
A tattoo is a form of
body modification made by inserting
tattoo ink, dyes, and/or
pigments, either indelible or temporary, into the
dermis layer of the
skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
to form a design.
Tattoo artists create these designs using several
tattooing processes and techniques, including hand-tapped traditional tattoos and modern
tattoo machines. The
history of tattooing goes back to
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several pa ...
times, practiced across the globe by many cultures, and the symbolism and impact of tattoos varies in different places and cultures.
Tattoos may be decorative (with no specific meaning), symbolic (with a specific meaning to the wearer), or pictorial (a depiction of a specific person or item). Many tattoos serve as
rites of passage, marks of status and rank, symbols of religious and spiritual devotion, decorations for bravery, marks of
fertility
Fertility is the capability to produce offspring through reproduction following the onset of sexual maturity. The fertility rate is the average number of children born by a female during her lifetime and is quantified demographically. Ferti ...
, pledges of love,
amulet
An amulet, also known as a good luck charm or phylactery, is an object believed to confer protection upon its possessor. The word "amulet" comes from the Latin word amuletum, which Pliny's ''Natural History'' describes as "an object that protect ...
s and talismans, protection, and as punishment, like the marks of outcasts, slaves and convicts. Extensive decorative tattooing has also been part of the work of performance artists such as
tattooed ladies.
Today, people choose to be tattooed for artistic, cosmetic, sentimental/
memorial,
religious, and spiritual reasons, and family and to symbolize their belonging to or identification with particular groups, including criminal gangs (see
criminal tattoos) or a particular ethnic group or law-abiding subculture. Tattoos may show how a person feels about a relative (commonly a parent or child) or about an unrelated person.
Tattoos can also be used for functional purposes, such as identification,
permanent makeup, and
medical purposes.
Terminology
The word ''tattoo'', or ''tattow'' in the 18th century, is a
loanword
A loanword (also loan word or loan-word) is a word at least partly assimilated from one language (the donor language) into another language. This is in contrast to cognates, which are words in two or more languages that are similar because ...
from the
Samoan word ''tatau'', meaning "to strike",
from
Proto-Oceanic *''sau''₃ referring to a
wingbone
The scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on eithe ...
from a
flying fox used as an instrument for the tattooing process. The ''
Oxford English Dictionary
The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED'') is the first and foundational historical dictionary of the English language, published by Oxford University Press (OUP). It traces the historical development of the English language, providing a c ...
'' gives the
etymology
Etymology () The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p. 633 "Etymology /ˌɛtɪˈmɒlədʒi/ the study of the class in words and the way their meanings have changed throughout time". is the study of the history of the form of words ...
of tattoo as "In 18th c. tattaow, tattow. From
Polynesian (Samoan,
Tahitian,
Tongan, etc.) tatau. In
Marquesan
The Marquesas Islands (; french: Îles Marquises or ' or '; Marquesan: ' ( North Marquesan) and ' (South Marquesan), both meaning "the land of men") are a group of volcanic islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France in t ...
, tatu." Before the importation of the Polynesian word, the practice of tattooing had been described in the West as painting, scarring, or staining.
The etymology of the body modification term is not to be confused with the origins of the word for the military drumbeat or performance — see ''
military tattoo
A military tattoo is a performance of music or display of armed forces in general. The term comes from the early 17th-century Dutch phrase ''doe den tap toe'' ("turn off the tap"), a signal sounded by drummers or trumpeters to instruct innkeeper ...
''. In this case, the English word ''tattoo'' is derived from the Dutch word ''taptoe''.
Copyrighted tattoo designs that are mass-produced and sent to tattoo artists are known as "
flash".
Flash sheets are prominently displayed in many tattoo parlors for the purpose of providing both inspiration and ready-made tattoo images to customers.
The Japanese word ''
irezumi'' means "insertion of ink" and can mean tattoos using ''tebori'', the traditional Japanese hand method, a Western-style machine or any method of tattooing using insertion of ink. The most common word used for traditional Japanese tattoo designs is ''
horimono''.
Japanese may use the word ''tattoo'' to mean non-Japanese styles of tattooing.
British anthropologist
Ling Roth in 1900 described four methods of skin marking and suggested they be differentiated under the names "tatu", "
moko", "
cicatrix", and "
keloid". The first is by pricking that leaves the skin smooth as found in places including the Pacific Islands. The second is a tattoo combined with chiseling to leave furrows in the skin as found in places including New Zealand. The third is scarification using a knife or chisel as found in places including West Africa. The fourth and the last is scarification by irritating and re-opening a preexisting wound, and re-scarification to form a raised scar as found in places including Tasmania, Australia, Melanesia, and Central Africa.
[McDougall, Russell and Davidson, Iain; eds. (2016). ]
The Roth Family, Anthropology, and Colonial Administration
', p.97. Routledge. .
Types
The
American Academy of Dermatology
The American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) is a non-profit professional organization of dermatologists in the United States and Canada, based in Rosemont, Illinois, near Chicago. It was founded in 1938 and has more than 20,500 members. The Academ ...
distinguishes five types of tattoos: traumatic tattoos that result from injuries, such as asphalt from road injuries or pencil lead; amateur tattoos; professional tattoos, both via traditional methods and modern tattoo machines; cosmetic tattoos, also known as "
permanent makeup"; and
medical tattoos.
Traumatic tattoos
A traumatic tattoo occurs when a substance such as asphalt or gunpowder is rubbed into a
wound as the result of some kind of accident or trauma.
When this involves
carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon ma ...
, dermatologists may call the mark a
carbon stain instead of a tattoo.
could develop characteristic marks owing to
coal dust getting into wounds. These are particularly difficult to remove as they tend to be spread across several layers of skin, and scarring or permanent discoloration is almost unavoidable depending on the location. An
amalgam tattoo is when
amalgam
Amalgam most commonly refers to:
* Amalgam (chemistry), mercury alloy
* Amalgam (dentistry), material of silver tooth fillings
** Bonded amalgam, used in dentistry
Amalgam may also refer to:
* Amalgam Comics, a publisher
* Amalgam Digital, an in ...
particles are implanted in to the soft tissues of the mouth, usually the gums, during dental filling placement or removal.
Another example of such accidental tattoos is the result of a deliberate or accidental stabbing with a pencil or pen, leaving graphite or ink beneath the skin.
Identification
Forcible tattooing for identification

A well-known example is the
Nazi
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in ...
practice of forcibly tattooing
concentration camp inmates with identification numbers during
the Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europ ...
as part of
the Nazis' identification system, beginning in fall 1941. The
SS introduced the practice at
Auschwitz concentration camp
Auschwitz concentration camp ( (); also or ) was a complex of over 40 concentration and extermination camps operated by Nazi Germany in occupied Poland (in a portion annexed into Germany in 1939) during World War II and the Holocaust. I ...
in order to identify the bodies of registered prisoners in the concentration camps. During registration, guards would pierce the outlines of the serial-number digits onto the prisoners' arms. Of the Nazi concentration camps, only Auschwitz put tattoos on inmates. The tattoo was the prisoner's camp number, sometimes with a special symbol added: some
Jews had a triangle, and
Romani
Romani may refer to:
Ethnicities
* Romani people, an ethnic group of Northern Indian origin, living dispersed in Europe, the Americas and Asia
** Romani genocide, under Nazi rule
* Romani language, any of several Indo-Aryan languages of the Roma ...
had the letter "Z" (from
German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
''Zigeuner'' for "Gypsy"). In May 1944, Jewish men received the letters "A" or "B" to indicate a particular series of numbers.
As early as the
Zhou, Chinese authorities would employ facial tattoos as a punishment for certain crimes or to mark prisoners or slaves.
During the
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
, gladiators and slaves were tattooed: exported slaves were tattooed with the words "tax paid", and it was a common practice to tattoo "fugitive" (denoted by the letters "FUG") on the foreheads of runaway slaves. Owing to the
Biblical
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of ...
strictures against the practice, Emperor
Constantine I
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterran ...
banned tattooing the face around AD 330, and the
Second Council of Nicaea
The Second Council of Nicaea is recognized as the last of the first seven ecumenical councils by the Eastern Orthodox Church and the Catholic Church. In addition, it is also recognized as such by the Old Catholics, the Anglican Communion, an ...
banned all body markings as a
pagan practice in AD 787.
Cultural identification
In the period of early contact between the Māori and Europeans, the Māori people hunted and decapitated each other for their
moko tattoos, which they traded for European items including axes and firearms. Moko tattoos were facial designs worn to indicate lineage, social position, and status within the tribe. The tattoo art was a sacred marker of identity among the Māori and also referred to as a vehicle for storing one's
tapu, or spiritual being, in the afterlife.
Postmortem identification

Tattoos are sometimes used by
forensic pathologists to help them identify burned, putrefied, or mutilated bodies. As tattoo pigment lies encapsulated deep in the skin, tattoos are not easily destroyed even when the skin is burned.
Identification of animals
Pets, show animals,
thoroughbred horses, and
livestock
Livestock are the domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to provide labor and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The term is sometimes used to refer solely to ani ...
are sometimes tattooed with
animal identification marks. Ear tattoos are a method of identification for
beef cattle. Tattooing with a 'slap mark' on the shoulder or on the ear is the standard identification method in commercial pig farming.
Branding
Branding may refer to:
Physical markings
* Making a mark, typically by charring:
** Wood branding, permanently marking, by way of heat, typically of wood (also applied to plastic, cork, leather, etc.)
** Livestock branding, the marking of animals ...
is used for similar reasons and is often performed without anesthesia, but is different from tattooing as no ink or dye is inserted during the process, the mark instead being caused by permanent scarring of the skin.
Pet dogs and cats are sometimes tattooed with a serial number (usually in the ear, or on the inner thigh) via which their owners can be identified. However, the use of a microchip has become an increasingly popular choice and since 2016 is a legal requirement for all 8.5 million pet dogs in the UK.
Cosmetic
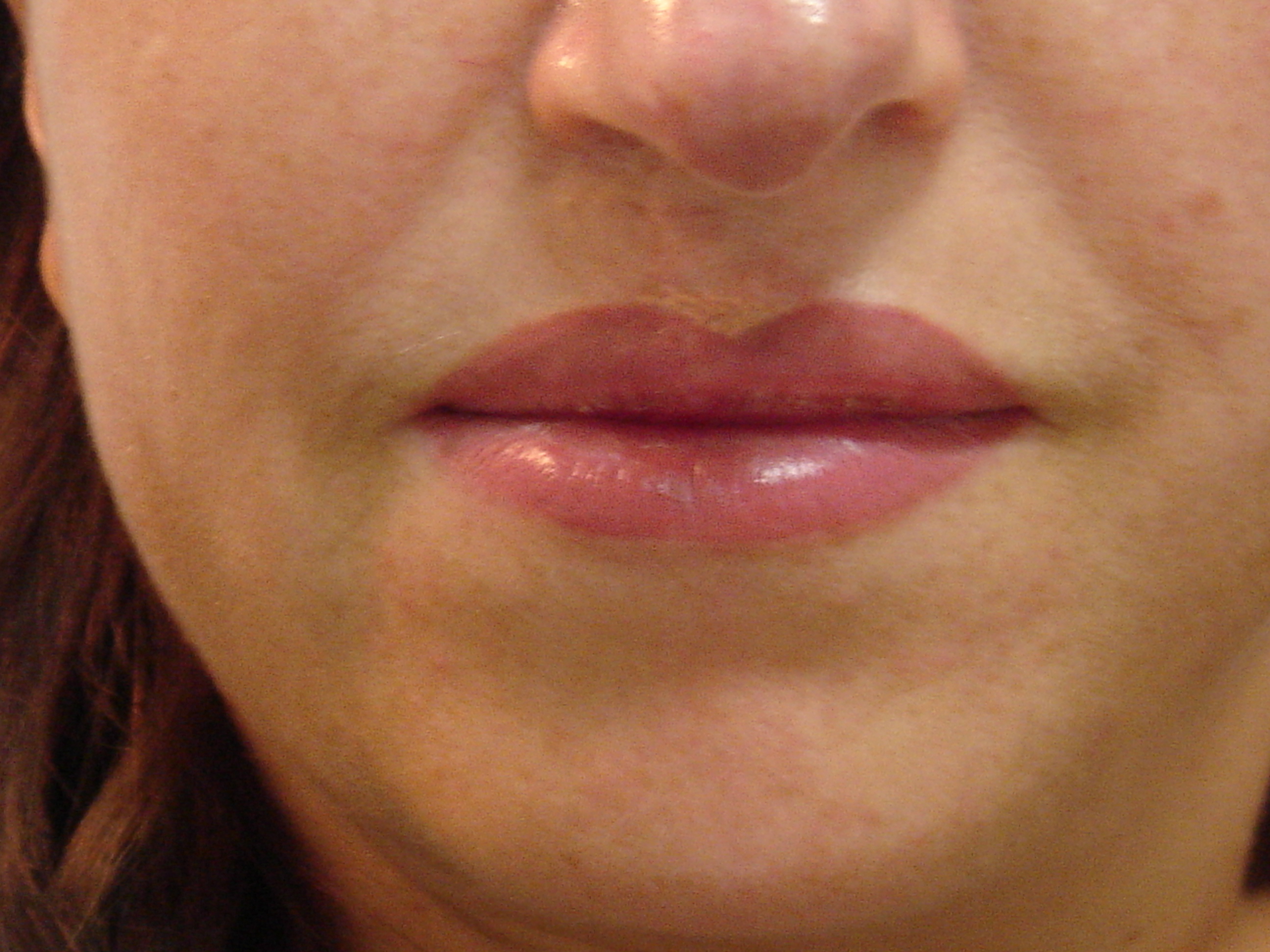
Permanent makeup is the use of tattoos to enhance eyebrows, lips (liner and/or lipstick), eyes (liner), and even
moles Moles can refer to:
* Moles de Xert, a mountain range in the Baix Maestrat comarca, Valencian Community, Spain
*The Moles (Australian band)
*The Moles, alter ego of Scottish band Simon Dupree and the Big Sound
People
* Abraham Moles, French engin ...
, usually with natural colors, as the designs are intended to resemble makeup.
A growing trend in the US and UK is to place artistic
tattoos
A tattoo is a form of body modification made by inserting tattoo ink, dyes, and/or pigments, either indelible or temporary, into the dermis layer of the skin to form a design. Tattoo artists create these designs using several tattooing ...
over the surgical scars of a
mastectomy. "More women are choosing not to reconstruct after a mastectomy and tattoo over the scar tissue instead... The mastectomy tattoo will become just another option for post cancer patients and a truly personal way of regaining control over post cancer bodies..." However, the tattooing of nipples on reconstructed breasts remains in high demand.
Medical
Medical tattoos are used to ensure instruments are properly located for repeated application of radiotherapy and for the areola in some forms of breast reconstruction. Tattooing has also been used to convey medical information about the wearer (e.g., blood group, medical condition, etc.).
Alzheimer
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As t ...
patients may be tattooed with their names, so they may be easily identified if they go missing. Additionally, tattoos are used in skin tones to cover
vitiligo, a skin pigmentation disorder.
SS blood group tattoos (german: Blutgruppentätowierung) were worn by members of the
Waffen-SS in Nazi Germany during World War II to identify the individual's
blood type. After the war, the tattoo was taken to be
prima facie, if not perfect, evidence of being part of the Waffen-SS, leading to potential arrest and prosecution. This led a number of ex-Waffen-SS to shoot themselves through the arm with a gun, removing the tattoo and leaving scars like the ones resulting from pox inoculation, making the removal less obvious.
Tattoos were probably also used in ancient medicine as part of the treatment of the patient. In 1898, Daniel Fouquet, a medical doctor, wrote an article on "medical tattooing" practices in
Ancient Egypt, in which he describes the tattooed markings on the female mummies found at the
Deir el-Bahari
Deir el-Bahari or Dayr al-Bahri ( ar, الدير البحري, al-Dayr al-Baḥrī, the Monastery of the North) is a complex of mortuary temples and tombs located on the west bank of the Nile, opposite the city of Luxor, Egypt. This is a part o ...
site. He speculated that the tattoos and other
scarifications observed on the bodies may have served a medicinal or therapeutic purpose: "The examination of these scars, some white, others blue, leaves in no doubt that they are not, in essence, ornament, but an established treatment for a condition of the pelvis, very probably chronic
pelvic peritonitis."
Ötzi the iceman had a total of 61 tattoos, which may have been a form of
acupuncture used to relieve pain.
Radiological examination of Ötzi's bones showed "age-conditioned or strain-induced degeneration" corresponding to many tattooed areas, including
osteochondrosis and slight
spondylosis in the lumbar spine and wear-and-tear degeneration in the knee and especially in the ankle joints. If so, this is at least 2,000 years before acupuncture's previously known earliest use in
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
(c. 100 BCE).
History

Preserved tattoos on ancient
mummified human remains reveal that tattooing has been practiced throughout the world for thousands of years.
In 2015, scientific re-assessment of the age of the two oldest known tattooed mummies identified
Ötzi as the oldest example then known. This body, with 61 tattoos, was found embedded in glacial ice in the
Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Sw ...
, and was dated to 3250 BCE.
In 2018, the oldest
figurative tattoos in the world were discovered on two mummies from Egypt which are dated between 3351 and 3017 BCE.
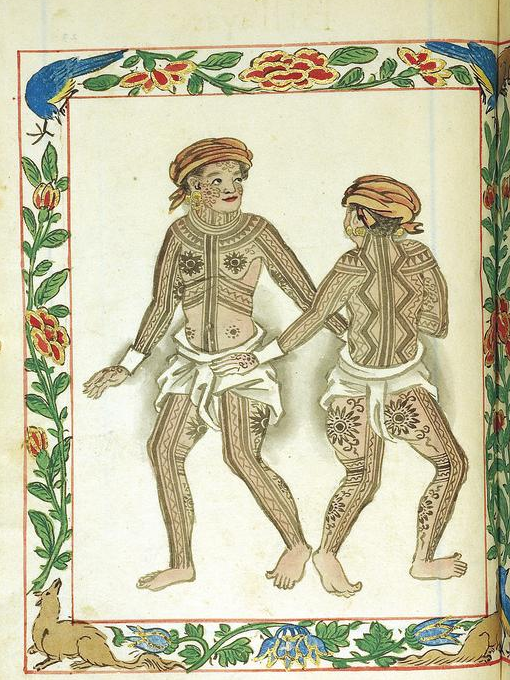
Ancient tattooing was most widely practiced among the
Austronesian people. It was one of the early technologies developed by the Proto-Austronesians in
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the no ...
and coastal
South China
South China () is a geographical and cultural region that covers the southernmost part of China. Its precise meaning varies with context. A notable feature of South China in comparison to the rest of China is that most of its citizens are not n ...
prior to at least 1500 BCE, before the Austronesian expansion into the islands of the
Indo-Pacific
The Indo-Pacific is a vast biogeographic region of Earth.
In a narrow sense, sometimes known as the Indo-West Pacific or Indo-Pacific Asia, it comprises the tropical waters of the Indian Ocean, the western and central Pacific Ocean, and the ...
.
It may have originally been associated with
headhunting.
Tattooing traditions, including facial tattooing, can be found among all Austronesian subgroups, including
Taiwanese Aborigines
Taiwanese may refer to:
* Taiwanese language, another name for Taiwanese Hokkien
* Something from or related to Taiwan ( Formosa)
* Taiwanese aborigines, the indigenous people of Taiwan
* Han Taiwanese, the Han people of Taiwan
* Taiwanese peo ...
,
Islander Southeast Asians
The Austronesian peoples, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesia, Polynesia, and Madagascar that speak Austrone ...
,
Micronesians
The Micronesians or Micronesian peoples are various closely related ethnic groups native to Micronesia, a region of Oceania in the Pacific Ocean. They are a part of the Austronesian ethnolinguistic group, which has an Urheimat in Taiwan.
Ethn ...
,
Polynesians
Polynesians form an ethnolinguistic group of closely related people who are native to Polynesia (islands in the Polynesian Triangle), an expansive region of Oceania in the Pacific Ocean. They trace their early prehistoric origins to Island Sou ...
, and the
Malagasy people
The Malagasy (french: Malgache) are an Austronesian-speaking African ethnic group native to the island country of Madagascar. Traditionally, the population have been divided by subgroups (tribes or ethnicities). Examples include "Highlander ...
. Austronesians used the characteristic hafted skin-puncturing technique, using a small mallet and a piercing implement made from ''
Citrus
''Citrus'' is a genus of flowering trees and shrubs in the rue family, Rutaceae. Plants in the genus produce citrus fruits, including important crops such as oranges, lemons, grapefruits, pomelos, and limes. The genus ''Citrus'' is native to ...
'' thorns, fish bone, bone, and oyster shells.
Ancient tattooing traditions have also been documented among
Papuans and
Melanesians
Melanesians are the predominant and indigenous inhabitants of Melanesia, in a wide area from Indonesia's New Guinea to as far East as the islands of Vanuatu and Fiji. Most speak either one of the many languages of the Austronesian language fam ...
, with their use of distinctive
obsidian skin piercers. Some archeological sites with these implements are associated with the Austronesian migration into
Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea (abbreviated PNG; , ; tpi, Papua Niugini; ho, Papua Niu Gini), officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea ( tpi, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niugini; ho, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niu Gini), is a country i ...
and
Melanesia
Melanesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from Indonesia's New Guinea in the west to Fiji in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea.
The region includes the four independent countries of Fiji, V ...
. But other sites are older than the Austronesian expansion, being dated to around 1650 to 2000 BCE, suggesting that there was a preexisting tattooing tradition in the region.
Among other ethnolinguistic groups, tattooing was also practiced among the
Ainu people
The Ainu are the indigenous people of the lands surrounding the Sea of Okhotsk, including Hokkaido Island, Northeast Honshu Island, Sakhalin Island, the Kuril Islands, the Kamchatka Peninsula and Khabarovsk Krai, before the arrival of the Ya ...
of Japan; some
Austroasian
The Austroasiatic languages , , are a large language family in Mainland Southeast Asia and South Asia. These languages are scattered throughout parts of Thailand, Laos, India, Myanmar, Malaysia, Bangladesh, Nepal, and southern China and are th ...
s of
Indochina
Mainland Southeast Asia, also known as the Indochinese Peninsula or Indochina, is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west an ...
;
Berber women of
Tamazgha
Tamazgha ( Berber: Tamazɣa, Arabic: تامازغا) is a fictitious entity and toponym in Berber languages denoting the lands traditionally inhabited by Berbers coined in the 1970s by the Berber Academy in Paris. The region claims the geographi ...
(North Africa);
the
Yoruba
The Yoruba people (, , ) are a West African ethnic group that mainly inhabit parts of Nigeria, Benin, and Togo. The areas of these countries primarily inhabited by Yoruba are often collectively referred to as Yorubaland. The Yoruba constitute ...
,
Fulani and
Hausa people of
Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
;
Native Americans of the
Pre-Columbian Americas;
[Evans, Susan, Toby. 2013. Ancient Mexico and Central America: Archaeology and Culture History. 3rd Edition.] and
Picts
The Picts were a group of peoples who lived in what is now northern and eastern Scotland (north of the Firth of Forth) during Late Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. Where they lived and what their culture was like can be inferred from ea ...
of
Iron Age Britain
The British Iron Age is a conventional name used in the archaeology of Great Britain, referring to the prehistoric and protohistoric phases of the Iron Age culture of the main island and the smaller islands, typically excluding prehistoric I ...
.
Europe

In 1566, French sailors abducted an Inuit woman and her child in modern-day
Labrador
, nickname = "The Big Land"
, etymology =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Canada
, subdivision_type1 = Province
, subdivision_name1 ...
and brought her to the city of
Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504, in the
Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands ( Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiograph ...
. The mother was tattooed while the child was unmarked. In Antwerp, the two were put on display at a local tavern at least until 1567, with handbills promoting the event being distributed in the city. In 1577, English
privateer
A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or deleg ...
Martin Frobisher captured two Inuit and brought them back to England for display. One of the Inuit was a tattooed woman from
Baffin Island
Baffin Island (formerly Baffin Land), in the Canadian territory of Nunavut, is the largest island in Canada and the fifth-largest island in the world. Its area is , slightly larger than Spain; its population was 13,039 as of the 2021 Canadia ...
, who was illustrated by the English cartographer
John White.
In 1691,
William Dampier
William Dampier (baptised 5 September 1651; died March 1715) was an English explorer, pirate, privateer, navigator, and naturalist who became the first Englishman to explore parts of what is today Australia, and the first person to circumnav ...
brought to London a Filipino man named
Jeoly or Giolo from the island of
Mindanao
Mindanao ( ) ( Jawi: مينداناو) is the second-largest island in the Philippines, after Luzon, and seventh-most populous island in the world. Located in the southern region of the archipelago, the island is part of an island group of ...
(Philippines) who had a tattooed body. Dampier exhibited Jeoly in a
human zoo to make a fortune and falsely branded him as a "prince" to draw large crowds. At the time of exhibition, Jeoly was still grieving his mother, who Dampier also enslaved and had died at sea during their exploitation to Europe. Dampier claimed that he became friends with Jeoly, but with the intention to make money, he continued to exploit his "friend" by exhibiting him in a human zoo, where Jeoly died three months later. Jeoly's dead body was afterwards skinned, and his skinless body was disposed, while the tattooed skin was sold and displayed at Oxford.

It is commonly held that the modern popularity of tattooing stems from Captain
James Cook's three voyages to the South Pacific in the late 18th century. Certainly, Cook's voyages and the dissemination of the texts and images from them brought more awareness about tattooing (and, as noted above, imported the word "tattow" into Western languages). On Cook's first voyage in 1768, his science officer and expedition botanist,
Sir Joseph Banks, as well as artist
Sydney Parkinson and many others of the crew, returned to England with a keen interest in tattoos with Banks writing about them extensively and Parkinson is believed to have gotten a tattoo himself in
Tahiti. Banks was a highly regarded member of the English aristocracy who had acquired his position with Cook by co-financing the expedition with ten thousand pounds, a very large sum at the time. In turn, Cook brought back with him a tattooed
Raiatea
Raiatea or Ra'iatea ( Tahitian: ''Ra‘iātea'') is the second largest of the Society Islands, after Tahiti, in French Polynesia. The island is widely regarded as the "centre" of the eastern islands in ancient Polynesia and it is likely that th ...
n man,
Omai, whom he presented to King George and the English Court. On subsequent voyages other crew members, from officers, such as American John Ledyard, to ordinary seamen, were tattooed.
The first documented professional tattooist in Britain was
Sutherland Macdonald
Sutherland Macdonald was a prominent English tattoo artist in the late 19th century and early 20th century, and the first tattooist in Britain with an identifiable premises open to the public. Operating in a salon in London's Jermyn Street, he ...
, who operated out of a salon in London beginning in 1894. In Britain, tattooing was still largely associated with sailors and the lower or even criminal class, but by the 1870s had become fashionable among some members of the upper classes, including royalty,
and in its upmarket form it could be an expensive and sometimes painful process. A marked
class division on the acceptability of the practice continued for some time in Britain.

Tattooing of
Catholic women in Bosnia and Herzegovina became widespread during the
Ottoman rule and continued to the mid 20th century. Among the Catholic population, there was a widespread tradition of tattooing crosses on the hands, arms, chest, and forehead of girls between the ages of 6 to 16.
This was done in order to prevent kidnapping by the Ottoman Turks and conversion to Islam.
Ethnographers believe that its origins predate both the
Slavic migration to the Balkans
The Slavic migrations to the Balkans began in the mid-6th century and first decades of the 7th century in the Early Middle Ages. The rapid demographic spread of the Slavs was followed by a population exchange, mixing and language shift to and from ...
and spread of
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global popula ...
, with evidence pointing far back to the prehistoric
Illyrian tribes.
North America
Many
Indigenous peoples of North America practice tattooing. European explorers and traders who met Native Americans noticed these tattoos and wrote about them, and a few Europeans chose to be tattooed by Native Americans.
See
history of tattooing in North America.
By the time of the
American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revoluti ...
, tattoos were already common among American sailors (see
sailor tattoos).
Tattoos were listed in
protection papers
Protection papers, also known as "Seamen Protection Papers", "Seamen Protection Certificates", or "Sailor's Protection Papers", were issued to American seamen during the last part of the 18th century through the first half of the 20th century. Thes ...
, an identity certificate issued to prevent
impressment
Impressment, colloquially "the press" or the "press gang", is the taking of men into a military or naval force by compulsion, with or without notice. European navies of several nations used forced recruitment by various means. The large size of ...
into the British
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Fr ...
.
Because protection papers were proof of American citizenship, Black sailors used them to show that they were freemen.

The first recorded professional tattoo shop in the US was established in the early 1870s by a German immigrant,
Martin Hildebrandt.
He had served as a Union soldier in the Civil War and tattooed many other soldiers.
Soon after the Civil War, tattoos became fashionable among upper-class young adults. This trend lasted until the beginning of World War I. The invention of the electric tattoo machine caused popularity of tattoos among the wealthy to drop off. The machine made the tattooing procedure both much easier and cheaper, thus, eliminating the status symbol tattoos previously held, as they were now affordable for all socioeconomic classes. The status symbol of a tattoo shifted from a representation of wealth to a mark typically seen on rebels and criminals. Despite this change, tattoos remained popular among military servicemen, a tradition that continues today.
In 1975, there were only 40 tattoo artists in the country; in 1980, there were more than 5,000 self-proclaimed tattoo artists,
appearing in response to sudden demand.
Many studies have been done of the tattooed population and society's view of tattoos. In June 2006, the ''
Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology'' published the results of a telephone survey of 2004: it found that 36% of Americans ages 18–29, 24% of those 30–40, and 15% of those 41–51 had a tattoo. In September 2006, the
Pew Research Center conducted a telephone survey that found that 36% of Americans ages 18–25, 40% of those 26–40 and 10% of those 41–64 had a tattoo. They concluded that
Generation X
Generation X (or Gen X for short) is the Western demographic cohort following the baby boomers and preceding the millennials. Researchers and popular media use the mid-to-late 1960s as starting birth years and the late 1970s to early 1980s ...
and
Millennials express themselves through their appearance, and tattoos are a popular form of self-expression. In January 2008, a survey conducted online by
Harris Interactive estimated that 14% of all adults in the United States have a tattoo, slightly down from 2003, when 16% had a tattoo. Among age groups, 9% of those ages 18–24, 32% of those 25–29, 25% of those 30–39 and 12% of those 40–49 have tattoos, as do 8% of those 50–64. Men are slightly more likely to have a tattoo than women.
Since the 1970s, tattoos have become a mainstream part of Western fashion, common both for men and women, and among all economic classes and to age groups from the later teen years to middle age. For many young Americans, the tattoo has taken on a decidedly different meaning than for previous generations. The tattoo has undergone "dramatic redefinition" and has shifted from a form of deviance to an acceptable form of expression.
As of 1 November 2006,
Oklahoma became the last state to legalize tattooing, having banned it since 1963.
Australia

Branding was used by European authorities for marking criminals throughout the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. The practice was also used by British authorities to mark army deserters and military personnel court-martialed in Australia. In nineteenth century Australia tattoos were generally the result of personal rather than official decisions but British authorities started to record tattoos along with scars and other bodily markings to describe and manage convicts assigned for transportation.
[Maxwell-Stewart, Hamish, in Caplan, J. (2000). Written on the body: The tattoo in European and American history / edited by Jane Caplan. London: Reaktion. ] The practice of tattooing appears to have been a largely non-commercial enterprise during the convict period in Australia. For example, James Ross in the Hobart Almanac of 1833 describes how the convicts on board ship commonly spent time tattooing themselves with gunpowder.
Out of a study of 10,180 convict records that were transported to then Van Diemen's Land (now Tasmania) between 1823 and 1853 about 37% of all men and about 15% of all women arrived with tattoos, making Australia at the time the most heavily tattooed English-speaking country.
By the beginning of the twentieth century, there were tattoo studios in Australia but they do not appear to have been numerous. For example, the Sydney tattoo studio of Fred Harris was touted as being the only tattoo studio in Sydney between 1916 and 1943. Tattoo designs often reflected the culture of the day and in 1923 Harris's small parlour experienced an increase in the number of women getting tattoos. Another popular trend was for women to have their legs tattooed so the designs could be seen through their stockings.
By 1937 Harris was one of Sydney's best-known tattoo artists and was inking around 2000 tattoos a year in his shop. Sailors provided most of the canvases for his work but among the more popular tattoos in 1938 were Australian flags and kangaroos for sailors of the visiting American Fleet.
In modern day Australia a popular tattoo design is the Southern Cross motif, or variations of it.
There are currently over 2000 official tattoo practitioners in Australia and over 100 registered parlours and clinics, with the number of unregistered parlours and clinics are estimated to be double that amount. The demand over the last decade for tattoos in Australia has risen over 440%, making it an in demand profession in the country.
There are several large
tattoo conventions held in Australia, some of which are considered the biggest in the southern hemisphere, with the best artists from around Oceana attending.
Process
Tattooing involves the placement of pigment into the skin's dermis, the layer of dermal tissue underlying the
epidermis. After initial injection, pigment is dispersed throughout a
homogenized damaged layer down through the epidermis and upper dermis, in both of which the presence of foreign material activates the
immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinte ...
's
phagocytes to engulf the pigment particles. As healing proceeds, the damaged epidermis flakes away (eliminating surface pigment) while deeper in the skin
granulation tissue
Granulation tissue is new connective tissue and microscopic blood vessels that form on the surfaces of a wound during the healing process. Granulation tissue typically grows from the base of a wound and is able to fill wounds of almost any siz ...
forms, which is later converted to connective tissue by
collagen growth. This mends the upper dermis, where pigment remains trapped within successive generations of
macrophages, ultimately concentrating in a layer just below the dermis/epidermis boundary. Its presence there is stable, but in the long term (decades) the pigment tends to migrate deeper into the dermis, accounting for the degraded detail of old tattoos.
Equipment

Some tribal cultures traditionally created tattoos by cutting designs into the skin and rubbing the resulting wound with ink, ashes or other agents; some cultures continue this practice, which may be an adjunct to
scarification. Some cultures create tattooed marks by hand-tapping the ink into the skin using sharpened sticks or animal bones (made into needles) with clay formed disks or, in modern times, actual needles.
The most common method of tattooing in modern times is the electric
tattoo machine, which inserts ink into the skin via a single needle or a group of needles that are
soldered onto a bar, which is attached to an oscillating unit. The unit rapidly and repeatedly drives the needles in and out of the skin, usually 80 to 150 times a second. The needles are single-use needles that come packaged individually, or manufactured by artists, on-demand, as groupings dictate on a per-piece basis.
In modern tattooing, an artist may use thermal stencil paper or
hectograph ink/stencil paper to first place a printed design on the skin before applying a tattoo design.
Practice regulation and health risk certification
Tattooing is regulated in many countries because of the associated health risks to client and practitioner, specifically local infections and virus transmission. Disposable plastic aprons and eye protection can be worn depending on the risk of blood or other secretions splashing into the eyes or clothing of the tattooist. Hand hygiene, assessment of risks and appropriate disposal of all sharp objects and materials contaminated with blood are crucial areas. The tattoo artist must wash his or her hands and must also wash the area that will be tattooed. Gloves must be worn at all times and the wound must be wiped frequently with a wet disposable towel of some kind. All equipment must be sterilized in a certified
autoclave before and after every use. It is good practice to provide clients with a printed consent form that outlines risks and complications as well as instructions for after care.
Associations
Historical associations

Among
Austronesian societies, tattoos had various functions. Among men, they were strongly linked to the widespread practice of
head-hunting raids. In head-hunting societies, like the
Ifugao
Ifugao, officially the Province of Ifugao ( ilo, Probinsia ti Ifugao; tl, Lalawigan ng Ifugao), is a landlocked province of the Philippines in the Cordillera Administrative Region in Luzon. Its capital is Lagawe and it borders Benguet to the ...
and
Dayak people, tattoos were records of how many heads the warriors had taken in battle, and were part of the
initiation rites into adulthood. The number, design, and location of tattoos, therefore, were indicative of a warrior's status and prowess. They were also regarded as magical wards against various dangers like evil spirits and illnesses. Among the
Visayans of the
pre-colonial Philippines
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose their relig ...
, tattoos were worn by the ''
tumao
The Tagalog ''maginoo'', the Kapampangan ''ginu'', and the Visayan ''tumao'' were the nobility social class among various cultures of the pre-colonial Philippines. Among the Visayans, the ''tumao'' were further distinguished from the immediate ...
'' nobility and the ''
timawa
The ''Timawa'' were the feudal warrior class of the ancient Visayan societies of the Philippines. They were regarded as higher than the '' uripon'' (commoners, serfs, and slaves) but below the '' Tumao'' (royal nobility) in the Visayan soci ...
'' warrior class as permanent records of their participation and conduct in maritime raids known as ''
mangayaw''.
In Austronesian women, like the facial tattoos among the women of the
Tayal and
Māori people
The Māori (, ) are the indigenous Polynesian people of mainland New Zealand (). Māori originated with settlers from East Polynesia, who arrived in New Zealand in several waves of canoe voyages between roughly 1320 and 1350. Over severa ...
, they were indicators of status, skill, and beauty.

The
Government of Meiji Japan had outlawed tattoos in the 19th century, a prohibition that stood for 70 years before being repealed in 1948. As of 6 June 2012, all new tattoos are forbidden for employees of the city of
Osaka
is a designated city in the Kansai region of Honshu in Japan. It is the capital of and most populous city in Osaka Prefecture, and the third most populous city in Japan, following Special wards of Tokyo and Yokohama. With a population of ...
. Existing tattoos are required to be covered with proper clothing. The regulations were added to Osaka's ethical codes, and employees with tattoos were encouraged to have them removed. This was done because of the strong connection of tattoos with the
yakuza, or Japanese organized crime, after an Osaka official in February 2012 threatened a schoolchild by showing his tattoo.
Tattoos had negative connotations in historical
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
, where criminals often had been marked by tattooing.
The association of tattoos with
criminals was transmitted from China to influence Japan.
Today, tattoos have remained a taboo in Chinese society.
The
Romans tattooed criminals and slaves, and in the 19th century released U.S. convicts,
Australian convicts and British army deserters were identified by tattoos. Prisoners in
Nazi concentration camps
From 1933 to 1945, Nazi Germany operated more than a thousand concentration camps, (officially) or (more commonly). The Nazi concentration camps are distinguished from other types of Nazi camps such as forced-labor camps, as well as con ...
were tattooed with an identification number. Today, many prison inmates still tattoo themselves as an indication of time spent in prison.
also used tattoos to represent their tribe. Catholic
Croats
The Croats (; hr, Hrvati ) are a South Slavic ethnic group who share a common Croatian ancestry, culture, history and language. They are also a recognized minority in a number of neighboring countries, namely Austria, the Czech Republic ...
of
Bosnia used religious
Christian tattooing, especially of children and women, for protection against conversion to
Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
during the Ottoman rule in the Balkans.
Modern associations
Tattoos are strongly
empirically associated with
deviance,
personality disorders
Personality disorders (PD) are a class of mental disorders characterized by enduring maladaptive patterns of behavior, cognition, and inner experience, exhibited across many contexts and deviating from those accepted by the individual's cultur ...
and criminality.
Although the general acceptance of tattoos is on the rise in Western society, they still carry a heavy stigma among certain social groups. Tattoos are generally considered an important part of the culture of the
Russian mafia.
Current cultural understandings of tattoos in Europe and North America have been greatly influenced by long-standing stereotypes based on deviant social groups in the 19th and 20th centuries. Particularly in North America, tattoos have been associated with stereotypes,
folklore
Folklore is shared by a particular group of people; it encompasses the traditions common to that culture, subculture or group. This includes oral traditions such as tales, legends, proverbs and jokes. They include material culture, rangin ...
and racism.
Not until the 1960s and 1970s did people associate tattoos with such societal outcasts as
bikers and prisoners. Today, in the United States many prisoners and criminal gangs use distinctive tattoos to indicate facts about their criminal behavior,
prison sentences and organizational affiliation. A
teardrop tattoo
The teardrop tattoo or tear tattoo is a symbolic tattoo of a tear that is placed underneath the eye. The teardrop is one of the most widely recognised prison tattoos and has various meanings.
It can signify that the wearer has spent time in pr ...
, for example, can be symbolic of murder, or each tear represents the death of a friend. At the same time, members of the
U.S. military have an equally well-established and longstanding
history of tattooing to indicate military units, battles, kills, etc., an association that remains widespread among older Americans. In Japan, tattoos are associated with
yakuza criminal groups, but there are non-yakuza groups such as
Fukushi Masaichi
was a Japanese physician, pathologist and Emeritus Professor of Nippon Medical School in Tokyo. He was the founder or nite of the world's only known collection of tattoos taken from the dead. Fukushi Masaichi and his son Fukushi Katsunari are kn ...
's tattoo association that sought to preserve the skins of dead Japanese who have extensive tattoos. Tattooing is also common in the
British Armed Forces
The British Armed Forces, also known as His Majesty's Armed Forces, are the military forces responsible for the defence of the United Kingdom, its Overseas Territories and the Crown Dependencies. They also promote the UK's wider interests, s ...
. Depending on vocation, tattoos are accepted in a number of professions in America. Companies across many fields are increasingly focused on diversity and inclusion. Mainstream art galleries hold exhibitions of both conventional and custom tattoo designs, such as ''Beyond Skin'', at the
Museum of Croydon
The Museum of Croydon is a museum located within the Croydon Clocktower arts facility in Central Croydon, England. It showcases historical and cultural artefacts relating to the London Borough of Croydon and its people. The museum is owned and ...
.

In Britain, there is evidence of women with tattoos, concealed by their clothing, throughout the 20th century, and records of women tattooists such as
Jessie Knight from the 1920s.
A study of "at-risk" (as defined by school absenteeism and truancy) adolescent girls showed a positive correlation between body modification and negative feelings towards the body and low self-esteem; however, the study also demonstrated that a strong motive for body modification is the search for "self and attempts to attain mastery and control over the body in an age of increasing alienation". The prevalence of women in the tattoo industry in the 21st century, along with larger numbers of women bearing tattoos, appears to be changing negative perceptions.
In ''Covered in Ink'' by Beverly Yuen Thompson, she interviews heavily tattooed women in Washington, Miami, Orlando, Houston, Long Beach, and Seattle from 2007 to 2010 using
participant observation and in-depth interviews of 70 women. Younger generations are typically more unbothered by heavily tattooed women, while older generation including the participants parents are more likely to look down on them, some even go to the extreme of disowning their children for getting tattoos. Typically how the family reacts is an indicator of their relationship in general. Family members who weren't accepting of tattoos often wanted to scrub the images off, pour holy water on them or have them surgically removed. Families who were emotionally accepting of their family members were able to maintain close bonds after tattooing.
Advertising and marketing
Former sailor
Rowland Hussey Macy, who formed
Macy's
Macy's (originally R. H. Macy & Co.) is an American chain of high-end department stores founded in 1858 by Rowland Hussey Macy. It became a division of the Cincinnati-based Federated Department Stores in 1994, through which it is affiliated wi ...
department stores, used a red star tattoo that he had on his hand for the store's logo.
Tattoos have also been used in marketing and advertising with companies paying people to have logos of brands like
HBO,
Red Bull,
ASOS.com
ASOS plc ( ) is a British online fashion and cosmetic retailer. The company was founded in 2000 in London, primarily aimed at young adults. The website sells over 850 brands as well as its own range of clothing and accessories, and ships to al ...
and
Sailor Jerry's rum tattooed in their bodies. This practice is known as "skinvertising".
B.T.'s Smokehouse, a barbecue restaurant located in Massachusetts, offered customers free meals for life if they had the logo of the establishment tattooed on a visible part of their bodies. Nine people took the business up on the offer.
Health risks
The pain of tattooing can range from uncomfortable to excruciating depending on the location of the tattooing the body. The pain can cause fainting.
Because it requires breaking the immunologic barrier formed by the skin, tattooing carries health risks including infection and allergic reactions. Modern tattooists reduce health risks by following universal precautions working with single-use items and sterilizing their equipment after each use. Many jurisdictions require that tattooists have
blood-borne pathogen training such as that provided through the
Red Cross
The International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is a Humanitarianism, humanitarian movement with approximately 97 million Volunteering, volunteers, members and staff worldwide. It was founded to protect human life and health, to ensure re ...
and
OSHA. As of 2009 (in the United States) there have been no reported cases of HIV contracted from tattoos.
In amateur tattooing, such as the practice in prisons, there is an elevated risk of infection. Infections that can theoretically be transmitted by the use of unsterilized tattoo equipment or contaminated ink include surface infections of the skin, fungal infections, some forms of
hepatitis
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver tissue. Some people or animals with hepatitis have no symptoms, whereas others develop yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes ( jaundice), poor appetite, vomiting, tiredness, abdominal ...
,
herpes simplex virus,
HIV,
staph
''Staphylococcus'' is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillales. Under the microscope, they appear spherical (cocci), and form in grape-like clusters. ''Staphylococcus'' species are facult ...
,
tetanus
Tetanus, also known as lockjaw, is a bacterial infection caused by ''Clostridium tetani'', and is characterized by muscle spasms. In the most common type, the spasms begin in the jaw and then progress to the rest of the body. Each spasm usually ...
, and
tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, ...
.

Tattoo inks have been described as "remarkably nonreactive histologically".
However, cases of allergic reactions to tattoo inks, particularly certain colors, have been medically documented. This is sometimes due to the presence of nickel in an ink pigment, which triggers a common metal allergy. Occasionally, when a
blood vessel
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide awa ...
is punctured during the tattooing procedure, a
bruise/
hematoma may appear. At the same time, a number of tattoo inks may contain hazardous substances, and a proposal has been submitted by the
European Chemicals Agency
The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA; ) is an agency of the European Union which manages the technical and administrative aspects of the implementation of the European Union regulation called Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restricti ...
(ECHA) to restrict the intentional use or concentration limit of approximately 4000 substances when contained in tattoo inks. According to a study by th
European Union Observatory for Nanomaterials (EUON, a number of modern-day tattoo inks contain nanomaterials. These engender significant
nanotoxicological concerns.
Certain colours – red or similar colours such as purple, pink, and orange – tend to cause more problems and damage compared to other colours. Red ink has even caused
skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
and
flesh damages so severe that the
amputation of a leg or an arm has been necessary. If part of a tattoo (especially if red) begins to cause even minor troubles, like becoming itchy or worse, lumpy, then Danish experts strongly suggest to remove the red parts.
In 2017, researchers from the
European Synchrotron Radiation Facility in France say the chemicals in tattoo ink can travel in the bloodstream and accumulate in the lymph nodes, obstructing their ability to fight infections. However, the authors noted in their paper that most tattooed individuals including the donors analyzed do not suffer from chronic inflammation.
Tattoo artists frequently recommend sun protection of skin to prevent tattoos from fading and to preserve skin integrity to make future tattooing easier.
Removal
While tattoos are considered permanent, it is sometimes possible to remove them, fully or partially, with laser treatments. Typically, carbon based pigments, or iron-oxide-based pigments, as well as some colored inks can be removed more completely than inks of other colors.
The expense and pain associated with removing tattoos are typically greater than the expense and pain associated with applying them. Methods other than laser tattoo removal methods include
dermabrasion
Dermabrasion is a type of surgical skin planing, generally with the goal of removing acne, scarring and other skin or tissue irregularities, typically performed in a professional medical setting by a dermatologist or plastic surgeon trained speci ...
, salabrasion (scrubbing the skin with
salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quant ...
), reduction techniques,
cryosurgery and
excision—which is sometimes still used along with
skin grafts for larger tattoos. These older methods, however, have been nearly completely replaced by laser removal treatment options.
Temporary tattoos
A temporary tattoo is a non-permanent image on the skin resembling a permanent tattoo. As a form of
body painting, temporary tattoos can be drawn, painted, or airbrushed.
Types
Decal-style temporary tattoos
Decal
A decal (, , ) or transfer is a plastic, cloth, paper, or ceramic substrate that has printed on it a pattern or image that can be moved to another surface upon contact, usually with the aid of heat or water.
The word is short for ''decalc ...
(press-on) temporary tattoos are used to decorate any part of the body. They may last for a day or for more than a week.
Metallic jewelry tattoos
Foil temporary tattoos are a variation of decal-style temporary tattoos, printed using a foil stamping technique instead of using ink. The foil design is printed as a mirror image in order to be viewed in the right direction once it is applied to the skin. Each metallic tattoo is protected by a transparent protective film.
Airbrush temporary tattoos
Although they have become more popular and usually require a greater investment, airbrush temporary tattoos are less likely to achieve the look of a permanent tattoo, and may not last as long as press-on temporary tattoos. An artist sprays on airbrush tattoos using a stencil with alcohol-based cosmetic inks. Like decal tattoos, airbrush temporary tattoos also are easily removed with rubbing alcohol or
baby oil
Baby oil is, in general terms, an inert oil for the purpose of keeping skin soft and supple. It is often used on babies for the purpose of maintaining "baby-soft" skin, but it is also often used by adults for skincare and massage.
The skin of an ...
.
Henna temporary tattoos

Another tattoo alternative is
henna-based tattoos, which generally contain no additives. Henna is a plant-derived substance which is painted on the skin, staining it a reddish-orange-to-brown color. Because of the semi-permanent nature of henna, they lack the realistic colors typical of decal temporary tattoos. Due to the time-consuming application process, it is a relatively poor option for children. Dermatological publications report that allergic reactions to natural henna are very rare and the product is generally considered safe for skin application. Serious problems can occur, however, from the use of henna with certain additives. The FDA and medical journals report that painted black henna temporary tattoos are especially dangerous.
Safety
Decal-style temporary tattoo safety
Decal temporary tattoos, when legally sold in the United States, have had their color additives approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as cosmetics – the FDA has determined these colorants are safe for "direct dermal contact". While the FDA has received some accounts of minor skin irritation, including redness and swelling, from this type of temporary tattoo, the agency has found these symptoms to be "child specific" and not significant enough to support warnings to the public. Unapproved pigments, however, which are sometimes used by non-US manufacturers, can provoke allergic reactions in anyone.
Airbrush tattoo safety
The types of airbrush paints manufactured for crafting, creating art or decorating clothing should never be used for tattooing. These paints can be allergenic or toxic.
Henna tattoo safety
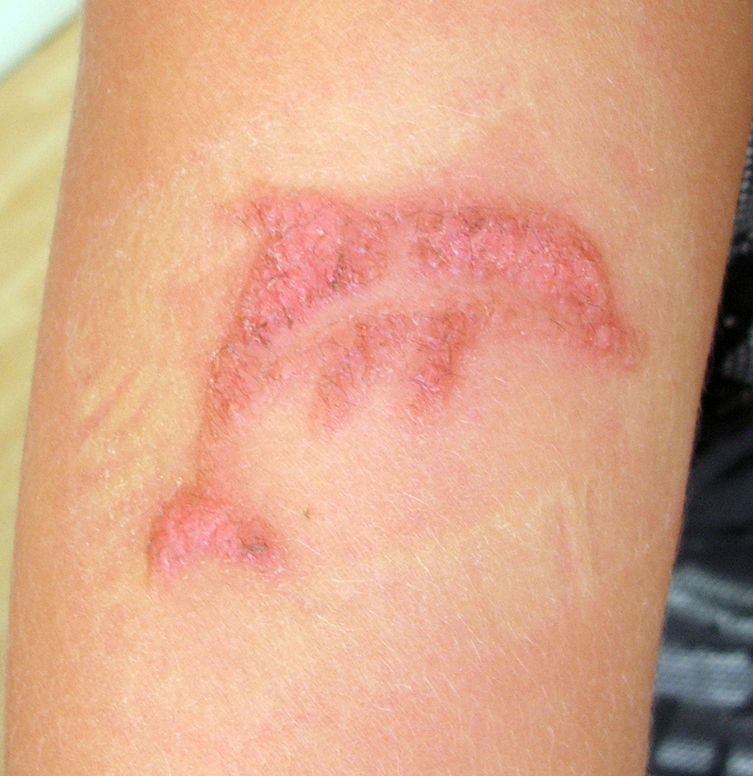
The
FDA regularly issues warnings to consumers about avoiding any temporary tattoos labeled as black henna or pre-mixed henna as these may contain potentially harmful ingredients including
silver nitrate
Silver nitrate is an inorganic compound with chemical formula . It is a versatile precursor to many other silver compounds, such as those used in photography. It is far less sensitive to light than the halides. It was once called ''lunar causti ...
,
carmine,
pyrogallol,
disperse orange dye and
chromium
Chromium is a chemical element with the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in group 6. It is a steely-grey, lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
Chromium metal is valued for its high corrosion resistance and hard ...
. Black henna gets its color from
paraphenylenediamine
''p''-Phenylenediamine (PPD) is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(NH2)2. This derivative of aniline is a white solid, but samples can darken due to air oxidation. It is mainly used as a component of engineering polymers and composites lik ...
(PPD), a
textile dye
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the ...
approved by the FDA for human use only in hair coloring. In Canada, the use of PPD on the skin, including hair dye, is banned. Research has linked these and other ingredients to a range of health problems including allergic reactions, chronic inflammatory reactions, and late-onset allergic reactions to related clothing and hairdressing dyes. They can cause these reactions long after application. Neither black henna nor pre-mixed henna are approved for cosmetic use by the FDA.
Religious views
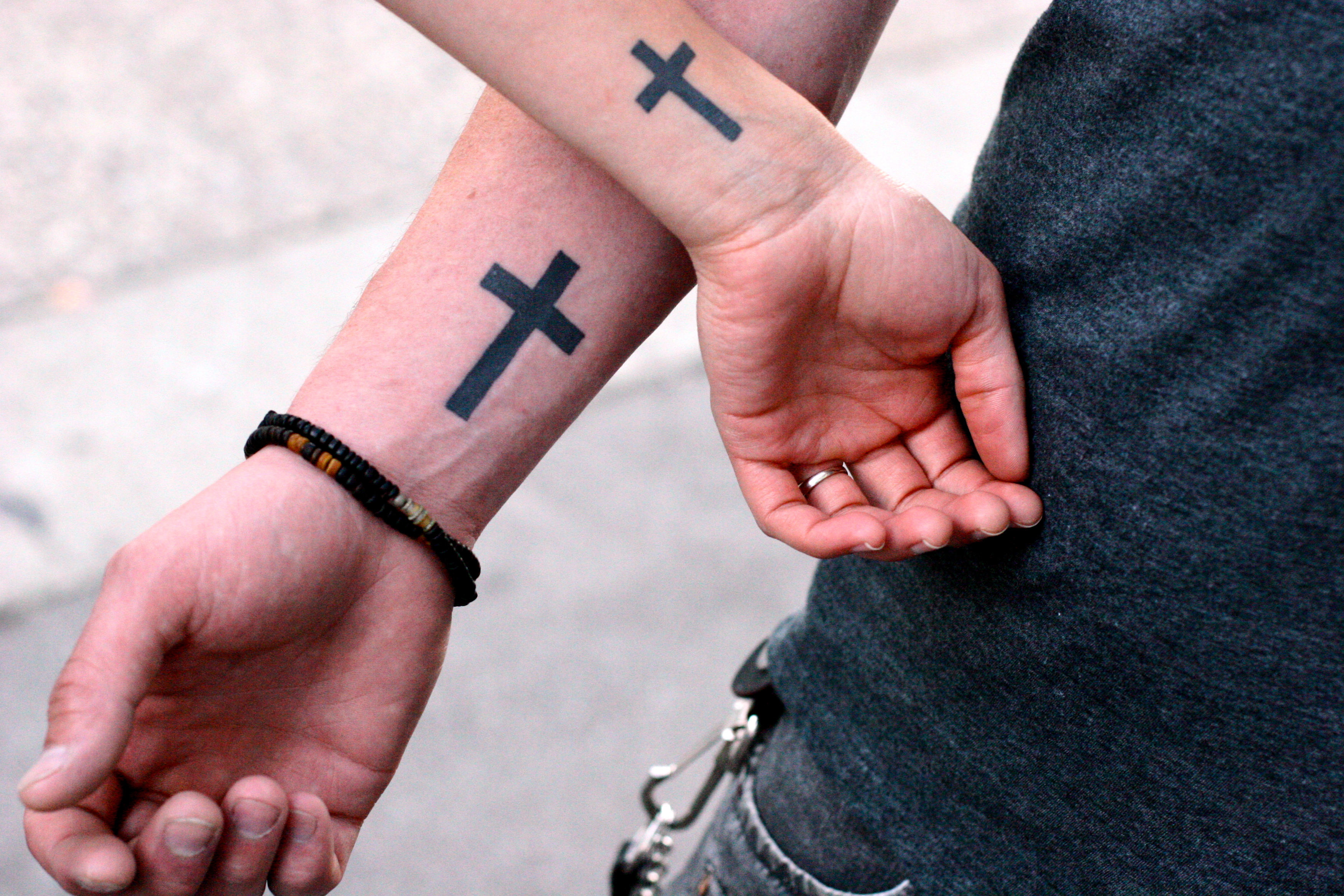 Egyptians
Egyptians originally used tattoos to show dedication to a god, and the tattoos were believed to convey divine protection. In
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
, Buddhism, and Neopaganism, tattoos are accepted.
Southeast Asia has a tradition of protective tattoos variously known as ''sak yant'' or
yantra tattoos that include Buddhist images, prayers, and symbols. Images of the Buddha or other religious figures have caused controversy in some Buddhist countries when incorporated into tattoos by Westerners who do not follow traditional customs regarding respectful display of images of Buddhas or deities.
Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in th ...
generally prohibits tattoos among its adherents based on the commandments in
Leviticus 19. Jews tend to believe this commandment only applies to Jews and not to
gentiles. However, an increasing number of young Jews are getting tattoos either for fashion, or an expression of their faith.
There is no specific teaching in the
New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Chris ...
prohibiting tattoos. Most
Christian denominations believe that the
Old Covenant ceremonial laws in Leviticus were
abrogated with the coming of the
New Covenant
The New Covenant (Hebrew '; Greek ''diatheke kaine'') is a biblical interpretation which was originally derived from a phrase which is contained in the Book of Jeremiah ( Jeremiah 31:31-34), in the Hebrew Bible (or the Old Testament of the ...
; that the prohibition of various cultural practices, including tattooing, was intended to distinguish the
Israelites
The Israelites (; , , ) were a group of Semitic-speaking tribes in the ancient Near East who, during the Iron Age, inhabited a part of Canaan.
The earliest recorded evidence of a people by the name of Israel appears in the Merneptah Stele o ...
from neighbouring peoples for a limited period of time, and was not intended as a universal law to apply to the gentiles for all time. Many
Coptic Christians in Egypt have a cross tattoo on their right wrist to differentiate themselves from Muslims. However, some
Evangelical
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide interdenominational movement within Protestant Christianity that affirms the centrality of being " born again", in which an individual expe ...
and
fundamentalist Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
denominations believe the commandment applies today for Christians and believe it is a
sin to get a tattoo. In
Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
teaching, what is said in Leviticus (19:28) is taught not binding upon Christians for the same reason that the verse "nor shall there come upon you a garment of cloth made of two kinds of stuff" (Lev. 19:19) is not binding upon Christians. It is a matter of what the tattoo depicts. The Catholic Church says the images should not be immoral, such as sexually explicit, Satanic, or in any way opposed to the truths and teachings of Christianity.
Tattoos are considered to be
haram for many
Sunni Muslims, based on rulings from scholars and passages in the Sunni
Hadith
Ḥadīth ( or ; ar, حديث, , , , , , , literally "talk" or "discourse") or Athar ( ar, أثر, , literally "remnant"/"effect") refers to what the majority of Muslims believe to be a record of the words, actions, and the silent approva ...
.
Shia Islam
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, mos ...
does not prohibit tattooing,
and many Shia Muslims (Lebanese, Iraqis, Yemenis, Iranians) have tattoos, specifically with religious themes.
In popular culture
*
''Inked'' (magazine), a tattoo lifestyle digital media company that bills itself as the outsiders' insider media
*See
List of tattoo TV shows
See also
Styles
*
Black-and-gray
*
Borneo traditional tattooing
Borneo traditional tattooing is a hand tapping style of tattooing with two sticks, developed by some of the ancient tribes of Borneo.
Borneo tattooing designs
The most common of Borneo designs are thick black tribal work, which all have differen ...
*
Chinese calligraphy tattoos
*
Christian tattooing in Bosnia and Herzegovina
or is a Serbo-Croatian name for a widespread custom mostly among Roman Catholic Croat women and girls of the central regions of Bosnia and Herzegovina, as well as the Dalmatia region of Croatia. The phenomenon predates the Slavic migration t ...
*
Criminal tattoo
*
Deq (tattoo)
Deq ( ku, deq, ) or xal ( ku, xał, ) are the traditional and unique tattoos pertaining to Kurds. Deq is more commonly found among Kurdish women, but is also observed among men. However, the practice of deq has become less common due to the influ ...
*
Irezumi, traditional Japanese tattoo
*
New school (tattoo)
*
Old school (tattoo)
*
Pe'a
*
Prison tattooing
Prison tattooing is the practice of creating and displaying tattoos in a prison environment. Present-day American and Russian prisoners may convey gang membership, code, or hidden meanings for origin or criminal deeds. Lack of proper equipment ...
*
Sailor tattoos
*
Scarification
*
Sleeve tattoo
*
Soot tattoo
*
SS blood group tattoo
Location
*
Body suit (tattoo)
A body suit or full body suit is an extensive tattoo, usually of a similar pattern, style or theme that covers the entire torso or the entire body. They are associated with traditional Japanese tattooing as well as with some freak show and circ ...
*
Genital tattooing
*
Lower back tattoo
Tattoos on the lower back became popular in the first decade of the 21st century, and gained a reputation for their erotic appeal. The tattoos were sometimes accentuated by low-rise jeans or crop tops. Their popularity was in part due to the ...
*
Scleral tattooing
Others
*
Biomechanical art Biomechanical art (also called Biomech) is a surrealistic style of art that combines elements of machines with organics. Rendered with distinct realism, biomechanical art expresses an internal fantasy world, most typically represented with human or ...
*
Body art
**
Body painting
**
Mehndi (also called
henna)
*
Foreign body granuloma
A foreign body reaction (FBR) is a typical tissue response to a foreign body within biological tissue. It usually includes the formation of a foreign body granuloma. Tissue-encapsulation of an implant is an example, as is inflammation around a sp ...
*
Fusen gum
*
Legal status of tattooing in European countries
Legislation controlling tattooing
A tattoo is a form of body modification made by inserting tattoo ink, dyes, and/or pigments, either indelible or temporary, into the dermis layer of the skin to form a design. Tattoo artists create these d ...
*
Legal status of tattooing in the United States
In the United States there is no federal law regulating the practice of tattooing. However, all 50 states and the District of Columbia have statutory laws requiring a person receiving a tattoo be at least 18 years old. This is partially based on t ...
*
List of tattoo artists
*
Lucky Diamond Rich
__NOTOC__
Gregory Paul McLaren (born 1971), who goes by the name of Lucky Diamond Rich, is a New Zealand-British performance artist, street performer and international performing arts festival performer, whose acts include sword swallowing and ...
, world's most tattooed person
*
Religious perspectives on tattooing
Some religions have perspectives on tattooing.
Buddhism
Southeast Asia has a tradition of protective tattoos known as ''sak yant'' or yantra tattoos that incorporate Buddhist symbols and images, as well as protective mantras or sutra verses in ...
*
Tattoo convention
*
Tattooed lady
References
Citations
General sources
; Anthropological
* Buckland, A. W. (1887). "On Tattooing", in ''Journal of the Royal Anthropological Institute of Great Britain and Ireland'', 1887/12, p. 318–328
* Caplan, Jane (ed.) (2000): ''Written on the Body: the Tattoo in European and American History'',
Princeton University Press
Princeton University Press is an independent publisher with close connections to Princeton University. Its mission is to disseminate scholarship within academia and society at large.
The press was founded by Whitney Darrow, with the financial ...
* DeMello, Margo (2000) ''Bodies of Inscription: a Cultural History of the Modern Tattoo Community'', California. Durham NC: Duke University Press
*
* Gell, Alfred (1993) ''Wrapping in Images: Tattooing in Polynesia'', Oxford: Clarendon Press
* Gilbert, Stephen G. (2001) ''Tattoo History: a Source Book'', New York: Juno Books
* Gustafson, Mark (1997) "''Inscripta in fronte'': Penal Tattooing in Late Antiquity", in ''Classical Antiquity'', April 1997, Vol. 16/No. 1, pp. 79–105
* Hambly, Wilfrid Dyson (1925) ''The History of Tattooing and Its Significance: With Some Account of Other Forms of Corporal Marking'', London:
H. F. & G. Witherby (reissued: Detroit 1974)
* Hesselt van Dinter, Maarten (2005) ''The World of Tattoo; An Illustrated History''. Amsterdam, KIT Publishers
* Jones, C. P. (1987) "Stigma: Tattooing and Branding in Graeco–Roman Antiquity", in ''Journal of Roman Studies'', 77/1987, pp. 139–155
* Juno, Andrea. ''Modern Primitives''. ''
Re/Search'' #12 (October 1989)
* Kächelen, Wolf-Peter (2004): ''Tatau und Tattoo – Eine Epigraphik der Identitätskonstruktion.''
Shaker Verlag, Aachen, .
* Kächelen, Wolf-Peter (2020): "Tatau und Tattoo Revisited: Tattoo pandemic: A forerunner of globel economic and social collapse." In
Wolf-Peter Kächelen – Tatau und Tattoo* Lombroso, Cesare (1896) "The Savage Origin of Tattooing", in ''Popular Science Monthly'', ''
Popular Science
''Popular Science'' (also known as ''PopSci'') is an American digital magazine carrying popular science content, which refers to articles for the general reader on science and technology subjects. ''Popular Science'' has won over 58 awards, incl ...
'' Vol. IV., 1896
Pang, Joey (2008) "Tattoo Art Expressions"* Raviv, Shaun (2006) "Marked for Life: Jews and Tattoos" (''
Moment Magazine''; June 2006)
"Comparative study about Ötzi's therapeutic tattoos" (L. Renaut, 2004, French and English abstract)* Robley, Horatio (1896) ''Moko, or, Maori tattooing''. London: Chapman and Hall
* Roth, H. Ling (1901) "Maori tatu and moko". In: ''Journal of the Anthropological Institute'' vol. 31, January–June 1901
* Rubin, Arnold (ed.) (1988) ''Marks of Civilization: Artistic Transformations of the Human Body'', Los Angeles:
UCLA Museum of Cultural History
* Sanders, Clinton R. (1989) ''Customizing the Body: the Art and Culture of Tattooing''. Philadelphia: Temple University Press
* Sinclair, A. T. (1909) "Tattooing of the North American Indians", in ''
American Anthropologist
''American Anthropologist'' is the flagship journal of the American Anthropological Association (AAA), published quarterly by Wiley. The "New Series" began in 1899 under an editorial board that included Franz Boas, Daniel G. Brinton, and John ...
'' 1909/11, No. 3, p. 362–400
* Thompson, Beverly Yuen (2015)
Covered in Ink: Tattoos, Women and the Politics of the Body'',
New York University Press
New York University Press (or NYU Press) is a university press that is part of New York University.
History
NYU Press was founded in 1916 by the then chancellor of NYU, Elmer Ellsworth Brown.
Directors
* Arthur Huntington Nason, 1916–1 ...
.
* Wianecki, Shannon (2011
"Marked"''
Maui No Ka 'Oi Magazine''.
; Popular and artistic
* Green, Terisa. ''Ink: The Not-Just-Skin-Deep Guide to Getting a Tattoo'' New York:
New American Library
* Green, Terisa. ''The Tattoo Encyclopedia: A Guide to Choosing Your Tattoo'' New York: New American Library
* Kraków, Amy. ''Total Tattoo Book'' New York:
Warner Books
; Medical
*
*
*
*
* Paola Piccinini, Laura Contor, Ivana Bianchi, Chiara Senaldi, Sazan Pakalin: ''Safety of tattoos and permanent make-up'',
Joint Research Centre, 2016, ,
doi:10.2788/011817.
Further reading
*
*
External links
Tattoos, The Permanent Art documentary produced by
Off Book
History, Inkproduced by Meghan Glass Hughes for The Valentine Richmond History Center
{{Authority control
1970s fashion
1980s fashion
1990s fashion
2000s fashion
2010s fashion
Articles containing video clips
Polynesian words and phrases
Skin conditions resulting from physical factors
 A tattoo is a form of body modification made by inserting tattoo ink, dyes, and/or pigments, either indelible or temporary, into the dermis layer of the
A tattoo is a form of body modification made by inserting tattoo ink, dyes, and/or pigments, either indelible or temporary, into the dermis layer of the  The word ''tattoo'', or ''tattow'' in the 18th century, is a
The word ''tattoo'', or ''tattow'' in the 18th century, is a  A well-known example is the
A well-known example is the  Tattoos are sometimes used by forensic pathologists to help them identify burned, putrefied, or mutilated bodies. As tattoo pigment lies encapsulated deep in the skin, tattoos are not easily destroyed even when the skin is burned.
Tattoos are sometimes used by forensic pathologists to help them identify burned, putrefied, or mutilated bodies. As tattoo pigment lies encapsulated deep in the skin, tattoos are not easily destroyed even when the skin is burned.
 Preserved tattoos on ancient mummified human remains reveal that tattooing has been practiced throughout the world for thousands of years. In 2015, scientific re-assessment of the age of the two oldest known tattooed mummies identified Ötzi as the oldest example then known. This body, with 61 tattoos, was found embedded in glacial ice in the
Preserved tattoos on ancient mummified human remains reveal that tattooing has been practiced throughout the world for thousands of years. In 2015, scientific re-assessment of the age of the two oldest known tattooed mummies identified Ötzi as the oldest example then known. This body, with 61 tattoos, was found embedded in glacial ice in the  In 1566, French sailors abducted an Inuit woman and her child in modern-day
In 1566, French sailors abducted an Inuit woman and her child in modern-day  It is commonly held that the modern popularity of tattooing stems from Captain James Cook's three voyages to the South Pacific in the late 18th century. Certainly, Cook's voyages and the dissemination of the texts and images from them brought more awareness about tattooing (and, as noted above, imported the word "tattow" into Western languages). On Cook's first voyage in 1768, his science officer and expedition botanist, Sir Joseph Banks, as well as artist Sydney Parkinson and many others of the crew, returned to England with a keen interest in tattoos with Banks writing about them extensively and Parkinson is believed to have gotten a tattoo himself in Tahiti. Banks was a highly regarded member of the English aristocracy who had acquired his position with Cook by co-financing the expedition with ten thousand pounds, a very large sum at the time. In turn, Cook brought back with him a tattooed
It is commonly held that the modern popularity of tattooing stems from Captain James Cook's three voyages to the South Pacific in the late 18th century. Certainly, Cook's voyages and the dissemination of the texts and images from them brought more awareness about tattooing (and, as noted above, imported the word "tattow" into Western languages). On Cook's first voyage in 1768, his science officer and expedition botanist, Sir Joseph Banks, as well as artist Sydney Parkinson and many others of the crew, returned to England with a keen interest in tattoos with Banks writing about them extensively and Parkinson is believed to have gotten a tattoo himself in Tahiti. Banks was a highly regarded member of the English aristocracy who had acquired his position with Cook by co-financing the expedition with ten thousand pounds, a very large sum at the time. In turn, Cook brought back with him a tattooed  Tattooing of Catholic women in Bosnia and Herzegovina became widespread during the Ottoman rule and continued to the mid 20th century. Among the Catholic population, there was a widespread tradition of tattooing crosses on the hands, arms, chest, and forehead of girls between the ages of 6 to 16. This was done in order to prevent kidnapping by the Ottoman Turks and conversion to Islam.
Ethnographers believe that its origins predate both the
Tattooing of Catholic women in Bosnia and Herzegovina became widespread during the Ottoman rule and continued to the mid 20th century. Among the Catholic population, there was a widespread tradition of tattooing crosses on the hands, arms, chest, and forehead of girls between the ages of 6 to 16. This was done in order to prevent kidnapping by the Ottoman Turks and conversion to Islam.
Ethnographers believe that its origins predate both the  The first recorded professional tattoo shop in the US was established in the early 1870s by a German immigrant, Martin Hildebrandt. He had served as a Union soldier in the Civil War and tattooed many other soldiers.
Soon after the Civil War, tattoos became fashionable among upper-class young adults. This trend lasted until the beginning of World War I. The invention of the electric tattoo machine caused popularity of tattoos among the wealthy to drop off. The machine made the tattooing procedure both much easier and cheaper, thus, eliminating the status symbol tattoos previously held, as they were now affordable for all socioeconomic classes. The status symbol of a tattoo shifted from a representation of wealth to a mark typically seen on rebels and criminals. Despite this change, tattoos remained popular among military servicemen, a tradition that continues today.
In 1975, there were only 40 tattoo artists in the country; in 1980, there were more than 5,000 self-proclaimed tattoo artists, appearing in response to sudden demand.
Many studies have been done of the tattooed population and society's view of tattoos. In June 2006, the '' Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology'' published the results of a telephone survey of 2004: it found that 36% of Americans ages 18–29, 24% of those 30–40, and 15% of those 41–51 had a tattoo. In September 2006, the Pew Research Center conducted a telephone survey that found that 36% of Americans ages 18–25, 40% of those 26–40 and 10% of those 41–64 had a tattoo. They concluded that
The first recorded professional tattoo shop in the US was established in the early 1870s by a German immigrant, Martin Hildebrandt. He had served as a Union soldier in the Civil War and tattooed many other soldiers.
Soon after the Civil War, tattoos became fashionable among upper-class young adults. This trend lasted until the beginning of World War I. The invention of the electric tattoo machine caused popularity of tattoos among the wealthy to drop off. The machine made the tattooing procedure both much easier and cheaper, thus, eliminating the status symbol tattoos previously held, as they were now affordable for all socioeconomic classes. The status symbol of a tattoo shifted from a representation of wealth to a mark typically seen on rebels and criminals. Despite this change, tattoos remained popular among military servicemen, a tradition that continues today.
In 1975, there were only 40 tattoo artists in the country; in 1980, there were more than 5,000 self-proclaimed tattoo artists, appearing in response to sudden demand.
Many studies have been done of the tattooed population and society's view of tattoos. In June 2006, the '' Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology'' published the results of a telephone survey of 2004: it found that 36% of Americans ages 18–29, 24% of those 30–40, and 15% of those 41–51 had a tattoo. In September 2006, the Pew Research Center conducted a telephone survey that found that 36% of Americans ages 18–25, 40% of those 26–40 and 10% of those 41–64 had a tattoo. They concluded that  Branding was used by European authorities for marking criminals throughout the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. The practice was also used by British authorities to mark army deserters and military personnel court-martialed in Australia. In nineteenth century Australia tattoos were generally the result of personal rather than official decisions but British authorities started to record tattoos along with scars and other bodily markings to describe and manage convicts assigned for transportation.Maxwell-Stewart, Hamish, in Caplan, J. (2000). Written on the body: The tattoo in European and American history / edited by Jane Caplan. London: Reaktion. The practice of tattooing appears to have been a largely non-commercial enterprise during the convict period in Australia. For example, James Ross in the Hobart Almanac of 1833 describes how the convicts on board ship commonly spent time tattooing themselves with gunpowder. Out of a study of 10,180 convict records that were transported to then Van Diemen's Land (now Tasmania) between 1823 and 1853 about 37% of all men and about 15% of all women arrived with tattoos, making Australia at the time the most heavily tattooed English-speaking country.
By the beginning of the twentieth century, there were tattoo studios in Australia but they do not appear to have been numerous. For example, the Sydney tattoo studio of Fred Harris was touted as being the only tattoo studio in Sydney between 1916 and 1943. Tattoo designs often reflected the culture of the day and in 1923 Harris's small parlour experienced an increase in the number of women getting tattoos. Another popular trend was for women to have their legs tattooed so the designs could be seen through their stockings.
By 1937 Harris was one of Sydney's best-known tattoo artists and was inking around 2000 tattoos a year in his shop. Sailors provided most of the canvases for his work but among the more popular tattoos in 1938 were Australian flags and kangaroos for sailors of the visiting American Fleet.
In modern day Australia a popular tattoo design is the Southern Cross motif, or variations of it.
There are currently over 2000 official tattoo practitioners in Australia and over 100 registered parlours and clinics, with the number of unregistered parlours and clinics are estimated to be double that amount. The demand over the last decade for tattoos in Australia has risen over 440%, making it an in demand profession in the country.
There are several large tattoo conventions held in Australia, some of which are considered the biggest in the southern hemisphere, with the best artists from around Oceana attending.
Branding was used by European authorities for marking criminals throughout the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. The practice was also used by British authorities to mark army deserters and military personnel court-martialed in Australia. In nineteenth century Australia tattoos were generally the result of personal rather than official decisions but British authorities started to record tattoos along with scars and other bodily markings to describe and manage convicts assigned for transportation.Maxwell-Stewart, Hamish, in Caplan, J. (2000). Written on the body: The tattoo in European and American history / edited by Jane Caplan. London: Reaktion. The practice of tattooing appears to have been a largely non-commercial enterprise during the convict period in Australia. For example, James Ross in the Hobart Almanac of 1833 describes how the convicts on board ship commonly spent time tattooing themselves with gunpowder. Out of a study of 10,180 convict records that were transported to then Van Diemen's Land (now Tasmania) between 1823 and 1853 about 37% of all men and about 15% of all women arrived with tattoos, making Australia at the time the most heavily tattooed English-speaking country.
By the beginning of the twentieth century, there were tattoo studios in Australia but they do not appear to have been numerous. For example, the Sydney tattoo studio of Fred Harris was touted as being the only tattoo studio in Sydney between 1916 and 1943. Tattoo designs often reflected the culture of the day and in 1923 Harris's small parlour experienced an increase in the number of women getting tattoos. Another popular trend was for women to have their legs tattooed so the designs could be seen through their stockings.
By 1937 Harris was one of Sydney's best-known tattoo artists and was inking around 2000 tattoos a year in his shop. Sailors provided most of the canvases for his work but among the more popular tattoos in 1938 were Australian flags and kangaroos for sailors of the visiting American Fleet.
In modern day Australia a popular tattoo design is the Southern Cross motif, or variations of it.
There are currently over 2000 official tattoo practitioners in Australia and over 100 registered parlours and clinics, with the number of unregistered parlours and clinics are estimated to be double that amount. The demand over the last decade for tattoos in Australia has risen over 440%, making it an in demand profession in the country.
There are several large tattoo conventions held in Australia, some of which are considered the biggest in the southern hemisphere, with the best artists from around Oceana attending.
 Some tribal cultures traditionally created tattoos by cutting designs into the skin and rubbing the resulting wound with ink, ashes or other agents; some cultures continue this practice, which may be an adjunct to scarification. Some cultures create tattooed marks by hand-tapping the ink into the skin using sharpened sticks or animal bones (made into needles) with clay formed disks or, in modern times, actual needles.
The most common method of tattooing in modern times is the electric tattoo machine, which inserts ink into the skin via a single needle or a group of needles that are soldered onto a bar, which is attached to an oscillating unit. The unit rapidly and repeatedly drives the needles in and out of the skin, usually 80 to 150 times a second. The needles are single-use needles that come packaged individually, or manufactured by artists, on-demand, as groupings dictate on a per-piece basis.
In modern tattooing, an artist may use thermal stencil paper or hectograph ink/stencil paper to first place a printed design on the skin before applying a tattoo design.
Some tribal cultures traditionally created tattoos by cutting designs into the skin and rubbing the resulting wound with ink, ashes or other agents; some cultures continue this practice, which may be an adjunct to scarification. Some cultures create tattooed marks by hand-tapping the ink into the skin using sharpened sticks or animal bones (made into needles) with clay formed disks or, in modern times, actual needles.
The most common method of tattooing in modern times is the electric tattoo machine, which inserts ink into the skin via a single needle or a group of needles that are soldered onto a bar, which is attached to an oscillating unit. The unit rapidly and repeatedly drives the needles in and out of the skin, usually 80 to 150 times a second. The needles are single-use needles that come packaged individually, or manufactured by artists, on-demand, as groupings dictate on a per-piece basis.
In modern tattooing, an artist may use thermal stencil paper or hectograph ink/stencil paper to first place a printed design on the skin before applying a tattoo design.
 Among Austronesian societies, tattoos had various functions. Among men, they were strongly linked to the widespread practice of head-hunting raids. In head-hunting societies, like the
Among Austronesian societies, tattoos had various functions. Among men, they were strongly linked to the widespread practice of head-hunting raids. In head-hunting societies, like the  The Government of Meiji Japan had outlawed tattoos in the 19th century, a prohibition that stood for 70 years before being repealed in 1948. As of 6 June 2012, all new tattoos are forbidden for employees of the city of
The Government of Meiji Japan had outlawed tattoos in the 19th century, a prohibition that stood for 70 years before being repealed in 1948. As of 6 June 2012, all new tattoos are forbidden for employees of the city of  In Britain, there is evidence of women with tattoos, concealed by their clothing, throughout the 20th century, and records of women tattooists such as Jessie Knight from the 1920s. A study of "at-risk" (as defined by school absenteeism and truancy) adolescent girls showed a positive correlation between body modification and negative feelings towards the body and low self-esteem; however, the study also demonstrated that a strong motive for body modification is the search for "self and attempts to attain mastery and control over the body in an age of increasing alienation". The prevalence of women in the tattoo industry in the 21st century, along with larger numbers of women bearing tattoos, appears to be changing negative perceptions.
In ''Covered in Ink'' by Beverly Yuen Thompson, she interviews heavily tattooed women in Washington, Miami, Orlando, Houston, Long Beach, and Seattle from 2007 to 2010 using participant observation and in-depth interviews of 70 women. Younger generations are typically more unbothered by heavily tattooed women, while older generation including the participants parents are more likely to look down on them, some even go to the extreme of disowning their children for getting tattoos. Typically how the family reacts is an indicator of their relationship in general. Family members who weren't accepting of tattoos often wanted to scrub the images off, pour holy water on them or have them surgically removed. Families who were emotionally accepting of their family members were able to maintain close bonds after tattooing.
In Britain, there is evidence of women with tattoos, concealed by their clothing, throughout the 20th century, and records of women tattooists such as Jessie Knight from the 1920s. A study of "at-risk" (as defined by school absenteeism and truancy) adolescent girls showed a positive correlation between body modification and negative feelings towards the body and low self-esteem; however, the study also demonstrated that a strong motive for body modification is the search for "self and attempts to attain mastery and control over the body in an age of increasing alienation". The prevalence of women in the tattoo industry in the 21st century, along with larger numbers of women bearing tattoos, appears to be changing negative perceptions.
In ''Covered in Ink'' by Beverly Yuen Thompson, she interviews heavily tattooed women in Washington, Miami, Orlando, Houston, Long Beach, and Seattle from 2007 to 2010 using participant observation and in-depth interviews of 70 women. Younger generations are typically more unbothered by heavily tattooed women, while older generation including the participants parents are more likely to look down on them, some even go to the extreme of disowning their children for getting tattoos. Typically how the family reacts is an indicator of their relationship in general. Family members who weren't accepting of tattoos often wanted to scrub the images off, pour holy water on them or have them surgically removed. Families who were emotionally accepting of their family members were able to maintain close bonds after tattooing.
 A temporary tattoo is a non-permanent image on the skin resembling a permanent tattoo. As a form of body painting, temporary tattoos can be drawn, painted, or airbrushed.
A temporary tattoo is a non-permanent image on the skin resembling a permanent tattoo. As a form of body painting, temporary tattoos can be drawn, painted, or airbrushed.
 Another tattoo alternative is henna-based tattoos, which generally contain no additives. Henna is a plant-derived substance which is painted on the skin, staining it a reddish-orange-to-brown color. Because of the semi-permanent nature of henna, they lack the realistic colors typical of decal temporary tattoos. Due to the time-consuming application process, it is a relatively poor option for children. Dermatological publications report that allergic reactions to natural henna are very rare and the product is generally considered safe for skin application. Serious problems can occur, however, from the use of henna with certain additives. The FDA and medical journals report that painted black henna temporary tattoos are especially dangerous.
Another tattoo alternative is henna-based tattoos, which generally contain no additives. Henna is a plant-derived substance which is painted on the skin, staining it a reddish-orange-to-brown color. Because of the semi-permanent nature of henna, they lack the realistic colors typical of decal temporary tattoos. Due to the time-consuming application process, it is a relatively poor option for children. Dermatological publications report that allergic reactions to natural henna are very rare and the product is generally considered safe for skin application. Serious problems can occur, however, from the use of henna with certain additives. The FDA and medical journals report that painted black henna temporary tattoos are especially dangerous.
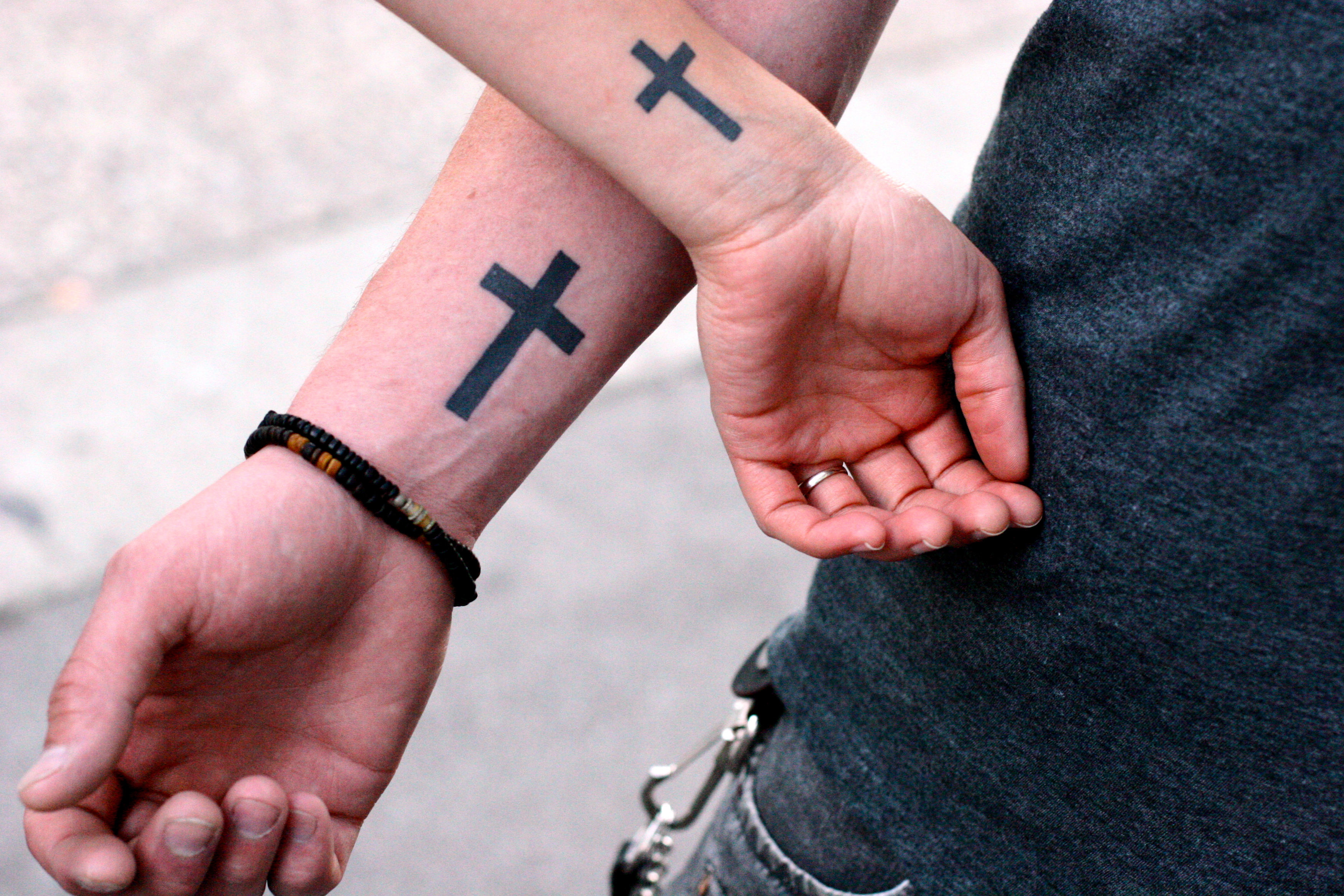 Egyptians originally used tattoos to show dedication to a god, and the tattoos were believed to convey divine protection. In
Egyptians originally used tattoos to show dedication to a god, and the tattoos were believed to convey divine protection. In