
Hunting is the
human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, or killing
wildlife
Wildlife refers to undomesticated animal species, but has come to include all organisms that grow or live wild in an area without being introduced by humans. Wildlife was also synonymous to game: those birds and mammals that were hunted ...
or
feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to harvest
food
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or fungal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. The substance is in ...
(i.e.
meat) and useful
animal product
An animal product is any material derived from the body of an animal. Examples are fat, flesh, blood, milk, eggs, and lesser known products, such as isinglass and rennet.
Animal by-products, as defined by the USDA, are products harvested or ma ...
s (
fur/
hide,
bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
/
tusks,
horn/
antler
Antlers are extensions of an animal's skull found in members of the Cervidae (deer) family. Antlers are a single structure composed of bone, cartilage, fibrous tissue, skin, nerves, and blood vessels. They are generally found only on ...
, etc.), for
recreation
Recreation is an activity of leisure, leisure being discretionary time. The "need to do something for recreation" is an essential element of human biology and psychology. Recreational activities are often done for enjoyment, amusement, or plea ...
/
taxidermy (see
trophy hunting
Trophy hunting is a form of hunting for sport in which parts of the hunted wild animals are kept and displayed as trophies. The animal being targeted, known as the " game", is typically a mature male specimen from a popular species of collectab ...
), to remove
predator
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill t ...
s dangerous to humans or
domestic animals (e.g.
wolf hunting), to
eliminate pests and
nuisance animal
Nuisance wildlife management is the selective removal of problem individuals or populations of specific species of wildlife. Other terms for the field include wildlife damage management, wildlife control, and animal damage control. Some wild ani ...
s that damage
crop
A crop is a plant that can be grown and harvested extensively for profit or subsistence. When the plants of the same kind are cultivated at one place on a large scale, it is called a crop. Most crops are cultivated in agriculture or hydropon ...
s/
livestock
Livestock are the domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to provide labor and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The term is sometimes used to refer solely to ani ...
/
poultry
Poultry () are domesticated birds kept by humans for their eggs, their meat or their feathers. These birds are most typically members of the superorder Galloanserae (fowl), especially the order Galliformes (which includes chickens, qu ...
or
spread diseases (see
varminting
Varmint hunting or varminting is the practice of hunting vermin — generally small/medium-sized wild mammals or birds — as a means of pest control, rather than as games for food or trophy. The targeted animals are culled because they are cons ...
), for trade/tourism (see
safari), or for
ecological conservation against
overpopulation
Overpopulation or overabundance is a phenomenon in which a species' population becomes larger than the carrying capacity of its environment. This may be caused by increased birth rates, lowered mortality rates, reduced predation or large scale ...
and
invasive species.
Recreationally hunted species are generally referred to as the ''
game
A game is a structured form of play, usually undertaken for entertainment or fun, and sometimes used as an educational tool. Many games are also considered to be work (such as professional players of spectator sports or games) or art (suc ...
'', and are usually
mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur ...
s and
bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
s. A person participating in a hunt is a hunter or (less commonly) huntsman; a
natural area used for hunting is called a
game reserve; an experienced hunter who helps organize a hunt and/or manage the game reserve is known as a
gamekeeper.
Many non-human animals also hunt (see
predation
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill ...
) as part of their
feeding and
parental
A parent is a caregiver of the offspring in their own species. In humans, a parent is the caretaker of a child (where "child" refers to offspring, not necessarily age). A ''biological parent'' is a person whose gamete resulted in a child, a mal ...
behaviors, sometimes
in quantities exceeding immediate dietary needs. The one that does the hunting is the ''
predator
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill t ...
'', and the one being hunted is the ''
prey
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill ...
''.

Hunting activities by humans arose in ''
Homo erectus
''Homo erectus'' (; meaning "upright man") is an extinct species of archaic human from the Pleistocene, with its earliest occurrence about 2 million years ago. Several human species, such as '' H. heidelbergensis'' and '' H. antecessor ...
'' or earlier, in the order of millions of years ago. Hunting has become deeply embedded in various
human cultures and was once an important part of the
rural
In general, a rural area or a countryside is a geographic area that is located outside towns and cities. Typical rural areas have a low population density and small settlements. Agricultural areas and areas with forestry typically are de ...
economies—classified by economists as part of
primary production
In ecology, primary production is the synthesis of organic compounds from atmospheric or aqueous carbon dioxide. It principally occurs through the process of photosynthesis, which uses light as its source of energy, but it also occurs through ...
alongside
forestry
Forestry is the science and craft of creating, managing, planting, using, conserving and repairing forests, woodlands, and associated resources for human and environmental benefits. Forestry is practiced in plantations and natural stands. ...
,
agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people ...
and
fishery
Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting fish and other aquatic life; or more commonly, the site where such enterprise takes place ( a.k.a. fishing ground). Commercial fisheries include wild fisheries and fish farms, ...
. Modern regulations (see
game law) distinguish lawful hunting activities from illegal
poaching, which involves the unauthorized and unregulated
killing
Killing, Killings, or The Killing may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* ''Killing'' (film), a 2018 Japanese film
* ''The Killing'' (film), a 1956 film noir directed by Stanley Kubrick Television
* ''The Killing'' (Danish TV serie ...
,
trapping or capture of animals.

Apart from
food
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or fungal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. The substance is in ...
provision, hunting can be a means of
population control
Population control is the practice of artificially maintaining the size of any population. It simply refers to the act of limiting the size of an animal population so that it remains manageable, as opposed to the act of protecting a species from ...
. Hunting advocates state that regulated hunting can be a necessary component of modern
wildlife management, for example to help maintain a healthy proportion of animal populations within an environment's ecological
carrying capacity when natural checks such as
natural predator
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill th ...
s are absent or insufficient, or to provide funding for
breeding programs and maintenance of
natural reserves and
conservation parks. However,
excessive hunting has also heavily contributed to the
endangerment,
extirpation and
extinction
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the Endling, last individual of the species, although the Functional ext ...
of many animals.
["Red List Overview". IUCN Red List. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 8 September 2010.] Some
animal rights
Animal rights is the philosophy according to which many or all sentient animals have moral worth that is independent of their utility for humans, and that their most basic interests—such as avoiding suffering—should be afforded the s ...
and
anti-hunting
Opposition to hunting is espoused by people or groups who object to the practice of hunting, often seeking anti-hunting legislation and sometimes taking on acts of civil disobedience, such as hunt sabotage. Anti-hunting laws, such as the Englis ...
activists regard hunting as a
cruel
Cruelty is the pleasure in inflicting suffering or inaction towards another's suffering when a clear remedy is readily available. Sadism can also be related to this form of action or concept. Cruel ways of inflicting suffering may involve viol ...
,
perverse and unnecessary
blood sport.
Certain hunting practices, such as
canned hunts and
ludicrously paid/
bribed trophy tours (especially to poor countries), are considered
unethical and
exploitative even by some hunters.

Marine mammal
Marine mammals are aquatic mammals that rely on the ocean and other marine ecosystems for their existence. They include animals such as seals, whales, manatees, sea otters and polar bears. They are an informal group, unified only by their ...
s such as
whale
Whales are a widely distributed and diverse group of fully aquatic placental marine mammals. As an informal and colloquial grouping, they correspond to large members of the infraorder Cetacea, i.e. all cetaceans apart from dolphins and ...
s and
pinniped
Pinnipeds (pronounced ), commonly known as seals, are a widely distributed and diverse clade of carnivorous, fin-footed, semiaquatic, mostly marine mammals. They comprise the extant families Odobenidae (whose only living member is the ...
s are also targets of hunting, both recreationally and commercially, often with heated controversies regarding the morality, ethics and legality of such practices. The pursuit, harvesting or
catch and release
Catch and release is a practice within recreational fishing where after capture, often a fast measurement and weighing of the fish is performed, followed by posing, posed photography as trophy, proof of the catch, and then the fish are unhooke ...
of
fish
Fish are Aquatic animal, aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack Limb (anatomy), limbs with Digit (anatomy), digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and Chondrichthyes, cartilaginous and bony fish as we ...
and
aquatic cephalopod
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda ( Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head ...
s and
crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapoda, decapods, ostracoda, seed shrimp, branchiopoda, branchiopods, argulidae, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopoda, isopods, barnacles, copepods, ...
s is called
fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment, but may also be caught from fish stocking, stocked bodies of water such as fish pond, ponds, canals, park wetlands and reservoirs. ...
, which however is widely accepted and not commonly categorised as a form of hunting, even though it essentially is. It is also not considered hunting to pursue animals without intent to kill them, as in
wildlife photography
Wildlife photography is a genre of photography concerned with documenting various forms of wildlife in their natural habitat.
As well as requiring photography skills, wildlife photographers may need field craft skills. For example, some anim ...
,
birdwatching, or scientific-research activities which involve
tranquilizing or
tagging of animals, although
green hunting Green hunting (also eco-hunting, green bullet concept, green darting or darting safari) is the practice of tracking and shooting game animals with non-lethal tranquilizer guns or bows and subsequently releasing the captured animals alive. Green h ...
is still called so. The practices of
netting or
trapping insect
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body ( head, thorax and abdomen), three pa ...
s and other
arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and cuticle made of chiti ...
s for
trophy collection, or the
foraging or
gathering
Gather, gatherer, or gathering may refer to:
Anthropology and sociology
*Hunter-gatherer, a person or a society whose subsistence depends on hunting and gathering of wild foods
*Intensive gathering, the practice of cultivating wild plants as a st ...
of
plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae excl ...
s and
mushroom
A mushroom or toadstool is the fleshy, spore-bearing fruiting body of a fungus, typically produced above ground, on soil, or on its food source. ''Toadstool'' generally denotes one poisonous to humans.
The standard for the name "mushroom" is ...
s, are also not regarded as hunting.

Skillful
tracking and acquisition of an elusive target has caused the word ''hunt'' to be used in the
vernacular
A vernacular or vernacular language is in contrast with a "standard language". It refers to the language or dialect that is spoken by people that are inhabiting a particular country or region. The vernacular is typically the native language, n ...
as a
metaphor
A metaphor is a figure of speech that, for rhetorical effect, directly refers to one thing by mentioning another. It may provide (or obscure) clarity or identify hidden similarities between two different ideas. Metaphors are often compared wi ...
for searching and obtaining something, as in "
treasure hunting", "
bargain hunting", "
hunting for votes" and even "
hunting down"
corruption and
waste
Waste (or wastes) are unwanted or unusable materials. Waste is any substance discarded after primary use, or is worthless, defective and of no use. A by-product, by contrast is a joint product of relatively minor economic value. A waste pr ...
.
Etymology
The word ''hunt'' serves as both a
noun
A noun () is a word that generally functions as the name of a specific object or set of objects, such as living creatures, places, actions, qualities, states of existence, or ideas.Example nouns for:
* Living creatures (including people, alive, ...
("the act of chasing game") and a
verb
A verb () is a word ( part of speech) that in syntax generally conveys an action (''bring'', ''read'', ''walk'', ''run'', ''learn''), an occurrence (''happen'', ''become''), or a state of being (''be'', ''exist'', ''stand''). In the usual descr ...
. The noun has been dated to the early 12th century, from the verb ''hunt''.
Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th ...
had ''huntung'', ''huntoþ''. The meaning of "a body of persons associated for the purpose of hunting with a pack of hounds" is first recorded in the 1570s. "The act of searching for someone or something" is from about 1600.
The verb, Old English ''huntian'' "to chase game" (
transitive and
intransitive), perhaps developed from ''hunta'' "hunter," is related to ''hentan'' "to seize," from
Proto-Germanic
Proto-Germanic (abbreviated PGmc; also called Common Germanic) is the reconstructed proto-language of the Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages.
Proto-Germanic eventually developed from pre-Proto-Germanic into three Germanic br ...
''huntojan'' (the source also of
Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken b ...
''hinþan'' "to seize, capture,"
Old High German
Old High German (OHG; german: Althochdeutsch (Ahd.)) is the earliest stage of the German language, conventionally covering the period from around 750 to 1050.
There is no standardised or supra-regional form of German at this period, and Old Hig ...
''hunda'' "booty"), which is of uncertain origin. The general sense of "search diligently" (for anything) is first recorded c. 1200.
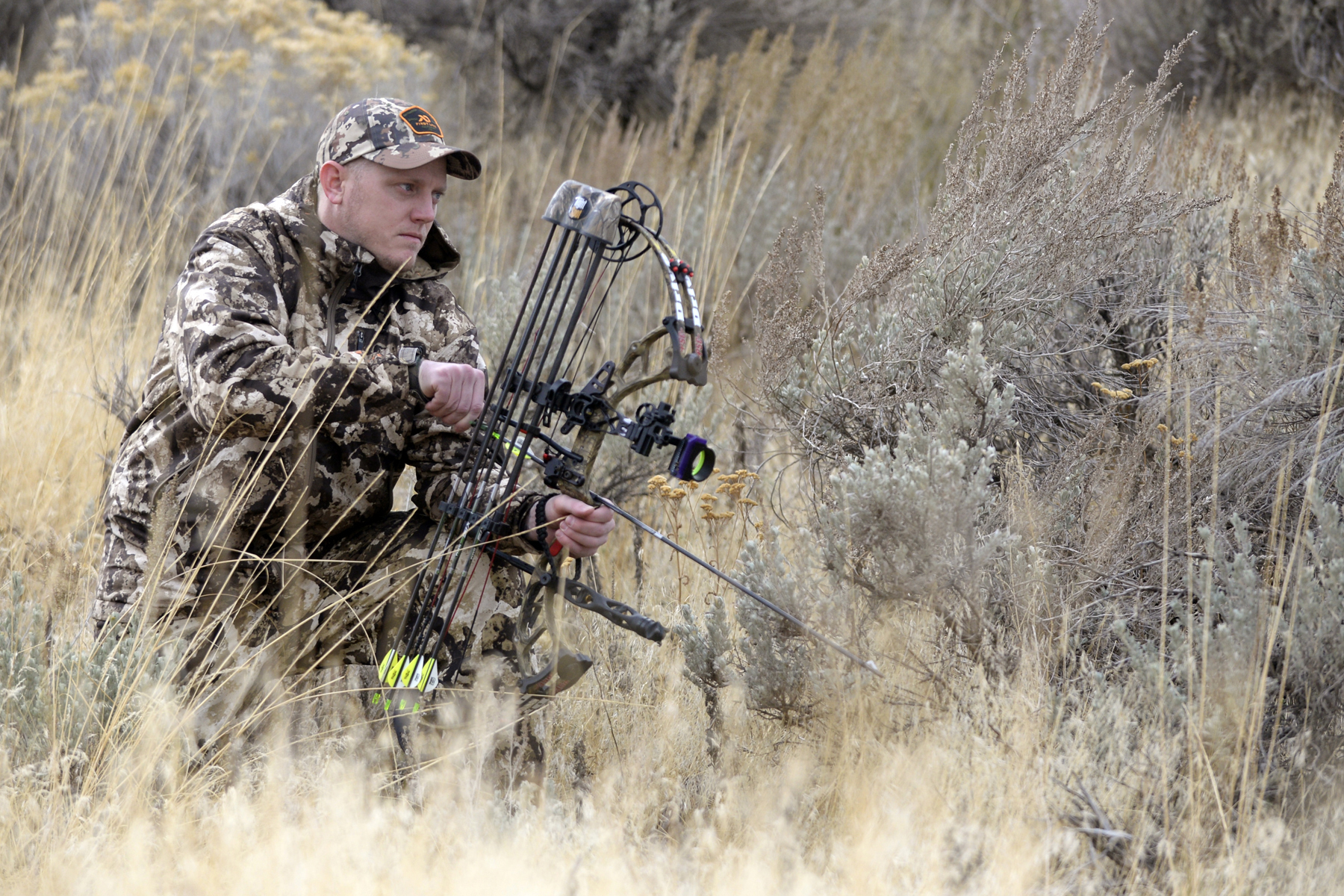
Types
* Recreational hunting, also known as
trophy hunting
Trophy hunting is a form of hunting for sport in which parts of the hunted wild animals are kept and displayed as trophies. The animal being targeted, known as the " game", is typically a mature male specimen from a popular species of collectab ...
,
sport hunting or "
sport
Sport pertains to any form of competitive physical activity or game that aims to use, maintain, or improve physical ability and skills while providing enjoyment to participants and, in some cases, entertainment to spectators. Sports can, ...
ing"
**
Big game hunting
Big-game hunting is the hunting of large game animals for meat, commercially valuable by-products (such as horns/antlers, furs, tusks, bones, body fat/oil, or special organs and contents), trophy/taxidermy, or simply just for recreation ...
***
Big Five game
In Africa, the Big Five game animals are the lion, leopard, black rhinoceros, African bush elephant, and African buffalo. They are examples of charismatic megafauna, featuring prominently in popular culture, and are among the most famous of Af ...
(
lion
The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large cat of the genus '' Panthera'' native to Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body; short, rounded head; round ears; and a hairy tuft at the end of its tail. It is sexually dimorphic; adu ...
,
elephant
Elephants are the largest existing land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantida ...
,
buffalo/
bison
Bison are large bovines in the genus ''Bison'' (Greek: "wild ox" (bison)) within the tribe Bovini. Two extant and numerous extinct species are recognised.
Of the two surviving species, the American bison, ''B. bison'', found only in North A ...
,
African leopard,
rhinoceros
A rhinoceros (; ; ), commonly abbreviated to rhino, is a member of any of the five extant species (or numerous extinct species) of odd-toed ungulates in the family Rhinocerotidae. (It can also refer to a member of any of the extinct specie ...
)
***
Bear hunting
***
Tiger hunting
***
Caribou hunting
** Medium/small game hunting
***
Fox hunting
***
Deer hunting/
stalking
***
Boar hunting
Boar hunting is the practice of hunting wild boar, feral pigs, warthogs, and peccaries. Boar hunting was historically a dangerous exercise due to the tusked animal's ambush tactics as well as its thick hide and dense bones rendering them diffic ...
***
Mink hunting Mink hunting is a country sport involving the hunting of American mink with scent hounds along the waterways which make up their habitat, in a manner similar to fox hunting.[Coon hunting
Coon hunting is the practice of hunting raccoons, most often for their meat and fur. It is almost always done with specially bred dogs called coonhounds, of which there are six breeds, and is most commonly associated with rural life in the Sout ...]
**
Fowling
***
Waterfowl hunting
Waterfowl hunting (also called wildfowling or waterfowl shooting in the UK) is the practice of hunting ducks, geese, or other waterfowl for food and sport.
Many types of ducks and geese share the same habitat, have overlapping or identical hunt ...
***
Shorebird
245px, A flock of Dunlins and Red knots">Red_knot.html" ;"title="Dunlins and Red knot">Dunlins and Red knots
Waders or shorebirds are birds of the order Charadriiformes commonly found wikt:wade#Etymology 1, wading along shorelines and mudflat ...
hunting (
snipe
A snipe is any of about 26 wading bird species in three genera in the family Scolopacidae. They are characterized by a very long, slender bill, eyes placed high on the head, and cryptic/ camouflaging plumage. The '' Gallinago'' snipes have ...
,
woodcock
The woodcocks are a group of seven or eight very similar living species of wading birds in the genus ''Scolopax''. The genus name is Latin for a snipe or woodcock, and until around 1800 was used to refer to a variety of waders. The English ...
,
curlew,
sandpiper
Sandpipers are a large family, Scolopacidae, of waders. They include many species called sandpipers, as well as those called by names such as curlew and snipe. The majority of these species eat small invertebrates picked out of the mud or soil ...
,
plover
Plovers ( , ) are a widely distributed group of wading birds belonging to the subfamily Charadriinae.
Description
There are about 66 species in the subfamily, most of them called "plover" or "dotterel". The closely related lapwing subf ...
)
***
Upland hunting (
quail,
pheasant,
grouse,
turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula ...
)
*
Pest control/
nuisance management
**
Predator
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill t ...
culling
In biology, culling is the process of segregating organisms from a group according to desired or undesired characteristics. In animal breeding, it is the process of removing or segregating animals from a breeding stock based on a specific tr ...
***
Wolf hunting
***
Jackal coursing
Jackal coursing involves the pursuit of jackals (usually the golden jackal and black-backed jackal) with dogs.
Jackal coursing was an occasional pastime for sportsmen in British India. English Foxhounds were usually imported to India for the pur ...
***
Coyote hunting
***
Bobcat hunting
**
Varmint hunting
***
Rabbiting
***
Squirrel hunting
***
Rook shooting
* Commercial hunting
**
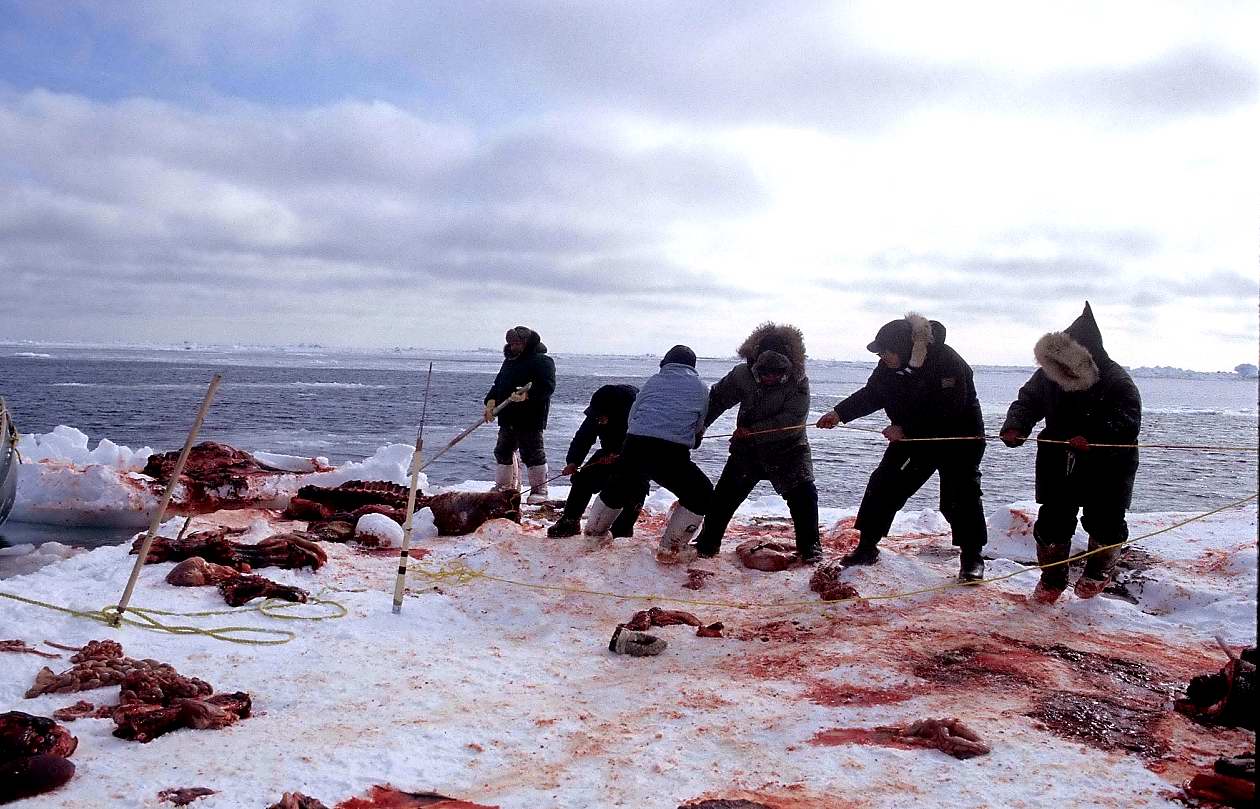
Seal hunting
Seal hunting, or sealing, is the personal or commercial hunting of seals. Seal hunting is currently practiced in ten countries: United States (above the Arctic Circle in Alaska), Canada, Namibia, Denmark (in self-governing Greenland only), Ice ...
**
Whaling
Whaling is the process of hunting of whales for their usable products such as meat and blubber, which can be turned into a type of oil that became increasingly important in the Industrial Revolution.
It was practiced as an organized industr ...
,
dolphin drive,
dugong hunting
**
Alligator hunting
Alligator hunting is the capture and killing of gators. With the appropriate licenses and tags, the American alligator can legally be hunted in the Southeastern United States.
The states of Florida, Georgia, Alabama, Arkansas, Mississippi, Louis ...
**
Kangaroo hunting
The kangaroo industry in Australia is based on the regulated harvesting of the large, abundant species of kangaroos. Limitation of the numbers of kangaroo can have environmental benefits, and is a way of meat production that does not involve in ...
*
Poaching
History
Lower to Middle Paleolithic
Hunting has a long history. It pre-dates the emergence of ''
Homo sapiens
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture ...
'' (
anatomically modern humans) and may even predate the
genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nom ...
''
Homo
''Homo'' () is the genus that emerged in the (otherwise extinct) genus '' Australopithecus'' that encompasses the extant species ''Homo sapiens'' ( modern humans), plus several extinct species classified as either ancestral to or closely rela ...
''.
The oldest undisputed evidence for hunting dates to the
Early Pleistocene
The Early Pleistocene is an unofficial sub-epoch in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, being the earliest division of the Pleistocene Epoch within the ongoing Quaternary Period. It is currently estimated to span the time ...
, consistent with the emergence and early dispersal of ''
Homo erectus
''Homo erectus'' (; meaning "upright man") is an extinct species of archaic human from the Pleistocene, with its earliest occurrence about 2 million years ago. Several human species, such as '' H. heidelbergensis'' and '' H. antecessor ...
'', about 1.7 million years ago (
Acheulean).
While it is undisputed that ''Homo erectus'' were hunters, the importance of this for the emergence of ''Homo erectus'' from its australopithecine ancestors, including the production of
stone tool
A stone tool is, in the most general sense, any tool made either partially or entirely out of stone. Although stone tool-dependent societies and cultures still exist today, most stone tools are associated with prehistoric (particularly Stone A ...
s and eventually the
control of fire, is emphasised in the so-called "
hunting hypothesis
In paleoanthropology, the hunting hypothesis is the hypothesis that human evolution was primarily influenced by the activity of hunting for relatively large and fast animals, and that the activity of hunting distinguished human ancestors from ot ...
" and de-emphasised in scenarios that stress omnivory and
social interaction
A social relation or also described as a social interaction or social experience is the fundamental unit of analysis within the social sciences, and describes any voluntary or involuntary interpersonal relationship between two or more individuals ...
.
There is no direct evidence for hunting predating ''Homo erectus'', in either ''
Homo habilis'' or in ''
Australopithecus
''Australopithecus'' (, ; ) is a genus of early hominins that existed in Africa during the Late Pliocene and Early Pleistocene. The genus ''Homo'' (which includes modern humans) emerged within ''Australopithecus'', as sister to e.g. ''Australo ...
''.
The early
hominid ancestors of humans were probably
frugivores or
omnivore
An omnivore () is an animal that has the ability to eat and survive on both plant and animal matter. Obtaining energy and nutrients from plant and animal matter, omnivores digest carbohydrates, protein, fat, and fiber, and metabolize the nu ...
s, with a partially carnivore diet from
scavenging rather than hunting.
Evidence for australopithecine meat consumption was presented in the 1990s.
It has nevertheless often been assumed that at least occasional hunting behavior may have been present well before the emergence of ''Homo''.
This can be argued on the basis of comparison with
chimpanzee
The chimpanzee (''Pan troglodytes''), also known as simply the chimp, is a species of great ape native to the forest and savannah of tropical Africa. It has four confirmed subspecies and a fifth proposed subspecies. When its close relative t ...
s, the closest extant relatives of humans, who also engage in hunting, indicating that the behavioral trait may have been present in the
Chimpanzee–human last common ancestor as early as 5 million years ago. The common chimpanzee (''
Pan troglodytes'') regularly engages in troop predation behaviour where bands of beta males are led by an
alpha male.
Bonobo
The bonobo (; ''Pan paniscus''), also historically called the pygmy chimpanzee and less often the dwarf chimpanzee or gracile chimpanzee, is an endangered great ape and one of the two species making up the genus '' Pan,'' the other being the comm ...
s (''
Pan paniscus
The bonobo (; ''Pan paniscus''), also historically called the pygmy chimpanzee and less often the dwarf chimpanzee or gracile chimpanzee, is an endangered great ape and one of the two species making up the genus '' Pan,'' the other being the comm ...
'') have also been observed to occasionally engage in group hunting, although more rarely than ''Pan troglodytes'', mainly subsisting on a
frugivorous
A frugivore is an animal that thrives mostly on raw fruits or succulent fruit-like produce of plants such as roots, shoots, nuts and seeds. Approximately 20% of mammalian herbivores eat fruit. Frugivores are highly dependent on the abundance an ...
diet.
Indirect evidence for
Oldowan era hunting, by early ''Homo'' or late ''Australopithecus'', has been presented in a 2009 study based on
an Oldowan site in southwestern Kenya.
Louis Binford (1986) criticised the idea that early hominids and early humans were hunters. On the basis of the analysis of the skeletal remains of the consumed animals, he concluded that hominids and early humans were mostly
scavengers, not hunters,
Blumenschine (1986) proposed the idea of ''confrontational scavenging'', which involves challenging and scaring off other
predator
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill t ...
s they have made a kill, which he suggests could have been the leading method of obtaining
protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
-rich meat by early humans.
Stone spearheads dated as early as 500,000 years ago were found in South Africa. Wood does not preserve well, however, and Craig Stanford, a primatologist and professor of anthropology at the
University of Southern California
, mottoeng = "Let whoever earns the palm bear it"
, religious_affiliation = Nonsectarian—historically Methodist
, established =
, accreditation = WSCUC
, type = Private research university
, academic_affiliations =
, endowment = $8.1 ...
, has suggested that the discovery of spear use by chimpanzees probably means that early humans used wooden spears as well, perhaps, five million years ago.
The earliest dated find of surviving wooden hunting
spear
A spear is a pole weapon consisting of a shaft, usually of wood, with a pointed head. The head may be simply the sharpened end of the shaft itself, as is the case with fire hardened spears, or it may be made of a more durable material fastene ...
s dates to the very end of the
Lower Paleolithic, just before 300,000 years ago. The
Schöningen spears, found in 1976 in
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
, are associated with ''
Homo heidelbergensis''.
The
hunting hypothesis
In paleoanthropology, the hunting hypothesis is the hypothesis that human evolution was primarily influenced by the activity of hunting for relatively large and fast animals, and that the activity of hunting distinguished human ancestors from ot ...
sees the emergence of
behavioral modernity in the
Middle Paleolithic as directly related to hunting, including
mating behaviour, the establishment of
language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of ...
, culture, and
religion
Religion is usually defined as a social- cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatur ...
,
mythology
Myth is a folklore genre consisting of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society, such as foundational tales or origin myths. Since "myth" is widely used to imply that a story is not objectively true, the identification of a narra ...
and
animal sacrifice
Animal sacrifice is the ritual killing and offering of one or more animals, usually as part of a religious ritual or to appease or maintain favour with a deity. Animal sacrifices were common throughout Europe and the Ancient Near East until th ...
. Sociologist
David Nibert of
Wittenberg University
Wittenberg University is a private liberal arts college in Springfield, Ohio. It has 1,326 full-time students representing 33 states and 9 foreign countries. Wittenberg University is associated with the Evangelical Lutheran Church in America ...
argues that the emergence of the organized hunting of animals undermined the communal, egalitarian nature of early human societies, with the status of women and less powerful males declining as the status of men quickly became associated with their success at hunting, which also increased human violence within these societies. However, 9000-year-old remains of a female hunter along with a toolkit of
projectile points and animal processing implements were discovered at the
Andean site of Wilamaya Patjxa,
Puno District in
Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
.
Upper Paleolithic to Mesolithic


Evidence exists that hunting may have been one of the multiple
environmental factors leading to the
Holocene extinction of
megafauna and their replacement by smaller
herbivores.
North American
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the ...
megafauna extinction was coincidental with the
Younger Dryas impact event
The Younger Dryas impact hypothesis (YDIH) or Clovis comet hypothesis is a speculative attempt to explain the onset of the Younger Dryas (YD) as an alternative to the long standing and widely accepted cause due to a significant reduction or shut ...
, possibly making hunting a less critical factor in prehistoric species loss than had been previously thought.
However, in other locations such as Australia, humans are thought to have played a very significant role in the extinction of the
Australian megafauna that was widespread prior to human occupation.
Hunting was a crucial component of hunter-gatherer societies before the
domestication of
livestock
Livestock are the domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to provide labor and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The term is sometimes used to refer solely to ani ...
and the
dawn of agriculture, beginning about 11,000 years ago in some parts of the world. In addition to the
spear
A spear is a pole weapon consisting of a shaft, usually of wood, with a pointed head. The head may be simply the sharpened end of the shaft itself, as is the case with fire hardened spears, or it may be made of a more durable material fastene ...
,
hunting weapon Hunting weapons are weapons designed or used primarily for hunting game animals for food or sport, as distinct from defensive weapons or weapons used primarily in warfare.
Characteristics
Since human beings are lacking in the natural weapons pos ...
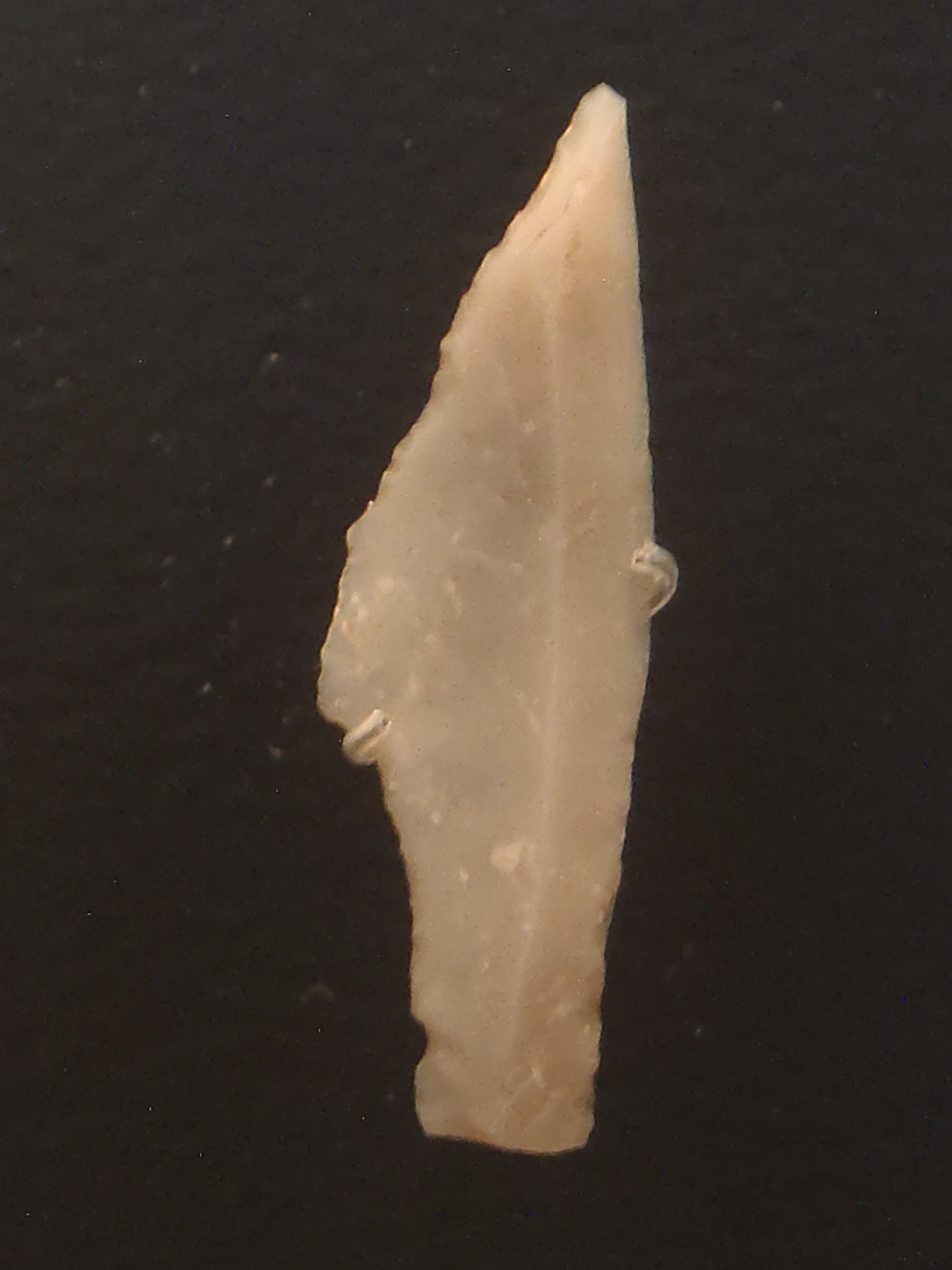
s developed during the Upper Paleolithic include the
atlatl (a spear-thrower; before 30,000 years ago) and the
bow (18,000 years ago). By the
Mesolithic,
hunting strategies had diversified with the development of these more far-reaching weapons and the
domestication of the dog about 15,000 years ago. Evidence puts the earliest known
mammoth
A mammoth is any species of the extinct elephantid genus ''Mammuthus'', one of the many genera that make up the order of trunked mammals called proboscideans. The various species of mammoth were commonly equipped with long, curved tusks an ...
hunting in Asia with
spears to approximately 16,200 years ago.

Many species of animals have been hunted throughout history. One theory is that in North America and
Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelag ...
,
caribou and wild reindeer "may well be the species of single greatest importance in the entire anthropological literature on hunting"
["In North America and Eurasia the species has long been an important resource—in many areas ''the'' most important resource—for peoples inhabiting the northern ]boreal forest
Taiga (; rus, тайга́, p=tɐjˈɡa; relates to Mongolic and Turkic languages), generally referred to in North America as a boreal forest or snow forest, is a biome characterized by coniferous forests consisting mostly of pines, spruc ...
and tundra regions. Known human dependence on caribou/wild reindeer has a long history, beginning in the Middle Pleistocene (Banfield 1961:170; Kurtén 1968:170) and continuing to the present. ��The caribou/wild reindeer is thus an animal that has been a major resource for humans throughout a tremendous geographic area and across a time span of tens of thousands of years." (see also
Reindeer Age
The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago (the beginning of the Holocene), according to some theories coin ...
), although the varying importance of different species depended on the geographic location.
 Mesolithic
Mesolithic hunter-gathering lifestyles remained prevalent in some parts of the
Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America, North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World. ...
,
Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
, and
Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part ...
, as well as all of Australia, until the European
Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (or the Age of Exploration), also known as the early modern period, was a period largely overlapping with the Age of Sail, approximately from the 15th century to the 17th century in European history, during which seafa ...
. They still persist in some
tribal societies
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide usage of the term in English is in the discipline of anthropology. This definition is contested, in part due to conflic ...
, albeit in rapid decline. Peoples that preserved Paleolithic hunting-gathering until the recent past include some
indigenous peoples of the Amazonas (
Aché
The Aché ( ) are an indigenous people of Paraguay. They are hunter-gatherers living in eastern Paraguay.
From the earliest Jesuit accounts of the Aché in the 17th century until their peaceful outside contacts in the 20th century, the Aché ...
), some Central and Southern African (
San people
The San peoples (also Saan), or Bushmen, are members of various Khoe, Tuu, or Kxʼa-speaking indigenous hunter-gatherer cultures that are the first cultures of Southern Africa, and whose territories span Botswana, Namibia, Angola, Zam ...
), some peoples of
New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the wide Torres ...
(
Fayu), the
Mlabri of
Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is b ...
and
Laos
Laos (, ''Lāo'' )), officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic ( Lao: ສາທາລະນະລັດ ປະຊາທິປະໄຕ ປະຊາຊົນລາວ, French: République démocratique populaire lao), is a socialist s ...
, the
Vedda people of
Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
, and a handful of
uncontacted peoples. In Africa, one of the last remaining hunter-gatherer tribes are the
Hadza of Tanzania.
Neolithic and Antiquity


Even as
animal domestication
The domestication of animals is the mutual relationship between non-human animals and the humans who have influence on their care and reproduction.
Charles Darwin recognized a small number of traits that made domesticated species different fro ...
became relatively widespread and after the development of agriculture, hunting was usually a significant contributor to the human food supply.
The supplementary meat and materials from hunting included
protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
,
bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
for implements,
sinew for
cordage,
fur,
feathers,
rawhide and leather used in clothing.
Hunting is still vital in marginal climates, especially those unsuited for
pastoral uses or agriculture. For example,
Inuit
Inuit (; iu, ᐃᓄᐃᑦ 'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territorie ...
in the
Arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar regions of Earth, polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenla ...
trap and hunt animals for clothing and use the skins of
sea mammals
Marine mammals are aquatic mammals that rely on the ocean and other marine ecosystems for their existence. They include animals such as seals, whales, manatees, sea otters and polar bears. They are an informal group, unified only by their re ...
to make
kayaks, clothing, and footwear.
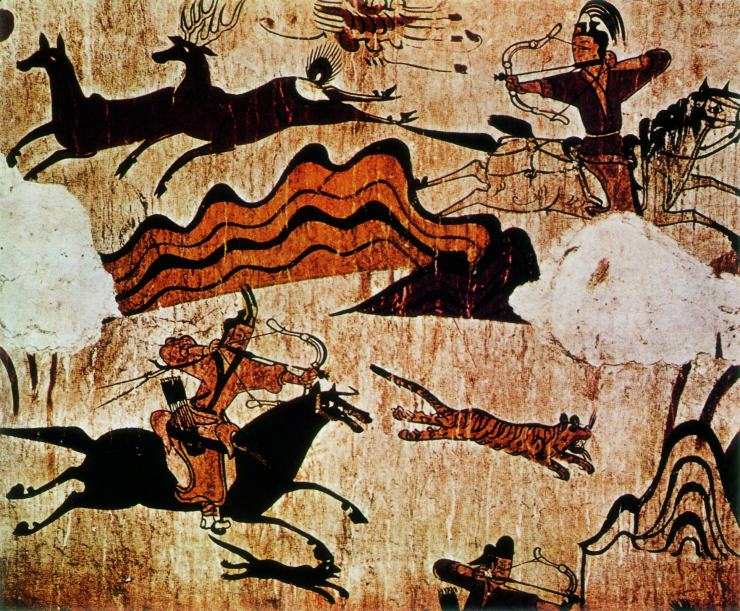
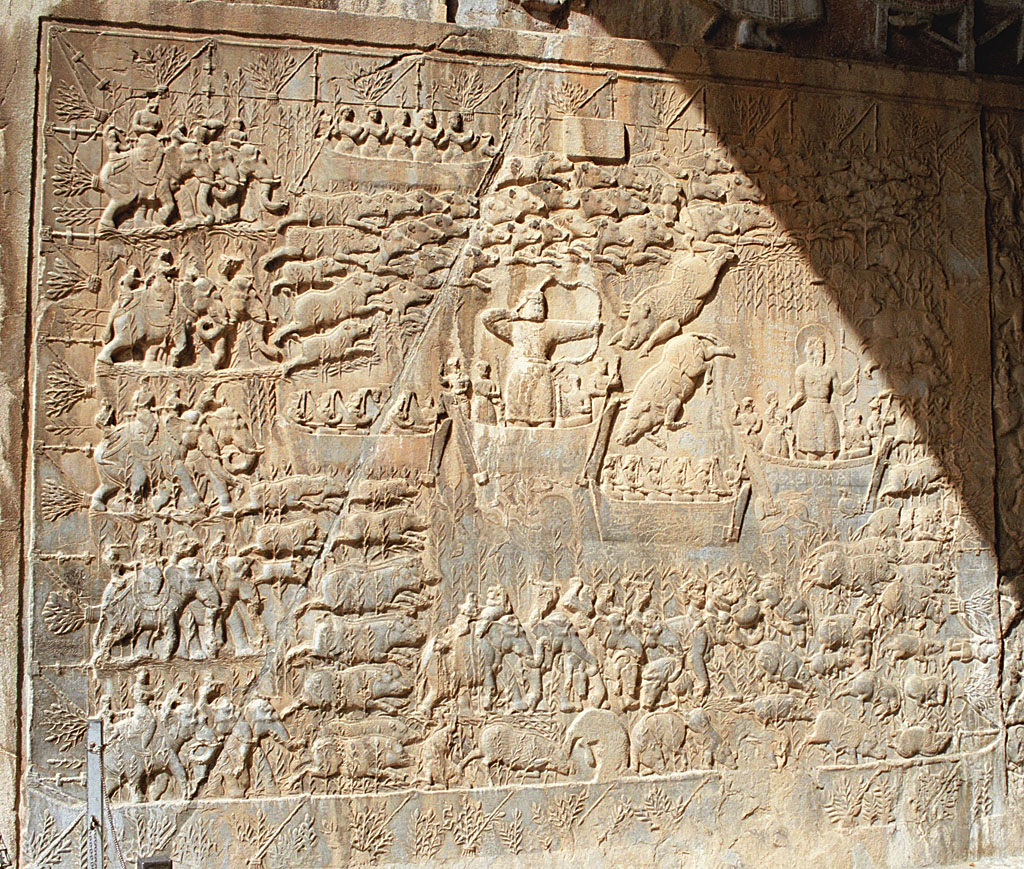
On ancient
reliefs, especially from
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
, kings are often depicted as hunters of
big game such as lions and are often portrayed hunting from a
war chariot. The cultural and
psychological
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Psychology includes the study of conscious and unconscious phenomena, including feelings and thoughts. It is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries bet ...
importance of hunting in ancient societies is represented by deities such as
the horned god Cernunnos and
lunar goddesses
Lunar most commonly means "of or relating to the Moon".
Lunar may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Lunar'' (series), a series of video games
* "Lunar" (song), by David Guetta
* "Lunar", a song by Priestess from the 2009 album '' Prior ...
of
classical antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ...
, the Greek
Artemis
In ancient Greek mythology and religion, Artemis (; grc-gre, Ἄρτεμις) is the goddess of the hunt, the wilderness, wild animals, nature, vegetation, childbirth, care of children, and chastity. She was heavily identified with ...
or Roman
Diana.
Taboos are often related to hunting, and mythological association of prey species with a
divinity
Divinity or the divine are things that are either related to, devoted to, or proceeding from a deity.[divine< ...](_blank)
could be reflected in hunting restrictions such as a
reserve
Reserve or reserves may refer to:
Places
* Reserve, Kansas, a US city
* Reserve, Louisiana, a census-designated place in St. John the Baptist Parish
* Reserve, Montana, a census-designated place in Sheridan County
* Reserve, New Mexico, a US ...
surrounding a temple.
Euripides
Euripides (; grc, Εὐριπίδης, Eurīpídēs, ; ) was a tragedian of classical Athens. Along with Aeschylus and Sophocles, he is one of the three ancient Greek tragedians for whom any plays have survived in full. Some ancient scholars ...
' tale of Artemis and
Actaeon, for example, may be seen as a caution against disrespect of prey or impudent boasting.

With the domestication of the dog,
birds of prey, and the
ferret
The ferret (''Mustela furo'') is a small, domesticated species belonging to the family Mustelidae. The ferret is most likely a domesticated form of the wild European polecat (''Mustela putorius''), evidenced by their interfertility. Other mus ...
, various forms of animal-aided hunting developed, including
venery (
scent hound
Franz Rudolf Frisching in the uniform of an officer of the Bernese Huntsmen Corps with his Berner Laufhund, painted by Jean Preudhomme in 1785
Scent hounds (or scenthounds) are a Dog type, type of hound that primarily hunts by scent rather than ...
hunting, such as
fox hunting),
coursing
Coursing by humans is the pursuit of game or other animals by dogs—chiefly greyhounds and other sighthounds—catching their prey by speed, running by sight, but not by scent. Coursing was a common hunting technique, practised by the nobility, ...
(
sight hound hunting),
falconry, and
ferreting
The ferret (''Mustela furo'') is a small, domesticated species belonging to the family Mustelidae. The ferret is most likely a domesticated form of the wild European polecat (''Mustela putorius''), evidenced by their interfertility. Other must ...
. While these are all associated with
medieval hunting
Throughout Western Europe in the Middle Ages, humans hunted wild animals. While game was at times an important source of food, it was rarely the principal source of nutrition. All classes engaged in hunting, but by the High Middle Ages, the nece ...
, over time, various
dog breeds were selected for very precise tasks during the hunt, reflected in such names as
pointer and
setter
The setter is a type of gundog used most often for hunting game such as quail, pheasant, and grouse.
In the UK, the four setter breeds, together with the pointers, usually form a subgroup within the gundog group as they share a common ...
.
Pastoral and agricultural societies
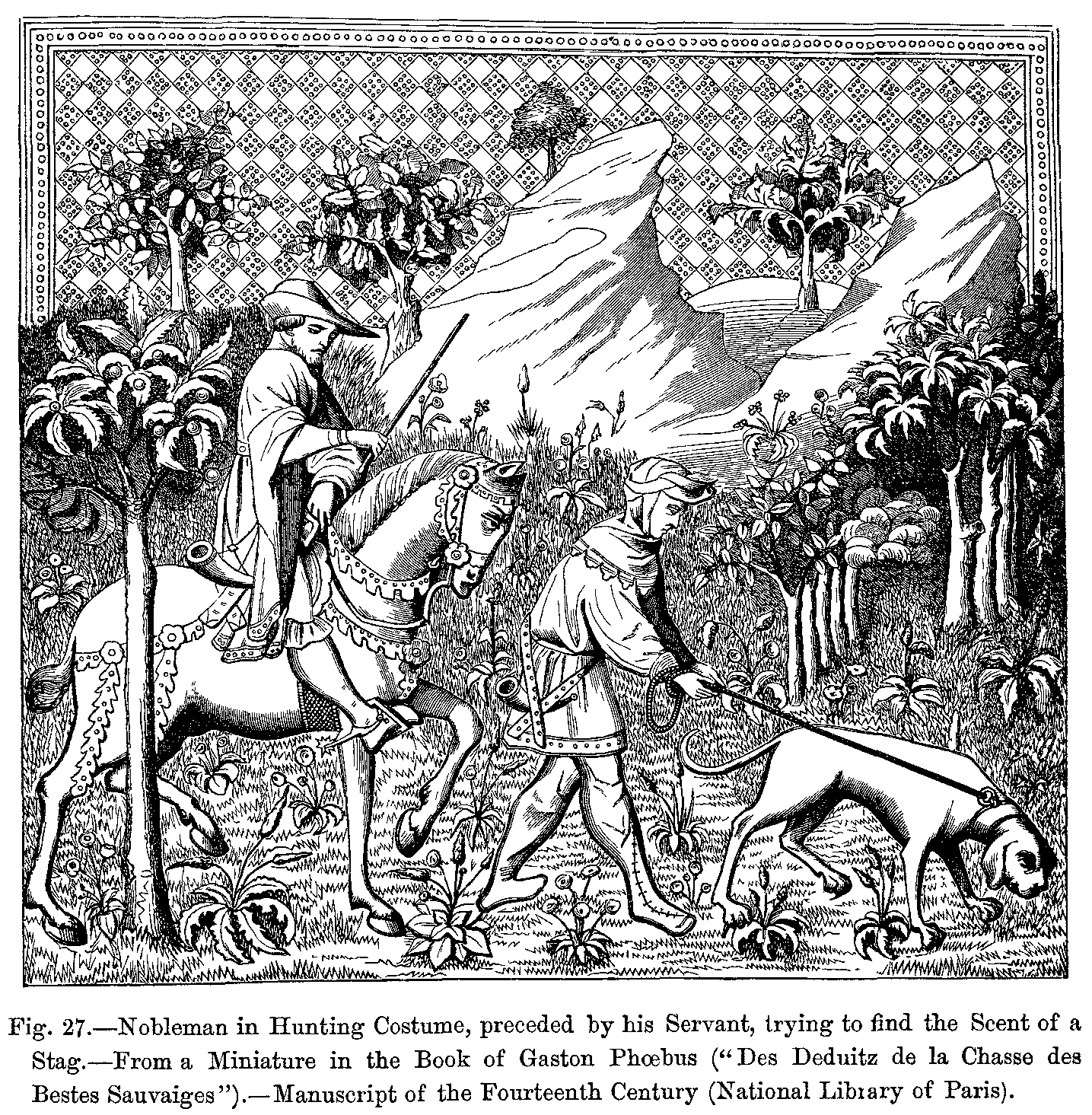
Even as agriculture and
animal husbandry became more prevalent, hunting often remained as a part of human culture where the environment and social conditions allowed. Hunter-gatherer societies persisted, even when increasingly confined to marginal areas. And within agricultural systems, hunting served to kill animals that prey upon
domestic and wild animals or to attempt to
extirpate animals seen by humans as competition for resources such as water or forage.
When hunting moved from a subsistence activity to a selective one, two trends emerged:
# the development of the role of the specialist hunter, with special training and equipment
# the option of hunting as a "sport" for members of an upper social class
The meaning of the word ''game'' in
Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old Englis ...
evolved to include an animal which is hunted. As the domestication of animals for meat grew, subsistence hunting remained among the lowest classes; however, the stylised pursuit of game in European societies became a luxury. Dangerous hunting, such as for lions or
wild boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The species i ...
s, often done on
horseback or from a
chariot
A chariot is a type of cart driven by a charioteer, usually using horses to provide rapid motive power. The oldest known chariots have been found in burials of the Sintashta culture in modern-day Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, dated to c. 2000&n ...
, had a function similar to
tournaments
A tournament is a competition involving at least three competitors, all participating in a sport or game. More specifically, the term may be used in either of two overlapping senses:
# One or more competitions held at a single venue and concentr ...
and manly sports. Hunting ranked as an honourable, somewhat competitive pastime to help the
aristocracy practice skills of war in times of peace.
In most parts of
medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
Europe, the upper class obtained the sole rights to hunt in certain areas of a feudal territory. Game in these areas was used as a source of food and furs, often provided via professional huntsmen, but it was also expected to provide a form of recreation for the aristocracy. The importance of this proprietary view of game can be seen in the
Robin Hood legends, in which one of the primary charges against the outlaws is that they "hunt the King's deer". In contrast, settlers in Anglophone colonies gloried democratically in hunting for all.
In medieval Europe, hunting was considered by
Johannes Scotus Eriugena to be part of the set of ''
seven mechanical arts''.
Use of dog

Although various other animals have been used to aid the hunter, such as
ferrets, the dog has assumed many very important uses to the hunter.
The domestication of the dog has led to a
symbiotic relationship in which the dog's independence from humans is deferred. Though dogs can survive independently of humans, and in many cases do ferrally, when raised or adopted by humans the species tends to defer to its control in exchange for habitation, food and support.
Dogs today are used to find, chase, retrieve, and sometimes kill game. Dogs allow humans to pursue and kill prey that would otherwise be very difficult or dangerous to hunt. Different breeds of specifically bred
hunting dog
A hunting dog is a canine that hunts with or for hunters. There are several different types of hunting dog developed for various tasks and purposes. The major categories of hunting dog include hounds, terriers, dachshunds, cur type dogs, and gu ...
are used for different types of hunting. Waterfowl are commonly hunted using retrieving dogs such as the
Labrador Retriever, the
Golden Retriever, the
Chesapeake Bay Retriever, the
Brittany Spaniel, and other similar breeds.
Game birds are flushed out using flushing
spaniels such as the
English Springer Spaniel, the various
Cocker Spaniels and similar breeds.
The hunting of wild mammals in England and Wales with dogs was banned under the
Hunting Act 2004
The Hunting Act 2004 (c 37) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which bans the hunting of most wild mammals (notably foxes, deer, hares and mink) with dogs in England and Wales, subject to some strictly limited exemptions; ...
. The wild mammals include fox, hare, deer and mink. There are, however, exceptions in the Act.
Religion
Many prehistoric deities are depicted as predators or prey of humans, often in a
zoomorphic form, perhaps alluding to the importance of hunting for most Palaeolithic cultures.
In many pagan religions, specific rituals are conducted before or after a hunt; the rituals done may vary according to the species hunted or the season the hunt is taking place. Often a hunting ground, or the hunt for one or more species, was reserved or prohibited in the context of a temple cult. In Roman religion,
Diana is the goddess of the hunt.

Indian and Eastern religions
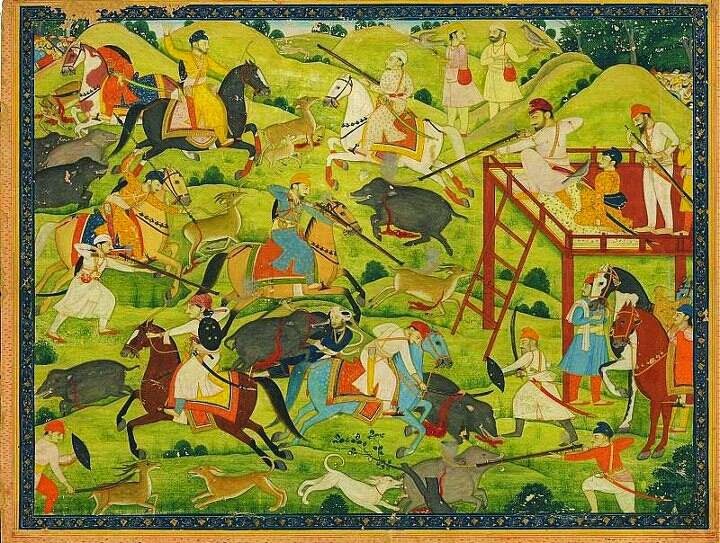

 Hindu scripture
Hindu scriptures describe hunting as an occupation, as well as a sport of the kingly. Even figures considered divine are described to have engaged in hunting. One of the names of the god
Shiva
Shiva (; sa, शिव, lit=The Auspicious One, Śiva ), also known as Mahadeva (; Help:IPA/Sanskrit, ɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐ, or Hara, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the Supreme Being in Shaivism, one o ...
is Mrigavyadha, which translates as "the deer hunter" (''mriga'' means deer; ''vyadha'' means hunter). The word ''Mriga'', in many Indian languages including Malayalam, not only stands for deer, but for all animals and animal instincts (Mriga Thrishna). Shiva, as Mrigavyadha, is the one who destroys the animal instincts in human beings. In the epic
Ramayana
The ''Rāmāyana'' (; sa, रामायणम्, ) is a Sanskrit epic composed over a period of nearly a millennium, with scholars' estimates for the earliest stage of the text ranging from the 8th to 4th centuries BCE, and later stages ...
,
Dasharatha
Dasharatha (Sanskrit: दशरथ, IAST: Daśaratha; born Nemi) was the king of the Kosala kingdom and a scion of the Suryavamsha dynasty in Hinduism. He ruled from this capital at Ayodhya. Dasharatha was the son of Aja and Indumati. He h ...
, the father of
Rama
Rama (; ), Ram, Raman or Ramar, also known as Ramachandra (; , ), is a major deity in Hinduism. He is the seventh and one of the most popular '' avatars'' of Vishnu. In Rama-centric traditions of Hinduism, he is considered the Supreme Bei ...
, is said to have the ability to hunt in the dark. During one of his hunting expeditions, he accidentally killed
Shravana
Shravana is the 22nd '' nakshatra'' (Devanagari नक्षत्र) or ''lunar mansion'' as used in Hindu astronomy, Hindu calendar and Hindu astrology. It belongs to the constellation Makara (Devanagari: मकर), a legendary sea creatu ...
, mistaking him for game. During Rama's exile in the forest,
Ravana
Ravana (; , , ) is a rakshasa king of the island of Lanka, and the chief antagonist of the Hindu epic '' Ramayana'' and its adaptations.
In the ''Ramayana'', Ravana is described to be the eldest son of sage Vishrava and rakshasi Kaikesi. He ...
kidnapped his wife,
Sita
Sita (; ) also called as Janaki and Vaidehi is a Hindu goddess and the female protagonist of the Hindu epic, ''Ramayana''. She is the consort of Rama, the avatar of the god Vishnu, and is regarded as a form of Vishnu's consort, Lakshmi. She ...
, from their hut, while Rama was asked by Sita to capture a golden deer, and his brother
Lakshman went after him. According to the
Mahabharat,
Pandu, the father of the
Pandavas
The Pandavas (Sanskrit: पाण्डव, IAST: Pāṇḍava) refers to the five legendary brothers— Yudhishthira, Bhima, Arjuna, Nakula and Sahadeva—who are the central characters of the Hindu epic ''Mahabharata''. They are acknowledge ...
, accidentally killed the sage Kindama and his wife with an arrow, mistaking them for a deer.
Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle bein ...
teaches followers to have tremendous respect for all of life. Prohibitions for hunting and meat eating are the fundamental conditions for being a
Jain
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle being ...
.
Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
's first
precept
A precept (from the la, præcipere, to teach) is a commandment, instruction, or order intended as an authoritative rule of action.
Religious law
In religion, precepts are usually commands respecting moral conduct.
Christianity
The term is en ...
is the respect for all sentient life. The general approach by all Buddhists is to avoid killing any living animals.
Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism.
According to Buddhist tradition, he was born in L ...
explained the issue by saying "all fear death; comparing others with oneself, one should neither kill nor cause to kill."
In
Sikhism
Sikhism (), also known as Sikhi ( pa, ਸਿੱਖੀ ', , from pa, ਸਿੱਖ, lit=disciple', 'seeker', or 'learner, translit=Sikh, label=none),''Sikhism'' (commonly known as ''Sikhī'') originated from the word ''Sikh'', which comes fro ...
, only meat obtained from hunting, or slaughtered with the
Jhatka
Jhatka, or Jhataka or chatka (' ), is the meat from an animal killed instantly, such as by a single strike of a sword or axe to sever the head within the Sikh religion. This type of slaughter is preferred by most Rajput in Hinduism Sikhs as well ...
is permitted. The
Sikh gurus, especially
Guru Hargobind and
Guru Gobind Singh were ardent hunters. Many old Sikh
Rehatnamas like
Prem Sumarag, recommend hunting
wild boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The species i ...
and
deer
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the re ...
. However, among modern Sikhs, the practise of hunting has died down; some even saying that all meat is forbidden.
Christianity, Judaism, and Islam
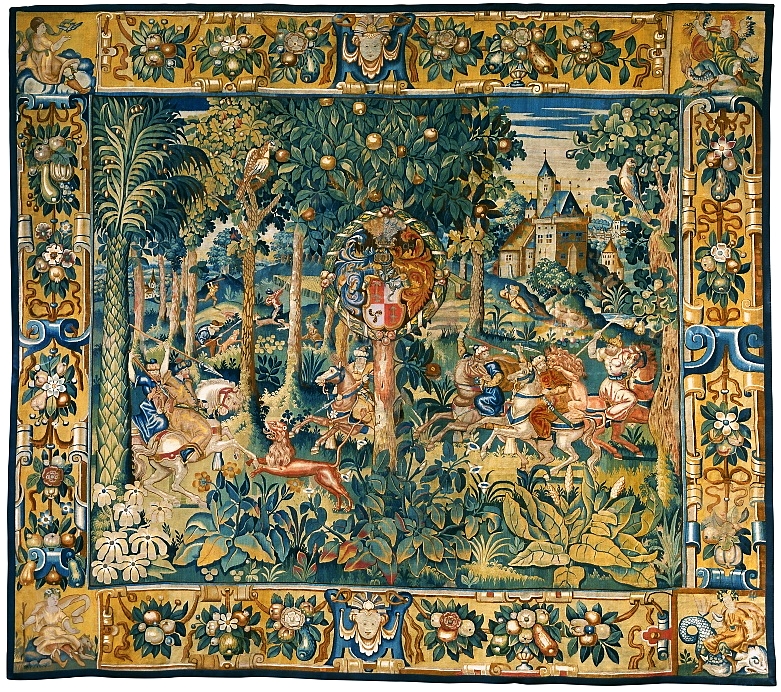


From
early Christian
Early Christianity (up to the First Council of Nicaea in 325) spread from the Levant, across the Roman Empire, and beyond. Originally, this progression was closely connected to already established Jewish centers in the Holy Land and the Jewis ...
times, hunting has been forbidden to Roman Catholic Church
clerics. Thus the ''
Corpus Juris Canonici'' (C. ii, X, De cleric. venat.) says, "We forbid to all servants of God hunting and expeditions through the woods with hounds; and we also forbid them to keep hawks or falcons." The
Fourth Council of the Lateran
The Fourth Council of the Lateran or Lateran IV was convoked by Pope Innocent III in April 1213 and opened at the Lateran Palace in Rome on 11 November 1215. Due to the great length of time between the Council's convocation and meeting, many b ...
, held under
Pope Innocent III
Pope Innocent III ( la, Innocentius III; 1160 or 1161 – 16 July 1216), born Lotario dei Conti di Segni (anglicized as Lothar of Segni), was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 8 January 1198 to his death in 16 ...
, decreed (canon xv): "We interdict hunting or hawking to all clerics." The decree of the
Council of Trent
The Council of Trent ( la, Concilium Tridentinum), held between 1545 and 1563 in Trent (or Trento), now in northern Italy, was the 19th ecumenical council of the Catholic Church. Prompted by the Protestant Reformation, it has been described a ...
is worded more mildly: "Let clerics abstain from illicit hunting and hawking" (Sess. XXIV, De reform., c. xii), which seems to imply that not all hunting is illicit, and canonists generally make a distinction declaring noisy (''clamorosa'') hunting unlawful, but not quiet (''quieta'') hunting.
Ferraris gives it as the general sense of canonists that hunting is allowed to clerics if it be indulged in rarely and for sufficient cause, as necessity, utility or "honest" recreation, and with that moderation which is becoming to the ecclesiastical state. Ziegler, however, thinks that the interpretation of the canonists is not in accordance with the letter or spirit of the laws of the church.
Nevertheless, although a distinction between lawful and unlawful hunting is undoubtedly permissible, it is certain that a bishop can absolutely prohibit all hunting to the clerics of his diocese, as was done by
synod
A synod () is a council of a Christian denomination, usually convened to decide an issue of doctrine, administration or application. The word '' synod'' comes from the meaning "assembly" or "meeting" and is analogous with the Latin word mean ...
s at
Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city ...
,
Avignon
Avignon (, ; ; oc, Avinhon, label= Provençal or , ; la, Avenio) is the prefecture of the Vaucluse department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region of Southeastern France. Located on the left bank of the river Rhône, the commune had ...
,
Liège,
Cologne
Cologne ( ; german: Köln ; ksh, Kölle ) is the largest city of the German western state of North Rhine-Westphalia (NRW) and the fourth-most populous city of Germany with 1.1 million inhabitants in the city proper and 3.6 millio ...
, and elsewhere.
Benedict XIV declared that such synodal decrees are not too severe, as an absolute prohibition of hunting is more conformable to the
ecclesiastical law
Canon law (from grc, κανών, , a 'straight measuring rod, ruler') is a set of ordinances and regulations made by ecclesiastical authority (church leadership) for the government of a Christian organization or church and its members. It is t ...
. In practice, therefore, the synodal statutes of various localities must be consulted to discover whether they allow quiet hunting or prohibit it altogether.
In Jewish law hunting is not forbidden although there is an aversion to it. The great 18th-century authority
Rabbi Yechezkel Landau after a study concluded although "hunting would not be considered cruelty to animals insofar as the animal is generally killed quickly and not tortured... There is an unseemly element in it, namely cruelty." The other issue is that hunting can be dangerous and Judaism places an extreme emphasis on the value of human life.
Islamic
Sharia Law permits hunting of lawful animals and birds if they cannot be easily caught and slaughtered. However, this is only for the purpose of food and not for trophy hunting.
National traditions
East Africa

A safari, from a
Swahili word meaning "a long journey", especially in Africa, is defined as an overland journey. Safari as a distinctive way of hunting was popularized by the US author
Ernest Hemingway
Ernest Miller Hemingway (July 21, 1899 – July 2, 1961) was an American novelist, short-story writer, and journalist. His economical and understated style—which he termed the iceberg theory—had a strong influence on 20th-century f ...
and President
Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt Jr. ( ; October 27, 1858 – January 6, 1919), often referred to as Teddy or by his initials, T. R., was an American politician, statesman, soldier, conservationist, naturalist, historian, and writer who served as the 26t ...
. A safari may consist of a several-days—or even weeks-long journey, with
camping
Camping is an outdoor activity involving overnight stays away from home, either without shelter or using basic shelter such as a tent, or a recreational vehicle. Typically, participants leave developed areas to spend time outdoors in more nat ...
in
the bush or
jungle
A jungle is land covered with dense forest and tangled vegetation, usually in tropical climates. Application of the term has varied greatly during the past recent century.
Etymology
The word ''jungle'' originates from the Sanskrit word ''ja� ...
, while pursuing
big game. Nowadays, it is often used to describe hunting tours through African wildlife.
Hunters are usually tourists, accompanied by
licensed and highly
regulated
Regulation is the management of complex systems according to a set of rules and trends. In systems theory, these types of rules exist in various fields of biology and society, but the term has slightly different meanings according to context. ...
professional hunters, local guides,
skinners, and
porters Porters may refer to:
* Porters, Virginia, an unincorporated community in Virginia, United States
* Porters, Wisconsin, an unincorporated community in Wisconsin, United States
* Porters Ski Area, a ski resort in New Zealand
* ''Porters'' (TV seri ...
in more difficult terrains. A special safari type is the solo-safari, where all the license acquiring, stalking, preparation, and outfitting is done by the hunter himself.
Indian subcontinent

During the
feudal and
colonial times in
British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
, hunting or ''shikar'' was regarded as a regal sport in the numerous
princely states, as many
maharaja
Mahārāja (; also spelled Maharajah, Maharaj) is a Sanskrit title for a "great ruler", "great king" or " high king".
A few ruled states informally called empires, including ruler raja Sri Gupta, founder of the ancient Indian Gupta Empire, a ...
s and
nawab
Nawab ( Balochi: نواب; ar, نواب;
bn, নবাব/নওয়াব;
hi, नवाब;
Punjabi : ਨਵਾਬ;
Persian,
Punjabi ,
Sindhi,
Urdu: ), also spelled Nawaab, Navaab, Navab, Nowab, Nabob, Nawaabshah, Nawabshah or Nobab, ...
s, as well as British officers, maintained a whole corps of ''shikari''s (
big-game hunters), who were native professional hunters. They would be headed by a master of the hunt, who might be styled ''mir-shikar''. Often, they recruited the normally low-ranking local tribes because of their
traditional knowledge
Traditional knowledge (TK), indigenous knowledge (IK) and local knowledge generally refer to knowledge systems embedded in the cultural traditions of regional, indigenous, or local communities. According to the World Intellectual Property Or ...
of the environment and hunting techniques. Big game, such as
Bengal tigers
The Bengal tiger is a population of the '' Panthera tigris tigris'' subspecies. It ranks among the biggest wild cats alive today. It is considered to belong to the world's charismatic megafauna.
The tiger is estimated to have been present i ...
, might be hunted from the back of an
Indian elephant.
Regional
social norms are generally antagonistic to hunting, while a few
sects, such as the
Bishnoi, lay special emphasis on the conservation of particular species, such as the
antelope. India's
Wildlife Protection Act of 1972 bans the killing of all wild animals. However, the
Chief Wildlife Warden may, if satisfied that any wild animal from a specified list has become dangerous to human life, or is so disabled or diseased as to be beyond recovery, permit any person to hunt such an animal. In this case, the body of any wild animal killed or wounded becomes government property.
The practice among the soldiers in British India during the 1770s of going out to hunt
snipe
A snipe is any of about 26 wading bird species in three genera in the family Scolopacidae. They are characterized by a very long, slender bill, eyes placed high on the head, and cryptic/ camouflaging plumage. The '' Gallinago'' snipes have ...
s, a
shorebird
245px, A flock of Dunlins and Red knots">Red_knot.html" ;"title="Dunlins and Red knot">Dunlins and Red knots
Waders or shorebirds are birds of the order Charadriiformes commonly found wikt:wade#Etymology 1, wading along shorelines and mudflat ...
considered extremely challenging for hunters due to its alertness, camouflaging color and erratic flight behavior, is believed to be the origin of the modern word for
sniper
A sniper is a military/paramilitary marksman who engages targets from positions of concealment or at distances exceeding the target's detection capabilities. Snipers generally have specialized training and are equipped with high-precision r ...
, as snipe-hunters needed to be stealthy in addition to having
tracking skills and
marksmanship.
The term was used in the nineteenth century, and had become common usage by the
First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
.
United Kingdom

Unarmed
fox hunting on horseback with hounds is the type of hunting most closely associated with the United Kingdom; in fact, "hunting" without qualification implies fox hunting. What in other countries is called "hunting" is called "shooting" (birds) or "stalking" (deer) in Britain. Originally a form of
vermin
Vermin ( colloquially varmint(s) or varmit(s)) are pests or nuisance animals that spread diseases or destroy crops or livestock. Since the term is defined in relation to human activities, which species are included vary by region and enterp ...
control to protect livestock, fox hunting became a popular social activity for newly wealthy upper classes in
Victorian times and a traditional rural activity for riders and foot followers alike. Similar to fox hunting in many ways is the chasing of hares with
hounds. Pairs of
sighthounds (or long-dogs), such as
greyhounds, may be used to pursue a hare in coursing, where the greyhounds are marked as to their skill in coursing the hare (but are not intended to actually catch it), or the hare may be pursued with
scent hound
Franz Rudolf Frisching in the uniform of an officer of the Bernese Huntsmen Corps with his Berner Laufhund, painted by Jean Preudhomme in 1785
Scent hounds (or scenthounds) are a Dog type, type of hound that primarily hunts by scent rather than ...
s such as
beagles or harriers. Other sorts of
foxhounds may also be used for hunting
stags (deer) or
mink
Mink are dark-colored, semiaquatic, carnivorous mammals of the genera '' Neogale'' and '' Mustela'' and part of the family Mustelidae, which also includes weasels, otters, and ferrets. There are two extant species referred to as "mink": ...
.
Deer stalking with rifles is carried out on foot without hounds, using stealth.
These forms of hunting have been controversial in the UK.
Animal welfare
Animal welfare is the well-being of non-human animals. Formal standards of animal welfare vary between contexts, but are debated mostly by animal welfare groups, legislators, and academics. Animal welfare science uses measures such as longevit ...
supporters believe that hunting causes unnecessary suffering to foxes, horses, and hounds. Proponents argue that it is culturally and perhaps economically important. Using dogs to chase wild mammals was
made illegal in February 2005 by the
Hunting Act 2004
The Hunting Act 2004 (c 37) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which bans the hunting of most wild mammals (notably foxes, deer, hares and mink) with dogs in England and Wales, subject to some strictly limited exemptions; ...
; there were a number of exemptions (under which the activity may not be illegal) in the act for hunting with hounds, but no exemptions at all for hare-coursing.
Shooting traditions
Game birds, especially
pheasants, are shot with shotguns for sport in the UK; the
British Association for Shooting and Conservation says that over a million people per year participate in shooting, including game shooting,
clay pigeon shooting, and
target shooting
Shooting sports is a group of competitive and recreational sporting activities involving proficiency tests of accuracy, precision and speed in shooting — the art of using ranged weapons, mainly small arms ( firearms and airguns, in forms suc ...
.
Shooting as practised in Britain, as opposed to traditional hunting, requires little questing for game—around thirty-five million birds are released onto shooting estates every year, some having been
factory farmed
Intensive animal farming or industrial livestock production, also known by its opponents as factory farming and macro-farms, is a type of intensive agriculture, specifically an approach to animal husbandry designed to maximize production, while ...
. Shoots can be elaborate affairs with guns placed in assigned positions and assistants to help load shotguns. When in position, "beaters" move through the areas of cover, swinging sticks or flags to drive the game out. Such events are often called "drives". The open season for
grouse in the UK begins on 12 August, the so-called
Glorious Twelfth. The definition of game in the United Kingdom is governed by the
Game Act 1831
The Game Act 1831 (1 & 2 Will 4 c 32) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which was passed to protect game birds by establishing a close season when they could not be legally taken. The Act also established the need for game licenc ...
.
A similar tradition, ', exists in Spain.
United States
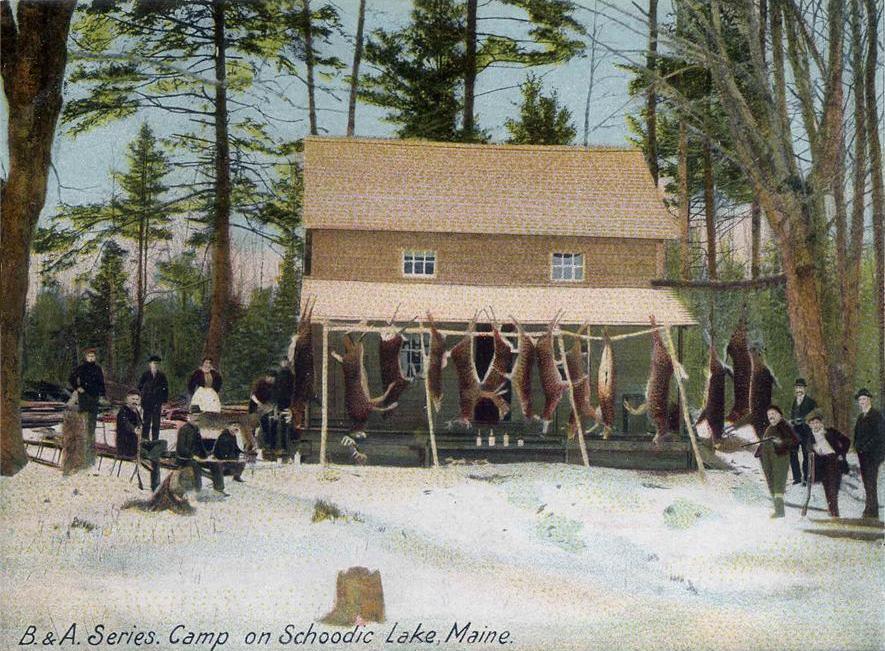

North American hunting pre-dates the United States by thousands of years and was an important part of many
pre-Columbian
In the history of the Americas, the pre-Columbian era spans from the original settlement of North and South America in the Upper Paleolithic period through European colonization, which began with Christopher Columbus's voyage of 1492. Usually, ...
Native American cultures. Native Americans retain some hunting rights and are exempt from some laws as part of Indian treaties and otherwise under
federal law
Federal law is the body of law created by the federal government of a country. A federal government is formed when a group of political units, such as states or provinces join in a federation, delegating their individual sovereignty and many ...
—examples include
eagle feather laws and exemptions in the
Marine Mammal Protection Act. This is considered particularly important in
Alaskan native communities.
Hunting is primarily regulated by
state law State law refers to the law of a federated state, as distinguished from the law of the federation
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, o ...
; additional regulations are imposed through
United States environmental law
United States environmental law concerns legal standards to protect human health and improve the natural environment of the United States. While subject to criticism at home and abroad on issues of protection, enforcement, and over-regulation, th ...
in the case of
migratory birds
Bird migration is the regular seasonal movement, often north and south along a flyway, between breeding and wintering grounds. Many species of bird migrate. Migration carries high costs in predation and mortality, including from hunting b ...
and
endangered species. Regulations vary widely from state to state and govern the areas, time periods, techniques and methods by which specific game animals may be hunted. Some states make a distinction between
protected species and unprotected species (often
vermin
Vermin ( colloquially varmint(s) or varmit(s)) are pests or nuisance animals that spread diseases or destroy crops or livestock. Since the term is defined in relation to human activities, which species are included vary by region and enterp ...
or
varmints for which there are no hunting regulations). Hunters of protected species require a
hunting license in all states, for which completion of a hunting safety course is sometimes a prerequisite.
Typically, game animals are divided into several categories for regulatory purposes. Typical categories, along with example species, are as follows:
* ''Big game'':
white-tailed deer,
mule deer,
moose
The moose (in North America) or elk (in Eurasia) (''Alces alces'') is a member of the New World deer subfamily and is the only species in the genus ''Alces''. It is the largest and heaviest extant species in the deer family. Most adult ma ...
,
elk,
caribou,
bear,
bighorn sheep
The bighorn sheep (''Ovis canadensis'') is a species of sheep native to North America. It is named for its large horns. A pair of horns might weigh up to ; the sheep typically weigh up to . Recent genetic testing indicates three distinct subsp ...
,
pronghorn,
boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The species is ...
,
javelina,
bison
Bison are large bovines in the genus ''Bison'' (Greek: "wild ox" (bison)) within the tribe Bovini. Two extant and numerous extinct species are recognised.
Of the two surviving species, the American bison, ''B. bison'', found only in North A ...
* ''Small game'':
rabbit
Rabbits, also known as bunnies or bunny rabbits, are small mammals in the family Leporidae (which also contains the hares) of the order Lagomorpha (which also contains the pikas). ''Oryctolagus cuniculus'' includes the European rabbit sp ...
, hare,
squirrel
Squirrels are members of the family Sciuridae, a family that includes small or medium-size rodents. The squirrel family includes tree squirrels, ground squirrels (including chipmunks and prairie dogs, among others), and flying squirrels. ...
,
opossum,
raccoon,
porcupine
Porcupines are large rodents with coats of sharp spines, or quills, that protect them against predation. The term covers two families of animals: the Old World porcupines of family Hystricidae, and the New World porcupines of family, Erethiz ...
,
skunk,
ring-tailed cat
The ringtail (''Bassariscus astutus'') is a mammal of the raccoon family native to arid regions of North America. It is widely distributed and well adapted to disturbed areas. It has been legally trapped for its fur. It is listed as Least Co ...
,
armadillo,
ruffed grouse
* ''Furbearers'':
beaver
Beavers are large, semiaquatic rodents in the genus ''Castor'' native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere. There are two extant species: the North American beaver (''Castor canadensis'') and the Eurasian beaver (''C. fiber''). Beavers a ...
,
red fox
The red fox (''Vulpes vulpes'') is the largest of the true foxes and one of the most widely distributed members of the Order (biology), order Carnivora, being present across the entire Northern Hemisphere including most of North America, Europe ...
,
mink
Mink are dark-colored, semiaquatic, carnivorous mammals of the genera '' Neogale'' and '' Mustela'' and part of the family Mustelidae, which also includes weasels, otters, and ferrets. There are two extant species referred to as "mink": ...
,
pine marten,
musk rat,
otter,
bobcat
The bobcat (''Lynx rufus''), also known as the red lynx, is a medium-sized cat native to North America. It ranges from southern Canada through most of the contiguous United States to Oaxaca in Mexico. It is listed as Least Concern on the ...
,
coyote
The coyote (''Canis latrans'') is a species of canine native to North America. It is smaller than its close relative, the wolf, and slightly smaller than the closely related eastern wolf and red wolf. It fills much of the same ecological nich ...
* ''Predators'':
cougar,
wolf
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; : wolves), also known as the gray wolf or grey wolf, is a large canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, and gray wolves, as popularly un ...
,
coyote
The coyote (''Canis latrans'') is a species of canine native to North America. It is smaller than its close relative, the wolf, and slightly smaller than the closely related eastern wolf and red wolf. It fills much of the same ecological nich ...
* ''
Upland game bird'':
grouse,
woodcock
The woodcocks are a group of seven or eight very similar living species of wading birds in the genus ''Scolopax''. The genus name is Latin for a snipe or woodcock, and until around 1800 was used to refer to a variety of waders. The English ...
,
chukar,
pheasant,
quail,
dove
* ''
Waterfowl
Anseriformes is an order of birds also known as waterfowl that comprises about 180 living species of birds in three families: Anhimidae (three species of screamers), Anseranatidae (the magpie goose), and Anatidae, the largest family, which ...
'':
duck
Duck is the common name for numerous species of waterfowl in the family Anatidae. Ducks are generally smaller and shorter-necked than swans and geese, which are members of the same family. Divided among several subfamilies, they are a form ...
,
teal,
merganser,
geese,
swan
Swans are birds of the family Anatidae within the genus ''Cygnus''. The swans' closest relatives include the geese and ducks. Swans are grouped with the closely related geese in the subfamily Anserinae where they form the tribe Cygnini. Som ...
Hunting big game typically requires a "tag" for each animal harvested. Tags must be purchased in addition to the hunting license, and the number of tags issued to an individual is typically limited. In cases where there are more prospective hunters than the quota for that species, tags are usually assigned by lottery. Tags may be further restricted to a specific area, or wildlife management unit.
Hunting migratory waterfowl requires a duck stamp from the
Fish and Wildlife Service in addition to the appropriate state hunting license.
Harvest of animals other than big game is typically restricted by a bag limit and a possession limit. A bag limit is the maximum number of a specific animal species that an individual can harvest in a single day. A possession limit is the maximum number of a specific animal species that can be in an individual's possession at any time.
Shooting

Gun usage in hunting is typically regulated by game category, area within the state, and time period. Regulations for
big-game hunting often specify a minimum
caliber or
muzzle energy
Muzzle energy is the kinetic energy of a bullet as it is expelled from the muzzle of a firearm. Without consideration of factors such as aerodynamics and gravity for the sake of comparison, muzzle energy is used as a rough indication of the de ...
for
firearm
A firearm is any type of gun designed to be readily carried and used by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries (see Legal definitions).
The first firearms originated in 10th-century China, when bamboo tubes ...
s. The use of
rifle
A rifle is a long-barreled firearm designed for accurate shooting, with a barrel that has a helical pattern of grooves ( rifling) cut into the bore wall. In keeping with their focus on accuracy, rifles are typically designed to be held with ...
s is often banned for safety reasons in areas with high
population densities
Population density (in agriculture: standing stock or plant density) is a measurement of population per unit land area. It is mostly applied to humans, but sometimes to other living organisms too. It is a key geographical term.Matt RosenberPo ...
or limited
topographic relief. Regulations may also limit or ban the use of
lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, ...
in
ammunition
Ammunition (informally ammo) is the material fired, scattered, dropped, or detonated from any weapon or weapon system. Ammunition is both expendable weapons (e.g., bombs, missiles, grenades, land mines) and the component parts of other we ...
because of environmental concerns. Specific seasons for
bow hunting or
muzzle-loading black-powder guns are often established to limit competition with hunters using more effective
weapons.
Hunting in the United States is not associated with any particular class or culture; a 2006 poll showed seventy-eight percent of Americans supported legal hunting, although relatively few Americans actually hunt. At the beginning of the 21st century, just six percent of Americans hunted.
Southerners in states along the eastern seaboard hunted at a rate of five percent, slightly below the national average, and while hunting was more common in other parts of the South at nine percent, these rates did not surpass those of the Plains states, where twelve percent of
Midwesterners
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of the United States. I ...
hunted. Hunting in other areas of the country fell below the national average. Overall, in the 1996–2006 period, the number of hunters over the age of sixteen declined by ten percent, a drop attributable to a number of factors including
habitat loss
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss and habitat reduction) is the process by which a natural habitat becomes incapable of supporting its native species. The organisms that previously inhabited the site are displaced or dead, thereby ...
and changes in recreation habits.
Regulation
Regulation of hunting within the United States dates from the 19th century. Some modern hunters see themselves as
conservationists
The conservation movement, also known as nature conservation, is a political, environmental, and social movement that seeks to manage and protect natural resources, including animal, fungus, and plant species as well as their habitat for the ...
and sportsmen in the mode of
Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt Jr. ( ; October 27, 1858 – January 6, 1919), often referred to as Teddy or by his initials, T. R., was an American politician, statesman, soldier, conservationist, naturalist, historian, and writer who served as the 26t ...
and the
Boone and Crockett Club. Local hunting clubs and national organizations provide hunter education and help protect the future of the sport by buying land for future hunting use. Some groups represent a specific hunting interest, such as
Ducks Unlimited,
Pheasants Forever
Pheasants Forever, Inc. (PF), a 501(c)(3) non-profit conservation organization, is dedicated to conserving wildlife habitat suitable for pheasants. Formed in 1982 as a response to the continuing decline of upland wildlife and habitat throughout th ...
, or the
Delta Waterfowl Foundation
Delta Waterfowl Foundation is a non-profit organization operating in both Canada and in the United States whose mission is to secure the future of waterfowl and waterfowl hunting. Delta provides knowledge, leaders, and science-based solutions ...
. Many hunting groups also participate in lobbying the federal government and state government.
Each year, nearly $200 million in hunters' federal excise taxes are distributed to state agencies to support wildlife management programs, the purchase of lands open to hunters, and hunter education and safety classes. Since 1934, the sale of
Federal Duck Stamps, a required purchase for migratory
waterfowl
Anseriformes is an order of birds also known as waterfowl that comprises about 180 living species of birds in three families: Anhimidae (three species of screamers), Anseranatidae (the magpie goose), and Anatidae, the largest family, which ...
hunters over sixteen years old, has raised over $700 million to help purchase more than of habitat for the
National Wildlife Refuge System
National Wildlife Refuge System is a designation for certain protected areas of the United States managed by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service. The National Wildlife Refuge System is the system of public lands and waters set aside to c ...
lands that support waterfowl and many other wildlife species and are often open to hunting. States also collect money from hunting licenses to assist with management of game animals, as designated by law. A key task of federal and state
park ranger
A ranger, park ranger, park warden, or forest ranger is a law enforcement person entrusted with protecting and preserving parklands – national, state, provincial, or local parks.
Description
"Parks" may be broadly defined by some systems in thi ...
s and
game warden
A conservation officer is a law enforcement officer who protects wildlife and the environment. A conservation officer may also be referred to as an environmental technician or technologist, game warden, forest ranger, forest watcher, forest g ...
s is to enforce laws and regulations related to hunting, including species protection,
hunting seasons, and hunting bans.
Varmint hunting

Varmint hunting is an American phrase for the selective killing of non-game animals seen as pests. While not always an efficient form of
pest control, varmint hunting achieves selective control of pests while providing recreation and is much less regulated. Varmint species are often responsible for detrimental effects on crops, livestock,
landscaping
Landscaping refers to any activity that modifies the visible features of an area of land, including the following:
# Living elements, such as flora or fauna; or what is commonly called gardening, the art and craft of growing plants with a goal ...
,
infrastructure
Infrastructure is the set of facilities and systems that serve a country, city, or other area, and encompasses the services and facilities necessary for its economy, households and firms to function. Infrastructure is composed of public and priv ...
, and pets. Some animals, such as wild rabbits or squirrels, may be utilised for fur or meat, but often no use is made of the carcass. Which species are varmints depends on the circumstance and area. Common varmints may include various
rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the order Rodentia (), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are n ...
s,
coyotes,
crows,
foxes,
feral cats, and feral
hogs. Some animals once considered varmints are now protected, such as wolves. In the US state of
Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is bord ...
, a
non-native rodent, the
coypu
The nutria (''Myocastor coypus''), also known as the coypu, is a large, herbivorous, semiaquatic rodent.
Classified for a long time as the only member of the family Myocastoridae, ''Myocastor'' is now included within Echimyidae, the family of t ...
, has become so destructive to the local ecosystem that the state has initiated a
bounty
Bounty or bounties commonly refers to:
* Bounty (reward), an amount of money or other reward offered by an organization for a specific task done with a person or thing
Bounty or bounties may also refer to:
Geography
* Bounty, Saskatchewan, a g ...
program to help control the population.
Beavers from North America constitute an invasive species in
Tierra del Fuego, where eradication attempts are ongoing.
Fair chase
The principles of the
fair chase have been a part of the American hunting tradition for over one hundred years. The role of the hunter-conservationist, popularised by Theodore Roosevelt, and perpetuated by Roosevelt's formation of the
Boone and Crockett Club, has been central to the development of the modern fair chase tradition. ''Beyond Fair Chase: The Ethic and Tradition of Hunting'', a book by Jim Posewitz, describes fair chase:
"Fundamental to ethical hunting is the idea of fair chase. This concept addresses the balance between the hunter and the hunted. It is a balance that allows hunters to occasionally succeed while animals generally avoid being taken."
When
Internet hunting
Internet hunting is the practice of hunting via remotely controlled firearms that can be aimed and shot using online webcams. The first internet hunting website, Live-Shot.com, was created in 2005 by John Lockwood, who saw it as a way to provide ...
was introduced in 2005, allowing people to hunt over the Internet using remotely controlled guns, the practice was widely criticised by hunters as violating the principles of fair chase. As a representative of the
National Rifle Association of America
The National Rifle Association of America (NRA) is a gun rights advocacy group based in the United States. Founded in 1871 to advance rifle marksmanship, the modern NRA has become a prominent gun rights lobbying organization while conti ...
(NRA) explained, "The NRA has always maintained that fair chase, being in the field with your firearm or bow, is an important element of hunting tradition. Sitting at your desk in front of your computer, clicking at a mouse, has nothing to do with hunting."
[Humane Society Wildlife Abuse Campaign]
Fact Sheet on Internet Hunting
/ref>
 One hunting club declares that a fair chase shall not involve the taking of animals under the following conditions:
* Helpless in a trap, deep snow or water, or on ice.
* From any power vehicle or power boat.
* By " jacklighting" or shining at night.
* By the use of any tranquilizers or poisons.
* While inside escape-proof fenced enclosures.
* By the use of any power vehicle or power boat for herding or driving animals, including use of aircraft to land alongside or to communicate with or direct a hunter on the ground.
* By the use of electronic devices for attracting, locating or pursuing game or guiding the hunter to such game, or by the use of a bow or arrow to which any electronic device is attached.
One hunting club declares that a fair chase shall not involve the taking of animals under the following conditions:
* Helpless in a trap, deep snow or water, or on ice.
* From any power vehicle or power boat.
* By " jacklighting" or shining at night.
* By the use of any tranquilizers or poisons.
* While inside escape-proof fenced enclosures.
* By the use of any power vehicle or power boat for herding or driving animals, including use of aircraft to land alongside or to communicate with or direct a hunter on the ground.
* By the use of electronic devices for attracting, locating or pursuing game or guiding the hunter to such game, or by the use of a bow or arrow to which any electronic device is attached.
Ranches
Animals such as blackbuck, nilgai
The nilgai (''Boselaphus tragocamelus'') (, literally meaning "blue cow") is the largest Asian antelope and is ubiquitous across the northern Indian subcontinent. It is the sole member of the genus ''Boselaphus'' and was described by Peter Si ...
, axis deer, fallow deer, zebras, barasingha, gazelle and many other exotic game species can now be found on game farm and ranch
A ranch (from es, rancho/Mexican Spanish) is an area of land, including various structures, given primarily to ranching, the practice of raising grazing livestock such as cattle and sheep. It is a subtype of a farm. These terms are most ofte ...
es in Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by ...
, where they were introduced for sport hunting. These hunters can be found paying in excess of $10,000 dollars to take trophy animals on these controlled ranches.
Russia
The Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
n imperial hunts evolved from hunting traditions of early Russian rulers— Grand Princes and Tsars—under the influence of hunting customs of European royal courts. The imperial hunts were organised mainly in Peterhof, Tsarskoye Selo, and Gatchina.

Australia
Hunting in Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
has evolved around the hunting and eradication of various animals considered to be pests or invasive species . All native animals are protected by law, and certain species such as kangaroo
Kangaroos are four marsupials from the family Macropodidae (macropods, meaning "large foot"). In common use the term is used to describe the largest species from this family, the red kangaroo, as well as the antilopine kangaroo, eastern ...
s and duck
Duck is the common name for numerous species of waterfowl in the family Anatidae. Ducks are generally smaller and shorter-necked than swans and geese, which are members of the same family. Divided among several subfamilies, they are a form ...
s can be hunted by license
A license (or licence) is an official permission or permit to do, use, or own something (as well as the document of that permission or permit).
A license is granted by a party (licensor) to another party (licensee) as an element of an agreeme ...
d shooters but only under a special permit on public lands during open seasons. The introduced species
An introduced species, alien species, exotic species, adventive species, immigrant species, foreign species, non-indigenous species, or non-native species is a species living outside its native distributional range, but which has arrived there ...
that are targeted include European rabbits, red fox
The red fox (''Vulpes vulpes'') is the largest of the true foxes and one of the most widely distributed members of the Order (biology), order Carnivora, being present across the entire Northern Hemisphere including most of North America, Europe ...
es, deer
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the re ...
s ( sambar, hog, red, fallow, chital and rusa), feral cat
A feral cat or a stray cat is an unowned domestic cat (''Felis catus'') that lives outdoors and avoids human contact: it does not allow itself to be handled or touched, and usually remains hidden from humans. Feral cats may breed over dozens ...
s, pigs, goat
The goat or domestic goat (''Capra hircus'') is a domesticated species of goat-antelope typically kept as livestock. It was domesticated from the wild goat (''C. aegagrus'') of Southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of the a ...
s, brumbies, donkeys and occasionally camel
A camel (from: la, camelus and grc-gre, κάμηλος (''kamēlos'') from Hebrew or Phoenician: גָמָל ''gāmāl''.) is an even-toed ungulate in the genus ''Camelus'' that bears distinctive fatty deposits known as "humps" on its back. ...
s, as well as introduced upland birds such as quails, pheasants and partridges.
New Zealand
New Zealand has a strong hunting culture. When humans arrived, the only mammals present on the islands making up New Zealand were bats, although seals and other marine mammals were present along the coasts. However, when humans arrived they brought other species with them. Polynesian voyagers introduced kuri (dogs), kiore (Polynesian rats), as well as a range of plant species. European explorers further added to New Zealand's biota, particularly pigs which were introduced by either Captain Cook or the French explorer De Surville in the 1700s. During the nineteenth century, as European colonisation took place, acclimatisation societies Acclimatisation societies were voluntary associations in the 19th and 20th centuries that encouraged the introduction of non-native species in various places around the world, in the hope that they would acclimatise and adapt to their new environ ...
were established. The societies introduced a large number of species with no use other than as prey for hunting. Species that adapted well to the New Zealand terrain include deer
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the re ...
, pigs, goats, hare
Hares and jackrabbits are mammals belonging to the genus ''Lepus''. They are herbivores, and live solitarily or in pairs. They nest in slight depressions called forms, and their young are able to fend for themselves shortly after birth. The g ...
, tahr and chamois
The chamois (''Rupicapra rupicapra'') or Alpine chamois is a species of goat-antelope native to mountains in Europe, from west to east, including the Alps, the Dinarides, the Tatra and the Carpathian Mountains, the Balkan Mountains, the R ...
. With wilderness areas, suitable forage, and no natural predators, their populations exploded. Government agencies view the animals as pests due to their effects on the natural environment
The natural environment or natural world encompasses all living and non-living things occurring naturally, meaning in this case not artificial. The term is most often applied to the Earth or some parts of Earth. This environment encompasses t ...
and on agricultural production, but hunters view them as a resource.
Iran
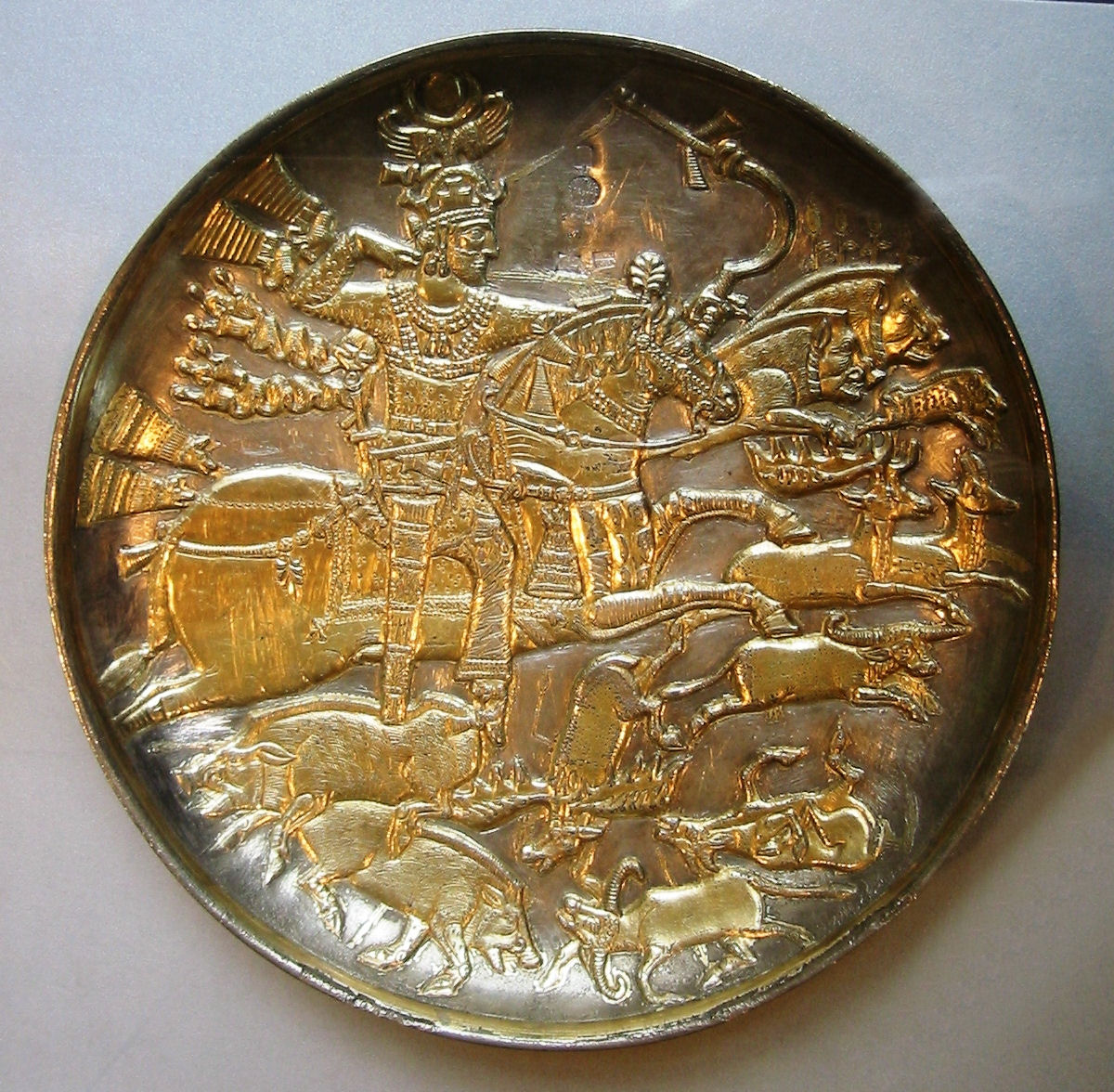 Iranian tradition regarded hunting as an essential part of a prince's education, and hunting was well recorded for the education of the upper-class youths during
Iranian tradition regarded hunting as an essential part of a prince's education, and hunting was well recorded for the education of the upper-class youths during pre-Islamic Persia
The history of Iran is intertwined with the history of a larger region known as Greater Iran, comprising the area from Anatolia in the west to the borders of Ancient India and the Syr Darya in the east, and from the Caucasus and the Eurasian Step ...
. As of October 2020, a hunting licence costs $20,000. The Department of Environment although do not report the number of permits issued.
Japan
The numbers of licensed hunters in Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
, including those using snares and guns, is generally decreasing, while their average age is increasing. , there were approximately 190,000 registered hunters, approximately 65% of whom were sixty years old or older.
Trinidad and Tobago
There is a very active tradition of hunting small to medium-sized wild game in Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago (, ), officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, is the southernmost island country in the Caribbean. Consisting of the main islands Trinidad and Tobago, and numerous much smaller islands, it is situated south of ...
. Hunting is carried out with firearms, slingshots and cage traps, and sometimes aided by the use of hounds. The illegal use of trap guns and snare nets also occurs. With approximately 12,000 to 13,000 hunters applying for and being granted hunting permits in recent years, there is some concern that the practice might not be sustainable. In addition there are at present no bag limits and the open season is comparatively very long (5 months – October to February inclusive). As such hunting pressure from legal hunters is very high. Added to that, there is a thriving and very lucrative black market for poached wild game (sold and enthusiastically purchased as expensive luxury delicacies) and the numbers of commercial poachers in operation is unknown but presumed to be fairly high. As a result, the populations of the five major mammalian game species ( red-rumped agouti, lowland paca
The lowland paca (''Cuniculus paca''), also known as the spotted paca, is a large rodent found in tropical and sub-tropical America, from east-central Mexico to northern Argentina, and has been introduced to Cuba and Algeria.
The animal is calle ...
, nine-banded armadillo, collared peccary and red brocket deer) are thought to be relatively low when compared to less-hunted regions in nearby mainland South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sou ...
(although scientifically conducted population studies are only just recently being conducted ). It appears that the red brocket deer population has been extirpated in Tobago
Tobago () is an island and ward within the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago. It is located northeast of the larger island of Trinidad and about off the northeastern coast of Venezuela. It also lies to the southeast of Grenada. The offic ...
as a result of over-hunting. By some time in the mid 20th century another extirpation due to over-hunting occurred in Trinidad
Trinidad is the larger and more populous of the two major islands of Trinidad and Tobago. The island lies off the northeastern coast of Venezuela and sits on the continental shelf of South America. It is often referred to as the southernmos ...
with its population of horned screamer (a large game bird). Various herons, ducks, doves, the green iguana, the cryptic golden tegu, the spectacled caiman, the common opossum
The common opossum (''Didelphis marsupialis''), also called the southern or black-eared opossum or gambá, and sometimes called a possum, is a marsupial species living from the northeast of Mexico to Bolivia (reaching the coast of the South Paci ...
and the capybara are also commonly hunted and poached. There is also some poaching of 'fully protected species', including red howler monkey and capuchin monkeys, southern tamandua, Brazilian porcupine
The Brazilian porcupine (''Coendou prehensilis'') is a porcupine found in Brazil, Argentina, Colombia, Venezuela, Guyana, French Guiana, Peru, Paraguay, Suriname, Bolivia and Trinidad, with a single record from Ecuador. It inhabits tropical for ...
, yellow-footed tortoise, the critically endangered island endemic Trinidad piping guan and even one of the national birds, the scarlet ibis
The scarlet ibis (''Eudocimus ruber'') is a species of ibis in the bird family Threskiornithidae. It inhabits tropical South America and part of the Caribbean. In form, it resembles most of the other twenty-seven extant species of ibis, but ...
. Legal hunters pay relatively small fees to obtain hunting licences and undergo no official basic conservation biology or hunting-ethics/ fair chase training, and are not assessed regarding their knowledge and comprehension of the local wildlife conservation laws. There is presumed to be relatively little subsistence hunting in the country (with most hunting for either sport or commercial profit). The local wildlife management authorities are under-staffed and under-funded, and as such little in the way of enforcement is done to uphold existing wildlife management laws, with hunting/poaching occurring both in and out of season and even in wildlife sanctuaries. There is some indication that the government is beginning to take the issue of wildlife management more seriously, with well drafted legislation being brought before Parliament in 2015. It remains to be seen if the drafted legislation will be fully adopted and financially supported by the current and future governments, and if the general populace will move towards a greater awareness of the importance of wildlife conservation and change the culture of wanton consumption to one of sustainable management.
Wildlife management
 Hunting is claimed to give resource managers an important tool in managing populations that might exceed the carrying capacity of their
Hunting is claimed to give resource managers an important tool in managing populations that might exceed the carrying capacity of their habitat
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical ...
and threaten the well-being of other species, or, in some instances, damage human health or safety.
In some cases, hunting actually can increase the population of predators such as coyotes by removing territorial bounds that would otherwise be established, resulting in excess neighbouring migrations into an area, thus artificially increasing the population. Hunting advocates assert that hunting reduces intraspecific competition for food and shelter, reducing mortality among the remaining animals. Some environmentalist
An environmentalist is a person who is concerned with and/or advocates for the protection of the environment. An environmentalist can be considered a supporter of the goals of the environmental movement, "a political and ethical movement that se ...
s assert that (re)introducing predator
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill t ...
s would achieve the same end with greater efficiency and less negative effect, such as introducing significant amounts of free lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, ...
into the environment and food chain.
In the United States, wildlife managers are frequently part of hunting regulatory and licensing bodies, where they help to set rules on the number, manner and conditions in which game may be hunted.
Management agencies sometimes rely on hunting to control specific animal populations, as has been the case with deer in North America. These hunts may sometimes be carried out by professional shooters, although others may include amateur hunters. Many US city and local governments hire professional and amateur hunters each year to reduce populations of animals such as deer that are becoming hazardous in a restricted area, such as neighbourhood parks and metropolitan
Metropolitan may refer to:
* Metropolitan area, a region consisting of a densely populated urban core and its less-populated surrounding territories
* Metropolitan borough, a form of local government district in England
* Metropolitan county, a typ ...
open spaces.
A large part of managing populations involves managing the number and, sometimes, the size or age of animals harvested so as to ensure the sustainability of the population. Tools that are frequently used to control harvest are bag limits and season closures, although gear restrictions such as archery-only seasons are becoming increasingly popular in an effort to reduce hunter success rates in countries that rely on bag limits per hunter instead of per area.
Laws
Illegal hunting and harvesting of wild species contrary to local and international conservation
Conservation is the preservation or efficient use of resources, or the conservation of various quantities under physical laws.
Conservation may also refer to:
Environment and natural resources
* Nature conservation, the protection and manageme ...
and wildlife management laws is called poaching. Game preservation
Game preservation is maintaining a stock of game to be hunted legally. It includes:
*Preventing poaching
*Preventing losses due to attack by predators.
*Encouraging breeding, and sometimes captive breeding for release.
Britain
Until hand-held gun ...
is one of the tactics used to prevent poaching. Violations of hunting laws and regulations involving poaching are normally punishable by law. Punishment can include Confiscation, confiscation of equipment, Fine (penalty), fines or a prison sentence.
Right to hunt
The right to hunt—sometimes in combination with the right to fish—is protected implicitly, as a consequence of the Property rights (economics), right of ownership, or explicitly, as a Rights, right on its own,
Bag limits
 Bag limits are provisions under the law that control how many animals of a given species or group of species can be killed, although there are often species for which bag limits do not apply. There are also jurisdictions where bag limits are not applied at all or are not applied under certain circumstances. The phrase ''bag limits'' comes from the custom among hunters of small game to carry successful kills in a small basket, similar to a fishing creel.
Where bag limits are used, there can be daily or seasonal bag limits; for example, ducks can often be harvested at a rate of six per hunter per day. Big game, like
Bag limits are provisions under the law that control how many animals of a given species or group of species can be killed, although there are often species for which bag limits do not apply. There are also jurisdictions where bag limits are not applied at all or are not applied under certain circumstances. The phrase ''bag limits'' comes from the custom among hunters of small game to carry successful kills in a small basket, similar to a fishing creel.
Where bag limits are used, there can be daily or seasonal bag limits; for example, ducks can often be harvested at a rate of six per hunter per day. Big game, like moose
The moose (in North America) or elk (in Eurasia) (''Alces alces'') is a member of the New World deer subfamily and is the only species in the genus ''Alces''. It is the largest and heaviest extant species in the deer family. Most adult ma ...
, most often have a seasonal bag limit of one animal per hunter. Bag limits may also regulate the size, sex, or age of animal that a hunter can kill. In many cases, bag limits are designed to allocate harvest among the hunting population more equitably rather than to protect animal populations, as protecting the population would necessitate regional density-dependent maximum bags.
Closed and open season
A closed season is a time during which hunting an animal of a given species is contrary to law. Typically, closed seasons are designed to protect a species when they are most vulnerable or to protect them during their breeding season. By extension, the period that is not the closed season is known as the Open season (hunting), open season.
Methods
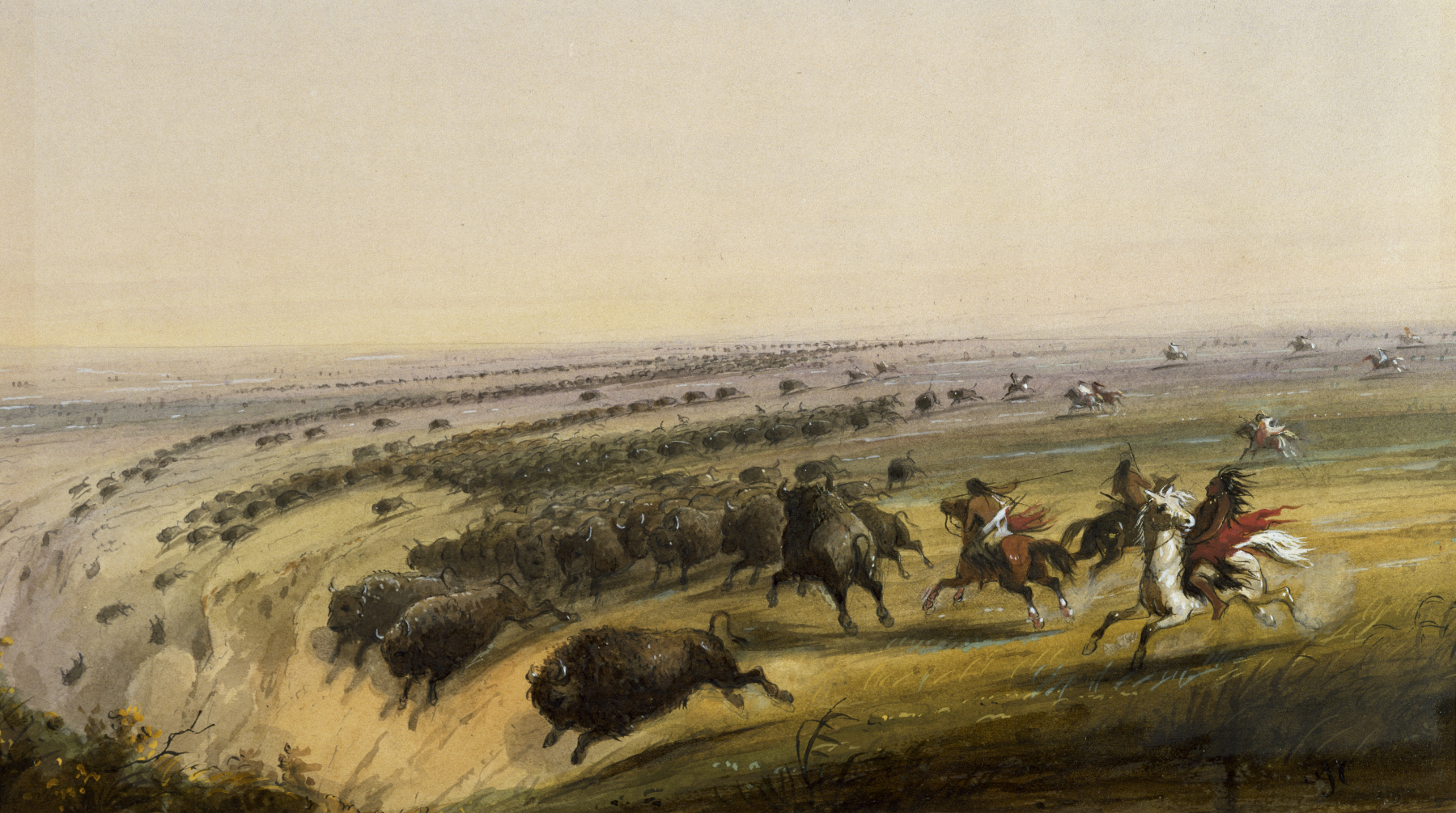
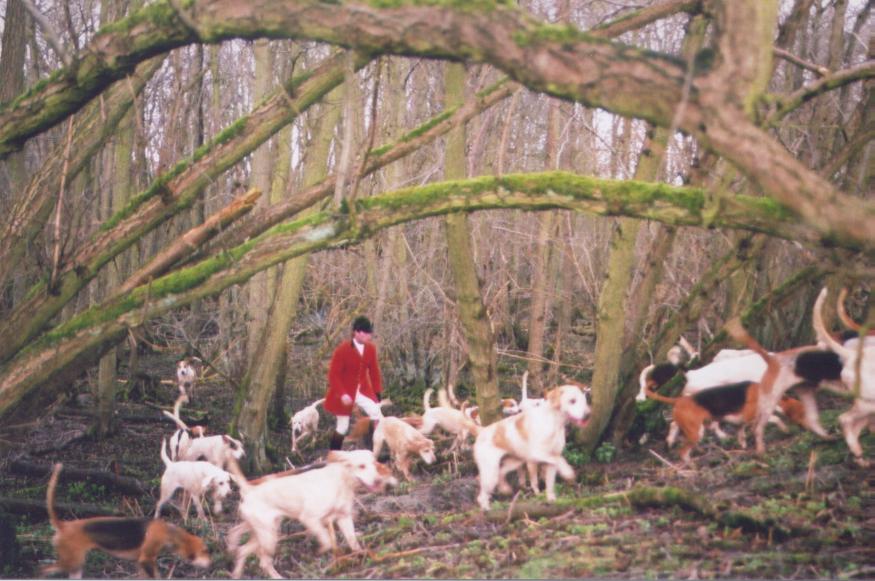

 Historical, subsistence, and sport hunting techniques can differ radically, with modern hunting regulations often addressing issues of where, when, and how hunts are conducted. Techniques may vary depending on government regulations, a hunter's personal ethics, local custom, hunting equipment, and the animal being hunted. Often a hunter will use a combination of more than one technique. Laws may forbid sport hunters from using some methods used primarily in poaching and wildlife management.
* ''Bait (luring substance), Baiting'' is the use of decoys, lures, scent, or food.
* ''wikt:battue, Battue'' involves scaring animals (by beating sticks) into a killing zone or ambush.
* ''Beagling'' is the use of beagles in hunting
Historical, subsistence, and sport hunting techniques can differ radically, with modern hunting regulations often addressing issues of where, when, and how hunts are conducted. Techniques may vary depending on government regulations, a hunter's personal ethics, local custom, hunting equipment, and the animal being hunted. Often a hunter will use a combination of more than one technique. Laws may forbid sport hunters from using some methods used primarily in poaching and wildlife management.
* ''Bait (luring substance), Baiting'' is the use of decoys, lures, scent, or food.
* ''wikt:battue, Battue'' involves scaring animals (by beating sticks) into a killing zone or ambush.
* ''Beagling'' is the use of beagles in hunting rabbit
Rabbits, also known as bunnies or bunny rabbits, are small mammals in the family Leporidae (which also contains the hares) of the order Lagomorpha (which also contains the pikas). ''Oryctolagus cuniculus'' includes the European rabbit sp ...
s, and sometimes in hunting foxes.
* ''Beating'' uses human beaters to flush out game from an area or drive it into position.
* ''Stand hunting'' or ''blind hunting'' is waiting for animals from a concealed or elevated position, for example from tree stands, hunting blinds or other types of shooting stands.
* ''Calling'' is the use of animal noises to attract or drive animals.
* ''Camouflage'' is the use of visual or odour concealment to blend with the environment.
* ''Hunting dog, Dogs'' may be used to coursing, course or to help flush, herd, drive, track, point at, pursue, or retrieve prey.
* ''Driving'' is the herding of animals in a particular direction, usually toward another hunter in the group.
* ''Flushing'' is the practice of scaring animals from concealed areas.
* ''Ghillie suit'' is a type of gear a person can wear to blend with environment.
* ''Glassing'' is the use of optics, such as binoculars, to locate animals more easily.
* ''Glue'' is an indiscriminate passive form to kill birds.
* ''Internet hunting
Internet hunting is the practice of hunting via remotely controlled firearms that can be aimed and shot using online webcams. The first internet hunting website, Live-Shot.com, was created in 2005 by John Lockwood, who saw it as a way to provide ...
'' is a method of hunting over the Internet using webcams and remotely controlled guns.
* ' involves using Net (device), nets, including active netting with the use of cannon netting, cannon nets and rocket nets.
* ''Persistence hunting'' is the use of running and tracking to pursue the prey to exhaustion.
*''Posting'' is done by sitting or standing in a particular place with the intentions of intercepting your game of choice along their travel corridor.
* ''Scouting'' for game is typically done prior to a hunt and will ensure the desired species are in a chosen area. Looking for animal sign such as tracks, scat, etc.... and utilizing "trail cameras" are commonly used tactics while scouting.
* ''Shooting'' is the use of a ranged weapon such as a gun, bow, crossbow, or slingshot.
* ''Solunar theory'' says that animals move according to the location of the moon in comparison to their bodies and is said to have been used long before this by hunters to know the best times to hunt their desired game.
* ''Spotlighting'' or ''shining'' is the use of artificial light to find or blind animals before killing.
* ''Game stalker, Stalking'' or ''still hunting'' is the practice of walking quietly in search of animals or in pursuit of an individual animal.
* ''Tracking (hunting), Tracking'' is the practice of reading physical evidence in pursuing animals.
* ''Animal trapping, Trapping'' is the use of devices such as snares, Trapping pit, pits, and deadfall trap, deadfalls to capture or kill an animal.
Statistics
Table
Graph

Trophy hunting

 Trophy hunting is the selective seeking and killing of wild game animals to take trophies for private collection, personal collection, boasting, bragging rights or as a status symbol. It may also include the controversial hunting of captive or semi-captive animals expressly bred and raised under controlled or semi-controlled conditions so as to attain trophy characteristics; this is sometimes known as canned hunts.
Trophy hunting is the selective seeking and killing of wild game animals to take trophies for private collection, personal collection, boasting, bragging rights or as a status symbol. It may also include the controversial hunting of captive or semi-captive animals expressly bred and raised under controlled or semi-controlled conditions so as to attain trophy characteristics; this is sometimes known as canned hunts.
History
In the 19th century, southern and central European sport hunters often pursued game only for a trophy, usually the head or fur, pelt of an animal, which was then displayed as a sign of prowess. The rest of the animal was typically discarded. Some cultures, however, disapprove of such waste. In Nordic countries, hunting for trophies was—and still is—frowned upon. Hunting in North America in the 19th century was done primarily as a way to supplement food supplies, although it is now undertaken mainly for sport. The Hunting#Africa, safari method of hunting was a development of sport hunting that saw elaborate travel in Africa, India and other places in pursuit of trophies. In modern times, trophy hunting
Trophy hunting is a form of hunting for sport in which parts of the hunted wild animals are kept and displayed as trophies. The animal being targeted, known as the " game", is typically a mature male specimen from a popular species of collectab ...
persists and is a significant industry in some areas.
Conservation tool
According to the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, hunting "provides an economic incentive" for ranchers to continue to breed those species, and that hunting "reduces the threat of the species' extinction."
A scientific study in the journal, ''Biological Conservation'', states that trophy hunting is of "major importance to conservation in Africa by creating economic incentives for conservation over vast areas, including areas which may be unsuitable for alternative wildlife-based land uses such as photographic ecotourism."green hunting Green hunting (also eco-hunting, green bullet concept, green darting or darting safari) is the practice of tracking and shooting game animals with non-lethal tranquilizer guns or bows and subsequently releasing the captured animals alive. Green h ...
, a trophy hunting alternative where hunters pay to dart animals that need to be tranquilized for conservation projects.
The U.S. House Committee on Natural Resources in 2016 concluded that trophy hunting may be contributing to the extinction of certain animals. Animal welfare organizations, including the IFAW, International Fund for Animal Welfare, claim that trophy hunting is a key factor in the "silent extinction" of giraffes.
According to a national survey that the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service conducts every five years, fewer people are hunting, even as population rises. National Public Radio reported, a graph shows 2016 statistics, that only about 5 percent of Americans, 16 years old and older, actually hunt, which is half of what it was 50 years ago. The decline in popularity of hunting is expected to accelerate over the next decade, which threatens how US will pay for conservation.
Controversy
Trophy hunting is most often criticised when it involves rare or endangered animals. Opponents may also see trophy hunting as an issue of morality or cruelty to animals, animal cruelty, criticising the killing of living creatures for recreation
Recreation is an activity of leisure, leisure being discretionary time. The "need to do something for recreation" is an essential element of human biology and psychology. Recreational activities are often done for enjoyment, amusement, or plea ...
. Victorian era dramatist W. S. Gilbert remarked, "Deer-stalking would be a very fine sport if only the deer had guns."
There is also debate about the extent to which trophy hunting benefits the local economy. Hunters pay substantial fees to the game outfitters and hunting guides which contributes to the local economy and provides value to animals that would otherwise be seen as competition for grazing, livestock, and crops. However, the argument is disputed by animal welfare organizations and other opponents of trophy hunting. It is argued that the animals are worth more to the community for ecotourism than hunting.
Economics
 A variety of industries benefit from hunting and support hunting on economic grounds. In Tanzania, it is estimated that a safari hunter spends fifty to one hundred times that of the average ecotourist. While the average photo tourist may seek luxury accommodation, the average safari hunter generally stays in tented camps. Safari hunters are also more likely to use remote areas, uninviting to the typical ecotourist. Advocates argue that these hunters allow for anti-poaching activities and revenue for local communities.
In the United Kingdom, the game hunting of birds as an industry is said to be extremely important to the rural economy. The Cobham Report of 1997 suggested it to be worth around £700 million, and hunting and shooting lobby groups claimed it to be worth over a billion pounds less than ten years later.
Hunting also has a significant financial impact in the United States, with many companies specialising in hunting sports equipment, equipment or speciality tourism. Many different technologies have been created to assist hunters. Today's hunters come from a broad range of economic, social, and cultural backgrounds. In 2001, over thirteen million hunters averaged eighteen days hunting, and spent over $20.5 billion on their sport. In the US, proceeds from hunting licences contribute to state game management programs, including preservation of wildlife habitat.
Hunting contributes to a portion of caloric intake of people and may have positive impacts on greenhouse gas emissions by avoidance of utilization of meat raised under industrial methods.
A variety of industries benefit from hunting and support hunting on economic grounds. In Tanzania, it is estimated that a safari hunter spends fifty to one hundred times that of the average ecotourist. While the average photo tourist may seek luxury accommodation, the average safari hunter generally stays in tented camps. Safari hunters are also more likely to use remote areas, uninviting to the typical ecotourist. Advocates argue that these hunters allow for anti-poaching activities and revenue for local communities.
In the United Kingdom, the game hunting of birds as an industry is said to be extremely important to the rural economy. The Cobham Report of 1997 suggested it to be worth around £700 million, and hunting and shooting lobby groups claimed it to be worth over a billion pounds less than ten years later.
Hunting also has a significant financial impact in the United States, with many companies specialising in hunting sports equipment, equipment or speciality tourism. Many different technologies have been created to assist hunters. Today's hunters come from a broad range of economic, social, and cultural backgrounds. In 2001, over thirteen million hunters averaged eighteen days hunting, and spent over $20.5 billion on their sport. In the US, proceeds from hunting licences contribute to state game management programs, including preservation of wildlife habitat.
Hunting contributes to a portion of caloric intake of people and may have positive impacts on greenhouse gas emissions by avoidance of utilization of meat raised under industrial methods.
Environmental problems
 Lead bullets that miss their target or remain in an unretrieved carcass could become a toxicant in the environment but lead in ammunition because of its metallic form has a lower solubility and higher resistance to corrosion than other forms of lead making it hardly available to biological systems. Waterfowl or other birds may ingest the lead and poison themselves with the neurotoxicant, but studies have demonstrated that effects of lead in ammunition are negligible on animal population size and growth. Since 1991, US federal law forbids lead shot in waterfowl hunts, and 30 states have some type of restriction.
Lead bullets that miss their target or remain in an unretrieved carcass could become a toxicant in the environment but lead in ammunition because of its metallic form has a lower solubility and higher resistance to corrosion than other forms of lead making it hardly available to biological systems. Waterfowl or other birds may ingest the lead and poison themselves with the neurotoxicant, but studies have demonstrated that effects of lead in ammunition are negligible on animal population size and growth. Since 1991, US federal law forbids lead shot in waterfowl hunts, and 30 states have some type of restriction.
Conservation
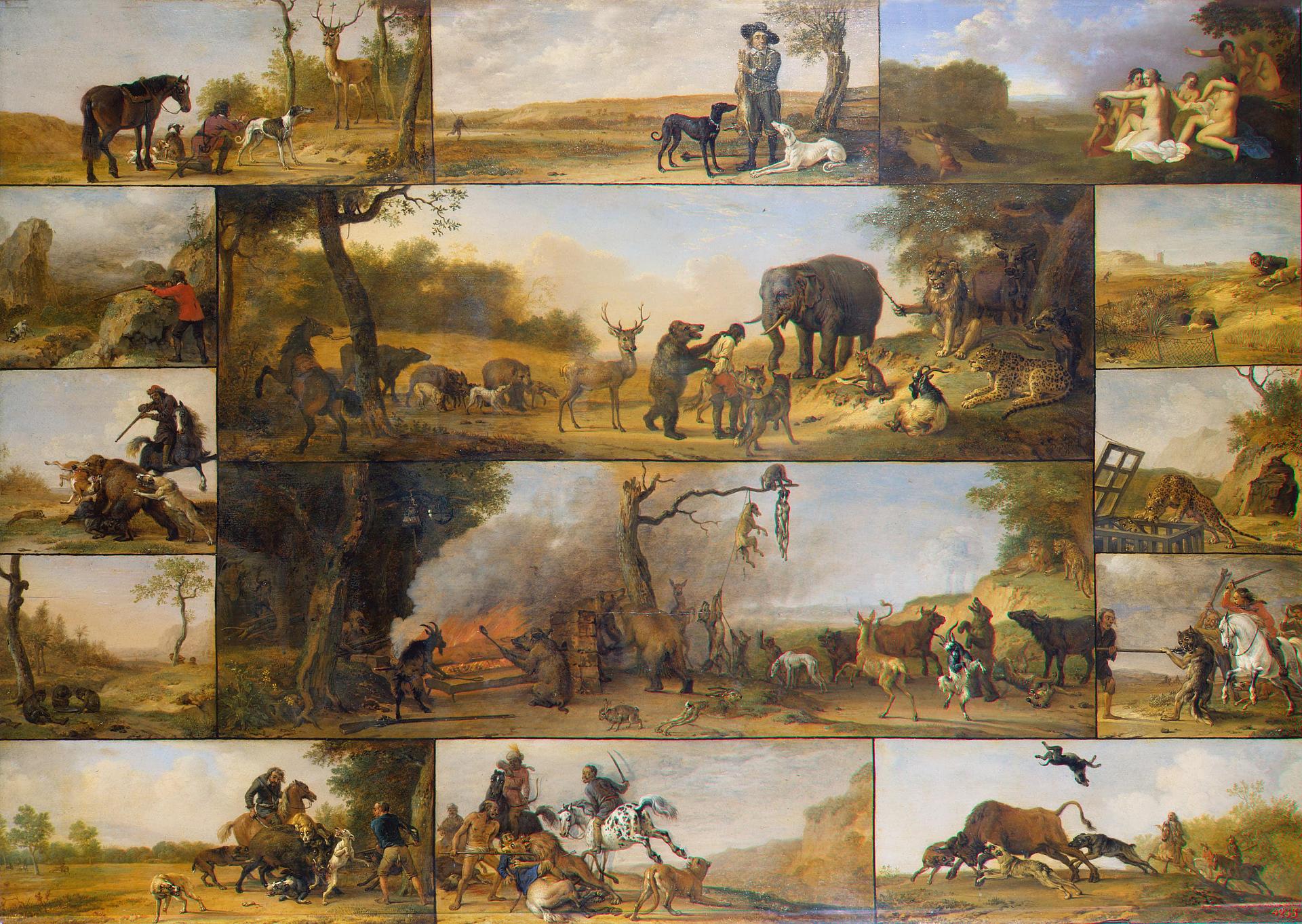 Hunters have been driving forces throughout history in the movement to ensure the preservation of Habitat (ecology), wildlife habitats and
Hunters have been driving forces throughout history in the movement to ensure the preservation of Habitat (ecology), wildlife habitats and wildlife
Wildlife refers to undomesticated animal species, but has come to include all organisms that grow or live wild in an area without being introduced by humans. Wildlife was also synonymous to game: those birds and mammals that were hunted ...
for further hunting. However, excessive hunting and poachers have also contributed heavily to the endangerment, extirpation and extinction of many animals, such as the quagga, the great auk, Steller's sea cow, the thylacine, the bluebuck, the Arabian oryx, the Caspian tiger, Caspian and Javan tigers, the markhor, the Sumatran rhinoceros, the bison, the North American cougar, the Altai argali sheep, the Asian elephant and many more, primarily for commercial sale or sport. All these animals have been hunted to endangerment or extinction. Poaching currently threatens bird and mammalian populations around the world. The 2019 ''Global Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services'' lists the direct exploitation of organisms, including hunting, as the second leading cause of biodiversity loss, after land use for agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people ...
. In 2022, IPBES released another report which stated that unsustainable hunting, along with unsustainable logging and fishing, are primary drivers of the global extinction crisis.
Legislation
Pittman–Robertson Wildlife Restoration Act of 1937
In 1937, American hunters successfully lobbied the US Congress to pass the Pittman–Robertson Federal Aid in Wildlife Restoration Act, Pittman-Robertson Wildlife Restoration Act, which placed an eleven percent tax on all hunting equipment. This self-imposed tax now generates over $700 million each year and is used exclusively to establish, restore and protect wildlife habitats. The act is named for Nevada Senator Key Pittman and Virginia Congressman Absalom Willis Robertson.
Federal Duck Stamp program
On 16 March 1934, Franklin D. Roosevelt, President Franklin D. Roosevelt signed the Migratory Bird Hunting Stamp Act, which requires an annual stamp purchase by all hunters over the age of sixteen. The stamps are created on behalf of the program by the US Postal Service and depict wildlife artwork chosen through an annual contest. They play an important role in habitat conservation because ninety-eight percent of all funds generated by their sale go directly toward the purchase or lease of wetland habitat for protection in the National Wildlife Refuge, National Wildlife Refuge System. In addition to waterfowl, it is estimated that one third of the nation's endangered species seek food and shelter in areas protected using Duck Stamp funds.
Since 1934, the sale of Federal Duck Stamps has generated $670 million, and helped to purchase or lease of habitat. The stamps serve as a license to hunt migratory birds, an entrance pass for all National Wildlife Refuge areas, and are also considered collectors items often purchased for aesthetic reasons outside of the hunting and birding communities. Although non-hunters buy a significant number of Duck Stamps, eighty-seven percent of their sales are contributed by hunters. Distribution of funds is managed by the Migratory Bird Conservation Commission (MBCC).
Species
Arabian oryx
The Arabian oryx, a species of large antelope, once inhabited much of the desert areas of the Middle East.
Markhor
The markhor is an endangered species of wild goat which inhabits the mountains of Central Asia and Pakistan. The colonization of these regions by British Empire, Britain gave British sport hunters access to the species, and they were hunted heavily, almost to the point of extinction. Only their willingness to breed in captivity and the inhospitability of their mountainous habitat prevented this. Despite these factors, the markhor is still endangered.
American bison
The American bison is a large bovid which inhabited much of western North America prior to the 1800s, living on the prairies in large herds. However, the vast herds of bison attracted market hunters, who killed dozens of bison for their hides only, leaving the rest to rot. Thousands of these hunters quickly eliminated the bison herds, bringing the population from several million in the early 1800s to a few hundred by the 1880s. Conservation efforts have allowed the population to increase, but the bison remains near-threatened due to lack of habitat.
White rhino
The ''Journal of International Wildlife Law and Policy'' cites that the legalization of white rhinoceros hunting in South Africa motivated private landowners to reintroduce the species onto their lands. As a result, the country saw an increase in white rhinos from fewer than one hundred individuals to more than 11,000, even while a limited number were killed as trophies.
However, the illegal hunting of rhinoceros for their horns is highly damaging to the population and is currently growing globally, with 1004 being killed in South Africa alone according to the most recent estimate. The White Rhino (along with the other 4 rhino species) are poached due to beliefs that the Rhinos horns can be used to cure Cancer, Arthritis and other diseases and illnesses, even though they are scientifically proven wrong.
Other species
According to Richard Conniff, Namibia is home to 1,750 of the roughly 5,000 black rhinos surviving in the wild because it allows trophy hunting of various species. Namibia's mountain zebra population has increased to 27,000 from 1,000 in 1982. Elephants, which "are gunned down elsewhere for their ivory", have gone to 20,000 from 15,000 in 1995. Lions, which were on the brink of extinction "from Senegal to Kenya", are increasing in Namibia.
In contrast, Botswana in 2012 banned trophy hunting following a precipitous wildlife decline. The numbers of antelope plummeted across Botswana, with a resultant decline in predator numbers, while elephant numbers remained stable and hippopotamus numbers rose. According to the government of Botswana, trophy hunting is at least partly to blame for this, but many other factors, such as poaching, drought and habitat loss are also to blame. Uganda recently did the same, arguing that "the share of benefits of sport hunting were lopsided and unlikely to deter poaching or improve [Uganda's] capacity to manage the wildlife reserves." In 2020, Botswana reopened trophy hunting on public lands.
Studies
 A study published by the Wildlife Society concluded that hunting and trapping are cost effective tools that reduce wildlife damage by reducing a population below the capacity of the environment to carry it and changing the behaviors of animals to stop them from causing damage. The study furthermore states that the cessation of hunting could cause wildlife to be severely harmed, rural property values to fall, and the incentive of landowners to maintain natural habitats to diminish.
Although deforestation and forest degradation have long been considered the most significant threats to tropical biodiversity, across Southeast Asia (Northeast India, Indochina, Sundaland, Philippines) substantial areas of natural habitat have few wild animals (>1 kg), bar a few hunting‐tolerant species.
A study published by the Wildlife Society concluded that hunting and trapping are cost effective tools that reduce wildlife damage by reducing a population below the capacity of the environment to carry it and changing the behaviors of animals to stop them from causing damage. The study furthermore states that the cessation of hunting could cause wildlife to be severely harmed, rural property values to fall, and the incentive of landowners to maintain natural habitats to diminish.
Although deforestation and forest degradation have long been considered the most significant threats to tropical biodiversity, across Southeast Asia (Northeast India, Indochina, Sundaland, Philippines) substantial areas of natural habitat have few wild animals (>1 kg), bar a few hunting‐tolerant species.
Opposition to hunting
It has been argued by animal rights activists that killing animals for sport is unethical, cruel, and unnecessary.Whether hunters try to justify their killing by citing human deaths caused by wild animals, by making conservationist claims, by claiming that it's acceptable to hunt as long as the animals' bodies are eaten, or simply because of the pleasure it brings them, the fact remains that hunting is morally unacceptable if we consider the interests of nonhuman animals. Hunted animals endure fear and pain, and then are deprived of their lives. Understanding the injustices of speciesism and the interests of nonhuman animals makes it clear that human pleasure cannot justify nonhuman animals' pain.
Hunting in the arts

 File:Larnax, hunting of deer and ibex, Prepalatial, AM, Rethymno, 076107.jpg, Hunting of deer and ibex, Minoan civilization, Minoan larnax, prepalatial period
File:TombofNebamun-2.jpg, Hunting in the papyrus thicket, mural from a tomb in Thebes, Egypt, before 1350 BC
File:Stag hunt mosaic, Pella.jpg, The Stag hunt mosaic, , Pella, Greece
File:Mosaico de Las Tiendas (MNAR Mérida) 01.jpg, Man hunting a boar, Roman mosaic, 4th century AD
File:Falconry Book of Frederick II 1240s.jpg, Illustration from the falconry book ''De arte venandi cum avibus'' written by Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor Frederick II,
File:Musée des Augustins Toulouse 14.JPG, Giovanni di Francesco (?),
File:Larnax, hunting of deer and ibex, Prepalatial, AM, Rethymno, 076107.jpg, Hunting of deer and ibex, Minoan civilization, Minoan larnax, prepalatial period
File:TombofNebamun-2.jpg, Hunting in the papyrus thicket, mural from a tomb in Thebes, Egypt, before 1350 BC
File:Stag hunt mosaic, Pella.jpg, The Stag hunt mosaic, , Pella, Greece
File:Mosaico de Las Tiendas (MNAR Mérida) 01.jpg, Man hunting a boar, Roman mosaic, 4th century AD
File:Falconry Book of Frederick II 1240s.jpg, Illustration from the falconry book ''De arte venandi cum avibus'' written by Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor Frederick II,
File:Musée des Augustins Toulouse 14.JPG, Giovanni di Francesco (?),
''La caccia'', , tempera on wood, detail
File:Hunt in the forest by paolo uccello.jpg, Paolo Uccello, ''The Hunt in the Forest, Caccia notturna (The Hunt in the Forest)'',
File:Carpaccio, caccia nella laguna, 1490-95 ca. 01.JPG, Vittore Carpaccio, ''Caccia in laguna (Hunt in the Lagoon)'',
File:Piero di Cosimo - Scena di caccia.jpg, Piero di Cosimo,
''A Hunting Scene'', 1508
File:Lucas Cranach d.Ä. - Hirschjagd des Kurfürsten Friedrich des Weisen (KHM Wien).jpg, Lucas Cranach the Elder, ''A Stag Hunt with the Elector Friedrich the Wise'', 1529
File:Peter Paul Rubens 083.jpg, Peter Paul Rubens, ''Hippopotamus and Crocodile Hunt'',
File:Peter Paul Rubens 110.jpg, Peter Paul Rubens, ''Tiger and Lion Hunt'', 1618
File:A Forest at Dawn with a Deer Hunt MET DT4532.jpg, Peter Paul Rubens, ''A Forest at Dawn with a Deer Hunt'',
File:Charles André van Loo, fermata durante la caccia, 1737, 01.jpg, Charles André van Loo, ''Halte de chasse (Halt During the Hunt)'', 1737
File:Partida de caza.jpg, Francisco Goya, ''The Quail Shoot'', 1775
File:Biche morte by Courbet.png, Gustave Courbet, ''Biche morte (Dead hind)'', 1857
File:Gustave Courbet - The Hunt Breakfast - WGA5468.jpg, Gustave Courbet, ''The Hunt Breakfast'', 1858
File:Eugène Delacroix - Chasse au lion (1858).jpg, Eugène Delacroix, ''Chasse au lion (Lion Hunt)'', 1858
File:After the Hunt MET DT1963.jpg, Gustave Courbet, ''Après la chasse (After the Hunt)'', 1859
File:Édouard Manet - Pertuiset, le chasseur de lions.jpg, Édouard Manet, ''Portrait of Monsieur Pertuiset the Lion-Hunter'', 1881
See also
* Air travel with firearms and ammunition
* Anti-hunting
* Bambi effect
* Blood sport
* Bowhunting
* Bushfood
* Bushmeat
* Chase (land), Chase
* Defaunation
* Federation of Associations for Hunting and Conservation of the EU
* Hiking equipment
* Human hunting
* Hunt Saboteurs Association (HSA)
* Hunting horn
* Nimrod
* Esau
* Sir Gawain and the Green Knight#Hunting and seduction, Sir Gawain and the Green Knight
* Tapetum lucidum eyeshine
* ''The Sound of His Horn''
* Backpacking (wilderness), Wilderness backpacking
References
Further reading
International Journal of Environmental Studies (2013) Special Edition: Conservation and Hunting in North America. IJES v 70.
International Journal of Environmental Studies (2015) Special Edition: Conservation and Hunting in North America II. IJES v72.
IUCN (2016) Briefing Paper: Informing Decisions on Trophy Hunting.
IUCN Species Survival Commission (2012) Guiding Principles on Trophy Hunting as a Tool for Creating Conservation Incentives.
* Dickson D. Bruce Jr., Mississippi Quarterly (Spring 1977).
* Kenneth S. Greenberg, Honor and Slavery: Lies, Duels, Noses, Masks, Dressing as a Woman, Gifts, Strangers, Humanitarianism, Death, Slave Rebellions, the Pro-Slavery Argument, Baseball, Hunting, and Gambling in the Old South (1996).
* Steven Hahn, Radical History Review (1982).
* Charles H. Hudson Jr., in Indians, Animals, and the Fur Trade, ed., Shephard Krech III (1981).
* Stuart A. Marks, Southern Hunting in Black and White: Nature, History, and Ritual in a Carolina Community (1991).
* Ted Ownby, Subduing Satan: Religion, Recreation, and Manhood in the Rural South, 1865–1920 (1990).
* Wiley C. Prewitt, "The Best of All Breathing: Hunting and Environmental Change in Mississippi, 1900–1980" M.A. thesis, (1991).
* Nicolas W. Proctor, Bathed in Blood: Hunting and Mastery in the Old South (2002).
* Jacob F. Rivers III, Cultural Values in the Southern Sporting Narrative (2002).
Salem, D.J., and A.N. Rowan, eds. 2003. ''The State of the Animals II: 2003''
. Washington, D.C.: Humane Society Press. ()
* Timothy Silver, A New Face on the Countryside: Indians, Colonists, and Slaves in South Atlantic Forests, 1500–1800 (1990).
* Richard C. Stedman and Thomas A. Heberlein, Rural Sociology (2001).
* Nancy L. Struna, People of Prowess: Sport, Leisure, and Labor in Early Anglo-America (1996).
* Marek Zukow-Karczewski, ''Polowania w dawnej Polsce'' (Hunting in the old Poland), "AURA" (A Monthly for the protection and shaping of human environment) 12 (1990).
External links
*
The Theodore Roosevelt Hunting Library
at the Library of Congress has 254 items on this topic.
{{Authority control
Hunting,
Cruelty to animals
Survival skills
Lifestyles
 Hunting is the human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, or killing
Hunting is the human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, or killing  Hunting activities by humans arose in ''
Hunting activities by humans arose in ''
 Skillful tracking and acquisition of an elusive target has caused the word ''hunt'' to be used in the
Skillful tracking and acquisition of an elusive target has caused the word ''hunt'' to be used in the 
 Evidence exists that hunting may have been one of the multiple environmental factors leading to the Holocene extinction of megafauna and their replacement by smaller herbivores.
Evidence exists that hunting may have been one of the multiple environmental factors leading to the Holocene extinction of megafauna and their replacement by smaller herbivores.
 Many species of animals have been hunted throughout history. One theory is that in North America and
Many species of animals have been hunted throughout history. One theory is that in North America and  Mesolithic hunter-gathering lifestyles remained prevalent in some parts of the
Mesolithic hunter-gathering lifestyles remained prevalent in some parts of the 
 Even as
Even as  With the domestication of the dog, birds of prey, and the
With the domestication of the dog, birds of prey, and the  Even as agriculture and animal husbandry became more prevalent, hunting often remained as a part of human culture where the environment and social conditions allowed. Hunter-gatherer societies persisted, even when increasingly confined to marginal areas. And within agricultural systems, hunting served to kill animals that prey upon domestic and wild animals or to attempt to extirpate animals seen by humans as competition for resources such as water or forage.
When hunting moved from a subsistence activity to a selective one, two trends emerged:
# the development of the role of the specialist hunter, with special training and equipment
# the option of hunting as a "sport" for members of an upper social class
The meaning of the word ''game'' in
Even as agriculture and animal husbandry became more prevalent, hunting often remained as a part of human culture where the environment and social conditions allowed. Hunter-gatherer societies persisted, even when increasingly confined to marginal areas. And within agricultural systems, hunting served to kill animals that prey upon domestic and wild animals or to attempt to extirpate animals seen by humans as competition for resources such as water or forage.
When hunting moved from a subsistence activity to a selective one, two trends emerged:
# the development of the role of the specialist hunter, with special training and equipment
# the option of hunting as a "sport" for members of an upper social class
The meaning of the word ''game'' in  Although various other animals have been used to aid the hunter, such as ferrets, the dog has assumed many very important uses to the hunter.
The domestication of the dog has led to a symbiotic relationship in which the dog's independence from humans is deferred. Though dogs can survive independently of humans, and in many cases do ferrally, when raised or adopted by humans the species tends to defer to its control in exchange for habitation, food and support.
Dogs today are used to find, chase, retrieve, and sometimes kill game. Dogs allow humans to pursue and kill prey that would otherwise be very difficult or dangerous to hunt. Different breeds of specifically bred
Although various other animals have been used to aid the hunter, such as ferrets, the dog has assumed many very important uses to the hunter.
The domestication of the dog has led to a symbiotic relationship in which the dog's independence from humans is deferred. Though dogs can survive independently of humans, and in many cases do ferrally, when raised or adopted by humans the species tends to defer to its control in exchange for habitation, food and support.
Dogs today are used to find, chase, retrieve, and sometimes kill game. Dogs allow humans to pursue and kill prey that would otherwise be very difficult or dangerous to hunt. Different breeds of specifically bred 

 Hindu scriptures describe hunting as an occupation, as well as a sport of the kingly. Even figures considered divine are described to have engaged in hunting. One of the names of the god
Hindu scriptures describe hunting as an occupation, as well as a sport of the kingly. Even figures considered divine are described to have engaged in hunting. One of the names of the god 
 From
From  A safari, from a Swahili word meaning "a long journey", especially in Africa, is defined as an overland journey. Safari as a distinctive way of hunting was popularized by the US author
A safari, from a Swahili word meaning "a long journey", especially in Africa, is defined as an overland journey. Safari as a distinctive way of hunting was popularized by the US author  During the feudal and colonial times in
During the feudal and colonial times in  Unarmed fox hunting on horseback with hounds is the type of hunting most closely associated with the United Kingdom; in fact, "hunting" without qualification implies fox hunting. What in other countries is called "hunting" is called "shooting" (birds) or "stalking" (deer) in Britain. Originally a form of
Unarmed fox hunting on horseback with hounds is the type of hunting most closely associated with the United Kingdom; in fact, "hunting" without qualification implies fox hunting. What in other countries is called "hunting" is called "shooting" (birds) or "stalking" (deer) in Britain. Originally a form of  North American hunting pre-dates the United States by thousands of years and was an important part of many
North American hunting pre-dates the United States by thousands of years and was an important part of many  Varmint hunting is an American phrase for the selective killing of non-game animals seen as pests. While not always an efficient form of pest control, varmint hunting achieves selective control of pests while providing recreation and is much less regulated. Varmint species are often responsible for detrimental effects on crops, livestock,
Varmint hunting is an American phrase for the selective killing of non-game animals seen as pests. While not always an efficient form of pest control, varmint hunting achieves selective control of pests while providing recreation and is much less regulated. Varmint species are often responsible for detrimental effects on crops, livestock,  One hunting club declares that a fair chase shall not involve the taking of animals under the following conditions:
* Helpless in a trap, deep snow or water, or on ice.
* From any power vehicle or power boat.
* By " jacklighting" or shining at night.
* By the use of any tranquilizers or poisons.
* While inside escape-proof fenced enclosures.
* By the use of any power vehicle or power boat for herding or driving animals, including use of aircraft to land alongside or to communicate with or direct a hunter on the ground.
* By the use of electronic devices for attracting, locating or pursuing game or guiding the hunter to such game, or by the use of a bow or arrow to which any electronic device is attached.
One hunting club declares that a fair chase shall not involve the taking of animals under the following conditions:
* Helpless in a trap, deep snow or water, or on ice.
* From any power vehicle or power boat.
* By " jacklighting" or shining at night.
* By the use of any tranquilizers or poisons.
* While inside escape-proof fenced enclosures.
* By the use of any power vehicle or power boat for herding or driving animals, including use of aircraft to land alongside or to communicate with or direct a hunter on the ground.
* By the use of electronic devices for attracting, locating or pursuing game or guiding the hunter to such game, or by the use of a bow or arrow to which any electronic device is attached.

 Hunting is claimed to give resource managers an important tool in managing populations that might exceed the carrying capacity of their
Hunting is claimed to give resource managers an important tool in managing populations that might exceed the carrying capacity of their  Bag limits are provisions under the law that control how many animals of a given species or group of species can be killed, although there are often species for which bag limits do not apply. There are also jurisdictions where bag limits are not applied at all or are not applied under certain circumstances. The phrase ''bag limits'' comes from the custom among hunters of small game to carry successful kills in a small basket, similar to a fishing creel.
Where bag limits are used, there can be daily or seasonal bag limits; for example, ducks can often be harvested at a rate of six per hunter per day. Big game, like
Bag limits are provisions under the law that control how many animals of a given species or group of species can be killed, although there are often species for which bag limits do not apply. There are also jurisdictions where bag limits are not applied at all or are not applied under certain circumstances. The phrase ''bag limits'' comes from the custom among hunters of small game to carry successful kills in a small basket, similar to a fishing creel.
Where bag limits are used, there can be daily or seasonal bag limits; for example, ducks can often be harvested at a rate of six per hunter per day. Big game, like 

 Historical, subsistence, and sport hunting techniques can differ radically, with modern hunting regulations often addressing issues of where, when, and how hunts are conducted. Techniques may vary depending on government regulations, a hunter's personal ethics, local custom, hunting equipment, and the animal being hunted. Often a hunter will use a combination of more than one technique. Laws may forbid sport hunters from using some methods used primarily in poaching and wildlife management.
* ''Bait (luring substance), Baiting'' is the use of decoys, lures, scent, or food.
* ''wikt:battue, Battue'' involves scaring animals (by beating sticks) into a killing zone or ambush.
* ''Beagling'' is the use of beagles in hunting
Historical, subsistence, and sport hunting techniques can differ radically, with modern hunting regulations often addressing issues of where, when, and how hunts are conducted. Techniques may vary depending on government regulations, a hunter's personal ethics, local custom, hunting equipment, and the animal being hunted. Often a hunter will use a combination of more than one technique. Laws may forbid sport hunters from using some methods used primarily in poaching and wildlife management.
* ''Bait (luring substance), Baiting'' is the use of decoys, lures, scent, or food.
* ''wikt:battue, Battue'' involves scaring animals (by beating sticks) into a killing zone or ambush.
* ''Beagling'' is the use of beagles in hunting 
 Trophy hunting is the selective seeking and killing of wild game animals to take trophies for private collection, personal collection, boasting, bragging rights or as a status symbol. It may also include the controversial hunting of captive or semi-captive animals expressly bred and raised under controlled or semi-controlled conditions so as to attain trophy characteristics; this is sometimes known as canned hunts.
Trophy hunting is the selective seeking and killing of wild game animals to take trophies for private collection, personal collection, boasting, bragging rights or as a status symbol. It may also include the controversial hunting of captive or semi-captive animals expressly bred and raised under controlled or semi-controlled conditions so as to attain trophy characteristics; this is sometimes known as canned hunts.
 A variety of industries benefit from hunting and support hunting on economic grounds. In Tanzania, it is estimated that a safari hunter spends fifty to one hundred times that of the average ecotourist. While the average photo tourist may seek luxury accommodation, the average safari hunter generally stays in tented camps. Safari hunters are also more likely to use remote areas, uninviting to the typical ecotourist. Advocates argue that these hunters allow for anti-poaching activities and revenue for local communities.
In the United Kingdom, the game hunting of birds as an industry is said to be extremely important to the rural economy. The Cobham Report of 1997 suggested it to be worth around £700 million, and hunting and shooting lobby groups claimed it to be worth over a billion pounds less than ten years later.
Hunting also has a significant financial impact in the United States, with many companies specialising in hunting sports equipment, equipment or speciality tourism. Many different technologies have been created to assist hunters. Today's hunters come from a broad range of economic, social, and cultural backgrounds. In 2001, over thirteen million hunters averaged eighteen days hunting, and spent over $20.5 billion on their sport. In the US, proceeds from hunting licences contribute to state game management programs, including preservation of wildlife habitat.
Hunting contributes to a portion of caloric intake of people and may have positive impacts on greenhouse gas emissions by avoidance of utilization of meat raised under industrial methods.
A variety of industries benefit from hunting and support hunting on economic grounds. In Tanzania, it is estimated that a safari hunter spends fifty to one hundred times that of the average ecotourist. While the average photo tourist may seek luxury accommodation, the average safari hunter generally stays in tented camps. Safari hunters are also more likely to use remote areas, uninviting to the typical ecotourist. Advocates argue that these hunters allow for anti-poaching activities and revenue for local communities.
In the United Kingdom, the game hunting of birds as an industry is said to be extremely important to the rural economy. The Cobham Report of 1997 suggested it to be worth around £700 million, and hunting and shooting lobby groups claimed it to be worth over a billion pounds less than ten years later.
Hunting also has a significant financial impact in the United States, with many companies specialising in hunting sports equipment, equipment or speciality tourism. Many different technologies have been created to assist hunters. Today's hunters come from a broad range of economic, social, and cultural backgrounds. In 2001, over thirteen million hunters averaged eighteen days hunting, and spent over $20.5 billion on their sport. In the US, proceeds from hunting licences contribute to state game management programs, including preservation of wildlife habitat.
Hunting contributes to a portion of caloric intake of people and may have positive impacts on greenhouse gas emissions by avoidance of utilization of meat raised under industrial methods.
 Lead bullets that miss their target or remain in an unretrieved carcass could become a toxicant in the environment but lead in ammunition because of its metallic form has a lower solubility and higher resistance to corrosion than other forms of lead making it hardly available to biological systems. Waterfowl or other birds may ingest the lead and poison themselves with the neurotoxicant, but studies have demonstrated that effects of lead in ammunition are negligible on animal population size and growth. Since 1991, US federal law forbids lead shot in waterfowl hunts, and 30 states have some type of restriction.
In December 2014, a federal appeals court denied a lawsuit by environmental groups that the EPA must use the Toxic Substances Control Act to regulate lead in shells and cartridges. The groups sought EPA to regulate "spent lead", yet the court found EPA could not regulate spent lead without also regulating cartridges and shells.
Lead bullets that miss their target or remain in an unretrieved carcass could become a toxicant in the environment but lead in ammunition because of its metallic form has a lower solubility and higher resistance to corrosion than other forms of lead making it hardly available to biological systems. Waterfowl or other birds may ingest the lead and poison themselves with the neurotoxicant, but studies have demonstrated that effects of lead in ammunition are negligible on animal population size and growth. Since 1991, US federal law forbids lead shot in waterfowl hunts, and 30 states have some type of restriction.
In December 2014, a federal appeals court denied a lawsuit by environmental groups that the EPA must use the Toxic Substances Control Act to regulate lead in shells and cartridges. The groups sought EPA to regulate "spent lead", yet the court found EPA could not regulate spent lead without also regulating cartridges and shells.
 Hunters have been driving forces throughout history in the movement to ensure the preservation of Habitat (ecology), wildlife habitats and
Hunters have been driving forces throughout history in the movement to ensure the preservation of Habitat (ecology), wildlife habitats and  A study published by the Wildlife Society concluded that hunting and trapping are cost effective tools that reduce wildlife damage by reducing a population below the capacity of the environment to carry it and changing the behaviors of animals to stop them from causing damage. The study furthermore states that the cessation of hunting could cause wildlife to be severely harmed, rural property values to fall, and the incentive of landowners to maintain natural habitats to diminish.
Although deforestation and forest degradation have long been considered the most significant threats to tropical biodiversity, across Southeast Asia (Northeast India, Indochina, Sundaland, Philippines) substantial areas of natural habitat have few wild animals (>1 kg), bar a few hunting‐tolerant species.
A study published by the Wildlife Society concluded that hunting and trapping are cost effective tools that reduce wildlife damage by reducing a population below the capacity of the environment to carry it and changing the behaviors of animals to stop them from causing damage. The study furthermore states that the cessation of hunting could cause wildlife to be severely harmed, rural property values to fall, and the incentive of landowners to maintain natural habitats to diminish.
Although deforestation and forest degradation have long been considered the most significant threats to tropical biodiversity, across Southeast Asia (Northeast India, Indochina, Sundaland, Philippines) substantial areas of natural habitat have few wild animals (>1 kg), bar a few hunting‐tolerant species.

