Tanja sail on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
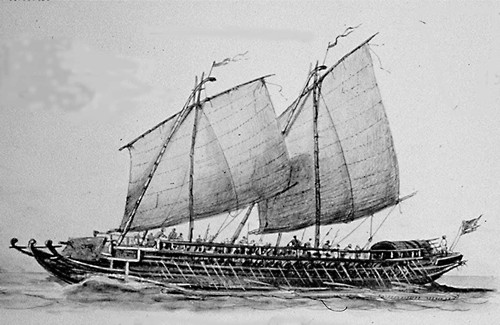 Tanja sail ( Malay: ''layar tanjak'') or tanja rig is a type of sail commonly used by the
Tanja sail ( Malay: ''layar tanjak'') or tanja rig is a type of sail commonly used by the
 There are several different theories regarding the origin of tanja sail.
The sail might be a derivative of the older Austronesian triangular
There are several different theories regarding the origin of tanja sail.
The sail might be a derivative of the older Austronesian triangular
 Tanja sail can be distinguished by its canted/oblique design. The sail face is
Tanja sail can be distinguished by its canted/oblique design. The sail face is  The 3rd century book "''Strange Things of the South''" (南州異物志) by Wan Chen (萬震) describes large ships which originates from ''K'un-lun'' (Southern country, either
The 3rd century book "''Strange Things of the South''" (南州異物志) by Wan Chen (萬震) describes large ships which originates from ''K'un-lun'' (Southern country, either
Cartas de Affonso de Albuquerque, Seguidas de Documentos que as Elucidam tomo I
' (pp. 29–65). Lisboa: Typographia da Academia Real das Sciencas. p. 64. Some examples of vessels that use tanja sails include: *
 Tanja sail ( Malay: ''layar tanjak'') or tanja rig is a type of sail commonly used by the
Tanja sail ( Malay: ''layar tanjak'') or tanja rig is a type of sail commonly used by the Austronesian people
The Austronesian peoples, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesia, Polynesia, and Madagascar that speak Au ...
, particularly in Maritime Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor. Maritime Southeast Asia is sometimes also referred to as Island Southeast Asia, Insular Southeast Asia or Oceanic Sout ...
. It is also known as the tilted square sail, canted rectangular sail, rectangular balance lug, or balance lug sail in English.Needham, Joseph (1971). ''Science and Civilisation in China: Volume 4, Physics and Physical Technology, Part III: Civil Engineering and Nautics''. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. In historical sources, tanja sail is sometimes incorrectly referred to as lateen sail or simply square sail.
Etymology
Also called tanjaq, tanjak, tanjaMandar people
The Mandarese are an ethnic group in the Indonesian province of West Sulawesi in Sulawesi. The Mandar language belongs to the Northern subgroup of the South Sulawesi languages group of the Malayo-Polynesian branch of the Austronesian language f ...
call it ''sombal tanjaq'' because when the wind blows the lower part of the sail (''peloang'') would "''mattanjaq''" (lit. "kick"). In colonial British records, it is sometimes written as "lyre ''tanjong''", a misspelling of ''layar tanjong'' (''layar'' means "sail" in Malay; ''layag'' in Philippine languages
The Philippine languages or Philippinic are a proposed group by R. David Paul Zorc (1986) and Robert Blust (1991; 2005; 2019) that include all the languages of the Philippines and northern Sulawesi, Indonesia—except Sama–Bajaw (language ...
).
Origin
crab-claw sail
The crab claw sail is a fore-and-aft triangular sail with spars along upper and lower edges. The crab claw sail was first developed by the Austronesian peoples some time around 1500 BC. It is used in many traditional Austronesian cultures in Isla ...
. It developed from the fixed mast version of the crab-claw sail and is functionally identical, with the only difference being that the upper and bottom spars of the tanja sail do not converge into a point in the leading edge.
Early contact with Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
ships in the Indian Ocean during Austronesian voyages is believed to have resulted in the development of the triangular Arabic lateen
A lateen (from French ''latine'', meaning "Latin") or latin-rig is a triangular sail set on a long yard mounted at an angle on the mast, and running in a fore-and-aft direction. The settee can be considered to be an associated type of the same ...
sail. Mahdi (1999) believed that in turn, Arab ships may have influenced the development of the Austronesian rectangular tanja sail. Research by Lynn White concludes that the Arab and Indian lateen sail may have been an adaptation of the lateen sail from the Portuguese ships (caravel
The caravel (Portuguese: , ) is a small maneuverable sailing ship used in the 15th century by the Portuguese to explore along the West African coast and into the Atlantic Ocean. The lateen sails gave it speed and the capacity for sailing w ...
), which arrived post-1498. According to H. Warington Smyth, the Malay tanja sail is an adaptation and development of the primitive square sail, with boom at the head and the foot. The Malay tilted the sail forward, to bring the tack right to the deck, turning the sail into the most powerful of lifting sails on a wind.
Characteristics
 Tanja sail can be distinguished by its canted/oblique design. The sail face is
Tanja sail can be distinguished by its canted/oblique design. The sail face is asymmetrical
Asymmetry is the absence of, or a violation of, symmetry (the property of an object being invariant to a transformation, such as reflection). Symmetry is an important property of both physical and abstract systems and it may be displayed in pre ...
in shape and most of the area is elongated to the sides, rather than upward like those of lug sail
The lug sail, or lugsail, is a fore-and-aft, four-cornered sail that is suspended from a spar, called a yard. When raised, the sail area overlaps the mast. For "standing lug" rigs, the sail may remain on the same side of the mast on both the port ...
.
 The 3rd century book "''Strange Things of the South''" (南州異物志) by Wan Chen (萬震) describes large ships which originates from ''K'un-lun'' (Southern country, either
The 3rd century book "''Strange Things of the South''" (南州異物志) by Wan Chen (萬震) describes large ships which originates from ''K'un-lun'' (Southern country, either Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mo ...
or Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
). The ships called ''K'un-lun po
K'un-lun po (also called Kun-lun po, Kunlun po, or K'un-lun bo) were ancient sailing ships used by Austronesian sailors from Maritime Southeast Asia, described by Chinese records from the Han Dynasty. In the first millennium AD, these ships con ...
'' (or ''K'un-lun bo''). He explains the ship's sail design as follows:
The four sails do not face directly forward, but are set obliquely, and so arranged that they can all be fixed in the same direction, to receive the wind and to spill it. Those sails which are behind the most windward one receiving the pressure of the wind, throw it from one to the other, so that they all profit from its force. If it is violent, (the sailors) diminish or augment the surface of the sails according to the conditions. This oblique rig, which permits the sails to receive from one another the breath of the wind, obviates the anxiety attendant upon having high masts. Thus these ships sail without avoiding strong winds and dashing waves, by the aid of which they can make great speed.
— Wan Chen, ''Nánzhōu Yìwùzhì'' (''Strange Things of the South'')
Usage
Most Southeast Asian and Austronesian vessels used the tanja sail. This type of sail may have brought Austronesian sailors as far as West Africa sometime in the 1st millennium CE, with its feasibility proved by an expedition carried out by a replica ship using such sail in 2003, and there is probability these sailor reached the New World as early as 1420 CE.Carta IX, 1 April 1512. In Pato, Raymundo Antonio de Bulhão (1884).Cartas de Affonso de Albuquerque, Seguidas de Documentos que as Elucidam tomo I
' (pp. 29–65). Lisboa: Typographia da Academia Real das Sciencas. p. 64. Some examples of vessels that use tanja sails include: *
Balangay
A Balangay, or barangay is a type of lashed-lug boat built by joining planks edge-to-edge using pins, dowels, and fiber lashings. They are found throughout the Philippines and were used largely as trading ships up until the colonial era. The ...
* Benawa
* Borobudur ship
A Borobudur ship is the 8th to 9th-century wooden double outrigger sailing vessel of Maritime Southeast Asia depicted in some bas reliefs of the Borobudur Buddhist monument in Central Java, Indonesia. It is a ship of Javanese people, derivative ...
* Djong
* Garay
* Kakap
* Karakoa
''Karakoa'' were large outrigger warships from the Philippines. They were used by native Filipinos, notably the Kapampangans and the Visayans, during seasonal sea raids. ''Karakoa'' were distinct from other traditional Philippine sailing vessels ...
* Kelulus
* Kora-kora
* K'un-lun po
K'un-lun po (also called Kun-lun po, Kunlun po, or K'un-lun bo) were ancient sailing ships used by Austronesian sailors from Maritime Southeast Asia, described by Chinese records from the Han Dynasty. In the first millennium AD, these ships con ...
* Lancaran
* Lanong
''Lanong'' were large outrigger warships used by the Iranun and the Banguingui people of the Philippines. They could reach up to in length and had two biped shear masts which doubled as boarding ladders. They also had one to three banks of oars ...
* Mayang
* Padewakang
Padewakang were traditional boats used by the Bugis, Mandar, and Makassar people of South Sulawesi. Padewakang were used for long distance voyages serving the south Sulawesi kingdoms.
Etymology
No-one quite seems to know the origin of the name ...
* Pajala
Pajala () is a locality and the seat of Pajala Municipality in Norrbotten County, Sweden, with 1,958 inhabitants in 2010. It is located in Swedish Lapland.
Pajala is in the Torne Valley and was dominated by people speaking a Finnish dialect unt ...
* Pangajava
Penjajap, also pangajava and pangayaw, were native outrigger warships used by several Austronesian ethnic groups in maritime Southeast Asia. They were typically very long and narrow, and were very fast. They are mentioned as being used by native f ...
* Patorani
Patorani (also prauw patorani or perahu patorani) is a traditional fishing boat from Makassar, Indonesia. It is used by Macassan people for fishing, transport, and trading since at least 17th century A.D. Historically this type of boat was used by ...
* Pencalang
Pencalang is a traditional merchant ship from Nusantara. Historically it was called as pantchiallang or pantjalang. It was originally built by Malay people from the area of Riau and the Malay Peninsula, but has been copied by Javanese shipwright ...
* Perahu
Proas are various types of multi-hull outrigger sailboats of the Austronesian peoples. The terms were used for native Austronesian ships in European records during the Colonial era indiscriminately, and thus can confusingly refer to the do ...
See also
*Crab claw sail
The crab claw sail is a fore-and-aft triangular sail with spars along upper and lower edges. The crab claw sail was first developed by the Austronesian peoples some time around 1500 BC. It is used in many traditional Austronesian cultures in Isla ...
* Lug sail
The lug sail, or lugsail, is a fore-and-aft, four-cornered sail that is suspended from a spar, called a yard. When raised, the sail area overlaps the mast. For "standing lug" rigs, the sail may remain on the same side of the mast on both the port ...
* Junk rig
* Lateen rig
* List of Indonesian inventions and discoveries
References
{{Indonesian traditional vessels Sailing rigs and rigging Indonesian inventions Austronesian culture