Greater Sudbury on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sudbury, officially the City of Greater Sudbury is the largest city in
 During construction of the railway in 1883, blasting and excavation revealed high concentrations of
During construction of the railway in 1883, blasting and excavation revealed high concentrations of  The open coke beds used in the early to mid 20th century and logging for fuel resulted in a near-total loss of native vegetation in the area. Consequently, the terrain was made up of exposed rocky outcrops permanently stained charcoal black by the air pollution from the roasting yards. Acid rain added more staining, in a layer that penetrates up to into the once pink-grey
The open coke beds used in the early to mid 20th century and logging for fuel resulted in a near-total loss of native vegetation in the area. Consequently, the terrain was made up of exposed rocky outcrops permanently stained charcoal black by the air pollution from the roasting yards. Acid rain added more staining, in a layer that penetrates up to into the once pink-grey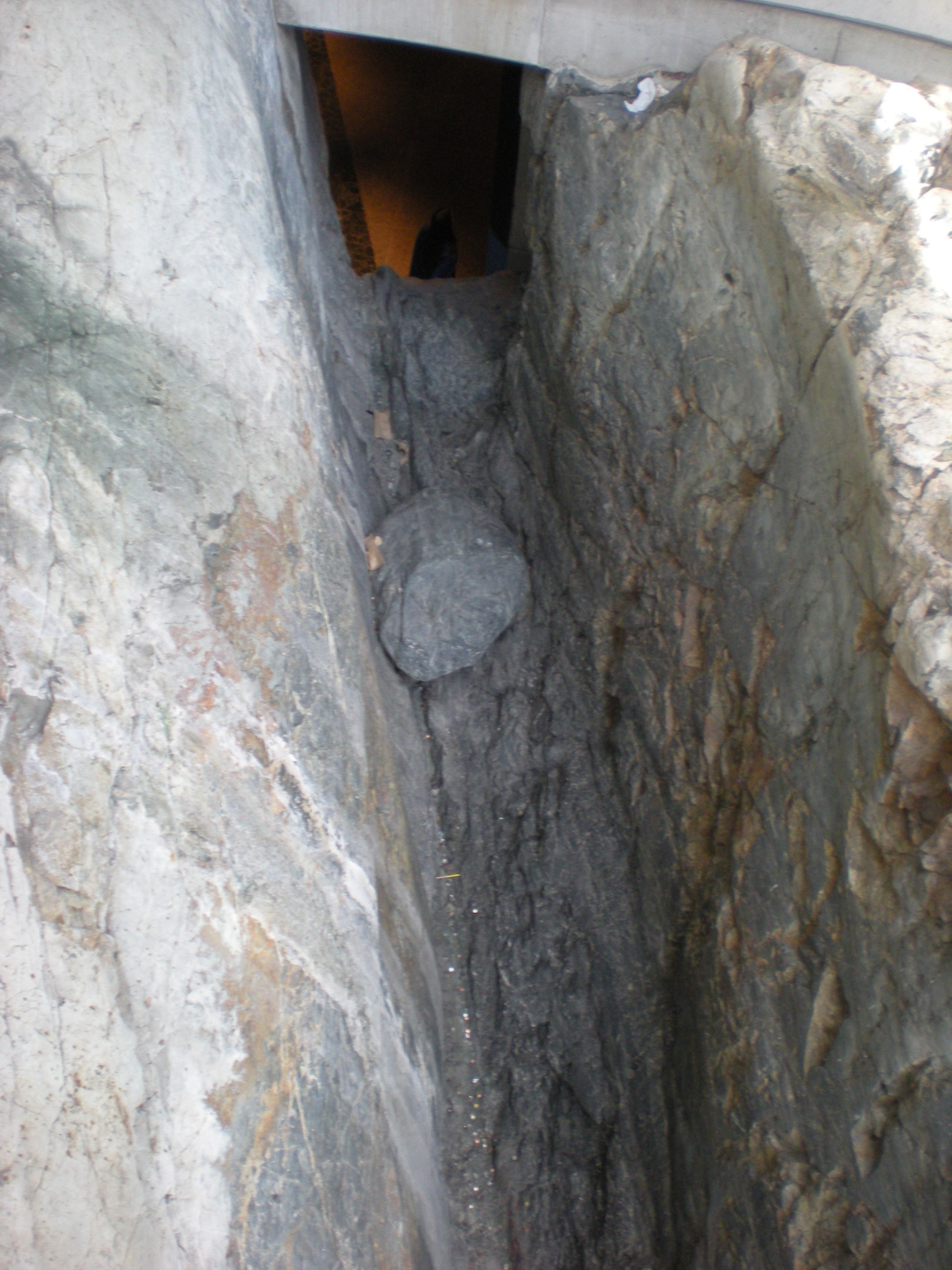  In 1978, the workers of Sudbury's largest mining corporation, Inco (now Vale), embarked on a strike over production and employment cutbacks. The strike, which lasted for nine months, badly damaged Sudbury's economy. The city government was spurred to launch a project to diversify the city's economy.
A unique and visionary project, Science North was inaugurated in 1984 with two-snowflake styled buildings connected by a tunnel through the Canadian shield where the Creighton fault intersects the shores of Lake Ramsey. The city tried to attract new employers and industries through the 1980s and 1990s with mixed success. The city of Sudbury and its suburban communities, which were reorganized into the Regional Municipality of Sudbury in 1973, was subsequently merged in 2001 into the single-tier city of Greater Sudbury.
In 1978, the workers of Sudbury's largest mining corporation, Inco (now Vale), embarked on a strike over production and employment cutbacks. The strike, which lasted for nine months, badly damaged Sudbury's economy. The city government was spurred to launch a project to diversify the city's economy.
A unique and visionary project, Science North was inaugurated in 1984 with two-snowflake styled buildings connected by a tunnel through the Canadian shield where the Creighton fault intersects the shores of Lake Ramsey. The city tried to attract new employers and industries through the 1980s and 1990s with mixed success. The city of Sudbury and its suburban communities, which were reorganized into the Regional Municipality of Sudbury in 1973, was subsequently merged in 2001 into the single-tier city of Greater Sudbury.
 In 2006, both of the city's major mining companies, Canadian-based Inco and Falconbridge, were taken over by new owners: Inco was acquired by the Brazilian company CVRD (now renamed
In 2006, both of the city's major mining companies, Canadian-based Inco and Falconbridge, were taken over by new owners: Inco was acquired by the Brazilian company CVRD (now renamed
 Sudbury is built around many small, rocky mountains with exposed
Sudbury is built around many small, rocky mountains with exposed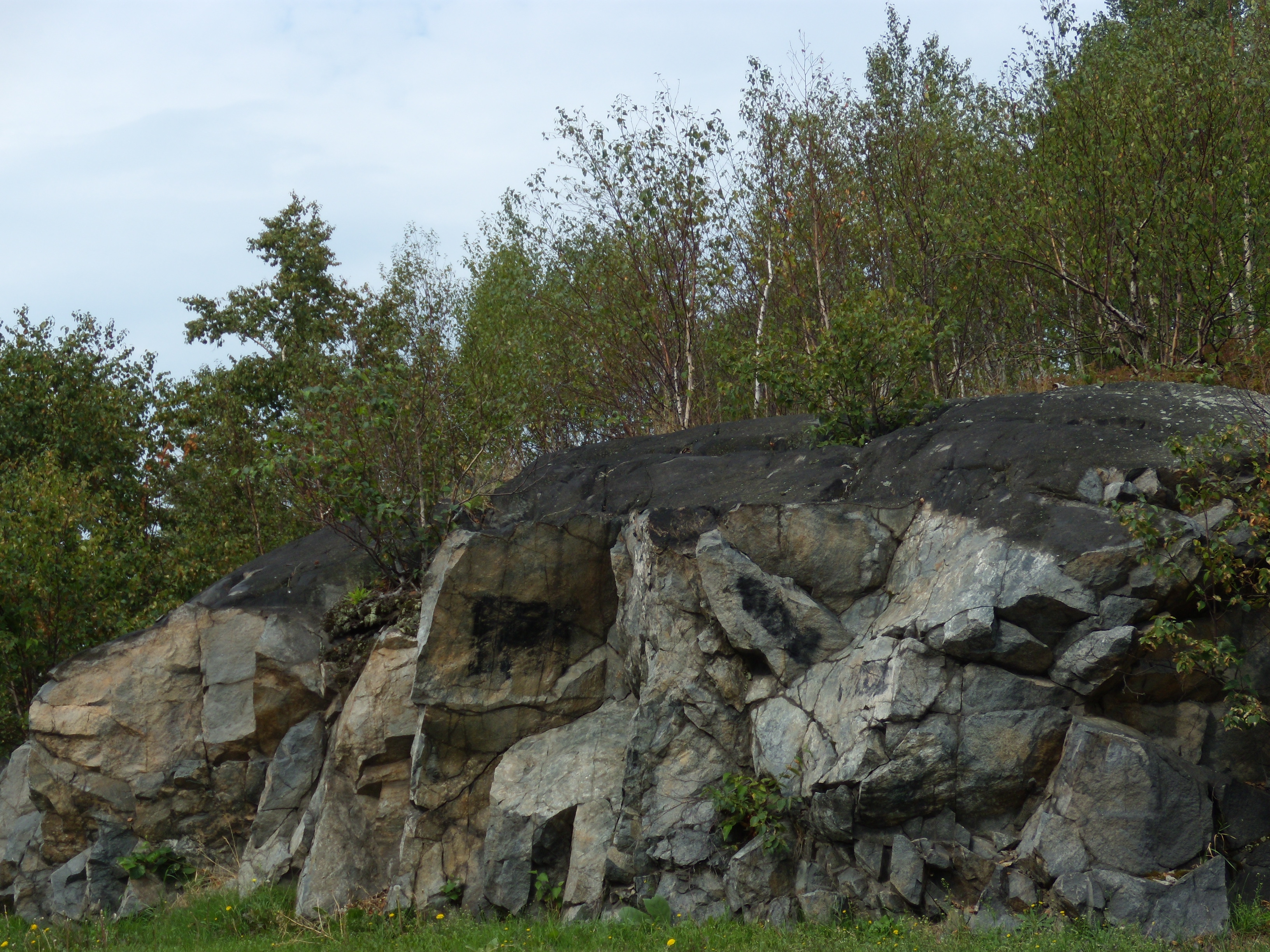  The resulting erosion exposed bedrock in many parts of the city, which was charred in most places to a pitted, dark black appearance. There was not a complete lack of vegetation in the region as paper birch and wild blueberry patches thrived in the acidic soils. During the
The resulting erosion exposed bedrock in many parts of the city, which was charred in most places to a pitted, dark black appearance. There was not a complete lack of vegetation in the region as paper birch and wild blueberry patches thrived in the acidic soils. During the
 The Sudbury Arts Council was established in 1974. Its mandate is to connect, communicate and celebrate the arts. It has an important role to provide a calendar of events and news about arts and culture activities. The city is home to two art galleries—the Art Gallery of Sudbury and
The Sudbury Arts Council was established in 1974. Its mandate is to connect, communicate and celebrate the arts. It has an important role to provide a calendar of events and news about arts and culture activities. The city is home to two art galleries—the Art Gallery of Sudbury and
CBC Northern Ontario, October 5, 2021.
CBC Sudbury, June 1, 2017. are also held each year. Mainstream commercial films are screened at the SilverCity theatre complex, which is also the primary venue for most Cinéfest screenings. Science North is home to an
. ''
 Sudbury's most successful artists have predominantly been in the country, folk and country-rock genres. These include
Sudbury's most successful artists have predominantly been in the country, folk and country-rock genres. These include
 Science North is an interactive
Science North is an interactive
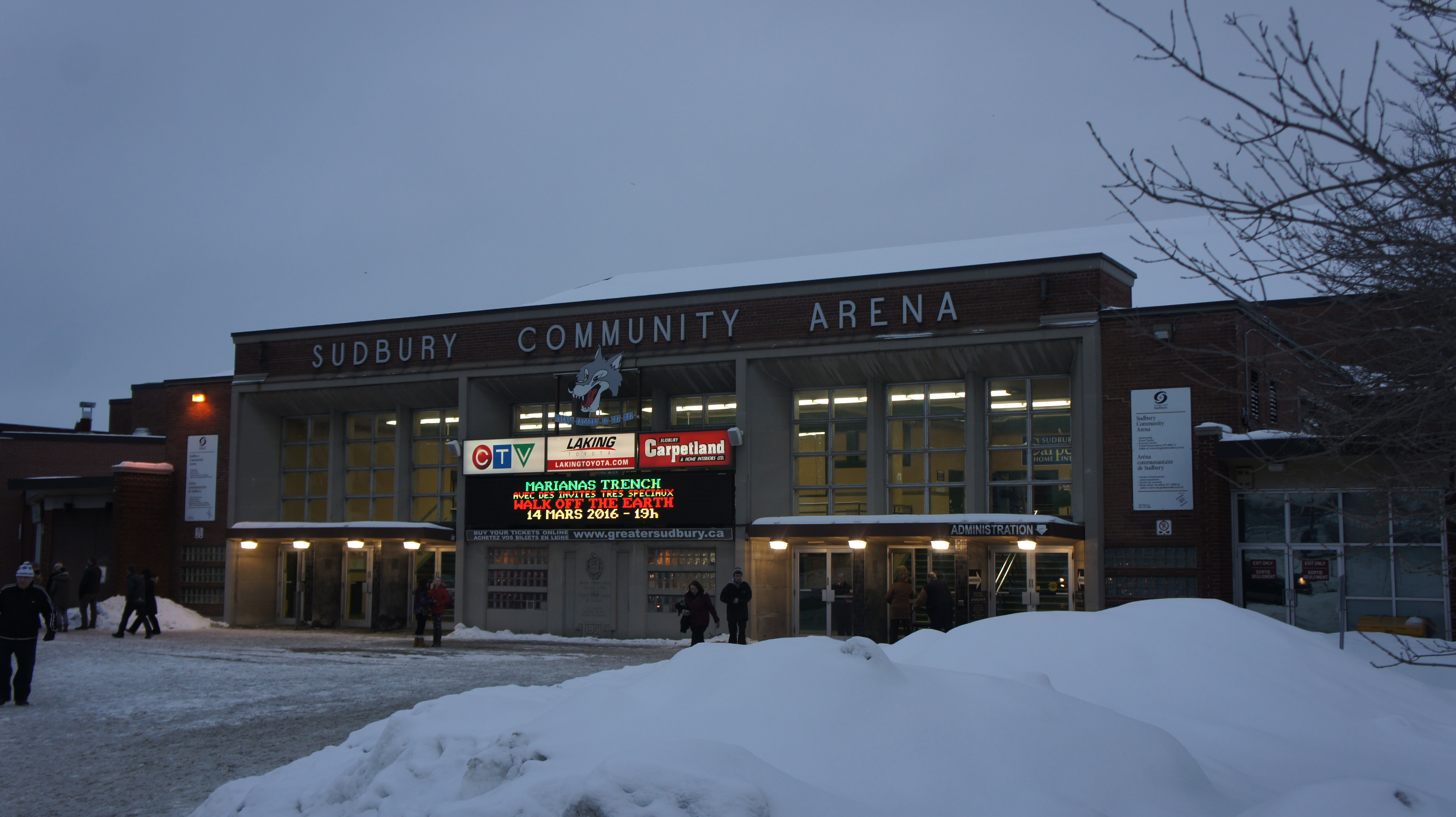 Sudbury has many trails that are used year-round. The Sudbury Trail Plan grooms almost of trails for snowmobiles in the winter. There are approximately of non-motorized trails in the city, many of which were built by Rainbow Routes Association. There is of diverse hiking, biking, and jogging trails found in the Lake Laurentian Conservation Area near downtown. Other trails link Sudbury to areas outside of the city including the Trans Canada Trail, which passes through the city, and the Voyageur Hiking Trail. The city is also home to Sudbury Downs, a harness racing track located in
Sudbury has many trails that are used year-round. The Sudbury Trail Plan grooms almost of trails for snowmobiles in the winter. There are approximately of non-motorized trails in the city, many of which were built by Rainbow Routes Association. There is of diverse hiking, biking, and jogging trails found in the Lake Laurentian Conservation Area near downtown. Other trails link Sudbury to areas outside of the city including the Trans Canada Trail, which passes through the city, and the Voyageur Hiking Trail. The city is also home to Sudbury Downs, a harness racing track located in
 After a brief period as a lumber camp, Sudbury's economy was dominated by the mining industry for much of the 20th century. By the 1970s, Inco employed a quarter of the local workforce."In Sudbury it's restive, not festive"
After a brief period as a lumber camp, Sudbury's economy was dominated by the mining industry for much of the 20th century. By the 1970s, Inco employed a quarter of the local workforce."In Sudbury it's restive, not festive"
''
CBC Northern Ontario, April 3, 2017. and the creation of The Junction, a multi-use complex which will incorporate the new home of the Art Gallery of Sudbury, the new main branch of the
Northern Ontario
Northern Ontario is a primary geographic and quasi-administrative region of the Canadian province of Ontario, the other primary region being Southern Ontario. Most of the core geographic region is located on part of the Superior Geological Pro ...
by population, with a population of 166,004 at the 2021 Canadian Census
The 2021 Canadian census was a detailed enumeration of the Canadian population with a reference date of May 11, 2021. It follows the 2016 Canadian census, which recorded a population of 35,151,728. The overall response rate was 98%, which is sl ...
. By land area, it is the largest in Ontario and the fifth largest in Canada. It is administratively a single-tier municipality
A unitary authority is a local authority responsible for all local government functions within its area or performing additional functions that elsewhere are usually performed by a higher level of sub-national government or the national governmen ...
and thus is not part of any district, county, or regional municipality. The City of Greater Sudbury is separate from, but entirely surrounded by the Sudbury District. The city is also referred to as "Grand Sudbury" among Francophones.
The Sudbury region was inhabited by the Ojibwe
The Ojibwe, Ojibwa, Chippewa, or Saulteaux are an Anishinaabe people in what is currently southern Canada, the northern Midwestern United States, and Northern Plains.
According to the U.S. census, in the United States Ojibwe people are one of ...
people of the Algonquin group for thousands of years prior to the founding of Sudbury after the discovery of nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow t ...
ore in 1883 during the construction of the transcontinental railway. Greater Sudbury was formed in 2001 by merging the cities and towns of the former Regional Municipality of Sudbury with several previously unincorporated townships. Being located inland, the local climate is extremely seasonal, with average January lows of around and average July highs of .
The population resides in an urban core and many smaller communities scattered around 330 lakes and among hills of rock blackened by historical smelting
Smelting is a process of applying heat to ore, to extract a base metal. It is a form of extractive metallurgy. It is used to extract many metals from their ores, including silver, iron, copper, and other base metals. Smelting uses heat and a c ...
activity. Sudbury was once a major lumber center and a world leader in nickel mining. Mining and related industries dominated the economy for much of the 20th century. The two major mining companies which shaped the history of Sudbury were Inco, now Vale Limited, which employed more than 25% of the population by the 1970s, and Falconbridge, now Glencore. Sudbury has since expanded from its resource-based economy to emerge as the major retail, economic, health, and educational center for Northeastern Ontario. Sudbury is also home to a large Franco-Ontarian population, which influences its arts and culture.
Toponymy
James Worthington, the superintendent of construction on the Northern Ontario segment of the railway, selected the name Sudbury after Sudbury, Suffolk, in England, which was the hometown of his wife Caroline Hitchcock. The city's official name was changed to Greater Sudbury in 2001, when it was amalgamated with its suburban towns into the current city, on the grounds of ensuring that the merger did not erase the longstanding community identities of the outlying towns. In everyday usage, however, the city is still more commonly referred to as just Sudbury.History
The Sudbury region was inhabited by theOjibwe
The Ojibwe, Ojibwa, Chippewa, or Saulteaux are an Anishinaabe people in what is currently southern Canada, the northern Midwestern United States, and Northern Plains.
According to the U.S. census, in the United States Ojibwe people are one of ...
people of the Algonquin group as early as 9,000 years ago following the retreat of the last continental ice sheet. In 1850, local Ojibwe chiefs entered into an agreement with the British Crown to share a large tract of land, including what is now Sudbury, as part of the Robinson Huron Treaty
The Robinson Treaties are two treaties signed between the Ojibwa chiefs and The Crown in 1850 in the Province of Canada. The first treaty involved Ojibwa chiefs along the north shore of Lake Superior, and is known as the Robinson Superior Treaty. ...
. In exchange the Crown pledged to pay an annuity to First Nations people, which was originally set at $1.60 per treaty member and increased incrementally; its last increase was in 1874, leaving it fixed at $4.
French Jesuits
, image = Ihs-logo.svg
, image_size = 175px
, caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits
, abbreviation = SJ
, nickname = Jesuits
, formation =
, founders = ...
were the first to establish a European settlement when they set up a mission called Sainte-Anne-des-Pins, just before the construction of the Canadian Pacific Railway
The Canadian Pacific Railway (french: Chemin de fer Canadien Pacifique) , also known simply as CPR or Canadian Pacific and formerly as CP Rail (1968–1996), is a Canadian Class I railway incorporated in 1881. The railway is owned by Canad ...
in 1883. The Sainte-Anne-des-Pins church played a prominent role in the development of Franco-Ontarian culture in the region. Coincidentally St -Anne is the Patron Saint of Miners.
 During construction of the railway in 1883, blasting and excavation revealed high concentrations of
During construction of the railway in 1883, blasting and excavation revealed high concentrations of nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow t ...
-copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pink ...
ore at Murray Mine on the edge of the Sudbury Basin. This discovery brought the first waves of European settlers, who arrived not only to work at the mines, but also to build a service station for railway workers.
Sudbury was incorporated as a town in 1893, and its first mayor was Joseph Étienne aka Stephen Fournier.Wallace, C. M.; & Thomson, Ashley (Eds.) (1993). ''Sudbury: Rail Town to Regional Capital'' (3rd ed.). Dundurn Press
Dundurn Press is one of the largest Canadian-owned book publishing companies of adult and children's fiction and non-fiction. The company publishes Canadian literature, history, biography, politics and arts. Dundurn has about 2500 books in prin ...
. .
The American inventor Thomas Edison
Thomas Alva Edison (February 11, 1847October 18, 1931) was an American inventor and businessman. He developed many devices in fields such as electric power generation, mass communication, sound recording, and motion pictures. These inventi ...
visited the Sudbury area as a prospector in 1901. He is credited with the original discovery of the ore body at Falconbridge. Rich deposits of nickel sulphide ore were discovered in the Sudbury Basin geological formation. The construction of the railway allowed exploitation of these mineral resources and shipment of the commodities to markets and ports, as well as large-scale lumber extraction.
Mining began to replace lumber as the primary industry as the area's transportation network was improved to include trams. These enabled workers to live in one community and work in another. Sudbury's economy was dominated by the mining industry for much of the 20th century. Two major mining companies were created: Inco in 1902 and Falconbridge in 1928. They became two of the city's major employers and two of the world's leading producers of nickel.
Through the decades that followed, Sudbury's economy went through boom and bust cycles as world demand for nickel fluctuated. Demand was high during the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, when Sudbury-mined nickel was used extensively in the manufacturing of artillery in Sheffield
Sheffield is a city in South Yorkshire, England, whose name derives from the River Sheaf which runs through it. The city serves as the administrative centre of the City of Sheffield. It is historically part of the West Riding of Yorkshire ...
, England. It bottomed out when the war ended and then rose again in the mid-1920s as peacetime uses for nickel began to develop. The town was reincorporated as a city in 1930.
The city recovered from the Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
much more quickly than almost any other city in North America due to increased demand for nickel in the 1930s. Sudbury was the fastest-growing city and one of the wealthiest cities in Canada for most of the decade. Many of the city's social problems in the Great Depression era were not caused by unemployment or poverty, but due to the difficulty in keeping up with all of the new infrastructure demands created by rapid growth — for example, employed mineworkers sometimes ended up living in boarding houses or makeshift shanty towns, because demand for new housing was rising faster than supply. Between 1936 and 1941, the city was ordered into receivership
In law, receivership is a situation in which an institution or enterprise is held by a receiver—a person "placed in the custodial responsibility for the property of others, including tangible and intangible assets and rights"—especially in c ...
by the Ontario Municipal Board
The Ontario Municipal Board (OMB) was an independent administrative board, operated as an adjudicative tribunal, in the province of Ontario, Canada. It heard applications and appeals on municipal and planning disputes, as well as other matters s ...
. Another economic slowdown affected the city in 1937, but the city's fortunes rose again with wartime demands during the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
. The Frood Mine
Frood-Stobie Mine is a nickel mine in Greater Sudbury, Ontario, named for Thomas Frood, an employee of the federal department of Crown lands who prospected and staked many of the early mining claims in the area. A major arterial road in the city i ...
alone accounted for 40 percent of all the nickel used in Allied artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during si ...
production during the war. After the end of the war, Sudbury was in a good position to supply nickel to the United States government when it decided to stockpile non-Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
supplies during the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
.
 The open coke beds used in the early to mid 20th century and logging for fuel resulted in a near-total loss of native vegetation in the area. Consequently, the terrain was made up of exposed rocky outcrops permanently stained charcoal black by the air pollution from the roasting yards. Acid rain added more staining, in a layer that penetrates up to into the once pink-grey
The open coke beds used in the early to mid 20th century and logging for fuel resulted in a near-total loss of native vegetation in the area. Consequently, the terrain was made up of exposed rocky outcrops permanently stained charcoal black by the air pollution from the roasting yards. Acid rain added more staining, in a layer that penetrates up to into the once pink-grey granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies un ...
.
The construction of the Inco Superstack
The Inco Superstack in Sudbury, Ontario, with a height of , is the tallest chimney in Canada and the Western hemisphere, and the second tallest freestanding chimney in the world after the GRES-2 Power Station in Kazakhstan. It is also the s ...
in 1972 dispersed sulphuric acid through the air over a much wider area, reducing the acidity of local precipitation. This enabled the municipality, province and Inco and academics from Laurentian University to begin an environmental recovery program in the late 1970s, labelled a "regreening" effort. Lime was spread over the charred soil by hand and by aircraft. Seeds of wild grasses
Poaceae () or Gramineae () is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos and the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in lawns ...
and other vegetation were also spread. As of 2010, 9.2 million new trees have been planted in the city. Vale
A vale is a type of valley.
Vale may also refer to:
Places Georgia
* Vale, Georgia, a town in the Samtskhe-Javakheti region
Norway
* Våle, a historic municipality
Portugal
* Vale (Santa Maria da Feira), a former civil parish in the municipa ...
has begun to rehabilitate the slag heaps that surrounds their smelter in the Copper Cliff area with the planting of grass and trees, as well as the use of biosolids
Biosolids are solid organic matter recovered from a sewage treatment process and used as fertilizer. In the past, it was common for farmers to use animal manure to improve their soil fertility. In the 1920s, the farming community began also to use ...
to stabilize and regreen tailings
In mining, tailings are the materials left over after the process of separating the valuable fraction from the uneconomic fraction ( gangue) of an ore. Tailings are different to overburden, which is the waste rock or other material that ove ...
areas.
 In 1978, the workers of Sudbury's largest mining corporation, Inco (now Vale), embarked on a strike over production and employment cutbacks. The strike, which lasted for nine months, badly damaged Sudbury's economy. The city government was spurred to launch a project to diversify the city's economy.
A unique and visionary project, Science North was inaugurated in 1984 with two-snowflake styled buildings connected by a tunnel through the Canadian shield where the Creighton fault intersects the shores of Lake Ramsey. The city tried to attract new employers and industries through the 1980s and 1990s with mixed success. The city of Sudbury and its suburban communities, which were reorganized into the Regional Municipality of Sudbury in 1973, was subsequently merged in 2001 into the single-tier city of Greater Sudbury.
In 1978, the workers of Sudbury's largest mining corporation, Inco (now Vale), embarked on a strike over production and employment cutbacks. The strike, which lasted for nine months, badly damaged Sudbury's economy. The city government was spurred to launch a project to diversify the city's economy.
A unique and visionary project, Science North was inaugurated in 1984 with two-snowflake styled buildings connected by a tunnel through the Canadian shield where the Creighton fault intersects the shores of Lake Ramsey. The city tried to attract new employers and industries through the 1980s and 1990s with mixed success. The city of Sudbury and its suburban communities, which were reorganized into the Regional Municipality of Sudbury in 1973, was subsequently merged in 2001 into the single-tier city of Greater Sudbury.
 In 2006, both of the city's major mining companies, Canadian-based Inco and Falconbridge, were taken over by new owners: Inco was acquired by the Brazilian company CVRD (now renamed
In 2006, both of the city's major mining companies, Canadian-based Inco and Falconbridge, were taken over by new owners: Inco was acquired by the Brazilian company CVRD (now renamed Vale
A vale is a type of valley.
Vale may also refer to:
Places Georgia
* Vale, Georgia, a town in the Samtskhe-Javakheti region
Norway
* Våle, a historic municipality
Portugal
* Vale (Santa Maria da Feira), a former civil parish in the municipa ...
), while Falconbridge was purchased by the Swiss company Xstrata, which itself was purchased by Anglo–Swiss Glencore, forming Glencore Xstrata
Glencore plc is a Swiss multinational commodity trading and mining company with headquarters in Baar, Switzerland. Glencore's oil and gas head office is in London and its registered office is in Saint Helier, Jersey. The current company was c ...
. Xstrata donated the historic Edison Building, the onetime head office of Falconbridge, to the city in 2007 to serve as the new home of the municipal archives. On September 19, 2008, a fire destroyed the historic Sudbury Steelworkers Hall on Frood Road. A strike at Vale's operations, which began on July 13, 2009, was tentatively resolved in July 2010. The 2009 strike lasted longer than the devastating 1978 strike, but had a much more modest effect on the city's economy than the earlier action—unlike in 1978, the local rate of unemployment
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work during the refe ...
''declined'' slightly during the 2009 strike.
The ecology of the Sudbury region has recovered dramatically, helped by regreening programs and improved mining practices. The United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoni ...
honoured twelve cities in the world, including Sudbury, with the Local Government Honours Award at the 1992 Earth Summit to recognise the city's community-based environmental reclamation strategies. By 2010, the regreening programs had successfully rehabilitated of land in the city; however, approximately of land have yet to be rehabilitated.
Geography
Sudbury has 330 lakes over within the city limits. The most prominent is Lake Wanapitei, the largest lake in the world completely contained within the boundaries of a single city.Ramsey Lake
Ramsey Lake (french: Lac Ramsey) is a lake in Sudbury, Ontario, located near the city's downtown core. Until 2001, Ramsey Lake was listed by the Guinness Book of World Records as the world's largest lake located entirely within the boundaries o ...
, a few kilometres south of downtown Sudbury, held the same record before the municipal amalgamation in 2001 brought Lake Wanapitei fully inside the city limits. Sudbury is divided into two main watersheds: to the east is the French River watershed which flows into Georgian Bay
Georgian Bay (french: Baie Georgienne) is a large bay of Lake Huron, in the Laurentia bioregion. It is located entirely within the borders of Ontario, Canada. The main body of the bay lies east of the Bruce Peninsula and Manitoulin Island. T ...
and to the west is the Spanish River watershed which flows into the North Channel of Lake Huron.
igneous rock
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma o ...
of the Canadian (Precambrian) Shield. The ore deposits in Sudbury are part of a large geological structure known as the Sudbury Basin, which are the remnants of a nearly two billion-year-old impact crater; long thought to be the result of a meteorite
A meteorite is a solid piece of debris from an object, such as a comet, asteroid, or meteoroid, that originates in outer space and survives its passage through the atmosphere to reach the surface of a planet or moon. When the original object ...
collision, more recent analysis has suggested that the crater may in fact have been created by a comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that, when passing close to the Sun, warms and begins to release gases, a process that is called outgassing. This produces a visible atmosphere or coma, and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena ...
.
Sudbury's pentlandite, pyrite
The mineral pyrite (), or iron pyrite, also known as fool's gold, is an iron sulfide with the chemical formula Iron, FeSulfur, S2 (iron (II) disulfide). Pyrite is the most abundant sulfide mineral.
Pyrite's metallic Luster (mineralogy), lust ...
and pyrrhotite ores contain profitable amounts of many elements—primarily nickel and copper, but also platinum, palladium and other valuable metals.
Local smelting of the ore releases this sulphur into the atmosphere where it combines with water vapour to form sulphuric acid, contributing to acid rain. As a result, Sudbury has had a widespread reputation as a wasteland. In parts of the city, vegetation was devastated by acid rain and logging to provide fuel for early smelting
Smelting is a process of applying heat to ore, to extract a base metal. It is a form of extractive metallurgy. It is used to extract many metals from their ores, including silver, iron, copper, and other base metals. Smelting uses heat and a c ...
techniques. To a lesser extent, the area's ecology was also impacted by lumber camps in the area providing wood for the reconstruction of Chicago after the Great Chicago Fire
The Great Chicago Fire was a conflagration that burned in the American city of Chicago during October 8–10, 1871. The fire killed approximately 300 people, destroyed roughly of the city including over 17,000 structures, and left more than 1 ...
of 1871. While other logging areas in Northeastern Ontario were also involved in that effort, the emergence of mining related processes in the following decade made it significantly harder for new trees to grow to full maturity in the Sudbury area than elsewhere.
Apollo
Apollo, grc, Ἀπόλλωνος, Apóllōnos, label=genitive , ; , grc-dor, Ἀπέλλων, Apéllōn, ; grc, Ἀπείλων, Apeílōn, label=Arcadocypriot Greek, ; grc-aeo, Ἄπλουν, Áploun, la, Apollō, la, Apollinis, label= ...
manned lunar exploration program, NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedin ...
astronauts trained in Sudbury to become familiar with impact breccia
Breccia () is a rock composed of large angular broken fragments of minerals or rocks cemented together by a fine-grained matrix.
The word has its origins in the Italian language, in which it means "rubble". A breccia may have a variety of ...
and shatter cones, rare rock formations produced by large meteorite impacts. However, the popular misconception that they were visiting Sudbury because it purportedly resembled the lifeless surface of the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
persists.
The city's Nickel District Conservation Authority operates a conservation area, the Lake Laurentian Conservation Area, in the city's south end. Other unique environmental projects in the city include the Fielding Bird Sanctuary, a protected area along Highway 17 near Lively that provides a managed natural habitat for birds, and a hiking and nature trail near Coniston, which is named in honour of scientist Jane Goodall
Dame Jane Morris Goodall (; born Valerie Jane Morris-Goodall on 3 April 1934), formerly Baroness Jane van Lawick-Goodall, is an English primatologist and anthropologist. Seen as the world's foremost expert on chimpanzees, Goodall is best kn ...
.
Six provincial park
Ischigualasto Provincial Park
A provincial park (or territorial park) is a park administered by one of the provinces of a country, as opposed to a national park. They are similar to state parks in other countries. They are typically open to t ...
s ( Chiniguchi River, Daisy Lake Uplands, Fairbank, Killarney Lakelands and Headwaters, Wanapitei and Windy Lake) and two provincial conservation reserves (MacLennan Esker Forest and Tilton Forest) are also located partially or entirely within the city boundaries.
Climate
Greater Sudbury has ahumid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freez ...
(Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, nota ...
: ''Dfb''). This region has warm and often hot, humid summers with long, cold and snowy winters. It is situated north of the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
, making it prone to arctic air masses. Monthly precipitation is equal year round, with snow cover expected six months of the year. Although extreme weather events are rare, one of the worst tornadoes in Canadian history struck the city and its suburbs on August 20, 1970, killing six people, injuring two hundred, and causing more than C$17 million in damages.
The highest temperature ever recorded in Greater Sudbury was on July 13, 1936. The lowest temperature ever recorded was on December 29, 1933.
Administration

Municipal politics
From the city hall at Tom Davies Square, the city is headed by twelvecouncil
A council is a group of people who come together to consult, deliberate, or make decisions. A council may function as a legislature, especially at a town, city or county/ shire level, but most legislative bodies at the state/provincial or nati ...
members and one mayor
In many countries, a mayor is the highest-ranking official in a municipal government such as that of a city or a town. Worldwide, there is a wide variance in local laws and customs regarding the powers and responsibilities of a mayor as well ...
both elected every four years. The current mayor is Paul Lefebvre, who was elected in the 2022 municipal election. The 2011 operating budget for Greater Sudbury was C$471 million, and the city employs 2006 full-time workers.
Federal and provincial politics
The city is divided between the federal electoral districts ofSudbury Sudbury may refer to:
Places Australia
* Sudbury Reef, Queensland
Canada
* Greater Sudbury, Ontario (official name; the city continues to be known simply as Sudbury for most purposes)
** Sudbury (electoral district), one of the city's federal el ...
and Nickel Belt in the House of Commons of Canada, and the provincial electoral districts of Sudbury Sudbury may refer to:
Places Australia
* Sudbury Reef, Queensland
Canada
* Greater Sudbury, Ontario (official name; the city continues to be known simply as Sudbury for most purposes)
** Sudbury (electoral district), one of the city's federal el ...
and Nickel Belt in the Legislative Assembly of Ontario. The federal and provincial districts do not have identical boundaries despite using the same names; most notably, the Walden
''Walden'' (; first published in 1854 as ''Walden; or, Life in the Woods'') is a book by American transcendentalist writer Henry David Thoreau. The text is a reflection upon the author's simple living in natural surroundings. The work is part ...
district of the city is located in Sudbury federally but in Nickel Belt provincially. The city is represented federally by Members of Parliament Viviane Lapointe
Viviane Lapointe is a Canadian politician, who was elected to the Canadian House of Commons in the 2021 Canadian federal election. She represents the electoral district of Sudbury as a member of the Liberal Party of Canada.
Biography
Lapointe ...
and Marc Serré, both of the Liberal Party of Canada, and provincially by Jamie West
Jamie West is a Canadian politician, who was elected to the Legislative Assembly of Ontario in the 2018 provincial election. He represents the riding of Sudbury as a member of the Ontario New Democratic Party.
Prior to his election to the leg ...
and France Gélinas of the Ontario New Democratic Party. The provincial Ministry of Energy, Northern Development and Mines
The Ministry of Energy, Northern Development and Mines (MENDM) was the ministry responsible for developing a safe, reliable and affordable energy supply across the province, overseeing Ontario’s mineral sector and promoting northern economic an ...
has its head office in the city.
Both federal and provincial politics in the city tend to be dominated by the Liberal and New Democratic parties. Historically, the Liberals have been stronger in the Sudbury riding, with the New Democrats dominant in Nickel Belt, although both ridings have elected members of both parties at different times.
Communities
The city of Sudbury and its suburban communities were reorganized into the Regional Municipality of Sudbury in 1973, which was subsequently merged in 2001 into the single-tier city of Greater Sudbury. In common usage, the city's urban core is still generally referred to as ''Sudbury'', while the outlying former towns are still referred to by their old names and continue in some respects to maintain their own distinct community identities despite their lack of political independence. Each of the seven former municipalities in turn encompasses numerous smaller neighbourhoods. Amalgamated cities (2001 Canadian census population) include: Sudbury (85,354) andValley East
A valley is an elongated low area often running between hills or mountains, which will typically contain a river or stream running from one end to the other. Most valleys are formed by erosion of the land surface by rivers or streams over ...
(22,374). Towns (2001 Canadian census population) include: Rayside-Balfour (15,046), Nickel Centre
Nickel Centre (1996 census population 13,017) was a town in Ontario, Canada, which existed from 1973 to 2000.
It was created as part of the Regional Municipality of Sudbury. On January 1, 2001, the town and the Regional Municipality were dissolve ...
(12,672), Walden
''Walden'' (; first published in 1854 as ''Walden; or, Life in the Woods'') is a book by American transcendentalist writer Henry David Thoreau. The text is a reflection upon the author's simple living in natural surroundings. The work is part ...
(10,101), Onaping Falls
Onaping Falls (1996 census population 5,277) was a town in the Canadian province of Ontario, which existed from 1973 to 2000. It was created as part of the Regional Municipality of Sudbury, and took its name from the waterfalls (High Falls) on the ...
(4,887), and Capreol (3,486). The Wanup
Wanup is a dispersed rural community and unincorporated place in the geographic township of Dill in the southeast of the city of Greater Sudbury, Ontario, Canada. Wanup became part of Greater Sudbury on January 1, 2001, when that city was create ...
area, formerly an unincorporated settlement outside of Sudbury's old city limits, was also annexed into the city in 2001, along with a large wilderness area on the northeastern shore of Lake Wanapitei.
Culture
Sudbury's culture is influenced by the large Franco-Ontarian community consisting of approximately 40 percent of the city's population, particularly in the amalgamated municipalities ofValley East
A valley is an elongated low area often running between hills or mountains, which will typically contain a river or stream running from one end to the other. Most valleys are formed by erosion of the land surface by rivers or streams over ...
and Rayside-Balfour and historically in the Moulin-à-Fleur neighbourhood. The French culture is celebrated with the Franco-Ontarian flag, recognized by the province as an official emblem, which was created in 1975 by a group of teachers at Laurentian University and after some controversy has flown at Tom Davies Square since 2006. The large francophone community plays a central role in developing and maintaining many of the cultural institutions of Sudbury including the Théâtre du Nouvel-Ontario
Théâtre du Nouvel-Ontario (''Theatre of New-Ontario'') is a Canadian professional theatre company. Located in Sudbury, Ontario, the company produces French language stage productions.
The company was founded in 1971 by the Coopérative des ...
, La Nuit sur l'étang La Nuit sur l'étang is a Canadian music festival, held annually in Sudbury, Ontario.
Established in 1973 by Fernand Dorais and a group of students from Laurentian University who were established as the Coopérative des artistes du Nouvel-Ontari ...
, La Galerie du Nouvel-Ontario
La Galerie du Nouvel-Ontario is an art gallery in Sudbury, Ontario, Canada.
Originally launched in 1974 by artists associated with the Cooperative des artistes du Nouvel-Ontario, the gallery was first established as part of La Slague, a local Fr ...
, Le Centre franco-ontarien de folklore and the Prise de parole publishing company. The city hosted Les Jeux de la francophonie canadienne in 2011.
Arts
 The Sudbury Arts Council was established in 1974. Its mandate is to connect, communicate and celebrate the arts. It has an important role to provide a calendar of events and news about arts and culture activities. The city is home to two art galleries—the Art Gallery of Sudbury and
The Sudbury Arts Council was established in 1974. Its mandate is to connect, communicate and celebrate the arts. It has an important role to provide a calendar of events and news about arts and culture activities. The city is home to two art galleries—the Art Gallery of Sudbury and La Galerie du Nouvel-Ontario
La Galerie du Nouvel-Ontario is an art gallery in Sudbury, Ontario, Canada.
Originally launched in 1974 by artists associated with the Cooperative des artistes du Nouvel-Ontario, the gallery was first established as part of La Slague, a local Fr ...
. Both are dedicated primarily to Canadian art, especially artists from Northern Ontario.
The city's two professional theatre companies are the anglophone Sudbury Theatre Centre
The Sudbury Theatre Centre is a professional theatre company, located in Greater Sudbury, Ontario, Canada.
Following an Ontario government report in 1967 which recommended the creation of a theatre company in Sudbury, local arts patrons Sonja Du ...
(STC) and the francophone Théâtre du Nouvel-Ontario
Théâtre du Nouvel-Ontario (''Theatre of New-Ontario'') is a Canadian professional theatre company. Located in Sudbury, Ontario, the company produces French language stage productions.
The company was founded in 1971 by the Coopérative des ...
(TNO). The STC has its own theatre venue downtown, while the TNO stages its productions at La salle André Paiement, a venue located on the campus of Collège Boréal. Theatre productions are also staged by students at Laurentian University's affiliated Thornloe faculty, by a community theatre company at Cambrian College
Cambrian College is a college of applied arts and technology in Greater Sudbury, Ontario, Canada. Established in 1967, and funded by the province of Ontario, Cambrian has campuses in Sudbury, Espanola and Little Current.
Cambrian works in p ...
, as well as by high school drama students at Sudbury Secondary School
Sudbury Secondary School is a high school in the downtown of Greater Sudbury, Ontario, Canada, well known for its Arts Education Program, featuring theatre arts, dance, vocal music, instrumental music, keyboard, media arts and visual art. Sudb ...
, Lo-Ellen Park Secondary School
Lo-Ellen Park Secondary School is a high school located on Loach's Road in the South End of Greater Sudbury, Ontario. It is administered by the Rainbow District School Board, and the current principal is Pamela Potvin and the current vice princi ...
, St. Charles College and École secondaire Macdonald-Cartier
École secondaire Macdonald-Cartier, in Sudbury, Ontario, opened its doors in 1969. École secondaire Macdonald-Cartier was the second public high school French language in Ontario to offer free education to all young francophones. The school is ...
with its troupe Les Draveurs. Sudbury also has numerous community theatre companies throughout the city, including its first and only for-charity theatre company, UP Theatre.
In 2021 the YES Theatre company unveiled plans for the Refettorio, which would convert a vacant lot on Durham Street near the YMCA into an outdoor theatrical and musical performance space. In 2022, YES and the Sudbury Theatre Centre announced a joint program as a "pilot" to explore the feasibility of a potential merger.
Place des Arts, a new project to provide a community hub for the city's francophone cultural institutions including a 300-seat concert hall, a 120-seat theatre studio, an art gallery, a bistro, a gift boutique and bookstore, a children's arts center and 10,000 square feet of studio space for artists, began construction in the downtown core in 2019, and opened in 2022."Sudbury's Place des Arts on track for a 2022 opening"CBC Northern Ontario, October 5, 2021.
Festivals
Cinéfest Sudbury International Film Festival, the city's primary annual film festival, has been staged in September each year since 1989."Extra seats needed at Cinefest". ''The Globe and Mail
''The Globe and Mail'' is a Canadian newspaper printed in five cities in western and central Canada. With a weekly readership of approximately 2 million in 2015, it is Canada's most widely read newspaper on weekdays and Saturdays, although it ...
'', September 27, 1989. Two smaller specialist film festivals, the Junction North International Documentary Film Festival for documentary films and the Queer North Film Festival The Queer North Film Festival is an annual film festival in Sudbury, Ontario, which presents an annual program of LGBT film. Presented by the Sudbury Indie Cinema Coop, the festival was staged for the first time in 2016. The same organization als ...
for LGBT
' is an initialism that stands for lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender. In use since the 1990s, the initialism, as well as some of its common variants, functions as an umbrella term for sexuality and gender identity.
The LGBT term ...
-themed films,"Queer North Film Festival announces lineup for second year"CBC Sudbury, June 1, 2017. are also held each year. Mainstream commercial films are screened at the SilverCity theatre complex, which is also the primary venue for most Cinéfest screenings. Science North is home to an
IMAX
IMAX is a proprietary system of high-resolution cameras, film formats, film projectors, and theaters known for having very large screens with a tall aspect ratio (approximately either 1.43:1 or 1.90:1) and steep stadium seating.
Graeme ...
theatre which screens a program of IMAX films, the Cavern at Science North hosts some gala screenings during Cinéfest and screens science documentaries during the year, and the Sudbury Indie Cinema programs a repertory cinema lineup of independent and international films as well as organizing both the Junction North and Queer North film festivals. In 2021 the Sudbury Indie Cinema Co-op also launched the Sudbury Outdoor Adventure Reels Film Festival, devoted to wilderness and adventure films, following several years of the city hosting an annual stop on the Banff Mountain Film Festival's touring circuit.
The city has hosted an annual Sudbury Pride festival since 1997.
The Up Here Festival, launched in 2015, blends a program of musical performance with the creation of both mural
A mural is any piece of graphic artwork that is painted or applied directly to a wall, ceiling or other permanent substrate. Mural techniques include fresco, mosaic, graffiti and marouflage.
Word mural in art
The word ''mural'' is a Spanis ...
s and installation art
Installation art is an artistic genre of three-dimensional works that are often site-specific and designed to transform the perception of a space. Generally, the term is applied to interior spaces, whereas exterior interventions are often called ...
projects throughout the downtown core, while PlaySmelter, a theatre festival devoted to theatrical and storytelling performances by local writers and actors, was launched in 2013, and is held at various venues in the city including the Sudbury Theatre Centre and Place des Arts.
In music, the city is home to the Northern Lights Festival Boréal
Northern Lights Festival Boréal is an annual summer music festival in Greater Sudbury, Ontario, Canada. It is one of Canada's oldest music festivals in continuous operation, having been staged every year since 1972 until the Covid-19 pandemic.
and La Nuit sur l'étang La Nuit sur l'étang is a Canadian music festival, held annually in Sudbury, Ontario.
Established in 1973 by Fernand Dorais and a group of students from Laurentian University who were established as the Coopérative des artistes du Nouvel-Ontari ...
festivals.
Sudbury also hosts Northern Ontario's only Japanese cultural Festival, Japan Festival Sudbury. It started in 2019, went on hiatus for two years during the COVID-19 pandemic in Ontario
The COVID-19 pandemic in Ontario is an ongoing viral pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 ( COVID-19), a novel infectious disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first confirmed case of COVID-19 i ...
, and returned to Sudbury's Bell Park Amphitheatre on July 16, 2022.
Literature
Works of fiction themed or set primarily or partially in Sudbury or its former suburbs include Robert J. Sawyer's '' The Neanderthal Parallax'' trilogy, Alistair MacLeod's novel '' No Great Mischief'', Paul Quarrington's '' Logan in Overtime'' andJean-Marc Dalpé
Jean-Marc Dalpé (born February 21, 1957) is a Canadian playwright and poet. He is one of the most important figures in Franco-Ontarian literature.
Dalpé studied theatre at the University of Ottawa, graduating in 1973. In 1979, he obtained grad ...
's play ''1932, la ville du nickel'' and his short story collection ''Contes sudburois''. The city is also fictionalized as "Chinookville" in several books by American comedy writer Jack Douglas, and as "Complexity" in Tomson Highway's musical play '' The (Post) Mistress''."A one-of-a-kind musical". ''
Sudbury Star
''The Sudbury Star'' is a Canadian daily regional newspaper published in Sudbury, Ontario. It is owned by the media company, Postmedia. It is the largest daily paper in Northeastern Ontario by circulation.
History
The ''Sudbury Star'' began as ...
'', October 25, 2012.
Noted writers who have lived in Sudbury include playwrights Jean-Marc Dalpé, Sandra Shamas
Sandra Shamas (born 1957) is a Canadian puppeteer, comedic actress, writer, director and producer.
Biography
Shamas was born in Sudbury, Ontario. She moved to Toronto in 1980, where she held a variety of jobs before a workshop at The Second City ...
and Brigitte Haentjens, poets Robert Dickson, Roger Nash, Gregory Scofield
Gregory Scofield (born July 20, 1966 in Maple Ridge, British Columbia)Gregory Scofield ...
and Margaret Christakos
Margaret Christakos (born 1962 in Sudbury, Ontario) is a Canadian poet who lives in Toronto.
Life
Christakos was born and raised in Sudbury, Ontario. She is a Canadian poet, fiction author, literary essayist and creative writing instructor. Sin ...
, fiction writers Kelley Armstrong, Sean Costello, Sarah Selecky, Matthew Heiti
Matthew Heiti is a Canadian actor, screenwriter, novelist and playwright. As cowriter with Ryan Ward of the film '' Son of the Sunshine'', he was a Genie Award nominee for Best Original Screenplay at the 32nd Genie Awards in 2012.
Born and rais ...
and Jeffrey Round, poet Patrice Desbiens
Patrice Desbiens (born 1948) is a Francophone Canadian poet. He was born in Timmins, Ontario and began his career as a journalist. Since making his literary debut in 1972, he has been regarded as one of Canada's most successful French-language po ...
, journalist Mick Lowe and academics Richard E. Bennett, Michel Bock
Michel Bock (born 1971) is a Canadian historian, who specializes in the history of Franco-Ontarian communities and cultures. His book ''Quand la nation débordait les frontières: les minorités françaises dans la pensée de Lionel Groulx'' was ...
, Rand Dyck Perry Rand Dyck (born 1943 in Calgary, Alberta) is the author of the Canadian Politics: Critical Approaches textbook which is used in many Canadian universities, and taught to students studying Political Science, Law, Economics, Women's Studies, Ph ...
, Graeme S. Mount and Gary Kinsman.
Music
Robert Paquette
Robert Paquette (born July 2, 1949) is a Canadian folk singer-songwriter.
In 1970, he worked with the student theatre group at Laurentian University, composing songs for the Franco-Ontarian stage musical ''Moé, j'viens du nord, 'stie!'' The t ...
, , Gil Grand, Kevin Closs
Kevin Closs (born 1963) is a Canadian singer-songwriter, and author ("OMAGEE") Closs was raised on Manitoulin Island
Manitoulin Island is an island in Lake Huron, located within the borders of the Canadian province of Ontario, in the biore ...
, CANO
CANO, a Canadian progressive rock band of the 1970s and 1980s, was the most successful popular musical group in Franco-Ontarian history.
Origins
CANO evolved out of the ''Coopérative des artistes du Nouvel-Ontario'' (''Artists' Cooperative
...
, Jake Mathews
Jake Mathews (born Jacques Lagrandeur born March 14, 1971 in Sudbury, Ontario, Canada) is a Canadian country music singer, songwriter and performer.
Career
Jake's self-titled debut CD (''Jake Mathews'') garnered six nationally charted hits: " ...
, Loma Lyns, Alex J. Robinson, Chuck Labelle
Jean-Guy (Chuck) Labelle (born 18 March 1954) is a Franco-Canadian singer-songwriter and guitarist who performs francophone New Country-Rock music. He is from Mattawa, Ontario. His first album, ''Chuck'', reached Gold status after two years and hi ...
, En Bref and Ox. The rap rock bands Project Wyze and Konflit Dramatik Konflit, formerly Konflit Dramatik, are a Canadian rap rock band, most prominent in the 2000s. One of the most prominent Franco-Ontarian musical groups of their era, the band had a varying lineup over its lifetime with vocalist Christian Berthiaume ...
were also based in Sudbury. High-profile musicians play at the Sudbury Community Arena
The Sudbury Community Arena is a multi-purpose arena in the downtown core of Greater Sudbury, Ontario, Canada. It was built in 1951, on the site of the former Central Public School, at a cost of $700,000. The approval and construction of the aren ...
. Bell Park's outdoor Grace Hartman Amphitheatre and Laurentian University's Fraser Auditorium are sometimes used for summer bookings. Smaller touring indie rock
Indie rock is a subgenre of rock music that originated in the United States, United Kingdom and New Zealand from the 1970s to the 1980s. Originally used to describe independent record labels, the term became associated with the music they produ ...
bands, as well as some local musicians, are usually booked at The Townehouse Tavern, while local bands play a number of small music venues across the city. The city is also home to annual music festivals including the Northern Lights Festival Boréal
Northern Lights Festival Boréal is an annual summer music festival in Greater Sudbury, Ontario, Canada. It is one of Canada's oldest music festivals in continuous operation, having been staged every year since 1972 until the Covid-19 pandemic.
, the Up Here Festival and La Nuit sur l'étang La Nuit sur l'étang is a Canadian music festival, held annually in Sudbury, Ontario.
Established in 1973 by Fernand Dorais and a group of students from Laurentian University who were established as the Coopérative des artistes du Nouvel-Ontari ...
. The local Sudbury Symphony Orchestra
The Sudbury Symphony Orchestra is a Canadian symphony orchestra based Sudbury, Ontario. Incorporated in 1975 as a not-for-profit registered charity, the orchestra performs a season of full orchestra concerts and chamber music concerts at a variet ...
performs six annual concerts of classical music
Classical music generally refers to the art music of the Western world, considered to be distinct from Western folk music or popular music traditions. It is sometimes distinguished as Western classical music, as the term "classical music" al ...
. Sudbury is also home to the Blue Saints Drum and Bugle Corps, a youth drum corps active since 1952.
One of Stompin' Tom Connors
Charles Thomas "Stompin' Tom" Connors, OC (February 9, 1936 – March 6, 2013) was a Canadian country and folk singer-songwriter. Focusing his career exclusively on his native Canada, he is credited with writing more than 300 songs and has re ...
' most famous songs, "Sudbury Saturday Night "Sudbury Saturday Night" is one of the most famous songs by Stompin' Tom Connors, which depicts the hard-drinking, hard-partying social life of hard rock miners in the Northern Ontario mining city of Sudbury.
The song's chorus is:
: ''Yeah, the g ...
", depicts the hard-drinking, hard-partying social life of hard rock miners
The Hard Rock Miners are a Canadian rockabilly/hillbilly/country/folk band based in Vancouver, British Columbia.
History
In 1987, members of The Hard Rock Miners started out busking on the streets of Vancouver, particularly on trendy Robson S ...
of Sudbury. Miriam Linna, who drummed in the Cramps, Nervus Rex and The A-Bones, was also born in Sudbury.
Attractions
 Science North is an interactive
Science North is an interactive science museum
A science museum is a museum devoted primarily to science. Older science museums tended to concentrate on static displays of objects related to natural history, paleontology, geology, industry and industrial machinery, etc. Modern trends in ...
and Northern Ontario
Northern Ontario is a primary geographic and quasi-administrative region of the Canadian province of Ontario, the other primary region being Southern Ontario. Most of the core geographic region is located on part of the Superior Geological Pro ...
's most popular tourist attraction with around 288,000 visitors per year (as of 2018). It consists of two snowflake-shaped buildings on the southwestern shore of Ramsey Lake
Ramsey Lake (french: Lac Ramsey) is a lake in Sudbury, Ontario, located near the city's downtown core. Until 2001, Ramsey Lake was listed by the Guinness Book of World Records as the world's largest lake located entirely within the boundaries o ...
and just south of the city's downtown core. There is also a former ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an ice skating rink with lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. In ice hockey, two opposing teams use ice ...
arena on-site, which includes the complex's entrance and an IMAX
IMAX is a proprietary system of high-resolution cameras, film formats, film projectors, and theaters known for having very large screens with a tall aspect ratio (approximately either 1.43:1 or 1.90:1) and steep stadium seating.
Graeme ...
theatre. The snowflake buildings are connected by a rock tunnel, which passes through a billion-year-old geologic fault. Sudbury's mining heritage is reflected in another major tourist attraction, Dynamic Earth. This interactive science museum focuses principally on geology and mining history exhibitions and is also home to the Big Nickel
The Big Nickel is a nine-metre (30 ft) replica of a 1951 Canadian nickel, located at the grounds of the Dynamic Earth science museum in Greater Sudbury, Ontario, Canada, and is the world's largest depiction of a coin. The twelve-sided nickel ...
, one of Sudbury's most famous landmarks. The city is also home to the Greater Sudbury Heritage Museums, a group of historical community museums, and a mining heritage monument overlooking the city's Bell Park.
The Inco Superstack
The Inco Superstack in Sudbury, Ontario, with a height of , is the tallest chimney in Canada and the Western hemisphere, and the second tallest freestanding chimney in the world after the GRES-2 Power Station in Kazakhstan. It is also the s ...
was the tallest freestanding chimney in the world at until the construction of the Ekibastuz GRES-2 Power Station
Ekibastuz ( kk, Екібастұз, translit=Ekıbastūz, , ەكئباستۇز; russian: Экибастуз) is a city in Pavlodar Region, northeastern Kazakhstan. The population was Ekibastuz is served by Ekibastuz Airport.
History
The history ...
, and is currently the second tallest structure in Canada after the CN Tower. It is almost the same height as the roof of the Empire State Building.
Sports
Azilda
Rayside-Balfour (1996 census population 16,050) was a town in Ontario, Canada, which existed from 1973 to 2000. It is now part of the city of Greater Sudbury.
The town was created as part of the Regional Municipality of Sudbury and took its name ...
.
There are a number of sports teams located in the city including the Sudbury Wolves who play at the Sudbury Community Arena
The Sudbury Community Arena is a multi-purpose arena in the downtown core of Greater Sudbury, Ontario, Canada. It was built in 1951, on the site of the former Central Public School, at a cost of $700,000. The approval and construction of the aren ...
. The Wolves are an ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an ice skating rink with lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. In ice hockey, two opposing teams use ice ...
team with the Ontario Hockey League
The Ontario Hockey League (OHL; french: Ligue de hockey de l'Ontario (LHO)) is one of the three major junior ice hockey leagues which constitute the Canadian Hockey League. The league is for players aged 16–19. There are exceptions for overa ...
. The Sudbury Spartans football club have played in the Northern Football Conference since 1954. Laurentian University participates in the U Sports
U Sports (stylized as U SPORTS) is the national sport governing body of university sport in Canada, comprising the majority of degree-granting universities in the country. Its equivalent body for organized sports at colleges in Canada is the ...
league by the Laurentian Voyageurs and the Laurentian Lady Vees. Cambrian College is represented in the Canadian Collegiate Athletic Association by the Cambrian Golden Shield, and Collège Boréal is represented by the Boréal Vipères. High school students compete in the Sudbury District Secondary School Athletic Association (SDSSAA), which is a division of Northern Ontario Secondary School Athletics (NOSSA). The city hosted the Pan American Junior Athletics Championships in 1980, the IAAF World Junior Championships in Athletics in 1988, the Brier: Canada's annual men's curling
Curling is a sport in which players slide stones on a sheet of ice toward a target area which is segmented into four concentric circles. It is related to bowls, boules, and shuffleboard. Two teams, each with four players, take turns slidi ...
championships, in 1953 and 1983, the 2001 Scott Tournament of Hearts
The 2001 Scott Tournament of Hearts Canadian women's national curling championship, was played at the Sudbury Community Arena in Sudbury, Ontario. The final pitted 1999 champions Colleen Jones and her Nova Scotia team against the defending champ ...
: the women's curling championship, and the 2010 Ontario Summer Games.
Greater Sudbury hosts a professional basketball team, the Sudbury Five
The Sudbury Five are a Canadian professional basketball team based in Sudbury that play in the National Basketball League of Canada (NBL Canada). The team is owned by Sudbury Wolves Sports and plays at the Sudbury Community Arena.
History
The t ...
, who play at the Sudbury Community Arena. The Five are owned by Sudbury Wolves Sports and Entertainment and began play in the National Basketball League of Canada in November 2018.
Demographics
In the 2021 Census of Population conducted byStatistics Canada
Statistics Canada (StatCan; french: Statistique Canada), formed in 1971, is the agency of the Government of Canada commissioned with producing statistics to help better understand Canada, its population, resources, economy, society, and cultu ...
, Greater Sudbury had a population of living in of its total private dwellings, a change of from its 2016 population of . With a land area of , it had a population density of in 2021.
At the census metropolitan area (CMA) level in the 2021 census, the Greater Sudbury CMA had a population of living in of its total private dwellings, a change of from its 2016 population of . With a land area of , it had a population density of in 2021.
In 2006, the median age was 41.1 years, slightly higher than the provincial average of 39.0 years.
Sudbury is a bilingual city with a large francophone
French became an international language in the Middle Ages, when the power of the Kingdom of France made it the second international language, alongside Latin. This status continued to grow into the 18th century, by which time French was the l ...
population, with 40% of Sudburians able to speak French. Some 80.1% of the population speak mostly English at home, followed by French at 16.3%, which is significantly higher than the Ontario average of 2.4%. According to the 2021 Census Profile, the residents of Greater Sudbury are predominantly Christian. Around 64% (down from 81% in 2011) of the population belongs to Christian denominations with Catholics composing the largest single group (47%, down from 59% in 2011). Those with no religious affiliation accounted for 33% (up from 18% in 2011) of the population. Other religions such as Islam, Judaism, and Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
constitute around 3% of the population in total, up from 1% in 2011.
Greater Sudbury has few visible minorities with reporting visible minority status on the 2016 census compared to the national average of , but a much higher percentage of indigenous Canadians () compared to the national average of . Visible minorities representing over 0.5% of the population include: 0.9% South Asian, 0.9% Black
Black is a color which results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without hue, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness. Black and white ha ...
, and 0.6% Chinese.
As of 2011, the population of Sudbury is less educated than the Canadian average, with 17.2% of the population holding a university degree (compared to 23.3% nationally) and 18.1% with no certificate, diploma or degree (compared to 17.3% nationally).
Economy
 After a brief period as a lumber camp, Sudbury's economy was dominated by the mining industry for much of the 20th century. By the 1970s, Inco employed a quarter of the local workforce."In Sudbury it's restive, not festive"
After a brief period as a lumber camp, Sudbury's economy was dominated by the mining industry for much of the 20th century. By the 1970s, Inco employed a quarter of the local workforce."In Sudbury it's restive, not festive"''
Toronto Star
The ''Toronto Star'' is a Canadian English-language broadsheet daily newspaper. The newspaper is the country's largest daily newspaper by circulation. It is owned by Toronto Star Newspapers Limited, a subsidiary of Torstar Corporation and par ...
'', December 19, 2009. However, in 2006, Inco and Falconbridge were taken over by foreign multinational corporations: Inco was acquired by the Brazilian company Vale
A vale is a type of valley.
Vale may also refer to:
Places Georgia
* Vale, Georgia, a town in the Samtskhe-Javakheti region
Norway
* Våle, a historic municipality
Portugal
* Vale (Santa Maria da Feira), a former civil parish in the municipa ...
, and Falconbridge was purchased by the Swiss company Xstrata which was in turn purchased by Anglo–Swiss Glencore forming Glencore Xstrata
Glencore plc is a Swiss multinational commodity trading and mining company with headquarters in Baar, Switzerland. Glencore's oil and gas head office is in London and its registered office is in Saint Helier, Jersey. The current company was c ...
. Several other mining companies, including First Nickel and KGHM, also have mining operations in the Sudbury area.
Mining now employs only 6,000 people in the city, although the mining supply and service sector employs a further 10,000. By 2006, 80% of Greater Sudbury's labour force was employed in services with 20% remaining in manufacturing. Over 345 mining supply and service companies are located in Sudbury. This includes a number of public and private firms pursuing research and development in new mining technologies such as Mining Innovation Rehabilitation and Applied Research Corporation (MIRARCO), the Northern Center for Advanced Technology (NORCAT), and the Centre for Excellence in Mining Innovation (CEMI).
While mining has decreased in relative importance, Sudbury's economy has diversified to establish itself as a major centre of finance, business, tourism, health care, education, government, and science and technology research. Many of these reflect Sudbury's position as a regional service center for Northeastern Ontario, a market of 550,000 people.
The top employers in Sudbury as of November 2010 include:
Many retail businesses in the city have moved outside of the downtown core in the late 20th century and the city has struggled to rebuild and maintain a vibrant downtown core. In the 2000s and early 2010s, projects aimed at revitalizing the downtown core included the creation of Market Square, a farmer's and craft market; the redevelopment of the Rainbow Center Mall; streetscape beautification projects; the conversion of several underutilized historic properties into mixed-use office and loft developments;"Sudbury developers tackle old downtown buildings"CBC News
CBC News is a division of the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation responsible for the news gathering and production of news programs on the corporation's English-language operations, namely CBC Television, CBC Radio, CBC News Network, and CBC.ca ...
, December 10, 2012. and the establishment and launch of the McEwen School of Architecture
The McEwen School of Architecture (french: link=no, l'École d'architecture McEwen), formerly the Laurentian School of Architecture, is an architecture school belonging to Laurentian University in Sudbury, Ontario, Canada.
, as well as cultural events such as Downtown Rotary Blues for Food, Sudbury's Largest Yard and Sidewalk Sale, Downtown Sudbury Ribfest and the Up Here art and music festival. New projects underway in the late 2010s include Place des Arts, a performing and visual arts center; the redesign and renovation of the central plaza at Tom Davies Square;"Bids for Tom Davies courtyard redesign come in millions over budget"CBC Northern Ontario, April 3, 2017. and the creation of The Junction, a multi-use complex which will incorporate the new home of the Art Gallery of Sudbury, the new main branch of the
Greater Sudbury Public Library
The Greater Sudbury Public Library is a public library system in Greater Sudbury, Ontario, Canada.
The library system has 13 branches throughout the city. The main branch is called "Mackenzie" and it is located on Mackenzie Street in the downtown ...
, and a convention and performance theatre space.
Despite these efforts a large percentage of the city's retail service sector is still found outside of the downtown core, in areas such as the Four Corners, the RioCan and Silver Hills power centres on the Kingsway, and the New Sudbury Centre, the largest shopping mall in Northern Ontario
Northern Ontario is a primary geographic and quasi-administrative region of the Canadian province of Ontario, the other primary region being Southern Ontario. Most of the core geographic region is located on part of the Superior Geological Pro ...
with 110 stores.
Film industry
Sudbury has an emerging film and television industry, with a number of projects filming in the city in the 2000s."Hollywood (Further) North? Sudbury, Ont., becoming hot spot for film crews"Canadian Press
The Canadian Press (CP; french: La Presse canadienne, ) is a Canadian national news agency headquartered in Toronto, Ontario. Established in 1917 as a vehicle for the time's Canadian newspapers to exchange news and information, The Canadian Pre ...
, June 25, 2015. Development of an active film and television production industry in Northern Ontario was initially undertaken by Cinéfest, the city's annual film festival, in the early 1990s, and is currently overseen by Music and Film in Motion, a non-profit organization based in Sudbury.
Films shot in the city have included '' Resident Evil: Welcome to Raccoon City'', '' Roadkill'', '' Shania: A Life in Eight Albums'', '' The Truth'', ''The Lesser Blessed
''The Lesser Blessed'' is a Canadian drama film, released in 2012.
"The Lesser Blessed tells universal story of alienation"
Government of Ontario, May 21, 2010. '' Hard Rock Medical'', '' Dark Rising: Warrior of Worlds'', '' Letterkenny'', ''
'' Huffington Post'', June 25, 2015. ''
. ''Broadcaster'', February 11, 2016. ''
''
 Greater Sudbury is home to three postsecondary institutions: Laurentian University, a primarily undergraduate bilingual university with approximately 9,000 students,
Greater Sudbury is home to three postsecondary institutions: Laurentian University, a primarily undergraduate bilingual university with approximately 9,000 students,  English-language public schooling is provided by the
English-language public schooling is provided by the
 The Greater Sudbury Airport maintains two paved runways and in length and serves 270,784 passengers per year (2017). The airport is served by three regional carrier lines:
The Greater Sudbury Airport maintains two paved runways and in length and serves 270,784 passengers per year (2017). The airport is served by three regional carrier lines:
 Several different agencies provide intercity transportation to Sudbury. Via Rail's
Several different agencies provide intercity transportation to Sudbury. Via Rail's
''
CBC News
CBC News is a division of the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation responsible for the news gathering and production of news programs on the corporation's English-language operations, namely CBC Television, CBC Radio, CBC News Network, and CBC.ca ...
, October 22, 2012. '' High Chicago'', '' Perspective'', '' The Captive'', ''Ice Soldiers
''Ice Soldiers'' is a 2013 Canadian action-science fiction film directed by Sturla Gunnarsson and starring Dominic Purcell, Adam Beach and Michael Ironside. In the film, Malraux (Purcell), and a team of Canadian scientists release a group of froze ...
'', '' Born to Be Blue'', '' Your Name Here'', ''Indian Horse
''Indian Horse'' () is a novel by Canadian writer Richard Wagamese, published by Douglas & McIntyre in 2012."Indian Horse is a dark ride". ''Calgary Herald'', February 28, 2012. The novel centres on Saul Indian Horse, a First Nations boy from Ont ...
'', '' The New Romantic'' and '' Men with Brooms''. Television series filmed in the city include ''Météo+
''Météo+'' is a Canadian television sitcom which aired on TFO, the French language public broadcaster in Ontario, from February 14, 2008 to April 28, 2011. The series is about the colourful crew of Météo+, a fictional francophone weather channe ...
'', ''Les Bleus de Ramville
''Les Bleus de Ramville'' (The Blues of Ramville) is a Canadian television series, which premiered on TFO in January 2012.
Set in the fictional town of Ramville near North Bay, Ontario, the series focuses on Gordie, Julie, Maureen and Christian, ...
'',New TV Series Produced In Sudbury And AreaGovernment of Ontario, May 21, 2010. '' Hard Rock Medical'', '' Dark Rising: Warrior of Worlds'', '' Letterkenny'', ''
St. Nickel
''St. Nickel'' is a Canadian television comedy series,
''Huffington Po ...
'',"«St-Nickel»: une première série originale pour Unis TV"''Huffington Po ...
'' Huffington Post'', June 25, 2015. ''
Cardinal
Cardinal or The Cardinal may refer to:
Animals
* Cardinal (bird) or Cardinalidae, a family of North and South American birds
**'' Cardinalis'', genus of cardinal in the family Cardinalidae
**'' Cardinalis cardinalis'', or northern cardinal, t ...
'',"CTV and Super Écran Partner on New Serialized Drama". ''Broadcaster'', February 11, 2016. ''
What Would Sal Do?
''What Would Sal Do?'' is a Canadian television comedy series,
'', '' Bad Blood''"Montreal Mafia TV series coming to a screen near you in fall 2017"''
Montreal Gazette
The ''Montreal Gazette'', formerly titled ''The Gazette'', is the only English-language daily newspaper published in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. Three other daily English-language newspapers shuttered at various times during the second half of t ...
'', January 12, 2017. and ''Shoresy
''Shoresy'' is a Canadian television comedy series created by and starring Jared Keeso that premiered on Crave on May 13, 2022. A spinoff of '' Letterkenny'', the series focuses on the titular character of Shoresy (Keeso) as he moves to Sudbur ...
''.
March Entertainment's studio in Sudbury has produced a number of animated television series, including ''Chilly Beach
''Chilly Beach'' is a Canadian animated series, which aired on CBC from 2003 to 2006. The series is a comedic depiction of life in the fictional Canadian town of Chilly Beach, described by the producers as "a bunch of Canadians doing the stuff th ...
'', '' Maple Shorts'', '' Yam Roll'', and '' Dex Hamilton: Alien Entomologist''.
The city's LGBT community has been profiled in two documentary films, the Genie Award-winning '' Mum's the Word (Maman et Ève)'' in 1996 and ''The Pinco Triangle
''The Pinco Triangle'' is a Canadian documentary film, directed by Patrick Crowe and Tristan R. Whiston and released in 1999.Gordon Bowness"Steelworkers, miners & faggots. Oh my" '' Daily Xtra'', May 19, 1999. A profile of LGBT life in Sudbury, ...
'' in 1999.
Sudbury is also home to the Science North Production Team, an award-winning producer of documentary films and multimedia presentations for museums. Independent film
An independent film, independent movie, indie film, or indie movie is a feature film or short film that is produced outside the major film studio system, in addition to being produced and distributed by independent entertainment companies (or, i ...
maker B. P. Paquette
Benjamin Patrick Paquette, commonly known as B. P. Paquette, is a Canadian film director, screenwriter, film producer and academic.
Background
Born in London, Ontario, Paquette spent his childhood and adolescence in Greater Sudbury. Shooting his ...
is based in Sudbury. Inner City Films, a production company owned by Sudbury native Robert Adetuyi
Robert Adetuyi is a Canadian screenwriter and film director who works in Hollywood. Born in Sudbury, Ontario,"Interview with Robert Adetuyi", ''Sudbury Star'', January 24, 2007. Adetuyi is a graduate of York University, where he studied communicat ...
, also has a production office in the city, as does Carte Blanche Films, the producer of ''Météo+'', ''Les Blues de Ramville'' and ''Hard Rock Medical''.
Architecture
With the construction of the Laurentian UniversityMcEwen School of Architecture
The McEwen School of Architecture (french: link=no, l'École d'architecture McEwen), formerly the Laurentian School of Architecture, is an architecture school belonging to Laurentian University in Sudbury, Ontario, Canada.
, as well as increasing development in the city, architecture has become a more increasingly important part of the economy in Sudbury.
Notable architecture in Greater Sudbury:
* Ledo Hotel, a historic building in downtown Sudbury, which has seen many uses since its construction in 1910.
* St. Andrew's Place, a church-community-complex which opened in 1972.
* Sudbury's Shaar Hashomayim Synagogue, is a community-led synagogue which was constructed in 1960 and is the only synagogue in Sudbury.
* Moses Block, Durham at Elgin, Sudbury's only flatiron building built in 1907
Education
 Greater Sudbury is home to three postsecondary institutions: Laurentian University, a primarily undergraduate bilingual university with approximately 9,000 students,
Greater Sudbury is home to three postsecondary institutions: Laurentian University, a primarily undergraduate bilingual university with approximately 9,000 students, Cambrian College
Cambrian College is a college of applied arts and technology in Greater Sudbury, Ontario, Canada. Established in 1967, and funded by the province of Ontario, Cambrian has campuses in Sudbury, Espanola and Little Current.
Cambrian works in p ...
, an English college of applied arts and technology with 4,500 full-time and 7,500 part-time students, and Collège Boréal, a francophone college with 2,000 enrolled. Laurentian University is home to the Sudbury campus of the Northern Ontario School of Medicine
Northern Ontario School of Medicine University (NOSM University; french: Université de l'École de médecine du Nord de l'Ontario) is a public medical university in the Canadian province of Ontario. It is mandated both to educate doctors and ...
. NOSM was the first medical school to be established in Canada in 30 years, having opened in September 2005. On September 4, 2013, Laurentian opened the McEwen School of Architecture
The McEwen School of Architecture (french: link=no, l'École d'architecture McEwen), formerly the Laurentian School of Architecture, is an architecture school belonging to Laurentian University in Sudbury, Ontario, Canada.
in downtown Sudbury—the first new architecture school to launch in Canada in more than 40 years. Opened in 2011 and located on the Laurentian University campus is the Vale Living with Lakes Centre
The Vale Living with Lakes Centre is a research center for The Cooperative Freshwater Ecology Unit in Greater Sudbury, Sudbury, Ontario, Canada. The centre consists of 2 buildings totalling 2,643m² (28,441 sq ft). The 2 storey main building (2,12 ...
which focuses on the research of stressors that can affect the health of water based ecosystems, contributing to the better ecological health of Sudbury. Canadian post-secondary institutions have also impacted the city's science and technology sectors. The Creighton Mine site in Sudbury is home to SNOLAB, the second-deepest (after China Jinping Underground Laboratory in China) underground laboratory in the world and the site of numerous dark matter
Dark matter is a hypothetical form of matter thought to account for approximately 85% of the matter in the universe. Dark matter is called "dark" because it does not appear to interact with the electromagnetic field, which means it does not ...
experiments. Originally constructed for the Sudbury Neutrino Observatory (now concluded), the underground laboratory has been expanded and continues to operate as SNOLAB. The SNO equipment has been refurbished for use in the SNO+ experiment.
 English-language public schooling is provided by the
English-language public schooling is provided by the Rainbow District School Board
Rainbow District School Board (known as English-language Public District School Board No. 3 prior to 1999) covers a geographic area of more than in the heart of the Rainbow Country and is the largest public school board in Northern Ontario. The ...
. The board operates 27 elementary and seven secondary schools in Sudbury, one school for students with special needs, and the Cecil Facer Youth Center for young offenders. The Sudbury Catholic District School Board
Sudbury Catholic District School Board (SCDSB, known as English-language Separate District School Board No. 32 prior to 1999) is a school board in north-central Ontario, Canada. The board is the school district administrator for English language ...
offers publicly funded English-language Catholic education, with 20 elementary schools, four high schools and an adult education center. French-language public schools are administered by the Conseil scolaire de district du Grand Nord de l'Ontario with seven elementary and two secondary schools and one alternative secondary school. Finally, the Conseil scolaire catholique du Nouvel-Ontario provides publicly funded French-language Catholic education, with 15 elementary, four secondary schools, and one adult education secondary school. There are also two Christian private schools (Glad Tidings Academy and King Christian Academy), as well two Montessori schools (King Montessori Academy and the Montessori School of Sudbury).
The Greater Sudbury Public Library
The Greater Sudbury Public Library is a public library system in Greater Sudbury, Ontario, Canada.
The library system has 13 branches throughout the city. The main branch is called "Mackenzie" and it is located on Mackenzie Street in the downtown ...
system has 13 branches throughout the city. The library system had 600,000 items as of 2011 and over 50% of the resident population are active library users. The Sudbury Tool Library and Makerspace are located at the main branch of the Greater Sudbury Public Library.
Infrastructure
Health care
Greater Sudbury serves as the health care center for much of northeastern Ontario through Health Sciences North. Sudbury is also the site of the Regional Cancer Program, which treats cancer patients from across the north. Sudbury's first General Hospital opened in 1950 and operated until 2010. Now, known as St. Joseph Health Center, the building remains abandoned and the new Sudbury Regional Hospital functions with Health Sciences North on Ramsey Lake Road. In 1968, the first successful coronary artery bypass surgery in Canada was performed at Sudbury Memorial Hospital. Adult mental health services are also provided to the area through Health Sciences North, primarily at the Kirkwood site (formerly the Sudbury Algoma Hospital) and at the Cedar site downtown. Children's mental health services are provided through the Regional Children's Psychiatric Center operated by the Northeast Mental Health Center, located onsite at the Kirkwood Site of Health Sciences North.Emergency services
Greater Sudbury is served by the Greater Sudbury Police Service, headquartered in downtown Sudbury. There is also a detachment of theOntario Provincial Police
The Ontario Provincial Police (OPP) is the provincial police service of Ontario, Canada. Under its provincial mandate, the OPP patrols provincial highways and waterways, protects provincial government buildings and officials, patrols unincorp ...
located in the McFarlane Lake area of the city's south end. Greater Sudbury Emergency Medical Services provides prehospital paramedic services with over 150 full-time and part-time paramedics. Greater Sudbury Fire Services operates from 24 fire stations located throughout the city, with a combination 103 career staff and 350 volunteer fire fighters. Prior to the municipal amalgamation of 2001, most of the suburban towns were served by separate volunteer fire department
A volunteer fire department (VFD) is a fire department of volunteers who perform fire suppression and other related emergency services for a local jurisdiction. Volunteer and retained (on-call) firefighters are expected to be on call to respon ...
s, which were amalgamated into the citywide service as part of the municipal restructuring. The municipally owned energy provider Greater Sudbury Utilities serves the city's urban core, while rural areas in the city continue to be served by Hydro One.
Transportation
Public transportation
The city maintains a bus-basedpublic transit
Public transport (also known as public transportation, public transit, mass transit, or simply transit) is a system of transport for passengers by group travel systems available for use by the general public unlike private transport, typi ...
system, GOVA, transporting 4.4 million passengers in 2012. The year 2000 marked the most significant change in Greater Sudbury's local transit history, as outlying townships were annexed into the municipality to form Greater Sudbury, expanding Greater Sudbury Transit's service area to one larger than most Ontario municipal and regional public transit agencies. The Downtown Transit Center is the primary hub for local transit in Sudbury.
Air
 The Greater Sudbury Airport maintains two paved runways and in length and serves 270,784 passengers per year (2017). The airport is served by three regional carrier lines:
The Greater Sudbury Airport maintains two paved runways and in length and serves 270,784 passengers per year (2017). The airport is served by three regional carrier lines: Air Canada Express
Air Canada Express is a brand name of regional feeder flights for Air Canada that are subcontracted to other airlines. As of March 2021, Jazz Aviation is the sole operator of Air Canada Express. They primarily connect smaller cities with Air Cana ...
to Toronto Pearson International Airport, Porter Airlines to Billy Bishop Toronto City Airport and Bearskin Airlines
Bearskin Lake Air Service LP, operating as Bearskin Airlines, is a regional airline based in Thunder Bay, Ontario, Canada. It is a division of Perimeter Aviation and operates services in northern Ontario and Manitoba. Its main base is at Thun ...
to several destinations in Northern Ontario including North Bay, Sault Ste. Marie, Timmins and Thunder Bay
Thunder Bay is a city in and the seat of Thunder Bay District, Ontario, Canada. It is the most populous municipality in Northwestern Ontario and the second most populous (after Greater Sudbury) municipality in Northern Ontario; its populati ...
.
Intercity transportation
 Several different agencies provide intercity transportation to Sudbury. Via Rail's
Several different agencies provide intercity transportation to Sudbury. Via Rail's Sudbury–White River train
The Sudbury–White River train, formerly the ''Lake Superior'', informally called the ''Budd Car'', is a Canadian passenger train operated by Via Rail serving communities between Sudbury and White River, Ontario three times a week. The timetabl ...
(a remnant of the old ''Lake Superior'' passenger service to Thunder Bay
Thunder Bay is a city in and the seat of Thunder Bay District, Ontario, Canada. It is the most populous municipality in Northwestern Ontario and the second most populous (after Greater Sudbury) municipality in Northern Ontario; its populati ...
) serves a number of remote interior communities, some of which are not accessible by road, from the downtown Sudbury station. To the north and east of the city, Capreol station and Sudbury Junction station are stops on Via Rail's transcontinental passenger service, the ''Canadian
Canadians (french: Canadiens) are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of ...
'', which passes through the area twice a week in each direction.
Intercity motor coach service is available at the Sudbury Ontario Northland Bus Terminal
The Sudbury Ontario Northland Bus Terminal (also known as the Ontario Northland Bus Depot or ONTC Terminal) is a bus station and depot in Sudbury, Ontario, Canada. It is operated by the Ontario Northland Transportation Commission (ONTC) and is a ...
, which is a stop for Ontario Northland
The Ontario Northland Transportation Commission (ONTC), or simply Ontario Northland, is a Crown agency of the Government of Ontario responsible for providing transportation services for passengers and goods in northern Ontario. It reports to ...
motor coaches. Destinations include North Bay, Sault Ste. Marie, Hearst, Barrie
Barrie is a city in Southern Ontario, Canada, about north of Toronto. The city is within Simcoe County and located along the shores of Kempenfelt Bay, the western arm of Lake Simcoe. Although physically in Simcoe County, Barrie is politicall ...
, Toronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the most populous city in Canada and the fourth most populous city in North America. The city is the anch ...
, and Ottawa
Ottawa (, ; Canadian French: ) is the capital city of Canada. It is located at the confluence of the Ottawa River and the Rideau River in the southern portion of the province of Ontario. Ottawa borders Gatineau, Quebec, and forms the c ...
.
Roads and highways
There are three highways connecting Sudbury to the rest of Ontario: Highway 17 is the main branch of theTrans-Canada Highway
The Trans-Canada Highway (Canadian French, French: ; abbreviated as the TCH or T-Can) is a transcontinental federal–provincial highway system that travels through all ten provinces of Canada, from the Pacific Ocean on the west coast to the A ...
, connecting the city to points east and west. An approximately segment of Highway 17, from Mikkola to Whitefish, is freeway
A controlled-access highway is a type of highway that has been designed for high-speed vehicular traffic, with all traffic flow—ingress and egress—regulated. Common English terms are freeway, motorway and expressway. Other similar terms ...
. The highway bypasses the city via two separately-constructed roads, the Southwest and Southeast Bypasses, that form a partial ring road around the southern end of the city's urban core for traffic travelling through Highway 17. The former alignment of Highway 17 through the city is now Municipal Road 55. Highway 69, also a branch of the Trans-Canada Highway, leads south to Parry Sound
Parry Sound is a sound or bay of Georgian Bay on Lake Huron, in Ontario, Canada. It is highly irregularly shaped with many deep bays and islands. Killbear Provincial Park is located on the large peninsula that separates the sound from Georgian ...
, where it connects to the Highway 400 freeway to Toronto; Highway 400 is being extended to Greater Sudbury and is scheduled for completion in the 2020s."Highway 69 to be delayed, province admits"''
Sudbury Star
''The Sudbury Star'' is a Canadian daily regional newspaper published in Sudbury, Ontario. It is owned by the media company, Postmedia. It is the largest daily paper in Northeastern Ontario by circulation.
History
The ''Sudbury Star'' began as ...
'', March 7, 2015. Highway 144 leads north to Highway 101 in Timmins.
Greater Sudbury is the only census division in Northern Ontario that maintains a system of numbered municipal roads, similar to the county road
A county highway (also county road or county route; usually abbreviated CH or CR) is a road in the United States and in the Canadian province of Ontario that is designated and/or maintained by the county highway department. Route numbering c ...
system in the southern part of the province. Secondary Highway 537, which essentially provides an outer bypass link between Highway 69 at Wanup and Highway 17 at Wahnapitae, is also the only remaining secondary highway in the province located in any census division which also has its own municipal or county road system.
Media
As the largest city in Northern Ontario, Greater Sudbury is the region's primary media center. Due to the relatively small size of the region's individual media markets, most of the region is served at least partially by Sudbury-based media. CICI-TV produces almost all local programming on the CTV Northern Ontario system, and the CBC Radio stations CBCS-FM and CBON-FM broadcast to the entire region through extensive rebroadcaster networks. As well, many of the commercial radio stations in Northeastern Ontario's smaller cities simulcast programming produced in Sudbury for at least a portion of their programming schedules, particularly in weekend and evening slots. Sudbury's daily newspaper, the ''Sudbury Star
''The Sudbury Star'' is a Canadian daily regional newspaper published in Sudbury, Ontario. It is owned by the media company, Postmedia. It is the largest daily paper in Northeastern Ontario by circulation.
History
The ''Sudbury Star'' began as ...
'' is owned by Postmedia, is published six days a week and has a weekday circulation of 17,530 as of 2006. The city's longtime community newspaper '' Northern Life'' ceased print publication in 2020, concurrently with its sale from Laurentian Media Group to Village Media, and remains in operation as the web-only publication ''Sudbury.com''.
There is also a weekly francophone publication, ''Le Voyageur
''Le Voyageur'' is a weekly community newspaper in Greater Sudbury, Ontario, serving the city's Franco-Ontarian community. The newspaper was launched on June 12, 1968, shortly after the demise of the region's earlier francophone community newspap ...
''. ''The South Side Story'' used to be a print and online publication but has been defunct since 2019.
Notable people
Notable people from Sudbury include television game-show ''Jeopardy!
''Jeopardy!'' is an American game show created by Merv Griffin. The show is a quiz competition that reverses the traditional question-and-answer format of many quiz shows. Rather than being given questions, contestants are instead given genera ...
'' host Alex Trebek
George Alexander Trebek (; July 22, 1940 – November 8, 2020) was a Canadian-American game show host and television personality. He is best known for hosting the syndicated general knowledge quiz game show ''Jeopardy!'' for 37 season ...
(which he hosted from 1984 to his death in 2020), architect Jason F. McLennan who created the Living Building Challenge and is CEO of McLennan Design, Power Corporation of Canada chairman Paul Desmarais Jr., mining speculator and philanthropist Frank Giustra, founder of Lionsgate Entertainment president of United Steelworkers, Leo Gerard, former Anaheim Ducks and Toronto Maple Leafs
The Toronto Maple Leafs (officially the Toronto Maple Leaf Hockey Club and often referred to as the Leafs) are a professional ice hockey team based in Toronto. They compete in the National Hockey League (NHL) as a member of the Atlantic Div ...
head coach Randy Carlyle, Olympic swimmer Alex Baumann
Alexander Baumann, (born April 21, 1964) is a Canadian sports administrator and former competitive swimmer who won two gold medals and set two world records at the 1984 Summer Olympics in Los Angeles. In 2007, he was regarded by the national b ...
, Rebecca Johnston
Rebecca Anne Johnston (born September 24, 1989) is a retired Canadian ice hockey player for the Calgary section of the PWHPA and, since 2007, the Canadian national team. She played four seasons at Cornell University and was selected second ov ...
who plays for the Canadian Women's Hockey Team, and Tessa Bonhomme
Tessa Bonhomme (born July 23, 1985) is a Canadian former professional ice hockey player and is a television sports reporter for The Sports Network (TSN). She was an Olympic gold medallist as a member of the Canadian national women's hockey team ...
was a former player. Sudbury has produced 81 National Hockey League
The National Hockey League (NHL; french: Ligue nationale de hockey—LNH, ) is a professional ice hockey sports league, league in North America comprising 32 teams—25 in the United States and 7 in Canada. It is considered to be the top ranke ...
hockey players, a number larger than any European city, including Hockey Hall of Fame inductees Eddie Giacomin
Edward "Ed" Giacomin (born June 6, 1939) is a Canadian retired professional ice hockey goaltender who played for the New York Rangers and Detroit Red Wings in the National Hockey League between 1965 and 1978.
Playing career
Giacomin began ...
, George Armstrong, Art Ross, and Al Arbour.Famous gaming Youtuber Quiil18 lives there.
See also
* List of tallest buildings in Greater Sudbury *List of francophone communities in Ontario
This is a list of francophone communities in the Canadian province of Ontario. Municipalities with a high percentage of French-speakers in Ontario are listed.
The provincial average of Ontarians whose mother tongue is French is 4.1%, with a t ...
Notes
References
Further reading
* Oiva W. Saarinen (2013). ''From Meteorite Impact to Constellation City: A Historical Geography of Greater Sudbury''.External links
* {{Authority control Cities in Ontario Hudson's Bay Company trading posts Mining communities in Ontario Single-tier municipalities in Ontario