Bone and cartilage on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most
 The hard outer layer of bones is composed of cortical bone, which is also called compact bone as it is much denser than cancellous bone. It forms the hard exterior (cortex) of bones. The cortical bone gives bone its smooth, white, and solid appearance, and accounts for 80% of the total bone mass of an adult human skeleton. It facilitates bone's main functions—to support the whole body, to protect organs, to provide
The hard outer layer of bones is composed of cortical bone, which is also called compact bone as it is much denser than cancellous bone. It forms the hard exterior (cortex) of bones. The cortical bone gives bone its smooth, white, and solid appearance, and accounts for 80% of the total bone mass of an adult human skeleton. It facilitates bone's main functions—to support the whole body, to protect organs, to provide
 Cancellous bone, also called trabecular or spongy bone, is the internal tissue of the skeletal bone and is an open cell
Cancellous bone, also called trabecular or spongy bone, is the internal tissue of the skeletal bone and is an open cell
 Bone is metabolically active tissue composed of several types of cells. These cells include osteoblasts, which are involved in the creation and mineralization of bone tissue,
Bone is metabolically active tissue composed of several types of cells. These cells include osteoblasts, which are involved in the creation and mineralization of bone tissue,
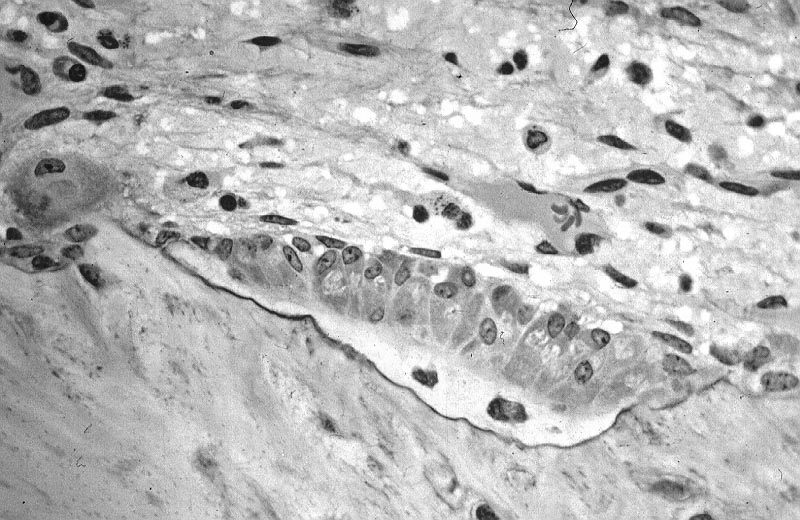 Osteoblasts are mononucleate bone-forming cells. They are located on the surface of osteon seams and make a
Osteoblasts are mononucleate bone-forming cells. They are located on the surface of osteon seams and make a
"The Structure of Bone Tissue"
pp. 12–14 in ''Bones: Structure and Mechanics''. Princeton University Press. Princeton, NJ. * Lamellar bone, which has a regular parallel alignment of collagen into sheets ("lamellae") and is mechanically strong. Woven bone is produced when osteoblasts produce osteoid rapidly, which occurs initially in all
Woven bone is produced when osteoblasts produce osteoid rapidly, which occurs initially in all
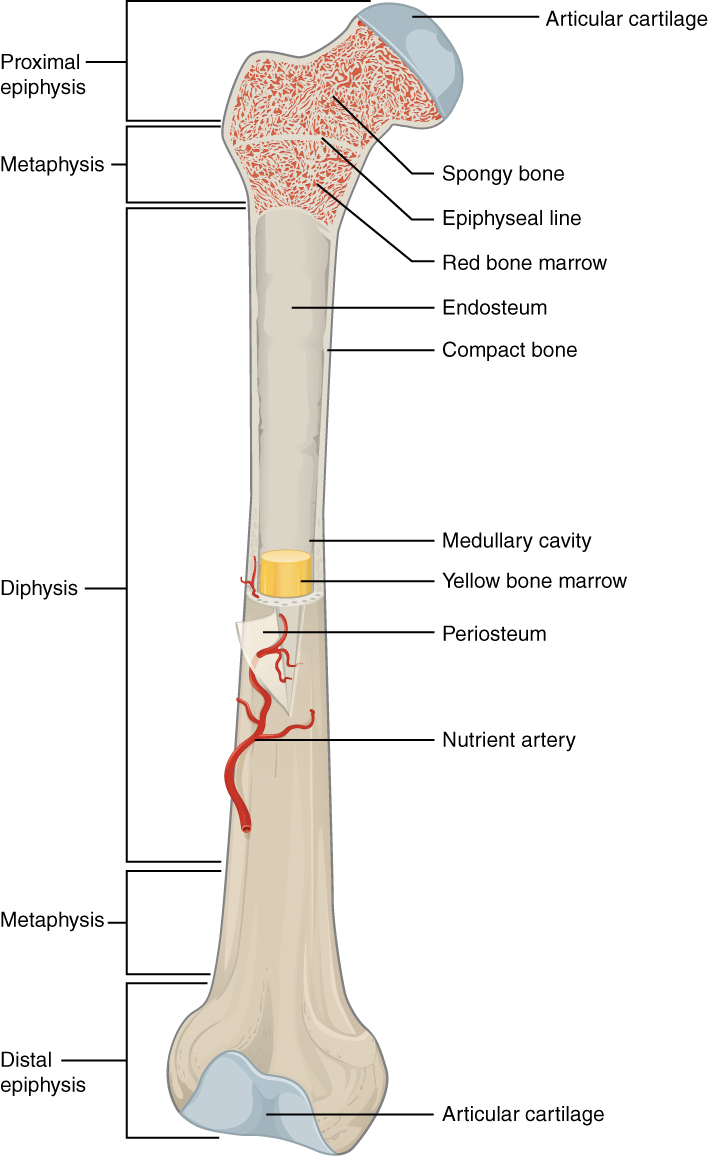
 There are five types of bones in the human body: long, short, flat, irregular, and sesamoid.
* Long bones are characterized by a shaft, the
There are five types of bones in the human body: long, short, flat, irregular, and sesamoid.
* Long bones are characterized by a shaft, the

 The formation of bone is called
The formation of bone is called
 In normal bone,
In normal bone,
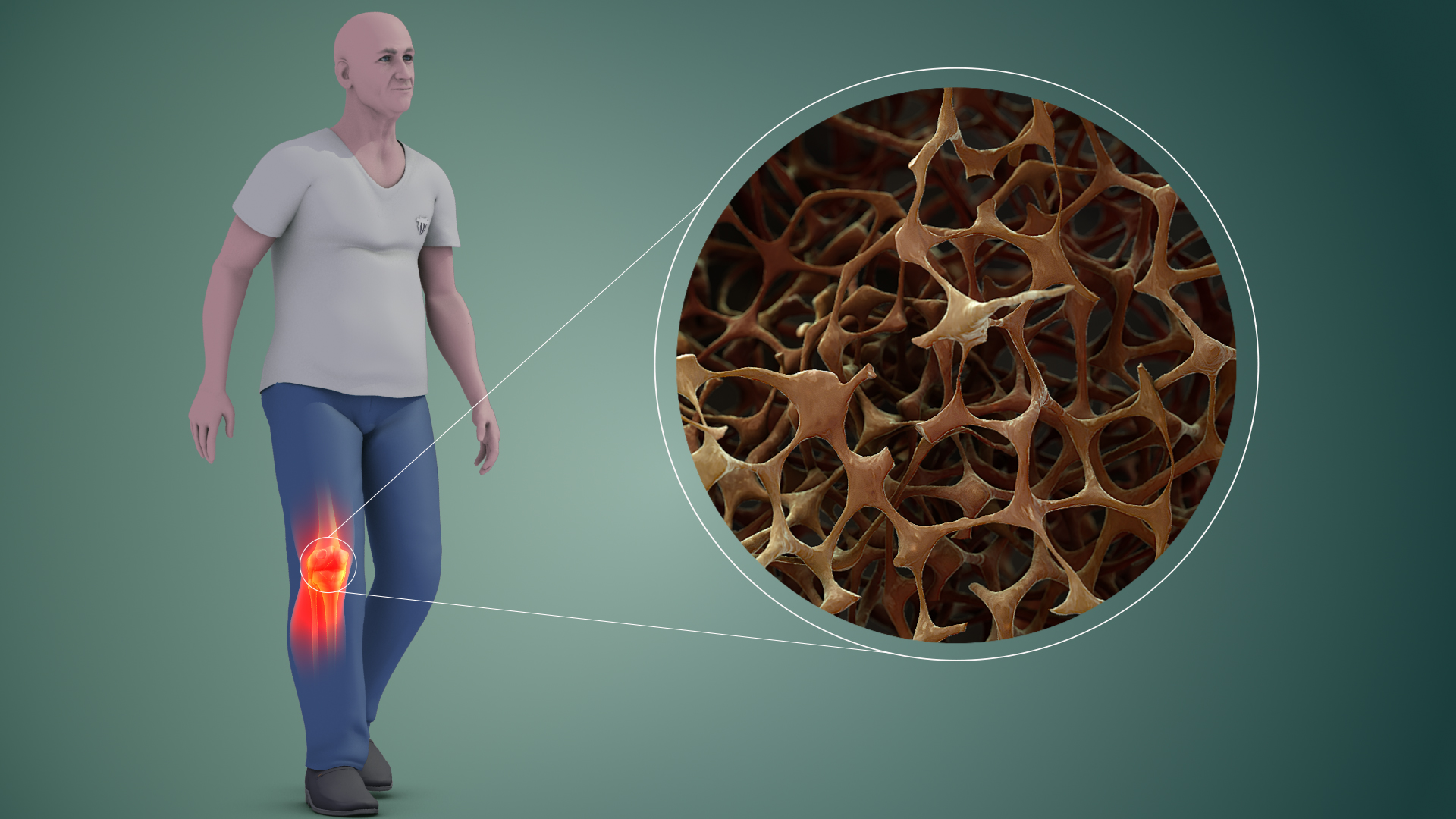 Osteoporosis is a disease of bone where there is reduced bone mineral density, increasing the likelihood of
Osteoporosis is a disease of bone where there is reduced bone mineral density, increasing the likelihood of

 Bones from slaughtered animals have a number of uses. In
Bones from slaughtered animals have a number of uses. In
File:Gray72-en.svg, Cells in bone marrow
File:Bertazzo S - SEM deproteined trabecular - wistar rat - x100.tif, Scanning electron microscope of bone at 100× magnification
File:Bone structure marco photo.jpg, Structure detail of an animal bone
Educational resource materials (including animations) by the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research
* [http://www.scq.ubc.ca/?p=400 A good basic overview of bone biology from the Science Creative Quarterly] *
Bone histology photomicrographs
{{Authority control Bones Skeletal system Connective tissue
vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with c ...
animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–740 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a secondar ...
and white blood cells, store mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2 ...
s, provide structure and support for the body, and enable mobility
Mobility may refer to:
Social sciences and humanities
* Economic mobility, ability of individuals or families to improve their economic status
* Geographic mobility, the measure of how populations and goods move over time
* Mobilities, a conte ...
. Bones come in a variety of shapes and sizes and have complex internal and external structures. They are lightweight yet strong and hard and serve multiple functions.
Bone tissue (osseous tissue), which is also called bone in the uncountable
In mathematics, an uncountable set (or uncountably infinite set) is an infinite set that contains too many elements to be countable. The uncountability of a set is closely related to its cardinal number: a set is uncountable if its cardinal num ...
sense of that word, is hard tissue Hard tissue, refers to "normal" calcified tissue, is the tissue which is mineralized and has a firm intercellular matrix. The hard tissues of humans are bone, tooth enamel, dentin, and cementum. The term is in contrast to soft tissue.
Bone
Bon ...
, a type of specialized connective tissue. It has a honeycomb
A honeycomb is a mass of hexagonal prismatic wax cells built by honey bees in their nests to contain their larvae and stores of honey and pollen.
Beekeepers may remove the entire honeycomb to harvest honey. Honey bees consume about of honey ...
-like matrix internally, which helps to give the bone rigidity. Bone tissue is made up of different types of bone cell
An osteocyte, an oblate shaped type of bone cell with dendritic processes, is the most commonly found cell in mature bone. It can live as long as the organism itself. The adult human body has about 42 billion of them. Osteocytes do not divide and ...
s. Osteoblasts and osteocyte
An osteocyte, an oblate shaped type of bone cell with dendritic processes, is the most commonly found cell in mature bone. It can live as long as the organism itself. The adult human body has about 42 billion of them. Osteocytes do not divide an ...
s are involved in the formation and mineralization of bone; osteoclast
An osteoclast () is a type of bone cell that breaks down bone tissue. This function is critical in the maintenance, repair, and remodeling of bones of the vertebral skeleton. The osteoclast disassembles and digests the composite of hydrated pro ...
s are involved in the resorption
Resorption is the absorption of cells or tissue into the circulatory system, usually by osteoclasts.
Types of resorption include:
* Bone resorption
* Herniated Disc Resorption
* Tooth resorption
* Fetal resorption
* Blood resorption
See also ...
of bone tissue. Modified (flattened) osteoblasts become the lining cells that form a protective layer on the bone surface. The mineralized matrix of bone tissue has an organic component of mainly collagen called ''ossein Ossein is the organic extracellular matrix of bone, which is made of 95% collagen. It can be isolated by treating bones with hydrochloric acid, which dissolves the inorganic matrix (calcium phosphate and calcium carbonate). This substance is used i ...
'' and an inorganic component of bone mineral
Bone mineral (also called inorganic bone phase, bone salt, or bone apatite) is the inorganic component of bone tissue. It gives bones their compressive strength. Bone mineral is formed predominantly from carbonated hydroxyapatite with lower cry ...
made up of various salts. Bone tissue is mineralized tissue
Mineralized tissues are biological tissues that incorporate minerals into soft matrices. Typically these tissues form a protective shield or structural support. Bone, mollusc shells, deep sea sponge ''Euplectella'' species, radiolarians, diato ...
of two types, cortical bone and cancellous bone. Other types of tissue found in bones include bone marrow, endosteum, periosteum
The periosteum is a membrane that covers the outer surface of all bones, except at the articular surfaces (i.e. the parts within a joint space) of long bones. Endosteum lines the inner surface of the medullary cavity of all long bones.
Structu ...
, nerves, blood vessel
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away ...
s and cartilage.
In the human body at birth, there are approximately 300 bones present; many of these fuse together during development, leaving a total of 206 separate bones in the adult, not counting numerous small sesamoid bones. The largest bone in the body is the femur
The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates wit ...
or thigh-bone, and the smallest is the stapes
The ''stapes'' or stirrup is a bone in the middle ear of humans and other animals which is involved in the conduction of sound vibrations to the inner ear. This bone is connected to the oval window by its annular ligament, which allows the foo ...
in the middle ear
The middle ear is the portion of the ear medial to the eardrum, and distal to the oval window of the cochlea (of the inner ear).
The mammalian middle ear contains three ossicles, which transfer the vibrations of the eardrum into waves in the ...
.
The Greek word for bone is ὀστέον ("osteon"), hence the many terms that use it as a prefix—such as osteopathy
Osteopathy () is a type of alternative medicine that emphasizes physical manipulation of the body's muscle tissue and bones. Practitioners of osteopathy are referred to as osteopaths.
Osteopathic manipulation is the core set of techniques in ...
. In anatomical terminology
Anatomical terminology is a form of scientific terminology used by anatomists, zoologists, and health professionals such as doctors.
Anatomical terminology uses many unique terms, suffixes, and prefixes deriving from Ancient Greek and Latin. ...
, including the Terminologia Anatomica
''Terminologia Anatomica'' is the international standard for human anatomical terminology. It is developed by the Federative International Programme on Anatomical Terminology, a program of the International Federation of Associations of Anatomi ...
international standard, the word for a bone is '' os'' (for example, os breve, os longum, os sesamoideum).
Structure
Bone is not uniformly solid, but consists of a flexible matrix (about 30%) and bound minerals (about 70%) which are intricately woven and endlessly remodeled by a group of specialized bone cells. Their unique composition and design allows bones to be relativelyhard
Hard may refer to:
* Hardness, resistance of physical materials to deformation or fracture
* Hard water, water with high mineral content
Arts and entertainment
* ''Hard'' (TV series), a French TV series
* Hard (band), a Hungarian hard rock supe ...
and strong, while remaining lightweight.
Bone matrix is 90 to 95% composed of elastic collagen fibers, also known as ossein, and the remainder is ground substance Ground substance is an amorphous gel-like substance in the extracellular space that contains all components of the extracellular matrix (ECM) except for fibrous materials such as collagen and elastin. Ground substance is active in the development, m ...
. The elasticity of collagen improves fracture resistance. The matrix is hardened by the binding of inorganic mineral salt, calcium phosphate
The term calcium phosphate refers to a family of materials and minerals containing calcium ions (Ca2+) together with inorganic phosphate anions. Some so-called calcium phosphates contain oxide and hydroxide as well. Calcium phosphates are whi ...
, in a chemical arrangement known as bone mineral
Bone mineral (also called inorganic bone phase, bone salt, or bone apatite) is the inorganic component of bone tissue. It gives bones their compressive strength. Bone mineral is formed predominantly from carbonated hydroxyapatite with lower cry ...
, a form of calcium hydroxylapatite
Hydroxyapatite, also called hydroxylapatite (HA), is a naturally occurring mineral form of calcium apatite with the formula Ca5(PO4)3(OH), but it is usually written Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 to denote that the crystal unit cell comprises two entities. ...
. It is the mineralization that gives bones rigidity.
Bone is actively constructed and remodeled throughout life by special bone cells known as osteoblasts and osteoclasts. Within any single bone, the tissue is woven into two main patterns, known as cortical and cancellous bone, each with a different appearance and characteristics.
Cortex
 The hard outer layer of bones is composed of cortical bone, which is also called compact bone as it is much denser than cancellous bone. It forms the hard exterior (cortex) of bones. The cortical bone gives bone its smooth, white, and solid appearance, and accounts for 80% of the total bone mass of an adult human skeleton. It facilitates bone's main functions—to support the whole body, to protect organs, to provide
The hard outer layer of bones is composed of cortical bone, which is also called compact bone as it is much denser than cancellous bone. It forms the hard exterior (cortex) of bones. The cortical bone gives bone its smooth, white, and solid appearance, and accounts for 80% of the total bone mass of an adult human skeleton. It facilitates bone's main functions—to support the whole body, to protect organs, to provide lever
A lever is a simple machine consisting of a beam or rigid rod pivoted at a fixed hinge, or '' fulcrum''. A lever is a rigid body capable of rotating on a point on itself. On the basis of the locations of fulcrum, load and effort, the lever is d ...
s for movement, and to store and release chemical elements, mainly calcium. It consists of multiple microscopic columns, each called an osteon
In osteology, the osteon or haversian system (; named for Clopton Havers) is the fundamental functional unit of much compact bone. Osteons are roughly cylindrical structures that are typically between 0.25 mm and 0.35 mm in diameter. Their ...
or Haversian system. Each column is multiple layers of osteoblasts and osteocyte
An osteocyte, an oblate shaped type of bone cell with dendritic processes, is the most commonly found cell in mature bone. It can live as long as the organism itself. The adult human body has about 42 billion of them. Osteocytes do not divide an ...
s around a central canal called the haversian canal
Haversian canals (sometimes canals of Havers) are a series of microscopic tubes in the outermost region of bone called cortical bone. They allow blood vessels and nerves to travel through them to supply the osteocytes.
Structure
Each Haversian ...
. Volkmann's canal
Volkmann's canals, also known as perforating holes or channels, are anatomic arrangements in cortical bones. Volkmann's canals are inside osteons. They interconnect the haversian canals with each other and the periosteum
The periosteum is a mem ...
s at right angles connect the osteons together. The columns are metabolically active, and as bone is reabsorbed and created the nature and location of the cells within the osteon will change. Cortical bone is covered by a periosteum
The periosteum is a membrane that covers the outer surface of all bones, except at the articular surfaces (i.e. the parts within a joint space) of long bones. Endosteum lines the inner surface of the medullary cavity of all long bones.
Structu ...
on its outer surface, and an endosteum on its inner surface. The endosteum is the boundary between the cortical bone and the cancellous bone. The primary anatomical and functional unit of cortical bone is the osteon
In osteology, the osteon or haversian system (; named for Clopton Havers) is the fundamental functional unit of much compact bone. Osteons are roughly cylindrical structures that are typically between 0.25 mm and 0.35 mm in diameter. Their ...
.
Trabecules
 Cancellous bone, also called trabecular or spongy bone, is the internal tissue of the skeletal bone and is an open cell
Cancellous bone, also called trabecular or spongy bone, is the internal tissue of the skeletal bone and is an open cell porous
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void (i.e. "empty") spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0 and 1, or as a percentage between 0% and 100%. Strictly speaking, some tests measure ...
network that follows the material properties of biofoams
Biofoams are biological or biologically derived foams, making up lightweight and porous cellular solids. A relatively new term, its use in academia began in the 1980s in relation to the scum that formed on activated sludge plants.
Biofoams is a br ...
. Cancellous bone has a higher surface-area-to-volume ratio
The surface-area-to-volume ratio, also called the surface-to-volume ratio and variously denoted sa/vol or SA:V, is the amount of surface area per unit volume of an object or collection of objects.
SA:V is an important concept in science and engin ...
than cortical bone and it is less dense
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the substance's mass per unit of volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' can also be used. Mathematically ...
. This makes it weaker and more flexible. The greater surface area also makes it suitable for metabolic activities such as the exchange of calcium ions. Cancellous bone is typically found at the ends of long bones, near joints, and in the interior of vertebrae. Cancellous bone is highly vascular
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away f ...
and often contains red bone marrow where hematopoiesis
Haematopoiesis (, from Greek , 'blood' and 'to make'; also hematopoiesis in American English; sometimes also h(a)emopoiesis) is the formation of blood cellular components. All cellular blood components are derived from haematopoietic stem cells ...
, the production of blood cells, occurs. The primary anatomical and functional unit of cancellous bone is the trabecula
A trabecula (plural trabeculae, from Latin for "small beam") is a small, often microscopic, tissue element in the form of a small beam, strut or rod that supports or anchors a framework of parts within a body or organ. A trabecula generally ha ...
. The trabeculae are aligned towards the mechanical load distribution that a bone experiences within long bones such as the femur
The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates wit ...
. As far as short bones are concerned, trabecular alignment has been studied in the vertebral
The vertebral column, also known as the backbone or spine, is part of the axial skeleton. The vertebral column is the defining characteristic of a vertebrate in which the notochord (a flexible rod of uniform composition) found in all chordates ...
pedicle
Pedicle or pedicel may refer to:
Human anatomy
*Pedicle of vertebral arch, the segment between the transverse process and the vertebral body, and is often used as a radiographic marker and entry point in vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty procedures
...
. Thin formations of osteoblasts covered in endosteum create an irregular network of spaces, known as trabeculae. Within these spaces are bone marrow and hematopoietic stem cells that give rise to platelet
Platelets, also called thrombocytes (from Greek θρόμβος, "clot" and κύτος, "cell"), are a component of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping, thereby i ...
s, red blood cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "holl ...
s and white blood cells. Trabecular marrow is composed of a network of rod- and plate-like elements that make the overall organ lighter and allow room for blood vessels and marrow. Trabecular bone accounts for the remaining 20% of total bone mass but has nearly ten times the surface area of compact bone.
The words ''cancellous'' and ''trabecular'' refer to the tiny lattice-shaped units (trabeculae) that form the tissue. It was first illustrated accurately in the engravings of Crisóstomo Martinez
Crisóstomo Martínez (1638–1694) was a Spanish painter, engraver, anatomist and microscopist from Valencia, known for his atlas of anatomy. His work has been ascribed to the Spanish intellectual movement called "''Novator''" which refers to th ...
.
Marrow
Bone marrow, also known asmyeloid tissue
Myeloid tissue, in the bone marrow sense of the word ''wikt:myeloid#Adjective, myeloid'' (''wikt:myelo-#Prefix, myelo-'' + ''wikt:-oid#Suffix, -oid''), is tissue (biology), tissue of bone marrow, of bone marrow cell lineage, or resembling bone ...
in red bone marrow, can be found in almost any bone that holds cancellous tissue
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, an ...
. In newborns
An infant or baby is the very young offspring of human beings. ''Infant'' (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'unable to speak' or 'speechless') is a formal or specialised synonym for the common term ''baby''. The terms may also be used t ...
, all such bones are filled exclusively with red marrow or hematopoietic marrow, but as the child ages the hematopoietic fraction decreases in quantity and the fatty/ yellow fraction called marrow adipose tissue
Bone marrow adipose tissue (BMAT), sometimes referred to as marrow adipose tissue (MAT), is a type of fat deposit in bone marrow. It increases in states of low bone density -osteoporosis, anorexia nervosa/ caloric restriction, skeletal unweigh ...
(MAT) increases in quantity. In adults, red marrow is mostly found in the bone marrow of the femur, the ribs, the vertebrae and pelvic bones
The hip bone (os coxae, innominate bone, pelvic bone or coxal bone) is a large flat bone, constricted in the center and expanded above and below. In some vertebrates (including humans before puberty) it is composed of three parts: the ilium, ischi ...
.
Vascular supply
Bone receives about 10% of cardiac output. Blood enters the endosteum, flows through the marrow, and exits through small vessels in the cortex. In humans, blood oxygen tension in bone marrow is about 6.6%, compared to about 12% in arterial blood, and 5% in venous and capillary blood.Cells
 Bone is metabolically active tissue composed of several types of cells. These cells include osteoblasts, which are involved in the creation and mineralization of bone tissue,
Bone is metabolically active tissue composed of several types of cells. These cells include osteoblasts, which are involved in the creation and mineralization of bone tissue, osteocyte
An osteocyte, an oblate shaped type of bone cell with dendritic processes, is the most commonly found cell in mature bone. It can live as long as the organism itself. The adult human body has about 42 billion of them. Osteocytes do not divide an ...
s, and osteoclast
An osteoclast () is a type of bone cell that breaks down bone tissue. This function is critical in the maintenance, repair, and remodeling of bones of the vertebral skeleton. The osteoclast disassembles and digests the composite of hydrated pro ...
s, which are involved in the reabsorption of bone tissue. Osteoblasts and osteocytes are derived from osteoprogenitor
Osteoblasts (from the Greek language, Greek combining forms for "bone", ὀστέο-, ''osteo-'' and βλαστάνω, ''blastanō'' "germinate") are cell (biology), cells with a single Cell nucleus, nucleus that synthesize bone. However, in the p ...
cells, but osteoclast
An osteoclast () is a type of bone cell that breaks down bone tissue. This function is critical in the maintenance, repair, and remodeling of bones of the vertebral skeleton. The osteoclast disassembles and digests the composite of hydrated pro ...
s are derived from the same cells that differentiate to form macrophages and monocyte
Monocytes are a type of leukocyte or white blood cell. They are the largest type of leukocyte in blood and can differentiate into macrophages and conventional dendritic cells. As a part of the vertebrate innate immune system monocytes also ...
s. Within the marrow of the bone there are also hematopoietic stem cells. These cells give rise to other cells, including white blood cells, red blood cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "holl ...
s, and platelet
Platelets, also called thrombocytes (from Greek θρόμβος, "clot" and κύτος, "cell"), are a component of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping, thereby i ...
s.
Osteoblast
 Osteoblasts are mononucleate bone-forming cells. They are located on the surface of osteon seams and make a
Osteoblasts are mononucleate bone-forming cells. They are located on the surface of osteon seams and make a protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
mixture known as osteoid
In histology, osteoid is the unmineralized, organic portion of the bone matrix that forms prior to the maturation of bone tissue. Osteoblasts begin the process of forming bone tissue by secreting the osteoid as several specific proteins. When ...
, which mineralizes to become bone. The osteoid seam is a narrow region of a newly formed organic matrix, not yet mineralized, located on the surface of a bone. Osteoid is primarily composed of Type I collagen. Osteoblasts also manufacture hormone
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are require ...
s, such as prostaglandins, to act on the bone itself. The osteoblast creates and repairs new bone by actually building around itself. First, the osteoblast puts up collagen fibers. These collagen fibers are used as a framework for the osteoblasts' work. The osteoblast then deposits calcium phosphate which is hardened by hydroxide
Hydroxide is a diatomic anion with chemical formula OH−. It consists of an oxygen and hydrogen atom held together by a single covalent bond, and carries a negative electric charge. It is an important but usually minor constituent of water. I ...
and bicarbonate
In inorganic chemistry, bicarbonate (IUPAC-recommended nomenclature: hydrogencarbonate) is an intermediate form in the deprotonation of carbonic acid. It is a polyatomic anion with the chemical formula .
Bicarbonate serves a crucial biochem ...
ions. The brand-new bone created by the osteoblast is called osteoid
In histology, osteoid is the unmineralized, organic portion of the bone matrix that forms prior to the maturation of bone tissue. Osteoblasts begin the process of forming bone tissue by secreting the osteoid as several specific proteins. When ...
. Once the osteoblast is finished working it is actually trapped inside the bone once it hardens. When the osteoblast becomes trapped, it becomes known as an osteocyte. Other osteoblasts remain on the top of the new bone and are used to protect the underlying bone, these become known as lining cells.
Osteocyte
Osteocyte
An osteocyte, an oblate shaped type of bone cell with dendritic processes, is the most commonly found cell in mature bone. It can live as long as the organism itself. The adult human body has about 42 billion of them. Osteocytes do not divide an ...
s are cells of mesenchymal origin and originate from osteoblasts that have migrated into and become trapped and surrounded by a bone matrix that they themselves produced. The spaces the cell body of osteocytes occupy within the mineralized collagen type I matrix are known as lacunae, while the osteocyte cell processes occupy channels called canaliculi. The many processes of osteocytes reach out to meet osteoblasts, osteoclasts, bone lining cells, and other osteocytes probably for the purposes of communication. Osteocytes remain in contact with other osteocytes in the bone through gap junctions—coupled cell processes which pass through the canalicular channels.
Osteoclast
Osteoclast
An osteoclast () is a type of bone cell that breaks down bone tissue. This function is critical in the maintenance, repair, and remodeling of bones of the vertebral skeleton. The osteoclast disassembles and digests the composite of hydrated pro ...
s are very large multinucleate
Multinucleate cells (also known as multinucleated or polynuclear cells) are eukaryotic cells that have more than one nucleus per cell, i.e., multiple nuclei share one common cytoplasm. Mitosis in multinucleate cells can occur either in a coordina ...
cells that are responsible for the breakdown of bones by the process of bone resorption
Bone resorption is resorption of bone tissue, that is, the process by which osteoclasts break down the tissue in bones and release the minerals, resulting in a transfer of calcium from bone tissue to the blood.
The osteoclasts are multi-nuclea ...
. New bone is then formed by the osteoblasts. Bone is constantly remodeled by the resorption of osteoclasts and created by osteoblasts. Osteoclasts are large cells with multiple nuclei located on bone surfaces in what are called ''Howship's lacunae'' (or ''resorption pits''). These lacunae are the result of surrounding bone tissue that has been reabsorbed. Because the osteoclasts are derived from a monocyte
Monocytes are a type of leukocyte or white blood cell. They are the largest type of leukocyte in blood and can differentiate into macrophages and conventional dendritic cells. As a part of the vertebrate innate immune system monocytes also ...
stem-cell lineage, they are equipped with phagocytic
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is c ...
-like mechanisms similar to circulating macrophages. Osteoclasts mature and/or migrate to discrete bone surfaces. Upon arrival, active enzymes, such as tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase
Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP or TRAPase), also called acid phosphatase 5, tartrate resistant (ACP5), is a glycosylated monomeric metalloprotein enzyme expressed in mammals. It has a molecular weight of approximately 35kDa, a basic iso ...
, are secreted 440px
Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical ...
against the mineral substrate. The reabsorption of bone by osteoclasts also plays a role in calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar t ...
homeostasis
In biology, homeostasis (British also homoeostasis) (/hɒmɪə(ʊ)ˈsteɪsɪs/) is the state of steady internal, physical, and chemical conditions maintained by living systems. This is the condition of optimal functioning for the organism and ...
.
Composition
Bones consist of living cells (osteoblasts and osteocytes) embedded in a mineralized organic matrix. The primary inorganic component of human bone is hydroxyapatite, the dominantbone mineral
Bone mineral (also called inorganic bone phase, bone salt, or bone apatite) is the inorganic component of bone tissue. It gives bones their compressive strength. Bone mineral is formed predominantly from carbonated hydroxyapatite with lower cry ...
, having the nominal composition of Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2. The organic components of this matrix consist mainly of type I collagen
Type I collagen is the most abundant collagen of the human body. It forms large, eosinophilic fibers known as collagen fibers.
It is present in scar tissue, the end product when tissue heals by repair, as well as tendons, ligaments, the endomy ...
—"organic" referring to materials produced as a result of the human body—and inorganic components, which alongside the dominant hydroxyapatite phase, include other compounds of calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar t ...
and phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosph ...
including salts. Approximately 30% of the acellular component of bone consists of organic matter, while roughly 70% by mass is attributed to the inorganic phase. The collagen fibers give bone its tensile strength
Ultimate tensile strength (UTS), often shortened to tensile strength (TS), ultimate strength, or F_\text within equations, is the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking. In brittle materials t ...
, and the interspersed crystals of hydroxyapatite give bone its compressive strength. These effects are synergistic. The exact composition of the matrix may be subject to change over time due to nutrition and biomineralization
Biomineralization, also written biomineralisation, is the process by which living organisms produce minerals, often to harden or stiffen existing tissues. Such tissues are called mineralized tissues. It is an extremely widespread phenomenon; ...
, with the ratio of calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar t ...
to phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosph ...
varying between 1.3 and 2.0 (per weight), and trace minerals such as magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ta ...
, sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable ...
, potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin ''kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmosph ...
and carbonate
A carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid (H2CO3), characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion with the formula . The word ''carbonate'' may also refer to a carbonate ester, an organic compound containing the carbonate ...
also be found.
Type I collagen composes 90–95% of the organic matrix, with the remainder of the matrix being a homogenous liquid called ground substance Ground substance is an amorphous gel-like substance in the extracellular space that contains all components of the extracellular matrix (ECM) except for fibrous materials such as collagen and elastin. Ground substance is active in the development, m ...
consisting of proteoglycans such as hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate
Chondroitin sulfate is a sulfated glycosaminoglycan (GAG) composed of a chain of alternating sugars ( N-acetylgalactosamine and glucuronic acid). It is usually found attached to proteins as part of a proteoglycan. A chondroitin chain can have ov ...
, as well as non-collagenous proteins such as osteocalcin
Osteocalcin, also known as bone gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-containing protein (BGLAP), is a small (49-amino-acid) noncollagenous protein hormone found in bone and dentin, first identified as a calcium-binding protein.
Because osteocalcin has g ...
, osteopontin
Osteopontin (OPN), also known as bone /sialoprotein I (BSP-1 or BNSP), early T-lymphocyte activation (ETA-1), secreted phosphoprotein 1 (SPP1), 2ar and Rickettsia resistance (Ric), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SPP1'' gene (secr ...
or bone sialoprotein
Bone sialoprotein (BSP) is a component of mineralized tissues such as bone, dentin, cementum and calcified cartilage. BSP is a significant component of the bone extracellular matrix and has been suggested to constitute approximately 8% of all ...
. Collagen consists of strands of repeating units, which give bone tensile strength, and are arranged in an overlapping fashion that prevents shear stress. The function of ground substance is not fully known. Two types of bone can be identified microscopically according to the arrangement of collagen: woven and lamellar.
* Woven bone (also known as ''fibrous bone''), which is characterized by a haphazard organization of collagen fibers and is mechanically weak.Currey, John D. (2002)"The Structure of Bone Tissue"
pp. 12–14 in ''Bones: Structure and Mechanics''. Princeton University Press. Princeton, NJ. * Lamellar bone, which has a regular parallel alignment of collagen into sheets ("lamellae") and is mechanically strong.
 Woven bone is produced when osteoblasts produce osteoid rapidly, which occurs initially in all
Woven bone is produced when osteoblasts produce osteoid rapidly, which occurs initially in all fetal
A fetus or foetus (; plural fetuses, feti, foetuses, or foeti) is the unborn offspring that develops from an animal embryo. Following embryonic development the fetal stage of development takes place. In human prenatal development, fetal develo ...
bones, but is later replaced by more resilient lamellar bone. In adults, woven bone is created after fractures
Fracture is the separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacement discontinuity surfaces within the solid. If a displa ...
or in Paget's disease. Woven bone is weaker, with a smaller number of randomly oriented collagen fibers, but forms quickly; it is for this appearance of the fibrous matrix that the bone is termed ''woven''. It is soon replaced by lamellar bone, which is highly organized in concentric sheets with a much lower proportion of osteocytes to surrounding tissue. Lamellar bone, which makes its first appearance in humans in the fetus
A fetus or foetus (; plural fetuses, feti, foetuses, or foeti) is the unborn offspring that develops from an animal embryo. Following embryonic development the fetal stage of development takes place. In human prenatal development, fetal dev ...
during the third trimester,Salentijn, L. ''Biology of Mineralized Tissues: Cartilage and Bone'', Columbia University College of Dental Medicine
The Columbia University College of Dental Medicine, often abbreviated CDM, is one of the twenty graduate and professional schools of Columbia University. It is located at 630 West 168th Street in Manhattan, New York City. According to American ...
post-graduate dental lecture series, 2007 is stronger and filled with many collagen fibers parallel to other fibers in the same layer (these parallel columns are called osteons). In cross-section, the fibers run in opposite directions in alternating layers, much like in plywood, assisting in the bone's ability to resist torsion
Torsion may refer to:
Science
* Torsion (mechanics), the twisting of an object due to an applied torque
* Torsion of spacetime, the field used in Einstein–Cartan theory and
** Alternatives to general relativity
* Torsion angle, in chemistry
Bi ...
forces. After a fracture, woven bone forms initially and is gradually replaced by lamellar bone during a process known as "bony substitution." Compared to woven bone, lamellar bone formation takes place more slowly. The orderly deposition of collagen fibers restricts the formation of osteoid to about 1 to 2 µm per day. Lamellar bone also requires a relatively flat surface to lay the collagen fibers in parallel or concentric layers.
Deposition
The extracellular matrix of bone is laid down by osteoblasts, which secrete both collagen and ground substance. These synthesise collagen within the cell and then secrete collagen fibrils. The collagen fibers rapidlypolymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + ''-mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic a ...
ise to form collagen strands. At this stage, they are not yet mineralised, and are called "osteoid". Around the strands calcium and phosphate precipitate
In an aqueous solution, precipitation is the process of transforming a dissolved substance into an insoluble solid from a super-saturated solution. The solid formed is called the precipitate. In case of an inorganic chemical reaction leading ...
on the surface of these strands, within days to weeks becoming crystals of hydroxyapatite.
In order to mineralise the bone, the osteoblasts secrete vesicles
Vesicle may refer to:
; In cellular biology or chemistry
* Vesicle (biology and chemistry), a supramolecular assembly of lipid molecules, like a cell membrane
* Synaptic vesicle
; In human embryology
* Vesicle (embryology), bulge-like features o ...
containing alkaline phosphatase. This cleaves the phosphate groups and acts as the foci for calcium and phosphate deposition. The vesicles then rupture and act as a centre for crystals to grow on. More particularly, bone mineral is formed from globular and plate structures.
Types

 There are five types of bones in the human body: long, short, flat, irregular, and sesamoid.
* Long bones are characterized by a shaft, the
There are five types of bones in the human body: long, short, flat, irregular, and sesamoid.
* Long bones are characterized by a shaft, the diaphysis
The diaphysis is the main or midsection (shaft) of a long bone. It is made up of cortical bone and usually contains bone marrow and adipose tissue (fat).
It is a middle tubular part composed of compact bone which surrounds a central marrow cavit ...
, that is much longer than its width; and by an epiphysis
The epiphysis () is the rounded end of a long bone, at its joint with adjacent bone(s). Between the epiphysis and diaphysis (the long midsection of the long bone) lies the metaphysis, including the epiphyseal plate (growth plate). At the jo ...
, a rounded head at each end of the shaft. They are made up mostly of compact bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, and ...
, with lesser amounts of marrow, located within the medullary cavity
The medullary cavity (''medulla'', innermost part) is the central cavity of bone shafts where red bone marrow and/or yellow bone marrow ( adipose tissue) is stored; hence, the medullary cavity is also known as the marrow cavity.
Located in the m ...
, and areas of spongy, cancellous bone at the ends of the bones. Most bones of the limbs, including those of the fingers
A finger is a limb of the body and a type of digit, an organ of manipulation and sensation found in the hands of most of the Tetrapods, so also with humans and other primates. Most land vertebrates have five fingers (Pentadactyly). Chambers 1 ...
and toes
Toes are the digits (fingers) of the foot of a tetrapod. Animal species such as cats that walk on their toes are described as being '' digitigrade''. Humans, and other animals that walk on the soles of their feet, are described as being '' pl ...
, are long bones. The exceptions are the eight carpal bones of the wrist
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; "The wrist contains eight bones, roughly aligned in two rows, known as the carp ...
, the seven articulating tarsal bone
In the human body, the tarsus is a cluster of seven articulating bones in each foot situated between the lower end of the tibia and the fibula of the lower leg and the metatarsus. It is made up of the midfoot (cuboid, medial, intermediate, and la ...
s of the ankle
The ankle, or the talocrural region, or the jumping bone (informal) is the area where the foot and the leg meet. The ankle includes three joints: the ankle joint proper or talocrural joint, the subtalar joint, and the inferior tibiofibular joi ...
and the sesamoid bone of the kneecap
The patella, also known as the kneecap, is a flat, rounded triangular bone which articulates with the femur (thigh bone) and covers and protects the anterior articular surface of the knee joint. The patella is found in many tetrapods, such as m ...
. Long bones such as the clavicle, that have a differently shaped shaft or ends are also called ''modified long bones''.
* Short bone
Short bones are designated as those bones that are as wide as they are long. Their primary function is to provide support and stability with little to no movement. They are one of five types of bones: short, long, flat, irregular and sesamoid ...
s are roughly cube-shaped, and have only a thin layer of compact bone surrounding a spongy interior. The bones of the wrist and ankle are short bones.
* Flat bone
Flat bones are bones whose principal function is either extensive protection or the provision of broad surfaces for muscular attachment. These bones are expanded into broad, flat plates,''Gray's Anatomy'' (1918). (See infobox) as in the cranium ...
s are thin and generally curved, with two parallel layers of compact bone sandwiching a layer of spongy bone. Most of the bones of the skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, th ...
are flat bones, as is the sternum
The sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. Sha ...
.
* Sesamoid bones are bones embedded in tendons. Since they act to hold the tendon further away from the joint, the angle of the tendon is increased and thus the leverage of the muscle is increased. Examples of sesamoid bones are the patella
The patella, also known as the kneecap, is a flat, rounded triangular bone which articulates with the femur (thigh bone) and covers and protects the anterior articular surface of the knee joint. The patella is found in many tetrapods, such as ...
and the pisiform
The pisiform bone ( or ), also spelled pisiforme (from the Latin ''pisifomis'', pea-shaped), is a small knobbly, sesamoid bone that is found in the wrist. It forms the ulnar border of the carpal tunnel.
Structure
The pisiform is a sesamoid bone, ...
.
* Irregular bone
The irregular bones are bones which, from their peculiar form, cannot be grouped as long, short, flat or sesamoid bones. Irregular bones serve various purposes in the body, such as protection of nervous tissue (such as the vertebrae protect th ...
s do not fit into the above categories. They consist of thin layers of compact bone surrounding a spongy interior. As implied by the name, their shapes are irregular and complicated. Often this irregular shape is due to their many centers of ossification or because they contain bony sinuses. The bones of the spine, pelvis, and some bones of the skull are irregular bones. Examples include the ethmoid
The ethmoid bone (; from grc, ἡθμός, hēthmós, sieve) is an unpaired bone in the skull that separates the nasal cavity from the brain. It is located at the roof of the nose, between the two orbits. The cubical bone is lightweight due to a ...
and sphenoid bones.
Terminology
In the study ofanatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having it ...
, anatomists use a number of anatomical terms to describe the appearance, shape and function of bones. Other anatomical terms are also used to describe the location of bones. Like other anatomical terms, many of these derive from Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
and Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
. Some anatomists still use Latin to refer to bones. The term "osseous", and the prefix "osteo-", referring to things related to bone, are still used commonly today.
Some examples of terms used to describe bones include the term "foramen" to describe a hole through which something passes, and a "canal" or "meatus" to describe a tunnel-like structure. A protrusion from a bone can be called a number of terms, including a "condyle", "crest", "spine", "eminence", "tubercle" or "tuberosity", depending on the protrusion's shape and location. In general, long bones are said to have a "head", "neck", and "body".
When two bones join, they are said to "articulate". If the two bones have a fibrous connection and are relatively immobile, then the joint is called a "suture".
Development

 The formation of bone is called
The formation of bone is called ossification
Ossification (also called osteogenesis or bone mineralization) in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells named osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in ...
. During the fetal stage of development this occurs by two processes: intramembranous ossification and endochondral ossification. Intramembranous ossification involves the formation of bone from connective tissue whereas endochondral ossification involves the formation of bone from cartilage.
Intramembranous ossification mainly occurs during formation of the flat bones of the skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, th ...
but also the mandible, maxilla, and clavicles; the bone is formed from connective tissue such as mesenchyme tissue rather than from cartilage. The process includes: the development of the ossification center
An ossification center is a point where ossification of the cartilage begins. The first step in ossification is that the cartilage cells at this point enlarge and arrange themselves in rows.Gray and Spitzka (1910), page 44.
The matrix in which t ...
, calcification
Calcification is the accumulation of calcium salts in a body tissue. It normally occurs in the formation of bone, but calcium can be deposited abnormally in soft tissue,Miller, J. D. Cardiovascular calcification: Orbicular origins. ''Nature Ma ...
, trabeculae formation and the development of the periosteum.
Endochondral ossification occurs in long bones and most other bones in the body; it involves the development of bone from cartilage. This process includes the development of a cartilage model, its growth and development, development of the primary and secondary ossification center
An ossification center is a point where ossification of the cartilage begins. The first step in ossification is that the cartilage cells at this point enlarge and arrange themselves in rows.Gray and Spitzka (1910), page 44.
The matrix in which t ...
s, and the formation of articular cartilage and the epiphyseal plate
The epiphyseal plate (or epiphysial plate, physis, or growth plate) is a hyaline cartilage plate in the metaphysis at each end of a long bone. It is the part of a long bone where new bone growth takes place; that is, the whole bone is alive, wit ...
s.
Endochondral ossification begins with points in the cartilage called "primary ossification centers." They mostly appear during fetal development, though a few short bones begin their primary ossification after birth
Birth is the act or process of bearing or bringing forth offspring, also referred to in technical contexts as parturition. In mammals, the process is initiated by hormones which cause the muscular walls of the uterus to contract, expelling the f ...
. They are responsible for the formation of the diaphyses of long bones, short bones and certain parts of irregular bones. Secondary ossification occurs after birth and forms the epiphyses
The epiphysis () is the rounded end of a long bone, at its joint with adjacent bone(s). Between the epiphysis and diaphysis (the long midsection of the long bone) lies the metaphysis, including the epiphyseal plate (growth plate). At the jo ...
of long bones and the extremities of irregular and flat bones. The diaphysis and both epiphyses of a long bone are separated by a growing zone of cartilage (the epiphyseal plate
The epiphyseal plate (or epiphysial plate, physis, or growth plate) is a hyaline cartilage plate in the metaphysis at each end of a long bone. It is the part of a long bone where new bone growth takes place; that is, the whole bone is alive, wit ...
). At skeletal maturity (18 to 25 years of age), all of the cartilage is replaced by bone, fusing the diaphysis and both epiphyses together (epiphyseal closure). In the upper limbs, only the diaphyses of the long bones and scapula are ossified. The epiphyses, carpal bones, coracoid process, medial border of the scapula, and acromion are still cartilaginous.
The following steps are followed in the conversion of cartilage to bone:
# Zone of reserve cartilage. This region, farthest from the marrow cavity, consists of typical hyaline cartilage that as yet shows no sign of transforming into bone.
# Zone of cell proliferation. A little closer to the marrow cavity, chondrocytes multiply and arrange themselves into longitudinal columns of flattened lacunae.
# Zone of cell hypertrophy. Next, the chondrocytes cease to divide and begin to hypertrophy (enlarge), much like they do in the primary ossification center of the fetus. The walls of the matrix between lacunae become very thin.
# Zone of calcification. Minerals are deposited in the matrix between the columns of lacunae and calcify the cartilage. These are not the permanent mineral deposits of bone, but only a temporary support for the cartilage that would otherwise soon be weakened by the breakdown of the enlarged lacunae.
# Zone of bone deposition. Within each column, the walls between the lacunae break down and the chondrocytes die. This converts each column into a longitudinal channel, which is immediately invaded by blood vessels and marrow from the marrow cavity. Osteoblasts line up along the walls of these channels and begin depositing concentric lamellae of matrix, while osteoclasts dissolve the temporarily calcified cartilage.
Functions
Bones have a variety of functions:Mechanical
Bones serve a variety of mechanical functions. Together the bones in the body form the skeleton. They provide a frame to keep the body supported, and an attachment point for skeletal muscles,tendon
A tendon or sinew is a tough, high-tensile-strength band of dense fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone. It is able to transmit the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system without sacrificing its ability ...
s, ligaments and joint
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw- ...
s, which function together to generate and transfer forces so that individual body parts or the whole body can be manipulated in three-dimensional space (the interaction between bone and muscle is studied in biomechanics
Biomechanics is the study of the structure, function and motion of the mechanical aspects of biological systems, at any level from whole organisms to organs, cells and cell organelles, using the methods of mechanics. Biomechanics is a branch of ...
).
Bones protect internal organs, such as the skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, th ...
protecting the brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a ve ...
or the ribs
The rib cage, as an enclosure that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum in the thorax of most vertebrates, protects vital organs such as the heart, lungs and great vessels.
The sternum, together known as the thoracic cage, is a semi- ...
protecting the heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to t ...
and lungs
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side ...
. Because of the way that bone is formed, bone has a high compressive strength of about , poor tensile strength
Ultimate tensile strength (UTS), often shortened to tensile strength (TS), ultimate strength, or F_\text within equations, is the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking. In brittle materials t ...
of 104–121 MPa, and a very low shear stress
Shear stress, often denoted by (Greek: tau), is the component of stress coplanar with a material cross section. It arises from the shear force, the component of force vector parallel to the material cross section. ''Normal stress'', on the ...
strength (51.6 MPa). This means that bone resists pushing (compressional) stress well, resist pulling (tensional) stress less well, but only poorly resists shear stress (such as due to torsional loads). While bone is essentially brittle
A material is brittle if, when subjected to stress, it fractures with little elastic deformation and without significant plastic deformation. Brittle materials absorb relatively little energy prior to fracture, even those of high strength. Br ...
, bone does have a significant degree of elasticity, contributed chiefly by collagen.
Mechanically, bones also have a special role in hearing
Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is audit ...
. The ossicles are three small bones in the middle ear
The middle ear is the portion of the ear medial to the eardrum, and distal to the oval window of the cochlea (of the inner ear).
The mammalian middle ear contains three ossicles, which transfer the vibrations of the eardrum into waves in the ...
which are involved in sound transduction.
Synthetic
The cancellous part of bones contain bone marrow. Bone marrow produces blood cells in a process calledhematopoiesis
Haematopoiesis (, from Greek , 'blood' and 'to make'; also hematopoiesis in American English; sometimes also h(a)emopoiesis) is the formation of blood cellular components. All cellular blood components are derived from haematopoietic stem cells ...
. Blood cells that are created in bone marrow include red blood cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "holl ...
s, platelet
Platelets, also called thrombocytes (from Greek θρόμβος, "clot" and κύτος, "cell"), are a component of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping, thereby i ...
s and white blood cells. Progenitor cells such as the hematopoietic stem cell divide in a process called mitosis to produce precursor cells. These include precursors which eventually give rise to white blood cells
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from mult ...
, and erythroblast
A nucleated red blood cell (NRBC), also known by several other names, is a red blood cell that contains a cell nucleus. Almost all vertebrate organisms have hemoglobin-containing cells in their blood, and with the exception of mammals, all of t ...
s which give rise to red blood cells. Unlike red and white blood cells, created by mitosis, platelets are shed from very large cells called megakaryocyte
A megakaryocyte (''mega-'' + '' karyo-'' + '' -cyte'', "large-nucleus cell") is a large bone marrow cell with a lobated nucleus responsible for the production of blood thrombocytes (platelets), which are necessary for normal blood clotting. In ...
s. This process of progressive differentiation occurs within the bone marrow. After the cells are matured, they enter the circulation. Every day, over 2.5 billion red blood cells and platelets, and 50–100 billion granulocytes are produced in this way.
As well as creating cells, bone marrow is also one of the major sites where defective or aged red blood cells are destroyed.
Metabolic
* Mineral storage – bones act as reserves of minerals important for the body, most notablycalcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar t ...
and phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Ear ...
.
Determined by the species, age, and the type of bone, bone cells make up to 15 percent of the bone. Growth factor
A growth factor is a naturally occurring substance capable of stimulating cell proliferation, wound healing, and occasionally cellular differentiation. Usually it is a secreted protein or a steroid hormone. Growth factors are important for regul ...
storage—mineralized bone matrix stores important growth factors such as insulin-like growth factors, transforming growth factor, bone morphogenetic proteins and others.
* Fat
In nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
The term often refers specifically to triglycerides (triple est ...
storage – marrow adipose tissue
Bone marrow adipose tissue (BMAT), sometimes referred to as marrow adipose tissue (MAT), is a type of fat deposit in bone marrow. It increases in states of low bone density -osteoporosis, anorexia nervosa/ caloric restriction, skeletal unweigh ...
(MAT) acts as a storage reserve of fatty acid
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, ...
s.
* Acid- base balance – bone buffers the blood against excessive pH changes by absorbing or releasing alkaline salts.
* Detoxification – bone tissues can also store heavy metals and other foreign elements, removing them from the blood and reducing their effects on other tissues. These can later be gradually released for excretion
Excretion is a process in which metabolic waste
is eliminated from an organism. In vertebrates this is primarily carried out by the lungs, kidneys, and skin. This is in contrast with secretion, where the substance may have specific tasks after ...
.
* Endocrine organ – bone controls phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosph ...
metabolism by releasing fibroblast growth factor 23
Fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) is a protein and member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family which participates in the regulation of phosphate in plasma and vitamin D metabolism. In humans it is encoded by the gene. FGF23 decreases rea ...
(FGF-23), which acts on kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blo ...
s to reduce phosphate reabsorption
In renal physiology, reabsorption or tubular reabsorption is the process by which the nephron removes water and solutes from the tubular fluid (pre-urine) and returns them to the circulating blood. It is called ''reabsorption'' (and not ''absorp ...
. Bone cells also release a hormone called osteocalcin
Osteocalcin, also known as bone gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-containing protein (BGLAP), is a small (49-amino-acid) noncollagenous protein hormone found in bone and dentin, first identified as a calcium-binding protein.
Because osteocalcin has g ...
, which contributes to the regulation of blood sugar
Glycaemia, also known as blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, or blood glucose level is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood of humans or other animals. Approximately 4 grams of glucose, a simple sugar, is present in the blo ...
(glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, u ...
) and fat deposition. Osteocalcin increases both the insulin secretion and sensitivity, in addition to boosting the number of insulin-producing cells and reducing stores of fat.
* Calcium balance – the process of bone resorption by the osteoclasts releases stored calcium into the systemic circulation and is an important process in regulating calcium balance. As bone formation actively ''fixes'' circulating calcium in its mineral form, removing it from the bloodstream, resorption actively ''unfixes'' it thereby increasing circulating calcium levels. These processes occur in tandem at site-specific locations.
Remodeling
Bone is constantly being created and replaced in a process known as remodeling. This ongoing turnover of bone is a process of resorption followed by replacement of bone with little change in shape. This is accomplished through osteoblasts and osteoclasts. Cells are stimulated by a variety ofsignals
In signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. Any quantity that can vary over space or time can be used as a signal to share messages between observers. The ''IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing'' ...
, and together referred to as a remodeling unit. Approximately 10% of the skeletal mass of an adult is remodelled each year. The purpose of remodeling is to regulate calcium homeostasis
Calcium metabolism is the movement and regulation of calcium ions (Ca2+) ''in'' (via the gut) and ''out'' (via the gut and kidneys) of the body, and ''between'' body compartments: the blood plasma, the extracellular and intracellular fluids, and ...
, repair microdamaged bones from everyday stress, and to shape the skeleton during growth. Repeated stress, such as weight-bearing exercise or bone healing, results in the bone thickening at the points of maximum stress (Wolff's law
Wolff's law, developed by the German anatomist and surgeon Julius Wolff (1836–1902) in the 19th century, states that bone in a healthy animal will adapt to the loads under which it is placed. If loading on a particular bone increases, the bon ...
). It has been hypothesized that this is a result of bone's piezoelectric
Piezoelectricity (, ) is the electric charge that accumulates in certain solid materials—such as crystals, certain ceramics, and biological matter such as bone, DNA, and various proteins—in response to applied mechanical stress. The word '' ...
properties, which cause bone to generate small electrical potentials under stress.
The action of osteoblasts and osteoclasts are controlled by a number of chemical enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products ...
s that either promote or inhibit the activity of the bone remodeling cells, controlling the rate at which bone is made, destroyed, or changed in shape. The cells also use paracrine signalling Paracrine signaling is a form of cell signaling, a type of cellular communication in which a cell produces a signal to induce changes in nearby cells, altering the behaviour of those cells. Signaling molecules known as paracrine factors diffuse over ...
to control the activity of each other. For example, the rate at which osteoclasts resorb bone is inhibited by calcitonin
Calcitonin is a 32 amino acid peptide hormone secreted by parafollicular cells (also known as C cells) of the thyroid (or endostyle) in humans and other chordates. in the ultimopharyngeal body. It acts to reduce blood calcium (Ca2+), opposing th ...
and osteoprotegerin
Osteoprotegerin (OPG), also known as osteoclastogenesis inhibitory factor (OCIF) or tumour necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 11B (TNFRSF11B), is a cytokine receptor of the tumour necrosis factor (TNF) receptor superfamily encoded by the ...
. Calcitonin is produced by parafollicular cell
Parafollicular cells, also called C cells, are neuroendocrine cells in the thyroid. The primary function of these cells is to secrete calcitonin. They are located adjacent to the thyroid follicles and reside in the connective tissue. These cells a ...
s in the thyroid gland, and can bind to receptors on osteoclasts to directly inhibit osteoclast activity. Osteoprotegerin is secreted by osteoblasts and is able to bind RANK-L, inhibiting osteoclast stimulation.
Osteoblasts can also be stimulated to increase bone mass through increased secretion of osteoid
In histology, osteoid is the unmineralized, organic portion of the bone matrix that forms prior to the maturation of bone tissue. Osteoblasts begin the process of forming bone tissue by secreting the osteoid as several specific proteins. When ...
and by inhibiting the ability of osteoclasts to break down osseous tissue
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
. Increased secretion of osteoid is stimulated by the secretion of growth hormone
Growth hormone (GH) or somatotropin, also known as human growth hormone (hGH or HGH) in its human form, is a peptide hormone that stimulates growth, cell reproduction, and cell regeneration in humans and other animals. It is thus important in h ...
by the pituitary
In vertebrate anatomy, the pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland, about the size of a chickpea and weighing, on average, in humans. It is a protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain. The hypoph ...
, thyroid hormone and the sex hormones (estrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal ac ...
s and androgen
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning "man") is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This in ...
s). These hormones also promote increased secretion of osteoprotegerin. Osteoblasts can also be induced to secrete a number of cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrin ...
s that promote reabsorption of bone by stimulating osteoclast activity and differentiation from progenitor cells. Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of fat-soluble secosteroids responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, and many other biological effects. In humans, the most important compounds in this group are vitamin D3 (c ...
, parathyroid hormone
Parathyroid hormone (PTH), also called parathormone or parathyrin, is a peptide hormone secreted by the parathyroid glands that regulates the serum calcium concentration through its effects on bone, kidney, and intestine.
PTH influences bone ...
and stimulation from osteocytes induce osteoblasts to increase secretion of RANK-ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule ( functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's elec ...
and interleukin 6
Interleukin 6 (IL-6) is an interleukin that acts as both a pro-inflammatory cytokine and an anti-inflammatory myokine. In humans, it is encoded by the ''IL6'' gene.
In addition, osteoblasts secrete IL-6 to stimulate osteoclast formation. Smooth ...
, which cytokines then stimulate increased reabsorption of bone by osteoclasts. These same compounds also increase secretion of macrophage colony-stimulating factor by osteoblasts, which promotes the differentiation of progenitor cells into osteoclasts, and decrease secretion of osteoprotegerin.
Volume
Bone volume is determined by the rates of bone formation and bone resorption. Recent research has suggested that certain growth factors may work to locally alter bone formation by increasing osteoblast activity. Numerous bone-derived growth factors have been isolated and classified via bone cultures. These factors include insulin-like growth factors I and II, transforming growth factor-beta, fibroblast growth factor, platelet-derived growth factor, and bone morphogenetic proteins. Evidence suggests that bone cells produce growth factors for extracellular storage in the bone matrix. The release of these growth factors from the bone matrix could cause the proliferation of osteoblast precursors. Essentially, bone growth factors may act as potential determinants of local bone formation. Research has suggested that cancellous bone volume in postmenopausal osteoporosis may be determined by the relationship between the total bone forming surface and the percent of surface resorption.Clinical significance
A number of diseases can affect bone, including arthritis, fractures, infections, osteoporosis and tumors. Conditions relating to bone can be managed by a variety of doctors, including rheumatologists for joints, andorthopedic
Orthopedic surgery or orthopedics ( alternatively spelt orthopaedics), is the branch of surgery concerned with conditions involving the musculoskeletal system. Orthopedic surgeons use both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal ...
surgeons, who may conduct surgery to fix broken bones. Other doctors, such as rehabilitation specialists may be involved in recovery, radiologists
Radiology ( ) is the medical discipline that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide their treatment, within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography (which is why its name has a root referring to radiat ...
in interpreting the findings on imaging, and pathologist
Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in t ...
s in investigating the cause of the disease, and family doctor
Family medicine is a medical specialty within primary care that provides continuing and comprehensive health care for the individual and family across all ages, genders, diseases, and parts of the body. The specialist, who is usually a primary ...
s may play a role in preventing complications of bone disease such as osteoporosis.
When a doctor sees a patient, a history and exam will be taken. Bones are then often imaged, called radiography
Radiography is an imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical radiography ("diagnostic" and "therapeu ...
. This might include ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies ...
X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
, CT scan, MRI scan
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves ...
and other imaging such as a Bone scan
A bone scan or bone scintigraphy is a nuclear medicine imaging technique of the bone. It can help diagnose a number of bone conditions, including cancer of the bone or metastasis, location of bone inflammation and fractures (that may not be vi ...
, which may be used to investigate cancer. Other tests such as a blood test for autoimmune markers may be taken, or a synovial fluid aspirate may be taken.
Fractures
fractures
Fracture is the separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacement discontinuity surfaces within the solid. If a displa ...
occur when there is significant force applied or repetitive trauma over a long time. Fractures can also occur when a bone is weakened, such as with osteoporosis, or when there is a structural problem, such as when the bone remodels excessively (such as Paget's disease) or is the site of the growth of cancer. Common fractures include wrist fracture
A distal radius fracture, also known as wrist fracture, is a break of the part of the radius bone which is close to the wrist. Symptoms include pain, bruising, and rapid-onset swelling. The ulna bone may also be broken.
In younger people, thes ...
s and hip fracture
A hip fracture is a break that occurs in the upper part of the femur (thigh bone). Symptoms may include pain around the hip, particularly with movement, and shortening of the leg. Usually the person cannot walk.
They most often occur as a res ...
s, associated with osteoporosis, vertebral fracture
A spinal fracture, also called a vertebral fracture or a broken back, is a fracture affecting the vertebrae of the spinal column. Most types of spinal fracture confer a significant risk of spinal cord injury. After the immediate trauma, there i ...
s associated with high-energy trauma and cancer, and fractures of long-bones. Not all fractures are painful. When serious, depending on the fractures type and location, complications may include flail chest
Flail chest is a life-threatening medical condition that occurs when a segment of the rib cage breaks due to trauma and becomes detached from the rest of the chest wall. Two of the symptoms of flail chest are chest pain and shortness of breath ...
, compartment syndrome
Compartment syndrome is a condition in which increased pressure within one of the body's anatomical compartments results in insufficient blood supply to tissue within that space. There are two main types: acute and chronic. Compartments of the ...
s or fat embolism.
Compound fracture
A bone fracture (abbreviated FRX or Fx, Fx, or #) is a medical condition in which there is a partial or complete break in the continuity of any bone in the body. In more severe cases, the bone may be broken into several fragments, known as a '' ...
s involve the bone's penetration through the skin. Some complex fractures can be treated by the use of bone grafting
Bone grafting is a surgical procedure that replaces missing bone in order to repair bone fractures that are extremely complex, pose a significant health risk to the patient, or fail to heal properly. Some small or acute fractures can be cured wit ...
procedures that replace missing bone portions.
Fractures and their underlying causes can be investigated by X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
s, CT scans and MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves ...
s. Fractures are described by their location and shape, and several classification systems exist, depending on the location of the fracture. A common long bone fracture in children is a Salter–Harris fracture
A Salter–Harris fracture is a fracture that involves the epiphyseal plate (growth plate) of a bone, specifically the zone of provisional calcification. It is thus a form of child bone fracture. It is a common injury found in children, occurring ...
. When fractures are managed, pain relief is often given, and the fractured area is often immobilised. This is to promote bone healing
Bone healing, or fracture healing, is a proliferative physiological process in which the body facilitates the repair of a bone fracture.
Generally, bone fracture treatment consists of a doctor reducing (pushing) displaced bones back into place ...
. In addition, surgical measures such as internal fixation
Internal fixation is an operation in orthopedics that involves the surgical implementation of implants for the purpose of repairing a bone, a concept that dates to the mid-nineteenth century and was made applicable for routine treatment in the m ...
may be used. Because of the immobilisation, people with fractures are often advised to undergo rehabilitation.
Tumors
There are several types of tumor that can affect bone; examples of benignbone tumor
A bone tumor is an abnormal growth of tissue in bone, traditionally classified as noncancerous (benign) or cancerous (malignant). Cancerous bone tumors usually originate from a cancer in another part of the body such as from lung, breast, thyroi ...
s include osteoma
An osteoma (plural: "osteomata") is a new piece of bone usually growing on another piece of bone, typically the skull. It is a benign tumor.
When the bone tumor grows on other bone it is known as "homoplastic osteoma"; when it grows on other tissu ...
, osteoid osteoma
An osteoid osteoma is a benign (non-cancerous) bone tumor that arises from osteoblasts and some components of osteoclasts. It was originally thought to be a smaller version of an osteoblastoma. Osteoid osteomas tend to be less than 1.5 cm ...
, osteochondroma
Osteochondromas are the most common benign tumors of the bones.
The tumors take the form of cartilage-capped bony projections or outgrowth on the surface of bones exostoses. It is characterized as a type of overgrowth that can occur in any bone w ...
, osteoblastoma
Osteoblastoma is an uncommon osteoid tissue-forming primary neoplasm of the bone.
It has clinical and histologic manifestations similar to those of osteoid osteoma; therefore, some consider the two tumors to be variants of the same disease, wit ...
, enchondroma
Enchondroma is a type of benign bone tumor belonging to the group of cartilage tumors. There may be no symptoms, or it may present typically in the short tubular bones of the hands with a swelling, pain or pathological fracture.
Diagnosis is by ...
, giant-cell tumor of bone
Giant-cell tumor of the bone (GCTOB), is a relatively uncommon tumor of the bone. It is characterized by the presence of multinucleated giant cells (osteoclast-like cells). Malignancy in giant-cell tumor is uncommon and occurs in about 2% of all ...
, and aneurysmal bone cyst
Aneurysmal bone cyst (ABC) is a non-cancerous bone tumor composed of multiple varying sizes of spaces in a bone which are filled with blood. The term is a misnomer, as the lesion is neither an aneurysm nor a cyst. It generally presents with pai ...
.
Cancer
Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
can arise in bone tissue, and bones are also a common site for other cancers to spread (metastasise
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then, ...
) to. Cancers that arise in bone are called "primary" cancers, although such cancers are rare. Metastases within bone are "secondary" cancers, with the most common being breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or a r ...
, lung cancer
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma (since about 98–99% of all lung cancers are carcinomas), is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. Lung carcinomas derive from transformed, malign ...
, prostate cancer, thyroid cancer
Thyroid cancer is cancer that develops from the tissues of the thyroid gland. It is a disease in which cells grow abnormally and have the potential to spread to other parts of the body. Symptoms can include swelling or a lump in the neck. C ...
, and kidney cancer
Kidney cancer, also known as renal cancer, is a group of cancers that starts in the kidney. Symptoms may include blood in the urine, lump in the abdomen, or back pain. Fever, weight loss, and tiredness may also occur. Complications can include sp ...
. Secondary cancers that affect bone can either destroy bone (called a "lytic
The lytic cycle ( ) is one of the two cycles of viral reproduction (referring to bacterial viruses or bacteriophages), the other being the lysogenic cycle. The lytic cycle results in the destruction of the infected cell and its membrane. Bacter ...
" cancer) or create bone (a " sclerotic" cancer). Cancers of the bone marrow inside the bone can also affect bone tissue, examples including leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia and pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and result in high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or ...
and multiple myeloma. Bone may also be affected by cancers in other parts of the body. Cancers in other parts of the body may release parathyroid hormone
Parathyroid hormone (PTH), also called parathormone or parathyrin, is a peptide hormone secreted by the parathyroid glands that regulates the serum calcium concentration through its effects on bone, kidney, and intestine.
PTH influences bone ...
or parathyroid hormone-related peptide
Parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP) is a proteinaceous hormone and a member of the parathyroid hormone family secreted by mesenchymal stem cells. It is occasionally secreted by cancer cells (for example, breast cancer, certain types of ...
. This increases bone reabsorption, and can lead to bone fractures.
Bone tissue that is destroyed or altered as a result of cancers is distorted, weakened, and more prone to fracture. This may lead to compression of the spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the sp ...
, destruction of the marrow resulting in bruising
A bruise, also known as a contusion, is a type of hematoma of tissue, the most common cause being capillaries damaged by trauma, causing localized bleeding that extravasates into the surrounding interstitial tissues. Most bruises occur clos ...
, bleeding
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vag ...
and immunosuppression
Immunosuppression is a reduction of the activation or efficacy of the immune system. Some portions of the immune system itself have immunosuppressive effects on other parts of the immune system, and immunosuppression may occur as an adverse reacti ...
, and is one cause of bone pain. If the cancer is metastatic, then there might be other symptoms depending on the site of the original cancer. Some bone cancers can also be felt.
Cancers of the bone are managed according to their type, their stage
Stage or stages may refer to:
Acting
* Stage (theatre), a space for the performance of theatrical productions
* Theatre, a branch of the performing arts, often referred to as "the stage"
* ''The Stage'', a weekly British theatre newspaper
* Sta ...
, prognosis, and what symptoms they cause. Many primary cancers of bone are treated with radiotherapy. Cancers of bone marrow may be treated with chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs ( chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemothe ...
, and other forms of targeted therapy such as immunotherapy
Immunotherapy or biological therapy is the treatment of disease by activating or suppressing the immune system. Immunotherapies designed to elicit or amplify an immune response are classified as ''activation immunotherapies,'' while immunotherap ...
may be used. Palliative care
Palliative care (derived from the Latin root , or 'to cloak') is an interdisciplinary medical caregiving approach aimed at optimizing quality of life and mitigating suffering among people with serious, complex, and often terminal illnesses. Wit ...
, which focuses on maximising a person's quality of life
Quality of life (QOL) is defined by the World Health Organization as "an individual's perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards ...
, may play a role in management, particularly if the likelihood of survival within five years is poor.
Other painful conditions
*Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis (OM) is an infection of bone. Symptoms may include pain in a specific bone with overlying redness, fever, and weakness. The long bones of the arms and legs are most commonly involved in children e.g. the femur and humerus, while the ...
is inflammation of the bone or bone marrow due to bacterial infection.
* Osteomalacia
Osteomalacia is a disease characterized by the softening of the bones caused by impaired bone metabolism primarily due to inadequate levels of available phosphate, calcium, and vitamin D, or because of resorption of calcium. The impairment of bon ...
is a painful softening of adult bone caused by severe vitamin D deficiency.
* Osteogenesis imperfecta
Osteogenesis imperfecta (; OI), colloquially known as brittle bone disease, is a group of genetic disorders that all result in bones that break easily. The range of symptoms—on the skeleton as well as on the body's other organs—may b ...
* Osteochondritis dissecans
Osteochondritis dissecans (OCD or OD) is a joint disorder primarily of the subchondral bone in which cracks form in the articular cartilage and the underlying subchondral bone. OCD usually causes pain during and after sports. In later stages ...
* Ankylosing spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a type of arthritis characterized by long-term inflammation of the joints of the spine typically where the spine joins the pelvis. Occasionally areas affected may include other joints such as the shoulders or hi ...
* Skeletal fluorosis
Skeletal fluorosis is a bone disease caused by excessive accumulation of fluoride leading to weakened bones. In advanced cases, skeletal fluorosis causes painful damage to bones and joints.
Symptoms
Symptoms are mainly promoted in the bone structu ...
is a bone disease caused by an excessive accumulation of fluoride in the bones. In advanced cases, skeletal fluorosis damages bones and joints and is painful.
Osteoporosis
 Osteoporosis is a disease of bone where there is reduced bone mineral density, increasing the likelihood of
Osteoporosis is a disease of bone where there is reduced bone mineral density, increasing the likelihood of fractures
Fracture is the separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacement discontinuity surfaces within the solid. If a displa ...
. Osteoporosis is defined in women by the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of ...
as a bone mineral density of 2.5 standard deviations below peak bone mass, relative to the age and sex-matched average. This density is measured using dual energy X-ray absorptiometry
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA, or DEXA) is a means of measuring bone mineral density (BMD) using Spectral imaging (radiography), spectral imaging. Two X-ray beams, with different energy levels, are aimed at the patient's bones. When soft ...
(DEXA), with the term "established osteoporosis" including the presence of a fragility fracture
A pathologic fracture is a bone fracture caused by weakness of the bone structure that leads to decrease mechanical resistance to normal mechanical loads. This process is most commonly due to osteoporosis, but may also be due to other pathologie ...
. Osteoporosis is most common in women after menopause
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time in women's lives when menstrual periods stop permanently, and they are no longer able to bear children. Menopause usually occurs between the age of 47 and 54. Medical professionals often ...
, when it is called "postmenopausal osteoporosis", but may develop in men and premenopausal women in the presence of particular hormonal disorders and other chronic diseases or as a result of smoking and medications, specifically glucocorticoid
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every verteb ...
s. Osteoporosis usually has no symptoms until a fracture occurs. For this reason, DEXA scans are often done in people with one or more risk factors, who have developed osteoporosis and are at risk of fracture.
One of the most important risk factors for osteoporosis is advanced age. Accumulation of oxidative DNA damage
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA d ...
in osteoblastic
Osteoblasts (from the Greek combining forms for "bone", ὀστέο-, ''osteo-'' and βλαστάνω, ''blastanō'' "germinate") are cells with a single nucleus that synthesize bone. However, in the process of bone formation, osteoblasts functio ...
and osteoclast
An osteoclast () is a type of bone cell that breaks down bone tissue. This function is critical in the maintenance, repair, and remodeling of bones of the vertebral skeleton. The osteoclast disassembles and digests the composite of hydrated pro ...
ic cells appears to be a key factor in age-related osteoporosis.
Osteoporosis treatment includes advice to stop smoking, decrease alcohol consumption, exercise regularly, and have a healthy diet. Calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar t ...
and trace mineral
In the context of nutrition, a mineral is a chemical element required as an essential nutrient by organisms to perform functions necessary for life. However, the four major structural elements in the human body by weight (oxygen, hydrogen, carbon, ...
supplements may also be advised, as may Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of fat-soluble secosteroids responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, and many other biological effects. In humans, the most important compounds in this group are vitamin D3 (c ...
. When medication is used, it may include bisphosphonate
Bisphosphonates are a class of drugs that prevent the loss of bone density, used to treat osteoporosis and similar diseases. They are the most commonly prescribed drugs used to treat osteoporosis. They are called bisphosphonates because they ...
s, Strontium ranelate
Strontium ranelate, a strontium(II) salt of ranelic acid, is a medication for osteoporosis marketed as Protelos or Protos by Servier. Studies indicate it can also slow the course of osteoarthritis of the knee. The drug is unusual in that it bo ...
, and hormone replacement therapy
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT), also known as menopausal hormone therapy or postmenopausal hormone therapy, is a form of hormone therapy used to treat symptoms associated with female menopause. These symptoms can include hot flashes, vaginal ...
.
Osteopathic medicine
Osteopathic medicine
Osteopathy () is a type of alternative medicine that emphasizes physical manipulation of the body's muscle tissue and bones. Practitioners of osteopathy are referred to as osteopaths.
Osteopathic manipulation is the core set of techniques in ...
is a school of medical thought originally developed based on the idea of the link between the musculoskeletal system and overall health, but now very similar to mainstream medicine. , over 77,000 physicians in the United States are trained in osteopathic medical schools.
Osteology
The study of bones and teeth is referred to as osteology. It is frequently used inanthropology
Anthropology is the scientific study of humanity, concerned with human behavior, human biology, cultures, societies, and linguistics, in both the present and past, including past human species. Social anthropology studies patterns of be ...
, archeology and forensic science for a variety of tasks. This can include determining the nutritional, health, age or injury status of the individual the bones were taken from. Preparing fleshed bones for these types of studies can involve the process of maceration.
Typically anthropologists and archeologists study bone tool
In archaeology, a bone tool is a tool created from bone. A bone tool can conceivably be created from almost any bone, and in a variety of methods.
Bone tools have been documented from the advent of '' Homo sapiens'' and are also known from ''Ho ...
s made by ''Homo sapiens
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
'' and ''Homo neanderthalensis
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. While the ...
''. Bones can serve a number of uses such as projectile points or artistic pigments, and can also be made from external bones such as antlers.
Other animals


Bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
skeletons are very lightweight. Their bones are smaller and thinner, to aid flight. Among mammals, bat
Bats are mammals of the order Chiroptera.''cheir'', "hand" and πτερόν''pteron'', "wing". With their forelimbs adapted as wings, they are the only mammals capable of true and sustained flight. Bats are more agile in flight than most ...
s come closest to birds in terms of bone density, suggesting that small dense bones are a flight adaptation. Many bird bones have little marrow due to them being hollow.
A bird's beak
The beak, bill, or rostrum is an external anatomical structure found mostly in birds, but also in turtles, non-avian dinosaurs and a few mammals. A beak is used for eating, preening, manipulating objects, killing prey, fighting, probing for foo ...
is primarily made of bone as projections of the mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone ...
s which are covered in keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, ho ...
.
Some bones, primarily formed separately in subcutaneous tissues, include headgears (such as bony core of horns, antlers, ossicones), osteoderm, and os penis
The baculum (also penis bone, penile bone, or ''os penis'', ''os genitale'' or ''os priapi'') is a bone found in the penis of many placental mammals. It is absent from the human penis, but present in the penises of some primates, such as the ...
/ os clitoris The os clitoridis (also called the os clitoris or baubellum) is a bone inside the clitoris of many mammalian taxa. It is absent from the human clitoris, but present in the clitoris of some primates, such as the ring-tailed lemurs. It is homologo ...
. A deer
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the re ...
's antlers are composed of bone which is an unusual example of bone being outside the skin of the animal once the velvet is shed.
The extinct predatory fish ''Dunkleosteus
''Dunkleosteus'' is an extinct genus of large armored, jawed fishes that existed during the Late Devonian period, about 382–358 million years ago. It consists of ten species, some of which are among the largest placoderms to have ever lived: ...
'' had sharp edges of hard exposed bone along its jaws.
The proportion of cortical bone that is 80% in the human skeleton may be much lower in other animals, especially in marine mammal
Marine mammals are aquatic mammals that rely on the ocean and other marine ecosystems for their existence. They include animals such as seals, whales, manatees, sea otters and polar bears. They are an informal group, unified only by their ...
s and marine turtles
Sea turtles (superfamily Chelonioidea), sometimes called marine turtles, are reptiles of the order Testudines and of the suborder Cryptodira. The seven existing species of sea turtles are the flatback, green, hawksbill, leatherback, loggerhead, ...
, or in various Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretace ...
marine reptiles, such as ichthyosaurs, among others. This proportion can vary quickly in evolution; it often increases in early stages of returns to an aquatic lifestyle, as seen in early whale
Whales are a widely distributed and diverse group of fully aquatic placental marine mammals. As an informal and colloquial grouping, they correspond to large members of the infraorder Cetacea, i.e. all cetaceans apart from dolphins and ...
s and pinniped
Pinnipeds (pronounced ), commonly known as seals, are a widely range (biology), distributed and diverse clade of carnivorous, fin-footed, semiaquatic, mostly marine mammal, marine mammals. They comprise the extant taxon, extant family (biology ...
s, among others. It subsequently decreases in pelagic taxa, which typically acquire spongy bone, but aquatic taxa that live in shallow water can retain very thick, pachyostotic, osteosclerotic, or pachyosteosclerotic bones, especially if they move slowly, like sea cows. In some cases, even marine taxa that had acquired spongy bone can revert to thicker, compact bones if they become adapted to live in shallow water, or in hypersaline
A hypersaline lake is a landlocked body of water that contains significant concentrations of sodium chloride, brines, and other salts, with saline levels surpassing that of ocean water (3.5%, i.e. ).
Specific microbial species can thrive in hi ...
(denser) water.
Many animals, particularly herbivores, practice osteophagy
Osteophagy is the practice in which animals, usually herbivores, consume bones. Most vegetation around the world lacks sufficient amounts of phosphate. Phosphorus is an essential mineral for all animals, as it plays a major role in the formation o ...
—the eating of bones. This is presumably carried out in order to replenish lacking phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosph ...
.
Many bone diseases that affect humans also affect other vertebrates—an example of one disorder is skeletal fluorosis.
Society and culture
 Bones from slaughtered animals have a number of uses. In
Bones from slaughtered animals have a number of uses. In prehistoric times
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of ...
, they have been used for making bone tool
In archaeology, a bone tool is a tool created from bone. A bone tool can conceivably be created from almost any bone, and in a variety of methods.
Bone tools have been documented from the advent of '' Homo sapiens'' and are also known from ''Ho ...
s. They have further been used in bone carving
Grazing caribou made in Alaska 1910 - Linden Museum
Bone carving is creating art, tools, and other goods by carving animal bones, antlers, and horns. It can result in the ornamentation of a bone by engraving, painting or another technique, ...
, already important in prehistoric art
In the history of art, prehistoric art is all art produced in preliterate, prehistorical cultures beginning somewhere in very late geological history, and generally continuing until that culture either develops writing or other methods of rec ...
, and also in modern time as crafting materials for buttons, beads, handles, bobbins, Napier's bones, calculation aids, head nuts, dice, poker chips, pick-up sticks, arrows, scrimshaw, ornaments, etc.
Bone glue can be made by prolonged boiling of ground or cracked bones, followed by filtering and evaporation to thicken the resulting fluid. Historically once important, bone glue and other animal glues today have only a few specialized uses, such as in antiques restoration. Essentially the same process, with further refinement, thickening and drying, is used to make gelatin.
Broth is made by simmering several ingredients for a long time, traditionally including bones.
Bone char, a porous, black, granular material primarily used for filtration and also as a black pigment, is produced by charring mammal bones.
Oracle bone script was a writing system used in Ancient China based on inscriptions in bones. Its name originates from oracle bones, which were mainly ox clavicle. The Ancient Chinese (mainly in the Shang dynasty), would write their questions on the oracle bone, and burn the bone, and where the bone cracked would be the answer for the questions.
To :wikt:point the bone, point the bone at someone is considered bad luck in some cultures, such as Australian aborigines, such as by the Kurdaitcha#Bone pointing, Kurdaitcha.
The Furcula, wishbones of fowl have been used for divination, and are still customarily used in a tradition to determine which one of two people pulling on either prong of the bone may make a wish.
Various cultures throughout history have adopted the custom of shaping an infant's head by the practice of artificial cranial deformation. A widely practised custom in China was that of foot binding to limit the normal growth of the foot.
Additional images
See also
* Artificial bone * Bone health * Distraction osteogenesis * National Bone Health Campaign * SkeletonReferences
Further reading
* * * * – ''drawings by Philip J.'' * * – ''Anthony edits the current version; Harrison edited previous versions.''External links
Educational resource materials (including animations) by the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research
* [http://www.scq.ubc.ca/?p=400 A good basic overview of bone biology from the Science Creative Quarterly] *
Bone histology photomicrographs
{{Authority control Bones Skeletal system Connective tissue