Tau Herculis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Tau Herculis, a name Latinized from τ Herculis, is a 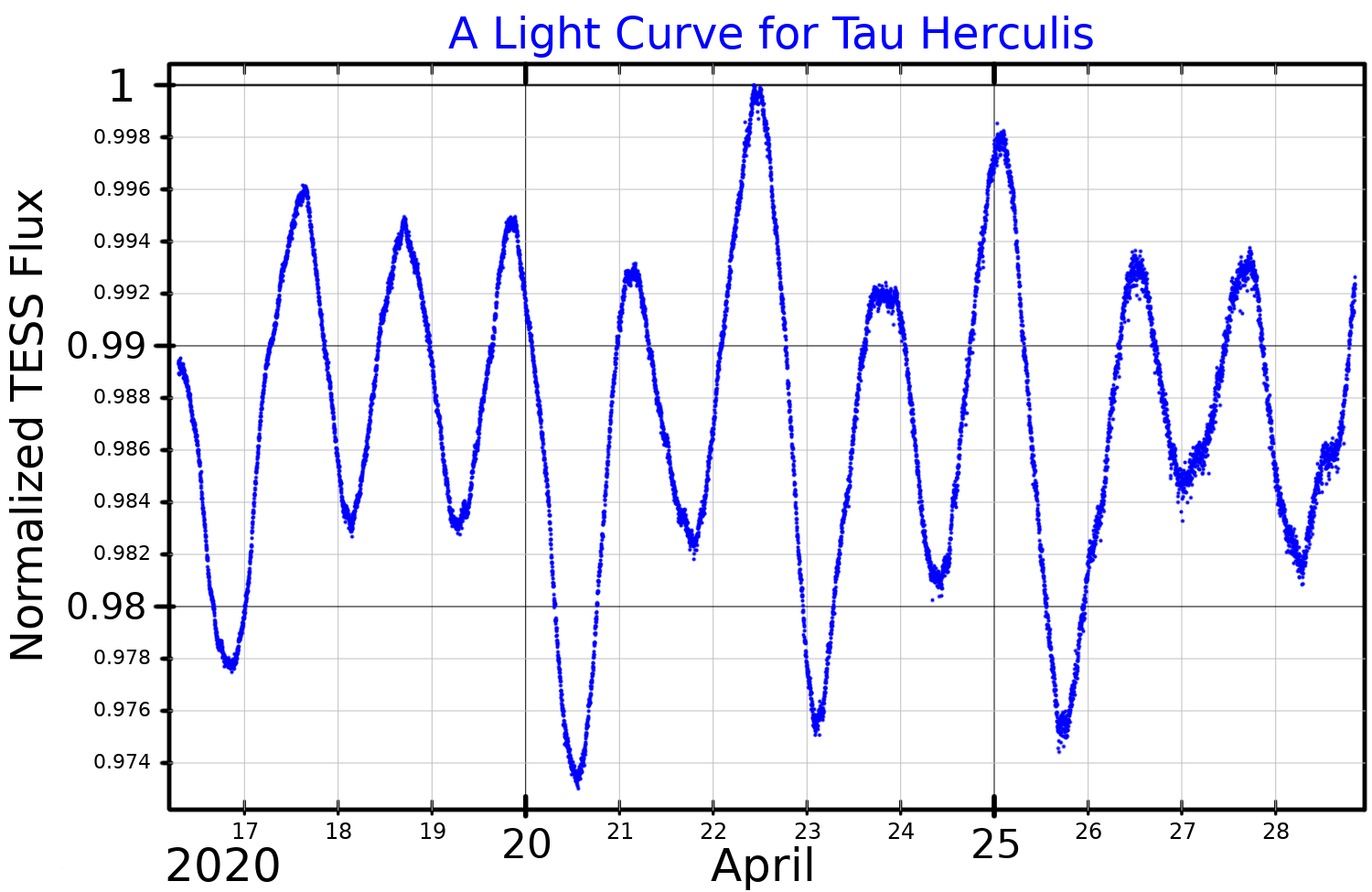 The stellar classification of Tau Hercules is B5 IV, and it serves as a standard
The stellar classification of Tau Hercules is B5 IV, and it serves as a standard
 Tau Herculis is located within 1° of the precessional path traced across the celestial sphere by the Earth's
Tau Herculis is located within 1° of the precessional path traced across the celestial sphere by the Earth's
variable star
A variable star is a star whose brightness as seen from Earth (its apparent magnitude) changes with time. This variation may be caused by a change in emitted light or by something partly blocking the light, so variable stars are classified as e ...
in the northern constellation of Hercules
Hercules (, ) is the Roman equivalent of the Greek divine hero Heracles, son of Jupiter and the mortal Alcmena. In classical mythology, Hercules is famous for his strength and for his numerous far-ranging adventures.
The Romans adapted the ...
. It has a blue-white hue and is visible to the naked eye at night with an apparent visual magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the brightness of a star or other astronomical object observed from Earth. An object's apparent magnitude depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance from Earth, and any extinction of the object's lig ...
that fluctuates around 3.91. The star is located at a distance of approximately 307 light years from the Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
based on parallax, but it is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −16 km/s.
 The stellar classification of Tau Hercules is B5 IV, and it serves as a standard
The stellar classification of Tau Hercules is B5 IV, and it serves as a standard spectrum
A spectrum (plural ''spectra'' or ''spectrums'') is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary, without gaps, across a continuum. The word was first used scientifically in optics to describe the rainbow of colors ...
in the modern Morgan–Keenan (MK) classification. It is estimated to be just 26 million years old with a relatively low projected rotational velocity
Stellar rotation is the angular motion of a star about its axis. The rate of rotation can be measured from the spectrum of the star, or by timing the movements of active features on the surface.
The rotation of a star produces an equatorial bulg ...
of 32 km/s. Slowly rotating B-type stars are often chemically peculiar, so the mostly normal spectra of this star suggests we may be viewing it from near pole-on. The abundance of most heavier elements in this star are about 85% of those in the Sun. The star has four times the mass of the Sun and around 3.8 times the Sun's radius. On average, it is radiating 574 times the luminosity of the Sun
The solar luminosity (), is a unit of radiant flux ( power emitted in the form of photons) conventionally used by astronomers to measure the luminosity of stars, galaxies and other celestial objects in terms of the output of the Sun.
One nominal ...
from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 15,615 K.
During the Hipparcos mission, Tau Hercules was discovered to be a variable star
A variable star is a star whose brightness as seen from Earth (its apparent magnitude) changes with time. This variation may be caused by a change in emitted light or by something partly blocking the light, so variable stars are classified as e ...
of the slowly pulsating B-type. These are mid-B main sequence stars that vary with a period of about a day; the brightness of Tau Hercules varies by 0.03 magnitude over a period of days. The radial velocity of the star varies at a different rate than the photometric period, with the object showing both radial and non-radial pulsation modes.
Historical significance and etymology
 Tau Herculis is located within 1° of the precessional path traced across the celestial sphere by the Earth's
Tau Herculis is located within 1° of the precessional path traced across the celestial sphere by the Earth's North pole
The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is the point in the Northern Hemisphere where the Earth's rotation, Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface. It is called the True North Pole to distingu ...
. It could have served the northern pole star
A pole star or polar star is a star, preferably bright, nearly aligned with the axis of a rotating astronomical body.
Currently, Earth's pole stars are Polaris (Alpha Ursae Minoris), a bright magnitude-2 star aligned approximately with its ...
around the year 7400 BCE, a phenomenon which is expected to reoccur in the year 18,400 due to precession
Precession is a change in the orientation of the rotational axis of a rotating body. In an appropriate reference frame it can be defined as a change in the first Euler angle, whereas the third Euler angle defines the rotation itself. In oth ...
.
Its traditional name, ''Rukbalgethi Shemali'', is of Arabic origin and shares certain etymological characteristics with the stars Ruchbah and Zubeneschamali
Beta Librae (β Librae, abbreviated Beta Lib, β Lib), formally named Zubeneschamali , is (despite its 'beta' designation) the brightest star in the zodiac constellation of Libra. From parallax measurements, its distance can be estimated ...
, signifying Hercules' "northern knee".
In Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
, (), meaning '' Seven Excellencies'', refers to an asterism consisting of τ Herculis, 42 Herculis, φ Herculis, χ Herculis, ν1 Boötis, μ1 Boötis and δ Boötis. ''中國星座神話'', written by 陳久金. Published by 台灣書房出版有限公司, 2005, . Consequently, the Chinese name
Chinese names or Chinese personal names are names used by individuals from Greater China and other parts of the Chinese-speaking world throughout East and Southeast Asia (ESEA). In addition, many names used in Japan, Korea and Vietnam are ofte ...
for τ Herculis itself is (, en, the Second Star of Seven Excellencies.)
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Tau Herculis B-type subgiants Slowly pulsating B stars Hercules (constellation) Herculis, Tau Durchmusterung objects Herculis, 022 147394 079992 6092 Rukbalgethi Shemali ar:ركبة الجاثي الشمالية