Channel blockers on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A channel blocker is the biological mechanism in which a particular molecule is used to prevent the opening of ion channels in order to produce a physiological response in a cell. Channel blocking is conducted by different types of molecules, such as cations, anions, amino acids, and other chemicals. These blockers act as ion channel antagonists, preventing the response that is normally provided by the opening of the channel.
Ion channels permit the selective passage of ions through cell membranes by utilizing proteins that function as pores, which allow for the passage of electrical charge in and out of the cell. These ion channels are most often gated, meaning they require a specific stimulus to cause the channel to open and close. These ion channel types regulate the flow of charged ions across the membrane and therefore mediate membrane potential of the cell.
Molecules that act as channel blockers are important in the field of pharmacology, as a large portion of drug design is the use of ion channel antagonists in regulating physiological response. The specificity of channel block molecules on certain channels makes it a valuable tool in the treatment of numerous disorders.
A channel blocker is the biological mechanism in which a particular molecule is used to prevent the opening of ion channels in order to produce a physiological response in a cell. Channel blocking is conducted by different types of molecules, such as cations, anions, amino acids, and other chemicals. These blockers act as ion channel antagonists, preventing the response that is normally provided by the opening of the channel.
Ion channels permit the selective passage of ions through cell membranes by utilizing proteins that function as pores, which allow for the passage of electrical charge in and out of the cell. These ion channels are most often gated, meaning they require a specific stimulus to cause the channel to open and close. These ion channel types regulate the flow of charged ions across the membrane and therefore mediate membrane potential of the cell.
Molecules that act as channel blockers are important in the field of pharmacology, as a large portion of drug design is the use of ion channel antagonists in regulating physiological response. The specificity of channel block molecules on certain channels makes it a valuable tool in the treatment of numerous disorders.
 A channel blocker is the biological mechanism in which a particular molecule is used to prevent the opening of ion channels in order to produce a physiological response in a cell. Channel blocking is conducted by different types of molecules, such as cations, anions, amino acids, and other chemicals. These blockers act as ion channel antagonists, preventing the response that is normally provided by the opening of the channel.
Ion channels permit the selective passage of ions through cell membranes by utilizing proteins that function as pores, which allow for the passage of electrical charge in and out of the cell. These ion channels are most often gated, meaning they require a specific stimulus to cause the channel to open and close. These ion channel types regulate the flow of charged ions across the membrane and therefore mediate membrane potential of the cell.
Molecules that act as channel blockers are important in the field of pharmacology, as a large portion of drug design is the use of ion channel antagonists in regulating physiological response. The specificity of channel block molecules on certain channels makes it a valuable tool in the treatment of numerous disorders.
A channel blocker is the biological mechanism in which a particular molecule is used to prevent the opening of ion channels in order to produce a physiological response in a cell. Channel blocking is conducted by different types of molecules, such as cations, anions, amino acids, and other chemicals. These blockers act as ion channel antagonists, preventing the response that is normally provided by the opening of the channel.
Ion channels permit the selective passage of ions through cell membranes by utilizing proteins that function as pores, which allow for the passage of electrical charge in and out of the cell. These ion channels are most often gated, meaning they require a specific stimulus to cause the channel to open and close. These ion channel types regulate the flow of charged ions across the membrane and therefore mediate membrane potential of the cell.
Molecules that act as channel blockers are important in the field of pharmacology, as a large portion of drug design is the use of ion channel antagonists in regulating physiological response. The specificity of channel block molecules on certain channels makes it a valuable tool in the treatment of numerous disorders.
Background
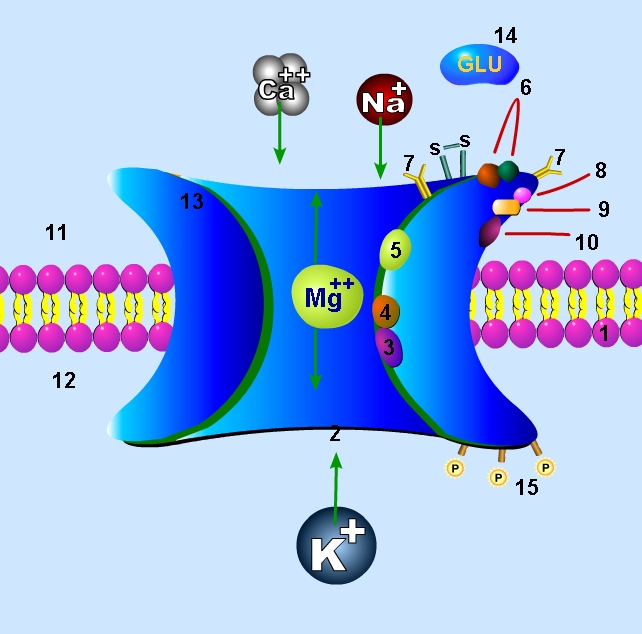
Ion channels
To comprehend the mechanism of channel blockers, it is critical to understand the composition of ion channels. Their main function is to contribute to theresting membrane potential A relatively static membrane potential which is usually referred to as the ground value for trans-membrane voltage.
The relatively static membrane potential of quiescent cells is called the resting membrane potential (or resting voltage), as oppo ...
of a cell via the flow of ions
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conven ...
through a cell membrane. To accomplish this task, ions must be able to cross the hydrophobic region of a lipid bilayer
The lipid bilayer (or phospholipid bilayer) is a thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules. These membranes are flat sheets that form a continuous barrier around all cells. The cell membranes of almost all organisms and many vir ...
membrane, an unfavorable process. To assist in ion transport, ion channels form a hydrophilic pore through the membrane which allows for the usually unfavorable transfer of hydrophilic molecules. Various ion channels have varying mechanisms of function. They include:
* voltage-gated ion channels
** Ion channels that are activated by changes in membrane potential
* ligand-gated ion channel
Ligand-gated ion channels (LICs, LGIC), also commonly referred to as ionotropic receptors, are a group of transmembrane ion-channel proteins which open to allow ions such as Na+, K+, Ca2+, and/or Cl− to pass through the membrane in res ...
** Ion channels mediated by the binding of small molecules to the channel protein
* mechanosensitive ion channels
** Ion channels that respond to stretch, vibration, or temperature changes
* light-gated ion channels
** Ion channels that open or close in response to light
Molecules that act as ion channel blockers can be used in relation to any of these various channels. For example, sodium channels, which are essential to the production of action potentials
An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell location rapidly rises and falls. This depolarization then causes adjacent locations to similarly depolarize. Action potentials occur in several types of animal cells ...
, are affected by many different toxins. Tetrodotoxin
Tetrodotoxin (TTX) is a potent neurotoxin. Its name derives from Tetraodontiformes, an order that includes pufferfish, porcupinefish, ocean sunfish, and triggerfish; several of these species carry the toxin. Although tetrodotoxin was discovere ...
(TTX), a toxin found in pufferfish, completely blocks sodium ion transportation by blocking the selectivity filter region of the channel. Much of the structure of the pores of ion channels has been elucidated from studies that used toxins to inhibit channel function.
Identity
Tools such asX-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles ...
and electrophysiology
Electrophysiology (from Ancient Greek, Greek , ''ēlektron'', "amber" ee the Electron#Etymology, etymology of "electron" , ''physis'', "nature, origin"; and , ''-logy, -logia'') is the branch of physiology that studies the electrical propertie ...
have been essential in locating the binding sites of open channel block molecules. By studying the biological and chemical makeup of ion channels, researchers can determine the makeup of the molecules that bind to certain regions. X-ray crystallography provides a structural image of the channel and molecule in question. Determining the hydrophobicity of channel domains through hydrophobicity plots also provides clues to the chemical makeup of the molecule and why it binds to a certain region. For example, if a protein binds to a hydrophobic region of the channel (and therefore, has a transmembrane region), the molecule in question might be composed of the amino acids alanine
Alanine (symbol Ala or A), or α-alanine, is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an amine group and a carboxylic acid group, both attached to the central carbon atom which also carries a methyl group side ...
, leucine
Leucine (symbol Leu or L) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Leucine is an α-amino acid, meaning it contains an α- amino group (which is in the protonated −NH3+ form under biological conditions), an α- ...
, or phenylalanine, as they are all hydrophobic themselves. Electrophysiology is also an important tool in identifying channel structure, as analyzing the ionic factors that lead to channel activation can be critical to understanding the inhibiting actions of open channel block molecules.
Physiology

Receptor antagonist
Channel blockers are antagonists for the respective ion channels. Many channels have binding spots for regulatory elements which can promote or repress normal function depending on the requirements within the cell and organism. The normal function of agonist binding is the generation of cellular changes leading to various downstream effects; these effects range from altering membrane potential to initiation of signaling cascades. Conversely, when open channel blockers bind to the cell they prevent the normal function of agonist binding. For example, voltage-gated channels open and close based on membrane potential and are critical in the generation of action potentials by their allowance of ions to flow down established gradients. However, open channels blockers can bind to these channels to prevent ions from flowing, thus inhibiting the initiation of an action potential.Specificity of molecules
Many differentorganic compounds
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The s ...
can act as channel blockers despite channel specificity. Channels have evolved structures that, due to their membrane spanning regions, can discriminate between various ions or compounds. For example, some objects are too large for to fit into channels that are structurally specified to transport smaller objects, such as a potassium ion attempting to fit into a sodium channel. Conversely, some objects are too small to be properly stabilized by certain channel pores, such as a sodium ion attempting to pass through a potassium channel. In both cases, channel flux is not permitted. However, as long as a particular compound possesses adequate chemical affinity to a channel, that compound may be able to bind and block the channel pore. For example, TTX can bind and inactivate voltage-gated sodium channels, despite the fact that TTX is much larger and chemically different than sodium ions. Given the disparities in size and chemical properties between TTX and a sodium ion, this is an example of structure being used to block usually specific channels.
Kinetics
A channel block can be induced by many different types of organic compounds as long as they can bind to some portion of the target channel's pore. The kinetics of channel blockers are primarily understood though their use asanesthetics
An anesthetic (American English) or anaesthetic (British English; see spelling differences) is a drug used to induce anesthesia — in other words, to result in a temporary loss of sensation or awareness. They may be divided into two ...
. Local anesthetics work by inducing a phasic block state in the targeted neurons. Initially, open channel blockers do not effectively prevent action potentials, as few channels are blocked and the blocker itself can be released from the channel either quickly or slowly depending on its characteristics. However, phasic blocks occur as repeated depolarization increases blockers’ affinity for channels in the neuron. The combination of an increase in available channels and the change in channel conformation to increase blocker binding affinity are responsible for this action.
Clinical significance
Therapeutic uses
Various neurodegenerative diseases have been associated with excessive NMDA receptor activation meant to mediate calcium dependent neurotoxicity. Researchers have examined many different NMDA antagonistmemantine
Memantine is a medication used to slow the progression of moderate-to-severe Alzheimer's disease. It is taken by mouth.
Common side effects include headache, constipation, sleepiness, and dizziness. Severe side effects may include blood clots ...
, as a treatment option for neurotoxicity. They hypothesized that the faster blocking and unblocking rates, and overall kinetics, of memantine could be the underlying reason for the clinical tolerance. As an uncompetitive antagonist, memantine should bring NMDA levels close to normal despite high glutamate concentration. Based on this information, researchers speculated that some day memantine could be used as an open channel block to prevent increasing glutamate levels associated with neurotoxicity with little to no side effects compared to other treatment options.
Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease, a specific neurodegenerative disorder, is linked to glutaminergicneurotransmission
Neurotransmission (Latin: ''transmissio'' "passage, crossing" from ''transmittere'' "send, let through") is the process by which signaling molecules called neurotransmitters are released by the axon terminal of a neuron (the presynaptic neuron), ...
interruptions that are believed to result in the staple cognitive symptoms of Alzheimer's. Researchers suggest that noncompetitive NMDA receptor agonists can be used to aid in the management of these symptoms without producing severe side effects. As one of the only drugs approved for Alzheimer's treatment, memantine has been shown to allow excitatory post synaptic currents to remain unaffected while decreasing the incidence and amplitude of inhibitory post-synatpic currents. Evidence supports the hypothesis that both the strong voltage dependency and fast kinetics of memantine may be responsible for the decreased side effects and cognitive progress.
Cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis is a progressive, genetic disease that is linked to CF transmembrane regulator (CFTR
Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) is a membrane protein and anion channel in vertebrates that is encoded by the ''CFTR'' gene.
Geneticist Lap-Chee Tsui and his team identified the CFTR gene in 1989 as the gene linked wi ...
) dysfunction. Blockage of this channel by certain cytoplasmic, negatively-charged substances results in reduced chloride ion and bicarbonate anion transport, as well as reduced fluid and salt secretion. This results in a buildup of thick mucus, which is characteristic of cystic fibrosis.
Pharmacology
Anesthetics
Channel blockers are essential in the field of anesthetics. Sodium channel inhibitors are used as bothantiepileptics
Anticonvulsants (also known as antiepileptic drugs or recently as antiseizure drugs) are a diverse group of pharmacological agents used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also increasingly being used in the treatment of ...
and antiarrhythmics, as they can inhibit the hyper-excitable tissues in a patient. Introducing specific sodium channel blockers into a tissue allows for the preferential binding of the blocker to sodium channels, which results in an ultimate inhibition of the flow of sodium into the tissue. Over time, this mechanism leads to an overall decrease in tissue excitation. Prolonged hyperpolarization interrupts normal channel recovery and allows for constant inhibition, providing dynamic control of the anesthetics in a given setting.
Alzheimer's disease
Excessive exposure to glutamate leads to neurotoxicity in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Specifically, over-activation of NMDA-type glutamate receptors have been linked to neural cell excitotoxicity and cell death. A potential solution to this is a decrease in NMDA receptor activity, without interfering so drastically as to cause clinical side effects. In an attempt to prevent further neurodegeneration, researchers have used memantine, an open channel block, as a form of treatment. Thus far, the use of memantine in patients with Alzheimer's disease quickly results in clinical progress across many different symptoms. Memantine is thought to work effectively due to its ability to quickly modify its kinetics, which prevents buildup in the channel and allows normal synaptic transmission. Other channel blockers have been found to block all NMDA receptor activity, leading to adverse clinical side effects.CFTR channel dysfunction
Cystic Fibrosis transmembrane regulators (CFTRepithelial
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercell ...
cells in respiratory, pancreatic, gastrointestinal, and reproductive tissues. Abnormally-elevated CFTR function results in excessive fluid secretion. High-affinity CFTR inhibitors, such as CFTRinh-172 and GlyH-101, have been shown to be efficient in treatment of secretory diarrheas. Theoretically, CFTR channel blockers may also be useful as male contraceptives. CFTR channels mediate bicarbonate anion entry which is essential for sperm capacitation.
Various types of substances have been known to block CFTR chloride ion channels. Some of the best-known and studied substances include sulfonylureas, arylaminobenzenoates, and disulfonic stilbenes. These blockers are side-dependent as they enter the pore exclusively from the cytoplasmic side, voltage-dependent as hyperpolarized membrane potentials favor negatively-charged substance entry into the pore from the cytoplasmic side, and chloride ion concentration-dependent as high extracellular chloride ions electrostatically repel negatively-charged blockers back into the cytoplasm.
Types
There are several different major classes of channel blockers, including: * Calcium (Ca2+) channel blockers * Chloride (Cl−) channel blockers * Potassium (K+) channel blockers * Sodium (Na+) channel blockers The following types which act onligand-gated ion channel
Ligand-gated ion channels (LICs, LGIC), also commonly referred to as ionotropic receptors, are a group of transmembrane ion-channel proteins which open to allow ions such as Na+, K+, Ca2+, and/or Cl− to pass through the membrane in res ...
s (LGICs) via binding to their pore also exist:
* 5-HT3 receptor antagonists
* GABAA receptor antagonists
* nACh receptor antagonists
* NMDA receptor antagonist
NMDA receptor antagonists are a class of drugs that work to antagonize, or inhibit the action of, the ''N''-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor ( NMDAR). They are commonly used as anesthetics for animals and humans; the state of anesthesia they induce ...
s
Channel blockers are also known to act at AMPA receptors, Glycine receptors, Kainate receptor
Kainate receptors, or kainic acid receptors (KARs), are ionotropic receptors that respond to the neurotransmitter glutamate. They were first identified as a distinct receptor type through their selective activation by the agonist kainate, a dru ...
s, P2X receptor
The ATP-gated P2X receptor cation channel familyTC# 1.A.7, or simply P2X receptor family, consists of cation-permeable ligand-gated ion channels that open in response to the binding of extracellular adenosine 5'-triphosphate ( ATP). They belong ...
s and Zinc (Zn2+)-activated channels. The type of inhibition mediated by channel blockers may be referred to as noncompetitive or uncompetitive.
See also
* Ion channel *Channel opener A channel opener, also known as a channel activator, is a type of drug which facilitates ion flow through ion channels.
They include the following:
* Potassium channel openers
* Calcium channel openers
* Sodium channel openers
* Chloride channel ...
References
{{Channel blockers Ion channel blockers