Durrës on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Durrës ( , ; sq-definite, Durrësi) is the second most populous city of the Republic of Albania and seat of Durrës County and Durrës Municipality. It is located on a flat plain along the Albanian Adriatic Sea Coast between the mouths of the
 Though surviving remains are minimal, Durrës is one of the oldest cities in Albania. In terms of mythology, the genealogy of the foundation of Dyrrhachium includes among the founders Illyrian men (the Illyrian king Epidamnos and his grandson Dyrrachos), Greek men (the Corinthian Falio, descendant of Heracles), heroes (
Though surviving remains are minimal, Durrës is one of the oldest cities in Albania. In terms of mythology, the genealogy of the foundation of Dyrrhachium includes among the founders Illyrian men (the Illyrian king Epidamnos and his grandson Dyrrachos), Greek men (the Corinthian Falio, descendant of Heracles), heroes ( After 323 BC Epidamnus-Dyrrhachium was involved in the intervention in Illyria of the Macedonians under Cassander, who clashed with the Illyrians under Glaukias. In 314 BC the Macedonian king seized the city but the garrison he established there was in turn besieged and driven out by the Illyrian king and the Corcyrans. In 312 BC, after another unsuccessful attack of Cassander in the region, the city came under the protection of Glaukias. Those events marked the end of
After 323 BC Epidamnus-Dyrrhachium was involved in the intervention in Illyria of the Macedonians under Cassander, who clashed with the Illyrians under Glaukias. In 314 BC the Macedonian king seized the city but the garrison he established there was in turn besieged and driven out by the Illyrian king and the Corcyrans. In 312 BC, after another unsuccessful attack of Cassander in the region, the city came under the protection of Glaukias. Those events marked the end of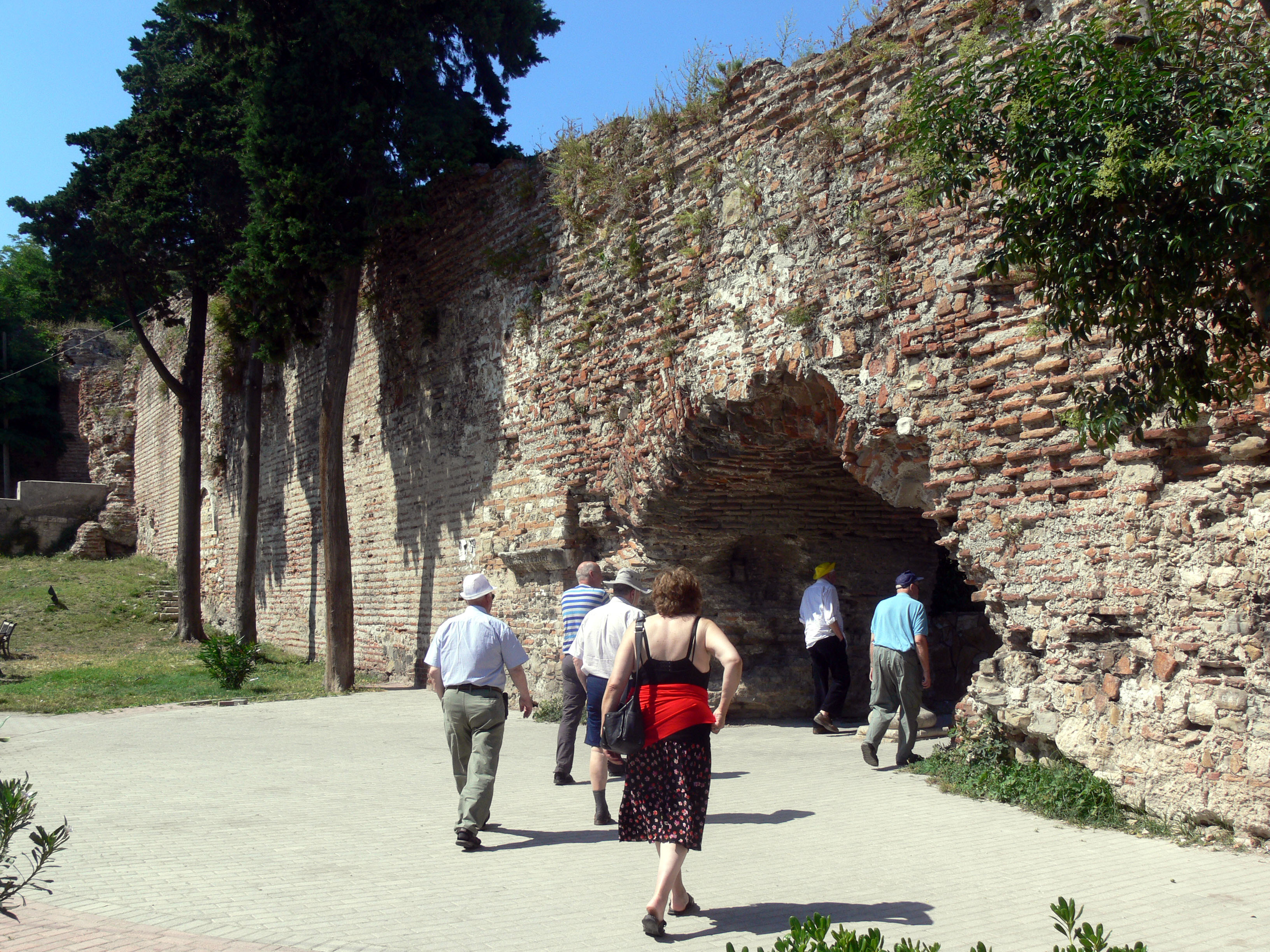  For
For  Like much of the rest of the
Like much of the rest of the
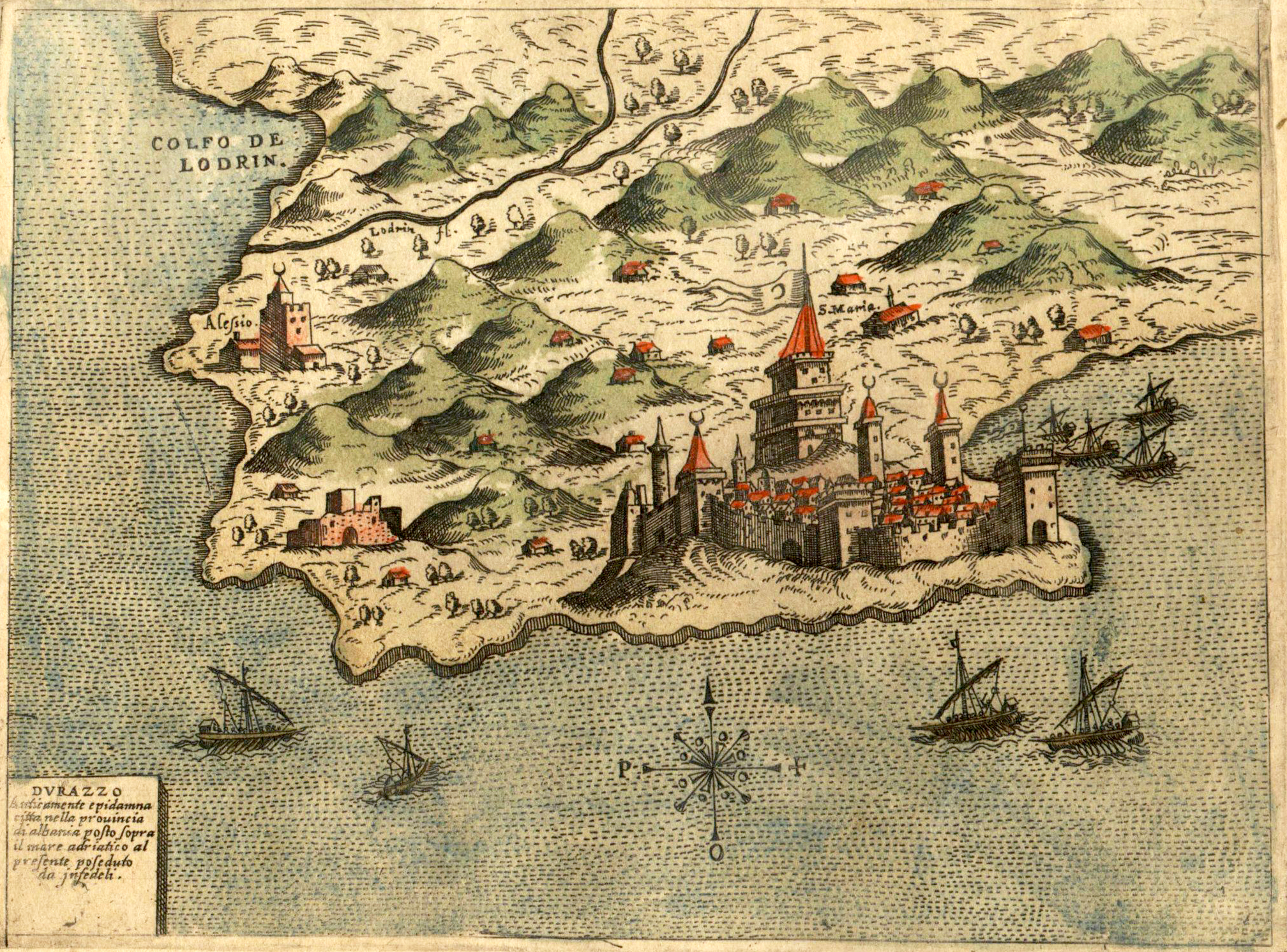 In the early 14th century, the city was ruled by a coalition of Anjous, Hungarians, and Albanians of the Thopia family. In 1317 or 1318, the area was taken by the Serbs and remained under their rule until the 1350s. At that time the Popes, supported by the Anjous, increased their diplomatic and political activity in the area, by using the Latin bishops, including the archbishop of Durrës. The city had been a religious center of Catholicism after the Anjou were installed in Durrës. In 1272, a Catholic archbishop was installed, and until the mid-14th century there were both Catholic and Orthodox archbishops of Durrës.
In the early 14th century, the city was ruled by a coalition of Anjous, Hungarians, and Albanians of the Thopia family. In 1317 or 1318, the area was taken by the Serbs and remained under their rule until the 1350s. At that time the Popes, supported by the Anjous, increased their diplomatic and political activity in the area, by using the Latin bishops, including the archbishop of Durrës. The city had been a religious center of Catholicism after the Anjou were installed in Durrës. In 1272, a Catholic archbishop was installed, and until the mid-14th century there were both Catholic and Orthodox archbishops of Durrës.
 Two Irish pilgrims who visited Albania on their way to Jerusalem in 1322, reported that Durrës was "inhabited by Latins, Greeks, perfidious Jews and barbaric Albanians".
When the Serbian Tsar
Two Irish pilgrims who visited Albania on their way to Jerusalem in 1322, reported that Durrës was "inhabited by Latins, Greeks, perfidious Jews and barbaric Albanians".
When the Serbian Tsar
, http://licodu.cois.it It remained Albania's capital until 11 February 1920, when the An earthquake in 1926 damaged some of the city and the rebuilding that followed gave the city its more modern appearance. During the 1930s, the
An earthquake in 1926 damaged some of the city and the rebuilding that followed gave the city its more modern appearance. During the 1930s, the  The
The
Erzen
The Erzen ( sq-definite, Erzeni) is a river in central Albania. The length of Erzen is , while the catchment area is including the southern Tirana District and eastern Durrës District.
Name
The ancient Illyrian name of the river was ''Ardaxa ...
and Ishëm at the southeastern corner of the Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to th ...
. Durrës' climate is profoundly influenced by a seasonal Mediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate (also called a dry summer temperate climate ''Cs'') is a temperate climate sub-type, generally characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, fairly wet winters; these weather conditions are typically experienced in the ...
.
Durrës was founded by Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic pe ...
colonists from Corinth
Corinth ( ; el, Κόρινθος, Kórinthos, ) is the successor to an ancient city, and is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it has been part ...
and Corcyra under the name of Epidamnos around the 7th century BC in cooperation with the local Illyrian Taulantii. Also known as Dyrrachium, Durrës essentially developed as it became an integral part of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
and its successor the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
. The Via Egnatia
The Via Egnatia was a road constructed by the Romans in the 2nd century BC. It crossed Illyricum, Macedonia, and Thracia, running through territory that is now part of modern Albania, North Macedonia, Greece, and European Turkey as a con ...
, the continuation of the Via Appia
The Appian Way (Latin and Italian: ''Via Appia'') is one of the earliest and strategically most important Roman roads of the ancient republic. It connected Rome to Brindisi, in southeast Italy. Its importance is indicated by its common name, ...
, started in the city and led across the interior of the Balkan Peninsula to Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
in the east.
In the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, Durrës was contested between Bulgarian, Venetian
Venetian often means from or related to:
* Venice, a city in Italy
* Veneto, a region of Italy
* Republic of Venice (697–1797), a historical nation in that area
Venetian and the like may also refer to:
* Venetian language, a Romance language s ...
and Ottoman dominions. The Ottomans ultimately prevailed, ruling the city for more than 400 years from 1501 until 1912. Following the Albanian Declaration of Independence
The Albanian Declaration of Independence ( Albanian: ''Deklarata e Pavarësisë'') was the declaration of independence of Albania from the Ottoman Empire. Independent Albania was proclaimed in Vlorë on 28 November 1912. Six days later the Ass ...
, the city served as the capital of the Principality of Albania for a short period of time. Subsequently, it was annexed by the Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy ( it, Regno d'Italia) was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946, when civil discontent led to ...
in the interwar period
In the history of the 20th century, the interwar period lasted from 11 November 1918 to 1 September 1939 (20 years, 9 months, 21 days), the end of the First World War to the beginning of the Second World War. The interwar period was relative ...
and was occupied by Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
during World War II. Durrës experienced a strong expansion in its demography and economic activity during the Communism in Albania.
The transport connections, concentration of economic institutions and industrial tradition underlie Durrës' leading economic position in Albania. It is served by the Port of Durrës
The Port of Durrës ( sq, Porti i Durrësit) is the largest seaport of Albania. The port is situated in the city of Durrës. It is an artificial basin that is formed between two moles, with a west-northwesterly oriented entrance approximately wid ...
, one of the largest on the Adriatic Sea, which connects the city to other neighbouring countries. Its most considerable attraction is the Amphitheatre of Durrës
The Amphitheatre of Durrës ( sq, Amfiteatri i Durrësit; la, Amphitheatrum Dyrrhachinum) is a Roman amphitheatre in the centre of the city of Durrës, Albania. Construction began under the emperor Trajan in the 2nd century AD and it was destroye ...
that is included on the Albanian tentative list for designation as a UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international coope ...
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
. Once having a capacity for 20,000 people, it is the largest amphitheatre in the Balkan Peninsula
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
.
Name
In antiquity, the city was known as () and () inclassical Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic pe ...
and then and in classical Latin
Classical Latin is the form of Literary Latin recognized as a literary standard by writers of the late Roman Republic and early Roman Empire. It was used from 75 BC to the 3rd century AD, when it developed into Late Latin. In some later period ...
. ''Epidamnos'' is the older known of the two Greek toponyms; it is widely considered to be of Illyrian origin, as first proposed by linguist Hans Krahe, and is attested in Thucydides
Thucydides (; grc, , }; BC) was an Athenian historian and general. His '' History of the Peloponnesian War'' recounts the fifth-century BC war between Sparta and Athens until the year 411 BC. Thucydides has been dubbed the father of " scienti ...
(5th century BC), Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of ...
(4th century BC), and Polybius
Polybius (; grc-gre, Πολύβιος, ; ) was a Greek historian of the Hellenistic period. He is noted for his work , which covered the period of 264–146 BC and the Punic Wars in detail.
Polybius is important for his analysis of the mixed ...
(2nd century BC). Etymologically, ''Epidamnos'' may be related to Proto-Albanian *dami (cub, young animal, young bull) > dem (modern Albanian) as proposed by linguist Eqrem Çabej
Eqrem Çabej () (6 August 1908 – 13 August 1980) was an Albanian historical linguist and scholar who, through the publication of numerous studies gained a reputation as a key expert in research on Albanian language, literature, ethnology and ...
. Although the name ''Epidamnos/Epidamnus'' was more commonly used among Ancient Greek authors, the coinage of the city only used the abbreviations for the name ''Dyrrhachion/Dyrrhachium''. ''Dyrrachium'' was chosen as the sole name of the city after the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
got control of the region after the Illyrian Wars
The Illyro-Roman Wars were a series of wars fought between the Roman Republic and the Ardiaei kingdom. In the ''First Illyrian War'', which lasted from 229 BC to 228 BC, Rome's concern was that the trade across the Adriatic Sea increased after the ...
in 229 BC. The Latin spelling of /y/ retained the form of Doric Greek
Doric or Dorian ( grc, Δωρισμός, Dōrismós), also known as West Greek, was a group of Ancient Greek dialects; its varieties are divided into the Doric proper and Northwest Doric subgroups. Doric was spoken in a vast area, that includ ...
Dyrrhachion, which was pronounced as /Durrakhion/. This change of the name is already attested in classical literature. Titus Livius, at the end of the first century BC, writes in Ab Urbe Condita Libri that at the time of the Illyrian Wars (roughly 200 years earlier) the city was not known as Dyrrachium, but as Epidamnus. Pomponius Mela, about 70 years later than Titus Livius, attributed the change of the name to the fact that the name Epidamnos reminded the Romans of the Latin word , which signified evil and bad luck; Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ' ...
, who lived in the same period, repeated this explanation in his own works. However, the Romans may have adopted the new name because it was already in more frequent use by citizens of the city.
The name ''Dyrrhachion'' is usually explained as a Greek compound from 'bad' and 'rocky shore, flood, roaring waves', an explanation already hinted at in antiquity by Cassius Dio, who writes it referred to the difficulties of the rocky coastline, while also reporting that other Roman authors linked it to the name of an eponymous
An eponym is a person, a place, or a thing after whom or which someone or something is, or is believed to be, named. The adjectives which are derived from the word eponym include ''eponymous'' and ''eponymic''.
Usage of the word
The term ''epon ...
hero ''Dyrrachius''. The mythological construction of the city's name was recorded by Appian
Appian of Alexandria (; grc-gre, Ἀππιανὸς Ἀλεξανδρεύς ''Appianòs Alexandreús''; la, Appianus Alexandrinus; ) was a Greek historian with Roman citizenship who flourished during the reigns of Emperors of Rome Trajan, Ha ...
(2nd century AD) who wrote that "the king of the barbarians of this country, Epidamnus gave the name to the city. His daughter's son Dyrrachius, built a port near the town that he called Dyrrachium". Stephanus of Byzantium
Stephanus or Stephan of Byzantium ( la, Stephanus Byzantinus; grc-gre, Στέφανος Βυζάντιος, ''Stéphanos Byzántios''; centuryAD), was a Byzantine grammarian and the author of an important geographical dictionary entitled ''Ethn ...
repeated this mythological construction in his work. It is unclear whether the two toponyms referred originally to different areas of the territory of the city or whether they referred to the same territory. Classical literature indicates that they more probably referred to different neighbouring areas originally. Gradually, the name Epidamnus fell out of use and Dyrrachium became the sole name for the city.
Archaeological research has shown that at the time of the foundation of Durrës, two distinct settlements existed on its territory. The first one is a hill site with no direct contact with the sea. It predates the colony and might represent the settlement which held the toponym known as ''Epidamnos'' in ancient literature. The hill site overlooks to its south the second site which is the territory of the port of Durrës, where the colony was founded. Its location on a rocky shore struck by waves on all sides reflects the description of the toponym Dyrrhachion. The distinction between these two districts of the city remained in place even much later. In the 19th century, ''Durrës proper'' was the district of the port, while the hill north of it was a separate settlement, Stani (Kodra e Stanit).
The modern names of the city in Albanian () and Italian (, ) are derived from ''Dyrrachium''/''Dyrrachion''. An intermediate, palatalized antecedent is found in the form ''Dyrratio'', attested in the early centuries AD. The palatalized /-tio/ ending probably represents a phonetic change in the way the inhabitants of the city pronounced its name. The preservation of old Doric /u/ indicates that the modern name derives from populations to whom the toponym was known in its original Doric pronunciation. By contrast, in Byzantine Greek, the name of the city is pronounced with the much later evolution of /u/ as /i/. The modern Italian name evolved in the sub-dialects that emerged from Colloquial Latin in northern Italy. The modern Albanian name evolved independently from the parent language of Albanian around the same period of the post-Roman era in the first centuries AD as the difference in stress in the two toponyms (first syllable in Albanian, second in Italian) highlights. In Aromanian, the city is known as .
In English usage, the Italian form ''Durazzo'' used to be widespread, but the local Albanian name ''Durrës'' has gradually replaced it in recent decades.
History
Earliest period
The territory of Durrës was populated at least starting from the Eneolithic and then, fromprotohistoric
Protohistory is a period between prehistory and history during which a culture or civilization has not yet developed writing, but other cultures have already noted the existence of those pre-literate groups in their own writings. For example, ...
times, it was inhabited by Illyrian peoples.
Antiquity
 Though surviving remains are minimal, Durrës is one of the oldest cities in Albania. In terms of mythology, the genealogy of the foundation of Dyrrhachium includes among the founders Illyrian men (the Illyrian king Epidamnos and his grandson Dyrrachos), Greek men (the Corinthian Falio, descendant of Heracles), heroes (
Though surviving remains are minimal, Durrës is one of the oldest cities in Albania. In terms of mythology, the genealogy of the foundation of Dyrrhachium includes among the founders Illyrian men (the Illyrian king Epidamnos and his grandson Dyrrachos), Greek men (the Corinthian Falio, descendant of Heracles), heroes (Heracles
Heracles ( ; grc-gre, Ἡρακλῆς, , glory/fame of Hera), born Alcaeus (, ''Alkaios'') or Alcides (, ''Alkeidēs''), was a divine hero in Greek mythology, the son of Zeus and Alcmene, and the foster son of Amphitryon.By his adoptiv ...
who was given part of the lands) and gods (Poseidon
Poseidon (; grc-gre, Ποσειδῶν) was one of the Twelve Olympians in ancient Greek religion and myth, god of the sea, storms, earthquakes and horses.Burkert 1985pp. 136–139 In pre-Olympian Bronze Age Greece, he was venerated as ...
, as father of Dyrrachos).
Several ancient people held the site: the presence of the Brygi appears to be confirmed by several ancient writers, the Illyrian Taulantii (their arrival has been estimated to have happened not later than the 10th century BC), probably the Liburni who expanded southwards in the 9th century BC. The city was founded by Greek colonists in 627 BC on the coast of the Taulantii. According to ancient authors, the Greek colonists helped the Taulantii to expel Liburnians and mixed with the local population establishing the Greek element to the port. A flourishing commercial centre emerged and the city grew rapidly. The fact that about the 6th century BC the citizens of Epidamnus constructed a Doric-style treasury at Olympia confirms that the city was among the richest of the Ancient Greek world
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cult ...
. An ancient account describes Epidamnos as 'a great power and very populated' city.
 After 323 BC Epidamnus-Dyrrhachium was involved in the intervention in Illyria of the Macedonians under Cassander, who clashed with the Illyrians under Glaukias. In 314 BC the Macedonian king seized the city but the garrison he established there was in turn besieged and driven out by the Illyrian king and the Corcyrans. In 312 BC, after another unsuccessful attack of Cassander in the region, the city came under the protection of Glaukias. Those events marked the end of
After 323 BC Epidamnus-Dyrrhachium was involved in the intervention in Illyria of the Macedonians under Cassander, who clashed with the Illyrians under Glaukias. In 314 BC the Macedonian king seized the city but the garrison he established there was in turn besieged and driven out by the Illyrian king and the Corcyrans. In 312 BC, after another unsuccessful attack of Cassander in the region, the city came under the protection of Glaukias. Those events marked the end of Macedon
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled ...
ian presence on the Adriatic coast for almost one century. The city probably came under the control of Pyrrhus of Epirus
Pyrrhus (; grc-gre, Πύρρος ; 319/318–272 BC) was a Greek king and statesman of the Hellenistic period.Plutarch. '' Parallel Lives'',Pyrrhus... He was king of the Greek tribe of Molossians, of the royal Aeacid house, and later he be ...
at the beginning of the 3rd century BC. From about 280 BC the Illyrian king Monunius, and his successor Mytilos minted in Dyrrhachion silver and bronze coins respectively, bearing the king's name and the symbol of the city. The fact that their coins were struck in the city mint of Dyrrhachion stresses that they exercised to some extent their authority over the city.
Epidamnus came under the control of the Illyrian Ardiaei
The Ardiaei were an Illyrian people who resided in the territory of present-day Albania, Serbia, Montenegro, Bosnia and Herzegovina and Croatia between the Adriatic coast on the south, Konjic on the north, along the Neretva river and its righ ...
under Agron, who fortified the city (c. 250–231 BC). When the Romans defeated the Illyrians, they replaced the rule of queen Teuta
Teuta ( Illyrian: *''Teutana'', 'mistress of the people, queen'; grc, Τεύτα; lat, Teuta) was the queen regent of the Ardiaei tribe in Illyria, who reigned approximately from 231 BC to 228/227 BC.
Following the death of her spouse Agr ...
with that of Demetrius of Pharos, one of her generals. He lost his kingdom, including Epidamnus, to the Romans in 219 BC at the Second Illyrian War. In the Third Illyrian War Epidamnus was attacked by Gentius
Gentius ( grc, Γένθιος, "Génthios"; 181168 BC) was an Illyrian king who belonged to the Labeatan dynasty. He ruled in 181–168 BC, being the last attested Illyrian king. He was the son of Pleuratus III, a king who kept positive relati ...
but he was defeated by the Romans at the same year.
 For
For Catullus
Gaius Valerius Catullus (; 84 - 54 BCE), often referred to simply as Catullus (, ), was a Latin poet of the late Roman Republic who wrote chiefly in the neoteric style of poetry, focusing on personal life rather than classical heroes. His ...
, the city was ''Durrachium Hadriae tabernam'', "the '' taberna'' of the Adriatic", one of the stopping places for a Roman traveling up the Adriatic
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to the ...
, as Catullus had done himself in the sailing season of 56.
After the Illyrian Wars
The Illyro-Roman Wars were a series of wars fought between the Roman Republic and the Ardiaei kingdom. In the ''First Illyrian War'', which lasted from 229 BC to 228 BC, Rome's concern was that the trade across the Adriatic Sea increased after the ...
with the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
in 229 BC ended in a decisive defeat for the Illyrians, the city passed to Roman rule, under which it was developed as a major military and naval base. The Romans preferred to use the name ''Dyrrachium'' (Greek: Δυρράχιον / ''Dyrrhachion'') for the city. They considered the name ''Epidamnos'' to be inauspicious because of its wholly coincidental similarities with the Latin word ''damnum'', meaning "loss" or "harm". The meaning of ''Dyrrachium'' ("bad spine" or "difficult ridge" in Greek) is unclear, but it has been suggested that it refers to the imposing cliffs near the city. During the Great Roman Civil War in Illyria, the Battle of Dyrrachium was undertaken by Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, an ...
against Gnaeus Pompey. The battle was a victory for Pompey, but it preceded the more decisive Battle of Pharsalus
The Battle of Pharsalus was the decisive battle of Caesar's Civil War fought on 9 August 48 BC near Pharsalus in central Greece. Julius Caesar and his allies formed up opposite the army of the Roman Republic under the command of Pompey ...
in Greece where Caesar won. Under Roman rule, Dyrrachium prospered; it became the western end of the ''Via Egnatia
The Via Egnatia was a road constructed by the Romans in the 2nd century BC. It crossed Illyricum, Macedonia, and Thracia, running through territory that is now part of modern Albania, North Macedonia, Greece, and European Turkey as a con ...
'', the great Roman road
Roman roads ( la, viae Romanae ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, and were built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Re ...
that led to Thessalonica
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area, and the capital of the geographic region of ...
and on to Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
. Another lesser road led south to the city of ''Buthrotum'', the modern Butrint. The Roman emperor Caesar Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
made the city a colony for veterans of his legions following the Battle of Actium
The Battle of Actium was a naval battle fought between a maritime fleet of Octavian led by Marcus Agrippa and the combined fleets of both Mark Antony and Cleopatra VII Philopator. The battle took place on 2 September 31 BC in the Ionian Sea, ...
, proclaiming it a ''civitas libera A free city ( la, civitas libera, urbs liberae condicionis; el, ) was a self-governed city during the Hellenistic and Roman Imperial eras. The status was given by the king or emperor, who nevertheless supervised the city's affairs through his '' e ...
'' (free town).
In the 4th century, Dyrrachium was made the capital of the Roman province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
of Epirus nova
sq, Epiri rup, Epiru
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = Historical region
, image_map = Epirus antiquus tabula.jpg
, map_alt =
, map_caption = Map of ancient Epirus by Heinric ...
. It was the birthplace of the emperor Anastasius I in c. 430. Sometime later that century, Dyrrachium was struck by a powerful earthquake which destroyed the city's defences. Anastasius I rebuilt and strengthened the city walls, thus creating the strongest fortifications in the western Balkans. The walls were so thick that, according to the Byzantine historian Anna Komnene
Anna Komnene ( gr, Ἄννα Κομνηνή, Ánna Komnēnḗ; 1 December 1083 – 1153), commonly Latinized as Anna Comnena, was a Byzantine princess and author of the ''Alexiad'', an account of the reign of her father, the Byzantine emperor, ...
, four horsemen could ride abreast on them. Significant portions of the ancient city defences still remain, although they have been much reduced over the centuries.
 Like much of the rest of the
Like much of the rest of the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
, Dyrrachium and the surrounding ''Dyrraciensis provinciae'' suffered considerably from barbarian
A barbarian (or savage) is someone who is perceived to be either uncivilized or primitive. The designation is usually applied as a generalization based on a popular stereotype; barbarians can be members of any nation judged by some to be less ...
incursions during the Migrations Period
The Migration Period was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories by various tribes, and the establishment of the post-Roman ...
. It was besieged in 481 by Theodoric the Great
Theodoric (or Theoderic) the Great (454 – 30 August 526), also called Theodoric the Amal ( got, , *Þiudareiks; Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ), was king of the Ostrogoths (471–526), and ruler of the independent Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy ...
, king of the Ostrogoth
The Ostrogoths ( la, Ostrogothi, Austrogothi) were a Roman-era Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Gothic kingdoms within the Roman Empire, based upon the large Gothic populations who ...
s, and in subsequent centuries had to fend off frequent attacks by the Bulgarians
Bulgarians ( bg, българи, Bǎlgari, ) are a nation and South Slavic ethnic group native to Bulgaria and the rest of Southeast Europe.
Etymology
Bulgarians derive their ethnonym from the Bulgars. Their name is not completely underst ...
. Unaffected by the fall of the Western Roman Empire
The fall of the Western Roman Empire (also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Rome) was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rule, and its va ...
, the city continued under the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
as an important port and a major link between the Empire and western Europe. During the sixth century based on accounts of Procopius
Procopius of Caesarea ( grc-gre, Προκόπιος ὁ Καισαρεύς ''Prokópios ho Kaisareús''; la, Procopius Caesariensis; – after 565) was a prominent late antique Greek scholar from Caesarea Maritima. Accompanying the Roman gen ...
, the city was mainly inhabited by a Greek population.
Middle Ages
The city and the surrounding coast became a Byzantine province, the Theme of Dyrrhachium, probably in the first decade of the 9th century. Durrës became aChristian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι� ...
city quite early on; its bishopric
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associate ...
was created around 58 and was raised to the status of an archbishopric
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associat ...
in 449. It was also the seat of an Orthodox metropolitan bishop
In Christian churches with episcopal polity, the rank of metropolitan bishop, or simply metropolitan (alternative obsolete form: metropolite), pertains to the diocesan bishop or archbishop of a metropolis.
Originally, the term referred to the ...
. The city remained in Byzantine hands until the late 10th century, when Samuel of Bulgaria
Samuel (also Samuil; bg, Самуил, ; mk, Самоил/Самуил, ; Old Church Slavonic: Самоилъ; died October 6, 1014) was the Tsar (''Emperor'') of the First Bulgarian Empire from 997 to 6 October 1014. From 977 to 997, he was a ...
gained control of the city, possibly through his marriage with Agatha, daughter of the local magnate John Chryselios John Chryselios ( el, ) was a provincial magnate in late 10th-century Dyrrhachium, and the father-in-law of Tsar Samuel of Bulgaria ().
Biography
Bulgarian in origin, Chryselios was the "leading man" (''proteuon'') of Dyrrhachium. According to a ...
. Samuel made his son-in-law Ashot Taronites, a Byzantine captive who had married his daughter Miroslava, governor of the city. In circa 1005, however, Ashot and Miroslava, with the connivance of Chryselios, fled to Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
, where they notified Emperor Basil II
Basil II Porphyrogenitus ( gr, Βασίλειος Πορφυρογέννητος ;) and, most often, the Purple-born ( gr, ὁ πορφυρογέννητος, translit=ho porphyrogennetos).. 958 – 15 December 1025), nicknamed the Bulgar S ...
of their intention to surrender the city to him. Soon, a Byzantine squadron appeared off the city under Eustathios Daphnomeles, and the city returned to Byzantine rule.
In the 11th–12th centuries, the city was important as a military stronghold and a metropolitan see
Metropolitan may refer to:
* Metropolitan area, a region consisting of a densely populated urban core and its less-populated surrounding territories
* Metropolitan borough, a form of local government district in England
* Metropolitan county, a t ...
rather than as a major economic center, and never recovered its late antique prosperity; Anna Komnene
Anna Komnene ( gr, Ἄννα Κομνηνή, Ánna Komnēnḗ; 1 December 1083 – 1153), commonly Latinized as Anna Comnena, was a Byzantine princess and author of the ''Alexiad'', an account of the reign of her father, the Byzantine emperor, ...
makes clear that medieval Dyrrhachium occupied only a portion of the ancient city. In the 1070s, two of its governors, Nikephoros Bryennios the Elder
Nikephoros Bryennios the Elder ( el, Νικηφόρος Βρυέννιος ο πρεσβύτερος), Latinized as Nicephorus Bryennius, was a Byzantine Greek general who tried to establish himself as Emperor in the late eleventh century. His c ...
and Nikephoros Basilakes, led unsuccessful rebellions trying to seize the Byzantine throne. Dyrrachium was lost in February 1082 when Alexios I Komnenos
Alexios I Komnenos ( grc-gre, Ἀλέξιος Κομνηνός, 1057 – 15 August 1118; Latinized Alexius I Comnenus) was Byzantine emperor from 1081 to 1118. Although he was not the first emperor of the Komnenian dynasty, it was during ...
was defeated by the Normans
The Normans ( Norman: ''Normaunds''; french: Normands; la, Nortmanni/Normanni) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norse Viking settlers and indigenous West Franks and Gallo-Romans. ...
under Robert Guiscard
Robert Guiscard (; Modern ; – 17 July 1085) was a Norman adventurer remembered for the conquest of southern Italy and Sicily. Robert was born into the Hauteville family in Normandy, went on to become count and then duke of Apulia and Calab ...
and his son Bohemund in the Battle of Dyrrhachium. Byzantine control was restored a few years later, but the Normans under Bohemund returned to besiege it in 1107–08, and sacked it again in 1185 under King William II of Sicily
William II (December 115311 November 1189), called the Good, was king of Sicily from 1166 to 1189. From surviving sources William's character is indistinct. Lacking in military enterprise, secluded and pleasure-loving, he seldom emerged from his ...
.
In 1205, after the Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid S ...
, the city was transferred to the rule of the Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia ...
, which formed the " Duchy of Durazzo". This Duchy was conquered in 1213 and the city taken by the Despotate of Epirus
The Despotate of Epirus ( gkm, Δεσποτᾶτον τῆς Ἠπείρου) was one of the Greek successor states of the Byzantine Empire established in the aftermath of the Fourth Crusade in 1204 by a branch of the Angelos dynasty. It clai ...
under Michael I Komnenos Doukas
Michael I Komnenos Doukas, Latinized as Comnenus Ducas ( el, Μιχαήλ Κομνηνός Δούκας, Mikhaēl Komnēnos Doukas), and in modern sources often recorded as Michael I Angelos, a name he never used, was the founder and first rule ...
. In 1257, Durrës was briefly occupied by the King of Sicily, Manfred of Hohenstaufen
Manfred ( scn, Manfredi di Sicilia; 123226 February 1266) was the last King of Sicily from the Hohenstaufen dynasty, reigning from 1258 until his death. The natural son of the Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II, Manfred became regent over the ...
. It was re-occupied by the Despot of Epirus Michael II Komnenos Doukas
Michael II Komnenos Doukas, Latinized as Comnenus Ducas ( el, Μιχαήλ Β΄ Κομνηνός Δούκας, ''Mikhaēl II Komnēnos Doukas''), often called Michael Angelos in narrative sources, was from 1230 until his death in 1266/68 the rule ...
until 1259, when the Despotate was defeated by the Byzantine Empire of Nicaea
The Empire of Nicaea or the Nicene Empire is the conventional historiographic name for the largest of the three Byzantine Greek''A Short history of Greece from early times to 1964'' by W. A. Heurtley, H. C. Darby, C. W. Crawley, C. M. Woodhous ...
in the Battle of Pelagonia
The Battle of Pelagonia or Battle of Kastoriae.g. ; . took place in early summer or autumn 1259, between the Empire of Nicaea and an anti-Nicaean alliance comprising Despotate of Epirus, Sicily and the Principality of Achaea. It was a decisive ev ...
. In the 1270s, Durrës was again controlled by Epirus under Nikephoros I Komnenos Doukas, the son of Michael II, who in 1278 was forced to yield the city to Charles d' Anjou (Charles I of Sicily
Charles I (early 1226/12277 January 1285), commonly called Charles of Anjou, was a member of the royal Capetian dynasty and the founder of the second House of Anjou. He was Count of Provence (1246–85) and Forcalquier (1246–48, 1256–85) i ...
). In c. 1273, it was wrecked by a devastating earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, fr ...
(according to George Pachymeres
George Pachymeres ( el, Γεώργιος Παχυμέρης, Geórgios Pachyméris; 1242 – 1310) was a Byzantine Greek historian, philosopher, music theorist and miscellaneous writer.
Biography
Pachymeres was born at Nicaea, in Bithynia, wher ...
) but soon recovered. It was briefly occupied by King Milutin Milutin ( sr, Милутин) is a Serbian masculine given name of Slavic origin. The name may refer to:
*Stephen Uroš II Milutin of Serbia
Stefan Uroš II Milutin ( sr-cyr, Стефан Урош II Милутин, Stefan Uroš II Milutin; 125 ...
of Serbia in 1296. In the thirteenth century, a Jewish community
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
existed in Durrës and was employed in the salt trade
A salt road (also known as a salt route, salt way, saltway, or salt trading route) refers to any of the prehistoric and historical trade routes by which essential salt was transported to regions that lacked it.
From the Bronze Age (in the 2nd m ...
.
 In the early 14th century, the city was ruled by a coalition of Anjous, Hungarians, and Albanians of the Thopia family. In 1317 or 1318, the area was taken by the Serbs and remained under their rule until the 1350s. At that time the Popes, supported by the Anjous, increased their diplomatic and political activity in the area, by using the Latin bishops, including the archbishop of Durrës. The city had been a religious center of Catholicism after the Anjou were installed in Durrës. In 1272, a Catholic archbishop was installed, and until the mid-14th century there were both Catholic and Orthodox archbishops of Durrës.
In the early 14th century, the city was ruled by a coalition of Anjous, Hungarians, and Albanians of the Thopia family. In 1317 or 1318, the area was taken by the Serbs and remained under their rule until the 1350s. At that time the Popes, supported by the Anjous, increased their diplomatic and political activity in the area, by using the Latin bishops, including the archbishop of Durrës. The city had been a religious center of Catholicism after the Anjou were installed in Durrës. In 1272, a Catholic archbishop was installed, and until the mid-14th century there were both Catholic and Orthodox archbishops of Durrës.
 Two Irish pilgrims who visited Albania on their way to Jerusalem in 1322, reported that Durrës was "inhabited by Latins, Greeks, perfidious Jews and barbaric Albanians".
When the Serbian Tsar
Two Irish pilgrims who visited Albania on their way to Jerusalem in 1322, reported that Durrës was "inhabited by Latins, Greeks, perfidious Jews and barbaric Albanians".
When the Serbian Tsar Dušan
Dušan ( sr-Cyrl, Душан) is a Slavic given name primarily used in countries of Yugoslavia; and among Slovaks and Czechs. The name is derived from the Slavic noun ''duša'' "soul".
Occurrence
In Serbia, it was the 29th most popular nam ...
died in 1355, the city passed into the hands of the Albanian family of Thopias. In 1376 the Navarrese Company Louis of Évreux, Duke of Durazzo
Louis of Évreux (also called "of Navarre"; 1341 – 1376) was the youngest son of Philip III of Navarre and Joan II of Navarre. He inherited the county of Beaumont-le-Roger from his father (1343) and became Duke of Durazzo in right of his sec ...
, who had gained the rights on the Kingdom of Albania from his second wife, attacked and conquered the city, but in 1383 Karl Topia regained control of the city. The Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia ...
regained control in 1392 and retained the city, known as ''Durazzo'' in those years, as part of the ''Albania Veneta
Venetian Albania ( vec, Albania vèneta, it, Albania Veneta, Serbian and Montenegrin: Млетачка Албанија / ''Mletačka Albanija'', ) was the official term for several possessions of the Republic of Venice in the southeastern Adri ...
''. It fended off a siege by the Ottoman Sultan Mehmed II
Mehmed II ( ota, محمد ثانى, translit=Meḥmed-i s̱ānī; tr, II. Mehmed, ; 30 March 14323 May 1481), commonly known as Mehmed the Conqueror ( ota, ابو الفتح, Ebū'l-fetḥ, lit=the Father of Conquest, links=no; tr, Fâtih Su ...
in 1466 but fell to Ottoman forces in 1501.
Under Ottoman rule, many of its inhabitants converted to Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
and many mosque
A mosque (; from ar, مَسْجِد, masjid, ; literally "place of ritual prostration"), also called masjid, is a place of prayer for Muslims. Mosques are usually covered buildings, but can be any place where prayers ( sujud) are performed, ...
s were erected. The city was renamed Dıraç but did not prosper under the Ottomans and its importance declined greatly. Following the establishment of Ottoman rule in 1501, the Durrës Jewish community experienced population growth.
By the mid-19th century, its population was said to have been only about 1,000 people living in some 200 households. In the late nineteenth century, Durrës contained 1,200 Orthodox Aromanians
The Aromanians ( rup, Armãnji, Rrãmãnji) are an ethnic group native to the southern Balkans who speak Aromanian, an Eastern Romance language. They traditionally live in central and southern Albania, south-western Bulgaria, northern and ...
(130 families) who lived among the larger population of Muslim Albanians alongside a significant number of Catholic Albanians. "Durrës... At the end of the nineteenth century, there were more than 130 Vlach families, some 1,200 Vlachs, who constituted the nucleus of the local Greek Orthodox community, amid the much more numerous Moslem Albanians and quite a number of Roman Catholics, also of Albanian stock." The decrepitude of Durrës was noted by foreign observers in the early 20th century: "The walls are dilapidated; plane-trees grow on the gigantic ruins of its old Byzantine citadel; and its harbour, once equally commodious and safe, is gradually becoming silted up." Durrës was a main centre in İşkodra Vilayet before 1912.
Modern
Durrës was an active city in the Albanian national liberation movement in the periods 1878–1881 and 1910–1912.Ismail Qemali
Ismail Qemal bey Vlora, mostly known as Ismail Qemali (; 16 January 184426 January 1919), was an Albanian diplomat, politician, rilindas, statesman and the Founding Father of modern Albania, and one of the most famous Southern Albanian perso ...
raised the Albanian flag
The flag of Albania ( sq, Flamuri i Republikës së Shqipërisë) is a red flag with a silhouetted black double-headed eagle in the center. The red stands for bravery, strength, valour and bloodshed, while the Eagle represents the sovereign state ...
on 26 November 1912 but the city was occupied by the Kingdom of Serbia
The Kingdom of Serbia ( sr-cyr, Краљевина Србија, Kraljevina Srbija) was a country located in the Balkans which was created when the ruler of the Principality of Serbia, Milan I, was proclaimed king in 1882. Since 1817, the Prin ...
three days later during the First Balkan War
The First Balkan War ( sr, Први балкански рат, ''Prvi balkanski rat''; bg, Балканска война; el, Αʹ Βαλκανικός πόλεμος; tr, Birinci Balkan Savaşı) lasted from October 1912 to May 1913 and invo ...
. On 29 November 1912 Durrës became the county town of the Durrës County
Durrës County ( sq, Qarku i Durrësit), officially the County of Durrës ( sq, Qarku i Durrësit, italic=unset), is a county in the Northern Region of the Republic of Albania. It is the smallest by area and the second most populous of the twe ...
( sr, Драчки округ) one of the counties of the Kingdom of Serbia
The Kingdom of Serbia ( sr-cyr, Краљевина Србија, Kraljevina Srbija) was a country located in the Balkans which was created when the ruler of the Principality of Serbia, Milan I, was proclaimed king in 1882. Since 1817, the Prin ...
established on the part of the territory of Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and share ...
occupied from Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
. The Durrës County had four districts ( sr, срез): Durrës, Lezha, Elbasan
Elbasan ( ; sq-definite, Elbasani ) is the fourth most populous city of Albania and seat of Elbasan County and Elbasan Municipality. It lies to the north of the river Shkumbin between the Skanderbeg Mountains and the Myzeqe Plain in central ...
and Tirana
Tirana ( , ; aln, Tirona) is the capital and largest city of Albania. It is located in the centre of the country, enclosed by mountains and hills with Dajti rising to the east and a slight valley to the northwest overlooking the Adriatic Sea ...
. The army of the Kingdom of Serbia retreated from Durrës in April 1913. The city became Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and share ...
's second national capital (after Vlora) on 7 March 1914 under the brief rule of Prince William of Wied
Prince Wilhelm of Wied ( German: ''Wilhelm Friedrich Heinrich Prinz zu Wied'', 26 March 1876 – 18 April 1945), reigned briefly as sovereign of the Principality of Albania as Vilhelm I from 7 March to 3 September 1914, when he left for exile. H ...
.Organic Statute of the Principality of Albania (in Albanian), http://licodu.cois.it It remained Albania's capital until 11 February 1920, when the
Congress of Lushnjë
The Congress of Lushnjë (), historically documented by the name ''Mbledhja Kombiare Lushnje'', was a conference of Albanian political leaders held from January 28 to January 31, 1920 in Lushnjë, Albania.
Its objective was to deal with the issue ...
made Tirana
Tirana ( , ; aln, Tirona) is the capital and largest city of Albania. It is located in the centre of the country, enclosed by mountains and hills with Dajti rising to the east and a slight valley to the northwest overlooking the Adriatic Sea ...
the new capital.
During the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, the city was occupied by Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
in 1915 and by Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
in 1916–1918. On 29 December 1915, a Naval Battle was fought off Durazzo. On 2 October 1918, several allied ships bombarded Durazzo and attacked the few Austrian ships in the harbour. Although civilians started to flee the city at the start of the bombardment, many casualties were inflicted on the innocent and neutral population. The Old City being adjacent to the harbour was largely destroyed, including the Royal Palace of Durrës and other primary public buildings. It was captured by Italian troops on 16 October 1918. Restored to Albanian sovereignty, Durrës became the country's temporary capital between 1918 and March 1920. It experienced an economic boom due to Italian investments and developed into a major seaport under the rule of King Zog, with a modern harbour being constructed in 1927. It was at this time the Royal Villa of Durrës was built by Zog as a summer palace, that still dominates the skyline from a hill close to the old city.
 An earthquake in 1926 damaged some of the city and the rebuilding that followed gave the city its more modern appearance. During the 1930s, the
An earthquake in 1926 damaged some of the city and the rebuilding that followed gave the city its more modern appearance. During the 1930s, the Bank of Athens
Over time, two Greek banks have been named the Bank of Athens. Both had their headquarters in Athens, Greece. The first Bank of Athens was founded in 1893 and operated in the Balkans and Eastern Mediterranean until its acquisition by the Nationa ...
had a branch in the city.
Durrës (called ''Durazzo'' again in Italian) and the rest of Albania were occupied in April 1939 and annexed to the Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy ( it, Regno d'Italia) was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946, when civil discontent led to ...
until 1943, then occupied by Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
until autumn 1944. Durrës's strategic value as a seaport made it a high-profile military target for both sides. It was the site of the initial Italian landings on 7 April 1939 (and was fiercely defended by Mujo Ulqinaku
Mujo Ulqinaku (born Mujo Cakuli; 1896 – 7 April 1939) was an Albanian sergeant of the Royal Albanian Navy, known for his resistance on 7 April 1939 to the Italian forces during the Italian invasion of Albania. He was given the People's Hero ...
) as well as the launch point for the ill-fated Italian invasion of Greece
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
. The city was heavily damaged by Allied bombing during the war and the port installations were blown up by retreating German soldiers in autumn 1944.
 The
The Communist
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society, ...
regime of Enver Hoxha
Enver Halil Hoxha ( , ; 16 October 190811 April 1985) was an Albanians, Albanian communist politician who was the authoritarian ruler of Albania from 1944 until his death in 1985. He was Secretary (title)#First secretary, First Secretary of t ...
rapidly rebuilt the city following the war, establishing a variety of heavy industries in the area and expanding the port. It became the terminus of Albania's first railway
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a p ...
, begun in 1947 ( Durrës–Tiranë railway). In the late 1980s, the city was briefly renamed Durrës-Enver Hoxha. The city was and continues to remain the center of Albanian mass beach tourism.
Following the collapse of communist rule in 1990, Durrës became the focus of mass emigrations from Albania with ships being hijacked in the harbour and sailed at gunpoint to Italy. In one month alone, August 1991, over 20,000 people migrated to Italy in this fashion. Italy intervened militarily, putting the port area under its control, and the city became the center of the European Community
The European Economic Community (EEC) was a regional organization created by the Treaty of Rome of 1957,Today the largely rewritten treaty continues in force as the ''Treaty on the functioning of the European Union'', as renamed by the Lis ...
's " Operation Pelican", a food-aid program.
In 1997, Albania slid into anarchy following the collapse of a massive pyramid scheme
A pyramid scheme is a business model that recruits members via a promise of payments or services for enrolling others into the scheme, rather than supplying investments or sale of products. As recruiting multiplies, recruiting becomes quickly i ...
which devastated the national economy. An Italian-led peacekeeping force was controversially deployed to Durrës and other Albanian cities to restore order, although there were widespread suggestions that the real purpose of "Operation Alba
Operation Alba ("Sunrise" or "Dawn" in Italian) was a multinational peacekeeping force sent to Albania in 1997. Led by Italy, it was intended to help the Albanian government restore law and order during the Albanian Civil War.
Geography
Durrës is located on the Bay of Durrës on a flatalluvial plain
An alluvial plain is a largely flat landform created by the deposition of sediment over a long period of time by one or more rivers coming from highland regions, from which alluvial soil forms. A floodplain is part of the process, being the smal ...
between the river mouth
A river mouth is where a river flows into a larger body of water, such as another river, a lake/reservoir, a bay/gulf, a sea, or an ocean. At the river mouth, sediments are often deposited due to the slowing of the current reducing the carrying ...
s of Erzen
The Erzen ( sq-definite, Erzeni) is a river in central Albania. The length of Erzen is , while the catchment area is including the southern Tirana District and eastern Durrës District.
Name
The ancient Illyrian name of the river was ''Ardaxa ...
and the Ishëm along the Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to th ...
within the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on ...
. The municipality of Durrës is encompassed in the County of Durrës within the Northern Region of Albania and consists of the adjacent administrative units of Ishëm
Ishëm is a former municipality in the Durrës County, northwestern Albania. At the 2015 local government reform it became a subdivision of the municipality Durrës. The population at the 2011 census was 5,001.Katund i Ri, Manëz,
 Durrës is an important link to
Durrës is an important link to

 Major roads and railways pass through the city of Durrës thank to its significant location and connect the northern part of the country to the south and the west with the east. Durrës is the starting point of Pan-European Corridor VIII, national roads SH2 and SH4, and serves as the
Major roads and railways pass through the city of Durrës thank to its significant location and connect the northern part of the country to the south and the west with the east. Durrës is the starting point of Pan-European Corridor VIII, national roads SH2 and SH4, and serves as the
 Durrës has a long tradition of education since the beginning of civil life from antiquity until today. After the fall of communism in Albania, a reorganization plan was announced in 1990, that would extend the compulsory education program from eight to ten years. The following year, major economic and political crisis in Albania, and the ensuing breakdown of public order, plunged the school system into chaos. Later, many schools were rebuilt or reconstructed, to improve learning conditions especially in larger cities of the country. Durrës is host to academic institutions such as the University of Durrës, Albanian College of Durrës, Kajtazi Brothers Educational Institute, Gjergj Kastrioti High School, Naim Frashëri High School, Sports mastery school Benardina Qerraxhiu and Jani Kukuzeli Artistic Lycee.
One of the city's main sights is the Byzantine city wall, also called
Durrës has a long tradition of education since the beginning of civil life from antiquity until today. After the fall of communism in Albania, a reorganization plan was announced in 1990, that would extend the compulsory education program from eight to ten years. The following year, major economic and political crisis in Albania, and the ensuing breakdown of public order, plunged the school system into chaos. Later, many schools were rebuilt or reconstructed, to improve learning conditions especially in larger cities of the country. Durrës is host to academic institutions such as the University of Durrës, Albanian College of Durrës, Kajtazi Brothers Educational Institute, Gjergj Kastrioti High School, Naim Frashëri High School, Sports mastery school Benardina Qerraxhiu and Jani Kukuzeli Artistic Lycee.
One of the city's main sights is the Byzantine city wall, also called
durres.gov.al
fficial Website {{DEFAULTSORT:Durres Cities in Albania Administrative units of Durrës Municipalities in Durrës County Populated coastal places in Albania 627 BC 7th-century BC establishments Populated places established in the 7th century BC Mediterranean port cities and towns in Albania Former national capitals Illyrian Albania Cities in ancient Illyria Greek colonies in Illyria Ancient Greek archaeological sites in Albania Hellenistic Albania Roman sites in Albania Territories of the Republic of Venice
Rrashbull
Rrashbull is a village and a former municipality in the Durrës County, western Albania. At the 2015 local government reform it became a subdivision of the municipality Durrës
Durrës ( , ; sq-definite, Durrësi) is the second most populous ...
, Sukth
Sukth is a village and a former municipality in the Durrës County, western Albania. At the 2015 local government reform it became a subdivision of the municipality Durrës. The population at the 2011 census was 15,966.
and Durrës as its seat. It stretches from the mouth of Ishëm River at the Cape of Rodon in the north across the Bay of Lalzi to the Shkëmbi i Kavajës
Shkëmbi i Kavajës (Rock of Kavajë) is a landmark named after the town of Kavajë, Albania. The outsized rock is about 6 kilometers from Kavajë and about 8 kilometers from Durrës. It is said to be the place where, in 48 BC, during Caesar's Civi ...
in the south.
Climate
According to theKöppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, nota ...
, Durrës is classified under the periphery of the hot-summer Mediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate (also called a dry summer temperate climate ''Cs'') is a temperate climate sub-type, generally characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, fairly wet winters; these weather conditions are typically experienced in the ...
(Csa) zone with an average annual temperature of . Its climate is influenced by its proximity to the Adriatic Sea in the Mediterranean Sea and the hills in the Western Lowlands
The Western Lowlands ( sq, Ultësira Bregdetare or Ultësira Perëndimore) is a physiogeographical region encompassing the western edge of Albania. It comprises the flat plains extending in the west along the Albanian Adriatic and Ionian Sea Co ...
in the hinterlands. The summers are predominantly hot and dry, the winters relatively mild, and falls and springs mainly stable, in terms of precipitation and temperatures. The mean monthly temperature ranges between in winter to in summer. The highest temperature of was recorded on 14 August 1957. The lowest temperature of was registered on 26 January 1954. Durrës receives most of the precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
in winter months and less in summer months. The mean annual precipitation ranges between and .
Politics
Durrës is amunicipality
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality'' may also mean the ...
governed by a mayor–council system with the mayor of Durrës and the members of the Durrës Municipal Council being responsible for the administration of Durrës Municipality. The mayor of Durrës is elected by its people to act as the executive officer of the municipality. The Durrës Municipal Council is the legislative body of the municipality and is also a democratically elected institution, comprising 51 councillors since the latest municipal election. Both, the mayor and members of the municipal council serve four-year terms without term limits.
Economy
 Durrës is an important link to
Durrës is an important link to Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
due to its port and its proximity to the Italian port cities, notably Bari, to which daily ferries run. As well as the dockyard, it also possesses an important shipyard and manufacturing industries, notably producing leather, plastic and tobacco products.
The southern coastal stretch of Golem is renowned for its traditional mass beach tourism having experienced uncontrolled urban development. The city's beaches are also a popular destination for many foreign and local tourists. In 2012, new water sanitation systems are being installed to eliminate sea water pollution. In contrast, the northern coastal stretch of Lalzit Bay is mostly unspoiled and set to become an elite tourism destination as a number of beach resorts are being built since 2009. Neighboring districts are known for the production of good wine and a variety of foodstuffs.
According to the World Bank, Durrës has made significant steps of starting a business in 2016. Durrës ranks ninth among 22 cities in Southeastern Europe
Southeast Europe or Southeastern Europe (SEE) is a geographical subregion of Europe, consisting primarily of the Balkans. Sovereign states and territories that are included in the region are Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia (a ...
before the capital Tirana
Tirana ( , ; aln, Tirona) is the capital and largest city of Albania. It is located in the centre of the country, enclosed by mountains and hills with Dajti rising to the east and a slight valley to the northwest overlooking the Adriatic Sea ...
, Belgrade
Belgrade ( , ;, ; names in other languages) is the capital and largest city in Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers and the crossroads of the Pannonian Plain and the Balkan Peninsula. Nearly 1,166,763 mi ...
, Serbia and Sarajevo
Sarajevo ( ; cyrl, Сарајево, ; ''see names in other languages'') is the capital and largest city of Bosnia and Herzegovina, with a population of 275,524 in its administrative limits. The Sarajevo metropolitan area including Sarajevo ...
, Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Transportation
 Major roads and railways pass through the city of Durrës thank to its significant location and connect the northern part of the country to the south and the west with the east. Durrës is the starting point of Pan-European Corridor VIII, national roads SH2 and SH4, and serves as the
Major roads and railways pass through the city of Durrës thank to its significant location and connect the northern part of the country to the south and the west with the east. Durrës is the starting point of Pan-European Corridor VIII, national roads SH2 and SH4, and serves as the main railway station
Central stations or central railway stations emerged in the second half of the nineteenth century as railway stations that had initially been built on the edge of city centres were enveloped by urban expansion and became an integral part of the ...
of the Albanian Railways (HSH).
The Pan-European Corridor VIII is one of the Pan-European corridors. It runs between Durrës, at the Adriatic
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to the ...
coast, and Varna, at the Bulgarian Black Sea coast. The National Road 2 (SH2) begins at the Port of Durrës
The Port of Durrës ( sq, Porti i Durrësit) is the largest seaport of Albania. The port is situated in the city of Durrës. It is an artificial basin that is formed between two moles, with a west-northwesterly oriented entrance approximately wid ...
at the Dajlani Overpass, bypasses the road to Tirana International Airport
Tirana ( , ; aln, Tirona) is the capital and largest city of Albania. It is located in the centre of the country, enclosed by mountains and hills with Dajti rising to the east and a slight valley to the northwest overlooking the Adriatic Sea ...
, and ends at the Kamza Overpass in the outskirts of Tirana
Tirana ( , ; aln, Tirona) is the capital and largest city of Albania. It is located in the centre of the country, enclosed by mountains and hills with Dajti rising to the east and a slight valley to the northwest overlooking the Adriatic Sea ...
where it meets National Road 1 (SH1) State Road heading to northern Albania. The Albania–Kosovo Highway is a four-lane highway constructed from 2006 to 2013 between Albania and Kosovo. As part of the South-East European Route 7, the highway will connect the Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to th ...
ports of Durrës via Pristina, with the E75/Corridor X near Niš
Niš (; sr-Cyrl, Ниш, ; names in other languages) is the third largest city in Serbia and the administrative center of the Nišava District. It is located in southern part of Serbia. , the city proper has a population of 183,164, whi ...
, Serbia. As most tourists come through Kosovo, the laying of the highway make it easier to travel to Durrës.
The Port of Durrës
The Port of Durrës ( sq, Porti i Durrësit) is the largest seaport of Albania. The port is situated in the city of Durrës. It is an artificial basin that is formed between two moles, with a west-northwesterly oriented entrance approximately wid ...
, in the south-west of the city, is one of the major ports of the Adriatic Sea and plays a very important role in the city's economy. The port is located on an artificial basin that is formed between two moles, with a west-northwesterly oriented entrance approximately wide as it passes between the ends of the moles. The port is also a key location for transit networks and passenger ferry, giving Durrës a strategic position with respect to the Pan-European Corridor VIII. The port has experienced major upgrades in recent years culminating with the opening of the new terminal in July 2012.
In 2012, The Globe and Mail
''The Globe and Mail'' is a Canadian newspaper printed in five cities in western and central Canada. With a weekly readership of approximately 2 million in 2015, it is Canada's most widely read newspaper on weekdays and Saturdays, although it ...
ranked Durrës at no. 1 among 8 exciting new cruise ports to explore. It is one of the largest passenger port on the Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to th ...
that handle more than 1.5 million passengers per year.
The railway station of Durrës is connected to other cities in Albania, including the capital of Tirana
Tirana ( , ; aln, Tirona) is the capital and largest city of Albania. It is located in the centre of the country, enclosed by mountains and hills with Dajti rising to the east and a slight valley to the northwest overlooking the Adriatic Sea ...
, Vlorë
Vlorë ( , ; sq-definite, Vlora) is the third most populous city of the Republic of Albania and seat of Vlorë County and Vlorë Municipality. Located in southwestern Albania, Vlorë sprawls on the Bay of Vlorë and is surrounded by the foo ...
, Elbasan
Elbasan ( ; sq-definite, Elbasani ) is the fourth most populous city of Albania and seat of Elbasan County and Elbasan Municipality. It lies to the north of the river Shkumbin between the Skanderbeg Mountains and the Myzeqe Plain in central ...
and Shkodër
Shkodër ( , ; sq-definite, Shkodra) is the fifth-most-populous city of the Republic of Albania and the seat of Shkodër County and Shkodër Municipality. The city sprawls across the Plain of Mbishkodra between the southern part of Lake Shko ...
. The Durrës–Tiranë railway was a railway
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a p ...
line which joined the two biggest cities in Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and share ...
: Durrës and Tiranë. The line connects to the Shkodër–Vorë railway halfway in Vorë, and to the Durrës–Vlorë railway in Durrës. In 2015, some rail stations and rolling stock along the Durrës-Tiranë line are being upgraded and latter colored red and white.
Demography
Durrës is the second most populous municipality in Albania and one of the most populous on theAdriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to th ...
with a growing number of inhabitants. According to the 2011 census, the municipal unit of Durrës had an estimated population of 113,249 of whom 56,511 were men and 56,738 women.
Albania is a secular state
A secular state is an idea pertaining to secularity, whereby a state is or purports to be officially neutral in matters of religion, supporting neither religion nor irreligion. A secular state claims to treat all its citizens equally regard ...
with no state religion
A state religion (also called religious state or official religion) is a religion or creed officially endorsed by a sovereign state. A state with an official religion (also known as confessional state), while not secular, is not necessarily a t ...
and the freedom of belief
Freedom of religion or religious liberty is a principle that supports the freedom of an individual or community, in public or private, to manifest religion or belief in teaching, practice, worship, and observance. It also includes the freedom ...
, conscience
Conscience is a cognitive process that elicits emotion and rational associations based on an individual's moral philosophy or value system. Conscience stands in contrast to elicited emotion or thought due to associations based on immediate sens ...
and religion
Religion is usually defined as a social- cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatur ...
is explicitly guaranteed in the constitution of the country. Durrës is therefore religiously diverse and has many places of worship catering to its religious population, whom are adherents of Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global popula ...
, Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
and Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in th ...
.
Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
was introduced to the city in the early 16th century during the Ottoman conquest. Much of the local population converted to Islam during the four centuries of Ottoman rule. The two most well-known mosques in the city are the Great Mosque of Durrës (built in 1931 on the site of an earlier Ottoman mosque) and the Fatih Mosque
The large Fatih Mosque ( tr, Fatih Camii, "Conqueror's Mosque" in English) is an Ottoman mosque off Fevzi Paşa Caddesi in the Fatih district of Istanbul, Turkey. The original mosque was constructed between 1463 and 1470 on the site of the Ch ...
, erected in 1502 just one year after the city became part of the Ottoman Empire.
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global popula ...
in Durrës and elsewhere in Albania has a presence dating back to classical antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ...
. Christian traditions relate that the archbishopric of Durrës was founded by the apostle Paul
Paul; grc, Παῦλος, translit=Paulos; cop, ⲡⲁⲩⲗⲟⲥ; hbo, פאולוס השליח (previously called Saul of Tarsus;; ar, بولس الطرسوسي; grc, Σαῦλος Ταρσεύς, Saũlos Tarseús; tr, Tarsuslu Pavlus; ...
while he was preaching in Illyria
In classical antiquity, Illyria (; grc, Ἰλλυρία, ''Illyría'' or , ''Illyrís''; la, Illyria, ''Illyricum'') was a region in the western part of the Balkan Peninsula inhabited by numerous tribes of people collectively known as the Illyr ...
and Epirus
sq, Epiri rup, Epiru
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = Historical region
, image_map = Epirus antiquus tabula.jpg
, map_alt =
, map_caption = Map of ancient Epirus by Heinri ...
and that there were possibly about seventy Christian families in the city as early as the time of the apostle
An apostle (), in its literal sense, is an emissary, from Ancient Greek ἀπόστολος (''apóstolos''), literally "one who is sent off", from the verb ἀποστέλλειν (''apostéllein''), "to send off". The purpose of such sending ...
s.http://biblicalstudies.org.uk/pdf/rcl/10-3_242.pdf The Orthodox Church of Albania, which has been autocephalous since 1923, was divided into the archbishopric of Tirana–Durrës, headed by the Metropolitan and sub-divided into the local church districts of Tirana
Tirana ( , ; aln, Tirona) is the capital and largest city of Albania. It is located in the centre of the country, enclosed by mountains and hills with Dajti rising to the east and a slight valley to the northwest overlooking the Adriatic Sea ...
, Durrës, Shkodër
Shkodër ( , ; sq-definite, Shkodra) is the fifth-most-populous city of the Republic of Albania and the seat of Shkodër County and Shkodër Municipality. The city sprawls across the Plain of Mbishkodra between the southern part of Lake Shko ...
and Elbasan
Elbasan ( ; sq-definite, Elbasani ) is the fourth most populous city of Albania and seat of Elbasan County and Elbasan Municipality. It lies to the north of the river Shkumbin between the Skanderbeg Mountains and the Myzeqe Plain in central ...
.
Culture
The theatrical and musical life of the city is centered on theAleksandër Moisiu Theatre
The Aleksandër Moisiu Theatre, or called also Durrës Theatre ( sq, Teatri Aleksandër Moisiu) is a theatre in the city centre of Durrës, Albania. The theatre took its name from Austrian actor Alexander Moissi, who was of Albanian descent.
Hist ...
, the Estrada Theatre, a puppet theatre, and the Philharmonic Orchestra. The annual International Film Summerfest of Durrës, founded in 2008, is held in late August or early September in the amphitheatre. In 2004 and 2009 Miss Globe International
Miss Globe is a global beauty pageant group that holds annual events. Currently, Miss Globe is produced simultaneously by three various organizations claiming to be the ''official'' organizers. The Miss Globe was first known to public in 1925. In ...
was held in Durrës.
The city is home to different architectural styles that represent influential periods in its history. The architecture is influenced by Illyrian, Greek, Roman and Italian architecture. In the 21st century, part of Durrës turned into a modernist city, with large blocks of flats, modern new buildings, new shopping centres and many green spaces.
Education
 Durrës has a long tradition of education since the beginning of civil life from antiquity until today. After the fall of communism in Albania, a reorganization plan was announced in 1990, that would extend the compulsory education program from eight to ten years. The following year, major economic and political crisis in Albania, and the ensuing breakdown of public order, plunged the school system into chaos. Later, many schools were rebuilt or reconstructed, to improve learning conditions especially in larger cities of the country. Durrës is host to academic institutions such as the University of Durrës, Albanian College of Durrës, Kajtazi Brothers Educational Institute, Gjergj Kastrioti High School, Naim Frashëri High School, Sports mastery school Benardina Qerraxhiu and Jani Kukuzeli Artistic Lycee.
One of the city's main sights is the Byzantine city wall, also called
Durrës has a long tradition of education since the beginning of civil life from antiquity until today. After the fall of communism in Albania, a reorganization plan was announced in 1990, that would extend the compulsory education program from eight to ten years. The following year, major economic and political crisis in Albania, and the ensuing breakdown of public order, plunged the school system into chaos. Later, many schools were rebuilt or reconstructed, to improve learning conditions especially in larger cities of the country. Durrës is host to academic institutions such as the University of Durrës, Albanian College of Durrës, Kajtazi Brothers Educational Institute, Gjergj Kastrioti High School, Naim Frashëri High School, Sports mastery school Benardina Qerraxhiu and Jani Kukuzeli Artistic Lycee.
One of the city's main sights is the Byzantine city wall, also called Durrës Castle
Durrës Castle ( sq, Kalaja e Durrësit) is the fortified old city of Durrës, Albania. It is enclosed by city walls built in the late 5th century, and repaired and reinforced in the Middle Ages and early modern periods.
History
The castle was bu ...
, while the largest amphitheatre
An amphitheatre (British English) or amphitheater (American English; both ) is an open-air venue used for entertainment, performances, and sports. The term derives from the ancient Greek ('), from ('), meaning "on both sides" or "around" and ...
in the Balkans is close to the city's harbour. This fifth-century construction is currently under consideration for listing as a UNESCO World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
.
Museums
Durrës is home to the largest archaeological museum in the country, the Durrës Archaeological Museum, located near the beach. North of the museum are the sixth-century Byzantine walls constructed after theVisigoth
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is kn ...
invasion of 481. The bulk of the museum's collection comprises artefacts from the nearby ancient site of Dyrrhachium and includes an extensive collection from the Illyrian, Ancient Greek, Hellenistic and Roman periods. Items of major note include Roman funeral steles and stone sarcophagi, a colourful elliptical mosaic measuring , known as The Beauty of Durrës
The Beauty of Durrës (also called The Beautiful Maiden of Durrës or The Belle of Durrës) is a polychromatic mosaic of the 4th century BC and is the most ancient and important mosaic discovered in Albania.BANK OF ALBANICoin with “The Beauty ...
, and a collection of miniature busts of Venus, testament to the time when Durrës was a centre of worship of the goddess. There are several other museums including the Royal Villa of Durrës and the Museum of History (in the house of the actor Aleksandër Moisiu
Alexander Moissi ( al, Aleksandër Moisiu; it, Alessandro Moissi; 2 April 1879 – 22/23 March 1935) was an Austrian stage actor of Albanian origin.
Early years
Moissi was born in Trieste to Moisi Moisiu from Kavaye, Ottoman Empire (today ...
).
International relations
In 2008,Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and ...
opened a consulate in the city considering that there is a community with Bosniak
The Bosniaks ( bs, Bošnjaci, Cyrillic: Бошњаци, ; , ) are a South Slavic ethnic group native to the Southeast European historical region of Bosnia, which is today part of Bosnia and Herzegovina, who share a common Bosnian ancestry, ...
ancestry that lives in Durres County. They are mostly concentrated in two neighborhoods of the city of Shijak
Shijak ( sq-definite, Shijaku) is a town and a municipality in Durrës County, west-central Albania. The municipality was formed at the 2015 local government reform by the merger of the former municipalities Gjepalaj, Maminas, Shijak and Xhafzot ...
, Borake and Koxhas. Nowadays it seems that the consulate is no longer active.
These countries have an honorary consulate in Durrës:
*
*
Twin and sister cities
Durrës is twinned with: *Bari
Bari ( , ; nap, label= Barese, Bare ; lat, Barium) is the capital city of the Metropolitan City of Bari and of the Apulia region, on the Adriatic Sea, southern Italy. It is the second most important economic centre of mainland Southern Ital ...
, Italy
* Bitonto
Bitonto (; nap, label= Bitontino, Vetònde) is a city and '' comune'' in the Metropolitan City of Bari ( Apulia region), Italy. It lies to the west of Bari. It is nicknamed the "City of Olives", due to the numerous olive groves surrounding the ...
, Italy
* Istanbul
)
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code = 34000 to 34990
, area_code = +90 212 (European side) +90 216 (Asian side)
, registration_plate = 34
, blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD
, blank_i ...
, Turkey
* Thessaloniki
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area, and the capital of the geographic region of ...
, Greece
Cooperation and friendship
Durrës has cooperation and friendship relationships with: *Kumanovo
Kumanovo ( mk, Куманово ; also known by other alternative names) is a city in North Macedonia and the seat of Kumanovo Municipality, the largest municipality in the country. Kumanovo lies above sea level and is surrounded by the Kar ...
, North Macedonia
* Shantou
Shantou, alternately romanized as Swatow and sometimes known as Santow, is a prefecture-level city on the eastern coast of Guangdong, China, with a total population of 5,502,031 as of the 2020 census (5,391,028 in 2010) and an administrative ...
, China
* Ulcinj, Montenegro
See also
*List of ancient cities in Illyria
This is a list of settlements in Illyria founded by Illyrians (southern Illyrians, Dardanians, Pannonians), Liburni, Ancient Greeks and the Roman Empire. A number of cities in Illyria and later Illyricum were built on the sites or close to the ...
* List of mayors of Durrës
* List of people from Durrës
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
durres.gov.al
fficial Website {{DEFAULTSORT:Durres Cities in Albania Administrative units of Durrës Municipalities in Durrës County Populated coastal places in Albania 627 BC 7th-century BC establishments Populated places established in the 7th century BC Mediterranean port cities and towns in Albania Former national capitals Illyrian Albania Cities in ancient Illyria Greek colonies in Illyria Ancient Greek archaeological sites in Albania Hellenistic Albania Roman sites in Albania Territories of the Republic of Venice