Regions of Switzerland on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The geography of Switzerland encompasses the geographical features of Switzerland, a mountainous and
The geography of Switzerland encompasses the geographical features of Switzerland, a mountainous and
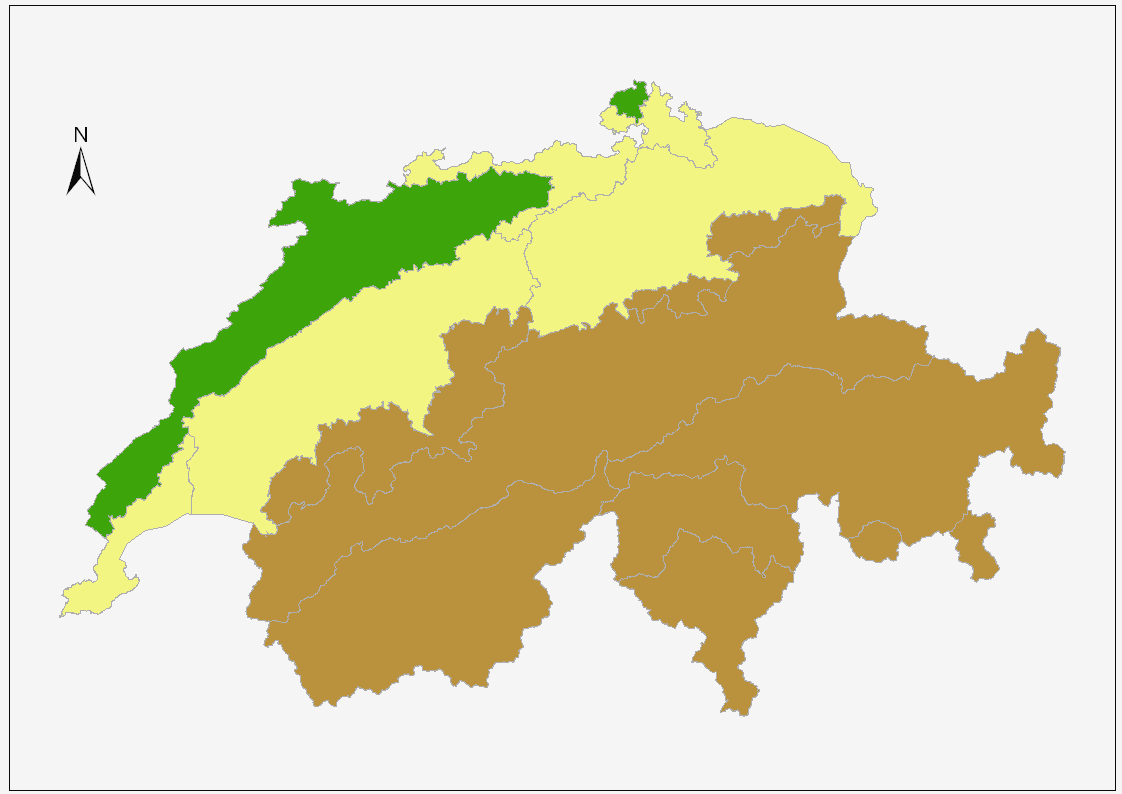 Switzerland is divided in three main geographic regions: the Swiss Alps, the Central Plateau and the Jura, each corresponding to very different geological realities. In addition, two small regions are not part of those three. The first, north of the
Switzerland is divided in three main geographic regions: the Swiss Alps, the Central Plateau and the Jura, each corresponding to very different geological realities. In addition, two small regions are not part of those three. The first, north of the
 The Swiss Plateau extends from Lake Geneva on the French border across central Switzerland to Lake Constance on the German and Austrian borders. In the north and northwest, the Swiss Plateau is sharply delimited geographically and geologically by the Jura Mountains. In the south, there is no clear border with the Alps. Usually, the rising of the terrain to altitudes above 1500 metres, which is very abrupt in certain places, is taken as a criterion for delimitation. The plateau has an average altitude of . Even though the Swiss Plateau forms a basin, it is by no means a flat territory and it is covered with rolling hills, lakes and rivers. Most of Switzerland's large lakes are located in the plateau. Both Lake Geneva () and Lake Constance () are located in the plateau but are shared with other countries. The largest lake totally in Switzerland,
The Swiss Plateau extends from Lake Geneva on the French border across central Switzerland to Lake Constance on the German and Austrian borders. In the north and northwest, the Swiss Plateau is sharply delimited geographically and geologically by the Jura Mountains. In the south, there is no clear border with the Alps. Usually, the rising of the terrain to altitudes above 1500 metres, which is very abrupt in certain places, is taken as a criterion for delimitation. The plateau has an average altitude of . Even though the Swiss Plateau forms a basin, it is by no means a flat territory and it is covered with rolling hills, lakes and rivers. Most of Switzerland's large lakes are located in the plateau. Both Lake Geneva () and Lake Constance () are located in the plateau but are shared with other countries. The largest lake totally in Switzerland,  The Swiss Plateau is crossed by three great river valleys (
The Swiss Plateau is crossed by three great river valleys (
 The Swiss Alps form part of a chain of mountains that stretch across southern Europe and isolate Northern Europe from the
The Swiss Alps form part of a chain of mountains that stretch across southern Europe and isolate Northern Europe from the  The Alps are a popular tourist destination and are one of the most recognizable symbols of Switzerland. The tallest point in Switzerland,
The Alps are a popular tourist destination and are one of the most recognizable symbols of Switzerland. The tallest point in Switzerland,
 The Jura is a
The Jura is a  Structurally, the Jura consists of a sequence of folds, the formation of which is facilitated by an evaporitic decollement layer. The box folds are still relatively young, evidenced by their defining the shape of the overlying landscape (meaning they have not existed long enough to experience
Structurally, the Jura consists of a sequence of folds, the formation of which is facilitated by an evaporitic decollement layer. The box folds are still relatively young, evidenced by their defining the shape of the overlying landscape (meaning they have not existed long enough to experience
 Often referred to as the water tower of Europe, Switzerland has 6% of all freshwater reserves of the continent, while only accounting for 0.4% of its total area. The country shares five river basins and some of the largest lakes in western Europe with its neighbours. It is the source of several major European rivers that ultimately flow into the
Often referred to as the water tower of Europe, Switzerland has 6% of all freshwater reserves of the continent, while only accounting for 0.4% of its total area. The country shares five river basins and some of the largest lakes in western Europe with its neighbours. It is the source of several major European rivers that ultimately flow into the  Switzerland has considerable reserves of groundwater and a large number of lakes, large and small, can be found in most areas. The two most extensive, those of
Switzerland has considerable reserves of groundwater and a large number of lakes, large and small, can be found in most areas. The two most extensive, those of 
 The geography of Switzerland encompasses a wide range of
The geography of Switzerland encompasses a wide range of
 The population of Switzerland is heavily urbanised. In 2009, 74% of the 7,785,800 inhabitants lived in urban areas. The distribution of population is shaped by the topography of the country, the plateau being the most populous area and including the major cities of Switzerland. With a population density of 450 inhabitants per km2, it is one of the most densely populated region in Europe. There are large disparities of population densities between the cantons lying in the plateau and those lying in the Alps. Thus, the population densities of the cantons of Lucerne,
The population of Switzerland is heavily urbanised. In 2009, 74% of the 7,785,800 inhabitants lived in urban areas. The distribution of population is shaped by the topography of the country, the plateau being the most populous area and including the major cities of Switzerland. With a population density of 450 inhabitants per km2, it is one of the most densely populated region in Europe. There are large disparities of population densities between the cantons lying in the plateau and those lying in the Alps. Thus, the population densities of the cantons of Lucerne,
accessed December 2, 2008 With these numbers, Switzerland is 31st to 33rd among the 45 nations listed by United Nations
 Switzerland is facing a
Switzerland is facing a
File:Lago di Lugano3.jpg,
CIA World Factbook
Official on-line maps of Switzerland
{{Authority control
 The geography of Switzerland encompasses the geographical features of Switzerland, a mountainous and
The geography of Switzerland encompasses the geographical features of Switzerland, a mountainous and landlocked country
A landlocked country is a country that does not have territory connected to an ocean or whose coastlines lie on endorheic basins. There are currently 44 landlocked countries and 4 landlocked de facto states. Kazakhstan is the world's largest ...
located in Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
and Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the a ...
. Switzerland's natural landscape is marked by its numerous lakes and mountains. It is surrounded by 5 countries: Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
and Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein (), officially the Principality of Liechtenstein (german: link=no, Fürstentum Liechtenstein), is a German-speaking microstate located in the Alps between Austria and Switzerland. Liechtenstein is a semi-constitutional monarch ...
to the east, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
to the west, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
to the south and Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
to the north. Switzerland has a maximum north–south length of and an east–west length of about .
Switzerland is well known for the Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Swi ...
in the south and south east. North of the Alps, the Swiss Plateau
The Swiss Plateau or Central Plateau (german: Schweizer Mittelland; french: plateau suisse; it, altopiano svizzero) is one of the three major landscapes in Switzerland, lying between the Jura Mountains and the Swiss Alps. It covers about 30% of ...
runs along the east–west axis of the country. Most of the population of Switzerland lives on the rolling hills and plains of the plateau. The smaller Jura Mountains are located on the north west side of the plateau. Much of the northern border with Germany follows the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
, through the Rhine enters Switzerland near Schaffhausen
Schaffhausen (; gsw, Schafuuse; french: Schaffhouse; it, Sciaffusa; rm, Schaffusa; en, Shaffhouse) is a town with historic roots, a municipality in northern Switzerland, and the capital of the canton of the same name; it has an estimate ...
. The eastern border with Germany and a portion of Austria is drawn through Lake Constance (german: Bodensee). A portion of the southwest border with France is drawn through Lake Geneva
, image = Lake Geneva by Sentinel-2.jpg
, caption = Satellite image
, image_bathymetry =
, caption_bathymetry =
, location = Switzerland, France
, coords =
, lake_type = Glacial la ...
.
Switzerland is divided into 26 sovereign cantons. The cantons along the Swiss Plateau tend to be the most populous, industrial and religiously Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
. The cantons in the Alps tend to be less populous, Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, and have an agrarian or tourism-based economy.
Switzerland is divided by language as well. There are four national languages: German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
(spoken by 63.7% of population), French (by 20.4% of population), Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
(by 6.5%) and Romansh (0.5%). From Bern east (except Ticino
Ticino (), sometimes Tessin (), officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino,, informally ''Canton Ticino'' ; lmo, Canton Tesin ; german: Kanton Tessin ; french: Canton du Tessin ; rm, Chantun dal Tessin . ...
) the population generally speaks German. West of Bern, the population generally speaks French. In the southern canton of Ticino, most people speak Italian. Romansh, a group of dialects descended from Vulgar Latin
Vulgar Latin, also known as Popular or Colloquial Latin, is the range of non-formal registers of Latin spoken from the Late Roman Republic onward. Through time, Vulgar Latin would evolve into numerous Romance languages. Its literary counterpa ...
, is spoken in several regions in the canton of Graubünden.
Physical description
Switzerland extends between the parallels 45°49'05 and 47°48'30 lat. and the meridians 5° 57'23 and 10°29'31 long. It forms an irregular quadrilateral, of which the greatest length from east to west is , and the greatest breadth from north to south is nearly . Switzerland is a landlocked country, the closest coastline being at theGulf of Genoa
The Gulf of Genoa (''Golfo di Genova'') is the northernmost part of the Ligurian Sea. This Italian gulf is about wide from the city of Imperia in the west to La Spezia in the east. The largest city on its coast is Genoa, which has an importan ...
, 160 km south of Chiasso
Chiasso (; lmo, Ciass ) is a municipality in the district of Mendrisio in the canton of Ticino in Switzerland.
As the southernmost of Switzerland's municipalities, Chiasso is on the border with Italy, in front of Ponte Chiasso (a frazione of Co ...
. Its political boundaries often do not coincide with those of nature. The entire canton of Ticino
Ticino (), sometimes Tessin (), officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino,, informally ''Canton Ticino'' ; lmo, Canton Tesin ; german: Kanton Tessin ; french: Canton du Tessin ; rm, Chantun dal Tessin . ...
is south of the Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Swi ...
, as are the valleys of Simplon (Valais
Valais ( , , ; frp, Valês; german: Wallis ), more formally the Canton of Valais,; german: Kanton Wallis; in other official Swiss languages outside Valais: it, (Canton) Vallese ; rm, (Chantun) Vallais. is one of the 26 cantons forming the S ...
), Mesocco
Mesocco ( Lombard: ''Mesòch'') is a municipality in the Moesa Region in the Swiss canton of Graubünden.
History
The first human settlement in the area dates back to the Mesolithic era. Stone tools dating to about 6000 BC have been found in the ...
, Bregaglia
Bregaglia (Italian and rm, ) is a municipality in the Maloja Region in the canton of Grisons in Switzerland. It was formed by the 2010 merger of the municipalities of Bondo, Castasegna, Soglio, Stampa and Vicosoprano, all located in the Val ...
, Poschiavo
Poschiavo ( it, Poschiavo, lmo, Pusciaaf, german: Puschlav, rm, Puschlav) is a municipality in the Bernina Region in the canton of Grisons in Switzerland.
History
Poschiavo is first mentioned in 824 as ''in Postclave'' though this comes fro ...
and Müstair (all in Graubünden); the whole canton of Schaffhausen
The canton of Schaffhausen, also canton of Schaffouse (german: Kanton Schaffhausen; rm, Chantun Schaffusa; french: Canton de Schaffhouse; it, Canton Sciaffusa) is the northernmost canton of Switzerland. The principal city and capital of the ca ...
and part of that of Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese
, neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (BS ...
are north of the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
, while a large part of Graubünden lies to the east of the Rhine basin, and Porrentruy
Porrentruy (, fc, Poérreintru , german: Pruntrut) is a Swiss municipality and seat of the district of the same name located in the canton of Jura.
Porrentruy is home to National League team, HC Ajoie.
History
The first trace of human pre ...
is far down on the western slope of the Jura. Putting these exceptional cases aside, the physical geography of Switzerland may thus be described:
*On the south runs the main chain of the Alps, which is joined (at Mont Dolent
Mont Dolent () is a mountain in the Mont Blanc massif and lies on the border between Italy, Switzerland and France.
As a mountain, Mont Dolent is regarded as the tripoint between Italy, Switzerland and France, although the tripoint itself lies a ...
near Martigny
Martigny (; german: Martinach, ; la, Octodurum) is the capital city of the district of Martigny, canton of Valais, Switzerland. It lies at an elevation of , and its population is approximately 15000 inhabitants (''Martignerains'' or "Octoduriens ...
) by the lower ranges that rise south of Lake Geneva
, image = Lake Geneva by Sentinel-2.jpg
, caption = Satellite image
, image_bathymetry =
, caption_bathymetry =
, location = Switzerland, France
, coords =
, lake_type = Glacial la ...
, and which continues partly Swiss till close to Piz Lad on the east.
*To the north of this main chain there is another great range of mountains (wholly Swiss) only slightly inferior in extent and height, which starts from the hills known as the Jorat
The Jorat (German: "der Jurten") is the area of the Canton of Vaud (Switzerland) located between the Gros-de-Vaud, West and the Broye, East.
Geography
It is a hill range that stretches from above Lausanne at the South and stretches toward Payer ...
range above Lausanne
, neighboring_municipalities= Bottens, Bretigny-sur-Morrens, Chavannes-près-Renens, Cheseaux-sur-Lausanne, Crissier, Cugy, Écublens, Épalinges, Évian-les-Bains (FR-74), Froideville, Jouxtens-Mézery, Le Mont-sur-Lausanne, Lugrin (FR ...
, reaches maximum in the great snowy summits of the Bernese Alps
, topo_map= Swiss Federal Office of Topography swisstopo
, photo=BerneseAlps.jpg
, photo_caption=The Eiger, Mönch, and Jungfrau
, country= Switzerland
, subdivision1_type= Cantons
, subdivision1=
, parent= Western Alps
, borders_on=
, ...
and the Tödi group, before trending to the north near Chur
, neighboring_municipalities= Arosa, Churwalden, Tschiertschen-Praden, Domat/Ems, Felsberg, Malix, Trimmis, Untervaz, Pfäfers
, twintowns = Bad Homburg (Germany), Cabourg (France), Mayrhofen (Austria), Mondorf-les-Bains (Luxe ...
and, after rising once more in the Säntis
At above sea level, Säntis is the highest mountain in the Alpstein massif of northeastern Switzerland. It is also the culminating point of the whole Appenzell Alps, between Lake Walen and Lake Constance. Shared by three cantons, the mounta ...
group, dies away on the southern shore of Lake Constance.
*The Swiss portion of the main chain of the Alps and the great northern outlier run parallel to each other from Martigny to near Chur, while for a short distance they actually unite near Pizzo Rotondo
Pizzo Rotondo is a mountain in the Lepontine Alps. At 3,190 metres above sea level, it is the highest mountain lying on the border between the cantons of Ticino and Valais, as well as the highest summit of the Lepontine Alps lying between Nufe ...
(west of the St Gotthard Pass
german: Gotthardpass
, photo = File:Gotthardpass 2008.jpg
, photo_caption = The area of the Gotthard Pass from the west
, elevation_m = 2106
, elevation_ref =
, traversed = National Road 2 Old paved road ( Tremola) Gotthard Rail Tunnel Go ...
), parting again near the Oberalp Pass
Oberalp Pass ( rm, Alpsu or ''Cuolm d'Ursera''; german: Oberalppass) (2044 meters above sea level) is a high mountain pass in the Swiss Alps connecting the cantons of Graubünden and Uri between Disentis/Mustér and Andermatt.
Winter closure
...
(east of the St Gotthard). Between these two great snowclad ranges flow two of the mightiest European rivers, the Rhône
The Rhône ( , ; wae, Rotten ; frp, Rôno ; oc, Ròse ) is a major river in France and Switzerland, rising in the Alps and flowing west and south through Lake Geneva and southeastern France before discharging into the Mediterranean Sea. At Ar ...
towards the west and the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
towards the east, their headwaters being only separated by the tangled mountain mass between Pizzo Rotondo and the Oberalp Pass, which sends the Reuss towards the north and the Ticino
Ticino (), sometimes Tessin (), officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino,, informally ''Canton Ticino'' ; lmo, Canton Tesin ; german: Kanton Tessin ; french: Canton du Tessin ; rm, Chantun dal Tessin . ...
towards the south.
*To the north of the great northern outlier rises the Jura range, a huge spur of the Alps (with which it is connected by the Jorat range), while between the northern outlier and the Jura extends what may be called the plains or plateau of Switzerland, consisting almost wholly of the undulating valley of the Aare
The Aare () or Aar () is a tributary of the High Rhine and the longest river that both rises and ends entirely within Switzerland.
Its total length from its source to its junction with the Rhine comprises about , during which distance it descen ...
(below Thun
, neighboring_municipalities= Amsoldingen, Heiligenschwendi, Heimberg, Hilterfingen, Homberg, Schwendibach, Spiez, Steffisburg, Thierachern, Uetendorf, Zwieselberg
, twintown =
, website = www.thun.ch
Thun (french: Thou ...
) with its numerous affluents. To that river valley, the valley of the Thur (a direct affluent of the Rhine), that lies between the Aare basin and the Rhine basin (Lake Constance) must be added.
Putting aside the valleys of the Ticino
Ticino (), sometimes Tessin (), officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino,, informally ''Canton Ticino'' ; lmo, Canton Tesin ; german: Kanton Tessin ; french: Canton du Tessin ; rm, Chantun dal Tessin . ...
and Inn
Inns are generally establishments or buildings where travelers can seek lodging, and usually, food and drink. Inns are typically located in the country or along a highway; before the advent of motorized transportation they also provided accommo ...
, Switzerland may thus be described as consisting of three great river valleys (Rhône, Rhine and Aare) with the smaller one of the Thur, which all lie to the north of the main chain of the Alps and include the region between the Alps and the Jura. If matters are examined more carefully, it can be noted that the Rhône and Rhine valleys are shut off from that of the Aare (and of the Thur) by the great northern outlier of the Alps, which consists of the Bernese and Glarus Alps. Two wide and undulating valleys (Aare and Thur) and two deeply cut trenches (Rhône and Rhine) thus lie on the northern slope of the Alps, to the north and south respectively of the great northern outlier of the Alps. The main chain of the Alps rises in Swiss territory to the height of in the loftiest summit or Dufourspitze (wholly Swiss) of Monte Rosa
:
, other_name = Monte Rosa massif
, translation = Mount Rose
, photo = Dufourspitze (Monte Rosa) and Monte Rosa Glacier as seen from Gornergrat, Wallis, Switzerland, 2012 August.jpg
, photo_caption = Central Mon ...
, though the Dom (), in the Mischabel range, is the highest mountain mass which is entirely within Switzerland. The great northern outlier attains a height of in the Finsteraarhorn
The Finsteraarhorn () is a mountain lying on the border between the cantons of Bern and Valais. It is the highest mountain of the Bernese Alps and the most prominent peak of Switzerland. The Finsteraarhorn is the ninth-highest mountain and thi ...
, while the lowest level () within the Confederation, is on Lake Maggiore
Lake Maggiore (, ; it, Lago Maggiore ; lmo, label=Western Lombard, Lagh Maggior; pms, Lagh Magior; literally 'Greater Lake') or Verbano (; la, Lacus Verbanus) is a large lake located on the south side of the Alps. It is the second largest l ...
(on the course of the Ticino). The highest permanently inhabited village in Switzerland is Juf
Juf () is a village in the municipality of Avers in the canton of Grisons, Switzerland. At above sea level, it is historically the highest village with permanent residents in Europe, as well as one of its coldest localities. As of 2016, Juf had ...
() at the head of the Avers valley (a tributary of the Rhine), while the lowest is Ascona (), on Lake Maggiore.
Geology
Different geological phenomena shaped the actual landscapes of Switzerland. The Alpine orogeny had the most visible effects on the landscape: this term covers entire geological movements contributing to the Alps’ formation. A crystalline basement formed at the beginning of thePaleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon.
The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838
by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ' ...
era, between 540 and 360 million years ago. Later, between 205 and 96 million years ago, the alpine ocean or Tethys Ocean
The Tethys Ocean ( el, Τηθύς ''Tēthús''), also called the Tethys Sea or the Neo-Tethys, was a prehistoric ocean that covered most of the Earth during much of the Mesozoic Era and early Cenozoic Era, located between the ancient continents ...
formed between Eurasia and Africa. The ocean reached its maximum width at the end of Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of ...
period, 135 million years ago. The collision between the Eurasian and African plates made it progressively disappear. This plate collision (still in progress) began 100 million years ago. The Alps resulted from this geological movement, the two plates creating folding zones. The Central Plateau is mainly composed of molasse
__NOTOC__
The term "molasse" () refers to sandstones, shales and conglomerates that form as terrestrial or shallow marine deposits in front of rising mountain chains. The molasse deposits accumulate in a foreland basin, especially on top of flysc ...
, a sedimentary rock that formed at the bottom of the Tethys ocean.
Switzerland is situated in a relatively tectonically inactive area, although the city of Basel was completely destroyed in 1356 by an earthquake, the largest historical seismic event in central Europe. The most seismically active regions are the Rhine Rift Valley
The Upper Rhine Plain, Rhine Rift Valley or Upper Rhine Graben (German: ''Oberrheinische Tiefebene'', ''Oberrheinisches Tiefland'' or ''Oberrheingraben'', French: ''Vallée du Rhin'') is a major rift, about and on average , between Basel in the so ...
(region of Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese
, neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (BS ...
) and the Valais
Valais ( , , ; frp, Valês; german: Wallis ), more formally the Canton of Valais,; german: Kanton Wallis; in other official Swiss languages outside Valais: it, (Canton) Vallese ; rm, (Chantun) Vallais. is one of the 26 cantons forming the S ...
.
Physiographic divisions
 Switzerland is divided in three main geographic regions: the Swiss Alps, the Central Plateau and the Jura, each corresponding to very different geological realities. In addition, two small regions are not part of those three. The first, north of the
Switzerland is divided in three main geographic regions: the Swiss Alps, the Central Plateau and the Jura, each corresponding to very different geological realities. In addition, two small regions are not part of those three. The first, north of the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
in the Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese
, neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (BS ...
area, is situated beyond the Jura. The second, on the south in the Mendrisio
Mendrisio (; lmo, label= Ticinese, Mendris ) is a municipality in the district of Mendrisio in the canton of Ticino in Switzerland.
Mendrisio is the seat of the Accademia di Architettura of the university of Italian-speaking Switzerland (U ...
area, is located in the Po Valley. But these two territories are not extensive in comparison to the total area of the country.
The Swiss Alps occupy the southern part of Switzerland. They were formed by the thrust of the African plate, which also caused the formation of the Jura in the north-east and the plateau between the two massifs. In terms of area the Alps constitute about 60% of the country, the plateau 30% and the Jura 10%.
The rugged terrain of the Jura and the Alps are very sparsely populated, except for some large valleys such as the Valais. Most of the population lives on the plateau where the country's major cities such as Geneva
, neighboring_municipalities= Carouge, Chêne-Bougeries, Cologny, Lancy, Grand-Saconnex, Pregny-Chambésy, Vernier, Veyrier
, website = https://www.geneve.ch/
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevr ...
, Zurich, Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese
, neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (BS ...
, Lucern
, neighboring_municipalities= Adligenswil, Ebikon, Emmen, Horw, Kriens, Malters, Meggen, Neuenkirch
Lucerne ( , ; High Alemannic: ''Lozärn'') or Luzern ()Other languages: gsw, Lozärn, label=Lucerne German; it, Lucerna ; rm, Lucerna . is ...
, and Bern are located.
Central Plateau
Lake Neuchâtel
Lake Neuchâtel (french: Lac de Neuchâtel ; frp, Lèc de Nôchâtél; german: Neuenburgersee) is a lake primarily in Romandy, in the French-speaking part of Switzerland. The lake lies mainly in the canton of Neuchâtel, but is also shared by t ...
(), is located in the Swiss Plateau.
 The Swiss Plateau is crossed by three great river valleys (
The Swiss Plateau is crossed by three great river valleys (Rhône
The Rhône ( , ; wae, Rotten ; frp, Rôno ; oc, Ròse ) is a major river in France and Switzerland, rising in the Alps and flowing west and south through Lake Geneva and southeastern France before discharging into the Mediterranean Sea. At Ar ...
, Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
and Aare
The Aare () or Aar () is a tributary of the High Rhine and the longest river that both rises and ends entirely within Switzerland.
Its total length from its source to its junction with the Rhine comprises about , during which distance it descen ...
) and the smaller Thur valley. While the headwaters
The headwaters of a river or stream is the farthest place in that river or stream from its estuary or downstream confluence with another river, as measured along the course of the river. It is also known as a river's source.
Definition
The ...
of these four rivers all lie in the Alps, they all cut across the plateau between the Alps and the Jura mountains. Near Schaffhausen
Schaffhausen (; gsw, Schafuuse; french: Schaffhouse; it, Sciaffusa; rm, Schaffusa; en, Shaffhouse) is a town with historic roots, a municipality in northern Switzerland, and the capital of the canton of the same name; it has an estimate ...
the Rhine passes through the Rhine Falls
, photo = File:SBB RABe 514 DTZ Rheinfall.jpg
, photo_width = 280
, photo_caption = Rhine Falls with Rheinfall Bridge and Laufen Castle
, location = On the border between the cantons of Schaffhausen and Zürich next to Schaffhausen, i ...
, Europe's largest waterfall. The Rhine Falls are wide and .
The plateau occupies about one third of the land area of Switzerland, and about two thirds of the population live in this area. The population density on the plateau averages about 450 people per km2 (1,166 per square mile). In the regions around Lake Geneva, Lake Zurich
__NOTOC__
Lake Zurich (Swiss German/ Alemannic: ''Zürisee''; German: ''Zürichsee''; rm, Lai da Turitg) is a lake in Switzerland, extending southeast of the city of Zürich. Depending on the context, Lake Zurich or ''Zürichsee'' can be used to ...
and other cities, the population density exceeds 1000 people per km2. As well as the majority of the population, the Swiss Plateau is also home to the majority of industry, manufacturing and farming in Switzerland. The farms are generally small and very organized. Most farms include small meadows alternating with fields with a variety of crops and small wooded areas.
Alps
 The Swiss Alps form part of a chain of mountains that stretch across southern Europe and isolate Northern Europe from the
The Swiss Alps form part of a chain of mountains that stretch across southern Europe and isolate Northern Europe from the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ...
. Several important passes through the Alps are located in Switzerland, and control of the passes has been important throughout Switzerland's history. The Alps have an average altitude of and cover nearly two thirds of the total surface area. Within the Alps there are 48 mountains that are or higher.
The Alps are the watershed of Western Europe. The Rhine, together with its tributaries the Aare and the Thur drain about two thirds of the water into the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea, epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the ...
. The Rhône
The Rhône ( , ; wae, Rotten ; frp, Rôno ; oc, Ròse ) is a major river in France and Switzerland, rising in the Alps and flowing west and south through Lake Geneva and southeastern France before discharging into the Mediterranean Sea. At Ar ...
and the Ticino
Ticino (), sometimes Tessin (), officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino,, informally ''Canton Ticino'' ; lmo, Canton Tesin ; german: Kanton Tessin ; french: Canton du Tessin ; rm, Chantun dal Tessin . ...
drain about 18% of the water into the Mediterranean Sea. The Inn
Inns are generally establishments or buildings where travelers can seek lodging, and usually, food and drink. Inns are typically located in the country or along a highway; before the advent of motorized transportation they also provided accommo ...
which flows into the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , p ...
outside of Switzerland drains about 4.4% of the water into the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
. The Swiss Alps also contain many of Central Europe's glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as ...
s. There are about 1,800 glaciers which cover of the total glaciated area of the Alps.
 The Alps are a popular tourist destination and are one of the most recognizable symbols of Switzerland. The tallest point in Switzerland,
The Alps are a popular tourist destination and are one of the most recognizable symbols of Switzerland. The tallest point in Switzerland, Monte Rosa
:
, other_name = Monte Rosa massif
, translation = Mount Rose
, photo = Dufourspitze (Monte Rosa) and Monte Rosa Glacier as seen from Gornergrat, Wallis, Switzerland, 2012 August.jpg
, photo_caption = Central Mon ...
() in Canton Valais
Valais ( , , ; frp, Valês; german: Wallis ), more formally the Canton of Valais,; german: Kanton Wallis; in other official Swiss languages outside Valais: it, (Canton) Vallese ; rm, (Chantun) Vallais. is one of the 26 cantons forming the S ...
, is located in the Alps as is tallest mountain wholly in Switzerland, the Dom (). One of the most recognizable symbols of Switzerland, the Matterhorn
The (, ; it, Cervino, ; french: Cervin, ; rm, Matterhorn) is a mountain of the Alps, straddling the main watershed and border between Switzerland and Italy. It is a large, near-symmetric pyramidal peak in the extended Monte Rosa area of the ...
, is also located in the Alps. The Matterhorn () is the seventh highest peak in the Swiss Alps and is the most photographed mountain in Switzerland. The tallest mountain in the northern outlier or Bernese Alps
, topo_map= Swiss Federal Office of Topography swisstopo
, photo=BerneseAlps.jpg
, photo_caption=The Eiger, Mönch, and Jungfrau
, country= Switzerland
, subdivision1_type= Cantons
, subdivision1=
, parent= Western Alps
, borders_on=
, ...
is the Finsteraarhorn
The Finsteraarhorn () is a mountain lying on the border between the cantons of Bern and Valais. It is the highest mountain of the Bernese Alps and the most prominent peak of Switzerland. The Finsteraarhorn is the ninth-highest mountain and thi ...
().
Switzerland encompasses a significant portion of the south side of the Alps. Most of it is constituted by the canton of Ticino
Ticino (), sometimes Tessin (), officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino,, informally ''Canton Ticino'' ; lmo, Canton Tesin ; german: Kanton Tessin ; french: Canton du Tessin ; rm, Chantun dal Tessin . ...
, almost reaching the plains of the Po and including Switzerland's lowest point on Lake Maggiore (). The canton of Graubünden is also partially located on the south side of the Alps with the four valleys of Misox
The ''Valle Mesolcina'', also known as the ''Val Mesolcina'' or ''Misox'' (German), is an alpine valley of the Grisons, Switzerland, stretching from the San Bernardino Pass to Grono where it joins the Calanca Valley. It is the valley formed by ...
, Bregaglia
Bregaglia (Italian and rm, ) is a municipality in the Maloja Region in the canton of Grisons in Switzerland. It was formed by the 2010 merger of the municipalities of Bondo, Castasegna, Soglio, Stampa and Vicosoprano, all located in the Val ...
, Poschiavo
Poschiavo ( it, Poschiavo, lmo, Pusciaaf, german: Puschlav, rm, Puschlav) is a municipality in the Bernina Region in the canton of Grisons in Switzerland.
History
Poschiavo is first mentioned in 824 as ''in Postclave'' though this comes fro ...
and Müstair. Finally, the canton of Valais
Valais ( , , ; frp, Valês; german: Wallis ), more formally the Canton of Valais,; german: Kanton Wallis; in other official Swiss languages outside Valais: it, (Canton) Vallese ; rm, (Chantun) Vallais. is one of the 26 cantons forming the S ...
comprises the upper Diveria
The Diveria (Walliser German: ''Churumm Bach'';In this part of the Haut-Valais, the language spoken is the Walliser German dialect. German: ''KrummBach'') is an Alpine river which flows through Switzerland ( Canton Valais) and Italy ( Provinc ...
valley, located south of the Simplon Pass
The Simplon Pass (french: Col du Simplon; german: Simplonpass; it, Passo del Sempione, Lombard: ''Pass del Sempiün'') () is a high mountain pass between the Pennine Alps and the Lepontine Alps in Switzerland. It connects Brig in the canto ...
.
Jura
 The Jura is a
The Jura is a limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
mountain range running from Lake Geneva to the Rhine river. This area makes up about 12% of Switzerland's land area. Located about above sea level, this region is characterized by a limestone highland with deep river valleys.
The limestone rock in the Jura is a Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of ...
period rock with numerous fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
s and dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
tracks. The name Jurassic actually refers to the Jura region where these fossils were studied at the end of the 18th century. The Jura is considered one of the most important sites for dinosaur footprints in the world. In one area near the village of Courtedoux, over 13,000 footprints were discovered in between 2002 and 2011.
The range is being continually built up and decreasing in width by mountain building, accommodating the compression from alpine folding as the main Alpine orogenic front moves roughly northwards. The deformation becomes less pervasive away from the younger, more active Alpine mountain building.
 Structurally, the Jura consists of a sequence of folds, the formation of which is facilitated by an evaporitic decollement layer. The box folds are still relatively young, evidenced by their defining the shape of the overlying landscape (meaning they have not existed long enough to experience
Structurally, the Jura consists of a sequence of folds, the formation of which is facilitated by an evaporitic decollement layer. The box folds are still relatively young, evidenced by their defining the shape of the overlying landscape (meaning they have not existed long enough to experience erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is dis ...
). The folds comprise three major ( lithological units) bands of building evidence dated roughly by era
An era is a span of time defined for the purposes of chronology or historiography, as in the regnal eras in the history of a given monarchy, a calendar era used for a given calendar, or the geological eras defined for the history of Earth.
Comp ...
: the Malm
is the administrative centre of the municipality of Steinkjer in Trøndelag county, Norway. The village of Malm is located along the Breistadsundet strait which flows into the Trondheimsfjorden. The village of Bartnes lies across the strait fro ...
, Dogger, and Lias
Lias may refer to:
Geology
* Lias Formation, a geologic formation in France
*Lias Group, a lithostratigraphic unit in western Europe
* Early Jurassic, an epoch
People
* Godfrey Lias, British author
* Mohd Shamsudin Lias (born 1953), Malaysian ...
(part of the Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of ...
Geologic period
The geologic time scale, or geological time scale, (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochr ...
). Each era of folding represents effects on a previously shallow marine environment as evidenced by beds with particular carbonate
A carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid (H2CO3), characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion with the formula . The word ''carbonate'' may also refer to a carbonate ester, an organic compound containing the carbonate ...
sequences, containing abundant bioclasts and oolitic divisions between layers (called horizons).
The Jura Mountains rise in Swiss territory to a height of at Mont Tendre
Mont Tendre is a mountain of the Jura, located between the valley of Joux and the basin of Lake Geneva in the canton of Vaud. With an elevation of 1,679 metres above sea level, it is the highest summit of the Swiss portion of the Jura Mountain ...
. Other high summits are La Dôle (), the Chasseron () and the Chasseral
The Chasseral is a mountain of the Jura Mountains, overlooking Lake Biel in the Swiss canton of Bern. With an elevation of 1,606 metres above sea level, the Chasseral is the highest summit in the canton of Bern outside the Alps. It is also both ...
(), all located in the western part of the range, in the cantons of Vaud
Vaud ( ; french: (Canton de) Vaud, ; german: (Kanton) Waadt, or ), more formally the canton of Vaud, is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of ten districts and its capital city is Lausanne. Its coat of arms b ...
, Neuchâtel and Bern.
Hydrology
 Often referred to as the water tower of Europe, Switzerland has 6% of all freshwater reserves of the continent, while only accounting for 0.4% of its total area. The country shares five river basins and some of the largest lakes in western Europe with its neighbours. It is the source of several major European rivers that ultimately flow into the
Often referred to as the water tower of Europe, Switzerland has 6% of all freshwater reserves of the continent, while only accounting for 0.4% of its total area. The country shares five river basins and some of the largest lakes in western Europe with its neighbours. It is the source of several major European rivers that ultimately flow into the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea, epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the ...
(Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
), into the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ...
(Rhône
The Rhône ( , ; wae, Rotten ; frp, Rôno ; oc, Ròse ) is a major river in France and Switzerland, rising in the Alps and flowing west and south through Lake Geneva and southeastern France before discharging into the Mediterranean Sea. At Ar ...
), into the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
(Inn
Inns are generally establishments or buildings where travelers can seek lodging, and usually, food and drink. Inns are typically located in the country or along a highway; before the advent of motorized transportation they also provided accommo ...
, through the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , p ...
) and into the Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to t ...
(Ticino
Ticino (), sometimes Tessin (), officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino,, informally ''Canton Ticino'' ; lmo, Canton Tesin ; german: Kanton Tessin ; french: Canton du Tessin ; rm, Chantun dal Tessin . ...
, through the Po and Rom
Rom, or ROM may refer to:
Biomechanics and medicine
* Risk of mortality, a medical classification to estimate the likelihood of death for a patient
* Rupture of membranes, a term used during pregnancy to describe a rupture of the amniotic sac
* ...
through the Adige
The Adige (; german: Etsch ; vec, Àdexe ; rm, Adisch ; lld, Adesc; la, Athesis; grc, Ἄθεσις, Áthesis, or , ''Átagis'') is the second-longest river in Italy, after the Po. It rises near the Reschen Pass in the Vinschgau in the pro ...
).
Most of the great Swiss rivers, being in their origin mere mountain torrents, tend to overflow their banks. Much has been done to prevent this by embanking them, regaining arable land: the Rhine (between Bad Ragaz and Lake Constance), the Rhône, the Aare, the Reuss and in particular the great works on the Linth
The Linth (pronounced "lint") is a Swiss river that rises near the village of Linthal in the mountains of the canton of Glarus, and eventually flows into the Obersee section of Lake Zurich. It is about in length.
The water power of the Lin ...
(carried out 1807–1810 by Hans Conrad Escher, earning him the surname of "Von der Linth") and the Zihl
The river Thielle (french: La Thielle, or La Thièle, german: Zihl), is a tributary to the Aare, in the Swiss Seeland.
The Thielle results from the merging of the Orbe and Talent, northeast of the little city of Orbe in the Swiss canton of Vaud ...
near the lakes of Neuchâtel and Biel
, french: Biennois(e)
, neighboring_municipalities= Brügg, Ipsach, Leubringen/Magglingen (''Evilard/Macolin''), Nidau, Orpund, Orvin, Pieterlen, Port, Safnern, Tüscherz-Alfermée, Vauffelin
, twintowns = Iserlohn (Germany) ...
, while the diversion of the Kander from its junction with the Aare to a channel by which it flows into Lake Thun
Lake Thun (german: Thunersee) is an Alpine lake in the Bernese Oberland in Switzerland named after the city of Thun, on its northern shore. At in surface area, it is the largest Swiss lake entirely within a single canton.
The lake was created af ...
was effected as early as 1714.
 Switzerland has considerable reserves of groundwater and a large number of lakes, large and small, can be found in most areas. The two most extensive, those of
Switzerland has considerable reserves of groundwater and a large number of lakes, large and small, can be found in most areas. The two most extensive, those of Geneva
, neighboring_municipalities= Carouge, Chêne-Bougeries, Cologny, Lancy, Grand-Saconnex, Pregny-Chambésy, Vernier, Veyrier
, website = https://www.geneve.ch/
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevr ...
and of Constance, balance each other, as it were, at the south-west and north-east corners of the land. But neither of these is wholly Swiss, this distinction being claimed by the next in size, that of Neuchâtel, Lake Maggiore
Lake Maggiore (, ; it, Lago Maggiore ; lmo, label=Western Lombard, Lagh Maggior; pms, Lagh Magior; literally 'Greater Lake') or Verbano (; la, Lacus Verbanus) is a large lake located on the south side of the Alps. It is the second largest l ...
(partly Swiss only) coming next in the list, and being followed by the wholly Swiss lakes of Lucerne and of Zurich. Then come Lake Lugano
__NOTOC__
Lake Lugano ( it, Lago di Lugano or , from la, Ceresius lacus; lmo, Lagh de Lugan) is a glacial lake which is situated on the border between southern Switzerland and northern Italy. The lake, named after the city of Lugano, is situated ...
, Lake Thun
Lake Thun (german: Thunersee) is an Alpine lake in the Bernese Oberland in Switzerland named after the city of Thun, on its northern shore. At in surface area, it is the largest Swiss lake entirely within a single canton.
The lake was created af ...
, Lake Biel
__NOTOC__
Lake Bienne or Lake Biel (french: Lac de Bienne ; german: Bielersee) is a lake in western Switzerland. Together with Lake Morat and Lake Neuchâtel, it is one of the three large lakes in the Jura region of Switzerland. It lies approxim ...
, Lake Zug
__NOTOC__
Lake Zug (german: Zugersee) is a lake in Central Switzerland, situated between Lake Lucerne and Lake Zurich. It stretches for 14 km between Arth and the Cham- Zug bay. The Lorze as the main feeder river empties its waters into the ...
, Lake Brienz
Lake Brienz (german: Brienzersee) is a lake just north of the Alps, in the canton of Bern in Switzerland. It has a length of about , a width of and a maximum depth of . Its area is ; the surface is above the sea-level. It is fed, among others, by ...
, Lake Walenstadt and Lake Murten. These thirteen only are over in extent. Ten of them are in the Rhine basin (also in that of the Aare), two (Maggiore and Lugano) in that of the Po, and one (Geneva) in that of the Rhône. There are no large lakes in the Swiss portion of the Inn
Inns are generally establishments or buildings where travelers can seek lodging, and usually, food and drink. Inns are typically located in the country or along a highway; before the advent of motorized transportation they also provided accommo ...
basin, the most extensive being that of Sils Sils or SILS may refer to:
Places
*Sils, Girona, a municipality in the ''comarca'' of Selva in Catalonia, Spain
** Lake Sils (Catalonia), an ancient lake near Sils, Catalonia, Spain
** Lake Sils, a lake in the Upper Engadine in the Grisons, Switzer ...
. Smaller Alpine lakes such as the Oeschinensee are innumerable, and often constitute popular tourist destination. Since the twentieth century a large number of dams have been built in the Alps and elsewhere, resulting in many artificial lakes. The largest are the Sihlsee
__NOTOC__
The Sihlsee (in English sometimes called ''Lake Sihl'') is an artificial lake in the Swiss canton of Schwyz, near the town of Einsiedeln. The lake was created by damming the river Sihl and flooding a section of the upper Sihl Valley.
T ...
and the Lake of Gruyère both approximately in extent. Also notable is Lac des Dix
Lac is the resinous secretion of a number of species of lac insects, of which the most commonly cultivated is ''Kerria lacca''.
Cultivation begins when a farmer gets a stick that contains eggs ready to hatch and ties it to the tree to be infes ...
, withheld by the Grande Dixence
__NOTOC__
The Grande Dixence Dam is a concrete gravity dam on the Dixence at the head of the Val d'Hérémence in the canton of Valais in Switzerland. At high, it is the tallest gravity dam in the world, sixth tallest dam overall, and the tall ...
, the tallest gravity dam in the world.
In total, lakes and reservoirs contain 50% of the stored water, glaciers 28%, groundwater 20% and rivers 2%.

Climate
climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in an area, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorologi ...
s, from subtropical to perennial snow climate. However, the lowlands are part of the temperate zone
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout t ...
and do typically neither experience extreme temperatures nor extreme weather conditions. In the Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
, the Swiss Plateau
The Swiss Plateau or Central Plateau (german: Schweizer Mittelland; french: plateau suisse; it, altopiano svizzero) is one of the three major landscapes in Switzerland, lying between the Jura Mountains and the Swiss Alps. It covers about 30% of ...
and most low-elevation areas are at the transition between oceanic climate (Cfb) and continental climate (Dfb). As a consequence, all four seasons (spring, summer, autumn and winter) are well marked and present distinct weather conditions. At the same time, the influence of the nearby seas (especially the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
) tends to prevent extreme temperatures in summer and winter, with changeable, often overcast weather. The Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Swi ...
, and in a minor way the Jura Mountains, have a considerable impact on the Swiss climate. They influence it both on a horizontal level, by compartmentalizing it into distinct areas, and on a vertical level, by stratificating it into distinct layers. As a result, four other Köppen climate types are also found in Switzerland: humid subtropical climate (Cfa), subarctic climate (Dfc), tundra climate
The tundra climate is a polar climate sub-type located in high latitudes and high mountains. undra climate https://www.britannica.com/science/tundra-climateThe Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica, 2019 It is classified as ET according to Köppen ...
(ET) and ice cap climate
An ice cap climate is a polar climate where no mean monthly temperature exceeds . The climate covers areas in or near the high latitudes (65° latitude) to polar regions (70–90° north and south latitude), such as Antarctica, some of the northe ...
(EF).
At lower altitudes, the weather is generally moderate. On the Plateau, freezing temperatures generally occur during December-early March with an average temperature of for elevations between . On the Plateau, the average precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
is with a range of about . Ticino, on the south side of the Alps, is usually warmer, and wetter than the Plateau, with often different weather conditions, which are particularly noticeable when crossing the Gotthard or other major tunnels through the Alps.
Horizontally, the low-elevation regions having a distinct climate are essentially the Plateau (north of the Alps), southern Switzerland (south of the Alps) and the inner valleys (neither really north of south of the Alps but well within them). To those can be added the northerly regions of Ajoie
The Ajoie (german: Elsgau, Franc-Comtois: ''Aidjoue'') is an historic region roughly coinciding with Porrentruy District in the canton of Jura in northwestern Switzerland.
It is a part of the Jura plain, composed of six geographic areas:
* th ...
, Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese
, neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (BS ...
and Schaffhausen
Schaffhausen (; gsw, Schafuuse; french: Schaffhouse; it, Sciaffusa; rm, Schaffusa; en, Shaffhouse) is a town with historic roots, a municipality in northern Switzerland, and the capital of the canton of the same name; it has an estimate ...
(well beyond the Jura Mountains), which are comparable to the Plateau. In those regions, the lowest averages temperatures can be found on the Plateau ( Bern: ) or north of the Jura Mountains (Fahy
Fahy is a municipality in the district of Porrentruy in the canton of Jura in Switzerland.
History
It was mentioned in 1177 as ''Fahyl'' when it was one of the possessions of the priory of Lanthenans. In 1477, the bishop of Basel affirmed th ...
: ). On the other hand, the highest average temperatures are found south of the Alps (Locarno
, neighboring_municipalities= Ascona, Avegno, Cadenazzo, Cugnasco, Gerra (Verzasca), Gambarogno, Gordola, Lavertezzo, Losone, Minusio, Muralto, Orselina, Tegna, Tenero-Contra
, twintowns =* Gagra, Georgia
* Karlovy Vary, Czech Republic
...
: , Lugano
Lugano (, , ; lmo, label=Ticinese dialect, Ticinese, Lugan ) is a city and municipality in Switzerland, part of the Lugano District in the canton of Ticino. It is the largest city of both Ticino and the Italian-speaking southern Switzerland. Luga ...
: ), which are partially subtropical. The precipitation levels are also deeply affected by the Alps, with the highest rainfalls being experienced south of the Alps (Locarno: , Lugano
Lugano (, , ; lmo, label=Ticinese dialect, Ticinese, Lugan ) is a city and municipality in Switzerland, part of the Lugano District in the canton of Ticino. It is the largest city of both Ticino and the Italian-speaking southern Switzerland. Luga ...
: ). In general, the proximity to the Alpine foothills increases the precipitations (Interlaken
Interlaken (; lit.: ''between lakes'') is a Swiss town and municipality in the Interlaken-Oberhasli administrative district in the canton of Bern. It is an important and well-known tourist destination in the Bernese Oberland region of the Swiss A ...
), Lucerne: ), while places further away from the Alps experience less precipitation (Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese
, neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (BS ...
: ). The driest regions of the country are, however, deep within the Alps (the inner valleys), particularly in Valais (Sion
Sion may refer to
* an alternative transliteration of Zion
People
* Sion (name) or Siôn, a Welsh and other given name and surname, including a list of people and fictional characters with the name
* Shion or Sion, a Japanese given name
Pl ...
: ), which is often described as "semi-arid", but also in Graubünden (Chur
, neighboring_municipalities= Arosa, Churwalden, Tschiertschen-Praden, Domat/Ems, Felsberg, Malix, Trimmis, Untervaz, Pfäfers
, twintowns = Bad Homburg (Germany), Cabourg (France), Mayrhofen (Austria), Mondorf-les-Bains (Luxe ...
: ). Precipitation levels do not always negatively correlate with sunshine hours. While Locarno is one of the wettest low-elevation locations in the country, it is also the one with the most sunshine hours (2,171). In comparison, the drier locations on the Plateau experience much less sunshine hours ( Lucerne: 1,570, Zurich: 1,544). Being sheltered by the mountains, the regions well within the Alps also naturally experience more sunshine hours than the north side of the Alps (Sion: 2,093, Chur: 1,692).
The widest range of climates in Switzerland is spread vertically. As the elevation above sea-level ranges from , many ecosystems
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syst ...
are naturally found, from the regions of olives, vines, oaks and beeches, pines and firs, to those of the high mountain pastures, rhododendrons, and of eternal snow. In general, rainfall increase with elevation, while temperature decrease with it. Just above the plains and the foothills zone, at roughly , is the montane zone, which still encompasses numerous inhabited regions of the Alps and Jura Mountains. In the montane zone, which comprehends a large diversity of ecosystems, coniferous trees and snowfall progressively replace deciduous tree and rainfall. At roughly is the tree line
The tree line is the edge of the habitat at which trees are capable of growing. It is found at high elevations and high latitudes. Beyond the tree line, trees cannot tolerate the environmental conditions (usually cold temperatures, extreme snow ...
, which marks the beginning of the Alpine zone
Alpine tundra is a type of natural region or biome that does not contain trees because it is at high elevation, with an associated alpine climate, harsh climate. As the latitude of a location approaches the poles, the threshold elevation for alp ...
. The latter marks the end of the inhabited regions as well, with a few exceptions, such as Juf
Juf () is a village in the municipality of Avers in the canton of Grisons, Switzerland. At above sea level, it is historically the highest village with permanent residents in Europe, as well as one of its coldest localities. As of 2016, Juf had ...
. The final layer lies above . It is the snow zone (ice cap climate
An ice cap climate is a polar climate where no mean monthly temperature exceeds . The climate covers areas in or near the high latitudes (65° latitude) to polar regions (70–90° north and south latitude), such as Antarctica, some of the northe ...
). It only concerns the high Alps, notably the Bernese Alps
, topo_map= Swiss Federal Office of Topography swisstopo
, photo=BerneseAlps.jpg
, photo_caption=The Eiger, Mönch, and Jungfrau
, country= Switzerland
, subdivision1_type= Cantons
, subdivision1=
, parent= Western Alps
, borders_on=
, ...
and Pennine Alps
The Pennine Alps (german: Walliser Alpen, french: Alpes valaisannes, it, Alpi Pennine, la, Alpes Poeninae), also known as the Valais Alps, are a mountain range in the western part of the Alps. They are located in Switzerland (Valais) and Italy ...
. The coldest meteorological station is at the Jungfraujoch
The Jungfraujoch (German: lit. "maiden saddle") is a saddle connecting two major 4000ers of the Bernese Alps: the Jungfrau and the Mönch. It lies at an elevation of above sea level and is directly overlooked by the rocky prominence of the Sphinx ...
, and overlook one of Europe's largest glaciers. The Jura and Alpine foothills have more precipitation than the plains, with an average of , while the high Alps may have over .
Political divisions and greater regions
As a federal state, Switzerland is composed of 26 cantons, which are further divided into districts andmunicipalities
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality'' may also mean the go ...
. Each canton was a fully sovereign state with its own borders, army and currency from the Treaty of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia (german: Westfälischer Friede, ) is the collective name for two peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought pea ...
(1648) until the establishment of the Swiss federal state in 1848. There are considerable differences between the individual cantons, most particularly in terms of population and geographical area; hence seven larger and more homogeneous regions have been defined. They do not, however, constitute administrative units and are mostly used for statistical and economic purposes.
Land use
The Swiss territory is divided into four major types ofland use
Land use involves the management and modification of natural environment or wilderness into built environment such as settlements and semi-natural habitats such as arable fields, pastures, and managed woods. Land use by humans has a long ...
. , 36.9% of the land in Switzerland was used for farming. 30.8% of the country is covered with forests and woodlands, with an additional 6.8% covered with houses or buildings. About one-fourth (25.5%) of the country is either mountains, lakes or rivers and is categorised as unproductive.
Surfaces of housing and infrastructure
The habitat is mainly developed in the Swiss Plateau and the northern slopes of the Alps, near lakes and along major rivers. It occupies 14.6% of the Plateau, the Jura (7.4%), the southern (4.3%) and the northern Alps (4%), and finally the western central Alps (2.9%) and Eastern Alps (1.6%). Habitat areas and infrastructure grow around the urban areas but also in the countryside, at the expense of agricultural land. This growth (called ''suburbanization
Suburbanization is a population shift from central urban areas into suburbs, resulting in the formation of (sub)urban sprawl. As a consequence of the movement of households and businesses out of the city centers, low-density, peripheral urba ...
'') is particularly pronounced along the main transport routes such as motorways and railways. New roads lead to a significant increase in construction activity in the affected regions. Many people who work in the city prefer to live in the countryside to take advantage of cheaper land and better quality of life. This is also reflected in the construction statistics: single-family homes arise mainly in rural areas, multi-family homes in the cities. Household structures are also evolving and tend to become smaller. In twelve years, the area devoted to housing increased by 25% while the increase of the population was only 9%.
Farmland
Although it is declining, agriculture represents the most important use of the territory in Switzerland. Farmlands dominates the Plateau, occupying just over half of the area. The situation is similar in the Jura (44%), on the northern slopes of the Alps (38.2%) and in the eastern Central Alps (31.4%). In the mountainous regions of the western Central Alps (Valais) and in the south, the agricultural areas (mostly pastures) are proportionately lower. In 1993 it was estimated that (or about 0.6%) of the entire country was irrigated meaning that most Swiss farms receive enough rainfall to grow. The protection of forested areas led to numerous conflicts of interests around the farmland, especially on the Plateau and near urban areas where the habitat area development and infrastructure tend to reduce the amount of arable land. Conversely, the number of farms in the mountains tend to decrease, many areas are left for the benefit of woodlands to the detriment of landscape diversity. This decline is particularly marked in Valais and Ticino.Forests
Forests cover less than a third of the territory, but the area is increasing year by year. Thereforestation
Reforestation (occasionally, reafforestation) is the natural or intentional restocking of existing forests and woodlands (forestation) that have been depleted, usually through deforestation, but also after clearcutting.
Management
A debat ...
is essentially natural, mainly in the Alps where the forest areas reoccupy those abandoned by farmers. Afforestation contributes 13% to reforestation, and is conducted for compensation following a clearance or to provide protection against natural hazards in the mountainous areas (avalanches, landslides). Forests are more predominant in the Jura and in the southern Alps, occupying respectively 47.7% and 47.2% of the soil in these regions. On the northern slopes of the Alps, Alpine forest occupy 33.2% and on the Plateau 24.6%. It is in the Central Alps that forest areas occupy less floor with about 22% coverage.
Switzerland is home to mixed maple-ash forests of fertile and deep earth that collects at the base of slopes. They replace the moist oak-hornbeam forests in areas with higher rainfall. This type of forest has been called "one of the most productive in Switzerland" and the tree growth has been described as "aggressive". It takes one third of the time for trees to reach the same height as it would in a mull-beech forest and within 100 years trees in maple-ash forests can reach a height of 35m, though the quality of wood will not be as high. The rich undergrowth of these forests is dominated by the ''allium ursinum
''Allium ursinum'', known as wild garlic, ramsons, cowleekes, cows's leek, cowleek, buckrams, broad-leaved garlic, wood garlic, bear leek, Eurasian wild garlic or bear's garlic, is a bulbous perennial flowering plant in the amaryllis family Amary ...
'' (wild garlic) common throughout Western Europe.
Unproductive areas
The unproductive areas correspond to all areas occupied by rocks, boulders, ice, snow fields and unproductive vegetation beyond the limits of forests. Lakes, rivers and wetlands are also unproductive areas. Occupying 25.5% of Swiss soil, these surfaces are in very slight decline (-0.1% over 10 years). They are predominant in the Central Alps (half of the soil), on the contrary they only cover 10% of the surface of the plateau and 1% of the Swiss Jura. The uncultivated mountain areas are exploited by the tourism and the production ofhydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined an ...
. Climatic conditions strongly affect the landscape of these areas: water seepage
Soil mechanics is a branch of soil physics and applied mechanics that describes the behavior of soils. It differs from fluid mechanics and solid mechanics in the sense that soils consist of a heterogeneous mixture of fluids (usually air and wat ...
, landslides
Landslides, also known as landslips, are several forms of mass wasting that may include a wide range of ground movements, such as rockfalls, deep-seated slope failures, mudflows, and debris flows. Landslides occur in a variety of environments, ...
, avalanches
An avalanche is a rapid flow of snow down a slope, such as a hill or mountain.
Avalanches can be set off spontaneously, by such factors as increased precipitation or snowpack weakening, or by external means such as humans, animals, and earth ...
, torrent
Torrent or torrents may refer to:
* A fast flowing stream
Animals
* Torrent duck, a species of the family Anatidae
* Torrent fish
* Torrent frog, various unrelated frogs
* Torrent robin, a bird species
* Torrent salamander, a family of s ...
s in spate. Man intervenes on 0.2% of this surface area to create infrastructure protecting against floods or avalanches. The channels of communication, with many works of art occupy a portion of these surfaces.
In the plains, lakes and streams near areas of habitat are used for recreation and relaxation. Habitats, damp or dry, and nature reserves are managed and these areas contribute to maintain biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic (''genetic variability''), species (''species diversity''), and ecosystem (''ecosystem diversity'') l ...
.
Population
 The population of Switzerland is heavily urbanised. In 2009, 74% of the 7,785,800 inhabitants lived in urban areas. The distribution of population is shaped by the topography of the country, the plateau being the most populous area and including the major cities of Switzerland. With a population density of 450 inhabitants per km2, it is one of the most densely populated region in Europe. There are large disparities of population densities between the cantons lying in the plateau and those lying in the Alps. Thus, the population densities of the cantons of Lucerne,
The population of Switzerland is heavily urbanised. In 2009, 74% of the 7,785,800 inhabitants lived in urban areas. The distribution of population is shaped by the topography of the country, the plateau being the most populous area and including the major cities of Switzerland. With a population density of 450 inhabitants per km2, it is one of the most densely populated region in Europe. There are large disparities of population densities between the cantons lying in the plateau and those lying in the Alps. Thus, the population densities of the cantons of Lucerne, Solothurn
Solothurn ( , ; french: Soleure ; it, Soletta ; rm, ) is a town, a municipality, and the capital of the canton of Solothurn in Switzerland. It is located in the north-west of Switzerland on the banks of the Aare and on the foot of the Weissens ...
and Zurich are respectively 261.0, 319.7 and 813.6 inhabitants per km2. On the other hand, the cantons of Uri and Graubünden have very low population densities, respectively 33.4 and 27.0 inhabitants per km2. In the southern Alps, the canton of Ticino
Ticino (), sometimes Tessin (), officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino,, informally ''Canton Ticino'' ; lmo, Canton Tesin ; german: Kanton Tessin ; french: Canton du Tessin ; rm, Chantun dal Tessin . ...
also has a population density less than the national average, with 122.5 inhabitants per km2 (against 194.7).
Environment
With the delicate alpine and glacial environments making up a significant portion of the country and providing a major industry, Switzerland has been concerned with environmental issues. Some of the main issues are listed below.Air
The main environmental issues in Switzerland's air isair pollution
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different typ ...
from vehicle emissions and open-air burning as well as acid rain. In 2004, the average amount of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is trans ...
(CO2) emissions per resident was and in 2005 was .United Nations Millennium Development Goals Indicatorsaccessed December 2, 2008 With these numbers, Switzerland is 31st to 33rd among the 45 nations listed by United Nations
Millennium Development Goals
The Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) were eight international development goals for the year 2015 that had been established following the Millennium Summit of the United Nations in 2000, following the adoption of the United Nations Millenn ...
Indicators as developed nation
A developed country (or industrialized country, high-income country, more economically developed country (MEDC), advanced country) is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy and advanced technological infrastruct ...
s and 69th worldwide. In 2009 Switzerland announced that they expected by 2010 to reduce their total greenhouse gas emissions by 8% to 10% over emissions in 1990.
The population () uses 3.76 tonnes of oil equivalent per person per year, of which 43.7% comes from petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crud ...
and 19% from nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced ...
.
Water
The major water issue in Switzerland iswater pollution
Water pollution (or aquatic pollution) is the contamination of water bodies, usually as a result of human activities, so that it negatively affects its uses. Water bodies include lakes, rivers, oceans, aquifers, reservoirs and groundwater. ...
from the increased use of agricultural fertilizers as well as hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic, and their odors are usually weak or ...
pollution from transport and industry. While improvements have been made, there are still issues with eutrophication
Eutrophication is the process by which an entire body of water, or parts of it, becomes progressively enriched with minerals and nutrients, particularly nitrogen and phosphorus. It has also been defined as "nutrient-induced increase in phytopla ...
(an increase in nitrogen and phosphates) in many lakes in the Swiss Plateau.
The total renewable water resources of Switzerland, , totals , of which the total freshwater withdrawal is per year. This breaks down to a ''per capita
''Per capita'' is a Latin phrase literally meaning "by heads" or "for each head", and idiomatically used to mean "per person". The term is used in a wide variety of social sciences and statistical research contexts, including government statistic ...
'' freshwater withdrawal of per year. Of that water (), 24% is used in households, 74% in industry and only 2% is used for agriculture.
In Switzerland, there are officially 38,000 polluted sites, 4,000 of which represent a real threat to groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available freshwater in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidated ...
.
Biodiversity
 Switzerland is facing a
Switzerland is facing a loss of biodiversity
Biodiversity loss includes the worldwide extinction of different species, as well as the local reduction or loss of species in a certain habitat, resulting in a loss of biological diversity. The latter phenomenon can be temporary or permanent, de ...
. While the country is quite small, the wide range of climates allow a variety of organisms to flourish. There are about 50,000 animal and plant species living in Switzerland. While most species that live on north and south foothills of the Alps are generally doing well, the Swiss Plateau is seeing a decrease in many species. The pressure from city and agricultural growth is reducing or eliminating the habitat of many species that once flourished along the plateau. There are about 60 species that are considered endangered that live in Switzerland. To help offset this, 28.6% of the country is set aside as a protected natural area. In 2001, the Federal Office for the Environment
The Federal Office for the Environment (german: Bundesamt für Umwelt; french: Office fédéral de l'environnement; it, Ufficio federale dell'ambiente) is the Swiss environmental agency, a division of the Federal Department of Environment, ...
FOEN launched a nationwide programme to systematically monitor biodiversity (Biodiversity Monitoring Switzerland The Biodiversity Monitoring Switzerland (BDM) is a Swiss Confederation programme for the long-term monitoring of species diversity in Switzerland.
Introduction
The Biodiversity Monitoring Switzerland surveys the long-term development of species ...
).
International agreements
''Party to:'' *Air Pollution
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different typ ...
* Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides
* Air Pollution-Sulphur 85, Air Pollution-Sulphur 94
* Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds
*Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants
*Antarctic Treaty
russian: link=no, Договор об Антарктике es, link=no, Tratado Antártico
, name = Antarctic Treaty System
, image = Flag of the Antarctic Treaty.svgborder
, image_width = 180px
, caption ...
*Biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic (''genetic variability''), species (''species diversity''), and ecosystem (''ecosystem diversity'') l ...
*Climate Change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
* Desertification
* Endangered Species
*Environmental Modification
The Environmental Modification Convention (ENMOD), formally the Convention on the Prohibition of Military or Any Other Hostile Use of Environmental Modification Techniques is an international treaty prohibiting the military or other hostile use ...
*Hazardous Wastes
Hazardous waste is waste that has substantial or potential threats to public health or the environment. Hazardous waste is a type of dangerous goods. They usually have one or more of the following hazardous traits: ignitability, reactivity, cor ...
* Marine Dumping
*Marine Life Conservation
The Convention on Fishing and Conservation of Living Resources of the High Seas is an agreement that was designed to solve through international cooperation the problems involved in the conservation of living resources of the high seas, consideri ...
*Nuclear Test Ban
The Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT) is a multilateral treaty to ban nuclear weapons test explosions and any other nuclear explosions, for both civilian and military purposes, in all environments. It was adopted by the United Nation ...
*Ozone Layer Protection
The Montreal Protocol is an international treaty designed to protect the ozone layer by phasing out the production of numerous substances that are responsible for ozone depletion. It was agreed on 16 September 1987, and entered into force o ...
*Ship Pollution
The environmental effects of shipping include air pollution, water pollution, acoustic, and oil pollution. Ships are responsible for more than 18 percent of some air pollutants.
As for greenhouse gas emissions, the International Maritime Orga ...
*Tropical Timber 83
The International Tropical Timber Agreement (ITTA), 1983) is an agreement to provide an effective framework for cooperation between tropical timber producers and consumers and to encourage the development of national policies aimed at sustainable ...
*Tropical Timber 94
The International Tropical Timber Agreement (ITTA), 1983) is an agreement to provide an effective framework for cooperation between tropical timber producers and consumers and to encourage the development of national policies aimed at sustainable ...
* Wetlands
*Whaling
Whaling is the process of hunting of whales for their usable products such as meat and blubber, which can be turned into a type of oil that became increasingly important in the Industrial Revolution.
It was practiced as an organized industr ...
''Signed, but not ratified:''
* Antarctic-Environmental Protocol
* Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol
* Law of the Sea
Area and boundaries
The borders of Switzerland were established by the original formation of the Helvetic Republic in 1798, the accession thereto ofValais
Valais ( , , ; frp, Valês; german: Wallis ), more formally the Canton of Valais,; german: Kanton Wallis; in other official Swiss languages outside Valais: it, (Canton) Vallese ; rm, (Chantun) Vallais. is one of the 26 cantons forming the S ...
and Grisons, and the incorporation of various remaining feudal territories such as the County of Neuchâtel, Prince-Bishopric of Basel
The Prince-Bishopric of Basel (german: Hochstift Basel, Fürstbistum Basel, Bistum Basel) was an ecclesiastical principality within the Holy Roman Empire, ruled from 1032 by prince-bishops with their seat at Basel, and from 1528 until 1792 at ...
, Abbey of St. Gall
The Abbey of Saint Gall (german: Abtei St. Gallen) is a dissolved abbey (747–1805) in a Catholic religious complex in the city of St. Gallen in Switzerland. The Carolingian-era monastery existed from 719, founded by Saint Othmar on the spot ...
, etc. The cantons largely had their current borders since 1815 (at accession of Valais
Valais ( , , ; frp, Valês; german: Wallis ), more formally the Canton of Valais,; german: Kanton Wallis; in other official Swiss languages outside Valais: it, (Canton) Vallese ; rm, (Chantun) Vallais. is one of the 26 cantons forming the S ...
, Neuchâtel and Geneva
, neighboring_municipalities= Carouge, Chêne-Bougeries, Cologny, Lancy, Grand-Saconnex, Pregny-Chambésy, Vernier, Veyrier
, website = https://www.geneve.ch/
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevr ...
), except for the notable change when Jura seceded from Berne in 1979.
The total length of the border is 1,899 km,
enclosing an area of (
land: , water: ).
The border of Switzerland has six tripoint
A tripoint, trijunction, triple point, or tri-border area is a geographical point at which the boundaries of three countries or subnational entities meet. There are 175 international tripoints as of 2020. Nearly half are situated in rivers, l ...
s, of which two are located in rivers, one undefined location in the Lake of Constance
Lake Constance (german: Bodensee, ) refers to three bodies of water on the Rhine at the northern foot of the Alps: Upper Lake Constance (''Obersee''), Lower Lake Constance (''Untersee''), and a connecting stretch of the Rhine, called the Lake ...
, and the three other in high mountains.
Elevation extremes
* Lowest point:Lake Maggiore
Lake Maggiore (, ; it, Lago Maggiore ; lmo, label=Western Lombard, Lagh Maggior; pms, Lagh Magior; literally 'Greater Lake') or Verbano (; la, Lacus Verbanus) is a large lake located on the south side of the Alps. It is the second largest l ...
:
* Highest point: Monte Rosa
:
, other_name = Monte Rosa massif
, translation = Mount Rose
, photo = Dufourspitze (Monte Rosa) and Monte Rosa Glacier as seen from Gornergrat, Wallis, Switzerland, 2012 August.jpg
, photo_caption = Central Mon ...
:
* Deepest point: in Lake Maggiore:
Western or Central Europe
No subdivision ofEurope
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
is universally accepted, therefore naming the different European regions and defining the borders between them is subject to debates. Depending on the definition chosen, Switzerland can be either part of Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
or Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the a ...
: both concepts depend heavily on context and carry cultural, economic and political connotations.
The term "Western Europe" commonly indicates the region west of the Baltic
Baltic may refer to:
Peoples and languages
* Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian
*Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originati ...
and Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to t ...
. Countries described as Western European (including Switzerland, according to the United Nations Statistics Division
The United Nations Statistics Division (UNSD), formerly the United Nations Statistical Office, serves under the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (DESA) as the central mechanism within the Secretariat of the United Nations ...
and the National Geographic Society
The National Geographic Society (NGS), headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States, is one of the largest non-profit scientific and educational organizations in the world.
Founded in 1888, its interests include geography, archaeology, an ...
) are invariably high-income developed countries, characterized by stable democratic political systems, mixed economies
A mixed economy is variously defined as an economic system blending elements of a market economy with elements of a planned economy, markets with state interventionism, or private enterprise with public enterprise. Common to all mixed economie ...
combining the free market
In economics, a free market is an economic system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand expressed by sellers and buyers. Such markets, as modeled, operate without the intervention of government or any ot ...
with aspects of the welfare state
A welfare state is a form of government in which the state (or a well-established network of social institutions) protects and promotes the economic and social well-being of its citizens, based upon the principles of equal opportunity, equita ...
. On the other hand, the term "Central Europe" refers to the region between Western and Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whic ...
. Central European countries (including Switzerland in the westernmost part, according to the World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a reference resource produced by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The official print version is available ...
and various encyclopedias such as Britannica and Columbia) show high disparities with regard to income but possibly share similar cultural characteristics. The concept came back into use by the end of the Cold War, which had divided Europe politically into the Western World
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to the various nations and states in the regions of Europe, North America, and Oceania.
and the East Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc and the Soviet Bloc, was the group of socialist states of Central and Eastern Europe, East Asia, Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America under the influence of the Soviet Union that existed du ...
, splitting Central Europe in half. Before World War I, the German-speaking world used the somewhat-related term ''Mitteleuropa
(), meaning Middle Europe, is one of the German terms for Central Europe. The term has acquired diverse cultural, political and historical connotations. University of Warsaw, Johnson, Lonnie (1996) ''Central Europe: Enemies, Neighbors, Friends'p ...
'' (from German: ''Middle Europe'') for an area larger than most conceptions of Central Europe, notably encompassing Switzerland among the other German-speaking countries.
Physically, Switzerland is situated approximately in the middle of the portion of Europe west of the Carpathian Mountains. Defining the Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western ...
as the eastern limit of the continent, Switzerland is located within the western third of Europe, approximately 15 degrees of longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east– west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek lette ...
away from the extreme west and 50 degrees away from extreme east. Phytogeographically
Phytogeography (from Greek φυτόν, ''phytón'' = "plant" and γεωγραφία, ''geographía'' = "geography" meaning also distribution) or botanical geography is the branch of biogeography that is concerned with the geographic distribution o ...
, the part of Switzerland that lies north of the Alps belongs to Central Europe, while the part south of the Alps belongs to Southern Europe
Southern Europe is the southern region of Europe. It is also known as Mediterranean Europe, as its geography is essentially marked by the Mediterranean Sea. Definitions of Southern Europe include some or all of these countries and regions: Alba ...
. Wolfgang Frey and Rainer Lösch; ''Lehrbuch der Geobotanik. Pflanze und Vegetation in Raum und Zeit''. Spektrum Akademischer Verlag, München 2004
Natural World Heritage Sites
Monte San Giorgio
Monte San Giorgio is a mountain and UNESCO World Heritage Site on the border between Switzerland and Italy. It is part of the Lugano Prealps, overlooking Lake Lugano in the Swiss Canton of Ticino.
Monte San Giorgio is a wooded mountain, rising ...
File:Sernftal.jpg, Glarus thrust
The Glarus thrust (german: Glarner Überschiebung) is a major thrust fault in the Alps of eastern Switzerland. Along the thrust the Helvetic nappes were thrust more than 100 km to the north over the external Aarmassif and Infrahelvetic compl ...
File:LakeOeschinen.jpg, Oeschinen Lake
Oeschinen Lake (German: ''Oeschinensee'') is a lake in the Bernese Oberland, Switzerland, east of Kandersteg in the Oeschinen valley. At an elevation of , it has a surface area of . Its maximum depth is .
The lake was created by a giant landsli ...
File:Oberaletsch.jpg, Oberaletsch Glacier
File:Great Aletsch Glacier.jpg, Aletsch Glacier
File:Aletschhorn from Konkordiaplatz.jpg, Konkordiaplatz
The Konkordiaplatz or Concordia Place (French: Place de la Concorde), is a flat area of snow and ice lying just to the south of the Jungfrau in the Bernese Alps in the Swiss canton of Valais. It is the junction of four large glaciers coming down ...
File:Jungfrau from Jungfraujoch.jpg, Jungfraujoch
The Jungfraujoch (German: lit. "maiden saddle") is a saddle connecting two major 4000ers of the Bernese Alps: the Jungfrau and the Mönch. It lies at an elevation of above sea level and is directly overlooked by the rocky prominence of the Sphinx ...
File:Lauteraarhütte.jpg, Unteraar Glacier
The Unteraargletscher (), literally "Lower Aare-Glacier", is the larger of the two sources of the Aare river in the Bernese Alps. It emerges from the association of the Finsteraargletscher (near the Finsteraarhorn) and the Lauteraargletscher (n ...
Topography
*Extreme points of Switzerland
This is a list of the extreme points of Switzerland.
Elevation
Latitude and longitude
References
See also
*Extreme points of Earth
This article lists extreme locations on Earth that hold geographical records or are otherwise know ...
*Geographical centre of Switzerland
The geographical centre of Switzerland has the coordinates ( Swiss Grid: 660158/183641). It is located at Älggi-Alp in the municipality of Sachseln, Obwalden. The point is the centre of mass determined in 1988 by Swisstopo.
As the point is di ...
*List of glaciers in Switzerland
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to:
People
* List (surname)
Organizations
* List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America
* SC Germania List, German rugby unio ...
* List of islands of Switzerland
*List of lakes in Switzerland
This article contains a sortable table listing all major lakes of Switzerland. The table includes all still water bodies, natural or artificial, that have a surface area of at least , regardless of water volume, maximum depth or other metric. T ...
*List of mountain passes in Switzerland
This is a list of mountain passes in Switzerland. They are generally situated in the Jura Mountains or in the Swiss Alps.
Pass roads
Trails
Railway
See also
* List of highest road passes in Switzerland
* List of highest paved roads in Sw ...
* List of mountain ranges in Switzerland
*List of mountains in Switzerland
This article contains a sortable table of many of the major mountains and hills of Switzerland. The table only includes those summits that have a topographic prominence of at least above other points, and ranks them by height and prominence. The ...
*List of rivers of Switzerland
The following is a list of rivers in Switzerland:
Rivers by length
(> 100 km, only the length in Switzerland)
#Rhine - 375 km - 36,494 km2
#Aare (or Aar) - 295 km - 17,779 km2
#Rhône - 264 km - 10,403 km2
#Reus ...
See also
*Geography of the Alps
The Alps form a large mountain range dominating Central Europe, including parts of Italy, France, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, Austria, Slovenia, Germany and possibly Hungary (if one includes the Kőszeg Mountains).
This article describes ...
* Swiss cartography
* Valleys of the Alps
The main valleys of the Alps, orographically by drainage basin.
Rhine basin (North Sea)
High Rhine
*Aare
**Limmat
***Linth (Glarus)
**** Lake Walen
***** Seeztal
**** Klöntal
**** Sernftal
**Reuss
***Lake Lucerne
**** Sarner Aa ( Brünig Pas ...
* Little Switzerland (landscape) A little Switzerland or ''Schweiz'' is a landscape, often of wooded hills. This Romantic aesthetic term is not a geographic category, but was widely used in the 19th century to connote dramatic natural scenic features that would be of interest to ...
* Swiss Federal Office of Topography
Swisstopo is the official name for the Swiss Federal Office of Topography (in German: ''Bundesamt für Landestopografie''; French: ''Office fédéral de topographie''; Italian: ''Ufficio federale di topografia''; Romansh: ''Uffizi federal da ...
Notes and references
Notes
References
Bibliography
* Martine Rebetez, ''La Suisse se réchauffe. Effet de serre et changement climatique'', fourth edition, collection « Le savoir suisse »,Presses polytechniques et universitaires romandes
The Presses polytechniques et universitaires romandes (PPUR, literally "Polytechnic and university press of French-speaking Switzerland") is a Swiss academic publishing house.
It is based in Lausanne, on the Lausanne campus, in the Rolex Learni ...
, 2011 ().
External links
* * *CIA World Factbook
Official on-line maps of Switzerland
{{Authority control