The transition from Ming to Qing, alternatively known as Ming–Qing transition or the Manchu conquest of China, from 1618 to 1683, saw the transition between two major
dynasties
A dynasty is a sequence of rulers from the same family,''Oxford English Dictionary'', "dynasty, ''n''." Oxford University Press (Oxford), 1897. usually in the context of a monarchical system, but sometimes also appearing in republics. A d ...
in
Chinese history. It was a decades-long conflict between the emerging
Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-spea ...
, the incumbent
Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peo ...
, and several smaller factions (like the
Shun dynasty
The Shun dynasty (), officially the Great Shun (), was a short-lived Chinese dynasty that existed during the Ming–Qing transition. The dynasty was founded in Xi'an on 8 February 1644, the first day of the lunar year, by Li Zicheng, the leade ...
and
Xi dynasty). It ended with the consolidation of Qing rule, and the fall of the Ming and several other factions.
Overview
The transition from the Ming to Qing was a decades-long period of conflict between:
# the
Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-spea ...
, established by the
Manchu clan
Aisin Gioro in contemporary
Northeast China
Northeast China or Northeastern China () is a geographical region of China, which is often referred to as "Manchuria" or "Inner Manchuria" by surrounding countries and the West. It usually corresponds specifically to the three provinces east of ...
;
# the
Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peo ...
, the incumbent dynasty led by the
Zhu clan;
# and various other rebel powers in China, such as the short-lived
Xi dynasty led by
Zhang Xianzhong and the short-lived
Shun dynasty
The Shun dynasty (), officially the Great Shun (), was a short-lived Chinese dynasty that existed during the Ming–Qing transition. The dynasty was founded in Xi'an on 8 February 1644, the first day of the lunar year, by Li Zicheng, the leade ...
led by
Li Zicheng
Li Zicheng (22 September 1606 – 1645), born Li Hongji, also known by the nickname, Dashing King, was a Chinese peasant rebel leader who overthrew the Ming dynasty in 1644 and ruled over northern China briefly as the emperor of the short-li ...
.
Leading up to the Qing, in 1618, the
Later Jin khan
Nurhaci
Nurhaci (14 May 1559 – 30 September 1626), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Taizu of Qing (), was a Jurchen chieftain who rose to prominence in the late 16th century in Manchuria. A member of the House of Aisin-Gioro, he reigned ...
commissioned a document entitled the
Seven Grievances
The ''Seven Grievances'' (Manchu: ''nadan koro''; ) was a manifesto announced by Nurhaci, khan of the Later Jin, on the thirteenth day of the fourth lunar month in the third year of the ''Tianming'' () era of his reign; 7 May 1618. It effectiv ...
, which enumerated grievances against the Ming. Many of the grievances dealt with conflicts against the Ming-backed
Yehe
Nara (Manchu: , Wade-Giles: nara hala, Chinese: , or ) is a clan name shared by a number of royal Manchu clans. The four tribes of the Hūlun confederation () – Hada (), Ula (), Hoifa () and Yehe () – were all ruled by clans bearing this ...
clan of the
Jurchens
Jurchen (Manchu: ''Jušen'', ; zh, 女真, ''Nǚzhēn'', ) is a term used to collectively describe a number of East Asian Tungusic-speaking peoples, descended from the Donghu people. They lived in the northeast of China, later known as Manch ...
. Nurhaci's demand that the Ming pay tribute to him to redress the seven grievances was effectively a declaration of war, as the Ming were not willing to pay money to a former tributary. Shortly afterwards, Nurhaci rebelled against
Ming rule in
Liaoning.
At the same time, the Ming dynasty was fighting for its survival against fiscal turmoil and peasant rebellions.
Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
officials urged Nurhaci's successor
Hong Taiji to crown himself
emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereignty, sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), ...
, which he did in 1636, declaring the new Qing dynasty. On 24 April 1644,
Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
fell to a rebel army led by
Li Zicheng
Li Zicheng (22 September 1606 – 1645), born Li Hongji, also known by the nickname, Dashing King, was a Chinese peasant rebel leader who overthrew the Ming dynasty in 1644 and ruled over northern China briefly as the emperor of the short-li ...
, a former minor Ming official who became the leader of the peasant revolt and then proclaimed the
Shun dynasty
The Shun dynasty (), officially the Great Shun (), was a short-lived Chinese dynasty that existed during the Ming–Qing transition. The dynasty was founded in Xi'an on 8 February 1644, the first day of the lunar year, by Li Zicheng, the leade ...
. The last Ming emperor, the
Chongzhen Emperor
The Chongzhen Emperor (; 6 February 1611 – 25 April 1644), personal name Zhu Youjian (), courtesy name Deyue (),Wang Yuan (王源),''Ju ye tang wen ji'' (《居業堂文集》), vol. 19. "聞之張景蔚親見烈皇帝神主題御諱字德� ...
, hanged himself from the
Zuihuai
The zuihuai () is a specimen of the pagoda tree (''Styphnolobium japonicum'') located in Jingshan Park, Beijing, China. It is a tourist attraction and national landmark in Jingshan Park. The Chongzhen Emperor Zhu Youjian, the last ruler of the Min ...
tree in the imperial garden outside the
Forbidden City
The Forbidden City () is a palace complex in Dongcheng District, Beijing, China, at the center of the Imperial City of Beijing. It is surrounded by numerous opulent imperial gardens and temples including the Zhongshan Park, the sacrifi ...
. When Li Zicheng moved against him, the Ming general
Wu Sangui shifted his allegiance to the Qing. Li Zicheng was defeated at the
Battle of Shanhai Pass
The Battle of Shanhai Pass, fought on May 27, 1644 at Shanhai Pass at the eastern end of the Great Wall, was a decisive battle leading to the beginning of the Qing dynasty rule in China proper. There, the Qing prince-regent Dorgon allied with ...
by the joint forces of Wu Sangui and Manchu prince
Dorgon
Dorgon (, ; 17 November 1612 – 31 December 1650), was a Manchu prince and regent of the early Qing dynasty. Born in the House of Aisin-Gioro as the 14th son of Nurhaci (the founder of the Later Jin dynasty, predecessor of the Qing dynast ...
. On 6 June, the mainly Han Chinese forces of Dorgon and Wu entered the capital.
The fall of the Ming dynasty was largely caused by a combination of factors. Scholars have argued that the fall of the Ming dynasty may have been partially caused by the droughts and famines caused by the
Little Ice Age. Historian
Kenneth Swope argues that one key factor was deteriorating relations between Ming Royalty and the
Ming Empire's military leadership. Other factors include repeated military expeditions to the North, inflationary pressures caused by spending too much from the imperial treasury, natural disasters and epidemics of disease. Contributing further to the chaos was a peasant rebellion throughout the country in 1644 and a series of weak emperors. Ming power would hold out in what is now southern China for years, though eventually would be overtaken by the Qing forces.
Other authors have linked the fall of the Ming with
the General Crisis
The General Crisis is a term used by some historians to describe an alleged period of widespread global conflict and instability that occurred from the early 17th century to the early 18th century in Europe, and in more recent historiography in ...
affecting the
Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
under
Philip IV, the
English Civil War
The English Civil War (1642–1651) was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Parliamentarians (" Roundheads") and Royalists led by Charles I ("Cavaliers"), mainly over the manner of England's governance and issues of re ...
and other polities.
However, the victory was far from complete as it required almost 40 more years before all of China was securely united under Qing rule. In 1661, the
Kangxi Emperor
The Kangxi Emperor (4 May 1654– 20 December 1722), also known by his temple name Emperor Shengzu of Qing, born Xuanye, was the third emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the second Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1661 to ...
ascended the throne, and in 1662 his regents launched the
Great Clearance
The Great Clearance (), also translated as the Great Evacuation or Great Frontier Shift, was caused by edicts issued in 1661, 1664, and 1679, which required the evacuation of the coastal areas of Guangdong, Fujian, Zhejiang, Jiangnan, and Shandong ...
to defeat the resistance of Ming loyalists in
South China. He then fought off several rebellions, such as the
Revolt of the Three Feudatories
The Revolt of the Three Feudatories, () also known as the Rebellion of Wu Sangui, was a rebellion in China lasting from 1673 to 1681, during the early reign of the Kangxi Emperor (r. 1661–1722) of the Qing dynasty (1644–1912). The revolt was ...
led by
Wu Sangui in southern China, starting in 1673, and then countered by launching a series of campaigns that expanded his empire. In 1662,
Zheng Chenggong
Zheng Chenggong, Prince of Yanping (; 27 August 1624 – 23 June 1662), better known internationally as Koxinga (), was a Ming loyalist general who resisted the Qing conquest of China in the 17th century, fighting them on China's southeastern ...
(Koxinga) drove out and defeated the
Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
and founded the
Kingdom of Tungning
The Kingdom of Tungning (), also known as Tywan by the British at the time, was a dynastic maritime state that ruled part of southwestern Taiwan and the Penghu islands between 1661 and 1683. It is the first predominantly Han Chinese state in ...
in
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
, a Ming loyalist state with the goal of reunifying China. However, Tungning was defeated in 1683 at the
Battle of Penghu
The Battle of Penghu () was a naval battle fought in 1683 between the Qing dynasty and the Kingdom of Tungning. The Qing admiral Shi Lang led a fleet to attack the Tungning forces in Penghu. Each side possessed more than 200 warships. The Tungn ...
by Han Chinese admiral
Shi Lang, a former admiral under Koxinga.
The Qing victory was overwhelmingly the result of the defection of the Ming dynasty's
Liaodong
The Liaodong Peninsula (also Liaotung Peninsula, ) is a peninsula in southern Liaoning province in Northeast China, and makes up the southwestern coastal half of the Liaodong region. It is located between the mouths of the Daliao River (the ...
military establishment and other defectors, with the Manchu military playing a very minor role (see below for specific examples).
[.][.]
Jurchens and the late Ming dynasty

The
Manchus
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
are sometimes described as a nomadic people, when in fact they were not nomads, but a sedentary agricultural people who lived in fixed villages, farmed crops, practiced hunting and mounted archery. Their main military formation was infantry wielding bows and arrows, swords, and pikes, while cavalry was kept in the rear.
Manchus were living in cities with walls surrounded by villages and adopting
Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
-style agriculture well before the Qing conquest of the Ming, and there was an established tradition of Han Chinese-Manchu mixing before 1644. The Han Chinese soldiers on the
Liaodong
The Liaodong Peninsula (also Liaotung Peninsula, ) is a peninsula in southern Liaoning province in Northeast China, and makes up the southwestern coastal half of the Liaodong region. It is located between the mouths of the Daliao River (the ...
frontier often mixed with non-Han tribesmen and were largely acculturated to their ways. The Jurchen Manchus accepted and assimilated Han soldiers who went over to them, and Han Chinese soldiers from Liaodong often adopted and used Manchu names. Indeed
Nurhaci
Nurhaci (14 May 1559 – 30 September 1626), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Taizu of Qing (), was a Jurchen chieftain who rose to prominence in the late 16th century in Manchuria. A member of the House of Aisin-Gioro, he reigned ...
's secretary Dahai may have been one such individual.


In the late
Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peo ...
, Ming army units had become dominated by officers who would spend long periods of 10 or 12 years in command instead of the usual practice of constant rotation, and the Central Military Command had lost much of its control over regional armies. ''Zongdu Junwu'', or Supreme Commanders, were appointed throughout the empire to oversee the fiscal and military affairs in the area of their jurisdiction. In the frontier areas these became increasingly autonomous, and especially in
Liaodong
The Liaodong Peninsula (also Liaotung Peninsula, ) is a peninsula in southern Liaoning province in Northeast China, and makes up the southwestern coastal half of the Liaodong region. It is located between the mouths of the Daliao River (the ...
, where military service and command became hereditary and
vassal
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerain ...
age-like personal bonds of loyalty grew between officers, their subordinates and troops. This military caste gravitated toward the
Jurchen tribal chieftains rather than the bureaucrats of the capital.
The
She-An Rebellion among the
Yi people
The Yi or Nuosu people,; zh, c=彝族, p=Yízú, l=Yi ethnicity historically known as the Lolo,; vi, Lô Lô; th, โล-โล, Lo-Lo are an ethnic group in China, Vietnam, and Thailand. Numbering nine million people, they are the sev ...
broke out in
Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of the ...
in 1621 against the Ming, requiring suppression, which was completed in 1629. In the early 1640s, mass rebellions led by many rebel leaders broke out in northwestern China's province of
Shaanxi
Shaanxi (alternatively Shensi, see § Name) is a landlocked province of China. Officially part of Northwest China, it borders the province-level divisions of Shanxi (NE, E), Henan (E), Hubei (SE), Chongqing (S), Sichuan (SW), Gansu (W), N ...
and spread throughout China in the 1640s. Major battles included the sacking of
Fengyang
Fengyang County () is a county in north-central Anhui, Anhui Province, China. It is under the administration of Chuzhou, a prefecture-level city. The county was home to 765,600 people as of 2013.
Administrative divisions
Fengyang County is divide ...
by
Li Zicheng
Li Zicheng (22 September 1606 – 1645), born Li Hongji, also known by the nickname, Dashing King, was a Chinese peasant rebel leader who overthrew the Ming dynasty in 1644 and ruled over northern China briefly as the emperor of the short-li ...
and
Zhang Xianzhong and a battle in
Kaifeng
Kaifeng () is a prefecture-level city in east-central Henan province, China. It is one of the Eight Ancient Capitals of China, having been the capital eight times in history, and is best known for having been the Chinese capital during the No ...
which led to the deliberately engineered
1642 Yellow River flood The 1642 Yellow River flood or Kaifeng flood was a man-made disaster in October, 1642, that principally affected Kaifeng and Xuzhou.
Kaifeng is located on the south bank of the Yellow River, prone to violent flooding throughout its history. During ...
by the Ming governor in an attempt to stop Li Zicheng.
Initial Jurchen conquests
Conquest of Liaodong and other Jurchen tribes (1601–1626)
The
Jianzhou Jurchen chief,
Nurhaci
Nurhaci (14 May 1559 – 30 September 1626), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Taizu of Qing (), was a Jurchen chieftain who rose to prominence in the late 16th century in Manchuria. A member of the House of Aisin-Gioro, he reigned ...
, is retrospectively identified as the founder of the
Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-spea ...
. In 1589 the
Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peo ...
appointed Nurhaci as paramount chieftain of the
Yalu Region, believing that his tribe was too weak to gain hegemony over the larger
Yehe
Nara (Manchu: , Wade-Giles: nara hala, Chinese: , or ) is a clan name shared by a number of royal Manchu clans. The four tribes of the Hūlun confederation () – Hada (), Ula (), Hoifa () and Yehe () – were all ruled by clans bearing this ...
and Hada. When the other tribes attacked him to check his power in 1591, he succeeded in defeating them and seized many of their warhorses.
In 1607 he declared himself ''
Khan''. Upon the advice of an Erdeni, most likely a Chinese transfrontiersman, he proclaimed the Jin State, named after
the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty that had ruled over northern China several centuries earlier. His unifying efforts gave the
Jurchen the strength to assert themselves backed by an army consisting of majority
Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
defectors as well as Ming produced firearms. In May 1618, Nurhaci proclaimed his
Seven Grievances
The ''Seven Grievances'' (Manchu: ''nadan koro''; ) was a manifesto announced by Nurhaci, khan of the Later Jin, on the thirteenth day of the fourth lunar month in the third year of the ''Tianming'' () era of his reign; 7 May 1618. It effectiv ...
against the Ming and departed his capital of
Hetu Ala with 20,000 men. The army attacked and
captured Fushun, located on the
Hun River about 10 kilometers east of
Shenyang.
The
Hulun tribes, a powerful confederacy of
Jurchen tribes, started recognizing the authority of Nurhaci by the beginning of the 17th century. In some cases, such as with
Bujantai
Bujantai (Manchu: ; ) (died 1618) was a Jurchen ''beile'' (chieftain) of the Ula tribal confederation.
Bujantai was descended from Nacibulu (納奇卜祿), the ancestor of the Nara lineages of Ula and Hada.
Tradition spoke of Nacibulu as havin ...
of the Ula, chieftains would attempt to reassert their independence and war would break out, but the
Jianzhou Jurchens
The Jianzhou Jurchens () were one of the three major groups of Jurchens as identified by the Ming dynasty. Although the geographic location of the Jianzhou Jurchens changed throughout history, during the 14th century they were located south of t ...
would defeat and assimilate all the tribes eventually (Hada 1601, Hoifa 1607, Ula 1613,
Yehe
Nara (Manchu: , Wade-Giles: nara hala, Chinese: , or ) is a clan name shared by a number of royal Manchu clans. The four tribes of the Hūlun confederation () – Hada (), Ula (), Hoifa () and Yehe () – were all ruled by clans bearing this ...
1619). The powerful Yehe Jurchens under
Gintaisi
Gintaisi (Manchu: ; died September 29, 1619), known as Jintaishi () or Jintaiji () in Chinese, was a Jurchen beile (chieftain) of the Yehe tribal confederation.
He was the younger brother of Narimbulu, and became one of the two beile of the Yeh ...
united with the forces of the Ming dynasty to combat the rise of Nurhaci but Gintaisi was defeated and died in 1619. The fur-trapping Warka peoples near the
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contine ...
coast were subjugated as tributary tribes from 1599 to 1641.
By summer 1621, the Ming's
Liaodong
The Liaodong Peninsula (also Liaotung Peninsula, ) is a peninsula in southern Liaoning province in Northeast China, and makes up the southwestern coastal half of the Liaodong region. It is located between the mouths of the Daliao River (the ...
fortress cities,
Fushun
Fushun (, formerly romanised as ''Fouchouen'', using French spelling, also as Fuxi ()) is a prefecture level city in Liaoning province, China, about east of Shenyang, with a total area of , of which is the city proper. Situated on the Hun Rive ...
,
Shenyang, and
Liaoyang
Liaoyang () is a prefecture-level city of east-central Liaoning province, China, situated on the Taizi River. It is approximately one hour south of Shenyang, the provincial capital, by car. Liaoyang is home to Liaoning University's College of F ...
, were all handed over to the
Later Jin by traitors and defectors. Fushun's commander surrendered after a single attack when promised that his troops and their families would not be enslaved or forced to change any of their customs (including hairstyle), but rather given high office. Shenyang fell with the aid of
Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
Ming soldiers in the city; Liaoyang fell after traitors let down ropes for the
Jurchens
Jurchen (Manchu: ''Jušen'', ; zh, 女真, ''Nǚzhēn'', ) is a term used to collectively describe a number of East Asian Tungusic-speaking peoples, descended from the Donghu people. They lived in the northeast of China, later known as Manch ...
to climb the wall in the night. The Ming general
Li Yongfang
Li Yongfang (; died 1634) was a Chinese general of the Ming dynasty and Qing dynasty known for defecting to the Qing dynasty, due to the Ming dynasty losing the city of Fushun in Liaoning to the Qing. Li Yongfang along with many other Han Chinese ...
who surrendered the city of
Fushun
Fushun (, formerly romanised as ''Fouchouen'', using French spelling, also as Fuxi ()) is a prefecture level city in Liaoning province, China, about east of Shenyang, with a total area of , of which is the city proper. Situated on the Hun Rive ...
in what is now
Liaoning province in
China's northeast did so after Nurhaci gave him an
Aisin Gioro princess in marriage and a noble title. The princess was one of Nurhaci's granddaughters. In April 1625, Nurhaci designated Shenyang the new capital city, which would hold that status until the Qing conquest of
Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
in 1644. In 1625, the Jurchens captured the port city of
Lüshun, thus controlling the whole
Liaodong peninsula
The Liaodong Peninsula (also Liaotung Peninsula, ) is a peninsula in southern Liaoning province in Northeast China, and makes up the southwestern coastal half of the Liaodong region. It is located between the mouths of the Daliao River ...
.
When the Jurchens were reorganized by Nurhaci into the
Eight Banners
The Eight Banners (in Manchu: ''jakūn gūsa'', ) were administrative and military divisions under the Later Jin and Qing dynasties of China into which all Manchu households were placed. In war, the Eight Banners functioned as armies, but the ...
, many
Manchu clans were artificially created from groups of unrelated people who would found a new Manchu clan (''mukun'') using a term of geographic origin such as a toponym for their ''hala'' (clan name). The irregularities over Jurchen and Manchu clan origin led to the Qing trying to document and systemize the creation of histories for Manchu clans, including manufacturing an entire legend around the origin of the Aisin Gioro clan by taking mythology from the northeast.
Nurhaci read the Chinese novels ''
Romance of the Three Kingdoms
''Romance of the Three Kingdoms'' () is a 14th-century historical novel attributed to Luo Guanzhong. It is set in the turbulent years towards the end of the Han dynasty and the Three Kingdoms period in Chinese history, starting in 184 AD ...
'' and ''
Water Margin
''Water Margin'' (''Shuihu zhuan'') is one of the earliest Chinese novels written in vernacular Mandarin, and is attributed to Shi Nai'an. It is also translated as ''Outlaws of the Marsh'' and ''All Men Are Brothers''.
The story, which is ...
'', learning all he knew about Chinese military and political strategies from them.
In February 1626, the Jurchens
besieged Ningyuan but suffered a defeat in which Nurhaci was mortally wounded.
First Joseon campaign
The
Later Jin had lost at the
Battle of Ningyuan
The Battle of Ningyuan () was a battle between the Ming dynasty and the Later Jin dynasty in 1626. The Later Jin had been waging war on the Ming for several years, and their leader Nurhaci had deemed Ningyuan to be a suitable target for his att ...
the previous year and their khan
Nurhaci
Nurhaci (14 May 1559 – 30 September 1626), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Taizu of Qing (), was a Jurchen chieftain who rose to prominence in the late 16th century in Manchuria. A member of the House of Aisin-Gioro, he reigned ...
died from his wounds afterwards. Peace negotiations with the
Ming
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peop ...
after the battle delayed an aggressive Ming response to the
Jurchen loss, and the Ming general
Yuan Chonghuan
Yuan Chonghuan (; 6 June 1584 – 22 September 1630), courtesy name Yuansu or Ziru, was a Chinese politician, military general and writer who served under the Ming dynasty. Widely regarded as a patriot in Chinese culture, he is best known for d ...
was busy fortifying the border garrisons and training new musketeers. The new khan
Hong Taiji was eager for a quick victory to consolidate his position as khan. By invading
Joseon he also hoped to extract much-needed resources for his army and subjects, who had suffered in the war against the Ming.
In 1627, Hong Taiji dispatched princes
Amin,
Jirgalang
Jirgalang or Jirhalang (Manchu: 19 November 1599 – June 11, 1655) was a Manchu noble, regent, and political and military leader of the early Qing dynasty. Born in the Aisin Gioro clan, he was the sixth son of Šurhaci, a younger brother of ...
,
Ajige
Ajige (Manchu:, Mölendroff: ajige; 28 August 1605 – 28 November 1651) was a Manchu prince and military general of the early Qing dynasty. He was born in the Aisin Gioro clan as the 12th son of Nurhaci, the khan of the Later Jin dynasty (the ...
and
Yoto to Joseon with 30,000 troops, under the guidance of
Gang Hong-rip and
Li Yongfang
Li Yongfang (; died 1634) was a Chinese general of the Ming dynasty and Qing dynasty known for defecting to the Qing dynasty, due to the Ming dynasty losing the city of Fushun in Liaoning to the Qing. Li Yongfang along with many other Han Chinese ...
. The Jurchens met sharp resistance at the border towns but Joseon border garrisons were quickly defeated. The Jurchen army advanced into
Uiju
Ŭiju County is a kun, or county, in North Pyongan Province, North Korea. The county has an area of 420 km², and a population of 110,018 (2008 data).
Name
Ŭiju appears as Uiju in South Korea's Revised Romanization and as Yizhou in Chinese ...
where Ming general
Mao Wenlong was stationed, and Mao quickly fled with his men into the
Bohai Sea
The Bohai Sea () is a marginal sea approximately in area on the east coast of Mainland China. It is the northwestern and innermost extension of the Yellow Sea, to which it connects to the east via the Bohai Strait. It has a mean depth of ...
. Next, the Jurchens attacked
Anju. When it became clear that defeat was inevitable, the Anju garrisons committed suicide by blowing up their gunpowder storehouse.
Pyongyang
Pyongyang (, , ) is the capital and largest city of North Korea, where it is known as the "Capital of the Revolution". Pyongyang is located on the Taedong River about upstream from its mouth on the Yellow Sea. According to the 2008 populat ...
fell without a fight and the Jin army crossed the
Taedong River
The Taedong River (Chosŏn'gŭl: ) is a large river in North Korea. The river rises in the Rangrim Mountains of the country's north where it then flows southwest into Korea Bay at Namp'o.Suh, Dae-Sook (1987) "North Korea in 1986: Strengthenin ...
. Joseon Korean King Injo asked the Ming to send cannons and hwagi rocket carts in addition to the Ming "southern army" to help against the 1627 Manchu invasion of Korea as Joseon forts fell and Joseon troops were wiped out.. He also said Korean commoners had to provide excessive rations to Ming general Mao Wenlong.
By this time news of the invasion had reached the Ming court, which immediately dispatched a relief contingent to Joseon, slowing the Jurchen advance into
Hwangju
Hwangju County is a county in North Hwanghae province, North Korea.
Geography
Hwangju is bordered to the northwest by Sariwŏn, to the northeast by Songrim and Kangnam, to the southwest by Yŏnt'an, to the south by Pongsan, and to the southeast ...
.
King Injo
Injo of Joseon (7 December 1595 – 17 June 1649), born Yi Jong, was the sixteenth ruler of the Joseon Dynasty of Korea. He was the grandson of King Seonjo and son of Prince Jeongwon. He was the king during the Later Jin invasion of Joseon, ...
then dispatched an envoy to negotiate a peace treaty, but by the time the messenger returned, Injo had already fled from
Hanseong
Seoul (; ; ), officially known as the Seoul Special City, is the capital and largest metropolis of South Korea.Before 1972, Seoul was the ''de jure'' capital of the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (North Korea) as stated iArticle 103 ...
to
Ganghwa Island
Ganghwa Island (Hangul ; Hanja ), also known by its native name Ganghwado, is a South Korean island in the estuary of the Han River. It is in the Yellow Sea, off Korea's west coast. The island is separated from Gimpo (on the South Korean mainlan ...
in panic.
Mongolia campaign (1625–1635)
The
Khorchin
The Khorchin ( mn, Хорчин, ''Horçin''; ''Qorčin''; ) are a subgroup of the Mongols that speak the Khorchin dialect of Mongolian and predominantly live in northeastern Inner Mongolia of China.
History
The Ming dynasty gave Borjigin p ...
Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal membe ...
allied with
Nurhaci
Nurhaci (14 May 1559 – 30 September 1626), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Taizu of Qing (), was a Jurchen chieftain who rose to prominence in the late 16th century in Manchuria. A member of the House of Aisin-Gioro, he reigned ...
and the
Jurchens
Jurchen (Manchu: ''Jušen'', ; zh, 女真, ''Nǚzhēn'', ) is a term used to collectively describe a number of East Asian Tungusic-speaking peoples, descended from the Donghu people. They lived in the northeast of China, later known as Manch ...
in 1626, submitting to his rule for protection against the
Khalkha
The Khalkha (Mongolian script, Mongolian: mn, Халх, Halh, , zh, 喀爾喀) have been the largest subgroup of Mongols, Mongol people in modern Mongolia since the 15th century. The Khalkha, together with Chahars, Ordos Mongols, Ordos and Tum ...
Mongols and
Chahar Mongols. Seven Khorchin nobles died at the hands of Khalkhas and Chahars in 1625. This started the Khorchin alliance with the
Qing.
The Chahar Mongols were fought against by
Dorgon
Dorgon (, ; 17 November 1612 – 31 December 1650), was a Manchu prince and regent of the early Qing dynasty. Born in the House of Aisin-Gioro as the 14th son of Nurhaci (the founder of the Later Jin dynasty, predecessor of the Qing dynast ...
in 1628 and 1635. An expedition against the Chahar Mongols in 1632 was ordered to establish a trading post at
Zhangjiakou
Zhangjiakou (; ; ) also known as Kalgan and by several other names, is a prefecture-level city in northwestern Hebei province in Northern China, bordering Beijing to the southeast, Inner Mongolia to the north and west, and Shanxi to the south ...
. The Qing defeated the armies of the Mongol khan
Ligdan, who was allied to the
Ming
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peop ...
, bringing an end to his rule over the
Northern Yuan
The Northern Yuan () was a dynastic regime ruled by the Mongol Borjigin clan based in the Mongolian Plateau. It existed as a rump state after the collapse of the Yuan dynasty in 1368 and lasted until its conquest by the Jurchen-led Later Jin ...
. The defeat of Ligdan Khan in 1634, in addition to winning the allegiance of the Southern Mongol hordes, brought a vast supply of horses to the Qing, while denying the same supply to the Ming. The Qing also captured the Great Seal of the Mongol Khans, giving them the opportunity to portray themselves as heirs of the
Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty (), officially the Great Yuan (; xng, , , literally "Great Yuan State"), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after its division. It was established by Kublai, the fift ...
as well.
Hong Taiji and formation of the Qing dynasty
 Hong Taiji
Hong Taiji was the eighth son of
Nurhaci
Nurhaci (14 May 1559 – 30 September 1626), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Taizu of Qing (), was a Jurchen chieftain who rose to prominence in the late 16th century in Manchuria. A member of the House of Aisin-Gioro, he reigned ...
, whom he succeeded as the second ruler of the
Later Jin dynasty in 1626. He organised
imperial examination
The imperial examination (; lit. "subject recommendation") refers to a civil-service examination system in Imperial China, administered for the purpose of selecting candidates for the state bureaucracy. The concept of choosing bureaucrats by ...
s to recruit scholar-officials from the
Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
, and adopted Chinese legal forms. He formed autonomous Han Chinese military colonies governed by Han Chinese officials, where
Manchus
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
were forbidden to trespass. Hong Taiji curtailed the power of the Manchu princes by relying on Han Chinese officials. He personally welcomed surrendered
Ming
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peop ...
commanders, eating side-by-side with them so as to build a rapport that was impossible with the Ming emperors. The Manchus, led by
Prince Amin, expressed their displeasure at the situation by massacring the population of
Qian'an and
Yongping. Hong Taiji responded by arresting and imprisoning Amin, who later died in prison. He then implemented, on the urging of his Han Chinese advisors, Chinese-style
Confucian
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China. Variously described as tradition, a philosophy, a religion, a humanistic or rationalistic religion, a way of governing, or ...
education, and Ming-style government ministries. When Zhang Chun, a Ming commander, was captured but refused to defect, Hong Taiji personally served him with food to show his sincerity (Zhang still refused but was kept in a temple until his death). With the surrender of
Dalinghe in 1631, the most capable army officers of the Ming became faithful followers of the new dynasty who would take over the preparation and planning of much of the war. From this episode onward, the Ming-Qing transition ceased to be an inter-nation conflict between Chinese and Manchus but rather a civil war between
Liaodong
The Liaodong Peninsula (also Liaotung Peninsula, ) is a peninsula in southern Liaoning province in Northeast China, and makes up the southwestern coastal half of the Liaodong region. It is located between the mouths of the Daliao River (the ...
and
Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
.
Meanwhile, in the Ming, the
Wuqiao mutiny broke out in 1631, led by
Kong Youde
Kong Youde ( zh, c=, p=Kǒng Yǒudé; mnc, , v=; Transliteration of Manchu: kung ioo de; died August 7, 1652) was a Chinese adventurer and Ming dynasty military officer who served under the warlord Mao Wenlong until Mao's death in 1629. Subsequen ...
and
Geng Zhongming
Geng Zhongming (; 1604–1649) was a Chinese military general who lived through the transition from the Ming (1368–1644) to the Qing (1644–1912) dynasty, during which he served both sides. His grandson Geng Jingzhong was one of the Three Fe ...
. Undersupplied and underpaid soldiers mutinied against the Ming dynasty. They subsequently sailed across
Bohai Gulf and defected to the
Jurchens
Jurchen (Manchu: ''Jušen'', ; zh, 女真, ''Nǚzhēn'', ) is a term used to collectively describe a number of East Asian Tungusic-speaking peoples, descended from the Donghu people. They lived in the northeast of China, later known as Manch ...
en masse. During the mutiny, they purged thousands of
Southern Chinese
South China () is a geographical and cultural region that covers the southernmost part of China. Its precise meaning varies with context. A notable feature of South China in comparison to the rest of China is that most of its citizens are not ...
, suspecting them to be loyal to the Ming.
Hong Taiji was reluctant to become Emperor of China. However, Han Chinese officials
Ning Wanwo Ning may refer to:
Places
* Ning County, county in Gansu, China
* Ning River, tributary of Mei River, originating and running through Xingning, China
* Ningxia, abbreviated as Ning, Hui autonomous region of China
* Nanjing, abbreviated as Ning, ca ...
,
Fan Wencheng
Fan Wencheng (, courtesy name: Xiandou 憲斗, 1597–1666) was a Qing dynasty Scholar-Official, Prime Minister and Grand Secretary ''(Daxue Shi)''. His official career went through four generation of Qing dynasty emperors through Nurhaci, Hong T ...
,
Ma Guozhu,
Zu Kefa,
Shen Peirui, and
Zhang Wenheng urged him to declare himself as Emperor of China. On 14 May 1636, he accepted this advice, changing the name of his regime from the Later Jin to the Qing dynasty, and enthroning himself as Emperor of China in an elaborate Confucian ceremony.
Hong Taiji's renaming of the
Jurchens
Jurchen (Manchu: ''Jušen'', ; zh, 女真, ''Nǚzhēn'', ) is a term used to collectively describe a number of East Asian Tungusic-speaking peoples, descended from the Donghu people. They lived in the northeast of China, later known as Manch ...
to
Manchus
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
was meant to hide the fact that the ancestors of the Manchus, the
Jianzhou Jurchens
The Jianzhou Jurchens () were one of the three major groups of Jurchens as identified by the Ming dynasty. Although the geographic location of the Jianzhou Jurchens changed throughout history, during the 14th century they were located south of t ...
, were ruled by the
Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
. The Qing dynasty carefully hid the two original editions of the books of "''Qing Taizu Wu Huangdi Shilu''" and the "''Manzhou Shilu Tu''" (Taizu Shilu Tu) in the Qing palace, forbidding them from public view, because they showed that the
Manchu Aisin-Gioro
The House of Aisin-Gioro was a Manchu people, Manchu clan that ruled the Later Jin (1616–1636), Later Jin dynasty (1616–1636), the Qing dynasty (1636–1912), and Manchukuo (1932–1945) in the history of China. Under the Ming dynasty, member ...
family had been ruled by the
Ming
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peop ...
dynasty. In the Ming period, the
Koreans
Koreans ( South Korean: , , North Korean: , ; see names of Korea) are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Korean Peninsula.
Koreans mainly live in the two Korean nation states: North Korea and South Korea (collectively and simply re ...
of
Joseon referred to the Jurchen-inhabited lands north of the
Korean peninsula
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic o ...
, above the rivers
Yalu and
Tumen, to be part of Ming China, as the "superior country" (sangguk), the name they used to refer to Ming China. The Qing deliberately excluded references and information from the ''
History of Ming
The ''History of Ming'' or the ''Ming History'' (''Míng Shǐ'') is one of the official Chinese historical works known as the ''Twenty-Four Histories''. It consists of 332 volumes and covers the history of the Ming dynasty from 1368 to 1644. It ...
'' that showed the Jurchens (Manchus) as subservient to the Ming dynasty, to hide their former subservient relationship to the Ming. The ''
Veritable Records of Ming
The ''Ming Shilu'' () contains the imperial annals of the emperors of the Ming dynasty (1368–1644). It is the single largest historical source for the dynasty. According to modern historians, it "plays an extremely important role in the histo ...
'' were not used to source the ''History of Ming'' because of this. Refusing to mention in the
Mingshi
The ''History of Ming'' or the ''Ming History'' (''Míng Shǐ'') is one of the official Chinese historical works known as the ''Twenty-Four Histories''. It consists of 332 volumes and covers the history of the Ming dynasty from 1368 to 1644. It ...
that the Qing founders were Ming China's subjects was meant to avoid the accusation of rebellion.
Han–Manchu marriages
Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
generals who defected to the
Manchus
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
were often
given women from the imperial Aisin-Gioro family in marriage. Manchu Aisin-Gioro princesses were also married to Han Chinese officials' sons. The Manchu leader
Nurhaci
Nurhaci (14 May 1559 – 30 September 1626), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Taizu of Qing (), was a Jurchen chieftain who rose to prominence in the late 16th century in Manchuria. A member of the House of Aisin-Gioro, he reigned ...
married one of his granddaughters (
Abatai
Abatai (Manchu: ; 27 July 1589 – 10 May 1646) was a Manchu prince and military general of the early Qing dynasty. Although an inconsistent and dissolute malcontent, he nevertheless showed considerable ability as a military leader and a ...
's daughter) to the
Ming
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peop ...
general
Li Yongfang
Li Yongfang (; died 1634) was a Chinese general of the Ming dynasty and Qing dynasty known for defecting to the Qing dynasty, due to the Ming dynasty losing the city of Fushun in Liaoning to the Qing. Li Yongfang along with many other Han Chinese ...
after he surrendered
Fushun
Fushun (, formerly romanised as ''Fouchouen'', using French spelling, also as Fuxi ()) is a prefecture level city in Liaoning province, China, about east of Shenyang, with a total area of , of which is the city proper. Situated on the Hun Rive ...
in
Liaoning to the Manchus in 1618. The offspring of Li Yongfang received the "Third Class Baron" () title. Li Yongfang was the great-great-great-grandfather of
Li Shiyao
Li, li, or LI may refer to:
Businesses and organizations
* Landscape Institute, a British professional body for landscape architects
* Leadership Institute, a non-profit organization located in Arlington, Virginia, US, that teaches "political tec ...
. The 4th daughter of
Kangxi
The Kangxi Emperor (4 May 1654– 20 December 1722), also known by his temple name Emperor Shengzu of Qing, born Xuanye, was the third emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the second Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1661 to 1 ...
was wedded to Sun Cheng'en, son of the Han Chinese Sun Sike. Other Aisin-Gioro women married the sons of the Han Chinese generals
Geng Jimao,
Shang Kexi, and
Wu Sangui. Meanwhile, the ordinary soldiers who defected were often given non-royal Manchu women as wives, and a mass marriage of Han Chinese officers and officials to Manchu women numbering 1,000 couples was arranged by Prince
Yoto and Khan
Hong Taiji in 1632 to promote harmony between the two ethnic groups.
This policy, which began before the invasion of 1644, was continued after it. A 1648 decree from
Shunzhi
The Shunzhi Emperor (15 March 1638 – 5 February 1661) was the second emperor of the Qing dynasty of China, and the first Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1644 to 1661. A committee of Manchu princes chose him to succee ...
allowed Han Chinese civilian men to marry Manchu women from the
Banners
A banner can be a flag or another piece of cloth bearing a symbol, logo, slogan or another message. A flag whose design is the same as the shield in a coat of arms (but usually in a square or rectangular shape) is called a banner of arms. Also ...
with the permission of the
Board of Revenue if they were registered daughters of officials or commoners or the permission of their banner company captain if they were unregistered commoners, and it was only later in the dynasty that these policies allowing intermarriage were done away with. The decree was formulated by Prince
Dorgon
Dorgon (, ; 17 November 1612 – 31 December 1650), was a Manchu prince and regent of the early Qing dynasty. Born in the House of Aisin-Gioro as the 14th son of Nurhaci (the founder of the Later Jin dynasty, predecessor of the Qing dynast ...
. In the beginning of the Qing dynasty the Qing government supported Han Chinese defectors weddings to Manchu girls. Han Chinese Bannermen wedded Manchus and there was no law against this.
The "Dolo efu" rank was given to husbands of Qing princesses.
Geng Zhongming
Geng Zhongming (; 1604–1649) was a Chinese military general who lived through the transition from the Ming (1368–1644) to the Qing (1644–1912) dynasty, during which he served both sides. His grandson Geng Jingzhong was one of the Three Fe ...
, a Han Chinese bannerman, was awarded the title of Prince Jingnan, and his son
Geng Jingmao managed to have both his sons
Geng Jingzhong
Geng Jingzhong (; died 1682) was a powerful military commander of the early Qing dynasty. He inherited the title of "King/Prince of Jingnan" (靖南王) from his father Geng Jimao, who had inherited it from Jingzhong's grandfather Geng Zhongming ...
and
Geng Zhaozhong become court attendants under the
Shunzhi Emperor and married
Aisin-Gioro
The House of Aisin-Gioro was a Manchu people, Manchu clan that ruled the Later Jin (1616–1636), Later Jin dynasty (1616–1636), the Qing dynasty (1636–1912), and Manchukuo (1932–1945) in the history of China. Under the Ming dynasty, member ...
women, with Prince
Abatai
Abatai (Manchu: ; 27 July 1589 – 10 May 1646) was a Manchu prince and military general of the early Qing dynasty. Although an inconsistent and dissolute malcontent, he nevertheless showed considerable ability as a military leader and a ...
's granddaughter marrying Geng Zhaozhong and
Haoge's (a son of
Hong Taiji) daughter marrying Geng Jingzhong. A daughter of the Manchu Aisin-Gioro Prince Yolo was wedded to
Geng Juzhong, who was another son of Geng Jingmao. Aisin-Gioro women were also offered to
Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal membe ...
who defected to the
Manchus
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
. The Manchu Prince Regent
Dorgon
Dorgon (, ; 17 November 1612 – 31 December 1650), was a Manchu prince and regent of the early Qing dynasty. Born in the House of Aisin-Gioro as the 14th son of Nurhaci (the founder of the Later Jin dynasty, predecessor of the Qing dynast ...
gave a Manchu woman as a wife to the Han Chinese official
Feng Quan, who had defected from the Ming to the Qing. Feng Quan willingly adopted the Manchu queue hairstyle before it was enforced on the Han Chinese population and he also learned the
Manchu language
Manchu (Manchu:, ) is a critically endangered East Asian Tungusic language native to the historical region of Manchuria in Northeast China.
As the traditional native language of the Manchus, it was one of the official languages of the Qin ...
.
Building a mixed military

When
Li Yongfang
Li Yongfang (; died 1634) was a Chinese general of the Ming dynasty and Qing dynasty known for defecting to the Qing dynasty, due to the Ming dynasty losing the city of Fushun in Liaoning to the Qing. Li Yongfang along with many other Han Chinese ...
surrendered, he was given much higher status than under the
Ming
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peop ...
, and even allowed to keep his troops as retainers.
Kong Youde
Kong Youde ( zh, c=, p=Kǒng Yǒudé; mnc, , v=; Transliteration of Manchu: kung ioo de; died August 7, 1652) was a Chinese adventurer and Ming dynasty military officer who served under the warlord Mao Wenlong until Mao's death in 1629. Subsequen ...
,
Shang Kexi and
Geng Zhongming
Geng Zhongming (; 1604–1649) was a Chinese military general who lived through the transition from the Ming (1368–1644) to the Qing (1644–1912) dynasty, during which he served both sides. His grandson Geng Jingzhong was one of the Three Fe ...
were also allowed to keep their personal armies. The warlord
Shen Zhixiang, who had unlawfully taken over command of his deceased uncle
Shen Shikui's troops as his private army, was unable to attain recognition from the Ming court. He then proceeded to lead his forces to switch allegiance to the
Qing, and they became critical assets to the Qing.
There were too few ethnic
Manchus
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
to rule
China, but they absorbed defeated
Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal membe ...
, and, more importantly, added
Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
to the
Eight Banners
The Eight Banners (in Manchu: ''jakūn gūsa'', ) were administrative and military divisions under the Later Jin and Qing dynasties of China into which all Manchu households were placed. In war, the Eight Banners functioned as armies, but the ...
. The Manchus had to create an entire "Jiu Han jun" (Old Han Army) due to the very large number of Han Chinese soldiers absorbed into the Eight Banners by both capture and defection. The Qing showed that the Manchus valued military skills in propaganda targeted towards the Ming military to get them to defect to the Qing, since the Ming civilian political system discriminated against the military. From 1618 to 1631 Manchus received Han Chinese defectors and their descendants became Han Bannermen and those killed in battle were commemorated as martyrs in biographies.
Hong Taiji recognized that Ming defectors were needed in order to defeat the Ming, explaining to other Manchus why he needed to treat the Ming defector general
Hong Chengchou
Hong Chengchou (; 1593–1665), courtesy name Yanyan and art name Hengjiu, was a Chinese official who served under the Ming and Qing dynasties. He was born in present-day Liangshan Village, Yingdu Town, Fujian Province, China. After obtaining t ...
leniently. Hong Taiji understood that the Ming would not be easily defeated unless Han Chinese troops wielding musket and cannon were included in the army.
Indeed, among the
Banners
A banner can be a flag or another piece of cloth bearing a symbol, logo, slogan or another message. A flag whose design is the same as the shield in a coat of arms (but usually in a square or rectangular shape) is called a banner of arms. Also ...
, gunpowder weapons like muskets and artillery were specifically used by the Han Chinese Banners. The Manchus established an artillery corps made out of Han Chinese soldiers in 1641. The use of artillery by Han Bannermen may have led to them being known as "heavy" soldiers (ujen cooha). The "
red coat cannon" were part of the Han army (
Liaodong
The Liaodong Peninsula (also Liaotung Peninsula, ) is a peninsula in southern Liaoning province in Northeast China, and makes up the southwestern coastal half of the Liaodong region. It is located between the mouths of the Daliao River (the ...
Han Chinese) serving the Qing.
Ming officers who defected to the Qing were allowed to retain their previous military rank. The Qing received the defection of
Shen Zhixiang in 1638. Among the other Han Chinese officers who defected to the Qing were
Ma Guangyuan,
Wu Rujie,
Zu Dashou
Zu Dashou (; d. 1656), courtesy name Fuyu (復宇), was a Chinese military general who served on the northern border of the Ming dynasty during the Ming–Qing transition period of Chinese history. He fought against the Qing dynasty in several ...
,
Quan Jie,
Geng Zhongming
Geng Zhongming (; 1604–1649) was a Chinese military general who lived through the transition from the Ming (1368–1644) to the Qing (1644–1912) dynasty, during which he served both sides. His grandson Geng Jingzhong was one of the Three Fe ...
,
Zu Zehong,
Zu Zepu,
Zu Zerun
Zu or ZU may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Fictional elements
* Zu, a mountain featured in the films ''Zu Warriors from the Magic Mountain'' and ''The Legend of Zu''
* ''ZU'', a " furry" anthology published by MU Press
* Zu, a large birdlike mo ...
,
Deng Changchun,
Wang Shixian
Wang Shixian (; ; born 13 February 1990) is a retired Chinese professional badminton player. She is a former World No. 1 in women's singles.
Career
Wang Shixian was admitted into Chinese Junior National Team in 2005 and was soon promoted t ...
,
Hong Chengchou
Hong Chengchou (; 1593–1665), courtesy name Yanyan and art name Hengjiu, was a Chinese official who served under the Ming and Qing dynasties. He was born in present-day Liangshan Village, Yingdu Town, Fujian Province, China. After obtaining t ...
,
Shang Kexi,
Liu Wuyuan,
Zu Kefa,
Zhang Cunren,
Meng Qiaofang
Meng may refer to:
* Meng (surname) (孟), a Chinese surname
* Master of Engineering (MEng or M.Eng.), an academic or professional master's degree in the field of engineering
* , "M with hook", letter used in the International Phonetic Alphabet
* ...
,
Kong Youde
Kong Youde ( zh, c=, p=Kǒng Yǒudé; mnc, , v=; Transliteration of Manchu: kung ioo de; died August 7, 1652) was a Chinese adventurer and Ming dynasty military officer who served under the warlord Mao Wenlong until Mao's death in 1629. Subsequen ...
,
Sun Dingliao. Aristocratic and military ranks, silver, horses and official positions were given to Han Chinese defectors like
Zhang Cunren,
Sun Dingliao,
Liu Wu,
Liu Liangchen,
Zu Zehong,
Zu Zepu,
Zu Kufa and
Zu Zerun
Zu or ZU may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Fictional elements
* Zu, a mountain featured in the films ''Zu Warriors from the Magic Mountain'' and ''The Legend of Zu''
* ''ZU'', a " furry" anthology published by MU Press
* Zu, a large birdlike mo ...
. Han Chinese defectors were primarily responsible for military strategy after 1631.
So many Han defected to the Qing and swelled up the ranks of the
Eight Banners
The Eight Banners (in Manchu: ''jakūn gūsa'', ) were administrative and military divisions under the Later Jin and Qing dynasties of China into which all Manchu households were placed. In war, the Eight Banners functioned as armies, but the ...
that ethnic
Manchus
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
became a minority within the Banners, making up only 16% in 1648, with
Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
Bannermen dominating at 75% and
Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
Bannermen making up the rest.
It was this multi-ethnic force in which Manchus were only a minority, which unified China for the Qing. The Qing takeover was done by the multi-ethnic Han Chinese Banners, Mongol Banners, and Manchu Banners which made up the Qing military. In 1644, Ming China was invaded by an army that had only a fraction of Manchus, being multi-ethnic, with Han Chinese Banners, Mongol Banners, and Manchu Banners. The political barrier was between the commoners made out of non-bannermen Han Chinese and the "conquest elite", made out of Han Chinese bannermen, nobles, and Mongols and Manchu. It was not ethnicity which was the factor. Han Chinese (Nikan) bannermen used banners of black color and
Nurhaci
Nurhaci (14 May 1559 – 30 September 1626), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Taizu of Qing (), was a Jurchen chieftain who rose to prominence in the late 16th century in Manchuria. A member of the House of Aisin-Gioro, he reigned ...
was guarded by Han Chinese soldiers. Other banners became a minority compared to the Han Chinese (Nikan) Black Banner detachments during Nurhaci's reign.
Lead-up to the Great Wall
Second Joseon campaign (1636–1637)
The
Later Jin had forced
Joseon to open markets near the borders because its conflicts with
Ming
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peop ...
had brought economic hardship and starvation to Jin subjects. Joseon was also forced to transfer suzerainty of the Warka tribe to Jin. Furthermore, a tribute of 100 horses, 100 tiger and leopard skins, 400 bolts of cotton, and 15,000 pieces of cloth was to be extracted and gifted to the Jin Khan.
King Injo
Injo of Joseon (7 December 1595 – 17 June 1649), born Yi Jong, was the sixteenth ruler of the Joseon Dynasty of Korea. He was the grandson of King Seonjo and son of Prince Jeongwon. He was the king during the Later Jin invasion of Joseon, ...
's brother was sent to deliver this tribute. However, in later letters to the Joseon king,
Hong Taiji would complain that the
Koreans
Koreans ( South Korean: , , North Korean: , ; see names of Korea) are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Korean Peninsula.
Koreans mainly live in the two Korean nation states: North Korea and South Korea (collectively and simply re ...
did not behave as if they had lost, and were not abiding by the terms of the agreement. Joseon merchants and markets continued to trade with Ming and actively aided Ming subjects by providing them with grain and rations. Hong Taiji rebuked them, saying that the food of Joseon should only be fed to Joseon subjects.
Prior to the invasion, Hong Taiji sent princes
Abatai
Abatai (Manchu: ; 27 July 1589 – 10 May 1646) was a Manchu prince and military general of the early Qing dynasty. Although an inconsistent and dissolute malcontent, he nevertheless showed considerable ability as a military leader and a ...
,
Jirgalang
Jirgalang or Jirhalang (Manchu: 19 November 1599 – June 11, 1655) was a Manchu noble, regent, and political and military leader of the early Qing dynasty. Born in the Aisin Gioro clan, he was the sixth son of Šurhaci, a younger brother of ...
, and
Ajige
Ajige (Manchu:, Mölendroff: ajige; 28 August 1605 – 28 November 1651) was a Manchu prince and military general of the early Qing dynasty. He was born in the Aisin Gioro clan as the 12th son of Nurhaci, the khan of the Later Jin dynasty (the ...
to secure the coastal approaches to Korea, so that Ming could not send reinforcements. On 9 December 1636,
Hong Taiji led
Manchu,
Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
, and
Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
Banners against Joseon. Chinese support was particularly evident in the army's artillery and naval contingents. The defected Ming mutineer
Kong Youde
Kong Youde ( zh, c=, p=Kǒng Yǒudé; mnc, , v=; Transliteration of Manchu: kung ioo de; died August 7, 1652) was a Chinese adventurer and Ming dynasty military officer who served under the warlord Mao Wenlong until Mao's death in 1629. Subsequen ...
, ennobled as the Qing's Prince Gongshun, joined the attacks on
Ganghwa and
Ka ("Pidao"). The defectors
Geng Zhongming
Geng Zhongming (; 1604–1649) was a Chinese military general who lived through the transition from the Ming (1368–1644) to the Qing (1644–1912) dynasty, during which he served both sides. His grandson Geng Jingzhong was one of the Three Fe ...
and
Shang Kexi also played prominent roles in the Korean invasion. Koreans continue to maintain anti-Manchu hatred and sentiments after the 1636 Qing invasion of Korea.
After the Second Manchu invasion of Korea,
Joseon Korea
Joseon (; ; Middle Korean: 됴ᇢ〯션〮 Dyǒw syéon or 됴ᇢ〯션〯 Dyǒw syěon), officially the Great Joseon (; ), was the last dynastic kingdom of Korea, lasting just over 500 years. It was founded by Yi Seong-gye in July 1392 and r ...
was forced to give several of their royal princesses as concubines to the Qing Manchu regent Prince
Dorgon
Dorgon (, ; 17 November 1612 – 31 December 1650), was a Manchu prince and regent of the early Qing dynasty. Born in the House of Aisin-Gioro as the 14th son of Nurhaci (the founder of the Later Jin dynasty, predecessor of the Qing dynast ...
. In 1650 Dorgon married the Korean
Princess Uisun
Princess Uisun (1635–1662; birth name Yi Ae-suk) was a Joseon Royal Family member who became the adopted daughter of Hyojong of Joseon and Queen Inseon, so she could marry the Aisin Gioro prince Dorgon and later, prince Bolo.
Biography Backgr ...
. The princess' name in Korean was Uisun and she was Prince Yi Kaeyoon's (Kumrimgoon) daughter. Dorgon married two Korean princesses at
Lianshan.
Campaigns against the Amur tribes
The
Qing defeated the
Evenk-
Daur federation led by Evenki chief
Bombogor and beheaded Bombogor in 1640, with Qing armies massacring and deporting Evenkis and absorbing the survivors into the
Banners
A banner can be a flag or another piece of cloth bearing a symbol, logo, slogan or another message. A flag whose design is the same as the shield in a coat of arms (but usually in a square or rectangular shape) is called a banner of arms. Also ...
. The
Nanais at first fought against
Nurhaci
Nurhaci (14 May 1559 – 30 September 1626), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Taizu of Qing (), was a Jurchen chieftain who rose to prominence in the late 16th century in Manchuria. A member of the House of Aisin-Gioro, he reigned ...
and the
Manchus
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
, led by their own Nanai Hurka chief Sosoku before surrendering to
Hong Taiji in 1631. Mandatory shaving of the front of all male heads was imposed on
Amur peoples conquered by the Qing like the Nanais. The Amur peoples already wore the queue on the back of their heads but did not shave the front until the Qing subjected them and ordered them to shave.
The Qing married off Manchu princesses to Amur chiefs who submitted to their rule.
The
Daurs
The Daur people (Khalkha Mongolian: Дагуур, ''Daguur''; ) are a Mongolic people in Northeast China. The Daur form one of the 56 ethnic groups officially recognised in the People's Republic of China. They numbered 131,992 according to the la ...
and
Tungusic peoples
Tungusic peoples are an ethno-linguistic group formed by the speakers of Tungusic languages (or Manchu–Tungus languages). They are native to Siberia and Northeast Asia.
The Tungusic phylum is divided into two main branches, northern (Evenic or ...
of the
Amur region
Amur Oblast ( rus, Аму́рская о́бласть, r=Amurskaya oblast, p=ɐˈmurskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast), located on the banks of the Amur and Zeya Rivers in the Russian Far East. The administrativ ...
(
Evenks
The Evenks (also spelled Ewenki or Evenki based on their endonym )Autonym: (); russian: Эвенки (); (); formerly known as Tungus or Tunguz; mn, Хамниган () or Aiwenji () are a Tungusic people of North Asia. In Russia, the Eve ...
,
Nanais) and other ethnicities of this region were absorbed into the Qing
Eight Banners
The Eight Banners (in Manchu: ''jakūn gūsa'', ) were administrative and military divisions under the Later Jin and Qing dynasties of China into which all Manchu households were placed. In war, the Eight Banners functioned as armies, but the ...
system.
Liaoxi campaign (1638–1642)
In 1638,
Qing armies raided deep into the interior of
China as far as
Jinan in
Shandong province and immediately retreated back across the
Great Wall
The Great Wall of China (, literally "ten thousand ''li'' wall") is a series of fortifications that were built across the historical northern borders of ancient Chinese states and Imperial China as protection against various nomadic groups ...
. The
Ming
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peop ...
emperor insisted on concentrating all efforts at fighting the rebel armies instead, likening the Qing to be a mere "skin rash" while the rebels were a "visceral disease". In 1641,
Jinzhou
Jinzhou (, ), formerly Chinchow, is a coastal prefecture-level city in central-west Liaoning province, China. It is a geographically strategic city located in the Liaoxi Corridor, which connects most of the land transports between North Chin ...
was besieged by a force of over 30 cannons of
Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
banner artillery under
Manchu prince
Jirgalang
Jirgalang or Jirhalang (Manchu: 19 November 1599 – June 11, 1655) was a Manchu noble, regent, and political and military leader of the early Qing dynasty. Born in the Aisin Gioro clan, he was the sixth son of Šurhaci, a younger brother of ...
, with supporting
Korean
Korean may refer to:
People and culture
* Koreans, ethnic group originating in the Korean Peninsula
* Korean cuisine
* Korean culture
* Korean language
**Korean alphabet, known as Hangul or Chosŏn'gŭl
**Korean dialects and the Jeju language
** ...
artillery under the command of
Yu Im. The Koreans, however, were incapacitated by outbreaks of disease. The fortress city of
Songshan fell next after a major battle, due to the defection and betrayal of Ming commander
Xia Chengde. The emperor responded by ordering the
Ningyuan garrison commander
Wu Sangui to go on the offense, but he was quickly repelled. Manchu prince
Abatai
Abatai (Manchu: ; 27 July 1589 – 10 May 1646) was a Manchu prince and military general of the early Qing dynasty. Although an inconsistent and dissolute malcontent, he nevertheless showed considerable ability as a military leader and a ...
then led another raid into the interior of China, reaching the northern
Jiangsu province and looting 12,000 gold
s and 2,200,000 silver taels. Ming
Grand Secretary
The Grand Secretariat (; Manchu: ''dorgi yamun'') was nominally a coordinating agency but ''de facto'' the highest institution in the imperial government of the Chinese Ming dynasty. It first took shape after the Hongwu Emperor abolished the o ...
Zhou Yanru refused to engage in battle, while fabricating reports of victory and extorting bribes to cover up for defeats. Prince-Regent
Dorgon
Dorgon (, ; 17 November 1612 – 31 December 1650), was a Manchu prince and regent of the early Qing dynasty. Born in the House of Aisin-Gioro as the 14th son of Nurhaci (the founder of the Later Jin dynasty, predecessor of the Qing dynast ...
later told his officials how "it was really very comical" reading captured Ming military reports, because most were fabricated stories of victory. Meanwhile, rebel "bandits" continued advancing. After the fall of Songshan, amid the urging of his brother and sons (formerly also Ming generals) to join them in defecting to the Qing, the commander of
Jinzhou
Jinzhou (, ), formerly Chinchow, is a coastal prefecture-level city in central-west Liaoning province, China. It is a geographically strategic city located in the Liaoxi Corridor, which connects most of the land transports between North Chin ...
,
Zu Dashou
Zu Dashou (; d. 1656), courtesy name Fuyu (復宇), was a Chinese military general who served on the northern border of the Ming dynasty during the Ming–Qing transition period of Chinese history. He fought against the Qing dynasty in several ...
, also defected on 8 April 1642, handing them the city. With the fall of Songshan and Jinzhou, the Ming defense system in
Liaoxi collapsed, leaving
Wu Sangui's forces near the
Shanhai Pass as the last barrier on the Qing armies' way to
Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
.
Beijing and the north (1644)
In their later years, the
Ming
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peop ...
faced a number of famines and floods as well as economic chaos, and rebellions.
Li Zicheng
Li Zicheng (22 September 1606 – 1645), born Li Hongji, also known by the nickname, Dashing King, was a Chinese peasant rebel leader who overthrew the Ming dynasty in 1644 and ruled over northern China briefly as the emperor of the short-li ...
rebelled in the 1630s in
Shaanxi
Shaanxi (alternatively Shensi, see § Name) is a landlocked province of China. Officially part of Northwest China, it borders the province-level divisions of Shanxi (NE, E), Henan (E), Hubei (SE), Chongqing (S), Sichuan (SW), Gansu (W), N ...
in the north, while a mutiny led by
Zhang Xianzhong broke out in
Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of the ...
in the 1640s. Historians estimated that up to one million people were killed in this self-proclaimed emperor's reign of terror.
Just as
Dorgon
Dorgon (, ; 17 November 1612 – 31 December 1650), was a Manchu prince and regent of the early Qing dynasty. Born in the House of Aisin-Gioro as the 14th son of Nurhaci (the founder of the Later Jin dynasty, predecessor of the Qing dynast ...
, whom historians have variously called "the mastermind of the
Qing conquest" and "the principal architect of the great
Manchu enterprise", and his advisors were pondering how to attack the
Ming
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peop ...
, the peasant rebellions ravaging northern China were approaching dangerously close to the
Ming
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peop ...
capital
Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
. In February 1644, rebel leader
Li Zicheng
Li Zicheng (22 September 1606 – 1645), born Li Hongji, also known by the nickname, Dashing King, was a Chinese peasant rebel leader who overthrew the Ming dynasty in 1644 and ruled over northern China briefly as the emperor of the short-li ...
had founded the
Shun dynasty
The Shun dynasty (), officially the Great Shun (), was a short-lived Chinese dynasty that existed during the Ming–Qing transition. The dynasty was founded in Xi'an on 8 February 1644, the first day of the lunar year, by Li Zicheng, the leade ...
in
Xi'an
Xi'an ( , ; ; Chinese: ), frequently spelled as Xian and also known by other names, is the capital of Shaanxi Province. A sub-provincial city on the Guanzhong Plain, the city is the third most populous city in Western China, after Chongqi ...
and proclaimed himself king. In March his armies had captured the important city of
Taiyuan in
Shanxi. Seeing the progress of the rebels, on 5 April the Ming
Chongzhen Emperor
The Chongzhen Emperor (; 6 February 1611 – 25 April 1644), personal name Zhu Youjian (), courtesy name Deyue (),Wang Yuan (王源),''Ju ye tang wen ji'' (《居業堂文集》), vol. 19. "聞之張景蔚親見烈皇帝神主題御諱字德� ...
requested the urgent help of any military commandant in the empire. On 24 April Li Zicheng breached the walls of Beijing, and the emperor hanged himself the next day on a hill behind the
Forbidden City
The Forbidden City () is a palace complex in Dongcheng District, Beijing, China, at the center of the Imperial City of Beijing. It is surrounded by numerous opulent imperial gardens and temples including the Zhongshan Park, the sacrifi ...
. He was the last Ming emperor to reign in Beijing.
The Qing made a proposal to Li Zicheng's Shun forces on 6 March 1644 that they should ally and divide northern China between the Shun and Qing, sending a delegation to propose a joint attack on the Ming to take over the
Central Plains. The Shun received the letter.
When Li Zicheng and his army reached Beijing, he had made an offer via the former Ming eunuch
Du Xun to the
Chongzhen Emperor
The Chongzhen Emperor (; 6 February 1611 – 25 April 1644), personal name Zhu Youjian (), courtesy name Deyue (),Wang Yuan (王源),''Ju ye tang wen ji'' (《居業堂文集》), vol. 19. "聞之張景蔚親見烈皇帝神主題御諱字德� ...
of the Ming dynasty that Li Zicheng would fight the Qing dynasty and eradicate all other rebels on behalf of the Ming, if the Ming dynasty would recognize Li Zicheng's control over his Shaanxi-Shanxi fief, pay him 1 million
s and confirm Li Zicheng's noble rank of Prince. Li Zicheng did not intend to overthrow the Ming Emperor or kill him. The Ming Emperor, however, fearful that accepting such political expediency would ruin his reputation tried to get
Wei Zaode, the Chief
Grand Secretary
The Grand Secretariat (; Manchu: ''dorgi yamun'') was nominally a coordinating agency but ''de facto'' the highest institution in the imperial government of the Chinese Ming dynasty. It first took shape after the Hongwu Emperor abolished the o ...
, to agree with the decision and shoulder the responsibility of the decision. Wei Zaode refused to answer, so the Chongzhen Emperor rejected Li Zicheng's terms. Li Zicheng marched into the capital as Ming officials surrendered and defected. Li Zicheng still did not intend to kill the Chongzhen Emperor and the Ming Crown Prince, intending to recognise them as nobles of the new
Shun dynasty
The Shun dynasty (), officially the Great Shun (), was a short-lived Chinese dynasty that existed during the Ming–Qing transition. The dynasty was founded in Xi'an on 8 February 1644, the first day of the lunar year, by Li Zicheng, the leade ...
. Li Zicheng lamented the death of the Chongzhen Emperor after discovering he committed suicide, saying that he had come to share power and rule together with him. Li Zicheng distrusted the Ming officials who defected to his side when the Ming fell, viewing them as the reason for the Ming demise. After declaring his own Shun dynasty in
Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
, Li Zicheng sent an offer to the powerful Ming general at the
Great Wall
The Great Wall of China (, literally "ten thousand ''li'' wall") is a series of fortifications that were built across the historical northern borders of ancient Chinese states and Imperial China as protection against various nomadic groups ...
,
Wu Sangui, to defect to his side in exchange for a high noble rank and title. Wu Sangui dallied for days before he decided to accept the rank and defect to Li Zicheng. Wu Sangui was on his way to formally capitulate and defect to Li Zicheng, but by that time Li Zicheng thought Wu Sangui's silence meant he had rejected the offer and ordered Wu Sangui's father to be beheaded. This caused Wu Sangui to defect to the Qing.

Soon after the emperor had called for help, Ming general
Wu Sangui had left his stronghold of
Ningyuan north of the
Great Wall
The Great Wall of China (, literally "ten thousand ''li'' wall") is a series of fortifications that were built across the historical northern borders of ancient Chinese states and Imperial China as protection against various nomadic groups ...
and started marching toward the capital. On 26 April, his armies had moved through the fortifications of the
Shanhai Pass (the eastern end of the Great Wall) and were marching toward
Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
when he heard that the city had fallen, whereupon he returned to the Shanhai Pass. Li Zicheng sent two armies to attack the pass but Wu's battle-hardened troops defeated them easily on 5 May and 10 May. Then on 18 May,
Li Zicheng
Li Zicheng (22 September 1606 – 1645), born Li Hongji, also known by the nickname, Dashing King, was a Chinese peasant rebel leader who overthrew the Ming dynasty in 1644 and ruled over northern China briefly as the emperor of the short-li ...
personally led 60,000 of his troops out of Beijing to attack Wu. At the same time, Wu Sangui wrote to
Dorgon
Dorgon (, ; 17 November 1612 – 31 December 1650), was a Manchu prince and regent of the early Qing dynasty. Born in the House of Aisin-Gioro as the 14th son of Nurhaci (the founder of the Later Jin dynasty, predecessor of the Qing dynast ...
to request the Qing's help in ousting the bandits and restoring the Ming dynasty.
Meanwhile, Wu Sangui's departure from the
stronghold of Ningyuan had left all the territory outside the Great Wall under Qing control. Two of Dorgon's most prominent Chinese advisors,
Hong Chengchou
Hong Chengchou (; 1593–1665), courtesy name Yanyan and art name Hengjiu, was a Chinese official who served under the Ming and Qing dynasties. He was born in present-day Liangshan Village, Yingdu Town, Fujian Province, China. After obtaining t ...
and
Fan Wencheng
Fan Wencheng (, courtesy name: Xiandou 憲斗, 1597–1666) was a Qing dynasty Scholar-Official, Prime Minister and Grand Secretary ''(Daxue Shi)''. His official career went through four generation of Qing dynasty emperors through Nurhaci, Hong T ...
, urged the Manchu prince to seize the opportunity of the fall of Beijing to present themselves as avengers of the fallen Ming and to claim the
Mandate of Heaven for the Qing. Therefore, when Dorgon received Wu's letter, he was already about to lead an expedition to attack northern China and had no intention to restore the Ming. When Dorgon asked Wu to work for the Qing instead, Wu had little choice but to accept.
After Wu formally surrendered to the Qing in the morning of 27 May, his elite troops charged the rebel army repeatedly, but were unable to break the enemy lines. Dorgon waited until both sides were weakened before ordering his cavalry to gallop around Wu's right wing to charge Li's left flank. Li Zicheng's troops were quickly routed and fled back toward Beijing. After their defeat at the
Battle of Shanhai Pass
The Battle of Shanhai Pass, fought on May 27, 1644 at Shanhai Pass at the eastern end of the Great Wall, was a decisive battle leading to the beginning of the Qing dynasty rule in China proper. There, the Qing prince-regent Dorgon allied with ...
, the Shun troops looted Beijing for several days until Li Zicheng left the capital on 4 June with all the wealth he could carry, one day after he had defiantly proclaimed himself
Emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereignty, sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), ...
of the Great Shun.
Ethnic situation

The easy transition between the Ming and Qing dynasties has been ascribed to the
Chongzhen Emperor
The Chongzhen Emperor (; 6 February 1611 – 25 April 1644), personal name Zhu Youjian (), courtesy name Deyue (),Wang Yuan (王源),''Ju ye tang wen ji'' (《居業堂文集》), vol. 19. "聞之張景蔚親見烈皇帝神主題御諱字德� ...
's refusal to move southward when his capital had been under rebel threat. This allowed the Qing dynasty to capture an entire corps of qualified civil servants to administer the country, and also ensured that the
Southern Ming
The Southern Ming (), also known as the Later Ming (), officially the Great Ming (), was an imperial dynasty of China and a series of rump states of the Ming dynasty that came into existence following the Jiashen Incident of 1644. Shun force ...
pretenders would suffer from infighting due to their weak claims on the throne. A large émigré elite of northerners in the south would also have increased the probability of an aggressive policy of reconquest to regain their northern homelands.
Imperial examinations started being organised almost immediately upon the Qing capture of Beijing. The early Qing government was dominated by scholars from
North China, and a strong factional rivalry between Northern and Southern scholars ensued. Ming dynasty officials in the finance, appointments and military departments largely joined the new dynasty and formed the core of the Qing civil service, but not the staff of rites, music and literature (the Qing may not have prioritised these either). These defectors were responsible for easing the transition of government without major setbacks. A large proportion of military officials and civilian officials in the
Board of War
The Board of War, also known as the Board of War and Ordinance, was created by the Second Continental Congress as a special standing committee to oversee the American Continental Army's administration and to make recommendations regarding the ar ...
were given promotions after defecting. The top positions were mainly in the hands of Han Chinese Bannermen from
Liaodong
The Liaodong Peninsula (also Liaotung Peninsula, ) is a peninsula in southern Liaoning province in Northeast China, and makes up the southwestern coastal half of the Liaodong region. It is located between the mouths of the Daliao River (the ...
.
When
Dorgon
Dorgon (, ; 17 November 1612 – 31 December 1650), was a Manchu prince and regent of the early Qing dynasty. Born in the House of Aisin-Gioro as the 14th son of Nurhaci (the founder of the Later Jin dynasty, predecessor of the Qing dynast ...
ordered
Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
civilians to vacate
Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
's inner city and move to the outskirts, he resettled the inner city with the Bannermen, including Han Chinese bannermen. Later, some exceptions were made, allowing Han Chinese civilians who held government or commercial jobs to also reside in the inner city. The civilian government was flooded by Han Chinese Bannermen. The Six Boards President and other major positions were filled with Han Chinese Bannermen chosen by the Qing.
It was Han Chinese Bannermen who were responsible for the successful Qing takeover. They made up the majority of governors in the early Qing and were the ones who governed and administered China, stabilizing Qing rule.
Han Chinese Bannermen dominated governor-general posts in the time of the
Shunzhi
The Shunzhi Emperor (15 March 1638 – 5 February 1661) was the second emperor of the Qing dynasty of China, and the first Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1644 to 1661. A committee of Manchu princes chose him to succee ...
and
Kangxi
The Kangxi Emperor (4 May 1654– 20 December 1722), also known by his temple name Emperor Shengzu of Qing, born Xuanye, was the third emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the second Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1661 to 1 ...
emperors, as well as governor posts, largely excluding ordinary Han Chinese civilians. Three
Liaodong
The Liaodong Peninsula (also Liaotung Peninsula, ) is a peninsula in southern Liaoning province in Northeast China, and makes up the southwestern coastal half of the Liaodong region. It is located between the mouths of the Daliao River (the ...
Han Chinese Bannermen officers who played a major role in southern China from the Ming were
Shang Kexi,
Geng Zhongming
Geng Zhongming (; 1604–1649) was a Chinese military general who lived through the transition from the Ming (1368–1644) to the Qing (1644–1912) dynasty, during which he served both sides. His grandson Geng Jingzhong was one of the Three Fe ...
, and
Kong Youde
Kong Youde ( zh, c=, p=Kǒng Yǒudé; mnc, , v=; Transliteration of Manchu: kung ioo de; died August 7, 1652) was a Chinese adventurer and Ming dynasty military officer who served under the warlord Mao Wenlong until Mao's death in 1629. Subsequen ...
. They governed southern China autonomously as viceroys for the Qing. The Qing deliberately avoided placing
Manchus
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
or
Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal membe ...
as provincial governors and governors-general, with not a single Manchu governor until 1658, and not a single governor-general until 1668.
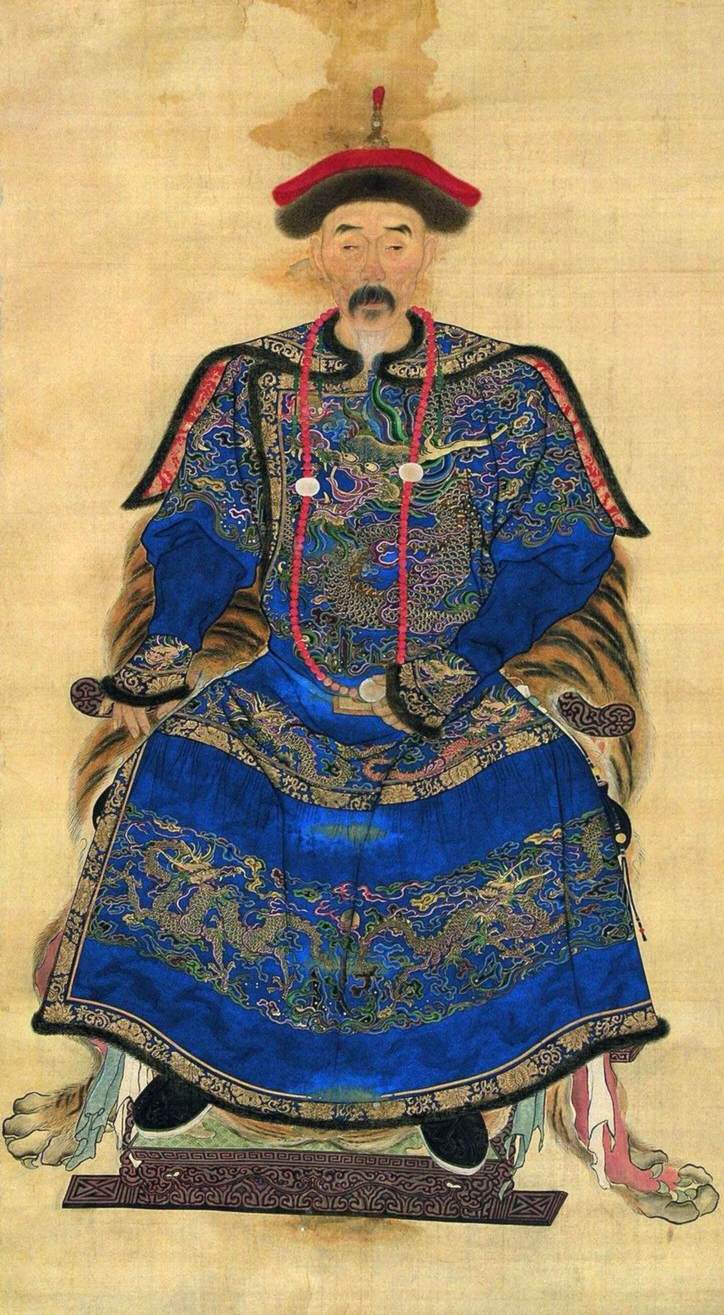

In addition to Han Chinese Banners, the Qing relied on the
Green Standard Army
The Green Standard Army (; Manchu: ''niowanggiyan turun i kūwaran'') was the name of a category of military units under the control of Qing dynasty in China. It was made up mostly of ethnic Han soldiers and operated concurrently with the Manchu ...
, composed of Han Chinese (Ming) military forces who defected to the Qing, in order to help rule northern China. It was these troops who provided day-to-day military governance in China, and supplied the forces used in the front-line fighting.
Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
Bannermen,
Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
Bannermen, and
Manchu Bannermen were only deployed to respond to emergency situations where there was sustained military resistance.
It was such a Qing army composed mostly of Han Chinese Bannermen which attacked
Koxinga
Zheng Chenggong, Prince of Yanping (; 27 August 1624 – 23 June 1662), better known internationally as Koxinga (), was a Ming loyalist general who resisted the Qing conquest of China in the 17th century, fighting them on China's southeastern ...
's Ming loyalists in
Nanjing
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu province of the People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and the second largest city in the East China region. T ...
. The Manchus sent Han Chinese Bannermen to fight against Koxinga's Ming loyalists in
Fujian
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its cap ...
. The Qing carried out a massive depopulation policy and
clearances, forcing people to evacuate the coast in order to deprive Koxinga's Ming loyalists of resources: this led to a myth that it was because Manchus were "afraid of water". In fact, in
Guangdong
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020) ...
and
Fujian
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its cap ...
, it was Han Bannermen who were the ones carrying out the fighting and killing for the Qing and this disproves the claim that "fear of water" on part of the Manchus had to do with the coastal evacuation to move inland and declare the sea ban. Most of the coastal population of
Fujian
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its cap ...
fled to the hills or to
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
to avoid the war;
Fuzhou was an empty city when the Qing forces entered it.
Consolidation in the north (1645)
Soon after entering
Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
in June 1644,
Dorgon
Dorgon (, ; 17 November 1612 – 31 December 1650), was a Manchu prince and regent of the early Qing dynasty. Born in the House of Aisin-Gioro as the 14th son of Nurhaci (the founder of the Later Jin dynasty, predecessor of the Qing dynast ...
despatched
Wu Sangui and his troops to pursue
Li Zicheng
Li Zicheng (22 September 1606 – 1645), born Li Hongji, also known by the nickname, Dashing King, was a Chinese peasant rebel leader who overthrew the Ming dynasty in 1644 and ruled over northern China briefly as the emperor of the short-li ...
, the rebel leader who had driven
the last Ming emperor to suicide, but had been defeated by the
Qing in late May at the
Battle of Shanhai Pass
The Battle of Shanhai Pass, fought on May 27, 1644 at Shanhai Pass at the eastern end of the Great Wall, was a decisive battle leading to the beginning of the Qing dynasty rule in China proper. There, the Qing prince-regent Dorgon allied with ...
. Wu managed to engage Li's rearguard many times, but Li still managed to cross the
Gu Pass into
Shanxi, and Wu returned to Beijing. Li Zicheng reestablished his power base in
Xi'an
Xi'an ( , ; ; Chinese: ), frequently spelled as Xian and also known by other names, is the capital of Shaanxi Province. A sub-provincial city on the Guanzhong Plain, the city is the third most populous city in Western China, after Chongqi ...
(
Shaanxi
Shaanxi (alternatively Shensi, see § Name) is a landlocked province of China. Officially part of Northwest China, it borders the province-level divisions of Shanxi (NE, E), Henan (E), Hubei (SE), Chongqing (S), Sichuan (SW), Gansu (W), N ...
province), where he had declared the foundation of his
Shun dynasty
The Shun dynasty (), officially the Great Shun (), was a short-lived Chinese dynasty that existed during the Ming–Qing transition. The dynasty was founded in Xi'an on 8 February 1644, the first day of the lunar year, by Li Zicheng, the leade ...
back in February 1644. In October of that year Dorgon sent several armies to root out Li Zicheng from his Shaanxi stronghold, after repressing revolts against Qing rule in
Hebei
Hebei or , (; alternately Hopeh) is a northern province of China. Hebei is China's sixth most populous province, with over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. The province is 96% Han Chinese, 3% Manchu, 0.8% Hui, and 0 ...
and
Shandong in the summer and autumn of 1644. Qing armies led by
Ajige
Ajige (Manchu:, Mölendroff: ajige; 28 August 1605 – 28 November 1651) was a Manchu prince and military general of the early Qing dynasty. He was born in the Aisin Gioro clan as the 12th son of Nurhaci, the khan of the Later Jin dynasty (the ...
,
Dodo
The dodo (''Raphus cucullatus'') is an extinct flightless bird that was endemic to the island of Mauritius, which is east of Madagascar in the Indian Ocean. The dodo's closest genetic relative was the also-extinct Rodrigues solitaire. The ...
, and
Shi Tingzhu won consecutive engagements against Shun forces in Shanxi and Shaanxi, forcing Li Zicheng to leave his Xi'an headquarters in February 1645. Pursued by Ajige, Li retreated down the
Han River into
Wuchang
Wuchang forms part of the urban core of and is one of 13 urban districts of the prefecture-level city of Wuhan, the capital of Hubei Province, China. It is the oldest of the three cities that merged into modern-day Wuhan, and stood on the ri ...
,
Hubei
Hubei (; ; alternately Hupeh) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, and is part of the Central China region. The name of the province means "north of the lake", referring to its position north of Dongting Lake. The ...
and further to
Tongcheng and the
Jiugong Mountains until he was killed in September 1645, either by his own hand or by a peasant group that had organized for self-defense in this time of rampant banditry.
Between
Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
and
Datong and in
Shanxi province
millenarianist groups of martial artist acolytes calling themselves the "Supreme Heaven's Clear and Pure Good Friends" and the "Society of Good Friends" respectively rose up in rebellion in 1645 against the new regime. These were suppressed by slaughtering anyone suspected of membership in such popular sects.
Other sectarian millenarian movements in Shanxi province broke out in rebellion in 1646–1648. Court fears of insurrection led them to crackdown on the sects led by
Zheng Dengqi, which in turn caused a major rebellion. The rebels were pacified through generous grants of amnesty.
Administrative policies
On the orders of
Nurhaci
Nurhaci (14 May 1559 – 30 September 1626), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Taizu of Qing (), was a Jurchen chieftain who rose to prominence in the late 16th century in Manchuria. A member of the House of Aisin-Gioro, he reigned ...
in 1629, a number of Chinese works considered to be of critical importance were translated into
Manchu by
Dahai.
The first works translated were all Chinese military texts dedicated to the arts of war due to the Manchu interests in the topic. They were the
''Liutao'', ''Su Shu'' (
素書), and
''Sanlüe'' followed by the military text ''
Wuzi
The ''Wuzi'' () is a classic Chinese work on military strategy attributed to Wu Qi. It is considered one of China's Seven Military Classics.
It is said there were two books on the art of war by Wu Qi, but one was lost, hence leaving the ''Wuzi ...
'' and ''
The Art of War
''The Art of War'' () is an ancient Chinese military treatise dating from the Late Spring and Autumn Period (roughly 5th century BC). The work, which is attributed to the ancient Chinese military strategist Sun Tzu ("Master Sun"), is com ...
''.
Other texts translated into Manchu by Dahai included the Ming penal code. The Manchus placed great significance on Chinese texts relating to military affairs and governance, and further Chinese texts of history, law and military theory were translated into Manchu during the rule of
Hong Taiji in
Mukden
Shenyang (, ; ; Mandarin pronunciation: ), formerly known as Fengtian () or by its Manchu name Mukden, is a major Chinese sub-provincial city and the provincial capital of Liaoning province. Located in central-north Liaoning, it is the prov ...
. A Manchu translation was made of the military themed Chinese novel ''
Romance of the Three Kingdoms
''Romance of the Three Kingdoms'' () is a 14th-century historical novel attributed to Luo Guanzhong. It is set in the turbulent years towards the end of the Han dynasty and the Three Kingdoms period in Chinese history, starting in 184 AD ...
''. As well as the translations by Dahai, other Chinese literature, military theory and legal texts were translated into Manchu by
Erdeni.
In order to pacify the population, the Qing authorities placed care to appoint good local officials. These were mainly ex-Ming non-Bannermen local magistrates who collaborated; virtually all county-level posts were filled by non-banner Han Chinese, who outnumbered Bannermen officials 12-to-1. There were in fact so many collaborators that the Qing court had to cut down on their numbers. The court also placed great attention to clamping down on administrative corruption through intensified inspections, and implemented a system of bureaucratic review (''kao cheng''). This helped to improve local government operations.
The Qing regime passed the Neighbourhood Security Investigation Law (''linbao jiancha fa'') which organised households into "mutual responsibility" groups of 10 and 100, and appointing leaders who were responsible for arresting fugitives. It was also used, initially at least, to stop the populace from moving in restive zones, and to stop arms and horse trading. From 1648 to 1649 civilian arms and horses were seized outright, but afterwards these were allowed for approved households in mutual responsibility units.
Conquest of the northwest (1644–1649)
The
Monguor Mongour, formerly also known by various names including Tu and Dchiahour, may refer to:
* Monguor people
* Monguor language
The Monguor language (; also written Mongour and Mongor) is a Mongolic language of its Shirongolic branch and is part of ...
s, who were
tusi
''Tusi'', often translated as "headmen" or "chieftains", were hereditary tribal leaders recognized as imperial officials by the Yuan, Ming, and Qing dynasties of China, and the Later Lê and Nguyễn dynasties of Vietnam. They ruled certain e ...
appointed by the Ming emperor, supported the
Ming
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peop ...
against a
Tibetan revolt and against
Li Zicheng
Li Zicheng (22 September 1606 – 1645), born Li Hongji, also known by the nickname, Dashing King, was a Chinese peasant rebel leader who overthrew the Ming dynasty in 1644 and ruled over northern China briefly as the emperor of the short-li ...
's rebels in 1642. They were unable to resist Li Zicheng and many tusi chiefs were massacred. When the
Qing forces under
Ajige
Ajige (Manchu:, Mölendroff: ajige; 28 August 1605 – 28 November 1651) was a Manchu prince and military general of the early Qing dynasty. He was born in the Aisin Gioro clan as the 12th son of Nurhaci, the khan of the Later Jin dynasty (the ...
and
Meng Qiaofang
Meng may refer to:
* Meng (surname) (孟), a Chinese surname
* Master of Engineering (MEng or M.Eng.), an academic or professional master's degree in the field of engineering
* , "M with hook", letter used in the International Phonetic Alphabet
* ...
fought against Li's forces after 1644 they quickly joined the Qing side. Meanwhile, Ming loyalist forces numbering 70,000 well-equipped troops were coalescing in the mountains south of
Xi'an
Xi'an ( , ; ; Chinese: ), frequently spelled as Xian and also known by other names, is the capital of Shaanxi Province. A sub-provincial city on the Guanzhong Plain, the city is the third most populous city in Western China, after Chongqi ...
, under former Ming commanders Sun Shoufa, He Zhen and Wu Dading, capturing the city of
Fengxiang. As they advanced toward Xi'an they were flanked by recent Ming defectors under Meng Qiaofang, and overrun with Bannermen. He Zhen's rebels were mainly bandits, and they continued operating out of small stockades in the forested, mountainous regions with 10 to 15 rebel families in every stockade, usually centered around a temple. They generally enjoyed popular support, and would retreat to the higher mountain safehouses upon receiving locals' notice of any military movements in the area. Groups of stockades congregated around a "King", who would grant commissions of Colonel or Major to other stockade leaders. They were finally pacified by forces led by
Ren Zhen.
Late in 1646, forces assembled by a
Muslim leader known in Chinese sources as
Milayin (米喇印) revolted against Qing rule in
Ganzhou
Ganzhou (), alternately romanized as Kanchow, is a prefecture-level city in the south of Jiangxi province, China, bordering Fujian to the east, Guangdong to the south, and Hunan to the west. Its administrative seat is at Zhanggong District.
Hist ...
(Gansu). He was soon joined by another Muslim named
Ding Guodong (丁國棟). Proclaiming that they wanted to restore the fallen Ming, they occupied a number of towns in Gansu, including the provincial capital
Lanzhou. These rebels' willingness to collaborate with non-Muslim Chinese suggests that they were not only driven by religion, and were not aiming to create an
Islamic state
An Islamic state is a state that has a form of government based on Islamic law (sharia). As a term, it has been used to describe various historical polities and theories of governance in the Islamic world. As a translation of the Arabic term ...
. To pacify the rebels, the Qing government quickly despatched
Meng Qiaofang
Meng may refer to:
* Meng (surname) (孟), a Chinese surname
* Master of Engineering (MEng or M.Eng.), an academic or professional master's degree in the field of engineering
* , "M with hook", letter used in the International Phonetic Alphabet
* ...
, governor of
Shaanxi
Shaanxi (alternatively Shensi, see § Name) is a landlocked province of China. Officially part of Northwest China, it borders the province-level divisions of Shanxi (NE, E), Henan (E), Hubei (SE), Chongqing (S), Sichuan (SW), Gansu (W), N ...
, a former Ming official who had surrendered to the Qing in 1631. The rebel leaders persuaded Zhu Shichuan, Ming Prince of
Yanchang, to legitimise them as a Ming loyalist force, and they quickly captured
Ganzhou
Ganzhou (), alternately romanized as Kanchow, is a prefecture-level city in the south of Jiangxi province, China, bordering Fujian to the east, Guangdong to the south, and Hunan to the west. Its administrative seat is at Zhanggong District.
Hist ...
and
Liangzhou, but were repelled at
Gongchang, Gansu. Milayin and Ding Guodong negotiated a truce in which they would become Qing commanders in April 1649, but less than four weeks later they rose up in revolt again. Milayan was swiftly killed when he attempted to break out of the Qing encirclement, while Ding Guodong holed up for a siege in
Suzhou and allied with the
Kumul Khanate
The Kumul Khanate was a semi-autonomous feudal Turkic khanate (equivalent to a banner in Mongolia) within the Qing dynasty and then the Republic of China until it was abolished by Xinjiang governor Jin Shuren in 1930. The Khanate was located in ...
by inviting Prince Sa'id Baba to rule in Suzhou. The Qing counterattack was interrupted by the Jiang Xiang mutiny (below).
Fall of the south
Conquest of Jiangnan (1645)
A few weeks after the
Chongzhen Emperor
The Chongzhen Emperor (; 6 February 1611 – 25 April 1644), personal name Zhu Youjian (), courtesy name Deyue (),Wang Yuan (王源),''Ju ye tang wen ji'' (《居業堂文集》), vol. 19. "聞之張景蔚親見烈皇帝神主題御諱字德� ...
committed suicide in
Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
in April 1644, descendants of the
Ming
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peop ...
imperial house started arriving in
Nanjing
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu province of the People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and the second largest city in the East China region. T ...
, which had been the auxiliary capital of the Ming dynasty. Agreeing that the Ming needed an imperial figure to rally support in the south, the
Nanjing
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu province of the People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and the second largest city in the East China region. T ...
Minister of War
Shi Kefa
Shi Kefa (4 February 1601 – 20 May 1645), courtesy names Xianzhi and Daolin, was a government official and calligrapher who lived in the late Ming dynasty. He was born in Xiangfu (祥符; present-day Kaifeng, Henan) and claimed ancestry from D ...
and the
Fengyang
Fengyang County () is a county in north-central Anhui, Anhui Province, China. It is under the administration of Chuzhou, a prefecture-level city. The county was home to 765,600 people as of 2013.
Administrative divisions
Fengyang County is divide ...
Governor-general
Ma Shiying agreed to form a loyalist Ming government around the
Prince of Fu
Prince of Fu ( zh, 福王), was a first-rank princely peerage used during Ming dynasty, this peerage title was created by Wanli Emperor. The first Prince of Fu was Zhu Changxun, 3rd son of Wanli Emperor. This peerage had 2 cadet commandery princel ...
,
Zhu Yousong
The Hongguang Emperor (; 1607–1646), personal name Zhu Yousong (), childhood nickname Fuba (福八), was the first emperor of the Chinese Southern Ming dynasty. He reigned briefly in southern China from 1644 to 1645. His era name, ''Hongguang'' ...
, a first cousin of the
Chongzhen Emperor
The Chongzhen Emperor (; 6 February 1611 – 25 April 1644), personal name Zhu Youjian (), courtesy name Deyue (),Wang Yuan (王源),''Ju ye tang wen ji'' (《居業堂文集》), vol. 19. "聞之張景蔚親見烈皇帝神主題御諱字德� ...
who had been next in line for succession after the dead emperor's sons, whose fates were still unknown. The Prince was
crowned as
emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereignty, sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), ...
on 19 June 1644 under the protection of Ma Shiying and his large war fleet. He would reign under the
era name
A regnal year is a year of the reign of a sovereign, from the Latin ''regnum'' meaning kingdom, rule. Regnal years considered the date as an ordinal, not a cardinal number. For example, a monarch could have a first year of rule, a second year of ...
"Hongguang" (弘光). The Hongguang regime was ridden with factional bickering that facilitated the
Qing conquest of
Jiangnan
Jiangnan or Jiang Nan (; formerly romanized Kiang-nan, literally "South of the River" meaning "South of the Yangtze") is a geographic area in China referring to lands immediately to the south of the lower reaches of the Yangtze River, incl ...
, which was launched from
Xi'an
Xi'an ( , ; ; Chinese: ), frequently spelled as Xian and also known by other names, is the capital of Shaanxi Province. A sub-provincial city on the Guanzhong Plain, the city is the third most populous city in Western China, after Chongqi ...
in April 1645. He set out from Xi'an on that very day. Greatly aided by the surrender of Southern Ming commanders
Li Chengdong
Li, li, or LI may refer to:
Businesses and organizations
* Landscape Institute, a British professional body for landscape architects
* Leadership Institute, a non-profit organization located in Arlington, Virginia, US, that teaches "political te ...
and
Liu Liangzuo
/ ( or ) is an East Asian surname. pinyin: in Mandarin Chinese, in Cantonese. It is the family name of the Han dynasty emperors. The character originally meant 'kill', but is now used only as a surname. It is listed 252nd in the classic t ...
, the Qing army took the key city of
Xuzhou
Xuzhou (徐州), also known as Pengcheng (彭城) in ancient times, is a major city in northwestern Jiangsu province, China. The city, with a recorded population of 9,083,790 at the 2020 census (3,135,660 of which lived in the built-up area ma ...
north of the
Huai River
The Huai River (), formerly romanized as the Hwai, is a major river in China. It is located about midway between the Yellow River and Yangtze, the two longest rivers and largest drainage basins in China, and like them runs from west to ea ...
in early May 1645, leaving
Shi Kefa
Shi Kefa (4 February 1601 – 20 May 1645), courtesy names Xianzhi and Daolin, was a government official and calligrapher who lived in the late Ming dynasty. He was born in Xiangfu (祥符; present-day Kaifeng, Henan) and claimed ancestry from D ...
in
Yangzhou
Yangzhou, postal romanization Yangchow, is a prefecture-level city in central Jiangsu Province (Suzhong), East China. Sitting on the north bank of the Yangtze, it borders the provincial capital Nanjing to the southwest, Huai'an to the north ...
as the main defender of the
Southern Ming
The Southern Ming (), also known as the Later Ming (), officially the Great Ming (), was an imperial dynasty of China and a series of rump states of the Ming dynasty that came into existence following the Jiashen Incident of 1644. Shun force ...
's northern frontiers. The betrayal of these commanders handed over the entire northwestern zone of the Southern Ming, helping the Qing forces to link up. Ming loyalist Ma Shiying had brought to
Nanjing
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu province of the People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and the second largest city in the East China region. T ...
troops from the western provinces made out of non-
Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
indigenous fierce tribal warriors called
"Sichuan" soldiers to defend the city against the Qing. These Ming loyalist non-Han Chinese "barbarian" fierce tribal warriors were slaughtered by the Han Chinese citizens of Nanjing after the Han Chinese people of Nanjing had peacefully defected and turned the city to Qing rule when the Southern Ming
Hongguang Emperor
The Hongguang Emperor (; 1607–1646), personal name Zhu Yousong (), childhood nickname Fuba (福八), was the first emperor of the Chinese Southern Ming dynasty. He reigned briefly in southern China from 1644 to 1645. His era name, ''Hongguang'' ...
left the city. The people also yelled "These are the son and daughter-in-law of the traitorous minister Ma Shiying!" when they paraded the daughter-in-law and son of Ma Shiying after storming
Ruan Dacheng
Ruan may refer to:
Buildings
*Ruan Center, office building in Des Moines, Iowa
*John Ruan House, historic mansion in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Places
*Ruan, County Clare, Ireland
*Ruan, Loiret, France
*Mont Ruan, Switzerland
*Ruan Major and Ru ...
and
Ma Shiying's houses and they also did it to
Wang Duo
Wang Duo () (died 884), courtesy name Zhaofan (), formally the Duke of Jin (), was a Chinese politician of the medieval Tang Dynasty, serving as a chancellor during the reigns of Emperor Yizong and Emperor Yizong's son Emperor Xizong. After th ...
's daughter-in-law and son. The
Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( nl, Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie, the VOC) was a chartered company established on the 20th March 1602 by the States General of the Netherlands amalgamating existing companies into the first joint-stock ...
secretary
Johann Nieuhof observed that
Nanjing
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu province of the People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and the second largest city in the East China region. T ...
city and its people were unharmed by the Qing and only the Ming palace suffered destruction. The damage inflicted to the Ming palace was largely done by the Han Chinese locals of Nanjing, and not the Qing army.
Qing Prince of Yu,
Dodo
The dodo (''Raphus cucullatus'') is an extinct flightless bird that was endemic to the island of Mauritius, which is east of Madagascar in the Indian Ocean. The dodo's closest genetic relative was the also-extinct Rodrigues solitaire. The ...
, later berated the Southern Ming Prince of Fu,
Zhu Yousong
The Hongguang Emperor (; 1607–1646), personal name Zhu Yousong (), childhood nickname Fuba (福八), was the first emperor of the Chinese Southern Ming dynasty. He reigned briefly in southern China from 1644 to 1645. His era name, ''Hongguang'' ...
, over his battle strategy in 1645, telling him that the Southern Ming would have defeated the Qing if only the Southern Ming assaulted the Qing military before they forded the
Yellow River
The Yellow River or Huang He (Chinese: , Mandarin: ''Huáng hé'' ) is the second-longest river in China, after the Yangtze River, and the sixth-longest river system in the world at the estimated length of . Originating in the Bayan Ha ...
instead of tarrying. The Prince of Fu could find no words to respond when he tried to defend himself.
In
Jiangnan
Jiangnan or Jiang Nan (; formerly romanized Kiang-nan, literally "South of the River" meaning "South of the Yangtze") is a geographic area in China referring to lands immediately to the south of the lower reaches of the Yangtze River, incl ...
, the Qing implemented peaceful takeovers for districts and cities who surrendered without any violent resistance, leaving the local Ming officials who defected in charge and the Qing
Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
-
Manchu army would not attack them nor kill or do any violence against peaceful defectors.
Several contingents of Qing forces converged on
Yangzhou
Yangzhou, postal romanization Yangchow, is a prefecture-level city in central Jiangsu Province (Suzhong), East China. Sitting on the north bank of the Yangtze, it borders the provincial capital Nanjing to the southwest, Huai'an to the north ...
on 13 May 1645. The majority of the Qing army which marched on the city were Ming defectors and they far outnumbered the
Manchus
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
and
Bannermen
Bannerman is a name of Scottish origin (see Clan Bannerman) and may refer to
Places
;Canada
* Bannerman, Edmonton, a neighbourhood in Edmonton, Canada
;United States
* Bannerman, Wisconsin, an unincorporated community
* Bannerman's Castle, an a ...
.
Shi Kefa
Shi Kefa (4 February 1601 – 20 May 1645), courtesy names Xianzhi and Daolin, was a government official and calligrapher who lived in the late Ming dynasty. He was born in Xiangfu (祥符; present-day Kaifeng, Henan) and claimed ancestry from D ...
's small force refused to surrender, but could not resist
Dodo
The dodo (''Raphus cucullatus'') is an extinct flightless bird that was endemic to the island of Mauritius, which is east of Madagascar in the Indian Ocean. The dodo's closest genetic relative was the also-extinct Rodrigues solitaire. The ...
's artillery: on 20 May Qing cannon wielded by the Han Chinese Bannermen (Ujen Coohai) breached the city wall and Dodo ordered the
"brutal slaughter" of Yangzhou's entire population to terrorize other Jiangnan cities into surrendering to the Qing. On 1 June Qing armies crossed the
Yangzi River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest river in Asia, the third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains (Tibetan Plateau) and flows ...
and easily took the garrison city of
Zhenjiang
Zhenjiang, alternately romanized as Chinkiang, is a prefecture-level city in Jiangsu Province, China. It lies on the southern bank of the Yangtze River near its intersection with the Grand Canal. It is opposite Yangzhou (to its north) and ...
, which protected access to
Nanjing
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu province of the People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and the second largest city in the East China region. T ...
. The Qing arrived at the gates of Nanjing a week later, but the
Hongguang Emperor
The Hongguang Emperor (; 1607–1646), personal name Zhu Yousong (), childhood nickname Fuba (福八), was the first emperor of the Chinese Southern Ming dynasty. He reigned briefly in southern China from 1644 to 1645. His era name, ''Hongguang'' ...
had already fled. The city surrendered without a fight on 16 June 1645 after its last defenders had made Dodo promise he would not hurt the population. Within less than a month, the Qing had captured the fleeing Ming emperor (he died in
Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
the following year) and seized
Jiangnan
Jiangnan or Jiang Nan (; formerly romanized Kiang-nan, literally "South of the River" meaning "South of the Yangtze") is a geographic area in China referring to lands immediately to the south of the lower reaches of the Yangtze River, incl ...
's main cities, including
Suzhou and
Hangzhou
Hangzhou ( or , ; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), also romanized as Hangchow, is the capital and most populous city of Zhejiang, China. It is located in the northwestern part of the province, sitting at the head of Hangzhou Bay, whic ...
. By then the frontier between the
Qing and the
Southern Ming
The Southern Ming (), also known as the Later Ming (), officially the Great Ming (), was an imperial dynasty of China and a series of rump states of the Ming dynasty that came into existence following the Jiashen Incident of 1644. Shun force ...
had been pushed south to the
Qiantang River.
Nieuhof observed that the city of
Nanjing
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu province of the People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and the second largest city in the East China region. T ...
was unharmed by
Qing soldiers.
Qing soldiers ransomed women captured from
Yangzhou
Yangzhou, postal romanization Yangchow, is a prefecture-level city in central Jiangsu Province (Suzhong), East China. Sitting on the north bank of the Yangtze, it borders the provincial capital Nanjing to the southwest, Huai'an to the north ...
back to their original husbands and fathers in
Nanjing
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu province of the People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and the second largest city in the East China region. T ...
after Nanjing peacefully surrendered, corralling the women into the city and whipping them hard with their hair containing a tag showing the price of the ransom, which was cheap at only 3 to 4
s for the best and 10 taels at most for those wearing good clothing.
During the factional struggles, the warlord
Zuo Liangyu Zuo Liangyu () (1599–1645) was a Ming dynasty and Southern Ming general. He was born in Linqing, Shandong Province.
Campaign against Zhang Xianzhong
After defeating peasant rebels at She County, Hebei, Huixian and Wu'an and eliminating their ...
had mutinied against
Ma Shiying who was in control at
Nanjing
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu province of the People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and the second largest city in the East China region. T ...
, accusing him of repression. With the arrival of the
Qing forces in
Jiujiang
Jiujiang (), formerly transliterated Kiukiang or Kew Keang, is a prefecture-level city located on the southern shores of the Yangtze River in northwest Jiangxi Province, People's Republic of China. It is the second-largest prefecture-level city ...
, almost the entire army of Zuo Liangyu defected to the Qing. This provided the Qing with a critical new pool of military leaders and troops. These were also officers from
Liaodong
The Liaodong Peninsula (also Liaotung Peninsula, ) is a peninsula in southern Liaoning province in Northeast China, and makes up the southwestern coastal half of the Liaodong region. It is located between the mouths of the Daliao River (the ...
, or had previously served there, who in the 1630s had been withdrawn to fight rebels in the interior provinces. The most important of these was
Jin Shenghuan
Jin Shenghuan (, ?–1 March 1649), courtesy name Huchen () was a soldier who served both the Ming and Qing dynasties. He was a native of Liaodong (modern-day Liaoyang).
Life
Jin was a brigadier-general under the Ming general Huang Long (黃� ...
who was later single-handedly responsible for the conquest of
Jiangxi
Jiangxi (; ; formerly romanized as Kiangsi or Chianghsi) is a landlocked province in the east of the People's Republic of China. Its major cities include Nanchang and Jiujiang. Spanning from the banks of the Yangtze river in the north int ...
. Other generals were Zuo Liangyu's son
Zuo Menggeng who later crushed rebels in
Datong,
Lu Guangzu
Lu Guangzu (; born on 19 October 1996) is a Chinese badminton player. In 2018, Lu made into his first final at the Lingshui China Masters. Since then, he both won Australian Open and Canada Open's titles.
Career
2022
Lu reached the final o ...
and
Li Guoying
Li Guoying (; born December 1963) is a Chinese hydraulic engineer-turned-politician, currently serving as governor of Anhui province. Li worked in his early career as a technician and administrator in the national ministry of water works, the Yel ...
who served in the
Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of the ...
campaign,
Xu Yong and
Hao Xiaozhong who served in the
Hunan
Hunan (, ; ) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the South Central China region. Located in the middle reaches of the Yangtze watershed, it borders the province-level divisions of Hubei to the north, Jiangxi ...
campaigns. Many of these became the most capable commanders against the
Southern Ming
The Southern Ming (), also known as the Later Ming (), officially the Great Ming (), was an imperial dynasty of China and a series of rump states of the Ming dynasty that came into existence following the Jiashen Incident of 1644. Shun force ...
loyalists.
The
Hongguang Emperor
The Hongguang Emperor (; 1607–1646), personal name Zhu Yousong (), childhood nickname Fuba (福八), was the first emperor of the Chinese Southern Ming dynasty. He reigned briefly in southern China from 1644 to 1645. His era name, ''Hongguang'' ...
fled into
Anhui
Anhui , (; formerly romanized as Anhwei) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the East China region. Its provincial capital and largest city is Hefei. The province is located across the basins of the Yangtze River ...
on the
Yangzi
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest river in Asia, the third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains (Tibetan Plateau) and flows ...
's southern bank at
Tongling
Tongling (; former names: Tunglinghsien, Tungkwanshan) is a prefecture-level city in southern Anhui province. A river port along the Yangtze River, Tongling borders Wuhu to the east, Chizhou to the southwest and Anqing to the west.
As of the 20 ...
, in
Huang Degong's military camp. Huang Degong told him that if he died fighting to the death in
Nanjing
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu province of the People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and the second largest city in the East China region. T ...
then all the ministers would have followed his lead in fighting against the
Qing, but now that he fled without a fight and listened to traitors his small army could not act as a guard for the emperor. Huang Degong then said "I am willing to devote my life to you" after the emperor said he could not rely on him as a minister resentfully. Then a group of Qing Han Chinese and Banner soldiers showed up to Huang Degong's camp in
Wuhu
Wuhu () is a prefecture-level city in southeastern Anhui province, China. Sitting on the southeast bank of the Yangtze River, Wuhu borders Xuancheng to the southeast, Chizhou and Tongling to the southwest, Hefei city to the northwest, Ma'ansh ...
on 15 June 1645, under
Zhang Tianlu, the
Guazhou
Guazhou County (), formerly (until 2006) Anxi County () or Ansichow, is a county in the northwest of Gansu province, the People's Republic of China. It is under the administration of Jiuquan City.
History
Emperor Wudi (140-87 BCE) had th ...
garrison commander, bannermen from
Dodo
The dodo (''Raphus cucullatus'') is an extinct flightless bird that was endemic to the island of Mauritius, which is east of Madagascar in the Indian Ocean. The dodo's closest genetic relative was the also-extinct Rodrigues solitaire. The ...
and general
Liu Liangzuo
/ ( or ) is an East Asian surname. pinyin: in Mandarin Chinese, in Cantonese. It is the family name of the Han dynasty emperors. The character originally meant 'kill', but is now used only as a surname. It is listed 252nd in the classic t ...
. Huang Degong rejected their demand to turn over the Hongguang Emperor but Zhang Tianlu then shot an arrow into Huang's throat and killed him.
Tian Xiong
''Tiān'' () is one of the oldest Chinese terms for heaven and a key concept in Chinese mythology, philosophy, and religion. During the Shang dynasty (17th―11th century BCE), the Chinese referred to their supreme god as '' Shàngdì'' (, "Lo ...
and
Ma Deong, the brigade commanders under Huang Degong then defected to the Qing and gave general Liu Liangzuo the Hongguang Emperor.
Queue order and Jiangnan resistance (1645-1646)

Resistance in the region was originally muted. As the heartland of the scholarly class, hundreds of
Jiangnan
Jiangnan or Jiang Nan (; formerly romanized Kiang-nan, literally "South of the River" meaning "South of the Yangtze") is a geographic area in China referring to lands immediately to the south of the lower reaches of the Yangtze River, incl ...
scholars committed suicide by drowning, hanging, self-immolation, or hunger strike on the news of the death of the
Hongguang Emperor
The Hongguang Emperor (; 1607–1646), personal name Zhu Yousong (), childhood nickname Fuba (福八), was the first emperor of the Chinese Southern Ming dynasty. He reigned briefly in southern China from 1644 to 1645. His era name, ''Hongguang'' ...
, sometimes entire families. Those who did not collaborate or commit suicide would have to join with bandits to resist the new regime. With the news of the fall of the capital back in 1644 and skyrocketing food prices, poor peasants had revolted against the local elite and indentured servitude, calling that "master and servant should address each other as brothers". They ransacked the villas and forced the wealthy to flee to the cities. Although the
Southern Ming
The Southern Ming (), also known as the Later Ming (), officially the Great Ming (), was an imperial dynasty of China and a series of rump states of the Ming dynasty that came into existence following the Jiashen Incident of 1644. Shun force ...
regime managed to restore order, the discontent persisted and coalesced as the Black Dragon Society, which immediately resumed their revolt once the Qing crushed the Southern Ming forces. Some of the gentry, associated with the
Donglin movement, resisted compromise, but most gentry and urban elites proceeded to collaborate with the Qing in order to acquire their help to suppress the revolt or other threats such as bandits. However, with the introduction of the queue order, anti-Qing resistance exploded once more.
On 21 July 1645, after the
Jiangnan
Jiangnan or Jiang Nan (; formerly romanized Kiang-nan, literally "South of the River" meaning "South of the Yangtze") is a geographic area in China referring to lands immediately to the south of the lower reaches of the Yangtze River, incl ...
region had been superficially pacified,
Dorgon
Dorgon (, ; 17 November 1612 – 31 December 1650), was a Manchu prince and regent of the early Qing dynasty. Born in the House of Aisin-Gioro as the 14th son of Nurhaci (the founder of the Later Jin dynasty, predecessor of the Qing dynast ...
issued "the most untimely promulgation of his career": he ordered all Chinese men to shave their forehead and to braid the rest of their hair into a
queue __NOTOC__
Queue () may refer to:
* Queue area, or queue, a line or area where people wait for goods or services
Arts, entertainment, and media
*''ACM Queue'', a computer magazine
* ''The Queue'' (Sorokin novel), a 1983 novel by Russian author ...
just like the
Manchus
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
. The punishment for non-compliance was death. In the queue order edict, Dorgon specifically emphasized the fact that Manchus and the Qing emperor himself all wore the queue and shaved their foreheads so that by following the queue order and shaving,
Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
would look like Manchus and the Qing Emperor, and invoked the
Confucian
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China. Variously described as tradition, a philosophy, a religion, a humanistic or rationalistic religion, a way of governing, or ...
notion that the people were like the sons of the emperor who was like the father, so the father and sons could not look different and to decrease differences in physical appearance between Manchus and Han Chinese.
The queue order was proposed by a number of Han Chinese officials in order to curry favour with
Dorgon
Dorgon (, ; 17 November 1612 – 31 December 1650), was a Manchu prince and regent of the early Qing dynasty. Born in the House of Aisin-Gioro as the 14th son of Nurhaci (the founder of the Later Jin dynasty, predecessor of the Qing dynast ...
. This policy of symbolic submission to the new dynasty helped the Manchus in telling friend from foe. However, for Han Chinese officials and literati, the new hairstyle was "a humiliating act of degradation" (because it breached a common
Confucian
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China. Variously described as tradition, a philosophy, a religion, a humanistic or rationalistic religion, a way of governing, or ...
directive to preserve one's body intact), whereas for common folk cutting their hair "was tantamount to the loss of their manhood." Because it united Chinese of all social backgrounds into resistance against Qing rule, the hair-cutting command "broke the momentum of the Qing
xpansion"
A minor scholar
Wang Zhan, in command of rural militia, besieged
Taicang
Taicang is a county-level city under the jurisdiction of Suzhou, Jiangsu province, China. The city located in the south of the Yangtze River estuary opposite Nantong, being bordered by Shanghai proper to the south, while the river also delineat ...
. In
Xiushui, the local military commander
Chen Wu and the local gentry mobilised militia and revolted, but they failed in an attack on
Jiaxing
Jiaxing (), alternately romanized as Kashing, is a prefecture-level city in northern Zhejiang province, China. Lying on the Grand Canal of China, Jiaxing borders Hangzhou to the southwest, Huzhou to the west, Shanghai to the northeast, and the p ...
. In
Kunshan
Kunshan is a county-level city in southeastern Jiangsu province with Shanghai bordering its eastern border and Suzhou on its western boundary. It is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Suzhou.
Name
There is a strong p ...
, the resistance forces under magistrate
Yang Yongyan, general
Wang Zuocai and scholar
Zhu Jihuang had been mostly unsuccessful until the queue order was passed, when they experienced a surge in popular support and succeeded in killing the local collaborationist magistrate. However the army of
Prince Dodo turned on the region and with the exception of a few holdouts such as
Jiangyin
Jiangyin (, Jiangyin dialect: ) is a county-level city on the southern bank of the Yangtze River, and is administered by Wuxi, Jiangsu province. Jiangyin is one of the most important transport hubs on the Yangtze River, it is also one of the most d ...
, the loyalists fell quickly and the population was massacred.
Resistance from marsh bandits, fishermen, gentry-led militia and ex-
Ming
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peop ...
soldiers coalesced around
Lake Tai
Taihu (), also known as Lake Tai or Lake Taihu, is a lake in the Yangtze Delta and one of the largest freshwater lakes in China. The lake is in Jiangsu province and a significant part of its southern shore forms its border with Zhejiang. Wi ...
. The region's bandits were infamous for kidnapping rich people and threatening to blind or bury them alive unless ransom was paid, while distributing food and money to the poor. Now their river craft were converted into an
ad hoc
Ad hoc is a Latin phrase meaning literally 'to this'. In English, it typically signifies a solution for a specific purpose, problem, or task rather than a generalized solution adaptable to collateral instances. (Compare with '' a priori''.)
C ...
naval raiding force and joined forces with their former gentry enemies. The gentry united these elements into the "White Headed Army" since they wore white turbans. East of the lake, loyalist gentry in
Songjiang District
Songjiang is a suburban district (formerly a county) of Shanghai. It has a land area of and a population of 1,582,398 (2010). Owing to a long history, Songjiang is known as the cultural root of Shanghai.
Songjiang Town, the urban center of the ...
under
Chen Zilong and the remaining
Ming navy at
Chongming Island
Chongming, formerly known as Chungming, is an alluvial island at the mouth of the Yangtze River in eastern China covering as of 2010. Together with the islands Changxing and Hengsha, it forms Chongming District, the northernmost area of the ...
under
Wu Zhikui coordinated to rise up and cut off the
Qing forces in
Zhejiang
Zhejiang ( or , ; , Chinese postal romanization, also romanized as Chekiang) is an East China, eastern, coastal Provinces of China, province of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Hangzhou, and other notable citie ...
. The loyalists aimed to serve as a linkage between the upstream resistance in
Hunan
Hunan (, ; ) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the South Central China region. Located in the middle reaches of the Yangtze watershed, it borders the province-level divisions of Hubei to the north, Jiangxi ...
and the coastal resistance in
Zhejiang
Zhejiang ( or , ; , Chinese postal romanization, also romanized as Chekiang) is an East China, eastern, coastal Provinces of China, province of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Hangzhou, and other notable citie ...
and
Fujian
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its cap ...
. The loyalists splintered over strategy disagreements. The loyalist navy, trying to sail for
Lake Mao, was destroyed at
Chushenpu by general
Li Chengdong
Li, li, or LI may refer to:
Businesses and organizations
* Landscape Institute, a British professional body for landscape architects
* Leadership Institute, a non-profit organization located in Arlington, Virginia, US, that teaches "political te ...
's light craft forces. The
Lake Tai
Taihu (), also known as Lake Tai or Lake Taihu, is a lake in the Yangtze Delta and one of the largest freshwater lakes in China. The lake is in Jiangsu province and a significant part of its southern shore forms its border with Zhejiang. Wi ...
resistance stormed
Suzhou but were trapped in the city when Qing forces under
Wang Guocai regrouped and closed the gates.
Songjiang Songjiang, from the Chinese for "Pine River" and formerly romanized as Sungkiang, usually refers to one of the following areas within the municipal limits of Shanghai:
* Songjiang Town (), the former principal town of the Shanghai area
* Songjia ...
fell after being deceived into opening the gates by Qing forces covering up their shaved heads. A group of loyalists fled to join the resistance in
Fuzhou.
The defiant population of
Jiading
Jiading is a suburban district of Shanghai. It had a population of 1,471,100 in 2010.
History
Historically, Jiading was a separate municipality/town, until, in 1958, becoming under the administration of Shanghai. In 1993, Jiading's designate ...
and
Songjiang Songjiang, from the Chinese for "Pine River" and formerly romanized as Sungkiang, usually refers to one of the following areas within the municipal limits of Shanghai:
* Songjiang Town (), the former principal town of the Shanghai area
* Songjia ...
was massacred by former Ming northern Chinese general Li Chengdong, respectively on 24 August and 22 September.
Jiangyin
Jiangyin (, Jiangyin dialect: ) is a county-level city on the southern bank of the Yangtze River, and is administered by Wuxi, Jiangsu province. Jiangyin is one of the most important transport hubs on the Yangtze River, it is also one of the most d ...
also held out against about 10,000 Qing troops for 83 days. When the city wall was finally breached on 9 October 1645, the Qing army led by northern Chinese Ming defector
Liu Liangzuo
/ ( or ) is an East Asian surname. pinyin: in Mandarin Chinese, in Cantonese. It is the family name of the Han dynasty emperors. The character originally meant 'kill', but is now used only as a surname. It is listed 252nd in the classic t ...
, who had been ordered to "fill the city with corpses before you sheathe your swords," massacred the entire population, killing between 74,000 and 100,000 people. Hundreds of thousands of people were killed before all of China was brought into compliance. Although
Manchu Bannermen were often associated with the
Jiangyin
Jiangyin (, Jiangyin dialect: ) is a county-level city on the southern bank of the Yangtze River, and is administered by Wuxi, Jiangsu province. Jiangyin is one of the most important transport hubs on the Yangtze River, it is also one of the most d ...
Massacre which targeted the Ming loyalists, the majority of those who had participated in Jiangyin Massacre were
Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
Bannermen. Ming defector Li Chengdong's Han Chinese soldiers, who were mostly former revolted refugees, peasants and bandits from the north called the Han Chinese anti-queue resisters and Ming loyalists in
Jiading
Jiading is a suburban district of Shanghai. It had a population of 1,471,100 in 2010.
History
Historically, Jiading was a separate municipality/town, until, in 1958, becoming under the administration of Shanghai. In 1993, Jiading's designate ...
"southern barbarians" (
manzi) threatening them, telling them "southern barbarian, hand over your valuables", raping, torturing and massacring. When the Qing imposed the
Queue Order in China, many Han Chinese defectors were appointed in the massacre of dissidents. Li Chengdong oversaw three massacres in
Jiading
Jiading is a suburban district of Shanghai. It had a population of 1,471,100 in 2010.
History
Historically, Jiading was a separate municipality/town, until, in 1958, becoming under the administration of Shanghai. In 1993, Jiading's designate ...
that occurred within the same month; together which resulted in tens of thousands of deaths and left cities depopulated.
In
Fuzhou, although former-Ming subjects were initially compensated with silver for complying to the Queue Order, the defected southern Chinese general
Hong Chengchou
Hong Chengchou (; 1593–1665), courtesy name Yanyan and art name Hengjiu, was a Chinese official who served under the Ming and Qing dynasties. He was born in present-day Liangshan Village, Yingdu Town, Fujian Province, China. After obtaining t ...
had enforced the policy thoroughly on the residents of
Jiangnan
Jiangnan or Jiang Nan (; formerly romanized Kiang-nan, literally "South of the River" meaning "South of the Yangtze") is a geographic area in China referring to lands immediately to the south of the lower reaches of the Yangtze River, incl ...
by 1645. The Han Chinese Banners were repeatedly assigned to enforce the Queue Order, often resulting in massacres such as the
Yangzhou Massacre
The Yangzhou massacre in May, 1645 in Yangzhou, Qing dynasty China, refers to the mass killings of innocent civilians by Manchu and defected northern Ming soldiers, commanded by the Manchu general Dodo.
The massacre is described in a contempora ...
, during which local residents were seen harassed by troops.
Chongming Island
Chongming, formerly known as Chungming, is an alluvial island at the mouth of the Yangtze River in eastern China covering as of 2010. Together with the islands Changxing and Hengsha, it forms Chongming District, the northernmost area of the ...
in the
Yangtzi estuary continued to harbour pirates and resistance forces, threatening to link up with the resistance in
Anqing and
Hubei
Hubei (; ; alternately Hupeh) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, and is part of the Central China region. The name of the province means "north of the lake", referring to its position north of Dongting Lake. The ...
-
Hunan
Hunan (, ; ) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the South Central China region. Located in the middle reaches of the Yangtze watershed, it borders the province-level divisions of Hubei to the north, Jiangxi ...
. The Qing authorities were only able to maintain control through working with corrupt former Ming officials such as
Qian Qianyi
Qian Qianyi (; Suzhou dialect: ; 1582–1664) was a Chinese historian, poet, and politician during the late Ming dynasty.Cihai: Page 1704. Qian was a famous author and poet; and along with Gong Dingzi and Wu Weiye was known as one of the Three ...
and
Ruan Dacheng
Ruan may refer to:
Buildings
*Ruan Center, office building in Des Moines, Iowa
*John Ruan House, historic mansion in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Places
*Ruan, County Clare, Ireland
*Ruan, Loiret, France
*Mont Ruan, Switzerland
*Ruan Major and Ru ...
. Loyalist marines continued fighting in the
Lake Tai
Taihu (), also known as Lake Tai or Lake Taihu, is a lake in the Yangtze Delta and one of the largest freshwater lakes in China. The lake is in Jiangsu province and a significant part of its southern shore forms its border with Zhejiang. Wi ...
area, under
Wu Yi and
Zhou Rui, mainly local fishermen and smugglers, which posed a problem for Qing forces who lacked competent sailors. These linked up gentry resistance all over the region, dealing severe losses on Qing forces of governor
Tu Guobao. Wu Yi attempted to link up with
Southern Ming
The Southern Ming (), also known as the Later Ming (), officially the Great Ming (), was an imperial dynasty of China and a series of rump states of the Ming dynasty that came into existence following the Jiashen Incident of 1644. Shun force ...
resistance in
Zhejiang
Zhejiang ( or , ; , Chinese postal romanization, also romanized as Chekiang) is an East China, eastern, coastal Provinces of China, province of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Hangzhou, and other notable citie ...
by entering negotiations with the
Qing official of
Jiashan
Jiashan County () is a county in the north of Zhejiang Province, bordering Shanghai to the northeast and Jiangsu province to the north. It is administered by the prefecture-level city of Jiaxing. Jiashan is nicknamed "The Land of Fish and Rice", ...
, but this was a trap; he was captured and executed. Resistance still carried on as the gentry continued near-open protest. In 1645, in
Liyang
Liyang () is a county-level city under the administration of Changzhou in the Jiangsu province of the People's Republic of China. In 2011, it had a population of about 781,500. It borders the prefecture-level divisions of Wuxi to the east, Xuanc ...
the poor peasants revolted, around
Tangshan
Tangshan () is a coastal, industrial prefecture-level city in the northeast of Hebei province. It is located in the eastern part of Hebei Province and the northeastern part of the North China Plain. It is located in the central area of the Boha ...
a scholar led a rebellion of local bandits, and from
Mount Yuntai to
Haizhou (Lianyungang) an insurgency was led by the Ming Prince of
Xinchang
Xinchang County () is a county in the east-central part of Zhejiang province, administratively under the municipal government of Shaoxing. 430,000 people live in Xinchang.
Administrative divisions
Subdistricts:
* Yulin Subdistrict (羽林街道) ...
. Ming Prince of
Rui'an
Rui'an (, Wenzhounese: ''zy iu'') is a county-level city along the southern coast of Zhejiang province, China, and is under the administration of Wenzhou City. It has a population of 1,125,000 people and covers a land area of , when including wat ...
and Prince of
Ruichang
Ruichang () is a county-level city under the jurisdiction of Jiujiang, in the north of Jiangxi province, along the Yangtze River, bordering Hubei province to the north.
Ruichang suffered deaths and extensive damage from the 2005 Ruichang earthqua ...
mobilised rebels in the
Huai'an
Huai'an (), formerly called Huaiyin () until 2001, is a prefecture-level city in the central part of Jiangsu province in East China, Eastern China. Huai'an is situated almost directly south of Lianyungang, southeast of Suqian, northwest of Yan ...
-
Yangzhou
Yangzhou, postal romanization Yangchow, is a prefecture-level city in central Jiangsu Province (Suzhong), East China. Sitting on the north bank of the Yangtze, it borders the provincial capital Nanjing to the southwest, Huai'an to the north ...
area and around
Nanjing
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu province of the People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and the second largest city in the East China region. T ...
for an assault on Nanjing in September 1646, but the Qing collaborators discovered the plan and defeated it.
Sichuan campaign (1646–1658)
In early 1646
Dorgon
Dorgon (, ; 17 November 1612 – 31 December 1650), was a Manchu prince and regent of the early Qing dynasty. Born in the House of Aisin-Gioro as the 14th son of Nurhaci (the founder of the Later Jin dynasty, predecessor of the Qing dynast ...
sent two expeditions to
Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of the ...
to try to destroy
Zhang Xianzhong's Great
Xi dynasty
Zhang Xianzhong (张献忠 or Chang Hsien-chung; 18 September 1606 – 2 January 1647), nickname Huanghu (literally 'Yellow Tiger'), was a Chinese peasant leader who led a peasant revolt from Yan'an wei, Shaanxi (today Yulin, Shaanxi province) ...
regime: the first expedition did not reach Sichuan because it was caught up against remnants; the second one, under the direction of
Hooge (the son of
Hong Taiji who had lost the succession struggle of 1643) reached Sichuan in October 1646. Hearing that a Qing army led by a major general was approaching, Zhang Xianzhong fled toward
Shaanxi
Shaanxi (alternatively Shensi, see § Name) is a landlocked province of China. Officially part of Northwest China, it borders the province-level divisions of Shanxi (NE, E), Henan (E), Hubei (SE), Chongqing (S), Sichuan (SW), Gansu (W), N ...
, splitting his troops into four divisions that were ordered to act independently if something were to happen to him. Before leaving, he ordered a massacre of the population of his capital
Chengdu
Chengdu (, ; simplified Chinese: 成都; pinyin: ''Chéngdū''; Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ), alternatively romanized as Chengtu, is a sub-provincial city which serves as the capital of the Chinese pro ...
.
The Qing forces advanced from
Xi'an
Xi'an ( , ; ; Chinese: ), frequently spelled as Xian and also known by other names, is the capital of Shaanxi Province. A sub-provincial city on the Guanzhong Plain, the city is the third most populous city in Western China, after Chongqi ...
into
Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of the ...
. Fearing Zhang's murderous tendencies, and with his Sichuanese troops unwilling to carry out Zhang's massacres on their fellow provincials, Zhang's commander
Liu Jinzhong defected to the Qing and guided them to Zhang. Liu was later granted the title of Baron.
En route
Zhang Xianzhong was surprised by a Qing army under
Hooge and
Li Guoying
Li Guoying (; born December 1963) is a Chinese hydraulic engineer-turned-politician, currently serving as governor of Anhui province. Li worked in his early career as a technician and administrator in the national ministry of water works, the Yel ...
at Mount Fenghuang, after being betrayed by one of his officers. Refusing to believe the scout's report, he rode out to see for himself and was killed by an arrow. This was witnessed by
Jesuit missionary
Gabriel de Magalhães Gabriel de Magalhães (; 1610 – 6 May 1677), or gallicized as Gabriel Magaillans, was an early Portuguese Jesuit missionary to China who was one of the first Catholic missionaries to reach Sichuan and founded the original St. Joseph's Church in ...
, who reported it. Zhang Xianzhong was killed in a battle against Qing forces near
Xichong in central Sichuan on 1 February 1647. In one account, he was betrayed by one of his officers,
Liu Jinzhong, who pointed him out to be shot by an archer. Hooge then easily took
Chengdu
Chengdu (, ; simplified Chinese: 成都; pinyin: ''Chéngdū''; Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ), alternatively romanized as Chengtu, is a sub-provincial city which serves as the capital of the Chinese pro ...
, but found it in a state of desolation he had not expected. Unable to find food in the countryside, his soldiers looted the area, killing resisters, and even resorted to cannibalism as food shortages grew acute.
Sun Kewang informally took over leadership, and he moved southward. In
Chongqing, the Ming general
Zeng Ying still held out. Xi dynasty boats under
Liu Wenxiu
/ ( or ) is an East Asian surname. pinyin: in Mandarin Chinese, in Cantonese. It is the family name of the Han dynasty emperors. The character originally meant 'kill', but is now used only as a surname. It is listed 252nd in the classic text ...
attacked Zeng's command boat on the
Yangtzi River, killed him and took the city, but continued moving southward to
Guizhou
Guizhou (; formerly Kweichow) is a landlocked province in the southwest region of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Guiyang, in the center of the province. Guizhou borders the autonomous region of Guangxi to the ...
. A young son of
Zhang Xianzhong was supposed to be enthroned as the next ruler but he died on the journey. The remnants of the Ming force moved eastward to
Fuling District
Fuling District () is a district in central Chongqing, China. The area is known for ''zha cai'', a hot pickled mustard tuber, as well as serving as the location of former U.S. Peace Corps teacher Peter Hessler's best-selling memoir '' River Tow ...
and
Yunyang County
Yunyang County () is a county in the northeast of Chongqing Municipality, China, bordering Hubei province to the south.
In eastern Chongqing is Yunyang County with over 1,400 years of history and a reputation as the 'Bright Pearl of Chongqing'. T ...
under
Li Zhanchun and
Yu Dahai. The remaining Ming forces under
Yang Zhan, now promoted to Marquis and
Ming
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peop ...
commander of Sichuan, moved south towards Guizhou and unsuccessfully attempted to contact the
Southern Ming
The Southern Ming (), also known as the Later Ming (), officially the Great Ming (), was an imperial dynasty of China and a series of rump states of the Ming dynasty that came into existence following the Jiashen Incident of 1644. Shun force ...
court for supplies, wandering in desperate search for supplies to
Jiading
Jiading is a suburban district of Shanghai. It had a population of 1,471,100 in 2010.
History
Historically, Jiading was a separate municipality/town, until, in 1958, becoming under the administration of Shanghai. In 1993, Jiading's designate ...
. Here he began stockpiling resources to prepare for war against the
Qing. Qing forces mainly left the province due to starvation and the remainder garrisoned at
Baoning in the north under
Li Guoying
Li Guoying (; born December 1963) is a Chinese hydraulic engineer-turned-politician, currently serving as governor of Anhui province. Li worked in his early career as a technician and administrator in the national ministry of water works, the Yel ...
, who moved to crush banditry, called for supplies to be shipped in and recultivated the land to relieve the famine-like conditions. After he was attacked and defeated by Li Zhanchun and Yu Dahai in 1647 in a land-riverine battle at
Zhangzhou
Zhangzhou (), alternately romanized as Changchow, is a prefecture-level city in Fujian Province, China. The prefecture around the city proper comprises the southeast corner of the province, facing the Taiwan Strait and surrounding the prefect ...
, he started building a riverine force of his own. The
Yongli Emperor
The Yongli Emperor (; 1623–1662; reigned 18 November 1646 – 1 June 1662), personal name Zhu Youlang, was a royal member to the imperial family of Ming dynasty, and the fourth and last commonly recognised emperor of the Southern Ming, reigni ...
in
Guangdong
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020) ...
sent his alleged distant relative
Zhu Rongfan to organise the Ming forces in Sichuan who instead became yet another warlord, establishing himself at
Kuizhou
Kui Prefecture, Kuizhou Circuit, or Kuizhou () was initially established in 619 CE, as a renaming of the existing Xin Prefecture. Kuizhou was an important area from the beginning and through the end of the Tang dynasty of China, when it was alter ...
. These groups started fighting among each other, which helped the Qing secure the northern and western parts of the province by 1652, and the rest of the province by 1658.
Jiangxi and Fujian campaigns (1646–1650)


The Qing advance into
Zhejiang
Zhejiang ( or , ; , Chinese postal romanization, also romanized as Chekiang) is an East China, eastern, coastal Provinces of China, province of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Hangzhou, and other notable citie ...
province was aided by the collaboration of
Tong Guoqi, who was appointed Governor of Zhejiang and
Fujian
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its cap ...
. Tong was originally from
Liaodong
The Liaodong Peninsula (also Liaotung Peninsula, ) is a peninsula in southern Liaoning province in Northeast China, and makes up the southwestern coastal half of the Liaodong region. It is located between the mouths of the Daliao River (the ...
, but lived in Zhejiang where he came into contact with Chinese Catholic scholars who, claiming that Europe was an ideal society and that all nations shared one morality, argued that Chinese culture was too
inward-looking and called for appreciation and imitation of foreign nations, and cooperation with them, whether Europeans or Manchus. This group therefore supported Manchu rule.
Meanwhile, the
Southern Ming
The Southern Ming (), also known as the Later Ming (), officially the Great Ming (), was an imperial dynasty of China and a series of rump states of the Ming dynasty that came into existence following the Jiashen Incident of 1644. Shun force ...
had not been eliminated. When
Hangzhou
Hangzhou ( or , ; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), also romanized as Hangchow, is the capital and most populous city of Zhejiang, China. It is located in the northwestern part of the province, sitting at the head of Hangzhou Bay, whic ...
fell to the
Qing on 6 July 1645, the Prince of Tang
Zhu Yujian
Zhu Yujian (; 1602 – 6 October 1646), nickname Changshou (長壽), originally the Prince of Tang, later reigned as the Longwu Emperor () of the Southern Ming from 18 August 1645, when he was enthroned in Fuzhou, to 6 October 1646, when he w ...
, a ninth-generation descendant of
Ming
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peop ...
founder
Zhu Yuanzhang
The Hongwu Emperor (21 October 1328 – 24 June 1398), personal name Zhu Yuanzhang (), courtesy name Guorui (), was the founding emperor of the Ming dynasty of China, reigning from 1368 to 1398.
As famine, plagues and peasant revolts i ...
, managed to escape by land to the southeastern province of Fujian. Crowned as the
Longwu Emperor
Zhu Yujian (; 1602 – 6 October 1646), nickname Changshou (長壽), originally the Prince of Tang, later reigned as the Longwu Emperor () of the Southern Ming from 18 August 1645, when he was enthroned in Fuzhou, to 6 October 1646, when he wa ...
in the coastal city of
Fuzhou on 18 August, he depended on the protection of talented seafarer
Zheng Zhilong
Zheng Zhilong, Marquis of Tong'an and Nan'an (; April 16, 1604 – November 24, 1661), baptismal name Nicholas Iquan Gaspard, was a Chinese admiral, merchant, military general, pirate, and politician of the late Ming dynasty who later defec ...
(also known as "Nicholas Iquan"). The childless emperor adopted Zheng's eldest son and granted him the imperial surname. "
Koxinga
Zheng Chenggong, Prince of Yanping (; 27 August 1624 – 23 June 1662), better known internationally as Koxinga (), was a Ming loyalist general who resisted the Qing conquest of China in the 17th century, fighting them on China's southeastern ...
", as his son is known to Westerners; it is a distortion of the title "Lord of the Imperial Surname" (Guoxingye 國姓爺). Upon Zheng Zhilong's request, the
Tokugawa Shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate (, Japanese 徳川幕府 ''Tokugawa bakufu''), also known as the , was the military government of Japan during the Edo period from 1603 to 1868. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"''Tokugawa-jidai''"in ''Japan Encyclopedia ...
in Japan quietly supported the Zheng clan's pro-Ming forces by quietly granting them access to mercenaries, weapons and other strategic materials. Zheng Zhilong drafted a plan entitled "Grand Strategy for ordering the country", in which he argued for the Southern Ming to reconquer territory through regional military commanders rather than a centralized fashion. This brought him at loggerheads with the Longwu Emperor. Famine also struck after drought and crops failed all along the southeastern coastal region, while Qing attacks on the Yangzi river delta had cut access to raw silk. In response, the Longwu emperor wanted to reconquer Huguang and Jiangxi provinces which were major producers of rice to help boost the southern Ming, but Zheng Zhilong refused to expand out of Fujian for fear of losing control of the regime.
In the meantime, another
Ming
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peop ...
claimant, the Prince of Lu
Zhu Yihai
Zhu Yihai (; 1618–1662), courtesy name Juchuan (巨川), art name Hengshan (恆山) and Changshizi (常石子), was a regent of the Southern Ming from 1645 to 1653.
Early life
Zhu Yihai was born in 1618, during the 46th year of the reign of th ...
, had named himself regent in
Zhejiang
Zhejiang ( or , ; , Chinese postal romanization, also romanized as Chekiang) is an East China, eastern, coastal Provinces of China, province of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Hangzhou, and other notable citie ...
, but the two loyalist regimes failed to cooperate, making their chances of success even lower than they already were.
In February 1646,
Qing armies seized land west of the
Qiantang River from the Lu regime and defeated a ragtag force representing the
Longwu Emperor
Zhu Yujian (; 1602 – 6 October 1646), nickname Changshou (長壽), originally the Prince of Tang, later reigned as the Longwu Emperor () of the Southern Ming from 18 August 1645, when he was enthroned in Fuzhou, to 6 October 1646, when he wa ...
in northeastern
Jiangxi
Jiangxi (; ; formerly romanized as Kiangsi or Chianghsi) is a landlocked province in the east of the People's Republic of China. Its major cities include Nanchang and Jiujiang. Spanning from the banks of the Yangtze river in the north int ...
. In May, they besieged
Ganzhou
Ganzhou (), alternately romanized as Kanchow, is a prefecture-level city in the south of Jiangxi province, China, bordering Fujian to the east, Guangdong to the south, and Hunan to the west. Its administrative seat is at Zhanggong District.
Hist ...
, the last Ming bastion in Jiangxi. In July, a new southern campaign led by
Prince Bolo sent Prince of Lu's
Zhejiang
Zhejiang ( or , ; , Chinese postal romanization, also romanized as Chekiang) is an East China, eastern, coastal Provinces of China, province of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Hangzhou, and other notable citie ...
regime into disarray and proceeded to attack the Longwu regime in
Fujian
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its cap ...
. Hoping to gain rewards from Prince Bolo,
Zheng Zhilong
Zheng Zhilong, Marquis of Tong'an and Nan'an (; April 16, 1604 – November 24, 1661), baptismal name Nicholas Iquan Gaspard, was a Chinese admiral, merchant, military general, pirate, and politician of the late Ming dynasty who later defec ...
betrayed the loyalists by contacting
Hong Chengchou
Hong Chengchou (; 1593–1665), courtesy name Yanyan and art name Hengjiu, was a Chinese official who served under the Ming and Qing dynasties. He was born in present-day Liangshan Village, Yingdu Town, Fujian Province, China. After obtaining t ...
and left northern Fujian undefended against a Qing army led by
Li Chengdong
Li, li, or LI may refer to:
Businesses and organizations
* Landscape Institute, a British professional body for landscape architects
* Leadership Institute, a non-profit organization located in Arlington, Virginia, US, that teaches "political te ...
and
Tong Yangjia. The Qing took control of Fujian in 1645.
On the pretext of relieving the siege of
Ganzhou
Ganzhou (), alternately romanized as Kanchow, is a prefecture-level city in the south of Jiangxi province, China, bordering Fujian to the east, Guangdong to the south, and Hunan to the west. Its administrative seat is at Zhanggong District.
Hist ...
, the Longwu court left their Fujian base in late September 1646, but the Qing army caught up with them. Longwu and his empress were summarily executed in
Tingzhou (western Fujian) on 6 October 1646. After the fall of
Fuzhou on 17 October,
Zheng Zhilong
Zheng Zhilong, Marquis of Tong'an and Nan'an (; April 16, 1604 – November 24, 1661), baptismal name Nicholas Iquan Gaspard, was a Chinese admiral, merchant, military general, pirate, and politician of the late Ming dynasty who later defec ...
surrendered to the Qing and his son
Koxinga
Zheng Chenggong, Prince of Yanping (; 27 August 1624 – 23 June 1662), better known internationally as Koxinga (), was a Ming loyalist general who resisted the Qing conquest of China in the 17th century, fighting them on China's southeastern ...
fled to the island of
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
with his fleet. When news arrived of the Longwu emperor's demise, the fortress of Ganzhou in southern Jiangxi under the command of
Yang Tinglin also caved in to Qing general
Jin Shenghuan
Jin Shenghuan (, ?–1 March 1649), courtesy name Huchen () was a soldier who served both the Ming and Qing dynasties. He was a native of Liaodong (modern-day Liaoyang).
Life
Jin was a brigadier-general under the Ming general Huang Long (黃� ...
by November 1646.
The Prince-Regent of Lu, with the aid of the sea-lord
Zhang Mingzhen, continued resistance at sea on the island of
Shacheng, between Zhejiang and Fujian. By July 1649 their base of operations shifted northward to Jiantiaosuo. After killing a rival naval commander
Huang Binqing, the base was moved to
Zhoushan in November. From there he attempted to raise a rebellion in
Jiangnan
Jiangnan or Jiang Nan (; formerly romanized Kiang-nan, literally "South of the River" meaning "South of the Yangtze") is a geographic area in China referring to lands immediately to the south of the lower reaches of the Yangtze River, incl ...
, but Zhoushan fell to the Qing in 1651 after being betrayed by Huang Binqing's former officers. Zhang Mingzhen, with all his family, fled to join
Zheng Chenggong
Zheng Chenggong, Prince of Yanping (; 27 August 1624 – 23 June 1662), better known internationally as Koxinga (), was a Ming loyalist general who resisted the Qing conquest of China in the 17th century, fighting them on China's southeastern ...
in
Xiamen
Xiamen ( , ; ), also known as Amoy (, from Hokkien pronunciation ), is a sub-provincial city in southeastern Fujian, People's Republic of China, beside the Taiwan Strait. It is divided into six districts: Huli, Siming, Jimei, Tong'an ...
.
Hunan, Guangdong and Guangxi campaign (1645–1650)
After the fall of
Nanjing
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu province of the People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and the second largest city in the East China region. T ...
, the old
Ming
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peop ...
governor of
Huguang
Huguang was a province of China during the Yuan and Ming dynasties. It was founded by the Yuan dynasty in 1274. During the Yuan dynasty it included the areas of modern Hubei south of the Yangtze river, Hunan, Guizhou, and Guangxi. During the Ming ...
(
Hubei
Hubei (; ; alternately Hupeh) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, and is part of the Central China region. The name of the province means "north of the lake", referring to its position north of Dongting Lake. The ...
and
Hunan
Hunan (, ; ) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the South Central China region. Located in the middle reaches of the Yangtze watershed, it borders the province-level divisions of Hubei to the north, Jiangxi ...
)
He Tengjiao, under the
Longwu
Longwu () (18 August 1645 – 4 February 1647) was the era name of the Longwu Emperor of the Southern Ming.
Comparison table
Other eras contemporaneous with Longwu
* China
** ''Shunzhi'' (順治, 1644–1661): Qing dynasty — era name of the ...
court, established the Thirteen Defense Commands ''(zhen)'' with
Shun
Shun may refer to one of the following:
*To shun, which means avoiding association with an individual or group
* Shun (given name), a masculine Japanese given name
*Seasonality in Japanese cuisine (''shun'', 旬)
Emperor Shun
* Emperor Shun (� ...
remnants in Hunan, which became famous for holding out against the
Qing. Qing forces under the early defector
Kong Youde
Kong Youde ( zh, c=, p=Kǒng Yǒudé; mnc, , v=; Transliteration of Manchu: kung ioo de; died August 7, 1652) was a Chinese adventurer and Ming dynasty military officer who served under the warlord Mao Wenlong until Mao's death in 1629. Subsequen ...
subdued Hunan in 1646. After the fall of the Longwu regime, He Tengjiao swore allegiance to the
Yongli Emperor
The Yongli Emperor (; 1623–1662; reigned 18 November 1646 – 1 June 1662), personal name Zhu Youlang, was a royal member to the imperial family of Ming dynasty, and the fourth and last commonly recognised emperor of the Southern Ming, reigni ...
, continuing resistance in
Hunan
Hunan (, ; ) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the South Central China region. Located in the middle reaches of the Yangtze watershed, it borders the province-level divisions of Hubei to the north, Jiangxi ...
and
Guizhou
Guizhou (; formerly Kweichow) is a landlocked province in the southwest region of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Guiyang, in the center of the province. Guizhou borders the autonomous region of Guangxi to the ...
provinces, and was finally killed at
Xiangtan
Xiangtan () is a prefecture-level city in east-central Hunan province, south-central China. The hometowns of several founding leaders of the Chinese Communist Party, including Chairman Mao Zedong, President Liu Shaoqi, and Marshal Peng Dehuai, a ...
in 1649.
The
Longwu Emperor
Zhu Yujian (; 1602 – 6 October 1646), nickname Changshou (長壽), originally the Prince of Tang, later reigned as the Longwu Emperor () of the Southern Ming from 18 August 1645, when he was enthroned in Fuzhou, to 6 October 1646, when he wa ...
's younger brother
Zhu Yuyue
Zhu Yuyue (; 1605 – 20 January 1647), the Prince of Tang (), reigned as the Shaowu Emperor () of the Southern Ming from 1646 to 1647.
Biography
He was a descendant of the first Ming emperor Zhu Yuanzhang. Before ascending to the throne he fol ...
, who had fled
Fuzhou by sea, soon founded another
Ming
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peop ...
regime in
Guangzhou
Guangzhou (, ; ; or ; ), also known as Canton () and alternatively romanized as Kwongchow or Kwangchow, is the capital and largest city of Guangdong province in southern China. Located on the Pearl River about north-northwest of Hong Kon ...
, the capital of
Guangdong
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020) ...
province, taking the reign title Shaowu (紹武) on 11 December 1646. Short of official costumes, the court had to purchase robes from local theater troops. On 24 December,
Prince of Gui
Prince of Gui ( zh, 桂王), was a first-rank princely peerage used during Ming dynasty, this peerage title was created by Wanli Emperor. The first Prince of Gui was Zhu Changying, 7th son of Wanli Emperor. This peerage had 6 cadet commandery pri ...
Zhu Youlang
The Yongli Emperor (; 1623–1662; reigned 18 November 1646 – 1 June 1662), personal name Zhu Youlang, was a royal member to the imperial family of Ming dynasty, and the fourth and last commonly recognised emperor of the Southern Ming, reign ...
established the
Yongli
Yongli () (5 February 1647 – 1 June 1662) was the era name of the Yongli Emperor of the Southern Ming.
Comparison table
Other eras contemporaneous with Yongli
* China
** '' Dingwu'' (定武, 1646–1664): Southern Ming — era name of Zhu B ...
(永曆) regime in the same vicinity. The Prince of Gui had fled from
Zhang Xianzhong's attack on
Hubei
Hubei (; ; alternately Hupeh) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, and is part of the Central China region. The name of the province means "north of the lake", referring to its position north of Dongting Lake. The ...
/
Hunan
Hunan (, ; ) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the South Central China region. Located in the middle reaches of the Yangtze watershed, it borders the province-level divisions of Hubei to the north, Jiangxi ...
to
Zhaoqing
Zhaoqing (), alternately romanized as Shiuhing, is a prefecture-level city in Guangdong Province, China. As of the 2020 census, its population was 4,113,594, with 1,553,109 living in the built-up (or metro) area made of Duanzhou, Dinghu ...
in
Guangdong
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020) ...
, but his retreat to
Guangxi led other loyalists to believe that he had abandoned them and they proceeded to enthrone the Shaowu emperor. The situation was complicated by the fact that the Shaowu court mainly consisted of local
Cantonese
Cantonese ( zh, t=廣東話, s=广东话, first=t, cy=Gwóngdūng wá) is a language within the Chinese (Sinitic) branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages originating from the city of Guangzhou (historically known as Canton) and its surrounding ar ...
while the Yongli court consisted of men of other provinces.
The two
Ming
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peop ...
regimes fought each other until 20 January 1647, when a small
Qing force led by former
Southern Ming
The Southern Ming (), also known as the Later Ming (), officially the Great Ming (), was an imperial dynasty of China and a series of rump states of the Ming dynasty that came into existence following the Jiashen Incident of 1644. Shun force ...
commander
Li Chengdong
Li, li, or LI may refer to:
Businesses and organizations
* Landscape Institute, a British professional body for landscape architects
* Leadership Institute, a non-profit organization located in Arlington, Virginia, US, that teaches "political te ...
captured
Guangzhou
Guangzhou (, ; ; or ; ), also known as Canton () and alternatively romanized as Kwongchow or Kwangchow, is the capital and largest city of Guangdong province in southern China. Located on the Pearl River about north-northwest of Hong Kon ...
, killing the
Shaowu Emperor and sending the
Yongli Emperor
The Yongli Emperor (; 1623–1662; reigned 18 November 1646 – 1 June 1662), personal name Zhu Youlang, was a royal member to the imperial family of Ming dynasty, and the fourth and last commonly recognised emperor of the Southern Ming, reigni ...
fleeing to
Nanning in
Guangxi.
In May 1648, however,
Li Chengdong
Li, li, or LI may refer to:
Businesses and organizations
* Landscape Institute, a British professional body for landscape architects
* Leadership Institute, a non-profit organization located in Arlington, Virginia, US, that teaches "political te ...
, disappointed at being made a mere regional commander after taking
Guangdong
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020) ...
province, mutinied against the Qing and rejoined the Ming. The reversion of another dissatisfied Ming defector in
Jiangxi
Jiangxi (; ; formerly romanized as Kiangsi or Chianghsi) is a landlocked province in the east of the People's Republic of China. Its major cities include Nanchang and Jiujiang. Spanning from the banks of the Yangtze river in the north int ...
,
Jin Shenghuan
Jin Shenghuan (, ?–1 March 1649), courtesy name Huchen () was a soldier who served both the Ming and Qing dynasties. He was a native of Liaodong (modern-day Liaoyang).
Life
Jin was a brigadier-general under the Ming general Huang Long (黃� ...
, who was also discontented at being appointed a regional commander after conquering Jiangxi province, helped the Yongli regime to retake most of southern China.
The Yongli emperor was encouraged by these developments and saw hope in a Ming reconquest, likening it to the revival of the
Han
Han may refer to:
Ethnic groups
* Han Chinese, or Han People (): the name for the largest ethnic group in China, which also constitutes the world's largest ethnic group.
** Han Taiwanese (): the name for the ethnic group of the Taiwanese p ...
and
Tang
Tang or TANG most often refers to:
* Tang dynasty
* Tang (drink mix)
Tang or TANG may also refer to:
Chinese states and dynasties
* Jin (Chinese state) (11th century – 376 BC), a state during the Spring and Autumn period, called Tang (唐) b ...
dynasties after the usurpations of
Wang Mang
Wang Mang () (c. 45 – 6 October 23 CE), courtesy name Jujun (), was the founder and the only emperor of the short-lived Chinese Xin dynasty. He was originally an official and consort kin of the Han dynasty and later seized the thron ...
and
An Lushan
An Lushan (; 20th day of the 1st month 19 February 703 – 29 January 757) was a general in the Tang dynasty and is primarily known for instigating the An Lushan Rebellion.
An Lushan was of Sogdian and Göktürk origin,Yang, Zhijiu, "An Lush ...
. Loyalists hoped to move the emperor to
Wuchang
Wuchang forms part of the urban core of and is one of 13 urban districts of the prefecture-level city of Wuhan, the capital of Hubei Province, China. It is the oldest of the three cities that merged into modern-day Wuhan, and stood on the ri ...
where he would lead a reconquest of
Nanjing
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu province of the People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and the second largest city in the East China region. T ...
and
Kaifeng
Kaifeng () is a prefecture-level city in east-central Henan province, China. It is one of the Eight Ancient Capitals of China, having been the capital eight times in history, and is best known for having been the Chinese capital during the No ...
. However, the Qing commander
Xu Yong (one of those who defected at
Jiangnan
Jiangnan or Jiang Nan (; formerly romanized Kiang-nan, literally "South of the River" meaning "South of the Yangtze") is a geographic area in China referring to lands immediately to the south of the lower reaches of the Yangtze River, incl ...
) repelled the loyalist counterattack at
Changsha
Changsha (; ; ; Changshanese pronunciation: (), Standard Chinese, Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is the Capital city, capital and the largest city of Hunan Province of China. Changsha is the 17th most populous city in China with a popul ...
as the populace did not side with the loyalists, and Qing forces advanced again. Xu Yong was later present at the capture of
He Tengjiao in
Xiangtan
Xiangtan () is a prefecture-level city in east-central Hunan province, south-central China. The hometowns of several founding leaders of the Chinese Communist Party, including Chairman Mao Zedong, President Liu Shaoqi, and Marshal Peng Dehuai, a ...
, and his army absorbed He's remaining troops.
This resurgence of loyalist hopes was short-lived. New
Han
Han may refer to:
Ethnic groups
* Han Chinese, or Han People (): the name for the largest ethnic group in China, which also constitutes the world's largest ethnic group.
** Han Taiwanese (): the name for the ethnic group of the Taiwanese p ...
-
Manchu-
Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
armies under
Kong Youde
Kong Youde ( zh, c=, p=Kǒng Yǒudé; mnc, , v=; Transliteration of Manchu: kung ioo de; died August 7, 1652) was a Chinese adventurer and Ming dynasty military officer who served under the warlord Mao Wenlong until Mao's death in 1629. Subsequen ...
,
Jirgalang
Jirgalang or Jirhalang (Manchu: 19 November 1599 – June 11, 1655) was a Manchu noble, regent, and political and military leader of the early Qing dynasty. Born in the Aisin Gioro clan, he was the sixth son of Šurhaci, a younger brother of ...
and
Lekedehun managed to reconquer the central province of
Huguang
Huguang was a province of China during the Yuan and Ming dynasties. It was founded by the Yuan dynasty in 1274. During the Yuan dynasty it included the areas of modern Hubei south of the Yangtze river, Hunan, Guizhou, and Guangxi. During the Ming ...
(present-day
Hubei
Hubei (; ; alternately Hupeh) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, and is part of the Central China region. The name of the province means "north of the lake", referring to its position north of Dongting Lake. The ...
and
Hunan
Hunan (, ; ) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the South Central China region. Located in the middle reaches of the Yangtze watershed, it borders the province-level divisions of Hubei to the north, Jiangxi ...
) in 1649, and the population of
Xiangtan
Xiangtan () is a prefecture-level city in east-central Hunan province, south-central China. The hometowns of several founding leaders of the Chinese Communist Party, including Chairman Mao Zedong, President Liu Shaoqi, and Marshal Peng Dehuai, a ...
was massacred.
Jiangxi
Jiangxi (; ; formerly romanized as Kiangsi or Chianghsi) is a landlocked province in the east of the People's Republic of China. Its major cities include Nanchang and Jiujiang. Spanning from the banks of the Yangtze river in the north int ...
fell to another army led by
Tantai,
Holhoi,
Shang Kexi and
Geng Zhongming
Geng Zhongming (; 1604–1649) was a Chinese military general who lived through the transition from the Ming (1368–1644) to the Qing (1644–1912) dynasty, during which he served both sides. His grandson Geng Jingzhong was one of the Three Fe ...
.
Guangdong
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020) ...
fell to Shang Kexi in November 1650. The
Yongli Emperor
The Yongli Emperor (; 1623–1662; reigned 18 November 1646 – 1 June 1662), personal name Zhu Youlang, was a royal member to the imperial family of Ming dynasty, and the fourth and last commonly recognised emperor of the Southern Ming, reigni ...
fled to
Nanning and from there to
Guizhou
Guizhou (; formerly Kweichow) is a landlocked province in the southwest region of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Guiyang, in the center of the province. Guizhou borders the autonomous region of Guangxi to the ...
. Finally on 24 November 1650, Qing forces led by Shang Kexi captured
Guangzhou
Guangzhou (, ; ; or ; ), also known as Canton () and alternatively romanized as Kwongchow or Kwangchow, is the capital and largest city of Guangdong province in southern China. Located on the Pearl River about north-northwest of Hong Kon ...
with 74 of his own cannons and the aid of
Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
gunners, and massacred the city's population, killing as many as 70,000 people. In Guangzhou, massacres of Ming loyalists and civilians in 1650 were carried out by Qing forces under the command of northern
Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
Banner generals
Shang Kexi and
Geng Jimao.
Ming loyalist revolts in the North (1647–1654)

A major revolt around
Zouping
Zouping () is a county-level city of Shandong province.
Geography
The city is located on the northern edge of the mountainous central portion of the province. It is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Binzhou, but is only w ...
,
Shandong broke out in March 1647. Shandong had been plagued by brigandage before the collapse of the
Ming
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peop ...
, and most Ming officials and their gentry-organised militia welcomed the new
Qing regime, cooperating with them against the bandits who now grew into sizeable rebel armies complete with guns and cannons, and whose leaders had declared themselves "kings". These were held off by the local gentry, who organised the local population into a defence force.
In March 1648, a bandit chief,
Yang Sihai, and a woman by the surname of Zhang claimed to be the Crown Prince of the
Tianqi Emperor
The Tianqi Emperor (23 December 1605 – 30 September 1627), personal name Zhu Youjiao (), was the 16th Emperor of the Ming dynasty, reigning from 1620 to 1627. He was the eldest son of the Taichang Emperor and a elder brother of the Chongzhe ...
and his consort, respectively. With the aid of another bandit chief called
Zhang Tianbao, they rebelled under the Ming flag in
Qingyun
Qingyun County () is a county of north-northwest Shandong province, People's Republic of China, bordering Hebei province to the north. It is the northernmost county-level division of the prefecture-level city of Dezhou
Dezhou () is a prefect ...
, south of
Tianjin
Tianjin (; ; Mandarin: ), alternately romanized as Tientsin (), is a municipality and a coastal metropolis in Northern China on the shore of the Bohai Sea. It is one of the nine national central cities in Mainland China, with a total popu ...
. The Qing was forced to send in "heavy troops" (artillery), as well as extra reinforcements. The Qing succeeded in subduing the rebellion in 1649, but with heavy losses. Further south, in the forests between
Shandong,
Hebei
Hebei or , (; alternately Hopeh) is a northern province of China. Hebei is China's sixth most populous province, with over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. The province is 96% Han Chinese, 3% Manchu, 0.8% Hui, and 0 ...
, and
Henan
Henan (; or ; ; alternatively Honan) is a landlocked province of China, in the central part of the country. Henan is often referred to as Zhongyuan or Zhongzhou (), which literally means "central plain" or "midland", although the name is al ...
provinces, 20 Ming loyalist brigades of 1,000 men each were amassing. This force was known as the "Elm Garden Army", equipped with Western cannons. Commander
Li Huajing had declared a distant relative of the Ming imperial family as the "Tianzheng Emperor", and besieged and captured the cities of
Caozhou,
Dingtao County
Dingtao District () is a district under the jurisdiction of Heze in Shandong province, China. Emperor Gaozu of Han's ill-fated consort Qi Consort Qi may refer to:
Consorts with the surname Qi
*Consort Qi (Han dynasty) (224–194 BC), concubine of ...
,
Chengwu County, and
Dongming County
Dongming County in Heze Prefecture is the westernmost county of Shandong Province in the People's Republic of China. It borders Henan Province to the west across the Yellow River. Dongming County had a population of 677,563 in 1999.
History
Mo ...
,
Lanyang and
Fengqiu
Fengqiu County () is a county in the north of Henan province, located on the north (left) bank of the Yellow River. It is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Xinxiang.
In ancient times, Pingqiu County () was located to the ea ...
. Heavy casualties were inflicted on the Qing. Defected Ming general
Gao Di led elite multi-ethnic Banner forces to crush the insurrection by 18 November.
In January 1649,
Jiang Xiang, the military governor in
Datong,
Shanxi, felt threatened that
Dorgon
Dorgon (, ; 17 November 1612 – 31 December 1650), was a Manchu prince and regent of the early Qing dynasty. Born in the House of Aisin-Gioro as the 14th son of Nurhaci (the founder of the Later Jin dynasty, predecessor of the Qing dynast ...
might be attempting to restrict his authority and rebelled, switching allegiance back to the Ming. Dorgon travelled to personally intervene against the rebels. The generals
Liu Denglou, commander of
Yulin, Shaanxi
Yulin () is a prefecture-level city in the Shanbei region of Shaanxi province, China, bordering Inner Mongolia to the north, Shanxi to the east, and Ningxia to the west. It has an administrative area of and as of the 2020 Chinese census had a pop ...
, and
Wang Yongqiang, top commander in
Yan'an
Yan'an (; ), alternatively spelled as Yenan is a prefecture-level city in the Shaanbei region of Shaanxi province, China, bordering Shanxi to the east and Gansu to the west. It administers several counties, including Zhidan (formerly Bao'an) ...
, Shaanxi, contacted Jiang Xiang, rebelled and switched back to the Ming. They were joined by
Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
leader
Zhamasu who rose up in the
Helan Mountains
The Helan Mountains, frequently called Alashan Mountains in older sources, are an isolated desert mountain range forming the border of Inner Mongolia's Alxa League and Ningxia. They run north-south parallel to the north-flowing Yellow River in t ...
. The revolt was defeated by the end of the year by a Banner force commanded by Prince
Bolo and
Wu Sangui. The Ming loyalist-held city of
Puzhou was subject to a massacre. Simultaneously,
Zhu Senfu, a man who claimed to be related to the Ming Imperial family, declared himself Prince of Qin in
Jiezhou,
Shaanxi
Shaanxi (alternatively Shensi, see § Name) is a landlocked province of China. Officially part of Northwest China, it borders the province-level divisions of Shanxi (NE, E), Henan (E), Hubei (SE), Chongqing (S), Sichuan (SW), Gansu (W), N ...
, near
Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of the ...
, backed by a local outlaw named
Zhao Ronggui with an army of 10,000 men. The rebels were crushed by
Wu Sangui's forces. In the chaos, many bandit groups expanded their raids. A local outlaw by the name of
Zhang Wugui rose up in
Shanxi and began handing out Ming ranks and documents, assembling an army. He attacked
Wutai in 1649, but was driven off. He continued marauding the province until he was killed in February 1655 when his headquarters was discovered by a
Manchu scout.
With the mutineers defeated, the Qing turned on the
Muslim rebels of
Ding Guodong at
Suzhou, Gansu and crushed them with ease in December 1649. Ding Guodong was killed. The population was appeased by strengthening judicial protections and, at the suggestion of supervisory secretary
He Bi,
Muslim communities were disarmed and shifted 150 ''li'' (75 km) away from
Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
communities. The
Jiayu Pass
Jiayu Pass or () is the first frontier fortress at the west end of the Ming dynasty Great Wall, near the city of Jiayuguan in Gansu province. Along with Juyong Pass and Shanhai Pass, it is one of the main passes of the Great Wall. In the Min ...
was blocked to severe all relations between the
Kumul Khanate
The Kumul Khanate was a semi-autonomous feudal Turkic khanate (equivalent to a banner in Mongolia) within the Qing dynasty and then the Republic of China until it was abolished by Xinjiang governor Jin Shuren in 1930. The Khanate was located in ...
and the
Gansu Muslims. By 1650 the Muslim rebels had been crushed in campaigns that inflicted heavy casualties.
The southeastern region of
Shaanxi
Shaanxi (alternatively Shensi, see § Name) is a landlocked province of China. Officially part of Northwest China, it borders the province-level divisions of Shanxi (NE, E), Henan (E), Hubei (SE), Chongqing (S), Sichuan (SW), Gansu (W), N ...
, a rural, untamed area, was beset by Ming colonel
Tang Zhongheng, accompanied by Ming princes
Zhu Changying
Zhu Changying (; 25 April 1597 – 21 December 1645), formally known as Prince Duan of Gui, was a prince of the Ming dynasty and the seventh son of the Wanli Emperor. He was the father of the Yongli Emperor, the last Southern Ming emperor.
Aft ...
and
Zhu Youdu and a Ming
Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
commander,
Shibulai. Other rebels, given the ready access to the Ming loyalists in neighbouring
Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of the ...
, were able to continue resistance.
Sun Shoujin, who called himself the Earl of
Xing'an, with the aid of general
Tan Qi, led an alliance of mountain fortresses around
Mount Banchang, just south of
Ziyang
Ziyang () prefecture-level city in eastern Sichuan province, China. It is bordered by the provincial capital of Chengdu to the northwest, Deyang to the north, Suining to the northeast, Chongqing municipality to the east, and Neijiang to the wes ...
. They resisted an intense Banner assault with their long rifles, but Tan Qi abandoned Sun in July 1652, leading to Sun's defeat and death. A bandit gang, the "Pole bandits", who were plundering the local population, were also defeated shortly afterward by the betrayal of one of their two chiefs.
Continued fighting in the south
Conquest of the southwest (1652–1661)

After the elimination of
Zhang Xianzhong's
Xi dynasty
Zhang Xianzhong (张献忠 or Chang Hsien-chung; 18 September 1606 – 2 January 1647), nickname Huanghu (literally 'Yellow Tiger'), was a Chinese peasant leader who led a peasant revolt from Yan'an wei, Shaanxi (today Yulin, Shaanxi province) ...
, his generals retreated southward to
Guizhou
Guizhou (; formerly Kweichow) is a landlocked province in the southwest region of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Guiyang, in the center of the province. Guizhou borders the autonomous region of Guangxi to the ...
province, where they encountered the
Southern Ming
The Southern Ming (), also known as the Later Ming (), officially the Great Ming (), was an imperial dynasty of China and a series of rump states of the Ming dynasty that came into existence following the Jiashen Incident of 1644. Shun force ...
forces retreating from
Guangxi province. The Ming emperor, in urgent need of reinforcements, requested the aid of the Xi dynasty's followers. Zhang Xianzhong's former deputy,
Sun Kewang, exterminated all his opponents in the Southern Ming court and kept the Ming emperor under ''
de facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with ''de jure'' ("by la ...
'' imprisonment, all the while continuing to refer to Zhang Xianzhong as a deceased emperor.
Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked province in the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the C ...
was still a frontier land where tribal chieftains
tusi
''Tusi'', often translated as "headmen" or "chieftains", were hereditary tribal leaders recognized as imperial officials by the Yuan, Ming, and Qing dynasties of China, and the Later Lê and Nguyễn dynasties of Vietnam. They ruled certain e ...
were still in power in many areas. The tusi were led by the
Mu family
The Chiefdom of Lijiang (; Naxi: ) was a Nakhi autonomous Tusi chiefdom that ruled Lijiang during Yuan, Ming and Qing dynasty.
History
At first, Lijiang was ruled by Yuexi Zhao (越巂詔). Later, it was annexed by Nanzhao. According to legen ...
who held the position of Duke of Qianguo. In the early Ming, it was Duke
Mu Sheng
Mu Sheng (; vi, Mộc Thạnh; 1368–1439), courtesy name Jingmao (), was a Chinese military general and politician of the Ming dynasty.
Mu Sheng was the second son of Mu Ying, the first Marquis of Xiping (). He was a solemn man of few w ...
who led the Ming armies in
Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
during the
Ming-Ho War. Now the Mu family were still in power in Yunnan and remained loyal to the Ming. However, due to discontent against their rule, local revolts broke out against them. Mu joined with the few remaining Ming officials and Sun Kewang to restore order.
Though the Qing under
Dorgon
Dorgon (, ; 17 November 1612 – 31 December 1650), was a Manchu prince and regent of the early Qing dynasty. Born in the House of Aisin-Gioro as the 14th son of Nurhaci (the founder of the Later Jin dynasty, predecessor of the Qing dynast ...
's leadership had successfully pushed the Southern Ming deep into southern China, Ming loyalism was not dead yet. In early August 1652,
Li Dingguo
Li Dingguo () (1621–1662) was a Chinese military general of the Southern Ming dynasty who fought against the Qing dynasty.
As Zhang Xianzhong's general
Li was an adopted son of the rebel leader Zhang Xianzhong, and appointed a general in Zhan ...
, who had served as general in
Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of the ...
under Zhang Xianzhong (d. 1647) and was now protecting the
Yongli Emperor
The Yongli Emperor (; 1623–1662; reigned 18 November 1646 – 1 June 1662), personal name Zhu Youlang, was a royal member to the imperial family of Ming dynasty, and the fourth and last commonly recognised emperor of the Southern Ming, reigni ...
of the Southern Ming, retook
Guilin
Guilin (Standard Zhuang: ''Gveilinz''; alternatively romanized as Kweilin) is a prefecture-level city in the northeast of China's Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region. It is situated on the west bank of the Li River and borders Hunan to the nort ...
(
Guangxi province) from the Qing. Within a month, most of the commanders who had been supporting the Qing in Guangxi reverted to the Ming side. Despite occasionally successful military campaigns in
Huguang
Huguang was a province of China during the Yuan and Ming dynasties. It was founded by the Yuan dynasty in 1274. During the Yuan dynasty it included the areas of modern Hubei south of the Yangtze river, Hunan, Guizhou, and Guangxi. During the Ming ...
and
Guangdong
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020) ...
in the next two years, Li Dingguo failed to retake important cities. In 1653, the Qing court put
Hong Chengchou
Hong Chengchou (; 1593–1665), courtesy name Yanyan and art name Hengjiu, was a Chinese official who served under the Ming and Qing dynasties. He was born in present-day Liangshan Village, Yingdu Town, Fujian Province, China. After obtaining t ...
in charge of retaking the southwest. Headquartered in
Changsha
Changsha (; ; ; Changshanese pronunciation: (), Standard Chinese, Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is the Capital city, capital and the largest city of Hunan Province of China. Changsha is the 17th most populous city in China with a popul ...
(in what is now
Hunan
Hunan (, ; ) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the South Central China region. Located in the middle reaches of the Yangtze watershed, it borders the province-level divisions of Hubei to the north, Jiangxi ...
province), he patiently built up his forces; only in late 1658 did well-fed and well-supplied Qing troops mount a multipronged campaign to take
Guizhou
Guizhou (; formerly Kweichow) is a landlocked province in the southwest region of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Guiyang, in the center of the province. Guizhou borders the autonomous region of Guangxi to the ...
and
Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked province in the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the C ...
. Infighting broke out between the forces of Li Dingguo and Sun Kewang. The Ming emperor, fearful that Sun intended to make himself emperor, asked Li Dingguo to liberate him. After Sun's forces were routed, he and his surviving troops defected to Hong Chengchou's Qing armies, giving the Qing their opening to strike.
The
Manchus
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
were not able to conquer southern China by their own accord; they only did so by delegating to Han Chinese. During the fighting to extinguish Ming loyalism in the south, the
Shunzhi Emperor came to rely increasingly on Han Chinese bannermen, some second or even third generation, to fill governor and governor-general posts as a kind of "provincial
janissaries". Virtually all posts were filled by professional military officers of the Han Chinese Banners rather than Manchus or Han Chinese civilians. Han Chinese bannermen were the main force that subdued southern China. This made the Qing extremely dependent on the private armies of the autonomous Han Chinese banner nobles. The reliance on Han Chinese was made obvious in 1660 when the emperor ruled in favour of
Lu Guangxu, a Han Chinese provincial censor who delivered a report criticizing Manchu military corruption, destroying the Manchu claim that Han Chinese officials should not be involved in military matters. This change was a reflection of the actual military importance of Han Chinese in the dynasty, as well as the determination of the Qing rulers not to allow the Manchu and Han Chinese
Bannermen
Bannerman is a name of Scottish origin (see Clan Bannerman) and may refer to
Places
;Canada
* Bannerman, Edmonton, a neighbourhood in Edmonton, Canada
;United States
* Bannerman, Wisconsin, an unincorporated community
* Bannerman's Castle, an a ...
class to dominate the government. Through this compromise, the bureaucracy versus military conflict that had helped to cause the downfall of the Ming dynasty was resolved.
Flight to Burma (1659–1662)

In late January 1659, a Qing army led by Manchu Prince
Doni (1636–1661),
Dodo
The dodo (''Raphus cucullatus'') is an extinct flightless bird that was endemic to the island of Mauritius, which is east of Madagascar in the Indian Ocean. The dodo's closest genetic relative was the also-extinct Rodrigues solitaire. The ...
's son, took the capital of
Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked province in the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the C ...
, sending the
Yongli Emperor
The Yongli Emperor (; 1623–1662; reigned 18 November 1646 – 1 June 1662), personal name Zhu Youlang, was a royal member to the imperial family of Ming dynasty, and the fourth and last commonly recognised emperor of the Southern Ming, reigni ...
fleeing into nearby
Burma
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
, which was then ruled by King
Pindale Min
Pindale Min ( my, ပင်းတလဲမင်း, ; 23 March 1608 – 3 June 1661) was king of the Toungoo dynasty of Burma (Myanmar) from 1648 to 1661. Prince of Pindale ascended to the Burmese throne after his father King Thalun died in 1648 ...
of the
Toungoo dynasty
, conventional_long_name = Toungoo dynasty
, common_name = Taungoo dynasty
, era =
, status = Empire
, event_start = Independence from Ava
, year_start ...
. The imperial retinue was disarmed by the
Burmese; many of the Ming retinue were killed or enslaved, and the remainder were housed in huts opposite the capital city
Ava, under a Burmese guard. In Yunnan, the banner troops had engaged in pillage and rape when moving through
Hmong
Hmong may refer to:
* Hmong people, an ethnic group living mainly in Southwest China, Vietnam, Laos, and Thailand
* Hmong cuisine
* Hmong customs and culture
** Hmong music
** Hmong textile art
* Hmong language, a continuum of closely related to ...
lands, and the chieftain
Nayan, under the promise of being given overall command of all the
tusi
''Tusi'', often translated as "headmen" or "chieftains", were hereditary tribal leaders recognized as imperial officials by the Yuan, Ming, and Qing dynasties of China, and the Later Lê and Nguyễn dynasties of Vietnam. They ruled certain e ...
chiefs, rose in rebellion on the side of the Yongli Emperor. His city of
Yuanjiang
Yuanjiang () is a county-level city in the Province of Hunan, China, it is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Yiyang.
Located in the north of the province, the city is bordered to the north by Nan County, to the northeast b ...
was taken by
Wu Sangui in 1659 amid a massacre of 100,000 people, and the next year was spent putting down the rest of the rebels. As the city fell Nayan bowed in the direction of the emperor and declared "Your minister has exerted himself to the utmost. I have nothing else to report to Your Highness." He then burned himself and his family.
Loyalist generals
Li Dingguo
Li Dingguo () (1621–1662) was a Chinese military general of the Southern Ming dynasty who fought against the Qing dynasty.
As Zhang Xianzhong's general
Li was an adopted son of the rebel leader Zhang Xianzhong, and appointed a general in Zhan ...
and
Bai Wenxuan
BAI or Bai may refer to:
BAI
Organizations
* BAI Communications, telecommunications infrastructure company
*BAI (organization), professional organization for financial services in the United States
*Badminton Association of India, India's gov ...
attempted to rescue the emperor from the
Burmese and attacked
Ava between 1660 and 1661. They opened fire with cannon on the Burmese army of 150,000 men with war elephants. The Burmese broke after a rear attack from Bai. The loyalists built boats and bridges to cross the
Irrawaddy River but these were burned by Burmese commandos. A long siege of Ava ensued but the Burmese increased their defenses after tricking the
Ming
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peop ...
forces into leaving. The king of Burma
Pindale Min
Pindale Min ( my, ပင်းတလဲမင်း, ; 23 March 1608 – 3 June 1661) was king of the Toungoo dynasty of Burma (Myanmar) from 1648 to 1661. Prince of Pindale ascended to the Burmese throne after his father King Thalun died in 1648 ...
was overthrown in a coup by his brother
Pye Min, who went on the offensive against the Ming loyalists. Under the guise of a 'spirit water' ritual during the king's enthronement, most of the men in the Ming imperial retinue were ambushed and killed. The Burmese contacted the
Qing to negotiate handing the emperor over. Subsequently, 100,000 Qing soldiers crossed into
Burma
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
. In 1662, the
Yongli Emperor
The Yongli Emperor (; 1623–1662; reigned 18 November 1646 – 1 June 1662), personal name Zhu Youlang, was a royal member to the imperial family of Ming dynasty, and the fourth and last commonly recognised emperor of the Southern Ming, reigni ...
was captured by
Wu Sangui near
Ava and executed by strangulation in
Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked province in the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the C ...
, the same Wu whose surrender to the
Manchus
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
in April 1644 had allowed
Dorgon
Dorgon (, ; 17 November 1612 – 31 December 1650), was a Manchu prince and regent of the early Qing dynasty. Born in the House of Aisin-Gioro as the 14th son of Nurhaci (the founder of the Later Jin dynasty, predecessor of the Qing dynast ...
to start the Qing expansion. Bai Wenxuan surrendered and was inducted into the Han Chinese banners. Li Dingguo, wrongly informed that the emperor had escaped, attempted to march for
Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
and contacted
Siam
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is bo ...
for an alliance, before finally dying of disease in August 1662. His final words were to tell his son to never surrender to the Qing (his son still did surrender, with the remainder of the army).
Seaborne resistance (1655–1663)

In 1656 a
Lake Mao bandit named Qian Ying managed to acquire blank commissions from the
Yongli
Yongli () (5 February 1647 – 1 June 1662) was the era name of the Yongli Emperor of the Southern Ming.
Comparison table
Other eras contemporaneous with Yongli
* China
** '' Dingwu'' (定武, 1646–1664): Southern Ming — era name of Zhu B ...
regime, and he therefore managed to become legitimized as a Ming loyalist fighter. He organised a marine resistance unit and established links with
Koxinga
Zheng Chenggong, Prince of Yanping (; 27 August 1624 – 23 June 1662), better known internationally as Koxinga (), was a Ming loyalist general who resisted the Qing conquest of China in the 17th century, fighting them on China's southeastern ...
's forces. The Qing governor-general Han Chinese bannerman
Lang Tingzuo
Lang may refer to:
*Lang (surname), a surname of independent Germanic or Chinese origin
Places
* Lang Island (Antarctica), East Antarctica
* Lang Nunatak, Antarctica
* Lang Sound, Antarctica
* Lang Park, a stadium in Brisbane, Australia
* Lan ...
quickly moved to suppress him, and launched a surprise attack which defeated him. Qian was hunted down and captured by March 1648. Only one year later did Koxinga launch an offensive, too late to join up with existing forces.
Zheng Chenggong
Zheng Chenggong, Prince of Yanping (; 27 August 1624 – 23 June 1662), better known internationally as Koxinga (), was a Ming loyalist general who resisted the Qing conquest of China in the 17th century, fighting them on China's southeastern ...
("Koxinga"), who had been adopted by the
Longwu Emperor
Zhu Yujian (; 1602 – 6 October 1646), nickname Changshou (長壽), originally the Prince of Tang, later reigned as the Longwu Emperor () of the Southern Ming from 18 August 1645, when he was enthroned in Fuzhou, to 6 October 1646, when he wa ...
in 1646 and ennobled by
Yongli
Yongli () (5 February 1647 – 1 June 1662) was the era name of the Yongli Emperor of the Southern Ming.
Comparison table
Other eras contemporaneous with Yongli
* China
** '' Dingwu'' (定武, 1646–1664): Southern Ming — era name of Zhu B ...
in 1655, also continued to defend the cause of the
Southern Ming
The Southern Ming (), also known as the Later Ming (), officially the Great Ming (), was an imperial dynasty of China and a series of rump states of the Ming dynasty that came into existence following the Jiashen Incident of 1644. Shun force ...
. From
Xiamen
Xiamen ( , ; ), also known as Amoy (, from Hokkien pronunciation ), is a sub-provincial city in southeastern Fujian, People's Republic of China, beside the Taiwan Strait. It is divided into six districts: Huli, Siming, Jimei, Tong'an ...
, he captured
Chaozhou in 1650. With his help, sea lord
Zhang Mingzhen had captured
Zhoushan Island
Zhoushan Island is the principal and namesake island in the Zhoushan Islands, formerly romanized as the ChusanIslands, an archipelago administered by Zhoushan Prefecture in Zhejiang Province in the People's Republic of China. It is the provinc ...
and
Taizhou in 1655. In 1658 he attacked the coastline of
Zhejiang
Zhejiang ( or , ; , Chinese postal romanization, also romanized as Chekiang) is an East China, eastern, coastal Provinces of China, province of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Hangzhou, and other notable citie ...
province and finally cut the cable protecting the
Yangtze
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest river in Asia, the third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains (Tibetan Plateau) and flows ...
estuary in 1659.
In 1659, just as
Shunzhi
The Shunzhi Emperor (15 March 1638 – 5 February 1661) was the second emperor of the Qing dynasty of China, and the first Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1644 to 1661. A committee of Manchu princes chose him to succee ...
was preparing to hold a special examination to celebrate the glories of his reign and the success of the southwestern campaigns, Zheng sailed up the
Yangtze River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest list of rivers of Asia, river in Asia, the list of rivers by length, third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in th ...
with a well-armed fleet, took several cities from Qing hands, and went so far as to threaten
Nanjing
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu province of the People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and the second largest city in the East China region. T ...
. Despite capturing many counties in his initial attack due to surprise and having the initiative, Koxinga announced the final battle in
Nanjing
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu province of the People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and the second largest city in the East China region. T ...
ahead of time giving plenty of time for the Qing to prepare because he wanted a decisive, single grand showdown like his father successfully did against the
Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
at the
Battle of Liaoluo Bay
The Battle of Liaoluo Bay () took place in 1633 off the coast of Fujian, China; involving the Dutch East India Company (VOC) and the Chinese Ming dynasty's navies. The battle was fought at the crescent-shaped Liaoluo Bay that forms the southe ...
, throwing away the surprise and initiative which led to its failure. Koxinga's attack on Qing held Nanjing which would interrupt the supply route of the
Grand Canal leading to possible starvation in
Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
caused such fear that the
Manchus
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
considered returning to
Manchuria
Manchuria is an exonym (derived from the endo demonym " Manchu") for a historical and geographic region in Northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day Northeast China (Inner Manchuria) and parts of the Russian Far East (Outer M ...
(Tartary) and abandoning
China according to a 1671 account by a
French missionary.
The commoners and officials in Beijing and Nanjing were waiting to support whichever side won. An official from Qing Beijing sent letters to family and another official in Nanjing, telling them all communication and news from Nanjing to Beijing had been cut off, that the Qing were considering abandoning Beijing and moving their capital far away to a remote location for safety since Koxinga's iron troops were rumored to be invincible. The letter said it reflected the grim situation being felt in Qing Beijing. The official told his children in Nanjing to prepare to defect to Koxinga which he himself was preparing to do. Koxinga's forces intercepted these letters and after reading them Koxinga may have started to regret his deliberate delays allowing the Qing to prepare for a final massive battle instead of swiftly attacking Nanjing. When the emperor heard of this sudden attack he is said to have slashed his throne with a sword in anger. But the siege of Nanjing was relieved and Zheng Chenggong repelled, forcing Zheng to take refuge in the southeastern coastal province of
Fujian
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its cap ...
. Koxinga's Ming loyalists fought against a majority Han Chinese Bannermen Qing army when attacking Nanjing. The siege lasted almost three weeks, beginning on 24 August. Koxinga's forces were unable to maintain a complete encirclement, which enabled the city to obtain supplies and even reinforcements—though cavalry attacks by the city's forces were successful even before reinforcements arrived. Koxinga's forces were defeated and "slipped back" (Wakeman's phrase) to the ships which had brought them. Koxinga's forces were pursued to
Xiamen
Xiamen ( , ; ), also known as Amoy (, from Hokkien pronunciation ), is a sub-provincial city in southeastern Fujian, People's Republic of China, beside the Taiwan Strait. It is divided into six districts: Huli, Siming, Jimei, Tong'an ...
where they were defeated in June 1660, and retreated to
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
.
After the admiral
Shi Lang disobeyed orders,
Koxinga
Zheng Chenggong, Prince of Yanping (; 27 August 1624 – 23 June 1662), better known internationally as Koxinga (), was a Ming loyalist general who resisted the Qing conquest of China in the 17th century, fighting them on China's southeastern ...
executed his family causing him to defect to the Qing. Admiral Shi later led the Qing navy to victory over Koxinga's descendants. Koxinga implemented extremely strict harsh discipline on his soldiers which caused many of them to defect to the Qing. Failure to listen to orders and failing in battle could bring death sentences with no leniency from Koxinga. The Qing implemented a lenient policy towards defectors who defected to the
Southern Ming
The Southern Ming (), also known as the Later Ming (), officially the Great Ming (), was an imperial dynasty of China and a series of rump states of the Ming dynasty that came into existence following the Jiashen Incident of 1644. Shun force ...
,
Koxinga
Zheng Chenggong, Prince of Yanping (; 27 August 1624 – 23 June 1662), better known internationally as Koxinga (), was a Ming loyalist general who resisted the Qing conquest of China in the 17th century, fighting them on China's southeastern ...
, and the
Three Feudatories, inviting and allowing them back into Qing ranks without punishment even after they initially betrayed the Qing and defected, and this policy was able to secure mass defections.
Pressured by Qing fleets,
Koxinga
Zheng Chenggong, Prince of Yanping (; 27 August 1624 – 23 June 1662), better known internationally as Koxinga (), was a Ming loyalist general who resisted the Qing conquest of China in the 17th century, fighting them on China's southeastern ...
fled to
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
in April 1661 and defeated the
Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
in the
Siege of Fort Zeelandia
The siege of Fort Zeelandia () of 1661–1662 ended the Dutch East India Company's rule over Taiwan and began the Kingdom of Tungning's rule over the island.
Prelude
From 1623 to 1624 the Dutch had been at war with Ming China over the Pescador ...
, expelling them from Taiwan and setting up the
Kingdom of Tungning
The Kingdom of Tungning (), also known as Tywan by the British at the time, was a dynastic maritime state that ruled part of southwestern Taiwan and the Penghu islands between 1661 and 1683. It is the first predominantly Han Chinese state in ...
. Great care was taken to symbolise support for the Ming legitimacy, an example being the use of the term ''guan'' instead of ''bu'' to name departments, since the latter is reserved for central government, whereas Taiwan was to be a regional office of the rightful Ming rule of
China.
Zheng Jing
Zheng Jing, Prince of Yanping (; 25 October 1642 – 17 March 1681), courtesy names Xianzhi () and Yuanzhi (), pseudonym Shitian (), was a 17th-century Chinese warlord, Ming dynasty loyalist and ruler of the Kingdom of Tungning in Taiwan.
Bi ...
dutifully complied with the prescribed procedures for Ming officials by regularly presenting reports and paying tribute to the absent Ming Emperor. His originally stated intentions for conquering Taiwan from the Dutch also included the desire to protect Chinese settlers in Taiwan from maltreatment by the Dutch. The Ming dynasty princes who accompanied Koxinga to Taiwan were the Prince
Zhu Shugui and Prince
Zhu Honghuan, son of
Zhu Yihai
Zhu Yihai (; 1618–1662), courtesy name Juchuan (巨川), art name Hengshan (恆山) and Changshizi (常石子), was a regent of the Southern Ming from 1645 to 1653.
Early life
Zhu Yihai was born in 1618, during the 46th year of the reign of th ...
.
The Qing agreed to an alliance with the
Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( nl, Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie, the VOC) was a chartered company established on the 20th March 1602 by the States General of the Netherlands amalgamating existing companies into the first joint-stock ...
against the remaining Ming loyalists in
Fujian
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its cap ...
and
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
. The Dutch intended to take a colonial outpost in Taiwan. In October 1663, the joint fleet succeeded in capturing
Xiamen
Xiamen ( , ; ), also known as Amoy (, from Hokkien pronunciation ), is a sub-provincial city in southeastern Fujian, People's Republic of China, beside the Taiwan Strait. It is divided into six districts: Huli, Siming, Jimei, Tong'an ...
and
Kinmen
Kinmen, alternatively known as Quemoy, is a group of islands governed as a county by the Republic of China (Taiwan), off the southeastern coast of mainland China. It lies roughly east of the city of Xiamen in Fujian, from which it is separat ...
(Quemoy) from the
Southern Ming
The Southern Ming (), also known as the Later Ming (), officially the Great Ming (), was an imperial dynasty of China and a series of rump states of the Ming dynasty that came into existence following the Jiashen Incident of 1644. Shun force ...
. However, the Qing grew suspicious of Dutch ambitions to maintain a colony in Taiwan and to push for trading privileges, so the alliance collapsed. Admiral
Shi Lang, who strongly objected to cession of Taiwan to the Dutch, offered to launch his own expedition instead. The Dutch looted relics and killed monks after attacking a
Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
complex at
Putuoshan
Mount Putuo (, from Sanskrit: " Mount Potalaka") is an island in Putuo District, Zhoushan, Zhejiang, China. It is a renowned site in Chinese Buddhism and is the bodhimaṇḍa of the bodhisattva Guanyin.
Mount Putuo is one of the four sacr ...
on the
Zhoushan Islands
Zhoushan , formerly romanized as Chusan, is an urbanized archipelago with the administrative status of a prefecture-level city in the eastern Chinese province of Zhejiang. It consists of an archipelago of islands at the southern mouth of ...
in 1665 during their war against
Koxinga
Zheng Chenggong, Prince of Yanping (; 27 August 1624 – 23 June 1662), better known internationally as Koxinga (), was a Ming loyalist general who resisted the Qing conquest of China in the 17th century, fighting them on China's southeastern ...
's son
Zheng Jing
Zheng Jing, Prince of Yanping (; 25 October 1642 – 17 March 1681), courtesy names Xianzhi () and Yuanzhi (), pseudonym Shitian (), was a 17th-century Chinese warlord, Ming dynasty loyalist and ruler of the Kingdom of Tungning in Taiwan.
Bi ...
. Zheng Jing's navy executed 34 Dutch sailors and drowned 8 Dutch sailors after looting, ambushing and sinking the Dutch
fluyt
A fluyt (archaic Dutch: ''fluijt'' "flute"; ) is a Dutch type of sailing vessel originally designed by the shipwrights of Hoorn as a dedicated cargo vessel. Originating in the Dutch Republic in the 16th century, the vessel was designed to faci ...
ship ''Cuylenburg'' in 1672 on northeastern Taiwan. Only 21 Dutch sailors escaped to
Japan. The ship was going from
Nagasaki
is the capital and the largest Cities of Japan, city of Nagasaki Prefecture on the island of Kyushu in Japan.
It became the sole Nanban trade, port used for trade with the Portuguese and Dutch during the 16th through 19th centuries. The Hi ...
to
Batavia
Batavia may refer to:
Historical places
* Batavia (region), a land inhabited by the Batavian people during the Roman Empire, today part of the Netherlands
* Batavia, Dutch East Indies, present-day Jakarta, the former capital of the Dutch East In ...
on a trade mission.
The Three Feudatories (1674–1681)
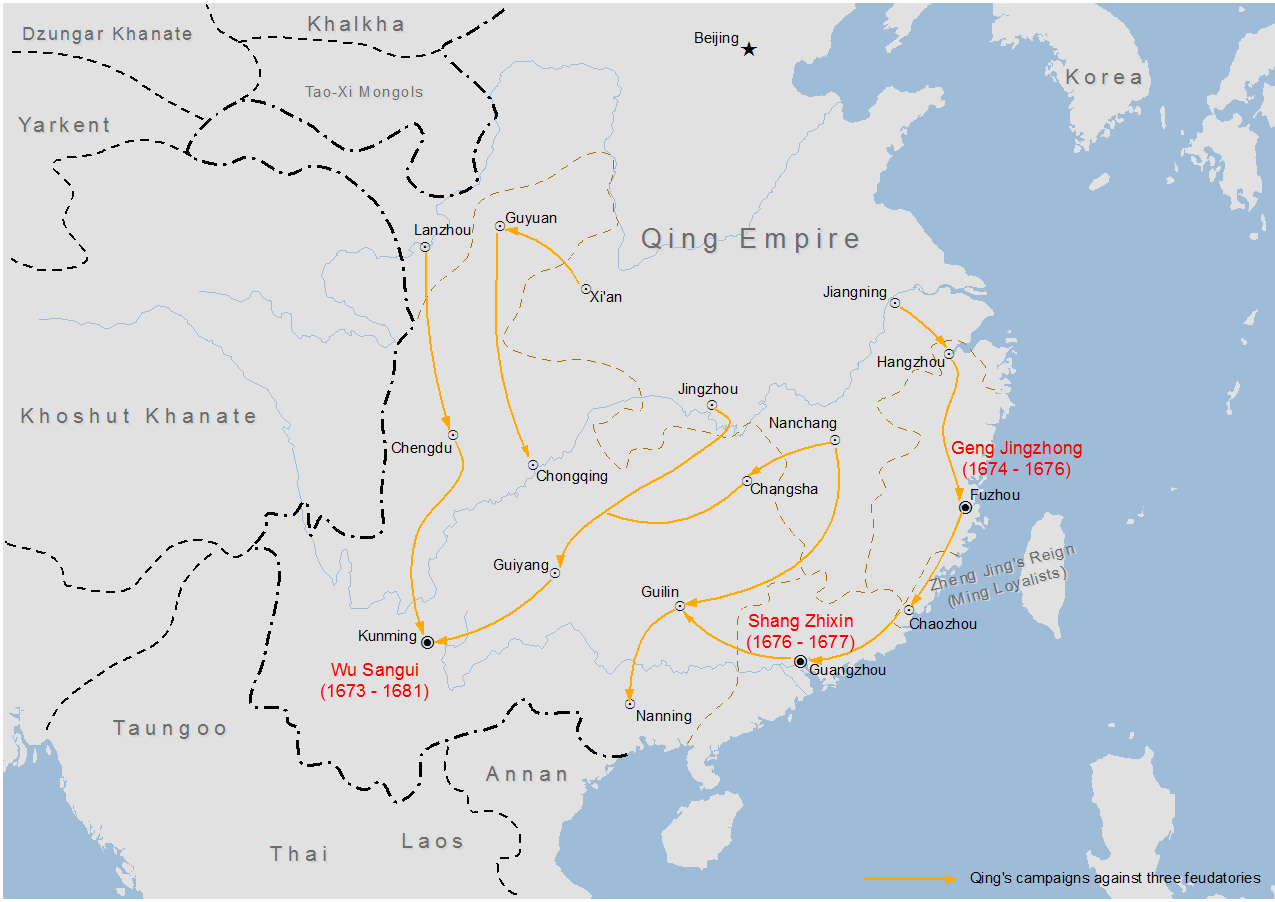

The Qing had relied on
Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
Banner generals to defeat
Li Chengdong
Li, li, or LI may refer to:
Businesses and organizations
* Landscape Institute, a British professional body for landscape architects
* Leadership Institute, a non-profit organization located in Arlington, Virginia, US, that teaches "political te ...
and defend against the resistance in
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
, and they were forced to grant these generals vast autonomy and subsidies. In 1673,
Wu Sangui,
Shang Zhixin, and
Geng Jimao, the "Three Feudatories", rebelled against the
Kangxi Emperor
The Kangxi Emperor (4 May 1654– 20 December 1722), also known by his temple name Emperor Shengzu of Qing, born Xuanye, was the third emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the second Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1661 to ...
. They were joined by generals
Sun Yanling in
Guangxi,
Wang Fuchen
Wang Fuchen () (d. 1681) was a participant in the Revolt of the Three Feudatories during the Qing dynasty against the Kangxi Emperor. Wang was born in Datong, Shanxi Province, he was born to a poor family and grew up to be a bandit. His original su ...
in
Shaanxi
Shaanxi (alternatively Shensi, see § Name) is a landlocked province of China. Officially part of Northwest China, it borders the province-level divisions of Shanxi (NE, E), Henan (E), Hubei (SE), Chongqing (S), Sichuan (SW), Gansu (W), N ...
and
Wang Pingfan in
Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of the ...
. Slaves revolted in Beijing as it was widely believed that the Qing would fall. The Kangxi Emperor called it the most harrowing experience in his life.
However, their disunity destroyed them.
Shang Zhixin and
Geng Jimao surrendered in 1681 after a massive Qing counteroffensive, in which the Han Chinese
Green Standard Army
The Green Standard Army (; Manchu: ''niowanggiyan turun i kūwaran'') was the name of a category of military units under the control of Qing dynasty in China. It was made up mostly of ethnic Han soldiers and operated concurrently with the Manchu ...
played the major role with the Bannermen taking a backseat.
The rebellion was defeated mainly due to the refusal of most Han Chinese commanders to turn against the Qing dynasty. Particularly repulsive to many was the blatant opportunism of
Wu Sangui, who had betrayed two dynasties in one lifetime: even
Ming
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peop ...
loyalists ridiculed his cause.
Fan Chengmo
Fan commonly refers to:
* Fan (machine), a machine for producing airflow, often used for cooling
** Hand fan, an implement held and waved by hand to move air for cooling
* Fan (person), short for fanatic; an enthusiast or supporter, especially wit ...
, son of
Fan Wencheng
Fan Wencheng (, courtesy name: Xiandou 憲斗, 1597–1666) was a Qing dynasty Scholar-Official, Prime Minister and Grand Secretary ''(Daxue Shi)''. His official career went through four generation of Qing dynasty emperors through Nurhaci, Hong T ...
, remained loyal to the Qing despite imprisonment and eventually death, and as one of leading military families of
Liaodong
The Liaodong Peninsula (also Liaotung Peninsula, ) is a peninsula in southern Liaoning province in Northeast China, and makes up the southwestern coastal half of the Liaodong region. It is located between the mouths of the Daliao River (the ...
, his example inspired other Liaodong generals to remain loyal.
The Qing forces were crushed by
Wu Sangui from 1673 to 1674. The Qing had the support of the majority of Han Chinese soldiers and Han Chinese elite against the
Three Feudatories, since they refused to join Wu Sangui in the revolt, while the
Eight Banners
The Eight Banners (in Manchu: ''jakūn gūsa'', ) were administrative and military divisions under the Later Jin and Qing dynasties of China into which all Manchu households were placed. In war, the Eight Banners functioned as armies, but the ...
and
Manchu officers fared poorly against Wu Sangui, so the Qing responded with using a massive army of more than 900,000
Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
(non-Banner) instead of the
Eight Banners
The Eight Banners (in Manchu: ''jakūn gūsa'', ) were administrative and military divisions under the Later Jin and Qing dynasties of China into which all Manchu households were placed. In war, the Eight Banners functioned as armies, but the ...
, to fight and crush the Three Feudatories. Wu Sangui's forces were crushed by the
Green Standard Army
The Green Standard Army (; Manchu: ''niowanggiyan turun i kūwaran'') was the name of a category of military units under the control of Qing dynasty in China. It was made up mostly of ethnic Han soldiers and operated concurrently with the Manchu ...
, made out of defected Ming soldiers. In the Three Feudatories rebellion, Han Chinese bannermen who stayed on the Qing side and died in battle were categorized as martyrs.
Surrender of Taiwan (1683)

Zheng Chenggong
Zheng Chenggong, Prince of Yanping (; 27 August 1624 – 23 June 1662), better known internationally as Koxinga (), was a Ming loyalist general who resisted the Qing conquest of China in the 17th century, fighting them on China's southeastern ...
(Koxinga) had died in 1662. His descendants resisted Qing rule until 1683, when the
Kangxi Emperor
The Kangxi Emperor (4 May 1654– 20 December 1722), also known by his temple name Emperor Shengzu of Qing, born Xuanye, was the third emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the second Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1661 to ...
dispatched
Shi Lang with a fleet of 300 ships to take the Ming loyalist
Kingdom of Tungning
The Kingdom of Tungning (), also known as Tywan by the British at the time, was a dynastic maritime state that ruled part of southwestern Taiwan and the Penghu islands between 1661 and 1683. It is the first predominantly Han Chinese state in ...
in
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
in 1683 from the Zheng family. The Tungning kingdom was coming under severe pressure in 1681-1682 from lack of food due to drought and overpopulation with limited food production as people were starving. There was factional rivalry within the Kingdom of Tungning between Feng Xifan who supported Zheng Kuan against Liu Guoxuan and Zheng Keshuang, so even though Taiwan could have easily withstood a Qing assault if Liu withdrew the navy back to the main island of Taiwan, Liu Guoxuan decided to gamble the entire navy in a battle at Penghu in 1683 instead against Shi Lang, so that if he won he would take over the affairs of the Tungning kingdom and if he lost the battle, he would be the one to surrender the Tunging kingdom to get favorable terms from the Qing. Zheng Chenggong's grandson
Zheng Keshuang
Zheng Keshuang, Prince of Yanping (; 13 August 1670 – 22 September 1707), courtesy name Shihong, art name Huitang, was the third and last ruler of the Kingdom of Tungning in Taiwan in the 17th century. He was the second son of Zheng Jing and ...
surrendered Taiwan to the
Kangxi Emperor
The Kangxi Emperor (4 May 1654– 20 December 1722), also known by his temple name Emperor Shengzu of Qing, born Xuanye, was the third emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the second Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1661 to ...
after the
Battle of Penghu
The Battle of Penghu () was a naval battle fought in 1683 between the Qing dynasty and the Kingdom of Tungning. The Qing admiral Shi Lang led a fleet to attack the Tungning forces in Penghu. Each side possessed more than 200 warships. The Tungn ...
. Having lost this battle, Zheng Keshuang surrendered and was rewarded by the Kangxi Emperor with the title "Duke of Haicheng" (). He and his soldiers were inducted into the
Eight Banners
The Eight Banners (in Manchu: ''jakūn gūsa'', ) were administrative and military divisions under the Later Jin and Qing dynasties of China into which all Manchu households were placed. In war, the Eight Banners functioned as armies, but the ...
. His rattan shield troops ( ''tengpaiying'') served
against Russian Cossacks at Albazin.
The Qing sent most of the 17 Ming princes still living on Taiwan back to mainland China where they spent the rest of their lives. The
Prince of Ningjing and his five concubines committed suicide rather than submit to capture. Their palace was used as
Shi Lang's headquarters in 1683 but he
memorialized the emperor to convert it into a
Mazu temple This is a list of Mazu temples, dedicated to Mazu (媽祖) also known as Tian Shang Sheng Mu (天上聖母) or Tian Hou (天后) Chinese Goddess of Sea and Patron Deity of fishermen, sailors and any occupations related to sea/ocean, also regarded as ...
as a propaganda measure in quieting remaining resistance on Taiwan. The emperor approved its dedication as the
Grand Matsu Temple the next year and, honoring the goddess
Mazu for her supposed assistance during the Qing expansion, promoted her to "Empress of Heaven" (''Tianhou'') from her previous status as a heavenly consort (''tianfei'').
The Ming loyalist Chinese pirate
Yang Yandi (Dương Ngạn Địch) and his fleet sailed to
Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
to leave the Qing dynasty in March 1682. Yang was a general of
Ming China, and swore allegiance to
Koxinga
Zheng Chenggong, Prince of Yanping (; 27 August 1624 – 23 June 1662), better known internationally as Koxinga (), was a Ming loyalist general who resisted the Qing conquest of China in the 17th century, fighting them on China's southeastern ...
. His position was Chief Commander of Longmen (a place in modern
Qinzhou
Qinzhou ( postal: Yamchow, , Jyutping: ''Jam1 zau1'' (Canton) /''Ham1 zau1'' ( Local) ) is a prefecture-level city in south-central Guangxi, southern China, lying on the Gulf of Tonkin and having a total population of 3,302,238 as of the 2020 c ...
,
Guangxi). In 1679, after the
Revolt of the Three Feudatories
The Revolt of the Three Feudatories, () also known as the Rebellion of Wu Sangui, was a rebellion in China lasting from 1673 to 1681, during the early reign of the Kangxi Emperor (r. 1661–1722) of the Qing dynasty (1644–1912). The revolt was ...
was put down by
Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-spea ...
, he led 3,000 soldiers and 50 ships to
Da Nang together with
Hoàng Tiến,
Trần Thượng Xuyên and
Trần An Bình. Dương Ngạn Địch and Hoàng Tiến were sponsored by
Nguyễn Phúc Tần to settle
Mỹ Tho
Mỹ Tho () is a city in the Tiền Giang province in the Mekong Delta region of South Vietnam. It has a population of approximately 169,000 in 2006 and 220,000 in 2012. It is the regional center of economics, education and technology. The majorit ...
, where Địch served as chief of a small Chinese community, while Trần Thượng Xuyên was sent to lead the community in Đông Phố (modern
Biên Hòa
Biên Hòa (Northern accent: , Southern accent: ) is the capital city of Đồng Nai Province, Vietnam and part of the Ho Chi Minh City metropolitan area and located about east of Ho Chi Minh City, to which Biên Hòa is linked by Vietnam Hi ...
).
['' Đại Nam liệt truyện tiền biên'', vol. 6]['']Việt Nam sử lược
( vi-hantu, 越南史略, french: Précis d'Histoire du Việt-Nam, lit. "Outline History of Vietnam"), was the first history text published in the Vietnamese and the Vietnamese alphabet. It was compiled by Vietnamese historian Trần Trọng Ki ...
'', Quyển 2, Tự chủ thời đại, Chương 6 The Nguyễn court allowed these resistance forces to resettle in
Nam Ky, which had been newly conquered from the
Khmers
The Khmer people ( km, ជនជាតិខ្មែរ, ) are a Southeast Asian ethnic group native to Cambodia. They comprise over 90% of Cambodia's population of 17 million. . These settlers named their settlements as "
Minh Huong", to recall their allegiance to the
Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peo ...
.
Dương was murdered by his assistant Hoàng Tiến in 1688, who then revolted against the Nguyễn lord but was put down.
[
]
Literature and thought
 The defeat of the
The defeat of the Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peo ...
posed practical and moral problems, especially for literati and officials. Confucian
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China. Variously described as tradition, a philosophy, a religion, a humanistic or rationalistic religion, a way of governing, or ...
teachings emphasized loyalty (忠 ''zhōng''), but the question arose as to whether Confucians should be loyal to the fallen Ming or to the new power, the Qing. Some, like the painter Bada Shanren, a descendant of the Ming ruling family, became recluses. Others, like Kong Shangren
Kong Shangren (; 1648 – 1718) was a Qing dynasty dramatist and poet best known for his '' chuanqi'' play ''The Peach Blossom Fan''"Frommer's China", Simon Foster et al., 2010, p. 383, about the last days of the Ming dynasty.
Born in Qufu, Kon ...
, who claimed to be a descendant of Confucius
Confucius ( ; zh, s=, p=Kǒng Fūzǐ, "Master Kǒng"; or commonly zh, s=, p=Kǒngzǐ, labels=no; – ) was a Chinese philosopher and politician of the Spring and Autumn period who is traditionally considered the paragon of Chinese sages. C ...
, supported the new regime. Kong wrote a poignant drama, The Peach Blossom Fan
''The Peach Blossom Fan'' () is a musical play and historical drama in 44 scenes that was completed in 1699 by the early Qing dynasty playwright Kong Shangren after more than 10 years of effort.
The play depicts the drama that resulted in ...
, which explored the moral decay of the Ming in order to explain its fall. Poets whose lives bridged the transition between Ming poetry
Ming poetry refers to the poetry of or typical of the Ming dynasty (1368–1644).Davis, lxxi With over one million specimens of Ming poetry surviving today, the poetry of the Ming dynasty represents one of the major periods of Classical Chinese ...
and Qing poetry
Qing poetry refers to the poetry of or typical of the Qing dynasty (1644–1911). Classical Chinese poetry continued to be the major poetic form of the Qing dynasty, during which the debates, trends and widespread literacy of the Ming period began ...
are attracting modern academic interest. Some of the most important first generation of Qing thinkers were Ming loyalists, at least in their hearts, including Gu Yanwu
Gu Yanwu () (July 15, 1613 – February 15, 1682), also known as Gu Tinglin (), was a Chinese philologist, geographer, and famous scholar-official in Qing dynasty. He spent his youth during the Manchu conquest of China in anti-Manchu activities a ...
, Huang Zongxi
Huang Zongxi (; September 24, 1610 – August 12, 1695), courtesy name Taichong (), was a Chinese naturalist, political theorist, philosopher, and soldier during the latter part of the Ming dynasty into the early part of the Qing.
Biography
Huan ...
, and Fang Yizhi. Partly in reaction and to protest the laxity and excess of the late Ming, they turned to evidential learning, which emphasized careful textual study and critical thinking. Another important group in this transitional period were the "Three Masters of Jiangdong The Three Masters of Jiangdong () were a group of Chinese literati who lived and wrote during the Manchu conquest of China, Ming-Qing transition. They were Gong Dingzi, Wu Weiye, Qian Qianyi.Zhang, 71 They are partly famous for reviving the ''Ci (po ...
"—Gong Dingzi Gong Dingzi () (1615–1673) was a Chinese poet and politician. He was a famous author and Classical Chinese poet. He was also a government official serving under the Ming Chongzhen Emperor
The Chongzhen Emperor (; 6 February 1611 – 25 April ...
, Wu Weiye
Wu Weiye (; 1609–1671) was a Chinese poet and politician. He was a poet in Classical Chinese poetry. He lived during the difficult times of the Ming-Qing transition. Along with Gong Dingzi and Qian Qianyi
Qian Qianyi (; Suzhou dialect: ; ...
and Qian Qianyi
Qian Qianyi (; Suzhou dialect: ; 1582–1664) was a Chinese historian, poet, and politician during the late Ming dynasty.Cihai: Page 1704. Qian was a famous author and poet; and along with Gong Dingzi and Wu Weiye was known as one of the Three ...
—who among other things contributed to a revival in the '' ci'' form of poetry.
The emperors, in order to legitimize their rule, encouraged Qing officials and literary figures to organize and appropriate the legacy of Chinese literature, producing anthologies and critical works. They also patronized the development of Manchu literature Manchu became a literary language after the creation of the Manchu script in 1599. Romance of the Three Kingdoms was translated by Dahai. Dahai translated Wanbao quanshu 萬寶全書.
Hong Taiji sponsored the translations of many Chinese language h ...
and the translation of Chinese classics into Manchu. Yet the phrase "defeat the Qing and restore the Ming" remained a byword for many.
Aftermath
''Dulimbai Gurun'' is the Manchu name for China (中國 Zhongguo; "Middle Kingdom"). After extinguishing the Ming, the Qing identified their state as "China" (Zhongguo), and referred to it as "Dulimbai Gurun" in Manchu. The Qing equated the lands of the Qing state (including present day Manchuria
Manchuria is an exonym (derived from the endo demonym " Manchu") for a historical and geographic region in Northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day Northeast China (Inner Manchuria) and parts of the Russian Far East (Outer M ...
, Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwest ...
, Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million, ...
, Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa, Taman ...
and other areas) as "China" in both the Chinese and Manchu languages, defining China as a multi-ethnic state, rejecting the idea that China only meant Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
areas, proclaiming that both Han and non-Han peoples were part of "China", using "China" to refer to the Qing in official documents, international treaties, and foreign affairs, and the "Chinese language" (Dulimbai gurun i bithe) referred to Han Chinese, Manchu, and Mongol languages, and the term "Chinese people" (中國人 Zhongguo ren; Manchu: Dulimbai gurun i niyalma) referred to all Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
, Manchu, and Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
subjects of the Qing.
During the Qing, many Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
later found themselves in positions of power and influence in Manchu administration and even had their own slaves.
 When the Qing defeated Dzungar Mongols in 1759, they proclaimed that the Oirats territorial lands were absorbed into "China" (Dulimbai Gurun) realm in a Manchu language memorial. They expounded the ideology that they were bringing together the "outer" non-Han Chinese like the
When the Qing defeated Dzungar Mongols in 1759, they proclaimed that the Oirats territorial lands were absorbed into "China" (Dulimbai Gurun) realm in a Manchu language memorial. They expounded the ideology that they were bringing together the "outer" non-Han Chinese like the Khalkha Mongols
The Khalkha ( Mongolian: mn, Халх, Halh, , zh, 喀爾喀) have been the largest subgroup of Mongol people in modern Mongolia since the 15th century. The Khalkha, together with Chahars, Ordos and Tumed, were directly ruled by Borjigin khan ...
, Inner Mongols
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. Its border includes most of the length of China's border with the country of Mongolia. Inner Mongolia also accounts for a ...
, Oirats (including Tibetans
The Tibetan people (; ) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Tibet. Their current population is estimated to be around 6.7 million. In addition to the majority living in Tibet Autonomous Region of China, significant numbers of Tibetans liv ...
, who were then under the rule of Oirat Khanates) together with the "inner" Han Chinese, into "one family" united under the Qing state. To show that the diverse subjects of the Qing were all part of one family, the Qing used the phrase "Zhongwai yijia" (中外一家, "central areas and outer areas as one realm") or "neiwei yijia" (內外一家, "interior and exterior of great-walls as one family"), to convey this idea of "unification" of the different peoples. A Manchu language version of a treaty with the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
concerning criminal jurisdiction over bandits called Qing subjects "people of the Central Kingdom (Dulimbai Gurun)". In the Manchu official Tulisen's Manchu language account of his meeting with the Torghut leader Ayuka Khan
Ayuka or Ayuki Khan (1669–1724) was a Kalmyk leader under whose rule the Kalmyk Khanate reached its zenith in terms of economic, military, and politic power. On behalf of Russia, Ayuka Khan protected the southern borders of Russia, engaging in ...
, it was mentioned that while the Torghut
The Torghut ( Mongolian: Торгууд, , Torguud), , "Guardsman" are one of the four major subgroups of the Four Oirats. The Torghut nobles traced its descent to the Keraite ruler Tooril; also many Torghuts descended from the Keraites.
Hist ...
s were unlike the Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 '' Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
, the "people of the Central Kingdom" (dulimba-i gurun 中國 Zhongguo) were like the Torghuts, and the "people of the Central Kingdom" referred to the Manchus
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
.
The rebellions led by Li Zicheng
Li Zicheng (22 September 1606 – 1645), born Li Hongji, also known by the nickname, Dashing King, was a Chinese peasant rebel leader who overthrew the Ming dynasty in 1644 and ruled over northern China briefly as the emperor of the short-li ...
, Zhang Xianzhong, and the subsequent expansion by the Qing was one of the most devastating wars in Chinese history. Examples of the devastation include the Yangzhou massacre
The Yangzhou massacre in May, 1645 in Yangzhou, Qing dynasty China, refers to the mass killings of innocent civilians by Manchu and defected northern Ming soldiers, commanded by the Manchu general Dodo.
The massacre is described in a contempora ...
, in which some 800,000 people, (although this number is now considered an exaggeration) including women and children, were massacred. The Qing carried out massacres in cities which resisted like Yangzhou
Yangzhou, postal romanization Yangchow, is a prefecture-level city in central Jiangsu Province (Suzhong), East China. Sitting on the north bank of the Yangtze, it borders the provincial capital Nanjing to the southwest, Huai'an to the north ...
and Guangzhou
Guangzhou (, ; ; or ; ), also known as Canton () and alternatively romanized as Kwongchow or Kwangchow, is the capital and largest city of Guangdong province in southern China. Located on the Pearl River about north-northwest of Hong Kon ...
but did not carry out violence in cities which surrendered and capitulated to Qing rule like Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
and Nanjing
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu province of the People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and the second largest city in the East China region. T ...
. Nanjing surrendered to the Qing without a violence as all officials surrendered and defected. Whole provinces, such as Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of the ...
, were thoroughly devastated and depopulated by the rebel Zhang Xianzhong. Zhang Xianzhong killed 600,000 to 6 million civilians. A massive famine in Shaanxi
Shaanxi (alternatively Shensi, see § Name) is a landlocked province of China. Officially part of Northwest China, it borders the province-level divisions of Shanxi (NE, E), Henan (E), Hubei (SE), Chongqing (S), Sichuan (SW), Gansu (W), N ...
had spurred Zhang Xianzhong and Li Zicheng to revolt and brutality by the rebels was widespread across northern China. Coastal China was devastated by the Qing coastal evacuation order. An estimated 25 million people died in the entire war. Some scholars estimate that the Chinese economy did not regain the level reached in the late Ming until 1750, a century after the foundation of the Qing dynasty.Yangtze delta
The Yangtze Delta or Yangtze River Delta (YRD, or simply ) is a triangle-shaped megalopolis generally comprising the Wu Chinese-speaking areas of Shanghai, southern Jiangsu and northern Zhejiang. The area lies in the heart of the Jiangnan reg ...
, China's richest province, was actually below Ming levels in 1820 (but equal to that of contemporary Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
).
Immediately before the Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peo ...
was overthrown by Li Zicheng
Li Zicheng (22 September 1606 – 1645), born Li Hongji, also known by the nickname, Dashing King, was a Chinese peasant rebel leader who overthrew the Ming dynasty in 1644 and ruled over northern China briefly as the emperor of the short-li ...
and the Qing entered Shanhai Pass, disease, famine, starvation and bandits ravaged the population of China. A disease killed half of the population in cities across China from 1640 to 1642 and three out of ten people in Huzhou died of plague and starvation. As the rural areas were hit by famine, peasants abandoned their homes by the millions, bandits took over Huguang
Huguang was a province of China during the Yuan and Ming dynasties. It was founded by the Yuan dynasty in 1274. During the Yuan dynasty it included the areas of modern Hubei south of the Yangtze river, Hunan, Guizhou, and Guangxi. During the Ming ...
, entire parts of the countryside were abandoned by peasants in the middle of China and theft and begging was widespread in cities by peasants looking for food and cannibalism spread all over famine hit Henan
Henan (; or ; ; alternatively Honan) is a landlocked province of China, in the central part of the country. Henan is often referred to as Zhongyuan or Zhongzhou (), which literally means "central plain" or "midland", although the name is al ...
. in 1641 northern China was hit by disease and plague spreading to Huangpi
Huangpi District () is one of 13 urban districts of the prefecture-level city of Wuhan, the capital of Hubei Province, China, situated on the northern (left) bank of the Yangtze River. The Sheshui enters the Yangtze at Huangpi. The district is ...
and the plague infected corpses were the only food available to the survivors. A massive drought in 1636 hit Huangpi amidst a series of natural disasters. Plague, locusts and famine spread all over. The plains and villages were hit by bandits and rebels as starving refugees, orphans who lost parents to disease and fired postal couriers and soldiers whose salary was cut off turned into rebels in 1642 all over China.
China's population growth led to devastating death tolls due to famine from cold weather, drought and floods. Soil and anything that was consumable was eaten by people in 1637 in Jiangxi
Jiangxi (; ; formerly romanized as Kiangsi or Chianghsi) is a landlocked province in the east of the People's Republic of China. Its major cities include Nanchang and Jiujiang. Spanning from the banks of the Yangtze river in the north int ...
in a massive famine. The massive disease epidemic devastated South Zhili
South Zhili, formerly romanized as or simply discussed under various romanizations of Nanjing, was a province of Imperial China, under the Ming dynasty. It was established around the "reserve capital" Nanjing and included parts of the modern ...
(Jiangnan
Jiangnan or Jiang Nan (; formerly romanized Kiang-nan, literally "South of the River" meaning "South of the Yangtze") is a geographic area in China referring to lands immediately to the south of the lower reaches of the Yangtze River, incl ...
) from 1641 to 1642 hitting the region twice, leaving corpses from the disease all over Zhili and killing 9 out of 10 across northern Zhejiang
Zhejiang ( or , ; , Chinese postal romanization, also romanized as Chekiang) is an East China, eastern, coastal Provinces of China, province of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Hangzhou, and other notable citie ...
after it spread there from the Grand Canal from northwestern China. Due to the loss in people, crops were not farmed further exacerbating the famine. The Yangtze
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest river in Asia, the third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains (Tibetan Plateau) and flows ...
river delta's urban regions, the coastal southeast and the northwest were all hit by massive famine as the grain producing regions lost productivity. Massive deflation blew up as silver bullion remained in Fujian
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its cap ...
and stopped grain and payments for famine relief from reaching famine victims. The rebellions broke out because of these famines. Famine hit Hangzhou
Hangzhou ( or , ; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), also romanized as Hangchow, is the capital and most populous city of Zhejiang, China. It is located in the northwestern part of the province, sitting at the head of Hangzhou Bay, whic ...
from 1640 to 1642, killing 50% of the population, forcing the impoverished to eat cocoons and silkworms, and forcing the rich to eat rice gruel. In multiple counties only three out of ten survived when Henan
Henan (; or ; ; alternatively Honan) is a landlocked province of China, in the central part of the country. Henan is often referred to as Zhongyuan or Zhongzhou (), which literally means "central plain" or "midland", although the name is al ...
was hit by the 1641 disease plague epidemic.
Over 1000 li of land were baked blood red in Shaanxi due to drought in 1627 and crimson skies appeared over the same province in 1628. Bandit ranks swelled from soldiers who deserted and starving people as plants died and cannibalism grew. Shaanxi was struck with a natural disaster every year for 60 years in a row until the final year of the Ming. Famines, frosts, earthquakes and windstorms also hit Shanxi province. Mass starvation also hit Henan province. Local government officials and the central government continued to levy taxes on the starving population. Bandit ranks swelled with the strong while the week died of starvation as no rain fell and the shoots of crops died. In 1622 in Shandong a White Lotus rebellion had broke out and they continued to recruit followers in Shaanxi. Lack of tax relief, floods and famine struck the common people while rebel ranks swelled with both peasants and former postal workers as the Ming state failed to pay rations and salaries to soldiers and fired postal workers. Highwaymen on horseback, poor and starving commoners, former postal workers, deserting rebel soldiers all filled the ranks of bandits and led to the peasant rebellions of Zhang Xianzhong and Li Zicheng which destroyed the Ming dynasty. Local magnates took over the fields of former tuntian military colonies in late Ming Shaanxi. Li Zicheng started squeezing corrupt former Ming officials for state funds as he noted the Ming dynasty which he defeated in Beijing, was toppled by massive corruption by officials.
In 1643-1644 Tianjin and Beijing were struck with two massive plague epidemics that helped destroy the Ming dynasty, which were recorded by Luo Yangxing, the governor general.
Selected groups of Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
bannermen were transferred en masse into Manchu Banners by the Qing, changing their ethnicity from Han Chinese to Manchu. Han Chinese bannermen of Tai Nikan 台尼堪 (watchpost Chinese) and Fusi Nikan 抚顺尼堪 (Fushun
Fushun (, formerly romanised as ''Fouchouen'', using French spelling, also as Fuxi ()) is a prefecture level city in Liaoning province, China, about east of Shenyang, with a total area of , of which is the city proper. Situated on the Hun Rive ...
Chinese) backgrounds into the Manchu banners in 1740 by order of the Qing Qianlong emperor. It was between 1618 and 1629 when the Han Chinese from Liaodong
The Liaodong Peninsula (also Liaotung Peninsula, ) is a peninsula in southern Liaoning province in Northeast China, and makes up the southwestern coastal half of the Liaodong region. It is located between the mouths of the Daliao River (the ...
who later became the Fushun Nikan and Tai Nikan defected to the Jurchens (Manchus). These Han Chinese-origin Manchu clans continue to use their original Han Chinese surnames and are marked as of Han Chinese origin on Qing lists of Manchu clans.
Accounts of atrocities during the transition from the Ming to Qing were used by revolutionaries in the anti-Qing Xinhai revolution
The 1911 Revolution, also known as the Xinhai Revolution or Hsinhai Revolution, ended China's last imperial dynasty, the Manchu-led Qing dynasty, and led to the establishment of the Republic of China. The revolution was the culmination of a ...
to fuel massacres against Manchus. Manchu bannermen and their families were massacred in several banner garrisons across China during the revolution, one of the massacres taking place in Xi'an
Xi'an ( , ; ; Chinese: ), frequently spelled as Xian and also known by other names, is the capital of Shaanxi Province. A sub-provincial city on the Guanzhong Plain, the city is the third most populous city in Western China, after Chongqi ...
. The Hui Muslim
The Hui people ( zh, c=, p=Huízú, w=Hui2-tsu2, Xiao'erjing: , dng, Хуэйзў, ) are an East Asian ethnoreligious group predominantly composed of Chinese-speaking adherents of Islam. They are distributed throughout China, mainly in the n ...
community was divided in its support for the 1911 Xinhai Revolution
The 1911 Revolution, also known as the Xinhai Revolution or Hsinhai Revolution, ended China's last imperial dynasty, the Manchu-led Qing dynasty, and led to the establishment of the Republic of China. The revolution was the culmination of a ...
. The Hui Muslims of Shaanxi
Shaanxi (alternatively Shensi, see § Name) is a landlocked province of China. Officially part of Northwest China, it borders the province-level divisions of Shanxi (NE, E), Henan (E), Hubei (SE), Chongqing (S), Sichuan (SW), Gansu (W), N ...
supported the revolutionaries and the Hui Muslims of Gansu supported the Qing. The local Hui Muslims (Mohammedans) of Xi'an
Xi'an ( , ; ; Chinese: ), frequently spelled as Xian and also known by other names, is the capital of Shaanxi Province. A sub-provincial city on the Guanzhong Plain, the city is the third most populous city in Western China, after Chongqi ...
(Shaanxi province
Shaanxi (alternatively Shensi, see § Name) is a landlocked province of China. Officially part of Northwest China, it borders the province-level divisions of Shanxi (NE, E), Henan (E), Hubei (SE), Chongqing (S), Sichuan (SW), Gansu (W), Ni ...
) joined the Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
revolutionaries in slaughtering the entire 20,000 Manchu population of Xi'an
Xi'an ( , ; ; Chinese: ), frequently spelled as Xian and also known by other names, is the capital of Shaanxi Province. A sub-provincial city on the Guanzhong Plain, the city is the third most populous city in Western China, after Chongqi ...
. The native Hui Muslims of Gansu province led by general Ma Anliang
Ma Anliang (, French romanization: Ma-ngan-leang, Xiao'erjing: ; 1855 – November 24, 1918) was a Hui born in Hezhou, Gansu, China. He became a general in the Qing dynasty army, and of the Republic of China. His father was Ma Zhan'a ...
sided with the Qing and prepared to attack the anti-Qing revolutionaries of Xi'an city. Only some wealthy Manchus who were ransomed and Manchu females survived. Wealthy Han Chinese seized Manchu girls to become their slaves and Han Chinese troops seized young Manchu women to be their wives. Young pretty Manchu girls were also seized by Hui Muslims of Xi'an during the massacre and brought up as Muslims.
See also
* Manchuria under Ming rule
Manchuria under Ming rule refers to the domination of the Ming dynasty over Manchuria, including today's Northeast China and Outer Manchuria. The Ming rule of Manchuria began with its conquest of Manchuria in the late 1380s after the fall of the ...
* Mongol invasion of China
The Mongol conquest of China was a series of major military efforts by the Mongol Empire to conquer various empires ruling over China. It spanned six decades in the 13th century and involved the defeat of the Jin dynasty, Western Liao, We ...
* Dzungar–Qing War
Mongolia, Tibet, and Xinjiang (c. 1620–1750)
* Dzungar–Qing Wars
The Dzungar–Qing Wars ( mn, Зүүнгар-Чин улсын дайн, ) were a decades-long series of conflicts that pitted the Dzungar Khanate against the Qing dynasty and its Mongol vassals. Fighting took place over a wide swath of Inner A ...
* Qing conquest of Mongolia
* Qing conquest of Tibet
* Qing dynasty in Inner Asia
The Qing dynasty in Inner Asia was the expansion of the Qing dynasty's realm in Inner Asia in the 17th and the 18th century AD, including both Inner Mongolia and Outer Mongolia, both Inner Manchuria and Outer Manchuria, Tibet, Qinghai and Xinjia ...
(Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwest ...
and parts of Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
)
* Tibet under Qing rule
Tibet under Qing rule refers to the Qing dynasty's relationship with Tibet from 1720 to 1912. The political status of Tibet during this period has been the subject of political debate. The Qing called Tibet a ''fanbang'' or ''fanshu'', which has ...
Explanatory notes
References
Citations
General and cited sources
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* .
*
* .
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
**
**
**
**
* .
*
*
*
* .
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
**
*
*
*
*
See profile at
Google Books
Google Books (previously known as Google Book Search, Google Print, and by its code-name Project Ocean) is a service from Google Inc. that searches the full text of books and magazines that Google has scanned, converted to text using optical ...
* .
*
*
*
*
* .
* .
* . In two volumes.
**
**
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
{{Qing dynasty topics
17th century in China
Eight Banners
History of Manchuria
History of Mongolia
Ming dynasty
Qing dynasty
Southern Ming
Wars involving the Ming dynasty
Wars involving the Qing dynasty
Wars of succession involving the states and peoples of Asia

 In the late
In the late  Hong Taiji was the eighth son of
Hong Taiji was the eighth son of  When
When  Soon after the emperor had called for help, Ming general Wu Sangui had left his stronghold of Ningyuan north of the
Soon after the emperor had called for help, Ming general Wu Sangui had left his stronghold of Ningyuan north of the  The easy transition between the Ming and Qing dynasties has been ascribed to the
The easy transition between the Ming and Qing dynasties has been ascribed to the  In addition to Han Chinese Banners, the Qing relied on the
In addition to Han Chinese Banners, the Qing relied on the  A few weeks after the
A few weeks after the  Resistance in the region was originally muted. As the heartland of the scholarly class, hundreds of
Resistance in the region was originally muted. As the heartland of the scholarly class, hundreds of  The Qing advance into
The Qing advance into  In 1656 a Lake Mao bandit named Qian Ying managed to acquire blank commissions from the
In 1656 a Lake Mao bandit named Qian Ying managed to acquire blank commissions from the 
 The Qing had relied on
The Qing had relied on 
 The defeat of the
The defeat of the