Tamil alphabet on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Tamil script ( , ) is an
 The Tamil script has 12
The Tamil script has 12
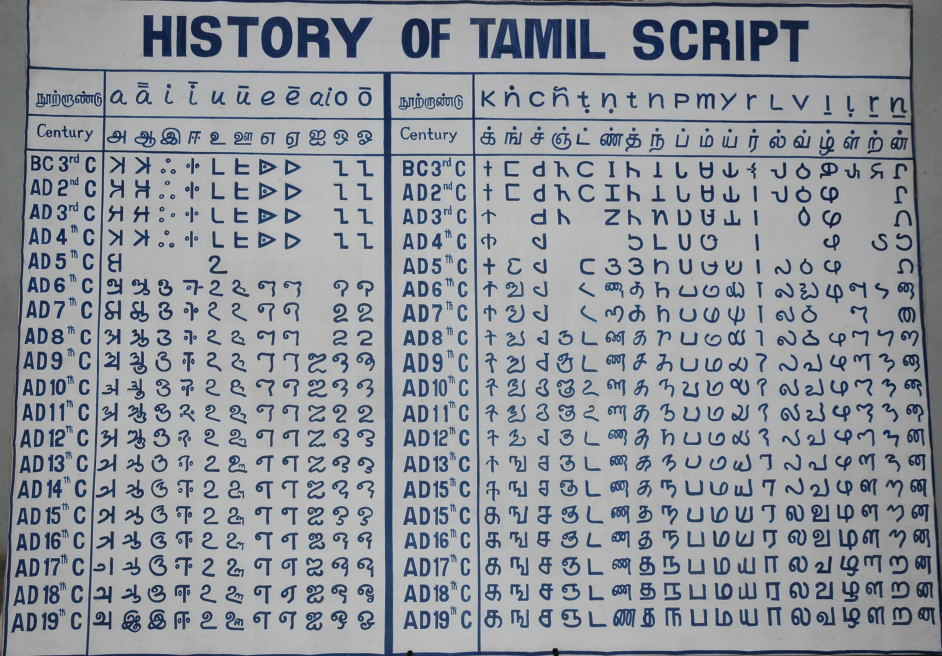
 The Tamil script, like the other
The Tamil script, like the other


''Proposal to encode characters for Extended Tamil''.
/ref>Sharma, Shriramana. (2010c)
''Follow-up #2 to Extended Tamil proposal''.
/ref> The Unicode Standard uses superscripted digits for the same purpose, as in , , and .
''Follow-up to Extended Tamil proposal L2/10-256R''.
/ref> however the proposals triggered discontent by some. Eventually, considering the sensitivity involved, it was determined that the two scripts should be encoded independently, except for the numerals. Proposals to encode characters used for fractional values in traditional accounting practices were submitted. Although discouraged by the ICTA of Sri Lanka, the proposal was recognized by the Government of
AnyTaFont2UTF8
using C#.
Findings at Keeladi Site dates back to 6th Century BCETamil Alphabet & Basics
PDF) *
Unicode Chart
- For Tamil ( PDF)
TACE 16
(PDF)
Learn TamilTamil LettersTamil Unicode Keyboard
{{DEFAULTSORT:Tamil Script Script, Tamil Brahmic scripts Officially used writing systems of India
abugida
An abugida (, from Ge'ez: ), sometimes known as alphasyllabary, neosyllabary or pseudo-alphabet, is a segmental writing system in which consonant-vowel sequences are written as units; each unit is based on a consonant letter, and vowel n ...
script that is used by Tamils
The Tamil people, also known as Tamilar ( ta, தமிழர், Tamiḻar, translit-std=ISO, in the singular or ta, தமிழர்கள், Tamiḻarkaḷ, translit-std=ISO, label=none, in the plural), or simply Tamils (), are a Drav ...
and Tamil speakers in India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, Sri Lanka, Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
, Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
, Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
and elsewhere to write the Tamil language
Tamil (; ' , ) is a Dravidian language natively spoken by the Tamil people of South Asia. Tamil is an official language of the Indian state of Tamil Nadu, the sovereign nations of Sri Lanka and Singapore, and the Indian territory of P ...
. Certain minority languages such as Saurashtra, Badaga, Irula and Paniya
Paniya is one of the Malayalam languages spoken in India. It is spoken by the Paniya people, a scheduled tribe with a majority of its speakers in the state of Kerala. The language is also known as ''Pania'', ''Paniyan'' and ''Panyah''. It belongs ...
are also written in the Tamil script.
Characteristics
 The Tamil script has 12
The Tamil script has 12 vowel
A vowel is a syllabic speech sound pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract. Vowels are one of the two principal classes of speech sounds, the other being the consonant. Vowels vary in quality, in loudness and also in quantity (leng ...
s (, , "soul-letters"), 18 consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract. Examples are and pronounced with the lips; and pronounced with the front of the tongue; and pronounced wi ...
s (, , "body-letters") and one special character, the (, ). is called "அக்கு", ''akku'' and is classified in Tamil orthography as being neither a consonant nor a vowel. However, it is listed at the end of the vowel set. The script is syllabic
Syllabic may refer to:
*Syllable, a unit of speech sound, considered the building block of words
**Syllabic consonant, a consonant that forms the nucleus of a syllable
*Syllabary, writing system using symbols for syllables
*Abugida, writing system ...
, not alphabet
An alphabet is a standardized set of basic written graphemes (called letters) that represent the phonemes of certain spoken languages. Not all writing systems represent language in this way; in a syllabary, each character represents a syllab ...
ic. The complete script, therefore, consists of the 31 letters in their independent form and an additional 216 combinatory letters, for a total of 247 (12+18+216+1) combinations (, , "soul-body-letters") of a consonant and a vowel, a mute consonant or a vowel alone. The combinatory letters are formed by adding a vowel marker to the consonant. Some vowels require the basic shape of the consonant to be altered in a way that is specific to that vowel. Others are written by adding a vowel-specific suffix to the consonant, yet others a prefix and still other vowels require adding both a prefix and a suffix to the consonant. In every case, the vowel marker is different from the standalone character for the vowel.
The Tamil script is written from left to right.
History

 The Tamil script, like the other
The Tamil script, like the other Brahmic scripts
The Brahmic scripts, also known as Indic scripts, are a family of abugida writing systems. They are used throughout the Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia and parts of East Asia. They are descended from the Brahmi script of ancient Ind ...
, is thought to have evolved from the original Brahmi script
Brahmi (; ; ISO: ''Brāhmī'') is a writing system of ancient South Asia. "Until the late nineteenth century, the script of the Aśokan (non-Kharosthi) inscriptions and its immediate derivatives was referred to by various names such as 'lath' ...
. The earliest inscriptions which are accepted examples of Tamil writing date to the Ashoka
Ashoka (, ; also ''Asoka''; 304 – 232 BCE), popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was the third emperor of the Maurya Empire of Indian subcontinent during to 232 BCE. His empire covered a large part of the Indian subcontinent, s ...
n period. The script used by such inscriptions is commonly known as the Tamil-Brahmi
Tamil-Brahmi, also known as Tamizhi or Damili, was a variant of the Brahmi script in southern India. It was used to write inscriptions in the early form of Old Tamil.Richard Salomon (1998) ''Indian Epigraphy: A Guide to the Study of Inscriptio ...
or "Tamili script" and differs in many ways from standard Ashokan Brahmi. For example, early Tamil-Brahmi, unlike Ashokan Brahmi, had a system to distinguish between pure consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract. Examples are and pronounced with the lips; and pronounced with the front of the tongue; and pronounced wi ...
s (''m'', in this example) and consonants with an inherent vowel
A vowel is a syllabic speech sound pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract. Vowels are one of the two principal classes of speech sounds, the other being the consonant. Vowels vary in quality, in loudness and also in quantity (leng ...
(''ma'', in this example). In addition, according to Iravatham Mahadevan
Iravatham Mahadevan (2 October 1930 – 26 November 2018) was an Indian epigraphist and civil servant, known for his decipherment of Tamil-Brahmi inscriptions and for his expertise on the epigraphy of the Indus Valley civilisation.
Early lif ...
, early Tamil Brahmi used slightly different vowel markers, had extra characters to represent letters not found in Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
and omitted letters for sounds not present in Tamil such as voiced consonants and aspirates. Inscriptions from the 2nd century use a later form of Tamil-Brahmi, which is substantially similar to the writing system described in the ''Tolkāppiyam
''Tolkāppiyam'', also romanised as ''Tholkaappiyam'' ( ta, தொல்காப்பியம், ''lit.'' "ancient poem"), is the most ancient extant Tamil grammar text and the oldest extant long work of Tamil literature. The surviving manus ...
'', an ancient Tamil grammar. Most notably, they used the ''puḷḷi'' to suppress the inherent vowel. The Tamil letters thereafter evolved towards a more rounded form and by the 5th or 6th century, they had reached a form called the ''early vaṭṭeḻuttu''.
The modern Tamil script does not, however, descend from that script. In the 4th century, the Pallava dynasty
The Pallava dynasty existed from 275 CE to 897 CE, ruling a significant portion of the Deccan, also known as Tondaimandalam. The dynasty rose to prominence after the downfall of the Satavahana dynasty, with whom they had formerly served as f ...
created a new script for Tamil and the Grantha alphabet
The Grantha script ( ta, கிரந்த எழுத்து, Granta eḻuttu; ml, ഗ്രന്ഥലിപി, granthalipi) is a South Indian script, found particularly in Tamil Nadu and Kerala. Originating from the Pallava script, th ...
evolved from it, adding the Vaṭṭeḻuttu alphabet for sounds not found to write Sanskrit. Parallel to Pallava script a new script (Chola-Pallava script, which evolved to modern Tamil script) again emerged in Chola territory resembling the same glyph development like Pallava script, but it did not evolve from that. By the 8th century, the new scripts supplanted Vaṭṭeḻuttu in the Chola resp. Pallava kingdoms which lay in the north portion of the Tamil-speaking region. However, Vaṭṭeḻuttu continued to be used in the southern portion of the Tamil-speaking region, in the Chera and Pandyan kingdoms until the 11th century, when the Pandyan kingdom was conquered by the Cholas.
With the fall of Pallava kingdom, the Chola dynasty pushed the Chola-Pallava script as the de facto script. Over the next few centuries, the Chola-Pallava script evolved into the modern Tamil script. The Grantha and its parent script influenced the Tamil script notably. The use of palm leaves
The Arecaceae is a family of perennial flowering plants in the monocot order Arecales. Their growth form can be climbers, shrubs, tree-like and stemless plants, all commonly known as palms. Those having a tree-like form are called palm trees. ...
as the primary medium for writing
Writing is a medium of human communication which involves the representation of a language through a system of physically inscribed, mechanically transferred, or digitally represented symbols.
Writing systems do not themselves constitute h ...
led to changes in the script. The scribe had to be careful not to pierce the leaves with the stylus while writing because a leaf with a hole was more likely to tear and decay faster. As a result, the use of the ''puḷḷi'' to distinguish pure consonants became rare, with pure consonants usually being written as if the inherent vowel were present. Similarly, the vowel marker for the ''kuṟṟiyal ukaram'', a half-rounded ''u'' which occurs at the end of some words and in the medial position in certain compound words, also fell out of use and was replaced by the marker for the simple ''u.'' The ''puḷḷi'' did not fully reappear until the introduction of printing
Printing is a process for mass reproducing text and images using a master form or template. The earliest non-paper products involving printing include cylinder seals and objects such as the Cyrus Cylinder and the Cylinders of Nabonidus. The ...
, but the marker ''kuṟṟiyal ukaram'' never came back into use although the sound itself still exists and plays an important role in Tamil prosody.
The forms of some of the letters were simplified in the 19th century to make the script easier to typeset. In the 20th century, the script was simplified even further in a series of reforms, which regularised the vowel markers used with consonants by eliminating special markers and most irregular forms.
Relationship with other Indic scripts
The Tamil script differs from other Brahmi-derived scripts in a number of ways. Unlike every other Brahmic script, it does not regularly represent voiced or aspirated stop consonants as these are notphoneme
In phonology and linguistics, a phoneme () is a unit of sound that can distinguish one word from another in a particular language.
For example, in most dialects of English, with the notable exception of the West Midlands and the north-wes ...
s of the Tamil language even though voiced and fricative allophone
In phonology, an allophone (; from the Greek , , 'other' and , , 'voice, sound') is a set of multiple possible spoken soundsor '' phones''or signs used to pronounce a single phoneme in a particular language. For example, in English, (as in '' ...
s of stops do appear in spoken Tamil. Thus the character ''k'', for example, represents but can also be pronounced [] or [] based on the rules of Tamil grammar. A separate set of characters appears for these sounds when the Tamil script is used to write Sanskrit or other languages.
Also unlike other Brahmi scripts, the Tamil script rarely uses typographic ligature
In writing and typography, a ligature occurs where two or more graphemes or letters are joined to form a single glyph. Examples are the characters æ and œ used in English and French, in which the letters 'a' and 'e' are joined for the firs ...
s to represent conjunct consonants, which are far less frequent in Tamil than in other Indian languages. Where they occur, conjunct consonants are written by writing the character for the first consonant, adding the ''puḷḷi'' to suppress its inherent vowel, and then writing the character for the second consonant. There are a few exceptions, namely ''kṣa'' and ''śrī''.
ISO 15919 is an international standard for the transliteration of Tamil and other Indic scripts into Latin characters. It uses diacritics to map the much larger set of Brahmic consonants and vowels to the Latin script.
Letters


Basic consonants
Consonants are called the "body" (''mei'') letters. The consonants are classified into three categories: ''vallinam'' (hard consonants), ''mellinam'' (soft consonants, including allnasals
In phonetics, a nasal, also called a nasal occlusive or nasal stop in contrast with an oral stop or nasalized consonant, is an occlusive consonant produced with a lowered velum, allowing air to escape freely through the nose. The vast majorit ...
), and ''itayinam'' (medium consonants).
There are some lexical rules for the formation of words. The ''Tolkāppiyam
''Tolkāppiyam'', also romanised as ''Tholkaappiyam'' ( ta, தொல்காப்பியம், ''lit.'' "ancient poem"), is the most ancient extant Tamil grammar text and the oldest extant long work of Tamil literature. The surviving manus ...
'' describes such rules. Some examples: a word cannot end in certain consonants, and cannot begin with some consonants including r-, l- and ḻ-; there are six nasal consonants in Tamil: a velar nasal
The voiced velar nasal, also known as agma, from the Greek word for 'fragment', is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. It is the sound of ''ng'' in English ''sing'' as well as ''n'' before velar consonants as in ''Englis ...
ங், a palatal nasal ஞ், a retroflex nasal
The voiced retroflex nasal is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is n`.
Like all the retroflex consona ...
ண், a dental nasal ந், a bilabial nasal ம், and an alveolar nasal
The voiced alveolar nasal is a type of consonantal sound used in numerous spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents dental, alveolar, and postalveolar nasals is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is ...
ன்.
The order of the alphabet (strictly abugida
An abugida (, from Ge'ez: ), sometimes known as alphasyllabary, neosyllabary or pseudo-alphabet, is a segmental writing system in which consonant-vowel sequences are written as units; each unit is based on a consonant letter, and vowel n ...
) in Tamil closely matches that of the nearby languages both in location and linguistics, reflecting the common origin of their scripts from Brahmi.
Grantha consonants used in Tamil
The Tamil speech has incorporated many phonemes which were not part of theTolkāppiyam
''Tolkāppiyam'', also romanised as ''Tholkaappiyam'' ( ta, தொல்காப்பியம், ''lit.'' "ancient poem"), is the most ancient extant Tamil grammar text and the oldest extant long work of Tamil literature. The surviving manus ...
classification. The letters used to write these sounds, known as Grantha, are used as part of Tamil. These are taught from elementary school and incorporated in Tamil All Character Encoding (TACE16).
There is also the compound (), equivalent to in Devanagari
Devanagari ( ; , , Sanskrit pronunciation: ), also called Nagari (),Kathleen Kuiper (2010), The Culture of India, New York: The Rosen Publishing Group, , page 83 is a left-to-right abugida (a type of segmental writing system), based on the ...
.
In recent times combinations of consonants with (, , equivalent to nuqta) are generally used to represent phonemes of foreign languages, especially to write Islamic and Christian texts. For example: asif = , azārutīn̠ = , Genghis Khan = .
A nuqta-like diacritic is used while writing the Badaga language
Badaga is a southern Dravidian language spoken by the Badaga people of the Nilgiris district of Tamil Nadu. The language is closely related to the Tamil and Kannada languages.
Of all the tribal languages spoken in Nilgiris (Badaga, Toda l ...
and double dot nuqta for the Irula language
Irula is a Dravidian language spoken by the Irulas who inhabit the area of the Nilgiri mountains, in the states of Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and Karnataka, India. It is closely related to Tamil. It is written in the Tamil script.
Origins
The langu ...
to transcribe its sounds.
There has also been effort to differentiate voiced and voiceless consonants through subscripted numbers – two, three, and four which stand for the unvoiced aspirated, voiced, voiced aspirated respectively. This was used to transcribe Sanskrit words in Sanskrit–Tamil books, as shown in the table below.Sharma, Shriramana. (2010a)''Proposal to encode characters for Extended Tamil''.
/ref>Sharma, Shriramana. (2010c)
''Follow-up #2 to Extended Tamil proposal''.
/ref> The Unicode Standard uses superscripted digits for the same purpose, as in , , and .
Vowels
Vowels are also called the 'life' (''uyir'') or 'soul' letters. Together with the consonants (''mei'', which are called 'body' letters), they form compound, syllabic (abugida
An abugida (, from Ge'ez: ), sometimes known as alphasyllabary, neosyllabary or pseudo-alphabet, is a segmental writing system in which consonant-vowel sequences are written as units; each unit is based on a consonant letter, and vowel n ...
) letters that are called 'living' or 'embodied' letters (''uyir mei'', i.e. letters that have both 'body' and 'soul').
Tamil vowels are divided into short and long (five of each type) and two diphthongs
Compound form
Using the consonant 'k' as an example: The special letter , represented by three dots and called ' or ''akh''. It traditionally served a purely grammatical function, but in modern times it has come to be used as a diacritic to represent foreign sounds. For example, is used for the English sound ''f'', not found in Tamil. Another archaic Tamil letter , represented by a small hollow circle and called ', is the ''Anusvara
Anusvara (Sanskrit: ') is a symbol used in many Indic scripts to mark a type of nasal sound, typically transliterated . Depending on its location in the word and the language for which it is used, its exact pronunciation can vary. In the context ...
''. It was traditionally used as a homorganic nasal when in front of a consonant, and either as a bilabial nasal () or alveolar nasal () at the end of a word, depending on the context.
The long (''nedil'') vowels are about twice as long as the short (''kuṟil'') vowels. The diphthongs are usually pronounced about one and a half times as long as the short vowels, though some grammatical texts place them with the long (''nedil'') vowels.
As can be seen in the compound form, the vowel sign can be added to the right, left or both sides of the consonants. It can also form a ligature
Ligature may refer to:
* Ligature (medicine), a piece of suture used to shut off a blood vessel or other anatomical structure
** Ligature (orthodontic), used in dentistry
* Ligature (music), an element of musical notation used especially in the me ...
. These rules are evolving and older use has more ligatures than modern use. What you actually see on this page depends on your font selection; for example, Code2000
Code2000 is a serif and pan- Unicode digital font, which includes characters and symbols from a very large range of writing systems. As of the current final version 1.171 released in 2008, Code2000 is designed and implemented by James Kass t ...
will show more ligatures than Latha.
There are proponents of script reform who want to eliminate all ligatures and let all vowel signs appear on the right side.
Unicode encodes the character in logical order (always the consonant first), whereas legacy 8-bit encodings (such as TSCII) prefer the written order. This makes it necessary to reorder when converting from one encoding to another; it is not sufficient simply to map one set of code points to the other.
Compound table of Tamil letters
The following table lists vowel (''uyir'' or life) letters across the top and consonant (''mei'' or body) letters along the side, the combination of which gives all Tamil compound (uyirmei) letters.Writing order
Numerals and symbols
Apart from the usual numerals (from 0 to 9), Tamil also has numerals for 10, 100 and 1000. Symbols for fraction and other number-based concepts can also be found.In Unicode
Tamil script was added to theUnicode
Unicode, formally The Unicode Standard,The formal version reference is is an information technology standard for the consistent encoding, representation, and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems. The standard, wh ...
Standard in October 1991 with the release of version 1.0.0. The Unicode block for Tamil is U+0B80–U+BFF. Grey areas indicate non-assigned code points. Most of the non-assigned code points are designated reserved because they are in the same relative position as characters assigned in other South Asian script blocks that correspond to phonemes that don't exist in the Tamil script.
Efforts to unify the Grantha script with Tamil have been made;Sharma, Shriramana. (2010b)''Follow-up to Extended Tamil proposal L2/10-256R''.
/ref> however the proposals triggered discontent by some. Eventually, considering the sensitivity involved, it was determined that the two scripts should be encoded independently, except for the numerals. Proposals to encode characters used for fractional values in traditional accounting practices were submitted. Although discouraged by the ICTA of Sri Lanka, the proposal was recognized by the Government of
Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is a state in southern India. It is the tenth largest Indian state by area and the sixth largest by population. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. Tamil Nadu is the home of the Tamil people, whose Tamil language ...
and were added to the Unicode Standard in March 2019 with the release of version 12.0. The Unicode block for Tamil Supplement is U+11FC0–U+11FFF:
Syllabary
Like other South Asian scripts in Unicode, the Tamil encoding was originally derived from theISCII
Indian Script Code for Information Interchange (ISCII) is a coding scheme for representing various writing systems of India. It encodes the main Indic scripts and a Roman transliteration. The supported scripts are: Bengali–Assamese, Devanagar ...
standard. Both ISCII
Indian Script Code for Information Interchange (ISCII) is a coding scheme for representing various writing systems of India. It encodes the main Indic scripts and a Roman transliteration. The supported scripts are: Bengali–Assamese, Devanagar ...
and Unicode
Unicode, formally The Unicode Standard,The formal version reference is is an information technology standard for the consistent encoding, representation, and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems. The standard, wh ...
encode Tamil as an abugida
An abugida (, from Ge'ez: ), sometimes known as alphasyllabary, neosyllabary or pseudo-alphabet, is a segmental writing system in which consonant-vowel sequences are written as units; each unit is based on a consonant letter, and vowel n ...
. In an abugida, each basic character represents a consonant and default vowel. Consonants with a different vowel or bare consonants are represented by adding a modifier character to a base character. Each code point representing a similar phoneme is encoded in the same relative position in each South Asian script block in Unicode, including Tamil. Because Unicode represents Tamil as an abugida all the pure consonants (consonants with no associated vowel) and syllables in Tamil can be represented by combining multiple Unicode code points, as can be seen in the Unicode Tamil Syllabary below. In Unicode 5.1, named sequences were added for all Tamil consonants and syllables.
Unicode 5.1 also has a named sequence for the Tamil ligature SRI (''śrī''), ஶ்ரீ, written using ஶ (''śa''). The name of this sequence is TAMIL SYLLABLE SHRII and is composed of the Unicode sequence U+0BB6 U+0BCD U+0BB0 U+0BC0. The ligature can also be written using ஸ (''sa'') to create an identical ligature ஸ்ரீ composed of the Unicode sequence U+0BB8 U+0BCD U+0BB0 U+0BC0; but this is discouraged by the Unicode standard.
Programmatic access
* Tamil script can be manipulated using thePython
Python may refer to:
Snakes
* Pythonidae, a family of nonvenomous snakes found in Africa, Asia, and Australia
** ''Python'' (genus), a genus of Pythonidae found in Africa and Asia
* Python (mythology), a mythical serpent
Computing
* Python (pro ...
library called open-Tamil.
* There is a Windows open source application available calleAnyTaFont2UTF8
using C#.
See also
* Simplified Tamil script *Tamil phonology
Tamil phonology is characterised by the presence of “true-subapical” retroflex consonants and multiple rhotic consonants. Its script does not distinguish between voiced and unvoiced consonants; phonetically, voice is assigned dependi ...
* Tamil Keyboard
*Tamil Braille
Tamil Braille is the smallest of the Bharati braille alphabets.UNESCO (2013World Braille Usage 3rd edition. (For the general system and for punctuation, see that article.)
Alphabet
Vowel letters are used rather than diacritics, and they occur ...
* Tamil letters (on Tamil Wikibooks)
*Tamil numerals
This article is about the number words of the Tamil language, as well as the dedicated symbols for them used in the Tamil script.
Basic numbering
Zero
Old Tamil possesses a special numerical character for zero ''(see Old Tamil numerals b ...
* Tamil units of measurement
*Grantha script
The Grantha script ( ta, கிரந்த எழுத்து, Granta eḻuttu; ml, ഗ്രന്ഥലിപി, granthalipi) is a South Indian script, found particularly in Tamil Nadu and Kerala. Originating from the Pallava script, th ...
* Vatteluttu script
*Tamil-Brahmi
Tamil-Brahmi, also known as Tamizhi or Damili, was a variant of the Brahmi script in southern India. It was used to write inscriptions in the early form of Old Tamil.Richard Salomon (1998) ''Indian Epigraphy: A Guide to the Study of Inscriptio ...
* Pallava script
* Kolezhuthu
*Arwi
Arwi or ArabuTamil (Arabic: , ; ta, அரபுத்தமிழ் is an Arabic influenced dialect of the Tamil language written with an extension of the Arabic alphabet, with extensive lexical and phonetic influences from the Arabic lang ...
*Tamil bell
__NOTOC__
The Tamil Bell is a broken bronze bell discovered in approximately 1836 by missionary William Colenso. It was being used as a pot to boil potatoes by Māori women near Whangarei in the Northland Region of New Zealand.
The bell is 1 ...
* Malayalam Script
* ISO 15919
Explanatory notes
Notes
References
* *External links
Findings at Keeladi Site dates back to 6th Century BCE
PDF) *
Unicode Chart
- For Tamil ( PDF)
TACE 16
(PDF)
Learn Tamil
{{DEFAULTSORT:Tamil Script Script, Tamil Brahmic scripts Officially used writing systems of India