Telecommunications in Kosovo on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Due to missing 3G/ LTE licenses in Kosovo, and a growing demand for mobile broadband services from subscribers, both telecommunication providers PTK and IPKO turned to
Due to missing 3G/ LTE licenses in Kosovo, and a growing demand for mobile broadband services from subscribers, both telecommunication providers PTK and IPKO turned to
 The Internet Exchange Point (KOSIX), the first of its kind in Kosovo, started operating on 23 June 2011, and it operates as a functional unit within Telecommunications Regulatory Authority (TRA). Its function is to provide the ISPs operating in Kosovo, an Internet exchange point for local traffic exchange.
Valuable and continuous contributions for the implementation of this project have given:
The Internet Exchange Point (KOSIX), the first of its kind in Kosovo, started operating on 23 June 2011, and it operates as a functional unit within Telecommunications Regulatory Authority (TRA). Its function is to provide the ISPs operating in Kosovo, an Internet exchange point for local traffic exchange.
Valuable and continuous contributions for the implementation of this project have given:
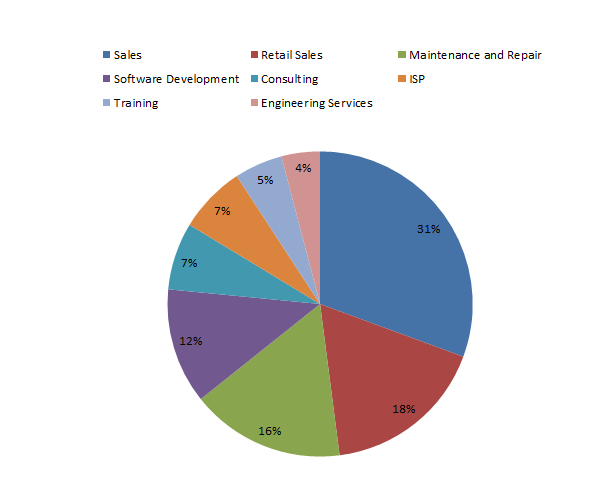 *Sales - 33%
*Retail Sales - 18.7%
*Maintenance and Repair - 17.6%
*Software Development - 13.2%
*Consulting - 7.7
*ISP - 7.7%
*Training - 5.5%
*Engineering Services - 4.4%
*Sales - 33%
*Retail Sales - 18.7%
*Maintenance and Repair - 17.6%
*Software Development - 13.2%
*Consulting - 7.7
*ISP - 7.7%
*Training - 5.5%
*Engineering Services - 4.4%

CACTTUS Education
- since 2016 has a number of programs in systems and software engineering offering two year professional vocational Education in ICT *Professional training centers and academies (Cisco, Microsoft, ECDL, Oracle, RedHat etc.) *Universities abroad.

History of IPKOLet's Outsource in KosovoDutch smartphone apps digitize wanted posters
Kosova Association of Information and Communication Technology
Free Libre Open Source Software Kosova
Regulatory Authority of Electronics and Postal Communication
Kosovo Internet Exchange
IPKO Foundation
Innovation Centre Kosovo (ICK)
Innovations Lab KosovoCACTTUS EducationTelecommunications Regulatory Authority (ART)
{{Kosovo topics Science and technology in Kosovo Telecommunications in Kosovo Information technology by country
Information and communication technology
Information and communications technology (ICT) is an extensional term for information technology (IT) that stresses the role of unified communications and the integration of telecommunications ( telephone lines and wireless signals) and computer ...
(ICT) in Kosovo
Kosovo ( sq, Kosova or ; sr-Cyrl, Косово ), officially the Republic of Kosovo ( sq, Republika e Kosovës, links=no; sr, Република Косово, Republika Kosovo, links=no), is a partially recognised state in Southeast Euro ...
has experienced a remarkable development since 1999. From being almost non-existent 10 years ago, Kosovar companies in the information technology
Information technology (IT) is the use of computers to create, process, store, retrieve, and exchange all kinds of Data (computing), data . and information. IT forms part of information and communications technology (ICT). An information te ...
(IT) domain offer today wide range of ICT services to their customers both local as well as to foreign companies. Kosovo has the youngest population in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
, with advanced knowledge in ICT.
Today, public and private education institutions in the IT field, through certified learning curricula by companies such as CISCO
Cisco Systems, Inc., commonly known as Cisco, is an American-based multinational digital communications technology conglomerate corporation headquartered in San Jose, California. Cisco develops, manufactures, and sells networking hardware, ...
and Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational technology corporation producing computer software, consumer electronics, personal computers, and related services headquartered at the Microsoft Redmond campus located in Redmond, Washin ...
, provide education to thousands of young Kosovars while the demand for this form of training is still rising.
Kosovo has two authorized mobile network operators
A mobile network operator (MNO), also known as a wireless service provider, wireless carrier, cellular company, or mobile network carrier, is a provider of wireless communications services that owns or controls all the elements necessary to sell ...
and is the only country in the region not having awarded any UMTS
The Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) is a third generation mobile cellular system for networks based on the GSM standard. Developed and maintained by the 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project), UMTS is a component of the In ...
license. Kosovo has neither awarded licenses for fixed wireless access, nor made the 900 and 1800 MHz bands technology neutral. Currently around 1,200,000 customers of "Vala" Post and Telecom of Kosovo
Post and Telecommunications of Kosovo (commonly abbreviated as PTK; sq, Posta dhe Telekomi i Kosovës) is the postal and telecommunications authority of Kosovo.
History
The company was founded in 1959, originally under the name of "The Post, ...
(PTK). As of March 2007 the second GSM
The Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) is a standard developed by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) to describe the protocols for second-generation ( 2G) digital cellular networks used by mobile devices such ...
license granted to IPKO
IPKO is a company that provides telecommunication services in Kosovo. It is the second mobile operator in the country. Amongst their services are: mobile telephony, fixed telephony, internet provider and cable TV. The main shareholder of the compa ...
– Telekom Slovenije
Telekom Slovenije d.d. (, "Telecom of Slovenia") is a telecommunications company based in Slovenia, with its headquarters in Ljubljana.
History
In 1994 PTT Slovenija separated postal and telecommunication activities and transferred all telecommuni ...
. Currently IPKO has over 1,000,000 users. Following the Brussels Agreement, Kosovo has its own telephone dialing code: 383. Before this assignment, network operators in Kosovo used either 387 (Monaco) or 386 (Slovenia). All other codes were to have been superseded by the new code on 15 January 2017, but some are still in use.
The infrastructure of ICT sector in Kosovo is mainly built of microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from about one meter to one millimeter corresponding to frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz respectively. Different sources define different frequency ra ...
network
Network, networking and networked may refer to:
Science and technology
* Network theory, the study of graphs as a representation of relations between discrete objects
* Network science, an academic field that studies complex networks
Mathematics ...
, optic
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultravio ...
and coaxial cable (DOCSIS
Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification (DOCSIS) is an international telecommunications standard that permits the addition of high-bandwidth data transfer to an existing cable television (CATV) system. It is used by many cable televisio ...
). The telecom industry is liberalized and legislation is introduced adopting European union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
regulatory principles and promoting competition. Some of the main internet providers are PTK, IPKO, Kujtesa and Artmotion
History
First ICT companies in Kosovo can be found as early 1984, these companies where mainly focused onradio
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmi ...
telecommunication
Telecommunication is the transmission of information by various types of technologies over wire, radio, optical, or other electromagnetic systems. It has its origin in the desire of humans for communication over a distance greater than that fe ...
and audio-video systems, while in early and mid '90s more companies were created, mainly specializing in personal computer
A personal computer (PC) is a multi-purpose microcomputer whose size, capabilities, and price make it feasible for individual use. Personal computers are intended to be operated directly by an end user, rather than by a computer expert or tec ...
sales. ICT industry in Kosovo boomed after 1999 with a lot of new companies being created, among which IPKO which now one of the major telecommunication
Telecommunication is the transmission of information by various types of technologies over wire, radio, optical, or other electromagnetic systems. It has its origin in the desire of humans for communication over a distance greater than that fe ...
providers and one of the biggest foreign investments in Kosovo.
Telecommunications
According to Regulatory Authority of Electronics and Postal Communication 2011 report, 86 telecommunication licenses have been issued since 2004.Mobile Telephony
In 2010, 74 percent of the population was subscribed to mobile phone services, or a total number of 1,537,164 In 2007, PTK reported growth of subscribers from 300,000 to 800,000 in less than a year. In 2006, the number was 562,000. You are required to show your ID to get a Sim card and pre-paid can be bought for 5 euros. There are many shops selling used mobile phones and sim unlocking services. Two licensed Mobile network operators offer their services in competition with twoMVNO
A mobile virtual network operator (MVNO) is a wireless communications services provider that does not own the wireless network infrastructure over which it provides services to its customers. An MVNO enters into a business agreement with a mobile ...
s. The market, however, remains concentrated with the incumbent‟s mobile subsidiary controlling over 65% of the market. Mobile broadband services are not available as no UMTS licenses have been awarded. So far, there are no plans to carry out the re-farming of 900/1800 MHz bands or assign frequency spectrum
The power spectrum S_(f) of a time series x(t) describes the distribution of power into frequency components composing that signal. According to Fourier analysis, any physical signal can be decomposed into a number of discrete frequencies, ...
for mobile broadband.
There are three virtual operators :
* D3 Mobile (virtual operator)-043 prefix
* Z Mobile (virtual operator)-045 prefix
* Zog Mobile (Powered by IPKO)-043 prefix
Fixed Telephony
Fixed telephony penetration rate is among the lowest in Europe about 5 lines per 100 inhabitants in 2011, in contrast with neighboring countries and European Union countries where penetration rates are 25% and 40% respectfully. There are currently three licensed Fixed Telephony providers in Kosovo: *PTK *IPKO *KONET (leased lines) PTK is by far the leading provider with market share of 94.4%, IPKO has only 5.6%. Number of subscribers dropped in 2011 to 86,014 from 88,372 in 2010, marking a drop of 2,358 or 2.67% of subscriber base.Dialing Code
After the breakup ofYugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
, with dialing code 38, Kosovo used the Serbian dialing code, 381 for new and existing landlines. As mobile networks were introduced, PTK adopted the code 377 (Monaco) and IPKO adopted the code 386 (Slovenia). This situation resulted in the highly unusual simultaneous use of three international dialing codes.
In September 2012 the Assembly of Kosovo
The Assembly of the Republic of Kosovo ( sq, Kuvendi i Republikës së Kosovës; sr, Скупштина Републике Косово, Skupština Republike Kosovo) is the unicameral legislature of the Republic of Kosovo that is directly electe ...
approved a resolution on replacing the various dialing codes in use with the Albanian country code 355. While this initiative draw a lot of media attention, it never saw the light of day.
In January 2016 after ongoing political discussions between Kosovo and Serbia, it was agreed that Kosovo would get its own country code: 383. This code is available for all mobile and fixed-line operators, all of whom were using other international telecom country code. The code 383 has now been formally assigned, and is in the process of adoption. This code was to have replaced all former codes on 15 January 2017, but the transition has yet to be complete.
Internet
Total of 38 licensed companies provide internet services in Kosovo, 6 of them with direct peering towards international gateways. Number of technologies are used to provide internet to end users, most popular being the cable DOCSIS technology with 68.95% of the market, followed by 25.43% xDSL and 5.62% other technologies like FTTX and wireless. In contrast with other countries, majority of market share is owned by private operators, with a total of 74.57%. The biggest operator being IPKO with 51.21% followed by Kujtesa with 19.08% and PTK with 25.43%. Others include: * Artmotion * ArdiNet * OrangeNet * I.T.S. * ComNet * NegeNet *Telekom Srbija
Telekom Srbija a.d. Beograd is a Serbian state-owned telecommunications operator. It was founded in May 1997 as a joint-stock company, by spinning off the telecommunications business from PTT Srbija (present-day „ Pošta Srbije"). In April 201 ...
Internet Penetration
Internet penetration in Kosovo is 96%. Laptops are the most frequent device found in almost half of the Kosovo households (48%), followed by a computer (39%). On average, households in Kosovo have a 20 Mbps download and 6 upload internet speed. Vast majority of the Kosovo population (81%) use the internet every day, and the internet is used by the absolute majority (96%) of the Kosovo population at least at some occasion. In addition, the internet usage is almost equally distributed across majority of age groups and is mostly used by students and employed people. Internet is used three and a half hours daily on average by the Kosovo citizens. Incomparably, mobile phones are the most frequent device (73%) used to access the internet. A very important discovery of the research is that 93% of Kosovo citizens use the internet for communication. All other reasons of usage are drastically lower compared to the communication. Consequently, as well as related to the reasons why the internet is used mostly in terms of applications and webpages visited, communication platforms are used the most. The vast majority of Kosovo citizens (98%) possess a mobile phone, and close to half of them (43%) possesses internet subscription on their phone.Digital Television
Digital television transition is still an ongoing process in Kosovo, limiting the analog television broadcast domain to only three national channels. Due to this conditions all four major telecommunications companies in Kosovo now broadcastdigital TV
Digital television (DTV) is the transmission of television signals using digital encoding, in contrast to the earlier analog television technology which used analog signals. At the time of its development it was considered an innovative adva ...
on other mediums. While IPKO and Kujtesa have chosen to reuse the existing coaxial network, PTK which offers xDSL services went for IPTV
Internet Protocol television (IPTV) is the delivery of television content over Internet Protocol (IP) networks. This is in contrast to delivery through traditional terrestrial, satellite, and cable television formats. Unlike downloaded med ...
, Artomotion offers digital TV to selected users in Pristina.
IPKO has recently launched an IPTV solution, tailored towards mobile customers. Currently platform is available in iOS
iOS (formerly iPhone OS) is a mobile operating system created and developed by Apple Inc. exclusively for its hardware. It is the operating system that powers many of the company's mobile devices, including the iPhone; the term also include ...
, Android and via a web browser.
Metro WiFi
Municipal wireless network
A municipal wireless network is a citywide wireless network. This usually works by providing municipal broadband via Wi-Fi to large parts or all of a municipal area by deploying a wireless mesh network. The typical deployment design uses hundred ...
(Muni Wi-Fi). Both operators cover the majority of cities around Kosovo and touristic destinations like Prekaz and Brezovica, with more cities to be covered later.
Kosovo Internet Exchange Point
United States Agency for International Development
The United States Agency for International Development (USAID) is an independent agency of the U.S. federal government that is primarily responsible for administering civilian foreign aid and development assistance. With a budget of over $27 b ...
(USAID) offered throughout their program Kosovo Private Enterprise Program, Norwegian government
The politics of Norway take place in the framework of a parliamentary, representative democratic constitutional monarchy. Executive power is exercised by the Council of State, the cabinet, led by the prime minister of Norway. Legislative power is ...
offered through Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Norwegian embassy respectively, Cisco Systems International BV, and University of Prishtina
The University of Pristina ( sq, Universiteti i Prishtinës) is a public university located in Pristina, Kosovo. It is the institution that emerged after the disestablishment of the University of Pristina (1969–99) as a result of the K ...
which have offered adequate space within the buildings of Electrical and Computer Engineering Faculty.
Currently four national ISPs are interconnected via KOSIX, there is no cost for peering.
Economical aspects
ICT in Kosovo consists of relatively young companies (most of them incorporated after 1999) and with predominantly small companies with less than 20 employees. 53.8 percent of ICT companies are individual business whilelimited Liability Company
A limited liability company (LLC for short) is the US-specific form of a private limited company. It is a business structure that can combine the pass-through taxation of a partnership or sole proprietorship with the limited liability of ...
(28.6 percent). Businesses specializing in maintenance and manufacturing are purely individual, while other sub-sectors are served by a mix of individual and LLC businesses. Other forms of incorporation are rare, with 4.4 percent being Limited Partnership, and 2.2 percent Joint-Stock Company. The rest (5.5) are either public companies
A public company is a company whose ownership is organized via shares of stock which are intended to be freely traded on a stock exchange or in over-the-counter markets. A public (publicly traded) company can be listed on a stock exchange (list ...
or have the unusual status of NGO
A non-governmental organization (NGO) or non-governmental organisation (see spelling differences) is an organization that generally is formed independent from government. They are typically nonprofit entities, and many of them are active in h ...
s.
Currently, the ICT companies are determined to grow and prosper within the Kosovo market, while very few companies seek expansion in markets outside Kosovo.
According to TRA report, ICT industry generated €239,518,037.36, 83.19 of which is generated by Mobile network operator, 8.37% from Fix telephony operators, 7.77% from Internet service providers and 0.68% from leased lines
A leased line is a private telecommunications circuit between two or more locations provided according to a commercial contract. It is sometimes also known as a private circuit, and as a data line in the UK. Typically, leased lines are used by ...
.
Market
The structure of the ICT market in Kosovo is diverse in the variety of activities, sales being the main activity 62 percent of the ICT companies have reported to import goods for retail, meanwhile their exports are minimal and their market share growth is seen to be within Kosovo, and could reach as far asNorth Macedonia
North Macedonia, ; sq, Maqedonia e Veriut, (Macedonia before February 2019), officially the Republic of North Macedonia,, is a country in Southeast Europe. It gained independence in 1991 as one of the successor states of Yugoslavia. It ...
and Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares ...
. The average annual turnover in the sector is 250,000 euros, with an increasing number of companies reporting turnovers in millions of euros.
 *Sales - 33%
*Retail Sales - 18.7%
*Maintenance and Repair - 17.6%
*Software Development - 13.2%
*Consulting - 7.7
*ISP - 7.7%
*Training - 5.5%
*Engineering Services - 4.4%
*Sales - 33%
*Retail Sales - 18.7%
*Maintenance and Repair - 17.6%
*Software Development - 13.2%
*Consulting - 7.7
*ISP - 7.7%
*Training - 5.5%
*Engineering Services - 4.4%
Ownership
The ICT sector is dominated by domestic firms. According to the survey, 80.2 percent of the respondents represented companies that are 100% domestically owned. Only 6.6 percent of the companies are entirely owned by foreigners. Mixed ownership is rare (3.3 percent). The other 3.3 percent that answered "Other" were either mostly owned by foreign companies or public/state-owned companies. Foreign investors are mostly present in the sub-sectors: consulting, information services, vendors, manufacturing/assembling, and retail.Size and Employment
The majority of ICT companies is small. More than three-quarters (77.1 percent) employ from one to twenty employees. Only a handful of the companies have more than 100 employees. Most of the employees working in the ICT sector are male, leaving the female employees in a tiny minority. Around 19 percent of the companies do not have any female employees at all. Over 93 per cent employ up to 10 women, 6 per cent of the firms employ between 11 and 20, and only 1.4 percent up to 30. There is one large company which employs 230 female workers.
Average Salary
This list is a result of a survey conducted by USAID, Kosovo Private Enterprise Program with 829 ICT companies.Kosovo Association of information and technology (STIKK)
According to statute, STIKK is a non-profit association founded and registered in accordance with the Law on Freedom of Association and Non-Governmental Organization. STIKK represents the interests of the information and communications technology of Kosova, and the interests of professionals in ITC industry.Educational aspects
The increasing number of vacancies for ICT professionals in Kosovo is reflecting the increasing progress of the industry, although thanks to the high quality of the university education of IT specialists, and the increasing interest of young people in modern technologies, there are no signs of systematic shortages in ICT employment, except a registered under-supply of specialists in the field of software development and programming. The number of ICT graduates grows each year and the leader in providing the needed skills to the industry is the Faculty of Electrical and Computer Engineering of the University of Pristina. ICT skilled professionals are also supplied by the University for Business and Technology, the American University in Kosovo, as well as a few vocational education providers. According to the Kosovo Accreditation Agency there are currently 13 higher education institutions, public and private, accredited to offer ICT related study programs in their curricula.The State University of Pristina
*Faculty of Electrical and Computer Engineering, *Faculty of Natural Sciences, Department of Computer Science, *Faculty of Applied Technical Sciences, Mitrovica.The State University of Prizren
*Faculty of Computer Science.Private Universities
* American University in Kosovo - has since 2003 an Information Technology program in bachelor studies, *University for Business and Technology - has an ICT related program both in bachelor and master studies. AAB College https://aab-edu.net/ AAB College is the first non-public institution of higher education in KosovoPrivate Colleges
*AAB Riinvest - has an ICT related program - Software Engineering in bachelor studies, and also the same one in the master studies. *European College Dukagjini - has two bachelor programs related to ICT as of 2011: Management and Informatics, and Applied Informatics. *College Iliria - has two programs related to ICT: Management and Informatics, and Applied Informatics. Even though they have few master programs, none of them is related to ICT. *Vizioni Per Arsim has a bachelor program related to ICT:– Computer Science.Other
CACTTUS Education
- since 2016 has a number of programs in systems and software engineering offering two year professional vocational Education in ICT *Professional training centers and academies (Cisco, Microsoft, ECDL, Oracle, RedHat etc.) *Universities abroad.
Legislation
For a short period Kosovo has managed to adopt few very important pieces of legislation and a strategic framework to support the government’s efforts to regulate, promote and improve the development of the ICT sector in Kosovo. Some of the most important legislative acts that have influenced the progress of the sector are:Laws
*Telecommunications law. – Adopted in 2002, the law governs all telecommunications services and all telecommunications service providers in Kosovo. The main objective of the Telecommunications law is to create a transparent legal and regulatory environment for the promotion of more investments in the sector and encourage competition. *Law on Information Society Services. – Approved in 2005 with the aim of enabling the legal use of electronic documentation, and facilitate the implementation of e-commerce, e-signature and personal data protection. *Law on Administrative Procedure – created to control the electronic implementation of the activities of public administration. *Law on Copyright and Related Rights. *Law on Scientific Research Activity. *Law on the Protection of Personal Data. *Law on Prevention and Fight against Cyber Crime. *Law for Privacy and Database Access. *Law on Digital Signatures *Postal Services LawStrategic Framework
*eSEE Agenda Plus for the Development of Information Society in SEE 2007-2012 - Kosovo is an active member of the regional eSEE Initiative - (Electronic South East Europe). The main objective of the initiative is to integrate SEE countries into the global, knowledge-based economy through development of the Information Society, in line with the European Union i2010 framework. *National Strategy for Information Society 2006-2012 – The Strategy was adopted by the Government of Kosovo in 2006. *Electronic Governance Strategy 2009-2015 – Published by the Department of Information Technology of the Ministry of Public Services of Kosovo in 2008, ensuring the provision of governmental institutions’ services through information technology and communication (WAN, Internet, mobile network) to citizens, businesses and others. *E-learning Strategy for Kosovo 2011 - 2015 – Prepared by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology with the main objective to transform e-learning into an integral part of the overall national educational system. *Strategy for Development of Pre-university Education 2007–2017 – Adopted by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology and used as a basis for the development of the education system of Kosovo. *Kosovo Education Strategic Plan 2011-2016 – Drafted in September 2010, the Strategic Plan is going to include eight priority programs among which are Capacity Building and Information and Communication Technology. The objective implemented in the ICT program is to fully develop and integrate ICT infrastructure and technical support needed to implement and sustain good educational practices.Agencies
Regulatory Authority of Electronics and Postal Communication
Law on Telecommunications adopted by the Assembly and promulgated by UNMIK, Regulation 2003/16,recognizes the need to improve the telecommunications sector of Kosovo, by establishing an independent regulatory agency responsible for licensing and supervising the providers of telecommunications services in Kosovo, encouraging the private sector participation and competition in the provision of services; setting standards for all service providers in Kosovo, and, establishing provisions for consumer protection. TRA officially started operating in January 2004. During its young development TRA went through some important milestones that represented a very important step towards a free, competitive market which promotes the development of the information society in Kosova.Digital Divide
Age
Due to the overly young population in Kosovo, digital divide is not very notable, this phenomenon is more notable with people in their fifties and above. This problem was evident with the educational system as well, to address this Government of Kosovo organized an ECDL course for about 27000 teachers across Kosovo.Gender
The labor force in the ICT sector is dominated by men with women comprising a marginal portion (although more significant in larger companies).Location
Most ICT firms are based in the Pristina, the economic, political, and social center of the country, where most businesses are located and where there is the highest concentration of customers, as much as 81 percent of all ICT companies have Prishtina as their head office location. The rest are fairly evenly spread out in the regional centers: Peja, Prizren, Gjilan, Gjakova, Podujeva, and Ferizaj.Open source
Over the years there have been a number of open source organizations including Albanian Linux user group (AlbaLinux). Due to lack of support, most of them are now "passive"; among the most active and successful open source groups is Free Libre Open Source Software Kosova (FLOSSK). *Free Libre Open Source Software Kosova (FLOSSK) FLOSSK began in March 2009 at the initiative of James Michael DuPont as a result of the desire to organize a conference on free and open software. After six difficult months and with the help of many supporters, FLOSSK organized the first conference of free and open software in Kosovo in August 2009. Apart from the conference, FLOSSK continued to work in various activities such as organizing Software Freedom Days in different cities of Kosovo, lectures on free software throughout Kosovo, translating software, collaborating with the media to promote free software and creating local free software groups in various cities. From the beginning, FLOSSK members and the general public learned about Linux operating system, FLOSS programs for solving everyday problems, map creation using OpenStreetMap, and met free software movement figures from around the world. * Software Freedom Kosova Software Freedom Kosova Conference is an annual conference on free and open source software and related developments in knowledge, culture and mapping held in Pristina, Kosovo. It is the largest conference of its kind in the region. The conference is organised by Free/Libre Open Source Software Kosova (FLOSSK), Kosovo Association of Information and Communication Technology, Ipko Foundation and Faculty of Electrical and Computer Engineering of the University of Prishtina.Outsourcing
A case study on ICT training in Kosovo performed by CISCO Networking Academy (NetAcad) states that the educated and experienced workforce as a whole is searching higher salaries and better working conditions abroad. If graduates are not experienced, they stay for a while in Kosovo and when they have gained experience they start searching opportunities for migration. It is exactly the findings that NetAcad case study revealed that make Kosovo a perfect ICT outsourcing country, and time difference with the USA makes it only more appealing for the U.S. market. Such is a story of 3CIS which provides highly specialized services to major telecommunication carriers across the globe. This includes network architecture design, planning, consulting, implementation, integration and testing with a strong expertise on mobile backhauling. 3CIS also provides on-site consulting ser- vices as well as manages and coordinates the activities in a multi-vendor environment during the life-cycle of the complete project. On top of this, 3CIS also offers Project management services that are tailored to suit client needs from initial planning to project completions. Kosovo has made it to other markets as well, both individually as well as established companies. Sprigs is the best example of a Kosovar start-up company established in Pristina. Anoniem is the highest-profile job to date for SPRIGS, which was founded in late 2010, by a Dutch entrepreneur, and this job was trusted to a half-dozen young Kosovar Albanian programmers, who work at computers at a repurposed apartment that now houses the technical brain trust of this IT outsourcing company.See also
*Economy of Kosovo
The economy of Kosovo is a transition economy. Kosovo was the poorest province of the former Yugoslavia with a modern economy established only after a series of federal development subsidies in the 1960s and the 1970s.
During the 1990s, the abolit ...
* Education in Kosovo
* American University in Kosovo
*Universiteti i Prishtinës
The University of Pristina ( sq, Universiteti i Prishtinës) is a public university located in Pristina, Kosovo. It is the institution that emerged after the disestablishment of the University of Pristina (1969–99) as a result of the K ...
* University of Prizren
* Media of Kosovo
* Telecommunications in Albania
Notes
References
Further reading
History of IPKO
External links
Kosova Association of Information and Communication Technology
Free Libre Open Source Software Kosova
Regulatory Authority of Electronics and Postal Communication
Kosovo Internet Exchange
IPKO Foundation
Innovation Centre Kosovo (ICK)
Innovations Lab Kosovo
{{Kosovo topics Science and technology in Kosovo Telecommunications in Kosovo Information technology by country
Kosovo
Kosovo ( sq, Kosova or ; sr-Cyrl, Косово ), officially the Republic of Kosovo ( sq, Republika e Kosovës, links=no; sr, Република Косово, Republika Kosovo, links=no), is a partially recognised state in Southeast Euro ...