Tartary on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
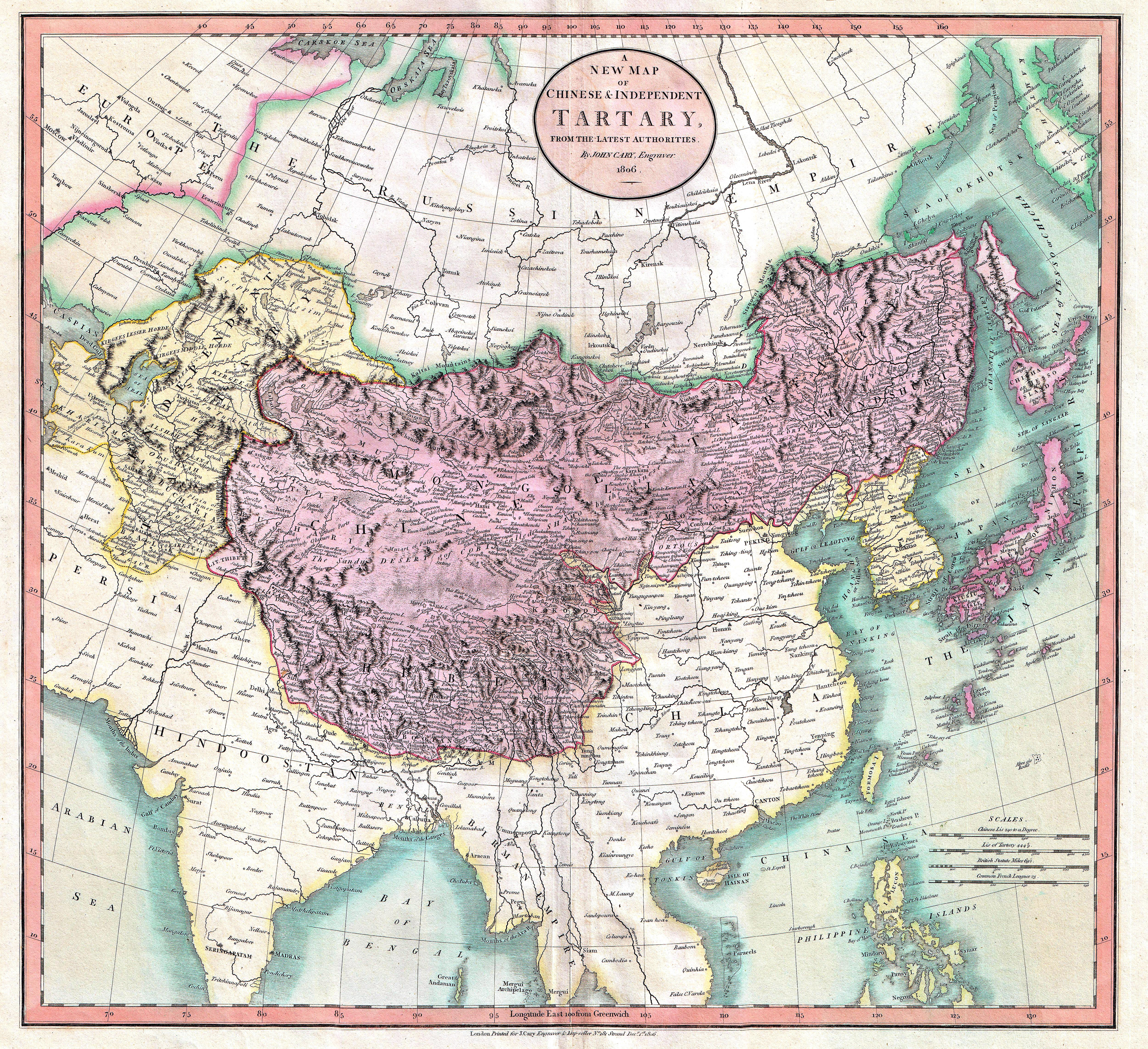 Tartary ( la, Tartaria, french: Tartarie, german: Tartarei, russian: Тартария, Tartariya) or Tatary (russian: Татария, Tatariya) was a blanket term used in
Tartary ( la, Tartaria, french: Tartarie, german: Tartarei, russian: Тартария, Tartariya) or Tatary (russian: Татария, Tatariya) was a blanket term used in
 Knowledge of
Knowledge of
1704 map of Tartary
* ttp://vlib.iue.it/carrie/texts/carrie_books/paksoy-6/cae02.html Nationality of Religion? Views of Central Asian Islam
Tatary – English World dictionary
Historical regions Geography of Russia History of Central Asia East Asia Mongol states Exonyms Pseudohistory Cartography
 Tartary ( la, Tartaria, french: Tartarie, german: Tartarei, russian: Тартария, Tartariya) or Tatary (russian: Татария, Tatariya) was a blanket term used in
Tartary ( la, Tartaria, french: Tartarie, german: Tartarei, russian: Тартария, Tartariya) or Tatary (russian: Татария, Tatariya) was a blanket term used in Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
an literature and cartography
Cartography (; from grc, χάρτης , "papyrus, sheet of paper, map"; and , "write") is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an i ...
for a vast part of Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
bounded by the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central A ...
, the Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western ...
, the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the conti ...
, and the northern borders of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
and Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, at a time when this region was largely unknown to European geographers.
The active use of the toponym
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of ''toponyms'' ( proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of ...
(place name) can be traced from the 13th to the 19th centuries. In European sources, Tartary became the most common name for Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the fo ...
that had no connection with the real polities or ethnic groups of the region; until the 19th century, European knowledge of the area remained extremely scarce and fragmentary. In modern English-speaking tradition, the region formerly known as Tartary is usually called Inner or Central Eurasia. Much of this area consists of arid plains, the main nomadic population of which in the past was engaged in animal husbandry
Animal husbandry is the branch of agriculture concerned with animals that are raised for meat, fibre, milk, or other products. It includes day-to-day care, selective breeding, and the raising of livestock. Husbandry has a long history, starti ...
.
Ignorance surrounding Tartary's use as a place name has spawned conspiracy theories including ideas of a "hidden past" and "mud flood
A flood is an overflow of water ( or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are an area of study of the discipline hydrol ...
s". Such theories assert that Tartary (or "Tartaria") was a lost civilization with advanced technology and culture. This ignores the well-documented history of Asia
The history of Asia can be seen as the collective history of several distinct peripheral coastal regions such as East Asia, South Asia, Southeast Asia and the Middle East linked by the interior mass of the Eurasian steppe. See History of the Mi ...
, which Tartary refers to. In the present day, the Tartary region covers a region spanning from central Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is borde ...
to northern Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
, as well as areas in present Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million ...
, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
and the Russian Far East
The Russian Far East (russian: Дальний Восток России, r=Dal'niy Vostok Rossii, p=ˈdalʲnʲɪj vɐˈstok rɐˈsʲiɪ) is a region in Northeast Asia. It is the easternmost part of Russia and the Asian continent; and is admin ...
in "Chinese Tartary
Chinese Tartary (see also Tartary) is an archaic geographical term used especially during the time of the Qing dynasty. The term "Tartar" was used by Europeans to refer to ethnicities living around China's north, northeast, and west, including ...
".
Geography and history
 Knowledge of
Knowledge of Manchuria
Manchuria is an exonym (derived from the endo demonym " Manchu") for a historical and geographic region in Northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day Northeast China (Inner Manchuria) and parts of the Russian Far East (Outer M ...
, Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part ...
and Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the fo ...
in Europe prior to the 18th century was limited. The entire area was known simply as "Tartary" and its inhabitants "Tartars". In the Early modern period, as understanding of the geography increased, Europeans began to subdivide Tartary into sections with prefixes denoting the name of the ruling power or the geographical location. Thus, Siberia was ''Great Tartary'' or ''Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
n Tartary'', the Crimean Khanate was ''Little Tartary'', Manchuria
Manchuria is an exonym (derived from the endo demonym " Manchu") for a historical and geographic region in Northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day Northeast China (Inner Manchuria) and parts of the Russian Far East (Outer M ...
was ''Chinese Tartary
Chinese Tartary (see also Tartary) is an archaic geographical term used especially during the time of the Qing dynasty. The term "Tartar" was used by Europeans to refer to ethnicities living around China's north, northeast, and west, including ...
'', and western Central Asia (prior to becoming Russian Central Asia) was known as ''Independent Tartary''. By the seventeenth century, however, largely under the influence of Catholic missionary writings, the word "Tartar" came to refer to the Manchus and the lands they ruled as "Tartary".
European opinions of the area were often negative, and reflected the legacy of the Mongol invasion
The Mongol invasions and conquests took place during the 13th and 14th centuries, creating history's largest contiguous empire: the Mongol Empire (1206-1368), which by 1300 covered large parts of Eurasia. Historians regard the Mongol devastati ...
s that originated from this region. The term originated in the wake of the widespread devastation spread by the Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire of the 13th and 14th centuries was the largest contiguous land empire in history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe, ...
. The adding of an extra "r" to "Tatar" was suggestive of Tartarus, a Hell
In religion and folklore, hell is a location in the afterlife in which evil souls are subjected to punitive suffering, most often through torture, as eternal punishment after death. Religions with a linear divine history often depict hell ...
-like realm in Greek mythology
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the origin and nature of the world, the lives and activities o ...
. In the 18th century, conceptions of Siberia or Tartary and its inhabitants as "barbarous" by Enlightenment-era writers tied into contemporary concepts of civilization
A civilization (or civilisation) is any complex society characterized by the development of a state, social stratification, urbanization, and symbolic systems of communication beyond natural spoken language (namely, a writing system).
...
, savagery and racism
Racism is the belief that groups of humans possess different behavioral traits corresponding to inherited attributes and can be divided based on the superiority of one race over another. It may also mean prejudice, discrimination, or antagoni ...
.
More positive opinions were also expressed by Europeans. Some saw Tartary as a possible source of spiritual knowledge lacking in contemporary European society. In ''Five Years of Theosophy'', edited by Theosophist and scholar G.R.S. Mead, polymath and "seer" Emanuel Swedenborg is quoted as having advised: "Seek for the Lost Word among the hierophants of Tartary, China, and Tibet."
Decline
The use of "Tartary" declined as the region became more known to European geographers; however, the term was still used long into the 19th century. Ethnographical data collected byJesuit
, image = Ihs-logo.svg
, image_size = 175px
, caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits
, abbreviation = SJ
, nickname = Jesuits
, formation =
, founders ...
missionaries in China contributed to the replacement of "Chinese Tartary
Chinese Tartary (see also Tartary) is an archaic geographical term used especially during the time of the Qing dynasty. The term "Tartar" was used by Europeans to refer to ethnicities living around China's north, northeast, and west, including ...
" with Manchuria
Manchuria is an exonym (derived from the endo demonym " Manchu") for a historical and geographic region in Northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day Northeast China (Inner Manchuria) and parts of the Russian Far East (Outer M ...
in European geography by the early 18th century. The voyages of Egor Meyendorff and Alexander von Humboldt
Friedrich Wilhelm Heinrich Alexander von Humboldt (14 September 17696 May 1859) was a German polymath, geographer, naturalist, explorer, and proponent of Romantic philosophy and science. He was the younger brother of the Prussian minister ...
into this region gave rise to the term Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the fo ...
in the early 19th century as well as supplementary terms such as Inner Asia, and Russian expansionism led to the term "Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part ...
" being coined for the Asian half of the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
.
By the 20th century, Tartary as a term for Siberia and Central Asia was obsolete. However, it lent the title to Peter Fleming's 1936 book '' News from Tartary'', which detailed his travels in Central Asia.
Tartaria conspiracy theory
The theory of Great Tartaria as a suppressed lost land or civilization originated inRussia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
, with aspects first appearing in Anatoly Fomenko
Anatoly Timofeevich Fomenko (russian: Анато́лий Тимофе́евич Фоме́нко) (born 13 March 1945 in Stalino, USSR) is a Soviet and Russian conspiracy theorist, mathematician, professor at Moscow State University, well-known as ...
’s New chronology, and then popularized by the racial occult history of Nikolai Levashov. In Russian pseudoscience
Pseudoscience consists of statements, beliefs, or practices that claim to be both scientific and factual but are incompatible with the scientific method. Pseudoscience is often characterized by contradictory, exaggerated or unfalsifiable claim ...
, known for its nationalism
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the State (polity), state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a in-group and out-group, group of peo ...
, Tartaria is presented as the "real" name for Russia, which was maliciously "ignored" in the West. The Russian Geographical Society
The Russian Geographical Society (russian: Ру́сское географи́ческое о́бщество «РГО»), or RGO, is a learned society based in Saint Petersburg, Russia. It promotes geography, exploration and nature protection wi ...
has debunked the conspiracy theory as an extremist fantasy, and far from denying the existence of the term, has used the opportunity to share numerous maps of "Tartary" in its collection. Since about 2016, conspiracy theories about the supposed lost empire of "Tartaria" have gained popularity on the Internet, divorced from its original Russian nationalist frame.
The globalized version of the conspiracy theory is based on an alternative view of architectural history
The history of architecture traces the changes in architecture through various traditions, regions, overarching stylistic trends, and dates. The beginnings of all these traditions is thought to be humans satisfying the very basic need of shelt ...
. Adherents propose that demolished buildings such as the Singer Building
The Singer Building (also known as the Singer Tower) was an office building and early skyscraper in Manhattan, New York City. The headquarters of the Singer Manufacturing Company, it was at the northwestern corner of Liberty Street and Broad ...
, the original New York Penn Station, or the temporary grounds of the 1915's World's Fair were actually the buildings of a vast empire based in Tartary that has been suppressed from history. Sumptuously styled Gilded Age
In United States history, the Gilded Age was an era extending roughly from 1877 to 1900, which was sandwiched between the Reconstruction era and the Progressive Era. It was a time of rapid economic growth, especially in the Northern and Wes ...
buildings are often held out as really having been built by the supposed Tartaria. Other buildings, such as the Great Pyramids
The Giza pyramid complex ( ar, مجمع أهرامات الجيزة), also called the Giza necropolis, is the site on the Giza Plateau in Greater Cairo, Egypt that includes the Great Pyramid of Giza, the Pyramid of Khafre, and the Pyramid of Men ...
and the White House
The White House is the official residence and workplace of the president of the United States. It is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue NW in Washington, D.C., and has been the residence of every U.S. president since John Adams in ...
, are further held out as Tartarian buildings. The conspiracy theory only vaguely describes how such a supposedly advanced civilization which had reputedly achieved world peace could have fallen and been hidden.
In the conspiracy theory, the idea that a "mud flood" wiped out much of the world via depopulation and thus old buildings is common, supported by the fact that many buildings across the world have architectural elements like doors, windows and archways submerged many feet below "ground level". Both World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
and II are cited as a way in which Tartaria was destroyed and hidden, reflecting the reality that the extensive bombing campaigns of World War II did destroy many historic buildings. The general evidence for the theory is that there are similar styles of building around the world, such as capitol buildings with domes, or star forts. Also many photographs from the turn of the 20th century appear to show deserted city streets in many capital cities across the world. When people do start to appear in the photographs there is a striking contrast between the horse and cart dwellers in the muddy streets and the elaborate, highly ornate stone mega-structures which tower above the inhabitants of the cities, which is seen even in modern cities where extreme poverty is contrasted with skyscrapers.
Zach Mortice writing for Bloomberg believes that the theory reflects a cultural discontent with modernism, and a supposition that traditional styles are inherently good and modern styles are bad. He describes the theory as "the QAnon of architecture".
See also
*Chinese Tartary
Chinese Tartary (see also Tartary) is an archaic geographical term used especially during the time of the Qing dynasty. The term "Tartar" was used by Europeans to refer to ethnicities living around China's north, northeast, and west, including ...
* Cossack
* Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fragmen ...
* Khanate of Crimea
* Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire of the 13th and 14th centuries was the largest contiguous land empire in history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe, ...
* Tatars
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different Turki ...
* Tatarstan
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different Turki ...
References
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * *External links
{{Commons category-inline1704 map of Tartary
* ttp://vlib.iue.it/carrie/texts/carrie_books/paksoy-6/cae02.html Nationality of Religion? Views of Central Asian Islam
Tatary – English World dictionary
Historical regions Geography of Russia History of Central Asia East Asia Mongol states Exonyms Pseudohistory Cartography