate Church of Saint Peter at Westminster, is an historic, mainly Gothic church in the City of Westminster, London, England, just to the west of the Palace of Westminster. It is one of the United ...
and St Paul's Cathedral
St Paul's Cathedral is an Anglicanism, Anglican cathedral in London and is the seat of the Bishop of London. The cathedral serves as the mother church of the Diocese of London. It is on Ludgate Hill at the highest point of the City of London ...
.
Redevelopment
A major 18-month redevelopment of the square led by W.S. Atkins withFoster and Partners
Foster + Partners is a British architectural, engineering, and integrated design practice founded in 1967 as Foster Associates by Norman Foster. It is the largest architectural firm in the UK with over 1,500 employees in 13 studios worldwide ...
as sub-consultants was completed in 2003. The work involved closing the eastbound road along the north side and diverting traffic around the other three sides of the square, demolishing the central section of the northern retaining wall and inserting a wide set of steps to the pedestrianised terrace in front of the National Gallery. The construction includes two lifts for disabled access, public toilets and a café. Access between the square and the gallery had been by two crossings at the northeast and northwest corners.
Statues and monuments
Plinths
 Barry's scheme provided two plinths for sculptures on the north side of the square. A bronze equestrian statue of
Barry's scheme provided two plinths for sculptures on the north side of the square. A bronze equestrian statue of George IV
George IV (George Augustus Frederick; 12 August 1762 – 26 June 1830) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and King of Hanover from the death of his father, King George III, on 29 January 1820, until his own death ten y ...
was designed by Sir Francis Chantrey and Thomas Earle Thomas Earle may refer to:
*Thomas Earle (American politician), American journalist and politician
*Thomas Earle (Canadian politician) (1837–1911), Canadian businessman and Conservative politician
* Thomas Earle (MP) (c. 1629–1696), English merc ...
. It was originally intended to be placed on top of the Marble Arch, but instead was installed on the eastern plinth in 1843. There are two other statues on plinths, both installed during the 19th century: General Sir Charles James Napier by George Cannon Adams in the south-west corner in 1855, and Major-General Sir Henry Havelock
Major-General Sir Henry Havelock (5 April 1795 – 24 November 1857) was a British general who is particularly associated with India and his recapture of Cawnpore during the Indian Rebellion of 1857 (First War of Independence, Sepoy Mutiny).
...
by William Behnes in the south-east in 1861. In 2000, the Mayor of London, Ken Livingstone, suggested replacing the statues with figures more familiar to the general public.
Fourth plinth
In the 21st century, the empty plinth in the north-west corner of the square, the "Fourth Plinth", has been used to show specially commissioned temporary artworks. The scheme was initiated by the Royal Society of Arts and continued by the Fourth Plinth Commission, appointed by the Mayor of London.Other sculptures
There are three busts of admirals against the north wall of the square. Those of Lord Jellicoe (by Sir Charles Wheeler) and Lord Beatty (by William MacMillan) were installed in 1948 in conjunction with the square's fountains, which also commemorate them. The third, of theSecond World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
First Sea Lord Admiral Cunningham (by Franta Belsky
František BÄ›lskĂ˝ (also known as Franta Belsky; 6 April 1921 – 5 July 2000) was a Czech sculptor.
He was known for large-scale abstract works of public art as well as more iconographic statues and busts of noted 20th-century figures suc ...
) was unveiled alongside them on 1967.
On the south side of Trafalgar Square, on the site of the original Charing Cross, is a bronze equestrian statue of Charles I by Hubert Le Sueur. It was cast in 1633, and placed in its present position in 1678.
The two statues on the lawn in front of the National Gallery are the statue of James II (designed by Peter van Dievoet
Peter van Dievoet (; French language, French: Pierre, Dutch language, Dutch: Peeter, Latin: Petrus; 16611729) was a sculptor, statuary, wood carver, and designer of ornamental architectural features from Brussels. He achieved fame for his work ...
and Laurens van der Meulen for the studio of Grinling Gibbons) to the west of the portico, and of George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Continental Congress as commander of ...
, a replica of a work by Jean-Antoine Houdon, to the east. The latter was a gift from the Commonwealth of Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth are ...
, installed in 1921.
Two statues erected in the 19th century have since been removed. One of Edward Jenner, pioneer of the smallpox vaccine, was set up in the south-west corner of the square in 1858, next to that of Napier. Sculpted by William Calder Marshall
William Calder Marshall ARSA (18 March 1813 – 16 June 1894) was a Scottish sculptor.
Life
He was born at Gilmour Place in Edinburgh, the eldest son of William Marshall a goldsmith with a shop at 1 South Bridge and his wife Annie Calder.
He ...
, it showed Jenner sitting in a chair in a relaxed pose, and was inaugurated at a ceremony presided over by Prince Albert. It was moved to Kensington Gardens in 1862. The other, of General Charles George Gordon by Hamo Thornycroft, was erected on an 18-foot high pedestal between the fountains in 1888. It was removed in 1943 and re-sited on the Victoria Embankment
Victoria Embankment is part of the Thames Embankment, a road and river-walk along the north bank of the River Thames in London. It runs from the Palace of Westminster to Blackfriars Bridge in the City of London, and acts as a major thoroughfar ...
ten years later.
Fountains
Ottawa
Ottawa (, ; Canadian French: ) is the capital city of Canada. It is located at the confluence of the Ottawa River and the Rideau River in the southern portion of the province of Ontario. Ottawa borders Gatineau, Quebec, and forms the c ...
's Confederation Park
Confederation Park ''(French: Parc de la Confédération)'' is a public park and National Historic Site of Canada, located in the downtown core of Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. It is bordered on the south by Laurier Avenue and Ottawa City Hall; on the ...
and Regina's Wascana Centre.
A programme of restoration was completed by . The pump system was replaced with one capable of sending an jet of water into the air. An LED lighting system that can project different combinations of colours on to the fountains was installed to reduce the cost of lighting maintenance and to coincide with the 2012 Summer Olympics.
Pigeons
 The square was once famous for
The square was once famous for feral pigeon
Feral pigeons (''Columba livia domestica'' or ''Columba livia forma urbana''), also called city doves, city pigeons, or street pigeons,Nagy, Kelsi, and Johnson, Phillip David. ''Trash animals: how we live with natures filthy, feral, invasive, an ...
s and feeding them was a popular activity. Pigeons began flocking to the square before construction was completed and feed sellers became well known in the Victorian era. The desirability of the birds' presence was contentious: their droppings disfigured the stonework and the flock, estimated at its peak to be 35,000, was considered a health hazard. A stall seller, Bernie Rayner, infamously sold bird seed to tourists at inflated prices.
In February 2001, the sale of bird seed in the square was stopped and other measures were introduced to discourage the pigeons including the use of birds of prey. Supporters continued to feed the birds but in 2003 the mayor, Ken Livingstone, enacted bylaws to ban feeding them in the square. In September 2007 Westminster City Council passed further bylaws banning feeding birds on the pedestrianised North Terrace and other pavements in the area. Nelson's column was repaired from years of damage from pigeon droppings at a cost of ÂŁ140,000.
Events
New Year
For many years, revellers celebrating theNew Year
New Year is the time or day currently at which a new calendar year begins and the calendar's year count increments by one. Many cultures celebrate the event in some manner. In the Gregorian calendar, the most widely used calendar system ...
have gathered in the square despite a lack of celebrations being arranged. The lack of official events was partly because the authorities were concerned that encouraging more partygoers would cause overcrowding. Since 2003, a firework display centred on the London Eye and South Bank of the Thames has been provided as an alternative. Since 2014, New Year celebrations have been organised by the Greater London Authority in conjunction with the charity Unicef, who began ticketing the event to control crowd numbers. The fireworks display has been cancelled during the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identi ...
, with an event due to take place in the Square to see in 2022. However the event was cancelled during the spread of the SARS-Cov-2 Omicron variant
Omicron (B.1.1.529) is a variant of SARS-CoV-2 first reported to the World Health Organization (WHO) by the Network for Genomics Surveillance in South Africa on 24 November 2021. It was first detected in Botswana and has spread to become the ...
.
Christmas
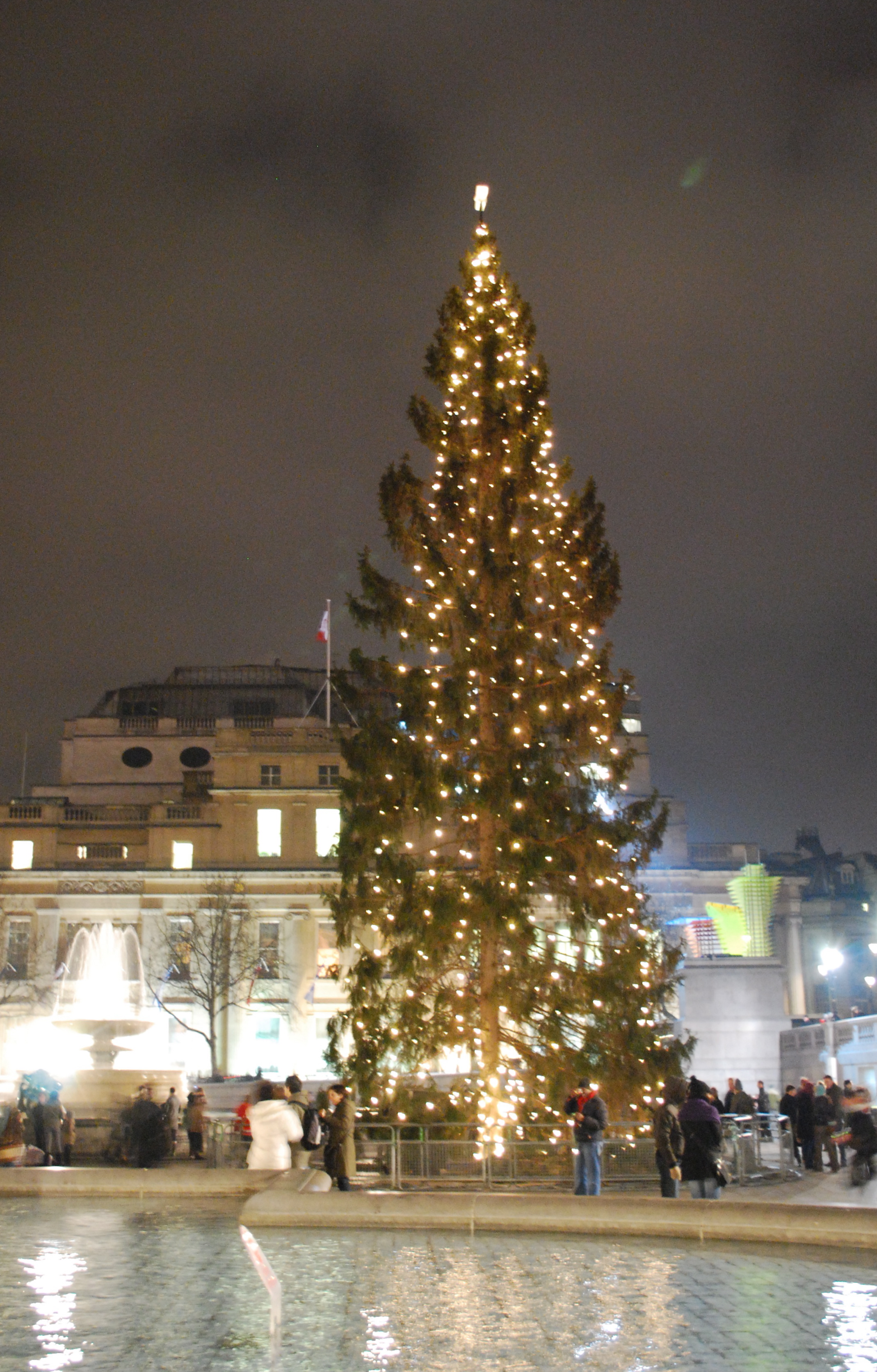
 A
A Christmas
Christmas is an annual festival commemorating the birth of Jesus Christ, observed primarily on December 25 as a religious and cultural celebration among billions of people around the world. A feast central to the Christian liturgical year ...
ceremony has been held in the square every year since 1947. A Norway spruce (or sometimes a fir) is presented by Norway's capital city, Oslo
Oslo ( , , or ; sma, Oslove) is the capital and most populous city of Norway. It constitutes both a county and a municipality. The municipality of Oslo had a population of in 2022, while the city's greater urban area had a population of ...
as London's Christmas tree, a token of gratitude for Britain's support during World War II. (Besides war-time support, Norway's Prince Olav and the country's government lived in exile in London throughout the war.)
The Christmas tree is decorated with lights that are switched on at a seasonal ceremony. It is usually held twelve days before Christmas Day. The festivity is open to the public and attracts a large number of people. The switch-on is usually followed by several nights of Christmas carol
A Christmas carol is a carol (a song or hymn) on the theme of Christmas, traditionally sung at Christmas itself or during the surrounding Christmas holiday season. The term noel has sometimes been used, especially for carols of French or ...
singing and other performances and events. On the twelfth night of Christmas, the tree is taken down for recycling. Westminster City Council threatened to abandon the event to save ÂŁ5,000 in 1980 but the decision was reversed.
The tree is selected by the Head Forester from Oslo's municipal forest and shipped, across the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian ...
to the Port of Felixstowe
The Port of Felixstowe, in Felixstowe, Suffolk, is the United Kingdom's busiest container port, dealing with 48% of Britain's containerised trade. In 2017, it was ranked as 43rd busiest container port in the world and 8th in Europe, with a ha ...
, then by road to Trafalgar Square. The first tree was tall, but more recently has been around . In 1987, protesters chained themselves to the tree. In 1990, a man sawed into the tree with a chainsaw a few hours before a New Year's Eve party was scheduled to take place. He was arrested and the tree was repaired by tree surgeons who removed gouged sections from the trunk while the tree was suspended from a crane.
Political demonstrations
 The square has become a social and political focus for visitors and Londoners, developing over its history from "an esplanade peopled with figures of national heroes, into the country's foremost ''place politique''", as historian Rodney Mace has written. Since its construction, it has been a venue for political demonstrations. The great Chartist rally in 1848, a campaign for social reform by the working class began in the square. A ban on political rallies remained in effect until the 1880s, when the emerging
The square has become a social and political focus for visitors and Londoners, developing over its history from "an esplanade peopled with figures of national heroes, into the country's foremost ''place politique''", as historian Rodney Mace has written. Since its construction, it has been a venue for political demonstrations. The great Chartist rally in 1848, a campaign for social reform by the working class began in the square. A ban on political rallies remained in effect until the 1880s, when the emerging Labour movement
The labour movement or labor movement consists of two main wings: the trade union movement (British English) or labor union movement (American English) on the one hand, and the political labour movement on the other.
* The trade union movement ...
, particularly the Social Democratic Federation, began holding protests. On 1886 (also known as "Black Monday"), protesters rallied against unemployment leading to a riot in Pall Mall. A larger riot (''"Bloody Sunday
Bloody Sunday may refer to:
Historical events Canada
* Bloody Sunday (1923), a day of police violence during a steelworkers' strike for union recognition in Sydney, Cape Breton Island, Nova Scotia
* Bloody Sunday (1938), police violence aga ...
"'') occurred in the square on 1887.
The Campaign for Nuclear Disarmament's first Aldermaston March
The Aldermaston marches were anti- nuclear weapons demonstrations in the 1950s and 1960s, taking place on Easter weekend between the Atomic Weapons Research Establishment at Aldermaston in Berkshire, England, and London, over a distance of fifty- ...
, protesting against the Atomic Weapons Establishment (AWE), began in the square in 1958. One of the first significant demonstrations of the modern era was held in the square on 1961 by the Committee of 100, which included the philosopher Bertrand Russell
Bertrand Arthur William Russell, 3rd Earl Russell, (18 May 1872 – 2 February 1970) was a British mathematician, philosopher, logician, and public intellectual. He had a considerable influence on mathematics, logic, set theory, linguistics, a ...
. The protesters rallied for peace and against war and nuclear weapons. In March 1968, a crowd of 10,000 demonstrated against US involvement in the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vie ...
before marching to the American Embassy in Grosvenor Square.
 Throughout the 1980s, a continuous anti-
Throughout the 1980s, a continuous anti-apartheid
Apartheid (, especially South African English: , ; , "aparthood") was a system of institutionalised racial segregation that existed in South Africa and South West Africa (now Namibia) from 1948 to the early 1990s. Apartheid was ...
protest was held outside South Africa House. In 1990, the Poll Tax Riots began by a demonstration attended by 200,000 people and ultimately caused rioting in the surrounding area. More recently, there have been anti-war demonstrations opposing the Afghanistan War and the Iraq War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Iraq War {{Nobold, {{lang, ar, Řرب العراق (Arabic) {{Nobold, {{lang, ku, Ř´Ű•Ú•ŰŚ عێراق (Kurdish languages, Kurdish)
, partof = the Iraq conflict (2003–present), I ...
. A large vigil was held shortly after the terrorist bombings in London on Thursday, 2005.
In December 2009, participants from the Camp for Climate Action occupied the square for the two weeks during which the UN Conference on Climate Change took place in Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( or .; da, København ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a proper population of around 815.000 in the last quarter of 2022; and some 1.370,000 in the urban area; and the wider Copenhagen metropolitan a ...
. It was billed as a UK base for direct action on climate change and saw various actions and protests stem from the occupation.
In March 2011, the square was occupied by a crowd protesting against the UK Budget and proposed budget cuts. During the night the situation turned violent as the escalation by riot police and protesters damaged portions of the square. In November 2015 a vigil against the terrorist attacks in Paris was held. Crowds sang the French national anthem
A national anthem is a patriotic musical composition symbolizing and evoking eulogies of the history and traditions of a country or nation. The majority of national anthems are marches or hymns in style. American, Central Asian, and Europea ...
, '' La Marseillaise'', and held banners in support of the city and country.
Every year on the anniversary of the Battle of Trafalgar (), the Sea Cadet Corps
Sea cadets are members of a sea cadet corps, a formal uniformed youth organisation for young people with an interest in waterborne activities and or the national navy. The organisation may be sponsored in whole or in part by the navy or a naval s ...
holds a parade in honour of Admiral Lord Nelson and the British victory over the combined fleets of Spain and France at Trafalgar. The Royal British Legion holds a Silence in the Square event on Armistice Day, 11 November, in remembrance of those who died in war. The event includes music and poetry readings, culminating in a bugler
The bugle is one of the simplest brass instruments, normally having no valves or other pitch-altering devices. All pitch control is done by varying the player's embouchure.
History
The bugle developed from early musical or communication i ...
playing the Last Post and a two-minute silence at 11 am.
In February 2019, hundreds of students participated in a protest against climate change as a part of the School strike for Climate campaign. The protest started in the nearby Parliament Square, and as the day went on, the demonstrators moved towards Trafalgar Square.
In July 2020, two members of the protest group Animal Rebellion were arrested on suspicion for criminal damage after releasing red dye
A dye is a colored substance that chemically bonds to the substrate to which it is being applied. This distinguishes dyes from pigments which do not chemically bind to the material they color. Dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution and ...
into the fountains.
In September 2020 anti-lockdown protests opposed to the imposition of regulations relating to the coronavirus outbreak took place in the square.
A police observation box has been in the Square since 1919, originally a wooden freestanding unit, it was replaced by hollowing out a lampstand at the southeastern corner of the Square into a permanent structure in 1928, but decommissioned in the 1970s.
Sport
In the 21st century, Trafalgar Square has been the location for several sporting events and victory parades. In June 2002, 12,000 people gathered to watchEngland
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
's FIFA World Cup
The FIFA World Cup, often simply called the World Cup, is an international association football competition contested by the senior men's national teams of the members of the ' ( FIFA), the sport's global governing body. The tournament has ...
quarter-final against Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
on giant video screens which had been erected for the occasion. The square was used by England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
on 2003 to celebrate their victory in the Rugby World Cup
The Rugby World Cup is a men's rugby union tournament contested every four years between the top international teams. The tournament is administered by World Rugby, the sport's international governing body. The winners are awarded the Webb ...
, and on 2005 for England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
's victory in the Ashes series.
On 6 July 2005 Trafalgar Square hosted the official watch party for London's bid to host the 2012 Summer Olympics at the 117th IOC Session in Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
, hosted by Katy Hill and Margherita Taylor
Margherita Taylor (born 26 April 1972) is an English TV and radio presenter. She is a freelancer with Global Group and currently presents on stations Smooth Radio and Classic FM.
Taylor studied media and communications at the University o ...
. A countdown clock was erected in March 2011, although engineering and weather-related faults caused it to stop a day later. In 2007, it hosted the opening ceremonies of the Tour de France and was part of the course for subsequent races.
Other uses
 The
The Sea Cadets
Sea cadets are members of a sea cadet corps, a formal uniformed youth organisation for young people with an interest in waterborne activities and or the national navy. The organisation may be sponsored in whole or in part by the navy or a naval s ...
hold a yearly Battle of Trafalgar victory parade running the north of Whitehall, from Horse Guard's Parade to Nelson's Column.
As an archetypal London location, Trafalgar Square featured in film and television productions during the Swinging London
The Swinging Sixties was a youth-driven cultural revolution that took place in the United Kingdom during the mid-to-late 1960s, emphasising modernity and fun-loving hedonism, with Swinging London as its centre. It saw a flourishing in art, mu ...
era of the late 1960s, including '' The Avengers'', '' Casino Royale'', '' Doctor Who'', and '' The Ipcress File''. It was used for filming several sketches and a cartoon backdrop in the BBC comedy series '' Monty Python's Flying Circus''. In May 2007, the square was grassed over with 2,000 square metres of turf for two days in a campaign by London authorities to promote "green spaces" in the city.
In July 2011, due to building works in Leicester Square, the world premiere of the final film in the ''Harry Potter'' series, '' Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows – Part 2'', was held in Trafalgar Square, with a red carpet linking the squares. Fans camped in Trafalgar Square for up to three days before the premiere, despite torrential rain. It was the first film premiere ever to be held there.
Cultural references
A Lego architecture set based on Trafalgar Square was released in 2019. It contains models of the National Gallery and Nelson's Column alongside miniature lions, fountains and double-decker buses. Trafalgar Square is one of the squares on the standard British Monopoly Board. It is in the red set alongside the Strand and Fleet Street. Several scenes in the dystopian future of George Orwell's '' Nineteen Eighty Four'' take place in Trafalgar Square, which was renamed "Victory Square" by the story's totalitarian regime and dominated by the giant statue of Big Brother which replaced Nelson. The square has seen controversy over busking and street theatre, which have attracted complaints over noise and public safety. In 2012, the Greater London Authority created a bylaw for regulating busking and associated tourism. In 2016, the National Gallery proposed to introduce licensing for such performances.Other Trafalgar Squares
 A Trafalgar Square in Stepney is recorded in ''
A Trafalgar Square in Stepney is recorded in ''Lockie's Topography of London
''Lockie's Topography of London'' gives a concise local description of and accurate direction to every square, street, lane, court, dock, wharf, public office, the metropolis, and its environs, including the new buildings to the present time, upon ...
'', published in 1810.
Trafalgar Square in Scarborough, North Yorkshire gives its name to the Trafalgar Square End at the town's North Marine Road cricket ground.
The square known as Chelsea Square, London SW3 was at one time known as Trafalgar Square and predated the one in Westminster.
National Heroes Square in Bridgetown
Bridgetown ( UN/LOCODE: BB BGI) is the capital and largest city of Barbados. Formerly The Town of Saint Michael, the Greater Bridgetown area is located within the parish of Saint Michael. Bridgetown is sometimes locally referred to as "The ...
, Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estima ...
, was named Trafalgar Square in 1813, before its better-known British namesake. It was renamed in 1999 to commemorate national heroes of Barbados. There is a life scale replica of the square in Bahria Town
Bahria Town (Private) Limited ( ur, ) is an Islamabad-based privately owned real-estate development company which owns, develops and manages properties across Pakistan.
It established its first gated community exclusively developed for the e ...
, Lahore
Lahore ( ; pnb, ; ur, ) is the second List of cities in Pakistan by population, most populous city in Pakistan after Karachi and 26th List of largest cities, most populous city in the world, with a population of over 13 million. It is th ...
, Pakistan where it is a tourist attraction and centre for local residents.
See also
*Canada House
Canada House (french: Maison du Canada) is a Greek Revival building on Trafalgar Square in London. It has been a Grade II* Listed Building since 1970. It has served as the offices of the High Commission of Canada in the United Kingdom since ...
* Parliament Square
*South Africa House
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunà ...
*Bloody Sunday (1887)
Bloody Sunday took place in London on 13 November 1887, when marchers protesting about unemployment and coercion in Ireland, as well as demanding the release of MP William O'Brien, clashed with the Metropolitan Police and the British Army. ...
– riots focused on Trafalgar Square.
* List of public art in Trafalgar Square and the vicinity
References
Notes Citations Sources * * * * * Second edition published as * * *Further reading
* * Book includes details of the Portland stone buildings around Trafalgar Square, including St Martin in the Fields, the National Gallery and Admiralty Arch. * * *External links
Official website of Trafalgar Square
on the Mayor of London's website
Trafalgar Square webcam
from Wxyz Webcams {{Authority control 1845 establishments in England Art gallery districts Battle of Trafalgar Cultural infrastructure completed in 1845 Fountains in the United Kingdom Horatio Nelson Monuments and memorials in London National squares Regency London Road junctions in London Tourist attractions in London Tourist attractions in the City of Westminster Works of Edwin Lutyens in England A4 road (England) Grade I listed parks and gardens in London Charles Barry buildings