Cork Harbour on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cork Harbour () is a natural
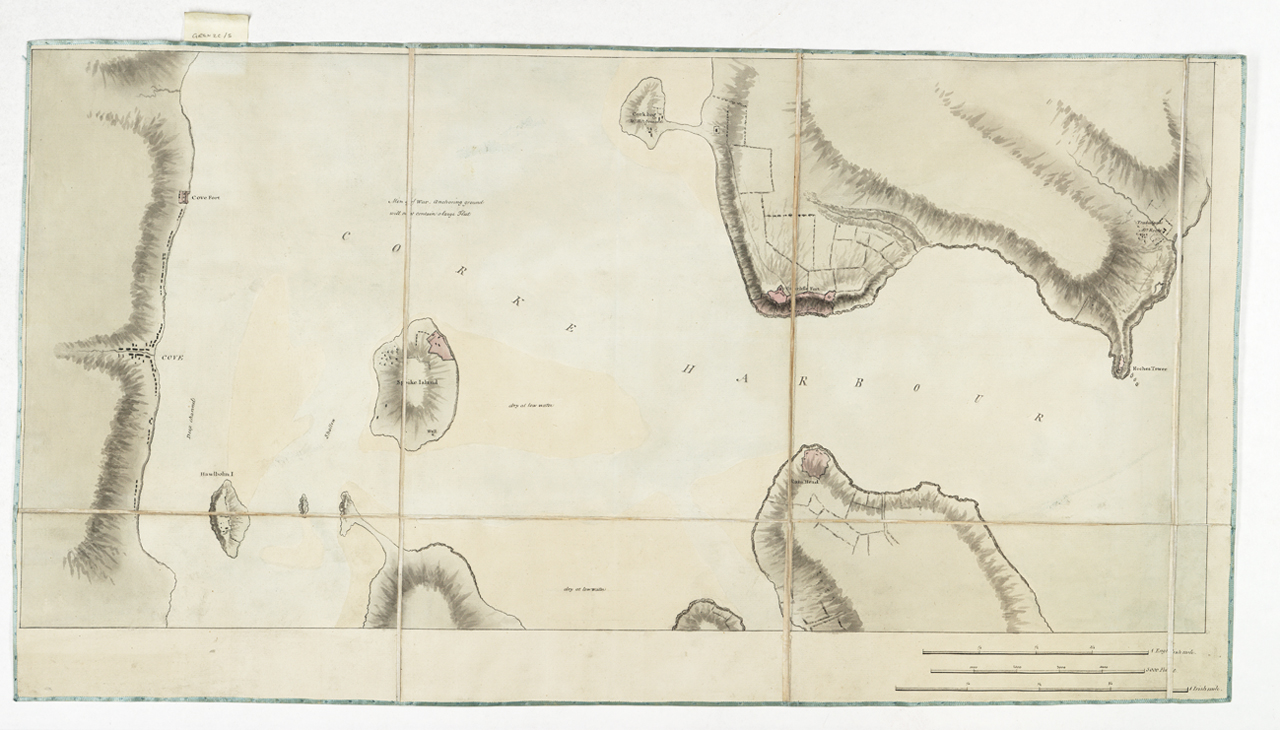 *
*
 Some of the first coastal defence fortifications built in Cork Harbour date to the 17th century, and were primarily intended to protect the approaches to Cork city. In the 18th century, fortifications were built on and opposite
Some of the first coastal defence fortifications built in Cork Harbour date to the 17th century, and were primarily intended to protect the approaches to Cork city. In the 18th century, fortifications were built on and opposite  The harbour's military significance increased during the
The harbour's military significance increased during the  The political uncertainty over the future of the treaty ports meant that the British government was not inclined to invest in their upgrade. Also, at the time of their construction, nobody had considered the possibility of air attack and as they were unable to expand, there was no possibility of adding adequate air cover. Finally, if the
The political uncertainty over the future of the treaty ports meant that the British government was not inclined to invest in their upgrade. Also, at the time of their construction, nobody had considered the possibility of air attack and as they were unable to expand, there was no possibility of adding adequate air cover. Finally, if the
 Historically, the navigation and port facilities of the harbour were managed by the ''Cork Harbour Commissioners''. Founded in 1814, the Cork Harbour Commissioners were reorganised as the Port of Cork Company in 1997.
Historically, the navigation and port facilities of the harbour were managed by the ''Cork Harbour Commissioners''. Founded in 1814, the Cork Harbour Commissioners were reorganised as the Port of Cork Company in 1997.
 Vessels up to are capable of coming through the harbour entrance. As the shipping channels get shallower the farther inland one travels, access becomes constricted, and only vessels up to can sail above
Vessels up to are capable of coming through the harbour entrance. As the shipping channels get shallower the farther inland one travels, access becomes constricted, and only vessels up to can sail above RTÉ News: Port of Cork €225m development rejected
/ref> Permission was later granted and work started (2018) on the new port. There has been an increase in cruise ship visits to Cork Harbour in the early 21st century, with 53 such ships visiting the port in 2011. The majority of these cruise ships berth at Cobh's Deepwater Quay. Historically, Cobh (under its former name Queenstown) was one of the principal ports through which flowed the stream of emigrants stemming from the Great Famine in the 1840s. There are also a number of private berths around the harbour, with several centred on Whitegate,
Port of Cork Company website
Cork Harbour Fortifications
{{Authority control Geography of Cork (city) Transport in County Cork Ports and harbours of the Republic of Ireland Tourist attractions in County Cork Ports and harbours of the Irish Sea Important Bird Areas of the Republic of Ireland Ramsar sites in the Republic of Ireland Tourist attractions in Cork (city) River Lee
harbour
A harbor (American English), harbour (British English; see spelling differences), or haven is a sheltered body of water where ships, boats, and barges can be docked. The term ''harbor'' is often used interchangeably with ''port'', which is ...
and river estuary
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environm ...
at the mouth of the River Lee in County Cork
County Cork ( ga, Contae Chorcaí) is the largest and the southernmost county of Ireland, named after the city of Cork, the state's second-largest city. It is in the province of Munster and the Southern Region. Its largest market towns a ...
, Ireland. It is one of several which lay claim to the title of "second largest natural harbour in the world by navigational area" (after Port Jackson
Port Jackson, consisting of the waters of Sydney Harbour, Middle Harbour, North Harbour and the Lane Cove and Parramatta Rivers, is the ria or natural harbour of Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. The harbour is an inlet of the Tasman S ...
, Sydney). Other contenders include Halifax Harbour in Canada, Trincomalee Harbour
Trincomalee Harbour is a seaport in Trincomalee Bay or Koddiyar Bay, a large natural harbour situated on the northeastern coast of Sri Lanka.
Located by Trincomalee, Sri Lanka, in the heart of the Indian Ocean, its strategic importance has sh ...
in Sri Lanka and Poole Harbour
Poole Harbour is a large natural harbour in Dorset, southern England, with the town of Poole on its shores. The harbour is a drowned valley ( ria) formed at the end of the last ice age and is the estuary of several rivers, the largest bei ...
in England.
The harbour has been a working port and a strategic defensive hub for centuries, and it has been one of Ireland's major employment hubs since the early 1900s. Traditional heavy industries have waned since the late 20th century, with the likes of the closure of Irish Steel in Haulbowline and shipbuilding at Verolme. It still has strategic significance in energy generation, shipping, refining and pharmaceuticals development.
Geography
The main tributary to the harbour is the River Lee which, after flowing through Cork city, passes through the upper harbour (Lough Mahon
Lough Mahon () is a sea lough in the north-western part of Cork Harbour. Its area is about .
Several Cork suburbs, such as Mahon, Douglas, Rochestown, Blackrock and Ballinlough as well as the town of Passage West are on its southern and west ...
) in the northwest before passing to the west of Great Island
Great Island () is an island in Cork Harbour, at the mouth of the River Lee and close to the city of Cork, Ireland. The largest town on the island is Cobh (called Queenstown from 1849 to 1922). The island's economic and social history has histo ...
with the main channel emerging into the lower harbour past Haulbowline Island
Haulbowline ( ga, Inis Sionnach; non, Ál-boling) is an island in Cork Harbour off the coast of Ireland. The world's first yacht club was founded on Haulbowline in 1720. The western side of the island is the main naval base and headquarters f ...
.
For conservation and navigation purposes, the harbour is often separated into "Upper Cork Harbour" (following the River Lee from Cork city to the towns of Passage West
Passage West (locally known as "Passage"; ) is a port town in County Cork, Ireland, situated on the west bank of Cork Harbour, some 10 km south-east of Cork city. The town has many services, amenities and social outlets. Passage West was ...
and Monkstown) and "Lower Cork Harbour" (separated from the upper harbour by Great Island
Great Island () is an island in Cork Harbour, at the mouth of the River Lee and close to the city of Cork, Ireland. The largest town on the island is Cobh (called Queenstown from 1849 to 1922). The island's economic and social history has histo ...
).
The depth of the harbour has been measured at between and .
Islands
Cork Harbour contains a number of islands of various sizes, some of which are connected to the mainland by bridges. Islands which are or have been inhabited include: *
* Great Island
Great Island () is an island in Cork Harbour, at the mouth of the River Lee and close to the city of Cork, Ireland. The largest town on the island is Cobh (called Queenstown from 1849 to 1922). The island's economic and social history has histo ...
– The largest island in Cork Harbour, which includes the town of Cobh
Cobh ( ,), known from 1849 until 1920 as Queenstown, is a seaport town on the south coast of County Cork, Ireland. With a population of around 13,000 inhabitants, Cobh is on the south side of Great Island in Cork Harbour and home to Ireland's ...
* Fota Island
Fota (statutory spelling Foaty; ga, Fóite) is an island in Cork Harbour, Ireland, just north of the larger island of Great Island. Fota Island is host to Ireland's only wildlife park – as well as the historical Fota House and gardens and go ...
– Containing Fota Wildlife Park, Fota House and the Fota Island Resort Hotel and golf course
* Little Island – A residential and industrial area
* Haulbowline Island
Haulbowline ( ga, Inis Sionnach; non, Ál-boling) is an island in Cork Harbour off the coast of Ireland. The world's first yacht club was founded on Haulbowline in 1720. The western side of the island is the main naval base and headquarters f ...
– Headquarters of the Irish Naval Service
The Naval Service ( ga, An tSeirbhís Chabhlaigh) is the maritime component of the Defence Forces of Ireland and is one of the three branches of the Irish Defence Forces. Its base is in Haulbowline, County Cork.
Though preceded by earlier ma ...
, and former home of the Cork Water Club (1720).
* Spike Island – Former prison island
* Harper's Island – Site of the Harper’s Island Wetland Centre
* Hop Island – Site of an equestrian centre
* Weir Island
* Brick Island
* Corkbeg Island – Site of Whitegate oil refinery
* Brown Island
* Rocky Island – Once housed a magazine building for the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Fr ...
. Used by Irish Steel for storage until 2002, and now home to 'The Island Crematorium'.
Settlements
Cork city is located slightly upstream on the River Lee on the northwest corner of Cork Harbour. Several of the city's suburbs, including Blackrock, Mahon,Douglas
Douglas may refer to:
People
* Douglas (given name)
* Douglas (surname)
Animals
*Douglas (parrot), macaw that starred as the parrot ''Rosalinda'' in Pippi Longstocking
* Douglas the camel, a camel in the Confederate Army in the American Civil ...
, Passage West
Passage West (locally known as "Passage"; ) is a port town in County Cork, Ireland, situated on the west bank of Cork Harbour, some 10 km south-east of Cork city. The town has many services, amenities and social outlets. Passage West was ...
and Rochestown lie on Lough Mahon
Lough Mahon () is a sea lough in the north-western part of Cork Harbour. Its area is about .
Several Cork suburbs, such as Mahon, Douglas, Rochestown, Blackrock and Ballinlough as well as the town of Passage West are on its southern and west ...
or the Douglas Estuary, both of which are parts of Upper Cork Harbour.
The Lower Harbour has a number of towns around its shores. Passage West, Monkstown, Ringaskiddy
Ringaskiddy () is a village in County Cork, Ireland. It is located on the western side of Cork Harbour, south of Cobh, and is 15 kilometres from Cork city, to which it is connected by the N28 road. The village is a port with passenger fer ...
and the smaller village of Raffeen are found on the western shore. On the southwestern shore is Crosshaven. Great Island
Great Island () is an island in Cork Harbour, at the mouth of the River Lee and close to the city of Cork, Ireland. The largest town on the island is Cobh (called Queenstown from 1849 to 1922). The island's economic and social history has histo ...
, which forms the northern shore of the lower harbour, houses the town of Cobh
Cobh ( ,), known from 1849 until 1920 as Queenstown, is a seaport town on the south coast of County Cork, Ireland. With a population of around 13,000 inhabitants, Cobh is on the south side of Great Island in Cork Harbour and home to Ireland's ...
. As of 2011, Cobh had a population of about 12,500. The eastern shore is less densely populated, but has two villages Whitegate and Aghada, both home to power plants.
The village of Ballinacurra is on the northeastern spur of the harbour, known as the Ballynacorra River. Due to the recent expansion of the town of Midleton, Ballinacurra has effectively become a suburb of Midleton, so it could also be said that Midleton lies on Cork Harbour.
Military
Cork Harbour hosts the headquarters of theIrish Naval Service
The Naval Service ( ga, An tSeirbhís Chabhlaigh) is the maritime component of the Defence Forces of Ireland and is one of the three branches of the Irish Defence Forces. Its base is in Haulbowline, County Cork.
Though preceded by earlier ma ...
. Prior to the transfer of the treaty ports in 1938, Cork Harbour was an important base for the British Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Fr ...
.
Haulbowline Island
Haulbowline ( ga, Inis Sionnach; non, Ál-boling) is an island in Cork Harbour off the coast of Ireland. The world's first yacht club was founded on Haulbowline in 1720. The western side of the island is the main naval base and headquarters f ...
to protect the anchorage in Cobh
Cobh ( ,), known from 1849 until 1920 as Queenstown, is a seaport town on the south coast of County Cork, Ireland. With a population of around 13,000 inhabitants, Cobh is on the south side of Great Island in Cork Harbour and home to Ireland's ...
- including Cove Fort (1743). Fort Camden and Fort Carlisle were built at opposite sides of the harbour entrance during the period of the American War of Independence
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
.
 The harbour's military significance increased during the
The harbour's military significance increased during the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fre ...
, when the naval establishment in Kinsale
Kinsale ( ; ) is a historic port and fishing town in County Cork, Ireland. Located approximately south of Cork City on the southeast coast near the Old Head of Kinsale, it sits at the mouth of the River Bandon, and has a population of 5,281 ( ...
was transferred to Cork Harbour. The harbour became an important anchorage, which could be used to guard the entrance to the English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" ( Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), ( Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Ka ...
and maintain the blockade of France. At this time, the naval dockyard on Haulbowline Island was constructed, as well as a fort on Spike Island (later to become Fort Westmoreland) and a number of Martello Towers and other fortifications were added or improved around the harbour.
The fortifications were developed throughout the 19th century and a further fort, Fort Templebreedy
Fort Templebreedy (Irish: ''Dún Theampall Bríde''), also known as Templebreedy Battery, was a coastal defence fortification close to Crosshaven, in County Cork, Ireland. Supplementing a number of earlier structures at Fort Camden and Fort Da ...
, was added to the south of Fort Camden at the beginning of the 20th century.
At the time of Irish independence, Cork Harbour was included, along with Berehaven and Lough Swilly, in a list of British naval establishments that would remain under the control of the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Fr ...
, although the naval dockyard on Haulbowline Island was handed over to the Irish Free State
The Irish Free State ( ga, Saorstát Éireann, , ; 6 December 192229 December 1937) was a state established in December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921. The treaty ended the three-year Irish War of Independence between ...
in 1923.
Although the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Fr ...
appreciated the location of Cork Harbour, particularly for submarines, which had a significantly shorter range in the 1920s, maintenance of the fortifications became an issue after Ireland became independent. The political uncertainty over the future of the treaty ports meant that the British government was not inclined to invest in their upgrade. Also, at the time of their construction, nobody had considered the possibility of air attack and as they were unable to expand, there was no possibility of adding adequate air cover. Finally, if the
The political uncertainty over the future of the treaty ports meant that the British government was not inclined to invest in their upgrade. Also, at the time of their construction, nobody had considered the possibility of air attack and as they were unable to expand, there was no possibility of adding adequate air cover. Finally, if the Irish Free State
The Irish Free State ( ga, Saorstát Éireann, , ; 6 December 192229 December 1937) was a state established in December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921. The treaty ended the three-year Irish War of Independence between ...
was hostile during any conflict, the treaty ports would have to be supplied by sea rather than land, wasting resources. In March 1938, the British government announced that the treaty ports would be handed over unconditionally, and on 11 July 1938, the defences at Cork Harbour were handed over to the Irish military authorities at a ceremony attended by Taoiseach
The Taoiseach is the head of government, or prime minister, of Ireland. The office is appointed by the president of Ireland upon the nomination of Dáil Éireann (the lower house of the Oireachtas, Ireland's national legislature) and the of ...
Éamon de Valera.
Since being handed over to the Irish military, most of the military installations have ceased to be used for military purposes. Fort Carlisle was renamed Fort Davis and is used by the Defence Forces for training - but is in a somewhat neglected state. Fort Camden became officially known as Fort Meagher and while no longer in military use, has been subject to renovation by local volunteers and enthusiasts, and can be visited by the public on certain days. The fort was officially renamed as of 11 July 2013 as Camden Fort Meagher, to account for both its British military and Irish military history. Locally, the two forts are sometimes known as "Camden" and "Carlisle", rather than their official titles. Fort Westmoreland became Fort Mitchell Spike Island prison, and has since ceased use for military or prison purposes. "Spike" was gifted to Cork County Council by the State and has been renovated as a tourist attraction by council workers and volunteers under the supervision of archaeologists. The fortifications on Haulbowline Island
Haulbowline ( ga, Inis Sionnach; non, Ál-boling) is an island in Cork Harbour off the coast of Ireland. The world's first yacht club was founded on Haulbowline in 1720. The western side of the island is the main naval base and headquarters f ...
however have been maintained, and are now the headquarters of the Irish Naval Service
The Naval Service ( ga, An tSeirbhís Chabhlaigh) is the maritime component of the Defence Forces of Ireland and is one of the three branches of the Irish Defence Forces. Its base is in Haulbowline, County Cork.
Though preceded by earlier ma ...
.
Industry
Cork Harbour is one of the most important industrial areas in Ireland. While several traditional industries such asshipbuilding
Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other floating vessels. It normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces its roots to bef ...
at Verolme Dockyards, steel-making on Haulbowline Island
Haulbowline ( ga, Inis Sionnach; non, Ál-boling) is an island in Cork Harbour off the coast of Ireland. The world's first yacht club was founded on Haulbowline in 1720. The western side of the island is the main naval base and headquarters f ...
and fertiliser manufacturing at IFI (Irish Fertiliser Industries) have ceased in recent years, they have been replaced with newer industries and Cork Harbour is now significant within the pharmaceutical
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy ( pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and ...
industry. Large international firms such as Pfizer
Pfizer Inc. ( ) is an American multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology corporation headquartered on 42nd Street in Manhattan, New York City. The company was established in 1849 in New York by two German entrepreneurs, Charles Pfize ...
, Novartis
Novartis AG is a Swiss-American multinational pharmaceutical corporation based in Basel, Switzerland and
Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States (global research).name="novartis.com">https://www.novartis.com/research-development/research-lo ...
, GlaxoSmithKline
GSK plc, formerly GlaxoSmithKline plc, is a British multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company with global headquarters in London, England. Established in 2000 by a merger of Glaxo Wellcome and SmithKline Beecham. GSK is the tent ...
and Janssen Pharmaceutica (a subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson
Johnson & Johnson (J&J) is an American multinational corporation founded in 1886 that develops medical devices, pharmaceuticals, and consumer packaged goods. Its common stock is a component of the Dow Jones Industrial Average and the company i ...
) are significant employers in the region. There has however been some concern since the post-2008 Irish economic downturn, as several of the pharmaceutical companies in Cork have shed jobs, notably Pfizer which announced the loss of 177 jobs in June 2012. There are in excess of 100 other pharmaceutical
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy ( pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and ...
firms operating in the Cork Harbour area. The main centres of the pharmaceutical industry are Little Island and Ringaskiddy
Ringaskiddy () is a village in County Cork, Ireland. It is located on the western side of Cork Harbour, south of Cobh, and is 15 kilometres from Cork city, to which it is connected by the N28 road. The village is a port with passenger fer ...
. Ireland's only oil refinery, Whitegate refinery, is located on the southeastern shore together with the adjacent Whitegate power station.
Marine activity
Commercial
 Historically, the navigation and port facilities of the harbour were managed by the ''Cork Harbour Commissioners''. Founded in 1814, the Cork Harbour Commissioners were reorganised as the Port of Cork Company in 1997.
Historically, the navigation and port facilities of the harbour were managed by the ''Cork Harbour Commissioners''. Founded in 1814, the Cork Harbour Commissioners were reorganised as the Port of Cork Company in 1997.
 Vessels up to are capable of coming through the harbour entrance. As the shipping channels get shallower the farther inland one travels, access becomes constricted, and only vessels up to can sail above
Vessels up to are capable of coming through the harbour entrance. As the shipping channels get shallower the farther inland one travels, access becomes constricted, and only vessels up to can sail above Cobh
Cobh ( ,), known from 1849 until 1920 as Queenstown, is a seaport town on the south coast of County Cork, Ireland. With a population of around 13,000 inhabitants, Cobh is on the south side of Great Island in Cork Harbour and home to Ireland's ...
.
The Port of Cork provides pilotage and towage facilities for vessels entering Cork Harbour. All vessels accessing the quays in Cork city must be piloted and all vessels exceeding 130 metres in length must be piloted once they pass within of the harbour entrance at a point marked by the Spit Bank Lighthouse
The Spit Bank Lighthouse close to Cobh in County Cork, Ireland is a screw-pile lighthouse which marks a shallow bank in the navigable channels of lower Cork Harbour. The platform was built by the blind Irish engineer Alexander Mitchell (who pio ...
which is the landmark boundary for compulsory pilotage.
The Port of Cork has berthing facilities at Cork city, Tivoli
Tivoli may refer to:
* Tivoli, Lazio, a town in Lazio, Italy, known for historic sites; the inspiration for other places named Tivoli
Buildings
* Tivoli (Baltimore, Maryland), a mansion built about 1855
* Tivoli Building (Cheyenne, Wyoming), ...
, Cobh and Ringaskiddy
Ringaskiddy () is a village in County Cork, Ireland. It is located on the western side of Cork Harbour, south of Cobh, and is 15 kilometres from Cork city, to which it is connected by the N28 road. The village is a port with passenger fer ...
. The facilities in Cork city are primarily used for grain and oil transport. Tivoli (downstream of the older city quays) provides container handling, facilities for oil, livestock and ore and a roll on-roll off (Ro-Ro) ramp. Prior to the opening of Ringaskiddy Ferry Port, car ferries sailed from here; now, the Ro-Ro ramp is used by companies importing cars into Ireland. In addition to the ferry terminal, which provides a service to Roscoff in France, Ringaskiddy has a deep water port.
The Port of Cork company is a commercial semi-state company responsible for the commercial running of the harbour as well as responsibility for navigation and berthage in the port. In 2011 the port had a turnover of €21.4 million and made pre-tax profits of €1.2 million. This was down from a turnover of €26.4 million and profits of €5.4 million in 2006. Container traffic increased by 6% in 2011 when 156,667teus
The twenty-foot equivalent unit (abbreviated TEU or teu) is an inexact unit of cargo capacity, often used for container ships and container ports.Rowlett, 2004. It is based on the volume of a intermodal container, a standard-sized metal box whic ...
were handled at the Tivoli container facility, however this was down from a peak of 185,000 TEUs in 2006. The 2006 figure saw the port at full capacity and the Port drew up plans for a new container facility capable of handling up to 400,000 teus per annum at Ringaskiddy. This was the subject of objections and after an oral planning hearing was held in 2008, the Irish planning board Bord Pleanala rejected the plan due to inadequate rail and road links at the location./ref> Permission was later granted and work started (2018) on the new port. There has been an increase in cruise ship visits to Cork Harbour in the early 21st century, with 53 such ships visiting the port in 2011. The majority of these cruise ships berth at Cobh's Deepwater Quay. Historically, Cobh (under its former name Queenstown) was one of the principal ports through which flowed the stream of emigrants stemming from the Great Famine in the 1840s. There are also a number of private berths around the harbour, with several centred on Whitegate,
Passage West
Passage West (locally known as "Passage"; ) is a port town in County Cork, Ireland, situated on the west bank of Cork Harbour, some 10 km south-east of Cork city. The town has many services, amenities and social outlets. Passage West was ...
, Rushbrooke, Ringaskiddy and Haulbowline.
Recreational
The Royal Cork Yacht Club, claimed as the world's oldest, was founded as 'The Water Club' on Haulbowline Island in the 1720s. When the British Navy took over Haulbowline in 1801, the club moved to Cobh, where their original clubhouse (built in the 1850s) still stands. In the 1960s, the club moved to Crosshaven. There are also boatyards at Crosshaven and two other marinas. There is another marina on Great Island opposite East Ferry, while Monkstown and Blackrock are used for boating,canoeing
Canoeing is an activity which involves paddling a canoe with a single-bladed paddle. Common meanings of the term are limited to when the canoeing is the central purpose of the activity. Broader meanings include when it is combined with other act ...
, windsurfing
Windsurfing is a wind propelled water sport that is a combination of sailing and surfing. It is also referred to as "sailboarding" and "boardsailing", and emerged in the late 1960s from the aerospace and surf culture of California. Windsurfing ga ...
and jet-skiing. A number of rowing clubs have facilities on the part of the River Lee between Cork city and Blackrock.
See also
* The Emergency *Plan W
Plan W, during World War II, was a plan of joint military operations between the governments of Ireland and the United Kingdom devised between 1940 and 1942, to be executed in the event of an invasion of Ireland by Nazi Germany.
Although Ir ...
* Joseph Wheeler for further information on 19th century shipbuilding in Cork.
References
Footnotes
Sources
*External links
Port of Cork Company website
Cork Harbour Fortifications
{{Authority control Geography of Cork (city) Transport in County Cork Ports and harbours of the Republic of Ireland Tourist attractions in County Cork Ports and harbours of the Irish Sea Important Bird Areas of the Republic of Ireland Ramsar sites in the Republic of Ireland Tourist attractions in Cork (city) River Lee